Autologous Blood Injections in Temporomandibular Hypermobility: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Rationale
1.3. Objectives
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Information Sources
2.3. Search Strategy
2.4. Selection and Data Collection Process
2.5. Data Items
2.6. Study Risk of Bias Assessment
2.7. Effect Measures and Synthesis Methods
3. Results
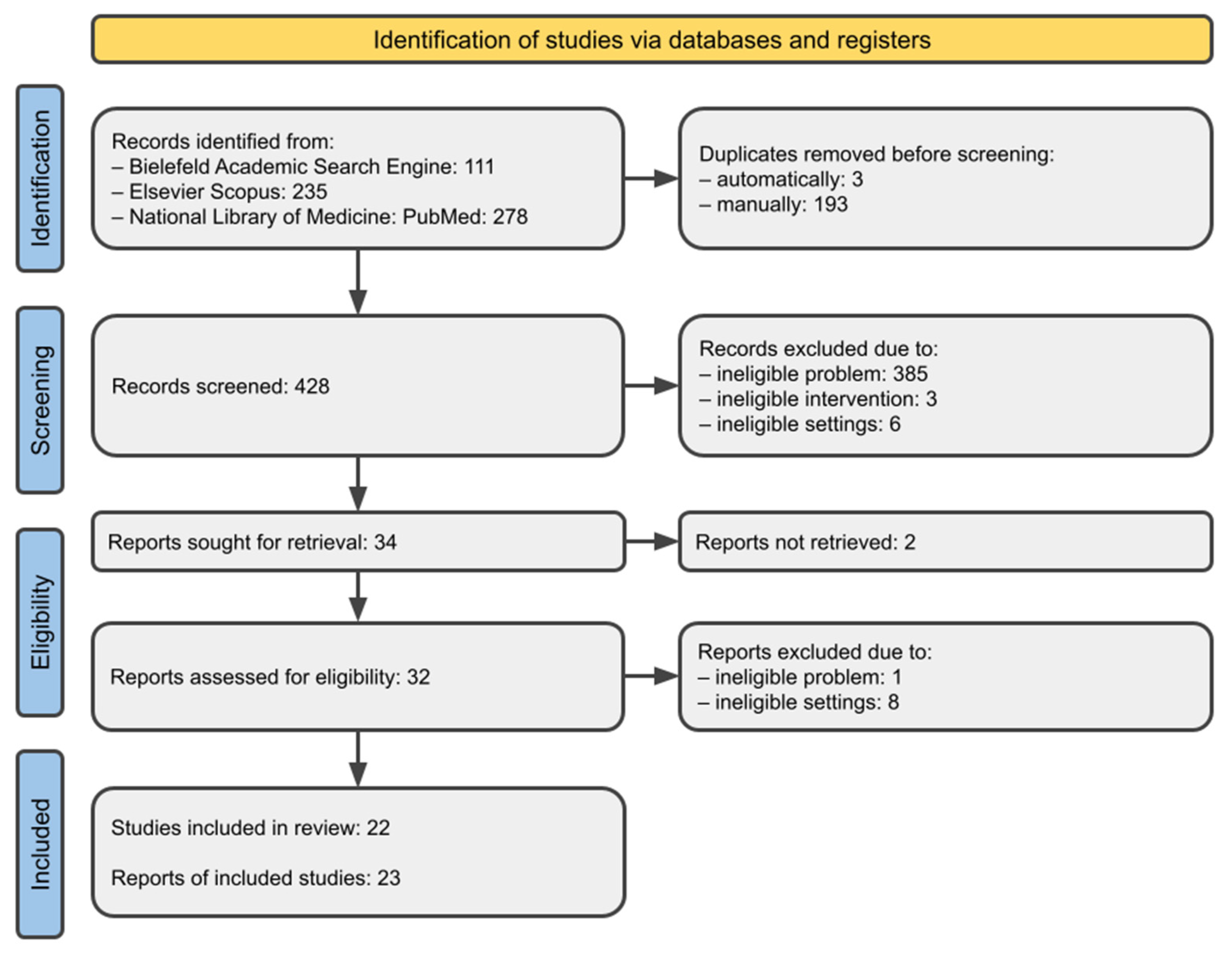
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
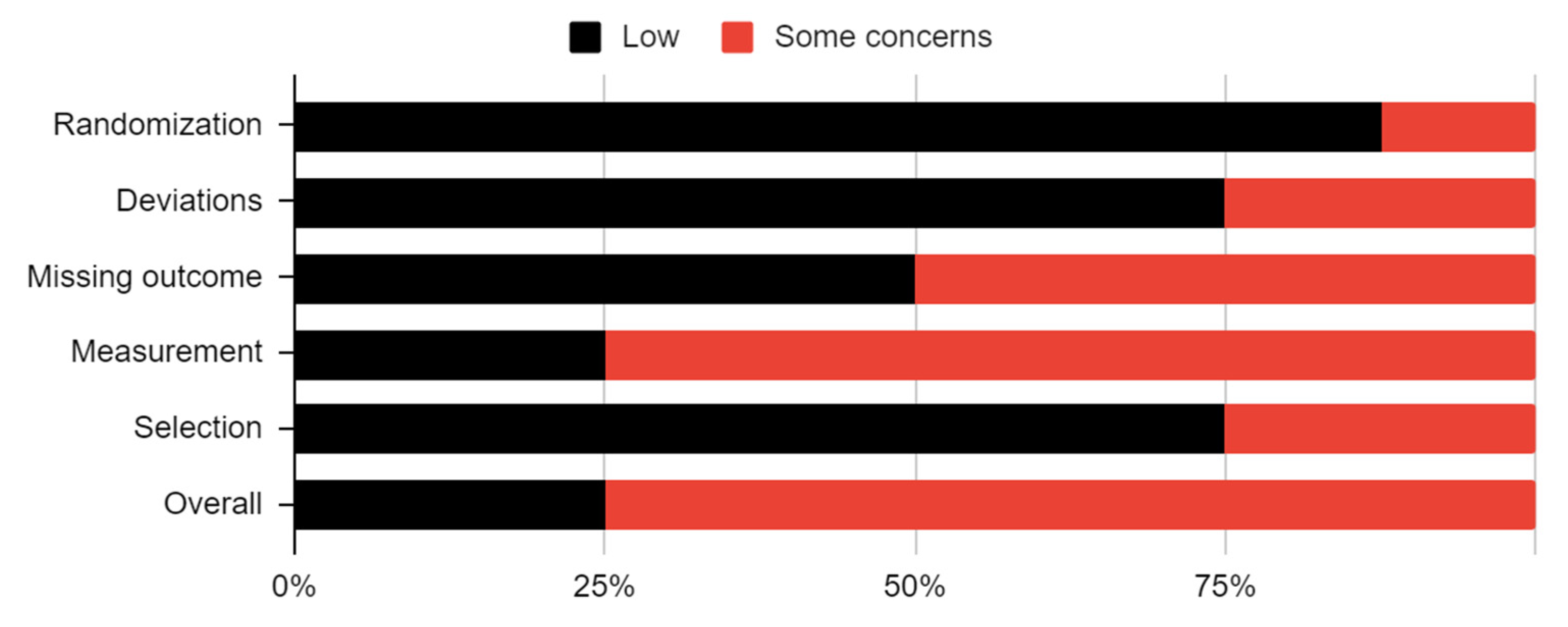
3.3. Risk of Bias in Studies
3.4. Results of Individual Studies
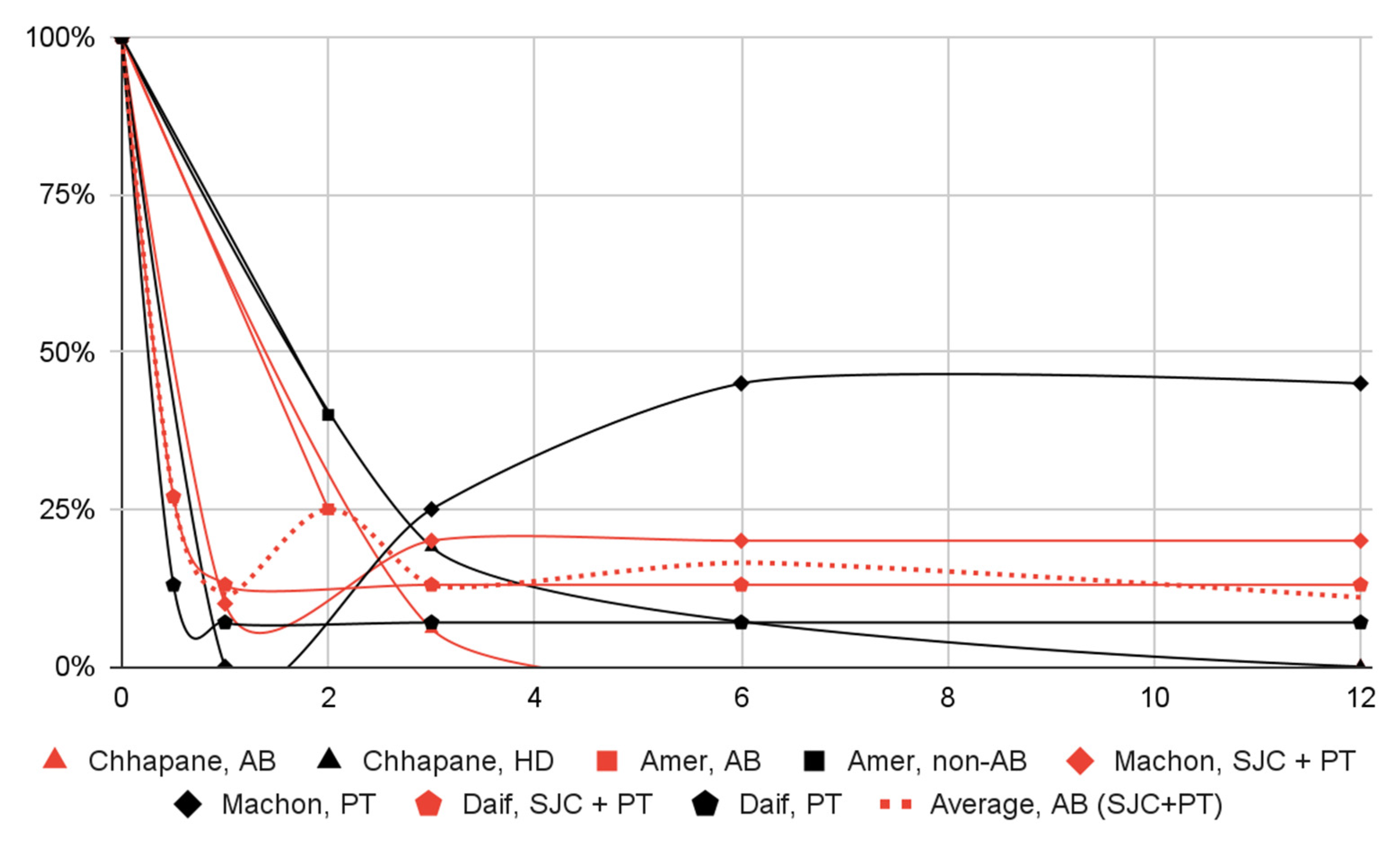
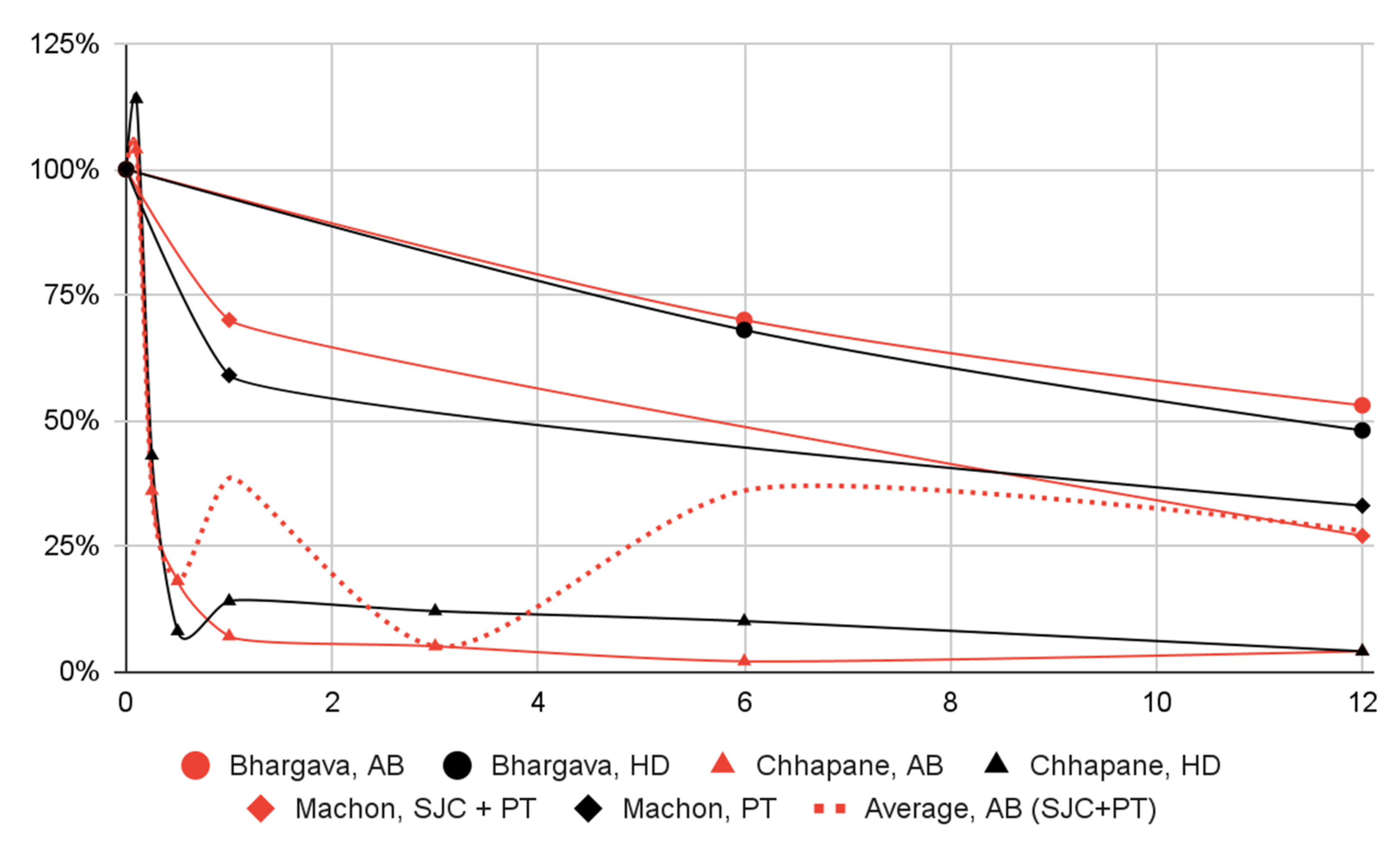
3.5. Results of Syntheses
4. Discussion
4.1. General Interpretation of the Results
4.1.1. Dislocation Episodes
4.1.2. Mandibular Mobility and Articular Pain
4.1.3. Autologous Blood Injections Compared to Hypertonic Dextrose Injections
4.1.4. Peri- and Intracapsular Injections versus Pericapsular Injection Alone
4.2. Limitations of the Evidence
4.3. Limitations of the Review Processes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schiffman, E.; Ohrbach, R.; Truelove, E.; Look, J.; Anderson, G.; Goulet, J.-P.; List, T.; Svensson, P.; Gonzalez, Y.; Lobbezoo, F.; et al. Diagnostic Criteria for Temporomandibular Disorders (DC/TMD) for Clinical and Research Applications: Recommendations of the International RDC/TMD Consortium Network* and Orofacial Pain Special Interest Group†. J. Oral Facial. Pain. Headache 2014, 28, 6–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tocaciu, S.; McCullough, M.J.; Dimitroulis, G. Surgical Management of Recurrent Dislocation of the Temporomandibular Joint: A New Treatment Protocol. