Prognostic Value of Fibrinogen-to-Albumin Ratio and Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients on Peritoneal Dialysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statements and Study Population
2.2. Data Collection and Laboratory Analyses
2.3. Outcome Measures
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CIn | Chronic inflammation |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| HD | Hemodialysis |
| ESKD | End-stage kidney disease |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| KRT | Kidney replacement therapy |
| PD | Peritoneal dialysis |
| NLR | Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| FAR | Fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio |
| UCCS | University Clinical Centre of Serbia |
| HTN | Hypertension |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| PVD | Peripheral vascular disease |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| IHD | Ischemic heart disease |
| PET | Peritoneal Equilibration Test |
| Ccr | Total weekly creatinine clearance |
| sGlc | Serum glucose |
| sUr | Serum urea |
| sCr | Serum creatinine |
| Chol | Total serum cholesterol |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| PTH | Parathyroid hormone |
| CCI | Charlson Comorbidity Index |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| CAPD | Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis |
| APD | Automated peritoneal dialysis |
| GN | Glomerulonephritis |
| ADPKD | Autosomal polycistic kidney disease |
| TIN | Tubulointerstitial nephritis |
| CMP | Cardiomyopathy |
| AMI | Acute myiocardial infarction |
| CVI | Cerebrovascular insult |
| AIDS | Acquired immune deficiency syndrome |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| GFR | Glomerular filtration rate |
| Kt/V | Peritoneal dialysis treatment adequacy |
| WBC | White blood cell count |
| CVE | Cardiovascular event |
| RKF | Residual kidney function |
| PLR | Platelet and lymphocyte ratio |
| hs | High-sensitivity |
| TNF-alpha | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| Alb | Albumin |
| Ly | Lymphocyte |
| Fib | Fibrinogen |
| IL-6 | interleukin 6 |
| CAR | C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio |
| MIA | malnutrition–inflammation–atherosclerosis |
References
- Yogesh, M.; Parmar, P.A.; Sharma, S.; Kakadiya, J.P.; Lakkad, D. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Novel Predictor of Sarcopenia in Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study Exploring Associations across Body Composition Categories. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2025, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Wu, X.; Li, H.; Ning, X.; Shi, Y.; Niu, H. Fibrinogen/Albumin Ratio: A More Powerful Prognostic Index for Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 50, e13266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Takeuchi, Y.; Matsuda, K.; Kagaya, S.; Saito, A.; Fukami, H.; Ojima, Y.; Nagasawa, T. Pre-Dialysis Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio, a Novel and Strong Short-Term Predictor of All-Cause Mortality in Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy: Results from a Single-Center Study. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2017, 21, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Liu, G.; Wang, R.; Li, D.; Wang, D. Fibrinogen/Albumin Ratio Is Associated with First-Ever Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Peritoneal Dialysis. Ann. Med. 2025, 57, 2499025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Nie, Y.; Guo, M.; Wang, L.; Shi, Y.; Jiang, X.; Ding, X.; Xu, X.; Ji, J. Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio as a Predictor of Long-Term Outcome in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients: A 5-Year Cohort Study. Blood Purif. 2021, 50, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, L.F.S.; Ng, J.K.; Fung, W.W.; Chan, G.C.; Cheng, P.M.-S.; Chow, K.M.; Leung, C.B.; Li, P.K.-T.; Szeto, C.C. Relationship between Serial Serum Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio, Cardiovascular Mortality, and All-Cause Mortality in Chinese Peritoneal Dialysis Patients. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2023, 48, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, E.; Wu, Y.; Ye, Z.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Shen, N.; Wang, F.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, J. Association of fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients on dialysis with acute coronary syndrome. Postgrad. Med. J. 2025, 101, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-H.; Liu, H.; Jin, D.-H.; Zou, J.; Xie, Y.-X.; Qiu, H.; Jia, M.; Li, D.-M.; Liu, B.-C. Fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio is related to the severity of coronary artery disease in chronic kidney disease patients undergoing coronary angiography. Nefrologia 2022, 42, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cnossen, T.T.; Smit, W.; Konings, C.J.; Kooman, J.P.; Leunissen, K.M.; Krediet, R.T. Quantification of Free Water Transport during the Peritoneal Equilibration Test. Perit. Dial. Int. 2009, 29, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baralić, M.; Pažitná, L.; Brković, V.; Laušević, M.; Gligorijević, N.; Katrlík, J.; Nedić, O.; Robajac, D. Prediction of Mortality in Patients on Peritoneal Dialysis Based on the Fibrinogen Mannosylation. Cells 2023, 12, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Eckardt, K.-U.; Dorman, N.M.; Christiansen, S.L.; Hoorn, E.J.; Ingelfinger, J.R.; Inker, L.A.; Levin, A.; Mehrotra, R.; Palevsky, P.M.; et al. Nomenclature for Kidney Function and Disease: Report of a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Consensus Conference. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 1117–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Khadda, Z.; Lahmamsi, H.; El Karmoudi, Y.; Ezrari, S.; El Hanafi, L.; Houssaini, T.S. Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology: A Global Health Threat in Rural Agricultural Communities—Prevalence, Suspected Causes, Mechanisms, and Prevention Strategies. Pathophysiology 2024, 31, 761–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.A.; Sharif, D.A.; Almukhtar, S.E.; Abd, K.H.; Saleem, Z.S.M.; Hughson, M.D. Incidence of Glomerulonephritis and Non-Diabetic End-Stage Renal Disease in a Developing Middle-East Region near Armed Conflict. BMC Nephrol. 2018, 19, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Q.; Axelsson, J.; Stenvinkel, P.; Lindholm, B. Chronic Systemic Inflammation in Dialysis Patients: An Update on Causes and Consequences. ASAIO J. 2004, 50, lii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Lindholm, B.; Stenvinkel, P. Inflammation as a Cause of Malnutrition, Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease, and Poor Outcome in Hemodialysis Patients. Hemodial. Int. 2004, 8, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, G.; Lindholm, B.; Stenvinkel, P. Chronic Inflammation in End-Stage Renal Disease and Dialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, iii35–iii40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.E.; Brunt, V.E.; Shiu, Y.T.; Bunsawat, K. Endothelial dysfunction in chronic kidney disease: A clinical perspective. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2025, 329, H135–H153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Lin, Y.L.; Hsu, B.G. Endothelial dysfunction in chronic kidney disease: Mechanisms, biomarkers, diagnostics, and therapeutic strategies. Tzu Chi Med. J. 2025, 37, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikami, R.; Mizutani, K.; Gohda, T.; Matsuyama, Y.; Gotoh, H.; Nakagawa, K.; Takemura, S.; Aoyama, N.; Matsuura, T.; Kido, D.; et al. Malnutrition-inflammation-atherosclerosis (MIA) syndrome associates with periodontitis in end-stage renal disease patients undergoing hemodialysis: A cross-sectional study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surma, S.; Banach, M. Fibrinogen and atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases—Review of the literature and clinical studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecoits-Filho, R.; Lindholm, B.; Stenvinkel, P. The malnutrition, inflammation, and atherosclerosis (MIA) syndrome–The heart of the matter. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2002, 17 (Suppl. 11), 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, F.C.; Sun, J.; Qureshi, A.R.; Dai, L.; Snaedal, S.; Bárány, P.; Heimbürger, O.; Lindholm, B.; Stenvinkel, P. The higher mortality associated with low serum albumin is dependent on systemic inflammation in end-stage kidney disease. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Fan, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, W. Fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio predicts mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1539114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Xu, W.; Zha, B.; Shi, J.; Wu, G.; Ding, H. Fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio as an independent risk factor for type 2 diabetic kidney disease. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obesity 2021, 14, 4557–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlacu, A.; Namolovan, C.A.; Brinza, C.; Covic, A.; Floria, M.; Voroneanu, L.; Covic, A. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR)—Independent prognostic marker of renal function decline in chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chermiti, R.; Burtey, S.; Dou, L. Role of uremic toxins in vascular inflammation associated with chronic kidney disease. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 7149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, W.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, P.; He, Q.; Deng, Z. The neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio predicts all-cause and cardiovascular mortality among United States adults with COPD: Results from NHANES 1999–2018. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1443749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, C.C.; Kacso, I.; Moldovan, D.; Potra, A.; Tirinescu, D.; Ticala, M.; Maslyennikov, Y.; Urs, A.; Bondor, C.I. Exploring the associations between inflammatory biomarkers, survival, and cardiovascular events in hemodialysis patients and the interrelationship with nutritional parameters—The experience of a single Transylvanian dialysis center. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, P.; Li, B.; Li, Y. Prognostic potential of inflammatory markers in chronic kidney disease patients combined with acute myocardial infarction. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 11, 1430215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Qiu, P.; Luo, L.; Jiang, L.; Chen, Y.; Yan, C.; Zhan, X. Serum C-Reactive Protein to Albumin Ratio and Mortality Associated with Peritoneal Dialysis. Ren. Fail. 2020, 42, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atas, D.B.; Asicioglu, E.; Tugcu, M.; Arikan, I.H.; Velioglu, A. Long-Term Predictors of Mortality in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients. Turk. J. Nephrol. 2021, 30, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atas, D.B.; Tugcu, M.; Velioglu, A.; Arikan, H.; Asicioglu, E. Ferritin to Albumin Ratio Predicts Mortality in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2025, 29, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Jang, H.M.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Kang, S.W.; Yang, C.W.; Kim, N.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Cho, J.H.; et al. Individualized Prediction of Mortality Using Multiple Inflammatory Markers in Patients on Dialysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
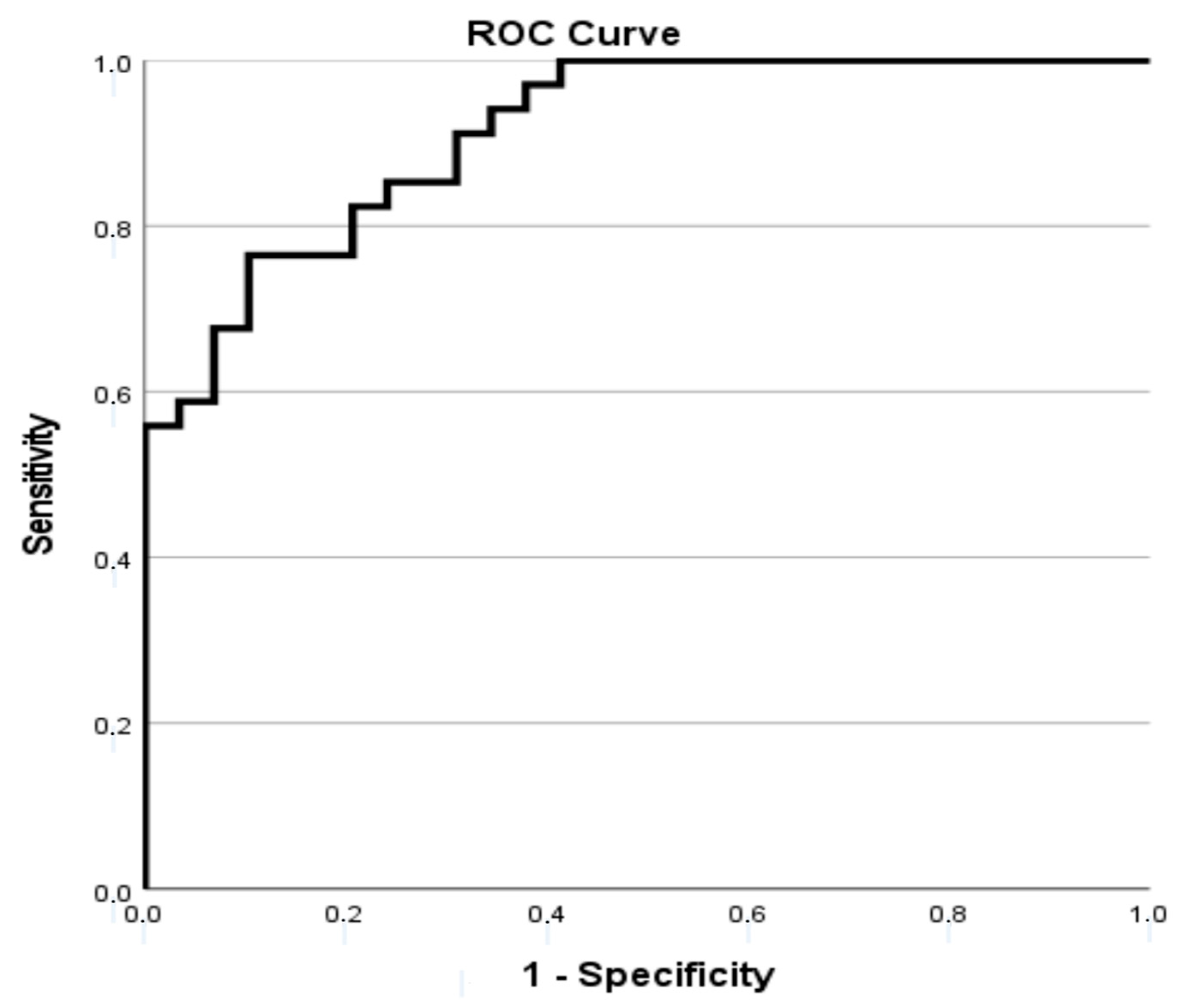
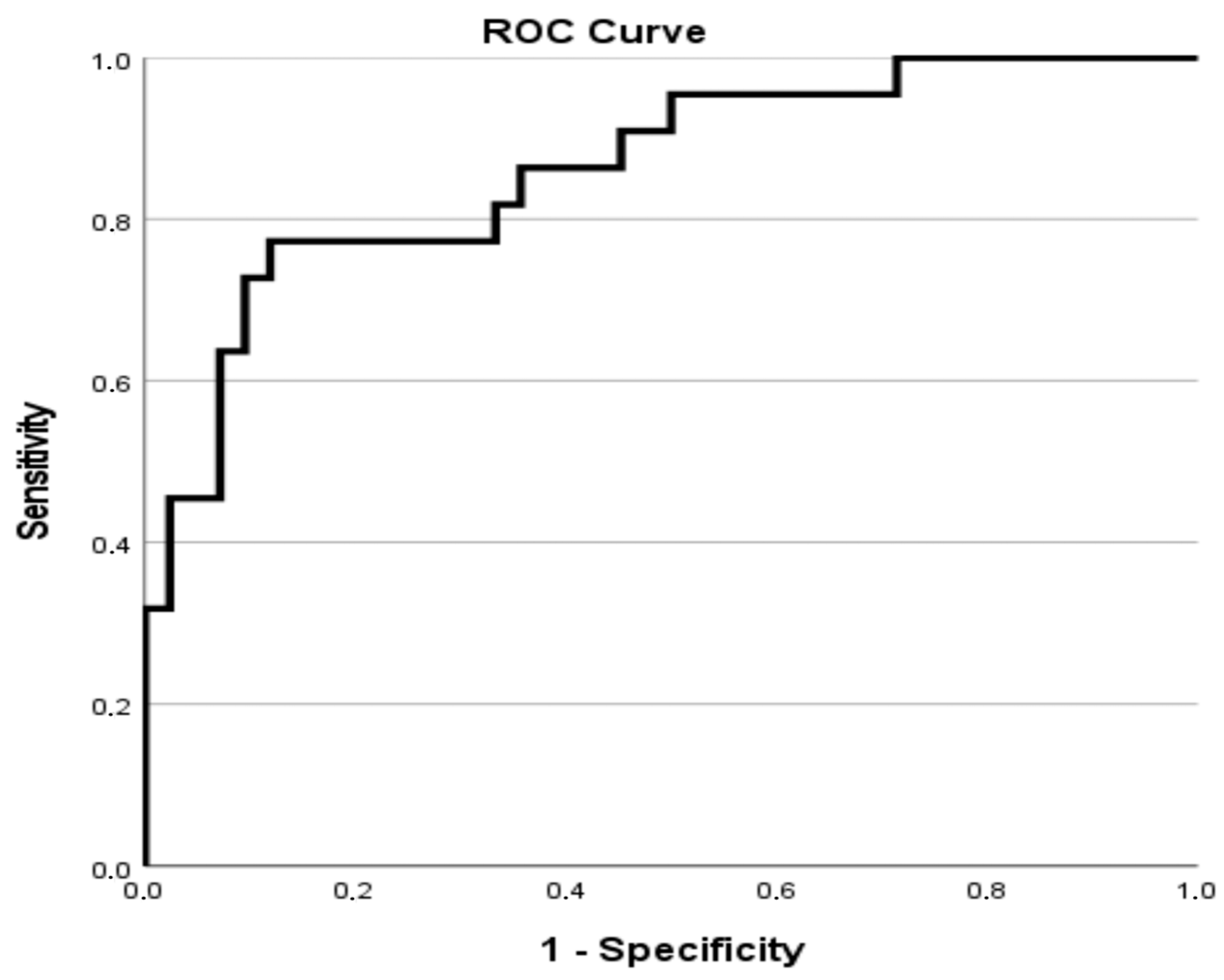
| Variables | Total |
|---|---|
| Age, years | 63 [16] |
| Female, n (%) | 30 (46.2) |
| Primary cause of ESKD, n (%) | |
| Hypertensive nephrosclerosis | 25 (38.4) |
| Diabetic nephropathy | 18 (27.7) |
| Chronic GN | 13 (20.0) |
| TIN | 2 (3.1) |
