Analysis and Prediction of Wear Resistance on Grind-Hardening Layer Considering Different Friction Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Grind-Hardening Experiment
2.1. Experimental Conditions
2.2. Microstructure
2.3. Microstructure Distribution Along the Cross-Section
3. Friction and Wear Experiment
3.1. Experimental Conditions
3.2. Friction Coefficient
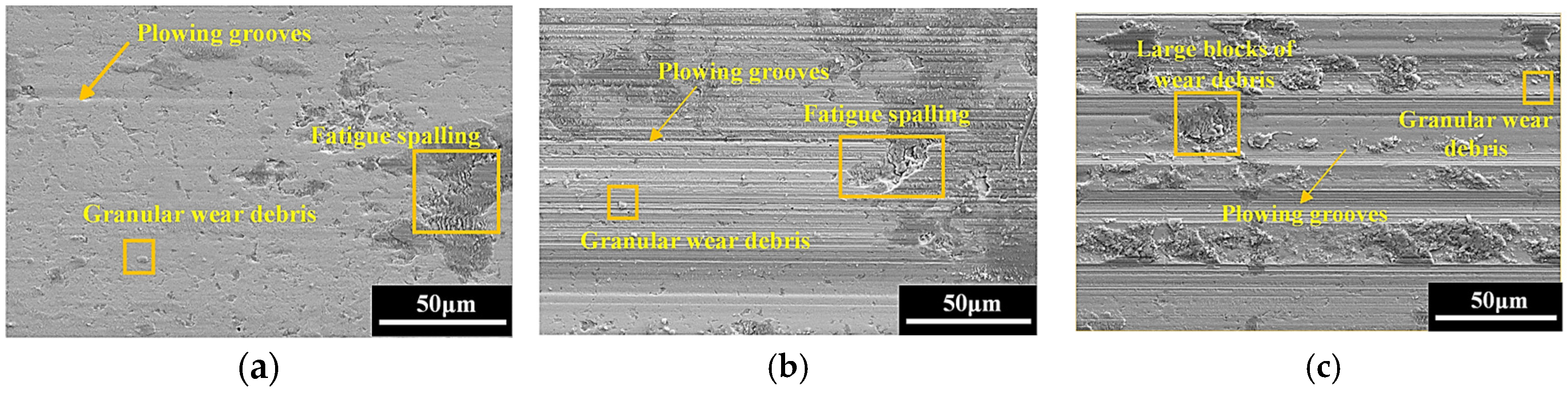
3.3. Worn Surface Morphology
3.4. Wear Measurement
4. Simulation of Friction and Wear
4.1. Methodology
4.2. Finite Element Simulation
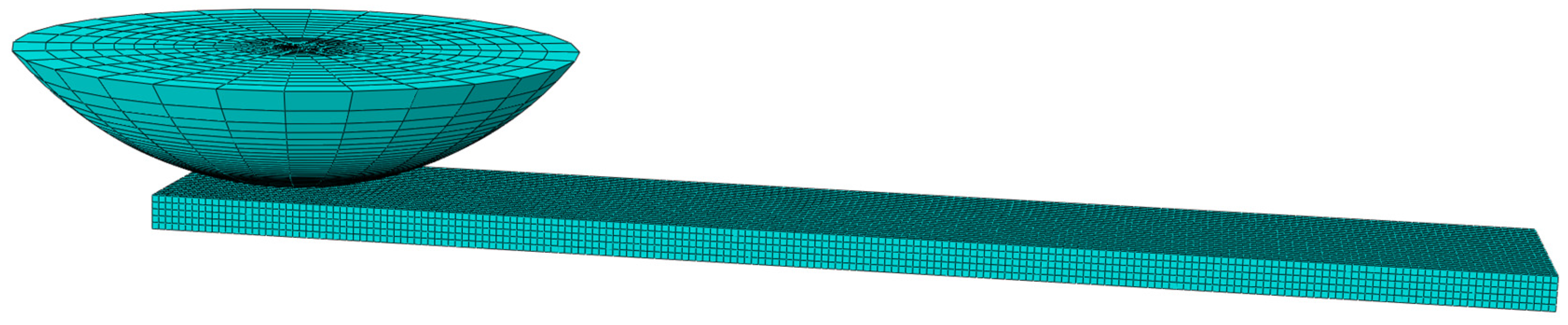
4.2.1. Finite Element Model
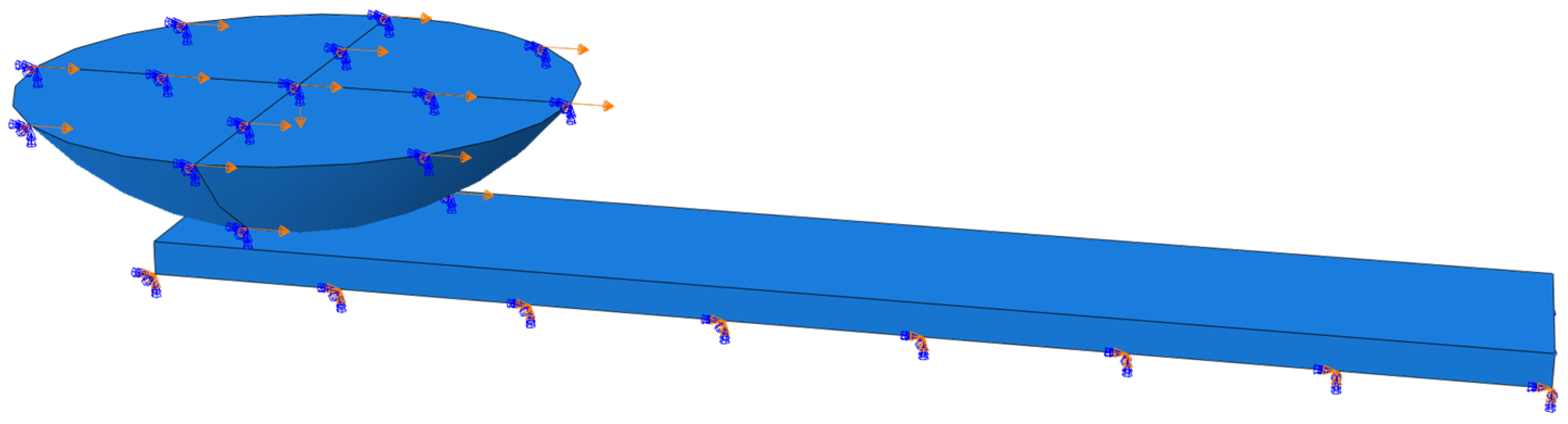
4.2.2. Boundary Conditions and Loading
4.2.3. Discussion
4.3. Validation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, Z.G.; Xu, N.W.; Zhang, Y.; Han, L.; Kang, R.K.; Wu, X.F.; Wang, Y. Mechanism of gradient strengthening layer formation based on microstructure and microhardness of Inconel 718 grinding surface. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 120, 2363–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fang, C.; Huang, G.; Xu, X. Modeling and simulation of the distribution of undeformed chip thicknesses in surface grinding. Int. J. Mach. Tools. Manuf. 2018, 127, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.Q.; Yi, H.; Shu, A.H.; Tang, L. Simulation of grinding surface topography considering wheel wear and wheel vibration. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 130, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Wang, X.R.; Song, Q.H.; Han, D.; Xiang, J.F. Exploring multi-deformation mechanism and control of arc thin-walled structures during supercritical CO2 assisted micro milling. J. Manuf. Process 2024, 132, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.L.; Zhang, X.M.; Xiu, S.C. A research on the mechanism and model of surface micro-damage in grinding hardening. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2021, 13, 16878140211044958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xiu, S.C.; Liu, M.H.; Shi, X.L. Uniformity mechanism investigation of hardness penetration depth during grind-hardening process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 89, 2001–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinksmeier, E.; Brockhoff, T. Surface heat treatment by using advanced grinding processes. Metall. Ital. 1999, 91, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Brockhoff, T. Grind-hardening: A comprehensive view. