Alternative Methods of Ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) Control with Emphasis on the Argentine Ant, Linepithema humile
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Pest Ant Control around Homes
2. Standard Ant Control Methods Can Be Problematic
3. Alternative Methods of Ant Control
3.1. Trail Pheromone
3.2. Use of Behavior-Modifying Chemicals
3.3. Mass Trapping
3.4. Hydrogels, “Virtual” Baiting, and Exceedingly-Low Bait Concentrations
3.5. Food Source Reduction
3.6. Deterrents
3.7. RNA Interference (RNAi)
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vega, S.J.; Rust, M.K. The Argentine ant: A significant invasive species in agricultural, urban and natural environments. Sociobiology 2001, 37, 3–25. [Google Scholar]
- Rust, M.; Reierson, D.A.; Klotz, J.H. Pest management of Argentine ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). J. Entomol. Sci. 2003, 38, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, J.H.; Rust, M.K.; Costa, H.S.; Reierson, D.A.; Kido, K. Strategies for controlling Argentine ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) with sprays and baits. J. Agric. Urban Entomol. 2002, 19, 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Klotz, J.H.; Rust, M.K.; Greenberg, L.; Field, H.C.; Kupfer, K. An evaluation of several urban pest management strategies to control Argentine ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Sociobiology 2007, 50, 391–398. [Google Scholar]
- Klotz, J.H.; Rust, M.K.; Field, H.C.; Greenberg, L.; Kupfer, K. Controlling Argentine ants in residential settings (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Sociobiology 2008, 51, 579–588. [Google Scholar]
- Klotz, J.H.; Rust, M.K.; Field, H.C.; Greenberg, L.; Kupfer, K. Low impact directed sprays and liquid baits to control Argentine ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Sociobiology 2009, 54, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Klotz, J.H.; Rust, M.K.; Greenberg, L.; Robertson, M.A. Developing low risk strategies for Argentine ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Sociobiology 2010, 55, 779–785. [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Hazard and General Labeling for Pyrethroid and Synergized Pyrethrins Non-Agricultural Outdoor Products; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ingredients-used-pesticide-products/environmental-hazard-and-general-labeling-pyrethroid-and (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Greenberg, L.; Rust, M.K. Chapter 23: Ant control and insecticide runoff around urban homes. In Pesticides in Surface Water: Monitoring Modeling, Risk Assessment, and Management; Goh, K.S., Gan, J., Young, D.F., Luo, Y., Eds.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; pp. 451–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, L.; Rust, M.K.; Klotz, J.H.; Haver, D.; Kabashima, J.N.; Bondarenko, S.; Gan, J. Impact of ant control technologies on insecticide runoff and efficacy. Pest Manag. Sci. 2010, 66, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Soeprono, A.; Rust, M.K.; Gan, J. Ant control efficacy of pyrethroids and fipronil on outdoor concrete surfaces. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Bondarenko, S.; Oki, L.; Haver, D.; Li, J.X. Occurrence of fipronil and its biologically active derivatives in urban residential runoff. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 1489–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, J.H.; Greenberg, L.; Storey, H.H.; Williams, D.F. Alternative control strategies for ants around homes. J. Entomol. Sci. 1997, 14, 249–257. [Google Scholar]