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 56, 936–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, S.; Chhabra, N.; Gupta, P. Recurrent Mandibular Dislocation in Geriatric Patients: Treatment and Prevention by a Simple and Non-Invasive Technique. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2015, 14, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquilina, P.; Vickers, R.; McKellar, G. Reduction of a Chronic Bilateral Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation with Intermaxillary Fixation and Botulinum Toxin A. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2004, 42, 272–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, C.M.; Haag, C.; Mühling, J. Treatment of Recurrent Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation with Intramuscular Botulinum Toxin Injection. Clin. Oral Investig. 2003, 7, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, Z.; Chęciński, M.; Nitecka-Buchta, A.; Bulanda, S.; Ilczuk-Rypuła, D.; Postek-Stefańska, L.; Baron, S. Intramuscular Injections and Dry Needling within Masticatory Muscles in Management of Myofascial Pain. Systematic Review of Clinical Trials. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2021, 18, 9552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, D.; Sivakumar, B.; Bhargava, P.G. A Comparative Preliminary Randomized Clinical Study to Evaluate Heavy Bupivacaine Dextrose Prolotherapy (HDP) and Autologous Blood Injection (ABI) for Symptomatic Temporomandibular Joint Hypermobility Disorder. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2023, 22, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhapane, A.; Wadde, K.; Sachdev, S.S.; Barai, S.; Landge, J.; Wadewale, M. Comparison of Autologous Blood Injection and Dextrose Prolotherapy in the Treatment of Chronic Recurrent