Role of Antioxidants in Modulating the Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis and Their Impact on Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
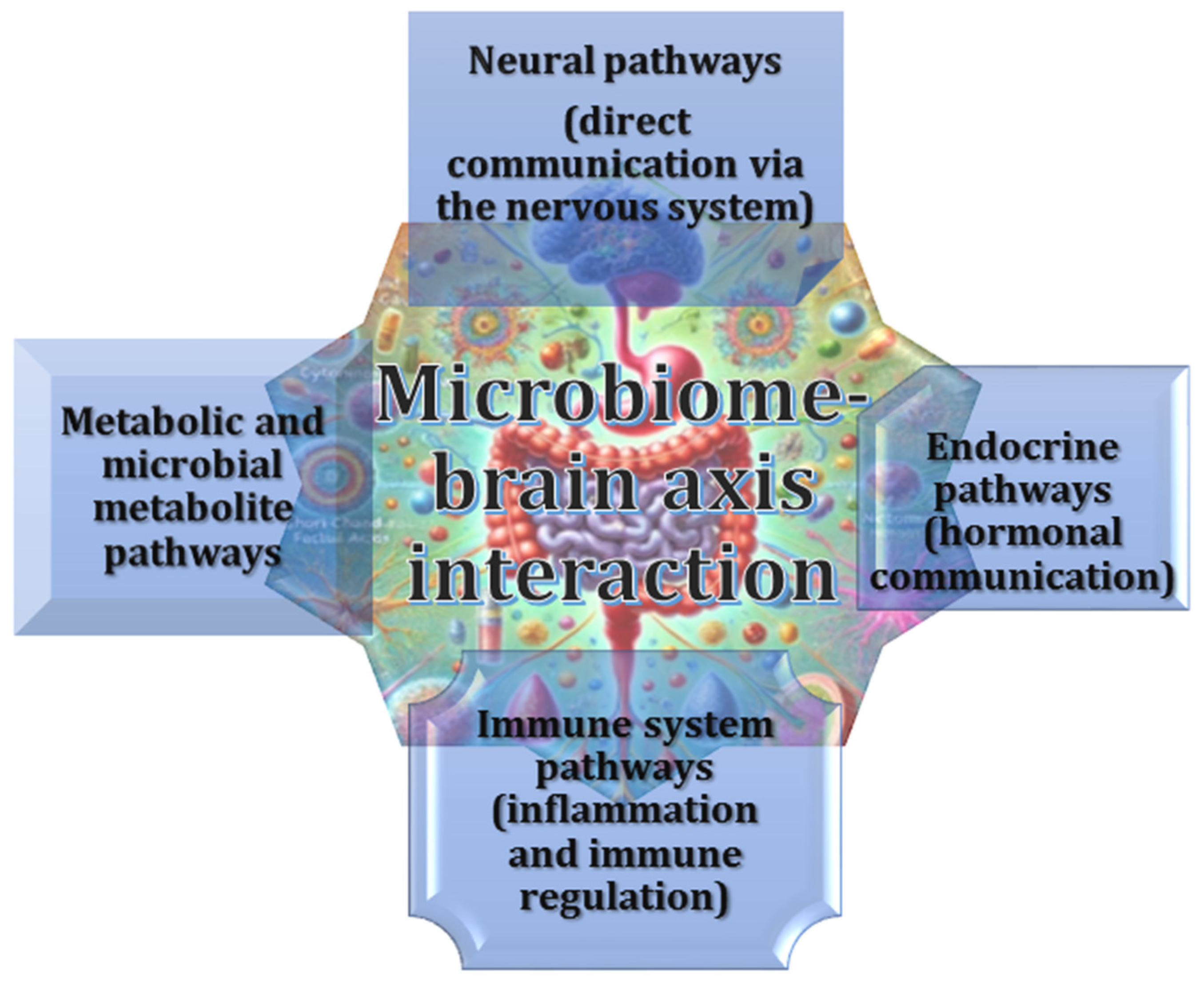
2.1. Gut–Brain Axis and Its Bidirectional Regulation
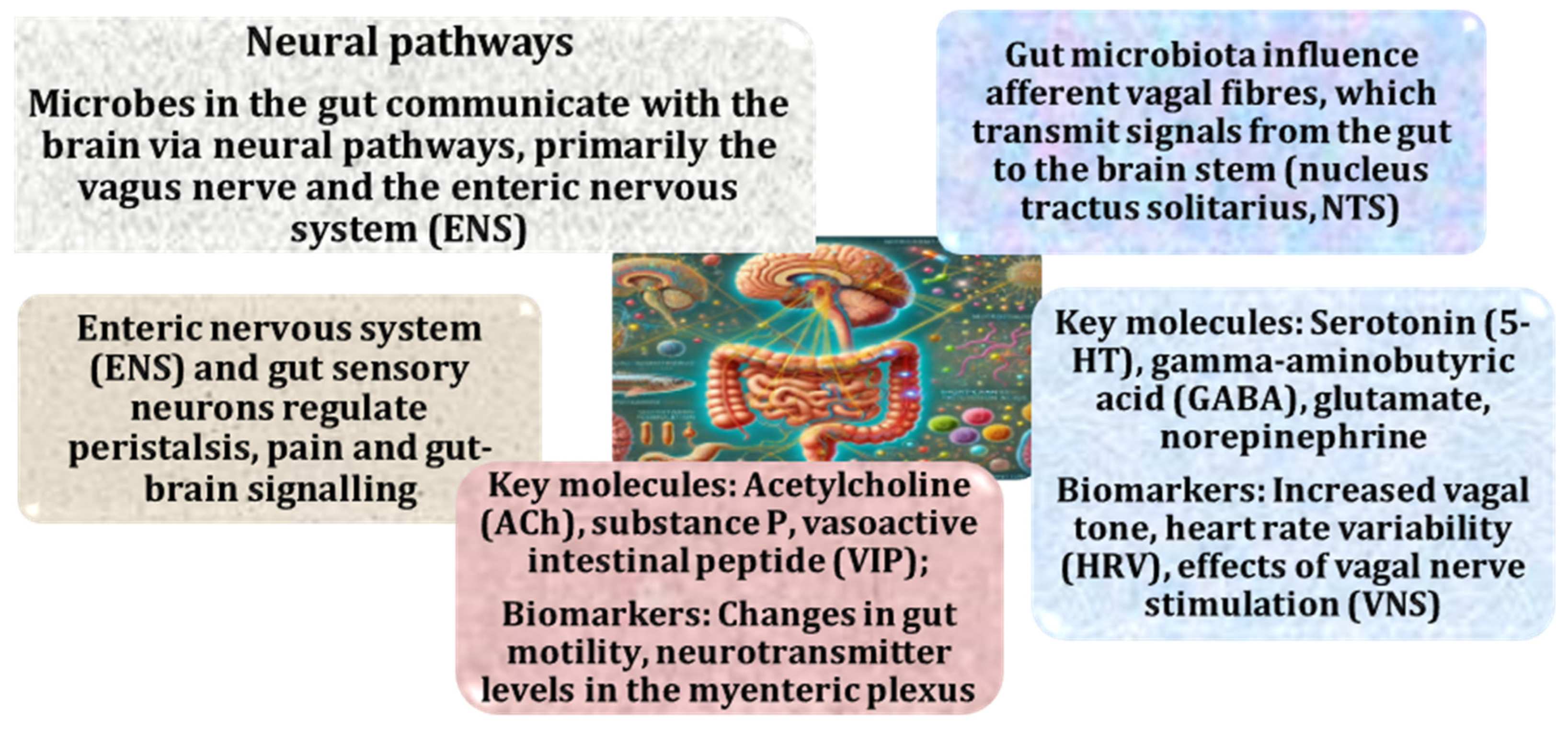