- Suckling, D.; Peck, R.; Manning, L.; Stringer, L.; Cappadonna, J.; El-Sayed, A. Pheromone disruption of Argentine ant trail integrity. J. Chem. Ecol. 2008, 34, 1602–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Nishisue, K.; Sunamura, E.; Suzuki, S.; Sakamoto, H.; Fukumoto, T.; Terayama, M.; Tatsuki, S. Trail-following disruption in the invasive Argentine ant with a synthetic trail pheromone component (Z)-9-hexadecenal. Sociobiology 2009, 54, 139–152. [Google Scholar]
- Suckling, D.M.; Peck, R.W.; Stringer, L.D.; Snook, K.; Banko, P.C. Trail pheromone disruption of Argentine ant trail formation and foraging. J. Chem. Ecol. 2010, 36, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishisue, K.; Sunamura, E.; Tanaka, Y.; Sakamoto, H.; Suzuki, S.; Fukumoto, T.; Terayama, M.; Tatsuki, S. Long-term field trial to control the invasive Argentine ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) with synthetic trail pheromone. J. Econ. Entomol. 2010, 103, 1784–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suckling, D.M.; Stringer, L.D.; Corn, J.E. Argentine ant trail pheromone disruption is mediated by trail concentration. J. Chem. Ecol. 2011, 37, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunamura, E.; Suzuki, S.; Nishisue, K.; Sakamoto, H.; Otsuka, M.; Utsumi, Y.; Mochizuki, F.; Fukumoto, T.; Ishikawa, Y.; Terayama, M.; et al. Combined use of a synthetic trail pheromone and insecticidal bait provides effective control of an invasive ant. Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 1230–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, D.H.; Villafuerte, D.B.; Tsutsui, N.D. Trail pheromone of the Argentine ant, Linepithema humile (Mayr) (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westermann, F.L.; Suckling, D.M.; Lester, P.J. Disruption of foraging by a dominant invasive species to decrease its competitive ability. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, L.; Klotz, J.H. Argentine ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) trail pheromone enhances consumption of liquid sucrose solution. J. Econ. Entomol. 2000, 93, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welzel, K.F.; Choe, D.H. Development of a pheromone-assisted baiting technique for Argentine ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, D.; Hwan, K.T.; Lopez, C.M.; Campbell, K. Pheromone-assisted techniques to improve the efficacy of insecticide sprays against Linepithema humile (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2014, 107, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soeprono, A.M.; Rust, M.K. Effect of horizontal transfer of barrier insecticides to control Argentine ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2004, 97, 1675–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, D.H.; Rust, M.K. Horizontal transfer of insecticides in laboratory colonies of the Argentine ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2008, 101, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiltz, B.; Suiter, D.; Gardner, W. Activity of bifenthrin, chlorfenapyr, fipronil, and thiamethoxam against Argentine ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2009, 102, 2279–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, D.H.; Millar, J.G.; Rust, M.K. Chemical signals associated with life inhibit necrophoresis in Argentine ants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 8251–8255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, E.O.; Durlach, N.I.; Roth, L.M. Chemical releaser of necrophoric behavior in ants. Psyche 1958, 65, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
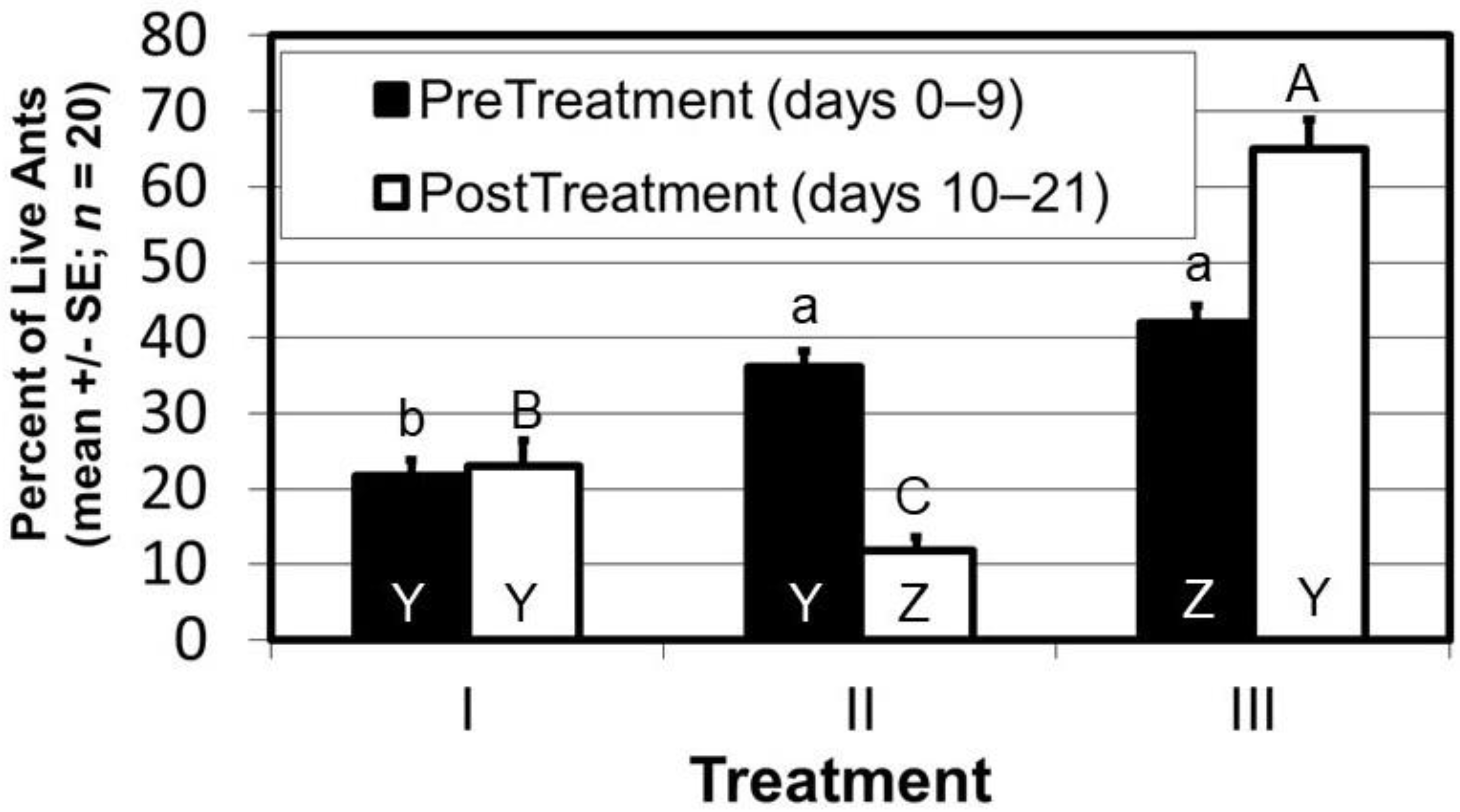