| ADPKD | 1 (1.5) |
| Other | 6 (9.2) |
| Comorbidities, n (%) | |
| CMP | 12 (18.5) |
| AMI | 12 (18.5) |
| CVI | 5 (7.7) |
| PVD | 10 (15.4) |
| Dementia | 2 (3.1) |
| COPD | 4 (6.1) |
| Peptic ulcer | 2 (3.1) |
| Liver disease | 1 (1.5) |
| CTD | 4 (6.2) |
| Cancer or AIDS | 9 (13.8) |
| Leukemia/Lymphoma | 1 (1.5) |
| Period on PD, months | 22.00 [42.00] |
| CAPD as dialysis modality, n (%) | 59 (90.8) |
| Icodextrine solution used, n (%) | 10 (15.4) |
| Daily ultrafiltration, L | 1.10 [0.90] |
| Daily urine volume, L | 0.80 [1.10] |
| Total Kt/V | 2.45 ± 0.59 |
| CCr, L/week | 78.80 [50.38] |
| PET | |
| Glc | 0.46 ± 0.15 |
| Cr | 0.65 ± 0.13 |
| CCI | 5.00 [4.00] |
| Composite outcome, n (%) | 36 (55.4) |
| Outcome Death, n (%) | 23 (35.4) |
| Variables | Total |
|---|---|
| FAR | 0.14 [0.04] |
| NLR | 3.27 [2.89] |
| CRP, mg/mol | 3.90 [6.90] |
| sGlc, mmol/L | 5.40 [2.40] |
| sUr, mmol/L | 15.13 ± 4.55 |
| sCr, mmol/L | 721.51 ± 207.44 |
| Chol, mmol/L | 4.73 [1.57] |
| TG, mmol/L | 1.56 [0.88] |
| PTH, pg/mL | 409.11 ± 248.92 |
| Alb (g/L) | 36 [28–40] |
| Ly (×109/L) | 1.6 [0.9–2.3] |
| Variable | PD Technique Survival (n = 29) | Composite Outcome (n = 36) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 61 [25] | 65 [12] | n.s. |
| Sex, n (%) Male Female | |||
| 15 (51.7) | 20 (55.6) | n.s. | |
| 14 (48.3) | 16 (44.4) | n.s. | |
| Icodextrine solution used, n (%) Yes No | 4 (13.8) 25 (86.2) | 30 (83.3) 6 (16.7) | n.s. |
| Dialysis modality, n (%) CAPD APD | 27 (93.1) 2 (6.9) | 32 (88.9) 4 (11.1) | n.s. |
| Period on PD, months | 24.00 [35] | 20.50 [53] | n.s. |
| Daily ultrafiltration, L | 1.10 [0.75] | 1.00 [1.05] | n.s. |
| Daily urine volume, L | 1.00 [1.10] | 0.60 [1.10] | n.s. |
| Total Kt/V | 2.52 ± 0.53 | 2.40 ± 0.64 | n.s. |
| CCr, L/week | 92.84 ± 36.49 | 83.29 ± 20.02 | n.s. |
| PET Glc | 0.46 ± 0.13 | 0.46 ± 0.17 | n.s. |
| PET Cr | 0.66 ± 0.13 | 0.65 ± 0.13 | n.s. |
| CCl | 5.59 ± 2.96 | 6.39 ± 2.50 | n.s. |
| Primary cause of ESKD, n (%) Hypertensive nephrosclerosis Diabetic nephropathy Chronic GN ADPKD TIN Other | 14 (56.0) 4 (22.2) 9 (69.2) 0 (0) 0 (0) 2 (33.3) | 11 (44.0) 14 (77.8) 4 (30.8) 1 (100) 2 (100) 4 (66.7) | 0.036 |
| Comorbidities, n (%) | |||
| CMP No Yes | 27 (50.9) 2 (16.7) | 26 (49.1) 10 (83.3) | 0.031 |
| AMI No Yes | 25 (47.2) 4 (33.3) | 28 (52.8) 8 (66.7) | n.s. |
| CVI No Yes | 26 (43.3) 3 (60.0) | 34 (56.7) 2 (40.0) | n.s. |
| PVD No Yes | 25 (45.5) 4 (40.0) | 30 (54.5) 6 (60.0) | n.s. |
| Dementia No Yes | 28 (44.4) 1 (50.0) | 35 (55.6) 1 (50.0) | n.s. |
| COPD No Yes | 27 (44.3) 1 (33.3) | 34 (55.7) 2 (66.7) | n.s. |
| Peptic ulcer No Yes | 29 (46.0) 0 (0) | 34 (54.0) 2 (100) | n.s. |
| Liver disease No Yes | 28 (43.8) 1 (100) | 36 (56.2) 0 (0) | n.s. |
| CTD No Yes | 26 (42.6) 3 (75.0) | 35 (57.4) 1 (25.0) | n.s. |
| Cancer or AIDS No Yes | 24 (42.9) 5 (55.6) | 32 (57.1) 4 (44.4) | n.s. |
| Leukemia/lymphoma No Yes | 29 (45.3) 0 (0) | 35 (54.7) 1 (100) | n.s. |
