Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of SUS 630 Stainless Steel: Effects of Age Hardening in a Tin Bath and Atmospheric Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methodology
2.3. Instrumental Methods
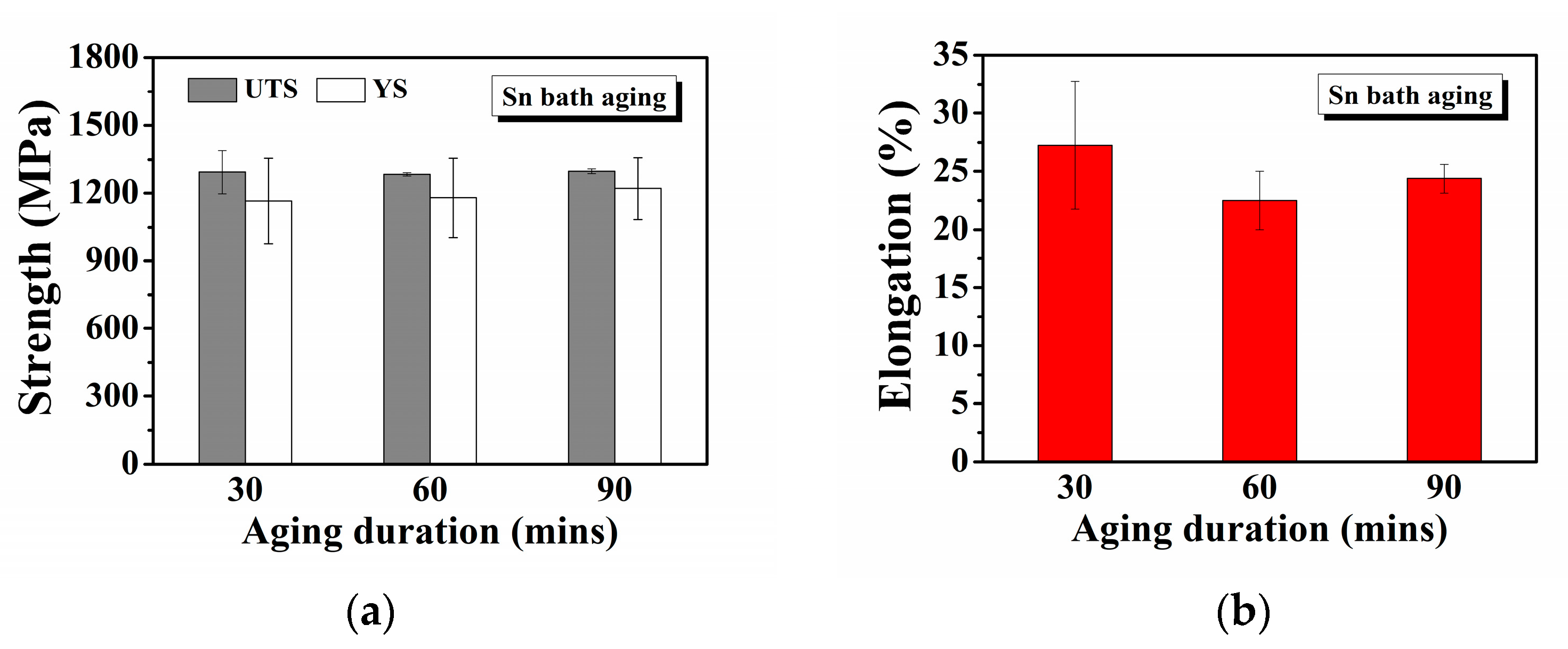
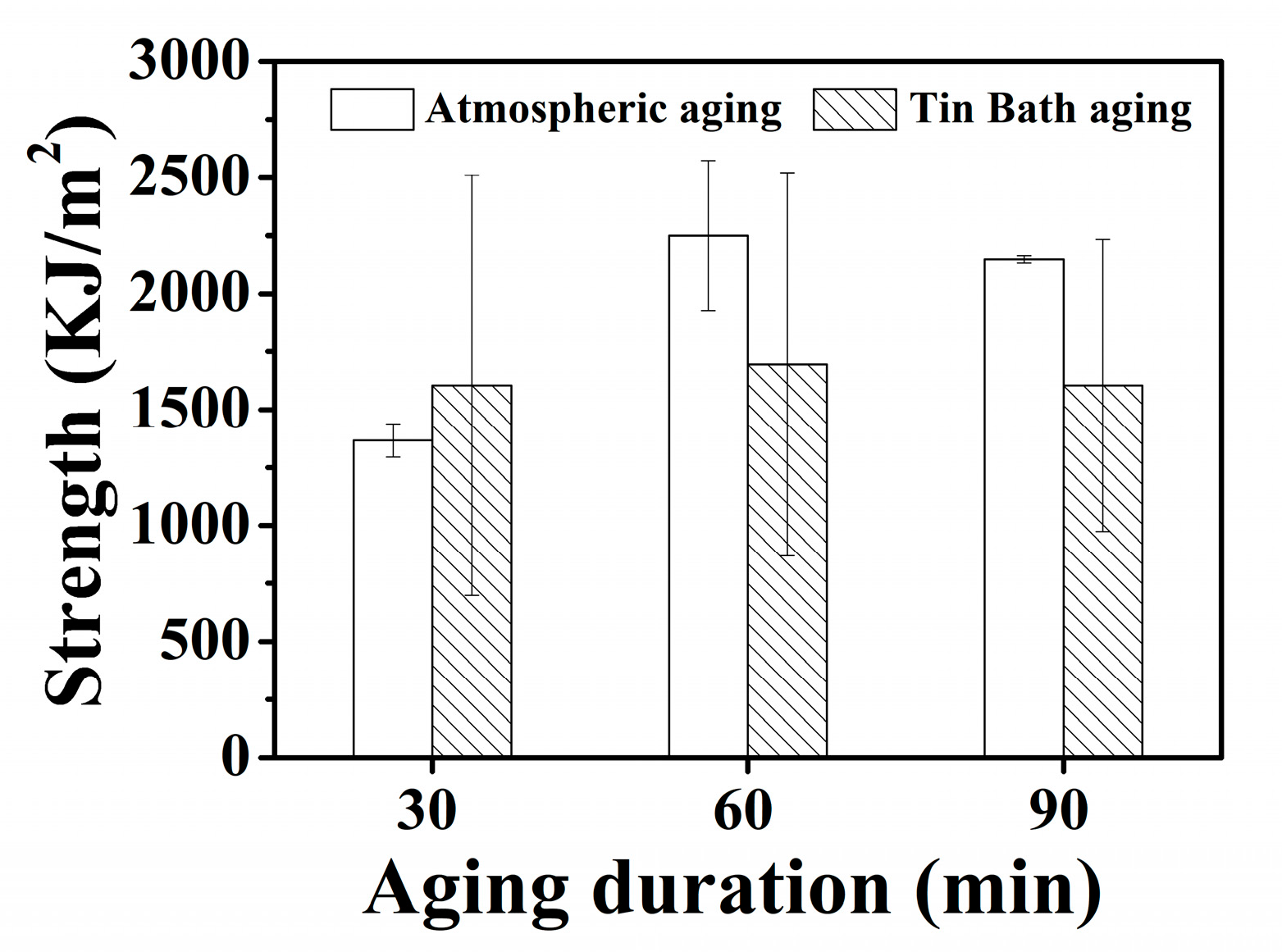
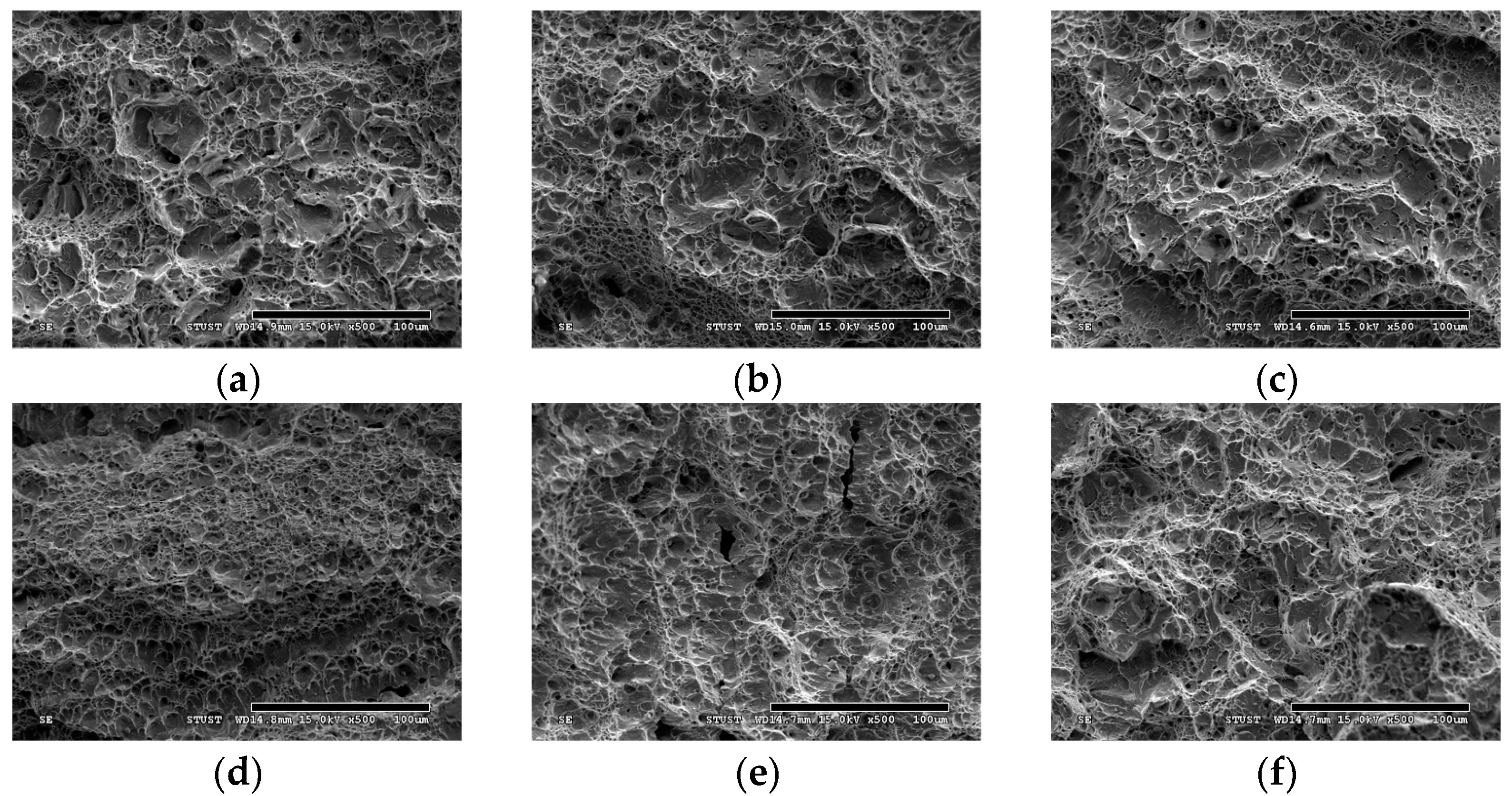
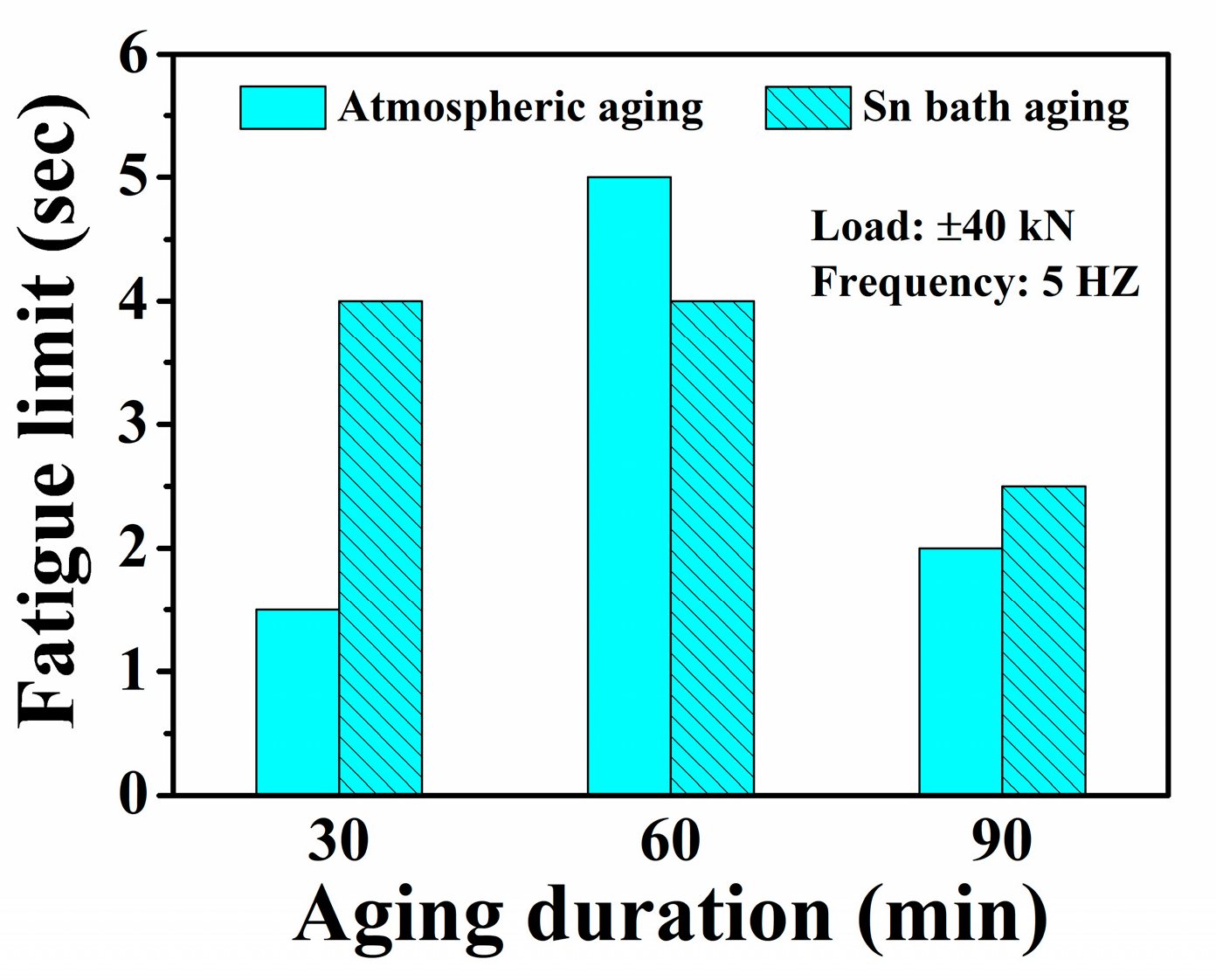
3. Results
- Q1 = Heating the solid tin from 25 °C to its melting point (231.9 °C)
- Q2 = Melting the tin at 231.9 °C
- Q3 = Heating the liquid tin from 231.9 to 500 °C
- m = 1 kg (mass of tin)
- c = 0.227 kJ/kg·°C (specific heat capacity of tin)
- ∆T1 = Temperature change from 25 to 231.9 °C
- Lf = 59.2 kJ/kg (latent heat of fusion of tin)
- ∆T2 = Temperature change from 231.9 to 500 °C
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- In the case of SUS 630 stainless steel, heat treatment induces a martensitic phase transformation, while the aging process promotes the formation of secondary precipitates, both of which are critical to enhancing the steel’s strength and hardness. The present study introduces liquid Sn metal as a medium for aging treatment to explore both the strengthening effects of Sn bath aging on 630 stainless steel and its contribution to environmental sustainability.