- Gochnour, B.M.; Suiter, D.R.; Davis, J.W.; Huang, Q. Use of an Argentine ant, Linepithema humile, semiochemical to deliver an acute toxicant. Insects 2018, 9, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiltz, B.A.; Suiter, D.R.; Gardner, W.A.; Berisford, C.W. A novel delivery method for ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) toxicants. Midsouth Entomol. 2010, 3, 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Buczkowski, G. The Trojan horse approach for managing invasive ants: A study with Asian needle ants, Pachycondyla chinensis. Biol. Invasions 2016, 18, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buczkowski, G. Prey-baiting as a conservation tool: Selective control of invasive ants with minimal non-target effects. Insect Conserv. Divers. 2017, 10, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buczkowski, G. Trap-treat-release: Horizontal transfer of fipronil in field colonies of black carpenter ants, Camponotus pennsylvanicus. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 2195–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buczkowski, G.; Mothapo, N.P.; Wossler, T.C. Let them eat termites-prey-baiting provides effective control of Argentine ants, Linepithema humile, in a biodiversity hotspot. J. Appl. Entomol. 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, W.; Barber, T. The Argentine ant. US Dep. Agric. Bur. Entomol. Bull. 1913, 122, 3–98. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, D.M.; Moses, L.; Falkovitz-Halpern, M.; Wong, E.H. Effect of weather on infestation of buildings by the invasive Argentine ant, Linepithema humile (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Am. Midl. Nat. 2001, 146, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilman, P.E.; Lighton, J.R.B.; Holway, D.A. Water balance in the Argentine ant (Linepithema humile) compared with five common native ant species from southern California. Physiol. Entomol. 2007, 32, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, A.C.; Mackay, D.A. An experimental study of the relative humidity preference and survival of the Argentine ant, Linepithema humile (Hymenoptera, Formicidae): Comparisons with a native Iridomyrmex species in South Australia. Insectes Soc. 2003, 50, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, N.E.; Gordon, D.M. Seasonal spatial dynamics and causes of nest movement in colonies of the invasive Argentine ant (Linepithema humile). Ecol. Entomol. 2006, 31, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, J.; Nsimba, B. Soil-free collection of Argentine ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) based on food-directed brood and queen movement. Fla. Entomol. 2000, 83, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scocco, C.; Suiter, D.; Gardner, W. Repellency of five essential oils to Linepithema humile (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). J. Entomol. Sci. 2012, 47, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiltz, B.; Suiter, D.; Gardner, W. Deterrency and toxicity of essential oils to Argentine and red imported fire ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). J. Entomol. Sci. 2007, 42, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, J.; Sorenson, C.E.; Waldvogel, M.G. Trap mulching Argentine ants. J. Econ. Entomol. 2006, 99, 1757–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enzmann, B.L.; Kepheim, K.M.; Wang, T.B.; Nonacs, P. Giving them what they want: Manipulating Argentine ant activity patterns with water. J. Appl. Entomol. 