| Variables | PD Technique Survival (n = 29) | Composite Outcome (n = 36) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| FAR | 0.14 [0.04] | 0.16 [0.04] | 0.07 |
| NLR | 3.00 [3.46] | 3.62 [2.77] | n.s. |
| CRP, mg/mol | 1.90 [4.40] | 6.25 [6.90] | 0.01 |
| sGlc, mmol/L | 5.20 [1.50] | 5.75 [3.10] | 0.022 |
| sUr, mmol/L | 14.46 ± 3.99 | 15.67 ± 4.94 | n.s. |
| sCr, mmol/L | 705.86 ± 226.66 | 734.11 ± 192.91 | n.s. |
| Chol, mmol/L | 4.97 [1.45] | 4.56 [1.80] | n.s. |
| TG, mmol/L | 1.84 [1.23] | 1.49 [0.84] | 0.040 |
| PTH, pg/mL | 341.00 [299] | 445.00 [294] | n.s. |
| Alb (g/L) | 37 [30–40] | 35 [29–40] | n.s. |
| Ly (×109/L) | 1.6 [0.9–2.3] | 1.55 [0.8–2.8] | n.s. |
| Variables | B | SE | Wald | p-Value | OR (Exp B) | 95% CI for OR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTH | 0.007 | 0.003 | 7.458 | 0.006 | 1.007 | 1.002–1.013 |
| CRP | 0.250 | 0.117 | 4.577 | 0.032 | 1.284 | 1.021–1.615 |
| FAR (Z-score) | 1.665 | 0.774 | 4.622 | 0.032 | 5.285 | 1.158–24.116 |
| TG | −1.313 | 0.705 | 3.462 | 0.063 | 0.269 | 0.068–1.073 |
| NLR | 0.302 | 0.174 | 3.007 | 0.083 | 1.352 | 0.961–1.902 |
| APD vs. CAPD | 4.332 | 2.001 | 4.685 | 0.030 | 76.059 | 1.506–3841.786 |
| Variables | B | SE | Wald | p-Value | OR (Exp(B)) | 95% CI for OR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTH | 0.005 | 0.002 | 5.947 | 0.015 | 1.005 | 1.001–1.009 |
| FAR (z-zone) | 1.384 | 0.626 | 4.889 | 0.027 | 3.990 | 1.170–13.605 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gajić, S.; Bontić, A.; Sič, A.; Karadžić-Ristanović, V.; Stojadinović, M.; Filić, K.; Pavlović, J.; Gavrilović, J.; Petrović, K.; Stanković, S.; et al. Prognostic Value of Fibrinogen-to-Albumin Ratio and Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients on Peritoneal Dialysis. Life 2025, 15, 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111728
Gajić S, Bontić A, Sič A, Karadžić-Ristanović V, Stojadinović M, Filić K, Pavlović J, Gavrilović J, Petrović K, Stanković S, et al. Prognostic Value of Fibrinogen-to-Albumin Ratio and Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients on Peritoneal Dialysis. Life. 2025; 15(11):1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111728
Chicago/Turabian StyleGajić, Selena, Ana Bontić, Aleksandar Sič, Vidna Karadžić-Ristanović, Milorad Stojadinović, Kristina Filić, Jelena Pavlović, Jovana Gavrilović, Kristina Petrović, Sanja Stanković, and et al. 2025. "Prognostic Value of Fibrinogen-to-Albumin Ratio and Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients on Peritoneal Dialysis" Life 15, no. 11: 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111728
APA StyleGajić, S., Bontić, A., Sič, A., Karadžić-Ristanović, V., Stojadinović, M., Filić, K., Pavlović, J., Gavrilović, J., Petrović, K., Stanković, S., Trnić, N., Simović, F., Popović, P., Jovičić-Pavlović, S., Kezić, A., & Baralić, M. (2025). Prognostic Value of Fibrinogen-to-Albumin Ratio and Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients on Peritoneal Dialysis. Life, 15(11), 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111728