Temporomandibular Dislocation: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2023, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Baidya, M.; Srivastava, A.; Garg, H. Comparison of Autologous Blood Prolotherapy and 25% Dextrose Prolotherapy for the Treatment of Chronic Recurrent Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation on the Basis of Clinical Parameters: A Retrospective Study. Natl. J. Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 13, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, N.S. (Ed.) Dislocation of the Temporomandibular Joint; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2018; ISBN 978-3-319-62651-2. [Google Scholar]
- Sikora, M.; Chęciński, M.; Nowak, Z.; Chlubek, D. Variants and Modifications of the Retroauricular Approach Using in Temporomandibular Joint Surgery: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Anchlia, S.; Sadhwani, B.S.; Bhatt, U.; Rajpoot, D. Arthrocentesis Followed by Autologous Blood Injection in the Treatment of Chronic Symptomatic Subluxation of Temporomandibular Joint. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2022, 21, 1218–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tocaciu, S. Surgical Management of Recurrent Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation-Systematic Literature Review and Development of a Treatment Protocol. Master’s Thesis, Melbourne Dental School, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Çandrl, C.; Yüce, S.; Yldrm, S.; Sert, H. Histopathologic Evaluation of Autologous Blood Injection to the Temporomandibular Joint. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2011, 22, 2202–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulses, A.; Bayar, G.R.; Aydintug, Y.S.; Sencimen, M.; Erdogan, E.; Agaoglu, R. Histological Evaluation of the Changes in Temporomandibular Joint Capsule and Retrodiscal Ligaments Following Autologous Blood Injection. J. Cranio. Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 41, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varedi, P.; Bohluli, B. Autologous Blood Injection for Treatment of Chronic Recurrent TMJ Dislocation: Is It Successful? Is It Safe Enough? A Systematic Review. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 19, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prechel, U.; Ottl, P.; Ahlers, O.M.; Neff, A. The Treatment of Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation. Dtsch. Ärztebl. Int. 2018, 115, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renapurkar, S.K.; Laskin, D.M. Injectable Agents Versus Surgery for Recurrent Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 30, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamsson, H.; Eriksson, L.; Abrahamsson, P.; Häggman-Henrikson, B. Treatment of Temporomandibular Joint Luxation: A Systematic Literature Review. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chęciński, M.; Chęcińska, K.; Nowak, Z.; Sikora, M.; Chlubek, D. Treatment of Mandibular Hypomobility by Injections into the Temporomandibular Joints: A Systematic Review of the Substances Used. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chęciński, M.; Chęcińska, K.; Turosz, N.; Brzozowska, A.; Chlubek, D.; Sikora, M. Current Clinical Research Directions on Temporomandibular Joint Intra-Articular Injections: A Mapping Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BASE-Bielefeld Academic Search Engine|What Is BASE? Available online: https://www.base-search.net/about/en/index.php (accessed on 4 May 2023).