2012, 136, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buczkowski, G.; Roper, E.; Chin, D. Polyacrylamide hydogels: An effective tool for delivering liquid baits to pest ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2014, 107, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buczkowski, G.; Roper, E.; Chin, D.; Mothapo, N.; Wossler, T. Hydrogel baits with low-dose thiamethoxam for sustainable Argentine ant management in commercial orchards. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2014, 153, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rust, M.K.; Soeprono, A.; Wright, S.; Greenberg, L.; Choe, D.H.; Boser, C.L.; Cory, C.; Hanna, C. Laboratory and field evaluations of polyacrylamide hydrogel baits against Argentine ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, J.W.; Hoddle, M.S.; Mulchandani, A.; Choe, D.H. Development of an alginate hydrogel to deliver aquaeous bait for pest ant management. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 2028–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, J.W.; Choe, D.H.; Mulchandani, A.; Rust, M.K. Hydrogels: From controlled release to a new bait delivery for insect pest management. J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 2061–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosavljevic, I.; Hoddle, M.S. Laboratory screening of selected synthetic and organic insecticides for efficacy against Argentine ants when incorporated into alginate hydrogel beads, 2021. Arthropod Manag. Tests 2021, 46, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCalla, K.A.; Tay, J.W.; Mulchandani, A.; Choe, D.H.; Hoddle, M.S. Biodegradable alginate hydrogel bait delivery system effectively controls high-density populations of Argentine ant in commercial citrus. J. Pest Sci. 2020, 93, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boser, C.L.; Hanna, C.; Faulkner, K.R.; Cory, C.; Randall, J.M.; Morrison, S.A. Argentine ant management in conservation areas: Results of a pilot study. Monogr. West. N. Am. Nat. 2014, 7, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, D.H.; Vetter, R.S.; Rust, M.K. Development of virtual bait stations to control Argentine ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in environmentally sensitive habitats. J. Econ. Entomol. 2010, 103, 1761–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brightwell, R.; Silverman, J. Effects of honeydew-producing hemipteran denial on local Argentine ant distribution and boric acid bait performance. J. Econ. Entomol. 2009, 102, 1170–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brightwell, R.; Bambara, S.B.; Silverman, J. Combined effect of hemipteran control and liquid bait on Argentine ant populations. J. Econ. Entomol. 2010, 103, 1790–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isman, M.B. Botanical insecticides, deterrents, and repellents in modern agriculture and an increasingly regulated world. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2006, 51, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regnault-Roger, C.; Philogene, B.J.R. Past and current prospects for the use of botanicals and plant allelochemicals in integrated pest management. Pharm. Biol. 2008, 46, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regnault-Roger, C.; Vincent, C.; Arnason, J.T. Essential oils in insect control: Low-risk products in a high-stakes world. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2012, 37, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, M.D.; Suiter, D.R.; Scocco, C.M. Topical toxicity of nine essential oils to Camponotus pennsylvanicus (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Sociobiology 2011, 58, 419–426. [Google Scholar]
