Influence of the Elastic Modulus on the Osseointegration of Dental Implants
Abstract
1. Introduction
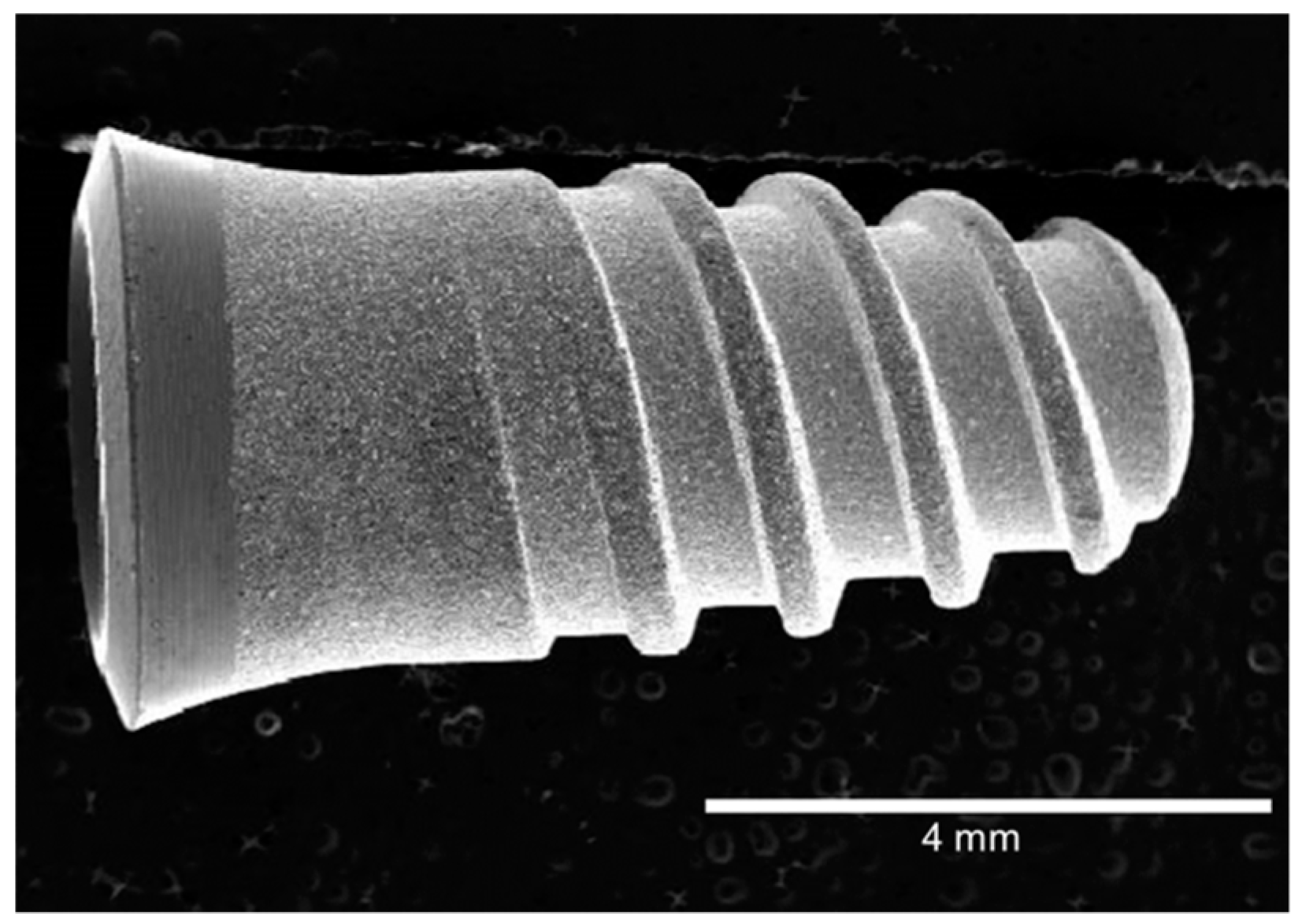
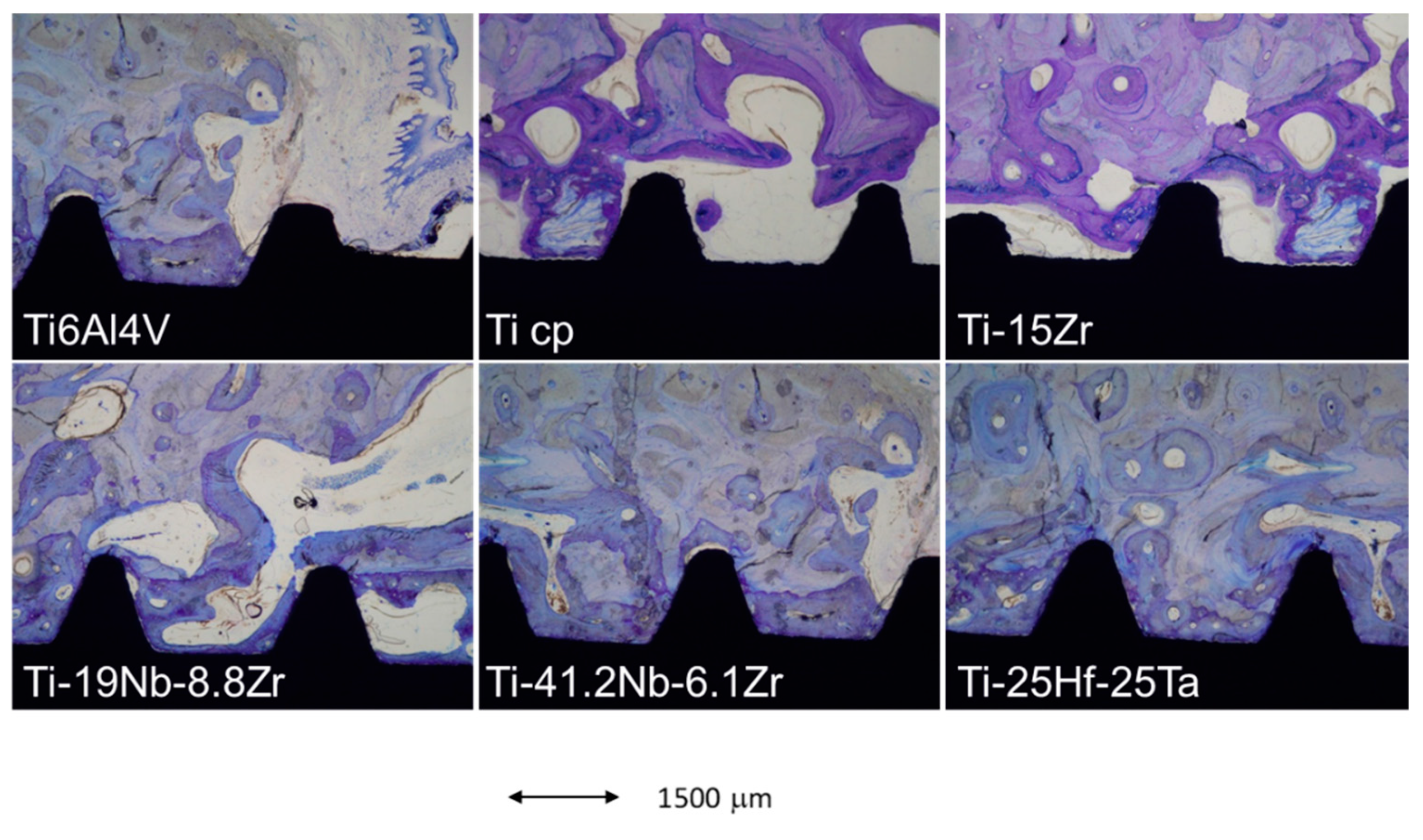
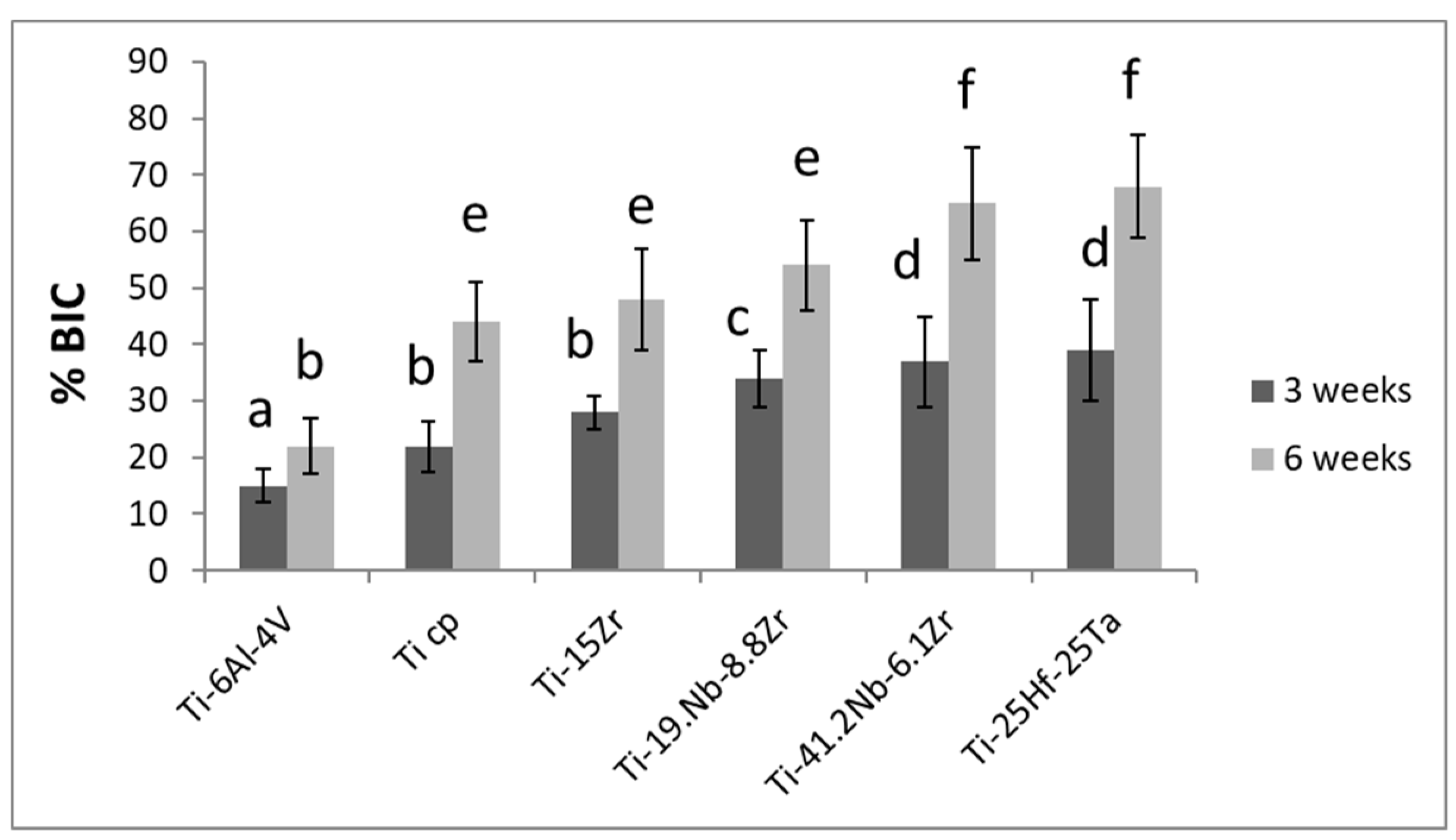
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sumner, D.R.; Turner, T.M.; Igloria, R.; Urban, R.M.; Galante, J.O. Functional adaptation and ingrowth of bone vary as a function of hip implant stiffness. J. Biomech. 1998, 31, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, M.; Singh, A.K.; Asokamani, R.; Gogia, A.K. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants—A review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2009, 54, 397–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niinomi, M.; Nakai, M.; Hieda, J. Development of new metallic alloys for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 