- About|Elsevier Scopus Blog. Available online: https://blog.scopus.com/about (accessed on 21 July 2023).
- PubMed Overview. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/about/ (accessed on 4 May 2023).
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—A Web and Mobile App for Systematic Reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howick, J.; Chalmers, I.; Glasziou, P.; Greenhalgh, T.; Heneghan, C.; Liberati, A.; Moschetti, I.; Phillips, B.; Thornton, H.; Goddard, O.; et al. OCEBM Levels of Evidence—Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine (CEBM); University of Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2011; Available online: https://www.cebm.ox.ac.uk/resources/levels-of-evidence/ocebm-levels-of-evidence (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A Revised Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Randomised Trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshioka, N.; Shimo, T.; Ibaragi, S.; Sasaki, A. Autologous Blood Injection for the Treatment of Recurrent Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation. Acta Med. Okayama 2016, 70, 291–294. [Google Scholar]
- Štembírek, J.; Vaněk, J.; Usvald, D.; Roubalíková, I.; Míšek, I. Blood Fate in Therapy of the Temporomandibular Joint Hypermobility Using an Injection of Autologous Blood. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 38, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindra, A.; Bithal, P.; Sokhal, N.; Arora, A. Pain Relief Can Be Painful. Indian J. Palliat. Care 2015, 21, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, A.; Cousin, G.C.S. Alice in Wonderland Syndrome and Hypermobility of the Temporomandibular Joint: Association or Coincidence? Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 53, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Rana, A.S.; Verma, V.K. Treatment of Recurrent TMJ Dislocation in Geriatric Patient by Autologous Blood–A Technique Revisited. J. Oral Biol. Craniofacial. Res. 2013, 3, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, A.; Matsumoto, K.; Kakimoto, N.; Yura, Y. Arthroscopic Findings after Autologous Blood Injection in the Treatment of Recurrent Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Med. Pathol. 2015, 27, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.S.R.; McVeigh, K.P.; Bainton, R. The Use of Autologous Blood and Adjunctive ‘Face Lift’ Bandage in the Management of Recurrent TMJ Dislocation. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 47, 323–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Shimoyama, T.; Nasu, D.; Kaneko, T.; Horie, N.; Kudo, I. Autologous Blood Injection into the Articular Cavity for the Treatment of Recurrent Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation: A Case Report. J. Oral Sci. 2007, 49, 237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobi-Hermanns, E.; Tetsch, P. [Pericapsular autologous blood injection as therapy for habitual temporomandibular joint luxation]. Dtsch. Zahnarztl. Z. 1981, 36, 187–190. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobi-Hermanns, E.; Wagner, G.; Tetsch, P. Investigations on Recurrent Condyle Dislocation in Patients with Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction: A Therapeutical Concept. Int. J. Oral Surg. 1981, 10, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hasson, O.; Nahlieli, O. Autologous Blood Injection for Treatment of Recurrent Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2001, 92, 390–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, J.; Joshi, K.; Jha, S.; Mathumathi, A. Comparative Analysis of Autologous Blood Injection and Conservative Therapy for the Management of Chronic Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation. J. Indian Acad. Oral Med. Radiol. 2022, 34, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertas, U.; Ascl, Y.; Yalcin, E.; Urvasizoglu, G. Evaluation of Intermaxillary Fixation (IMF) Screw Therapy with Craniomandibular Index Analysis for Chronic Recurrent Dislocation in the Temporomandibular Joint. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2022, 25, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amer, I.; Kukereja, P.; Gaber, A. Efficacy of Autologous Blood Injection for Treatment of Chronic Recurrent Temporo-Mandibular Joint Dislocation. Egypt. J. Ear. Nose Throat Allied Sci. 2021, 22, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, A.; Rahim, A. Comparison of Mean Decrease in Mouth Opening by Autologous Blood Injection in Superior Joint Space with and without Pericapsular Tissue in Treatment of Chronic Recurrent Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation in Mayo Hospital Lahore. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2020, 70, 1878–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnani, S.; Kholakiya, Y.; Arora, A.; Bhutia, O.; Seith, A.; Khandelwal, R.; Roychoudhury, A. Ultrasound-Guided Autologous Blood Injection in Patients with Chronic Recurrent Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation. Natl. J. Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machon, V.; Levorova, J.; Hirjak, D.; Wisniewski, M.; Drahos, M.; Sidebottom, A.; Foltan, R. A Prospective Assessment of Outcomes Following the Use of Autologous Blood for the Management of Recurrent Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 22, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Nakatani, Y.-i.; Gamoh, S.; Shimizutani, K.; Morita, S. Clinical Outcome after 36 Months of Treatment with Injections of Autologous Blood for Recurrent Dislocation of the Temporomandibular Joint. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 56, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.; Nilesh, K.; Parkar, M.; Vaghasiya, A. Clinical and Radiological Outcome of Arthrocentesis Followed by Autologous Blood Injection for Treatment of Chronic Recurrent Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2017, 9, e962–e969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.S.; Ansari, K. Treatment of Chronic Recurrent Dislocation of Temporomandibular Joint by Autologus Blood Injection. Plast. Aesthetic. Res. 2016, 3, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coser, R.; Da Silveira, H.; Medeiros, P.; Ritto, F.G. Autologous Blood Injection for the Treatment of Recurrent Mandibular Dislocation. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 44, 1034–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshiro, N.; Yoshida, H.; Uemura, M.; Suwa, F.; Morita, S. Analysis of MRI Findings in Minimum Invasive Treatment for Habitual Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation by Autologous Blood Injection around the Temporomandibular Joint Capsule. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 42, 1486–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayoumi, A.M.; Al-Sebaei, M.O.; Mohamed, K.M.; Al-Yamani, A.O.; Makrami, A.M. Arthrocentesis Followed by Intra-Articular Autologous Blood Injection for the Treatment of Recurrent Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 43, 1224–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candirli, C.; Korkmaz, Y.T.; Yuce, S.; Dayisoylu, E.H.; Taskesen, F. The Effect of Chronic Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation: Frequency on the Success of Autologous Blood Injection. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2013, 12, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegab, A.F. Treatment of Chronic Recurrent Dislocation of the Temporomandibular Joint with Injection of Autologous Blood Alone, Intermaxillary Fixation Alone, or Both Together: A Prospective, Randomised, Controlled Clinical Trial. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 51, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafillidou, K.; Venetis, G.; Markos, A. Short-Term Results of Autologous Blood Injection for Treatment of Habitual TMJ Luxation. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2012, 23, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candirli, C.; Yüce, S.; Cavus, U.Y.; Akin, K.; Cakir, B. Autologous Blood Injection to the Temporomandibular Joint: Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings. Imaging Sci. Dent. 2012, 42, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daif, E.T. Autologous Blood Injection as a New Treatment Modality for Chronic Recurrent Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2010, 109, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machon, V.; Abramowicz, S.; Paska, J.; Dolwick, M.F. Autologous Blood Injection for the Treatment of Chronic Recurrent Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 67, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sielski, M.; Chęcińska, K.; Chęciński, M.; Sikora, M. Injectable Platelet-Rich Fibrin (I-PRF) Administered to Temporomandibular Joint Cavities: A Scoping Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, C.; Zoghbi, A.; El Skaff, E.; Touma, J. Platelet-rich Plasma Injections for the Treatment of Temporomandibular Joint Disorders: A Systematic Review. J. Oral Rehabil. 