- (2)
- The aging process of 630 stainless steel promotes a dense distribution of carbides and precipitates within the martensite matrix, which are the primary contributors to the steel’s performance.
- (3)
- Following aging at 500 °C for 60 min in an atmospheric furnace, the 630 stainless steel demonstrates superior precipitation hardening and reliable ductility (>20%). When aged in a 500 °C Sn bath, the 630 stainless steel achieves similar mechanical enhancements in half the duration required by atmospheric aging, displaying improved fatigue limits due to its high tensile strength and ductility.
- (4)
- Additionally, incorporating liquid Sn as the aging medium significantly increases processing efficiency and contributes to environmental sustainability by reducing the time and energy required for heat treatment. This approach highlights Sn bath aging as a promising, low-emission alternative for the heat treatment industry, offering an efficient route to achieving both enhanced material properties and lower environmental impact.
- (5)
- The liquid Sn may chemically react with certain high-alloy steels or coatings, limiting its applications. Additionally, as a rare metal, tin is relatively expensive, resulting in higher maintenance costs for heat treatment, especially in large-scale applications.
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ščetinec, A.; Klobčar, D.; Nagode, A.; Vuherer, T.; Bračun, D.; Trdan, U. Optimisation of precipitation hardening for 15-5 PH martensitic stainless steel produced by wire arc directed energy deposition. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2023, 28, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milkereit, B.; Rowolt, C.; Chatterjee, D.; Holmestad, R.; Bjorge, R.; Villa, M.; Niessen, F.; Stark, A.; De Geuser, F.; Kessler, O. On the precipitation and transformation kinetics of precipitation-hardening steel X5CrNiCuNb16-4 in a wide range of heating and cooling rates. Materialia 2024, 38, 102254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallaradhya, H.M.; Vijay Kumar, M.; Veeresh Chandra, M.S. Optimization of parameters and prediction of response values using regression and ANN model in resistance spot welding of 17-4 precipitation hardened stainless steel. J. Adv. Manuf. Syst. 2022, 21, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manladan, S.M.