Gut–Liver Axis: How Do Gut Bacteria Influence the Liver?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Gut–Liver Axis
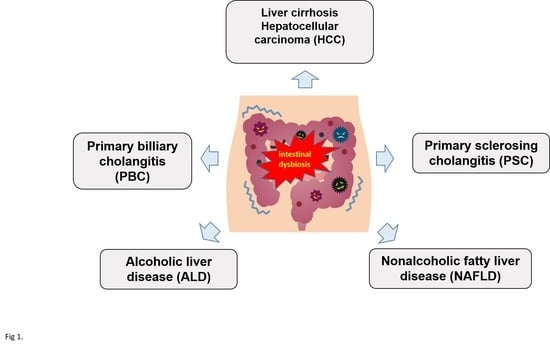
3. Dysbiosis and Liver Diseases
4. Gut Microbiota and Alcoholic Liver Disease
5. Gut Microbiota and Nonalcoholic Liver Disease
6. Gut Microbiota and Immune-Mediated Liver Diseases
7. Dysbiosis and Liver Cirrhosis
8. Targeting Gut Microbiota in Hepatocarcinogenesis
9. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jandhyala, S.M.; Talukdar, R.; Subramanyam, C.; Vuyyuru, H.; Sasikala, M.; Reddy, D.N. Role of the normal gut microbiota. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8787–8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Round, J.L.; Mazmanian, S.K. The gut microbiota shapes intestinal immune responses during health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W. Gut microbiomes and their metabolites shape human and animal health. J. Microbial. 2018, 56, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Chen, W.D.; Wang, Y.D. Gut Microbiota: An Integral Moderator in Health and Disease. Front. Microbial. 2018, 9, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattarai, Y.; Muniz Pedrogo, D.A.; Kashyap, P.C. Irritable bowel syndrome: A gut microbiota-related disorder? Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2017, 312, G52–G62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, F.; Backhed, F. The gut microbiota—Masters of host development and physiology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, B.O.; Backhed, F. Signals from the gut microbiota to distant organs in physiology and disease. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente, J.C.; Ursell, L.K.; Parfrey, L.W.; Knight, R. The impact of the gut microbiota on human health: An integrative view. Cell 2012, 148, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bretin, A.; Gewirtz, A.T.; Chassaing, B. Microbiota and Metabolism—What’s New in 2018. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hara, P.; Karlsen, T.H.; LaRusso, N.F. Cholangiocytes and the environment in primary sclerosing cholangitis: Where is the link? Gut 2017, 66, 1873–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponziani, F.R.; Zocco, M.A.; Cerrito, L.; Gasbarrini, A.; Pompili, M. Bacterial translocation in patients with liver cirrhosis: Physiology, clinical consequences, and practical implications. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carotti, S.; Guarino, M.P.L.; Vespasiani-Gentilucci, U.; Morini, S. Starring role of toll-like receptor-4 activation in the gut-liver axis. World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2015, 6, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandl, K.; Kumar, V.; Eckmann, L. Gut-liver axis at the frontier of host-microbial interactions. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2017, 312, G413–G419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betrapally, N.S.; Gillevet, P.M.; Bajaj, J.S. Gut microbiome and liver disease. Transl. Res. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 2017, 179, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathurin, P.; Lucey, M.R. Alcohol, liver disease, and transplantation: Shifting attitudes and new understanding leads to changes in practice. Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 2018, 23, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.; Stepanova, M.; Ong, J.P.; Jacobson, I.M.; Bugianesi, E.; Duseja, A.; Eguchi, Y.; Wong, V.W.; Negro, F.; Yilmaz, Y.; et al. Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis is the Fastest Growing Cause of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Liver Transplant Candidates. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimpin, L.; Cortez-Pinto, H.; Negro, F.; Corbould, E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Webber, L.; Sheron, N. Burden of liver disease in Europe: Epidemiology and analysis of risk factors to identify prevention policies. J. Hepatol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, R.; Kim, S.J.; Gao, B. Alcohol, adipose tissue and liver disease: Mechanistic links and clinical considerations. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassard, A.M.; Ciocan, D. Microbiota, a key player in alcoholic liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2018, 24, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, Y.; Moore, L.E.; Bradford, B.U.; Gao, W.; Thurman, R.G. Antibiotics prevent liver injury in rats following long-term exposure to ethanol. Gastroenterology 1995, 108, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morencos, F.C.; De las Heras Castano, G.; Ramos, L.M.; Arias, M.J.L.; Ledesma, F.; Romero, F.P. Small bowel bacterial overgrowth in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1996, 41, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Shanahan, E.; Macdonald, G.A.; Fletcher, L.; Ghasemi, P.; Morrison, M.; Jones, M.; Holtmann, G. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis: Prevalence of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Chronic Liver Disease. Semin. Liver Dis. 2017, 37, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quigley, E.M.; Stanton, C.; Murphy, E.F. The gut microbiota and the liver. Pathophysiological and clinical implications. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanduzzi Zamparelli, M.; Rocco, A.; Compare, D.; Nardone, G. The gut microbiota: A new potential driving force in liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2017, 5, 944–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopis, M.; Cassard, A.M.; Wrzosek, L.; Boschat, L.; Bruneau, A.; Ferrere, G.; Puchois, V.; Martin, J.C.; Lepage, P.; Le Roy, T.; et al. Intestinal microbiota contributes to individual susceptibility to alcoholic liver disease. Gut 2016, 65, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M.; Han, D.H.; Hong, J.; Kim, D.J.; Suk, K.T. Are Probiotics Effective in Targeting Alcoholic Liver Diseases? Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Duan, K.; Wang, C.; McClain, C.; Feng, W. Probiotics and Alcoholic Liver Disease: Treatment and Potential Mechanisms. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2016, 5491465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konturek, P.C. Therapy of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: The proven and the new. MMW Fortschritte der Medizin 2018, 160, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Evolution of inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The multiple parallel hits hypothesis. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1836–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doulberis, M.; Kotronis, G.; Gialamprinou, D. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An update with special focus on the role of gut microbiota. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2017, 71, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Faria Ghetti, F.; Oliveira, D.G.; de Oliveira, J.M.; de Castro, L.E.V.V.; Cesar, D.E.; Moreira, A.P.B. Influence of gut microbiota on the development and progression of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 861–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Zhou, Q.; Li, H. Gut Microbiota and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Insights on Mechanisms and Therapy. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolella, G.; Mandato, C.; Pierri, L.; Poeta, M.; Di Stasi, M.; Vajro, P. Gut-liver axis and probiotics: Their role in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 15518–15531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.Y.; Wan, Y.P.; Fang, Q.Y.; Lu, W.; Cai, W. Supplementation with probiotics modifies gut flora and attenuates liver fat accumulation in rat nonalcoholic fatty liver disease model. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2012, 50, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Wong, G.L.H.; Chim, A.M.L.; Chu, W.C.W.; Yeung, D.K.W.; Li, K.C.T.; Chan, H.L.Y. Treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with probiotics. A proof-of-concept study. Ann. Hepatol. 2013, 12, 256–262. [Google Scholar]
- Parnell, J.A.; Raman, M.; Rioux, K.P.; Reimer, R.A. The potential role of prebiotic fibre for treatment and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and associated obesity and insulin resistance. Liver Int. 2012, 32, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomhof, M.R.; Parnell, J.A.; Ramay, H.R.; Crotty, P.; Rioux, K.P.; Probert, C.S.; Jayakumar, S.; Raman, M.; Reimer, R.A. Histological improvement of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis with a prebiotic: A pilot clinical trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daubioul, C.A.; Horsmans, Y.; Lambert, P.; Danse, E.; Delzenne, N.M. Effects of oligofructose on glucose and lipid metabolism in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Results of a pilot study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 59, 723–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mofidi, F.; Poustchi, H.; Yari, Z.; Nourinayyer, B.; Merat, S.; Sharafkhah, M.; Malekzadeh, R.; Hekmatdoost, A. Synbiotic supplementation in lean patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A pilot, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalesi, S.; Johnson, D.W.; Campbell, K.; Williams, S.; Fenning, A.; Saluja, S.; Irwin, C. Effect of probiotics and synbiotics consumption on serum concentrations of liver function test enzymes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattner, J. Impact of Microbes on the Pathogenesis of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis (PBC) and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, R.; Wei, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, W.; Chen, H.; Wang, Q.; Yang, F.; Miao, Q.