2023, joor.13545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, M.; Sielski, M.; Chęciński, M.; Chęcińska, K.; Czerwińska-Niezabitowska, B.; Chlubek, D. Patient-Reported Quality of Life versus Physical Examination in Treating Temporomandibular Disorders with Intra-Articular Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections: An Open-Label Clinical Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 13299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vingender, S.; Dőri, F.; Schmidt, P.; Hermann, P.; Vaszilkó, M.T. Evaluation of the Efficiency of Hyaluronic Acid, PRP and I-PRF Intra-Articular Injections in the Treatment of Internal Derangement of the Temporomandibular Joint: A Prospective Study. J. Cranio. Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 51, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoneim, N.I.; Mansour, N.A.; Elmaghraby, S.A.; Abdelsameaa, S.E. Treatment of Temporomandibular Joint Disc Displacement Using Arthrocentesis Combined with Injectable Platelet Rich Fibrin versus Arthrocentesis Alone. J. Dent. Sci. 2022, 17, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, M.; Sielski, M.; Chęciński, M.; Nowak, Z.; Czerwińska-Niezabitowska, B.; Chlubek, D. Repeated Intra-Articular Administration of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) in Temporomandibular Disorders: A Clinical Case Series. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria | |
|---|---|---|
| Problem | Mandibular hypermobility | Cadaver and animal studies |
| Intervention | Unprocessed blood intra- or pericavitary injection(s) | More invasive interventions, such as arthroscopy or open surgery |
| Comparison | Arthrocentesis, placebo injection, hypertonic dextrose prolotherapy, immobilization, and physiotherapy | As above |
| Outcomes | Frequency or presence of dislocation episodes, range of mandibular mobility, articular pain | Not applicable |
| Timeframe | Any | Not applicable |
| Settings | Primary studies | Case reports and series of up to three cases |
| First author | Patients | Injection Site | Volume | Cointervention | Repetitions | Control | Evidence Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bhargava [7] | 60 | Bilateral | 3 mL | Immobilization | 1–4 | HD | 2 |
| Chhapane [8] | 32 | Unilateral or bilateral | 3 mL | None | 1–2 | HD | 2 |
| Sharma [12] | 30 | 14 unilateral16 bilateral | 3 mL | Arthrocentesis | 1–3 | None | 4 |
| Pandey [9] | 20 | Bilateral | 3 mL | Immobilization | 1 | HD | 3 |
| Shah [40] | 5 | N/S | 5 mL | Arthrocentesis | 1 | None | 4 |
| Ertas [41] | 300 | Bilateral | 5 mL | None | 1 | Placebo | 2 |
| Amer [42] | 140 | Bilateral | 3 mL | Arthrocentesis + immobilization | 1–2 | Arthrocentesis alone | 2 |
| Bukhari [43] | 80 | Bilateral | 3 mL | Immobilization | 1 | Intracapsular injections alone | 3 |
| Gagnani [44] | 19 | 4 unilateral15 bilateral | 3 mL | Immobilization | 1–2 | None | 4 |
| Machon (2018) [45] | 40 | Unilateral | 3 mL | None | 1 | Intracapsular injections alone | 2 |
| Yoshida [46] | 21 | 13 unilateral8 bilateral | N/S | N/S | 1–3 | None | 4 |
| Patel [47] | 10 | Bilateral | 3 mL | Arthrocentesis | 1 | None | 4 |
| Ahmed [48] | 11 | Bilateral | 4 mL | Arthrocentesis | 1 | None | 4 |
| Coser [49] | 11 | Bilateral | 3 mL | Arthrocentesis + immobilization | 1–2 | None | 4 |
| Oshiro [50] | 14 | Unilateral | 5 mL | None | 1 | None | 4 |
| Bayoumi [51] | 15 | Bilateral | 3 mL | Arthrocentesis + immobilization | 1 | None | 4 |
| Candirli (2013) [52] | 17 | 5 unilateral12 bilateral | 5 mL | Immobilization | 1–2 | None | 4 |
| Hegab [53] | 48 | Bilateral | 5 mL | Arthrocentesis | 1–3 | AB + Immobilization; immobilization alone | 2 |
| Triantafillidou [54] | 40 | 2 unilateral23 bilateral | 3 mL | None | 1–4 | Physiotherapy | 2 |
| Candirli (2012) [55] | 14 | 8 unilateral6 bilateral | 5 mL | Immobilization | 1 | None | 4 |
| Daif [56] | 30 | Bilateral | 3 mL | Arthrocentesis + immobilization | 1 | Intracapsular injections alone | 2 |
| Machon (2009) [57] | 25 | Bilateral | 3 mL | Arthrocentesis | 1–3 | None | 4 |
| Study | Randomization | Deviations | Missing Outcome | Measurement | Selection | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bhargava |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Chhapane |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Ertas |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Amer |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Machon |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Hegab |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Triantafillidou |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Daif |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Study | Population (Mean Age, Male/Female) | Dislocation Episodes | Mandibular Abduction | Articular Pain | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bhargava | 29.2 ± 8.5 33/27 | No | Yes | Yes | None |
| Chhapane | 36.6 ± 8.8 14/18 | Yes | Incorrect data * | Yes | Acoustic symptoms |
| Ertas | 31.0 ± 5.5 82/218 | No | No | No | Craniomandibular index |