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Z.; Wang, C.M. Effect of Ni addition on the microstructural evolution and lap-shear performance of AISI 630 martensitic stainless steel resistance spot welds. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 84, 494–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macha, J.H.; Kirby, M.L.; Hickey, W.F.; Riha, D.S.; Alston, J.K.; Holden, B.B. Investigation of thermal embrittlement of 17-4PH stainless steel main steam isolation valves. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 2021, 21, 1445–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, X.D.; Zhou, X.L.; Li, J.H.; Wang, Y.D.; Zhao, Y.F.; Brochu, M. Selective laser melting and heat treatment of precipitation hardening stainless steel with a refined microstructure and excellent mechanical properties. Scr. Mater. 2020, 178, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kun, L.; Jianbin, Z.; Tianbao, Y.; Albert, T.C.; Susheng, T.; Qian, T.; Huajun, C.; Lawrence, M.E. Homogenization timing effect on microstructure and precipitation strengthening of 17-4PH stainless steel fabricated by laser powder bed fusion. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 52, 102672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, W.; Ebrahimian, M.; Choi, K.; Kim, J.H. Influence of heat treatment on the microstructure and hardness of 17-4PH stainless steel fabricated through direct energy deposition. Met. Mater. Int. 2023, 29, 1750–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swietlicki, A.; Walczak, M.; Szala, M.; Turek, M.; Chocyk, D. Effects of aging heat treatment temperature on the properties of DMLS additive manufactured 17-4PH steel. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci.-Tech. Sci. 2023, 71, e146237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzadeh, H.; Najafizadeh, A. Aging kinetics of 17-4 PH stainless steel. Mater. Phys. Chem. 2009, 116, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.P.; Zhan, D.P.; Qi, X.W.; Jiang, Z.H. Effect of tempering temperature on the microstructure and properties of ultrahigh-strength stainless steel. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 1240–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressan, J.D.; Daros, D.P.; Sokolowski, A.; Mesquita, R.A.; Barbosa, C.A. Influence of hardness on the wear resistance of 17-4 PH stainless steel evaluated by the pin-on-disc testing. J. Mater. Process Technol. 