3888–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.Y.; Hashimoto, S.; Kim, J.L.L.; Hosoda, H.; Miyazaki, S. Mechanical Properties and Shape Memory Behavior of Ti-Nb Alloys. Mater. Trans. 2004, 45, 2443–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, H.; Watanabe, S.; Hanada, S. Beta TiNbSn Alloys with Low Young’s Modulus and High Strength. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, S.; Kim, H.Y.; Hosoda, H. Development and characterization of Ni-free Ti-base shape memory and superelastic alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 438, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoda, H.; Fukui, Y.; Inamura, T.; Wakashima, K.; Miyazaki, S.; Inoue, K. Mechanical Properties of Ti-Base Shape Memory Alloys. Mater. Sci. Forum. 2003, 426–432, 3121–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Ikehara, Y.; Kim, J.I.; Hosoda, H.; Miyazaki, S. Martensitic transformation, shape memory effect and superelasticity of Ti–Nb binary alloys. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 2419–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.; Gil, F.J.; Peña, J.; Manero, J.M. Characterization of two Ti-Nb-Hf-Zr alloys under different cold rolling conditions. J. Mater. Eng. Performance. 2011, 20, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.; Peña, J.; Manero, J.M.; Gil, F.J. Influence of Cold Work in the Elastic Modulus of the Ti-16.2Hf-24.8Nb-1Zr Alloy Characterized by Instrumented Nanoindentation. Key Eng. Mater. 2010, 423, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.; Peña, J.; Manero, J.M.; Arciniegas, M.; Gil, F.J. Optimization of the Ti-16.2Hf-24.8Nb-1Zr Alloy by Cold Working. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2009, 18, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.; Peña, J.; Manero, J.M.; Arciniegas, M.; Gil, F.J. Design and Characterization of New Ti-Nb-Hf Alloys. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2009, 18, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.; Peña, J.; Gil, F.J.; Manero, J.M. Low modulus Ti–Nb–Hf alloy for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 42, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, M.; Salvagni, E.; Rodríguez-Cabello, J.C.; Rupérez, E.; Gil, F.J.; Peña, J.; Manero, J.M. A low elastic modulus Ti-Nb-Hf alloy bioactivated with an elastin-like protein-based polymer enhances osteoblast cell adhesion and spreading. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2013, 101, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titanium alloy with extra-low modulus and superelasticity and its producing method and processing (2004). Available online: http://www.google.ch/patents/US20070137742?utm_source=gb-gplus-sharePatent (accessed on 12 May 2017).