- Appel, A.G.; Gehret, M.J.; Tanley, M.J. Repellency and toxicity of mint oil granules to red imported fire ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2004, 97, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, J.T.; Shelton, T.G.; Merchant, M.E.; Russell, S.A.; Tanley, M.J.; Appel, A.G. Efficacy of three citrus oil formulations against Solenopsis invicta Buren (Hymenoptera: Formicidae), the red imported fire ant. J. Agric. Urban Entomol. 2002, 19, 159–171. [Google Scholar]
- Meissner, H.E.; Silverman, J. Effects of aromatic cedar mulch on the Argentine ant and the odorous house ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2001, 94, 1526–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meissner, H.E.; Silverman, J. Effect of aromatic cedar mulch on Argentine ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) foraging activity and nest establishment. J. Econ. Entomol. 2003, 96, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sisk, C.B.; Shorey, H.H.; Gerber, R.G.; Gaston, L.K. Semiochemicals that disrupt foraging by the Argentine ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae): Laboratory bioassays. J. Econ. Entomol. 1996, 89, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorey, H.H.; Gaston, L.K.; Gerber, R.G.; Phillips, P.A.; Wood, D.L. Disruption of foraging by Argentine ants, Iridomyrmex humilis (Mayr) (Hymenoptera: Formicidae), in citrus trees through the use of semiochemicals and related chemicals. J. Chem. Ecol. 1992, 18, 2131–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorey, H.H.; Gaston, L.K.; Gerber, R.G.; Sisk, C.B.; Phillips, P.A. Formulating farnesol and other ant-repellent semiochemicals for exclusion of Argentine ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from citrus trees. Environ. Entomol. 1996, 25, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, G.; Blau, H. A brief history of RNAi: The silence of the genes. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 1293–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welzel, K.F. Exploration of Argentine ant (Linepithema humile) Biology for Pest Management. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California Riverside, Riverside, CA, USA, September 2017. Available online: https://escholarship.org/uc/item/2fn009vr (accessed on 23 May 2021).
- Meng, J.; Lei, J.; Davitt, A.; Holt, J.R.; Huang, J.; Gold, R.; Vargo, E.L.; Tarone, A.M.; Zhu-Salzman, K. Suppressing tawny crazy ant (Nylanderia fulva) by RNAi technology. Insect Sci. 2020, 27, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suiter, D.R.; Gochnour, B.M.; Holloway, J.B.; Vail, K.M. Alternative Methods of Ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) Control with Emphasis on the Argentine Ant, Linepithema humile. Insects 2021, 12, 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12060487
Suiter DR, Gochnour BM, Holloway JB, Vail KM. Alternative Methods of Ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) Control with Emphasis on the Argentine Ant, Linepithema humile. Insects. 2021; 12(6):487. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12060487
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuiter, Daniel R., Benjamin M. Gochnour, Jacob B. Holloway, and Karen M. Vail. 2021. "Alternative Methods of Ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) Control with Emphasis on the Argentine Ant, Linepithema humile" Insects 12, no. 6: 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12060487
APA StyleSuiter, D. R., Gochnour, B. M., Holloway, J. B., & Vail, K. M. (2021). Alternative Methods of Ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) Control with Emphasis on the Argentine Ant, Linepithema humile. Insects, 12(6), 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12060487