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 1999, 48, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarudi, I.; Zhang, L.C. Mechanical property improvement of quenchable steel by grinding. J. Mater. Sci. 2002, 37, 3935–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.C.; Liu, J.D.; Pei, H.J.; Jia, Z.H. Study on forming mechanism of surface hardening in two-pass grinding 40Cr steel. Key Eng. Mater. 2006, 304–305, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Zarudi, I.; Zhang, L.C. Grinding-hardening with liquid nitrogen: Mechanisms and technology. Int. J. Mach. Tools. Manuf. 2007, 47, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.H.; Zhang, K.; Xiu, S.C. Mechanism investigation of hardening layer hardness uniformity based on grind-hardening process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 88, 3185–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonitis, K. A hybrid cellular automata-finite element model for the simulation of the grind-hardening process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 93, 4007–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.S.; Xiu, S.C. Research on microstructure evolution of austenitization in grinding hardening by cellular automata simulation and experiment. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 93, 2599–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehle, L.; Kohls, E.; Richter, S.; Spille, J.; Schwedt, A. Grind hardening: Correlations between surface modifications and applied internal loads. Procedia CIRP 2018, 71, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.M.; Ren, Y.H.; Wu, W.; Li, T. Research on grind-hardening layer and residual stresses based on variable grinding forces. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 103, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, M.H.; Yan, Y.T. Hardness Prediction of Grind-Hardening Layer Based on Integrated Approach of Finite Element and Cellular Automata. Materials 2021, 14, 5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.L.; Xiu, S.C.; Liu, X. Experiment study on the corrosion resistance of the surface metamorphic layer of grinding. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerra, F.; Ascari, A.; Fortunato, A. Hardness penetration depth prediction in the grind-hardening process through a combined FEM model. Procedia CIRP 2022, 108, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Zhang, D.J.; Hu, Y.L.; Zhang, M.J.; Luo, Y.Q. Formation mechanisms of affected layers induced by grinding hardened AISI 52100 steel. Precis. Eng. 2024, 86, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmberg, K.; Erdemir, A. Influence of tribology on global energy consumption, costs and emissions. Friction 2017, 5, 263–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archard, J. Contact and rubbing of flat surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 1953, 24, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashish, S.; Kartik, J.; Piyush, C.V. Load-dependent Finite Element Wear Simulation of Semi-Metallic and Ceramic Friction Materials Using ANSYS. Trans. Indian. Inst. Met. 2023, 76, 2473–2482. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Ren, Z.; Su, X.; Shen, L.; Huang, J. Study on the Fretting Wear Evolution Model of Wires with Curvature Inside Metal Rubber. Tribol. Lett. 2023, 71, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wei, F.; Lin, S.; Sun, X.; Liu, L. Study on the Performance of Reciprocating Seals under the Coupling Effect of Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication and Rubber Wear. Eng. Res. Express 2024, 6, 015064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannopoulos, G.I.; Georgantzinos, S.K.; Anifantis, N.K. Coupled vibration response of a shaft with a breathing crack. J. Sound Vib. 2015, 336, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.J.; Shen, F.; Ke, L.L.; Wang, Y.S. Adaptive finite element simulation and experimental verification for fretting wear of PVDF piezoelectric thin films. Wear 2022, 502–503, 204395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Load F (N) | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Frequency f (Hz) | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 |
| Sliding distance s (mm) | 10 | ||||||||
| Time t (min) | 15 | ||||||||
| Item | Density (kg/m3) | Young’s Modulus (Mpa) | Poisson’s Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardened workpiece | 7.8 × 10−9 | 2 × 105 | 0.3 |
| Si3N4 ball | 3.3 × 10−9 | 3 × 105 | 0.26 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y. Analysis and Prediction of Wear Resistance on Grind-Hardening Layer Considering Different Friction Conditions. Materials 2025, 18, 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18050975
Guo Y, Liu M, Zhang Y. Analysis and Prediction of Wear Resistance on Grind-Hardening Layer Considering Different Friction Conditions. Materials. 2025; 18(5):975. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18050975
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yu, Minghe Liu, and Yiming Zhang. 2025. "Analysis and Prediction of Wear Resistance on Grind-Hardening Layer Considering Different Friction Conditions" Materials 18, no. 5: 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18050975
APA StyleGuo, Y., Liu, M., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Analysis and Prediction of Wear Resistance on Grind-Hardening Layer Considering Different Friction Conditions. Materials, 18(5), 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18050975