- Saito, T.; Furuta, T.; Hwang, J.H.; Kuramoto, S.; Nishino, K.; Suzuki, K.; Chen, R.; Yamada, A.; Ito, K.; Seno, Y.; et al. Multifunctional Alloys Obtained via a Dislocation-Free Plastic Deformation Mechanism. Science 2017, 80, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.L.; Li, S.J.; Sun, S.Y.; Zheng, C.Y.; Yang, R. Elastic deformation behaviour of Ti–24Nb–4Zr–7.9Sn for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 2007, 3, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feighan, J.E.; Goldberg, V.M.; Davy, D.; Parr, J.A.; Stevenson, S. The influence of surface-blasting on the incorporation of titanium-alloy implants in a rabbit intramedullary model. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1995, 77, 1380–1395. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Fan, X.; Li, X.; Fu, J.; Li, S.; Fan, H.; Guo, Z. Low elastic modulus contributes to the osteointegration of titanium alloy plug. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2013, 101B, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, M.; Huang, Y.; Heng, B.C.; Mo, X.; Liu, Y.; Wei, D.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. Synergistic effects of elastic modulus and surface topology of Ti-based implants on early osseointegration. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 43685–43696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuno, H.; Yokoyama, A.; Watari, F.; Uo, M.; Kawasaki, T. Biocompatibility and osteogenesis of refractory metal implants, titanium, hafnium, niobium, tantalum and rhenium. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arciniegas, M.; Manero, J.M.; Peña, J.; Gil, F.J.; Planell, J.A. Study of new multifunctional shape memory and low elastic modulus Ni-free Ti alloys”. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2008, 39, 742–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arciniegas, M.; Peña, J.; Manero, J.M.; Paniagua, J.C.; Gil, F.J. Quantum parameters for guiding the design of Ti alloys with shape memory and/or low elastic modulus”. Philos. Mag. 2008, 88, 2529–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, F.J.; Manzanares, N.; Badet, A.; Aparicio, C.; Ginebra, M.P. Biomimetic treatment on dental implants for short-term bone regeneration. Clin. Oral Investig. 2018, 18, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Ti alloys | E (GPa) |
|---|---|
| Ti-6Al-4V | 113 ± 3 |
| Ti cp | 107 ± 3 |
| Ti-15Zr | 103 ± 2 |
| Ti-19.1Nb-8.8Zr | 74 ± 2 |
| Ti-41.2Nb-6.1Zr | 67 ± 2 |
| Ti-25Hf-25Ta | 53 ± 3 |
| Ti Alloys | Before | Shot Blasting | After | Shot Blasting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ra (µm) | Pc (cm−1) | Ra (µm) | Pc (cm−1) | |
| Ti-6Al-4V | 0.56 ± 0.14 | 8.2 ± 0.3 | 1.99 ± 0.41 | 98.3 ± 2.4 |
| Ti cp | 0.43 ± 0.11 | 9.9 ± 1.2 | 2.33 ± 0.54 | 70.9 ± 9.2 |
| Ti-15Zr | 0.33 ± 0.07 | 8.4 ± 1.7 | 2.23 ± 0.76 | 88.1 ± 11.1 |
| Ti-19.1Nb-8.8Zr | 0.44 ± 0.10 | 7.3 ± 1.6 | 1.74 ± 0.25 | 82.1 ± 10.0 |
| Ti-41.2Nb-6.1Zr | 0.33 ± 0.07 | 8.8 ± 1.2 | 1.83 ± 0.33 | 92.1 ± 13.0 |
| Ti-25Hf-25Ta | 0.23 ± 0.05 | 6.9 ± 2.2 | 2.33 ± 0.53 | 70.9 ± 9.2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brizuela, A.; Herrero-Climent, M.; Rios-Carrasco, E.; Rios-Santos, J.V.; Pérez, R.A.; Manero, J.M.; Gil Mur, J. Influence of the Elastic Modulus on the Osseointegration of Dental Implants. Materials 2019, 12, 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12060980
Brizuela A, Herrero-Climent M, Rios-Carrasco E, Rios-Santos JV, Pérez RA, Manero JM, Gil Mur J. Influence of the Elastic Modulus on the Osseointegration of Dental Implants. Materials. 2019; 12(6):980. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12060980
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrizuela, Aritza, Mariano Herrero-Climent, Elisa Rios-Carrasco, Jose Vicente Rios-Santos, Roman A. Pérez, Jose Maria Manero, and Javier Gil Mur. 2019. "Influence of the Elastic Modulus on the Osseointegration of Dental Implants" Materials 12, no. 6: 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12060980
APA StyleBrizuela, A., Herrero-Climent, M., Rios-Carrasco, E., Rios-Santos, J. V., Pérez, R. A., Manero, J. M., & Gil Mur, J. (2019). Influence of the Elastic Modulus on the Osseointegration of Dental Implants. Materials, 12(6), 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12060980