2008, 205, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.Q.; Zhai, Y.C. Aging process optimization for a high strength and toughness of FV520B martensitic steel. Acta Metall. Sin. 2009, 45, 249–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.W.; Gong, X.F.; Wang, J.; Yan, J. Effects on the long-term aging of low temperature salt bath nitride AISI 321 stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 394, 032004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Moghazi, S.N.; Wolfe, T.; Ivey, D.G.; Henein, H. Plasma transfer arc additive manufacturing of 17-4 PH: Assessment of defects. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 108, 2301–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantazopoulos, G.; Papazoglou, T.; Psyllaki, P.; Sfantos, G.; Antoniou, S.; Papadimitriou, K.; Sideris, J. Sliding wear behavior of a liquid introcarburised precipitation-hardening (PH) stainless steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 187, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.H.; Zhuang, Y.; Ouyang, H.S.; Hao, J.H.; Han, X.H. Experimental investigation on optimization of the performance of gallium-based liquid metal with high thermal conductivity as thermal interface material for efficient electronic cooling. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 226, 125455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Z.; Repaka, D.V.M.; Suwardi, A.; Zhu, Q.; Wu, J.; Xu, J.W. Thermal and electrical properties of liquid metal gallium during phase transition. Trans. Tianjin. Univ. 2023, 29, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.L.; Wei, X.L.; Ding, J.; Wang, W.L.; Lu, J.F. Bi-Sn-In phase change material with low melting point and high cyclic stability for thermal energy storage and management. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 135055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, C.N.; Chiou, C.S.; Yang, J.R. Aging reactions in a 17-4 PH stainless steel. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2002, 74, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hebert, R.J.; Aindow, M. Effect of heat treatments on microstructural evolution of additively manufactured and wrought 17-4 PH stainless steel. Mater. Des. 2018, 156, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantazopoulos, G.; Papazoglou, T.; Antoniou, S.; Sideris, J. Tribological behavior of a liquid nitride precipitation-hardening (PH) stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Forum 2003, 426–432, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, U.K.; Banerjee, S.; Krishnan, R. Effects of aging on the microstructure of 17-4 PH stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1988, 104, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.S.; Fu, B.; Kong, L.L.; Wang, Y.Q.; Li, N. Microstructure and mechanical properties of 9Cr18Mo martensitic stainless steel fabricated by strengthening-toughening treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 869, 144783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, R.Z.; Sun, M.J.; Liu, W.Q. Atom probe characterization of Cu-rich precipitates in different phase of 15-5 PH stainless steel in over-aged condition. Mater. Charact. 2022, 191, 112184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.W.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Yang, L.H. Research and development of low carbon bainite steels. Mater. Rev. 2006, 20, 84–86. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zou, H.; Li, C.; Qiu, S.; Shen, B.L. The effect of microstructural evolution on hardening behavior of type 17-4PH stainless steel in long-term aging at 350 °C. Mater. Charact. 2006, 57, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.Y.; Lin, J.W.; Tai, C.L.; Chung, T.F.; Yang, Y.L.; Tsao, T.C.; Lu, S.Y.; Chen, J.J.; Chiu, P.H.; Chen, C.Y.; et al. Effect of repeated-tempering induced martensite o the microstructural evolution in 17-7 PH stainless steel. Mater. Charact. 2024, 214, 114091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. Heat treating of precipitation-hardenable stainless steels and iron-base superalloys. In ASM Handbook; ASM International: Tokyo, Japan, 2014; pp. 397–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, T.W. The heat capacity of liquid metals. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1966, 1, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutchak, V.I.; Osipenko, V.P.; Panasyuk, P.V. Thermal conductivity of Sn-Bi alloys in the solid and liquid states. Soviet Phys. J. 1968, 11, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plevachuk, Y.; Sklyarchuk, V.; Hoyer, W.; Kaban, I. Electrical conductivity, thermoelectric power and viscosity of liquid Sn-based alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 4632–4635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafat, S.; Ghoniem, N. Summary of Thermo-Physical Properties of Sn, and Compounds of Sn-H, Sn-O, Sn-C, Sn-Li, and Sn-Si and Comparison of Properties of Sn, Sn-Li, Li, and Pb-Li; Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering Department, University of California Los Angeles: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]