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, H.; et al. Gut microbial profile is altered in primary biliary cholangitis and partially restored after UDCA therapy. Gut 2018, 67, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, C.; Sahingur, S.E.; Bajaj, J.S. Microbiota, cirrhosis, and the emerging oral-gut-liver axis. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e94416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodhouse, C.A.; Patel, V.C.; Singanayagam, A.; Shawcross, D.L. Review article: The gut microbiome as a therapeutic target in the pathogenesis and treatment of chronic liver disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bass, N.M.; Mullen, K.D.; Sanyal, A.; Poordad, F.; Neff, G.; Leevy, C.B.; Sigal, S.; Sheikh, M.Y.; Beavers, K.; Frederick, T.; et al. Rifaximin treatment in hepatic encephalopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachogiannakos, J.; Viazis, N.; Vasianopoulou, P.; Vafiadis, I.; Karamanolis, D.G.; Ladas, S.D. Long-term administration of rifaximin improves the prognosis of patients with decompensated alcoholic cirrhosis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhiman, R.K.; Rana, B.; Agrawal, S.; Garg, A.; Chopra, M.; Thumburu, K.K.; Khattri, A.; Malhotra, S.; Duseja, A.; Chawla, Y.K. Probiotic VSL#3 reduces liver disease severity and hospitalization in patients with cirrhosis: A randomized, controlled trial. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 1327–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altamirano-Barrera, A.; Uribe, M.; Chávez-Tapia, N.C.; Nuño-Lámbarri, N. The role of the gut microbiota in the pathology and prevention of liver disease. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konturek, P.C.; Haziri, D.; Brzozowski, T.; Hess, T.; Heyman, S.; Kwiecien, S.; Konturek, S.J.; Koziel, J. Emerging role of fecal microbiota therapy in the treatment of gastrointestinal and extra-intestinal diseases. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015, 66, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Kassam, Z.; Fagan, A.; Gavis, E.A.; Liu, E.; Cox, I.J.; Kheradman, R.; Heuman, D.; Wang, J.; Gurry, T.; et al. Fecal microbiota transplant from a rational stool donor improves hepatic encephalopathy: A randomized clinical trial. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1727–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponziani, F.R.; Bhoori, S.; Castelli, C.; Putignani, L.; Rivoltini, L.; Del Chierico, F.; Sanguinetti, M.; Morelli, D.; Paroni Sterbini, F.; Petito, V.; et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with gut microbiota profile and inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Sung, C.Y.J.; Lee, N.; Ni, Y.; Pihlajamäki, J.; Panagiotou, G.; El-Nezami, H. Probiotics modulated gut microbiota suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma growth in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1306–E1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.X.; Yan, H.X.; Liu, Q.; Yang, W.; Wu, H.P.; Dong, W.; Tang, L.; Lin, Y.; He, Y.Q.; Zou, S.S.; et al. Endotoxin accumulation prevents carcinogen-induced apoptosis and promotes liver tumorigenesis in rodents. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Konturek, P.C.; Harsch, I.A.; Konturek, K.; Schink, M.; Konturek, T.; Neurath, M.F.; Zopf, Y. Gut–Liver Axis: How Do Gut Bacteria Influence the Liver? Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci6030079
Konturek PC, Harsch IA, Konturek K, Schink M, Konturek T, Neurath MF, Zopf Y. Gut–Liver Axis: How Do Gut Bacteria Influence the Liver? Medical Sciences. 2018; 6(3):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci6030079
Chicago/Turabian StyleKonturek, Peter Christopher, Igor Alexander Harsch, Kathrin Konturek, Monic Schink, Thomas Konturek, Markus F. Neurath, and Yurdaguel Zopf. 2018. "Gut–Liver Axis: How Do Gut Bacteria Influence the Liver?" Medical Sciences 6, no. 3: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci6030079
APA StyleKonturek, P. C., Harsch, I. A., Konturek, K., Schink, M., Konturek, T., Neurath, M. F., & Zopf, Y. (2018). Gut–Liver Axis: How Do Gut Bacteria Influence the Liver? Medical Sciences, 6(3), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci6030079