| Amer | 46.6 ± 8.5 and 49.3 ± 6.3 ** 56/84 | Yes | Yes | No | Acoustic symptoms, satisfaction |
| Machon | 29.9 *** 3/37 | Yes | Yes | Yes | None |
| Hegab | 33 *** 11/37 | Missing data | Yes | No | None |
| Triantafillidou | 33.5 and 34.3 **,*** 9/31 | No | Yes | No | Acoustic symptoms |
| Daif | 34 *** 12/18 | Yes | Yes | No | None |
| Patient Group | Group Size | Initial Value | 2 Weeks | 1 Month | 2 Months | 3 Months | 6 Months | 12 Months |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chhapane, AB | 16 | 16 100% | N/S | N/S | N/S | 1 6% | N/S | 0 0% |
| Chhapane, HD | 16 | 16 100% | N/S | N/S | N/S | 3 19% | N/S | 0 0% |
| Amer, AB | 70 | 70 100% | N/S | N/S | 18 * 25% | N/S | N/S | N/S |
| Amer, non-AB | 70 | 70 100% | N/S | N/S | 28 * 40% | N/S | N/S | N/S |
| Machon, SJC + PT | 20 | 20 100% | N/S | 210% | N/S | 4 20% | 4 20% | 4 20% |
| Machon, PT | 20 | 20 100% | N/S | 0 0% | N/S | 5 25% | 9 45% | 9 45% |
| Daif, SJC + PT | 15 | 15 100% | 4 27% | 2 13% | N/S | 2 13% | 2 13% | 2 13% |
| Daif, PT | 15 | 15 100% | 2 13% | 1 7% | N/S | 1 7% | 1 7% | 1 7% |
| Patient Group | Group Size | Initial Value | 1 Month | 2 Months | 3 Months | 6 Months | 12 Months |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bhargava, AB | 30 | 43 100% | N/S | N/S | N/S | 39 91% | 38 88% |
| Bhargava, HD | 30 | 43 100% | N/S | N/S | N/S | 39 91% | 38 88% |
| Amer, AB | 70 | 47 100% | N/S | 40 85% | N/S | N/S | N/S |
| Amer, non-AB | 70 | 44 100% | N/S | 40 91% | N/S | N/S | N/S |
| Machon, SJC + PT | 20 | N/S 100% | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S 86% |
| Machon, PT | 20 | N/S 100% | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S 88% |
| Hegab, AB | 16 | 50 100% | 40 80% | N/S | 41 82% | 41 82% | 42 84% |
| Hegab, IMF | 16 | 51 100% | 40 78% | N/S | 41 80% | 41 80% | 42 82% |
| Hegab, AB + IMF | 16 | 51 100% | 37 73% | N/S | 38 75% | 3976% | 40 78% |
| Triantafillidou, AB | 25 | 50 100% | N/S | N/S | 43 86% | N/S | N/S |
| Triantafillidou, P | 15 | 50 100% | N/S | N/S | 49 98% | N/S | N/S |
| Daif, SJC + PT | 15 | 41 * 100% | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | 37 90% |
| Daif, PT | 15 | 41 * 100% | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | 35 85% |
| Patient Group | Group Size | Initial Value | 3 Days | 1 Week | 2 Weeks | 1 Month | 3 Months | 6 Months | 12 Months |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bhargava, AB | 30 | 8.9 100% | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | 6.2 70% | 4.7 53% |
| Bhargava, HD | 30 | 8.4 100% | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | 5.7 68% | 4.0 48% |
| Chhapane, AB | 16 | 5.5 100% | 5.7 104% | 2.0 36% | 1.0 18% | 0.4 7% | 0.3 5% | 0.1 2% | 0.2 4% |
| Chhapane, HD | 16 | 5.1 100% | 5.8 114% | 2.2 43% | 0.4 8% | 0.7 14% | 0.6 12% | 0.5 10% | 0.2 4% |
| Machon, SJC + PT | 20 | 4.4 100% | N/S | N/S | N/S | 3.1 70% | N/S | N/S | 1.2 27% |
| Machon, PT | 20 | 4.2 100% | N/S | N/S | N/S | 2.5 59% | N/S | N/S | 1.4 33% |
| Outcome Domain | Number of Studies Presenting Outcomes after 1–6 Months | Total Number of Patients | Weighted Average of the Effect after 2–6 Months | Standard Deviation | Risk of Bias in Studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dislocation episodes | 4 | 121 | 20% of the initial number of patients presenting dislocation episodes | 8% | Some concerns |
| Mandibular abduction | 4 | 176 | 86% of initial mandibular abduction | 4% | Some concerns |
| Articular pain in visual analogue scale | 3 | 66 | 54% of initial severity of pain | 39% | Some concerns |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chęciński, M.; Chęcińska, K.; Rąpalska, I.; Turosz, N.; Chlubek, D.; Sikora, M. Autologous Blood Injections in Temporomandibular Hypermobility: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5590. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175590
Chęciński M, Chęcińska K, Rąpalska I, Turosz N, Chlubek D, Sikora M. Autologous Blood Injections in Temporomandibular Hypermobility: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(17):5590. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175590
Chicago/Turabian StyleChęciński, Maciej, Kamila Chęcińska, Iwona Rąpalska, Natalia Turosz, Dariusz Chlubek, and Maciej Sikora. 2023. "Autologous Blood Injections in Temporomandibular Hypermobility: A Systematic Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 17: 5590. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175590
APA StyleChęciński, M., Chęcińska, K., Rąpalska, I., Turosz, N., Chlubek, D., & Sikora, M. (2023). Autologous Blood Injections in Temporomandibular Hypermobility: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(17), 5590. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175590