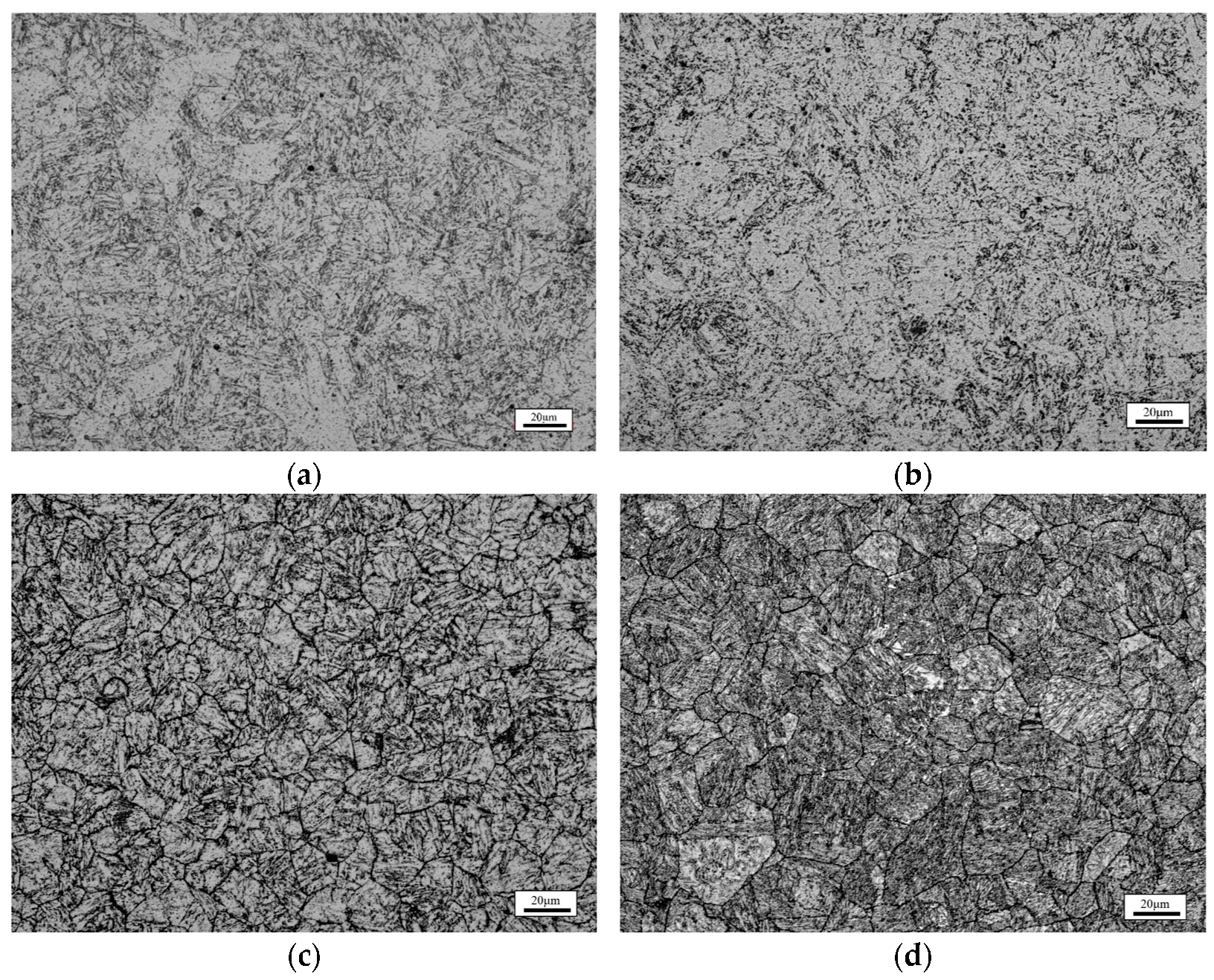
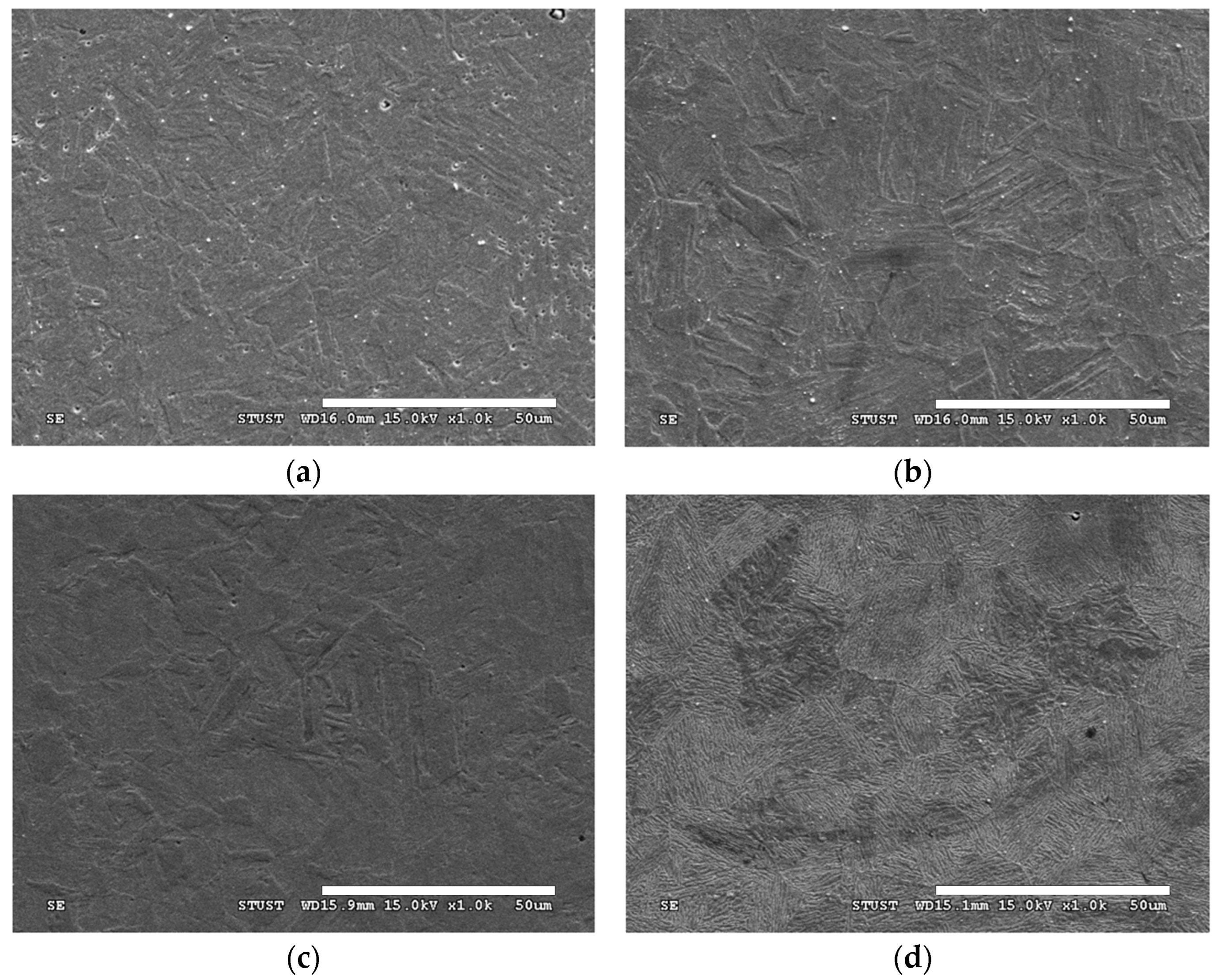
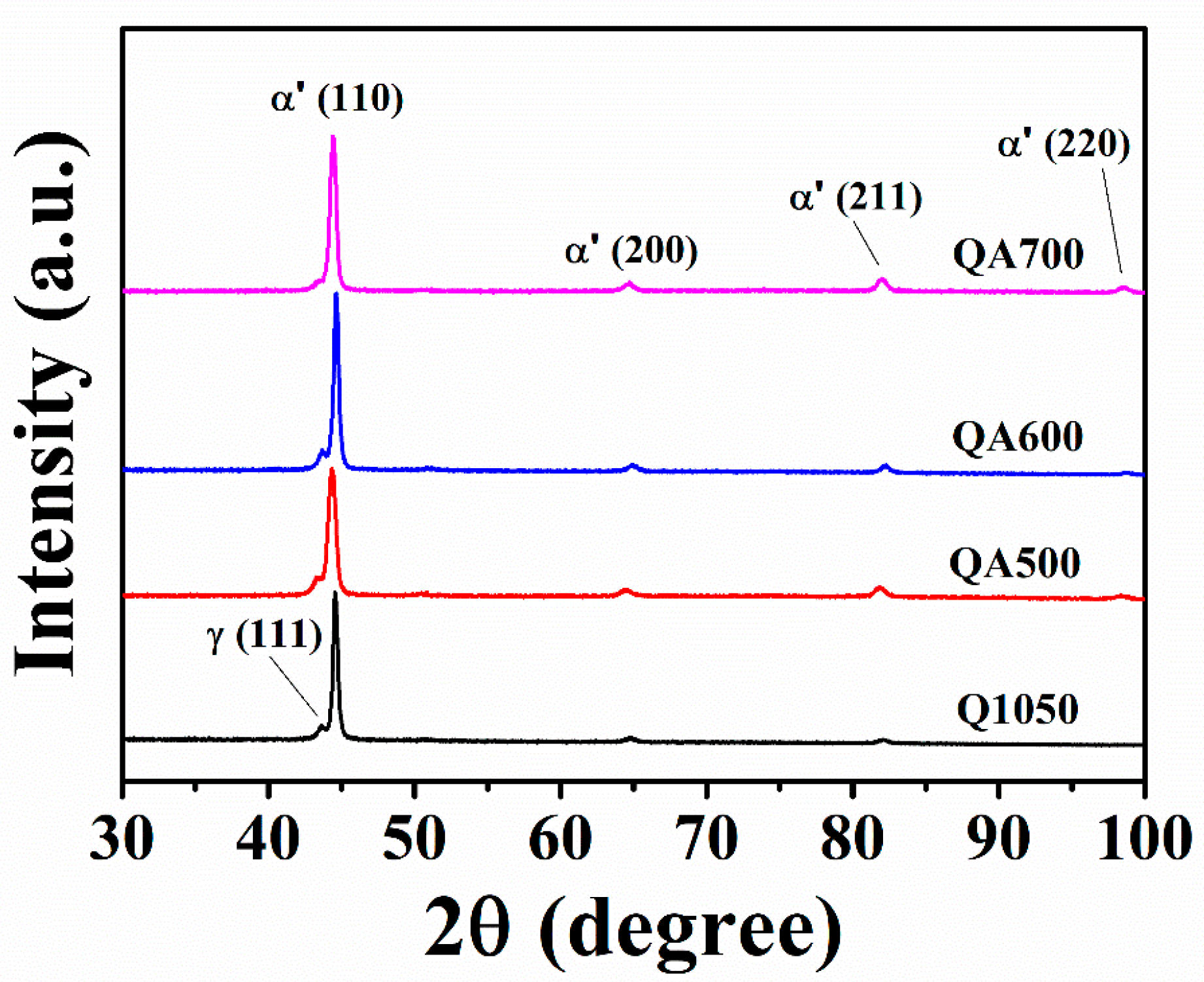

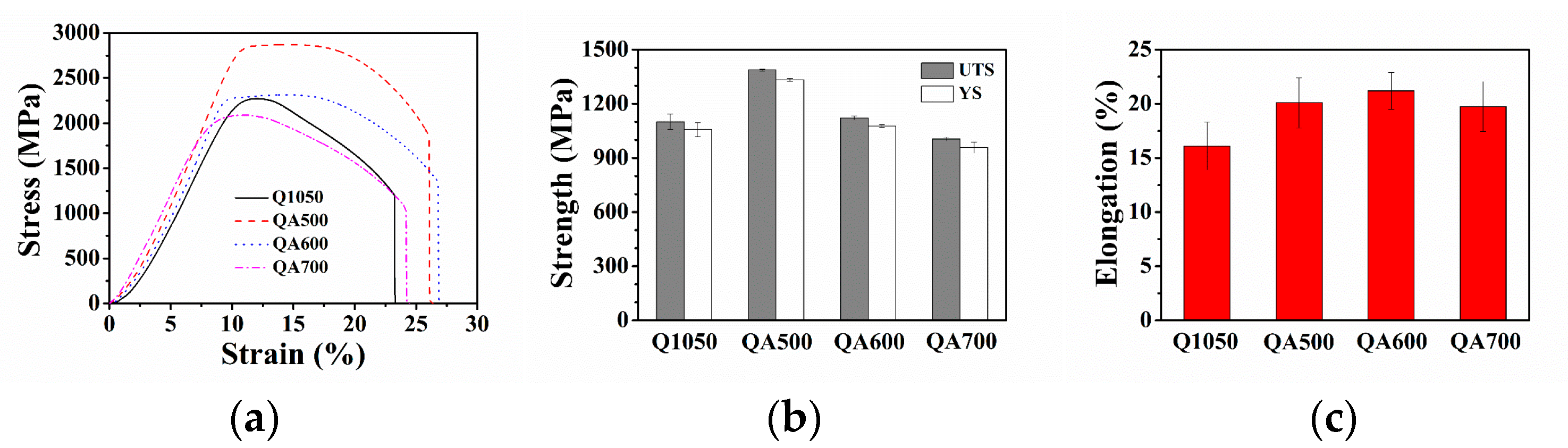
| Wt.% | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Ni | Cr | Cu | Nb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUS630 | <0.07 | <1.00 | <1.00 | <0.04 | <0.03 | 3.00–5.00 | 15.00–17.50 | 3.00–5.00 | 0.15–0.45 |
| Quenching Medium | Residual Stress (MPa) | Retained Austenite (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Air | −365 | 2.3 |
| Water | −437 | 1.1 |
| 30 min Sn Bath Aging | 60 min Atmospheric Aging | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical properties | Tensile strength | ○ | ◎ |
| Elongation | ◎ | ○ | |
| Hardness | ○ | ◎ | |
| Fatigue limits | ○ | ○ | |
| Benefits | Energy consumption (kWh) | 1920 | 3840 |
| Carbon emissions (tCO2e/year) | 0.9772 | 1.8970 | |
| Economics (TWD) | 8256 | 16,512 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, K.-J.; Chuang, F.-S. Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of SUS 630 Stainless Steel: Effects of Age Hardening in a Tin Bath and Atmospheric Environments. Materials 2025, 18, 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18030574
Chen K-J, Chuang F-S. Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of SUS 630 Stainless Steel: Effects of Age Hardening in a Tin Bath and Atmospheric Environments. Materials. 2025; 18(3):574. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18030574
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Kuan-Jen, and Fu-Sung Chuang. 2025. "Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of SUS 630 Stainless Steel: Effects of Age Hardening in a Tin Bath and Atmospheric Environments" Materials 18, no. 3: 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18030574
APA StyleChen, K.-J., & Chuang, F.-S. (2025). Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of SUS 630 Stainless Steel: Effects of Age Hardening in a Tin Bath and Atmospheric Environments. Materials, 18(3), 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18030574