2.2. Role of the Vagus Nerve in the Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis and Its Implications for Neurodegenerative Diseases
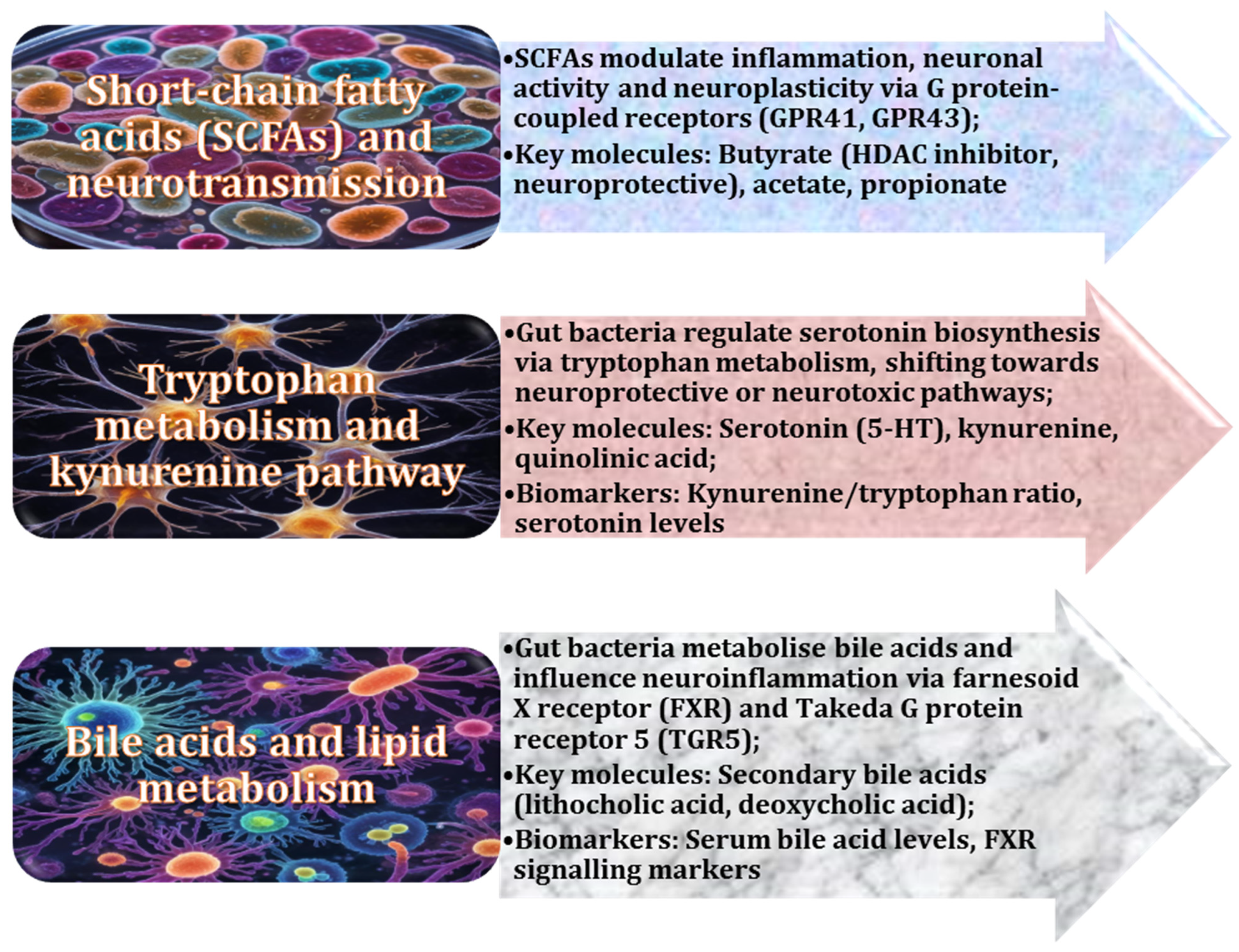
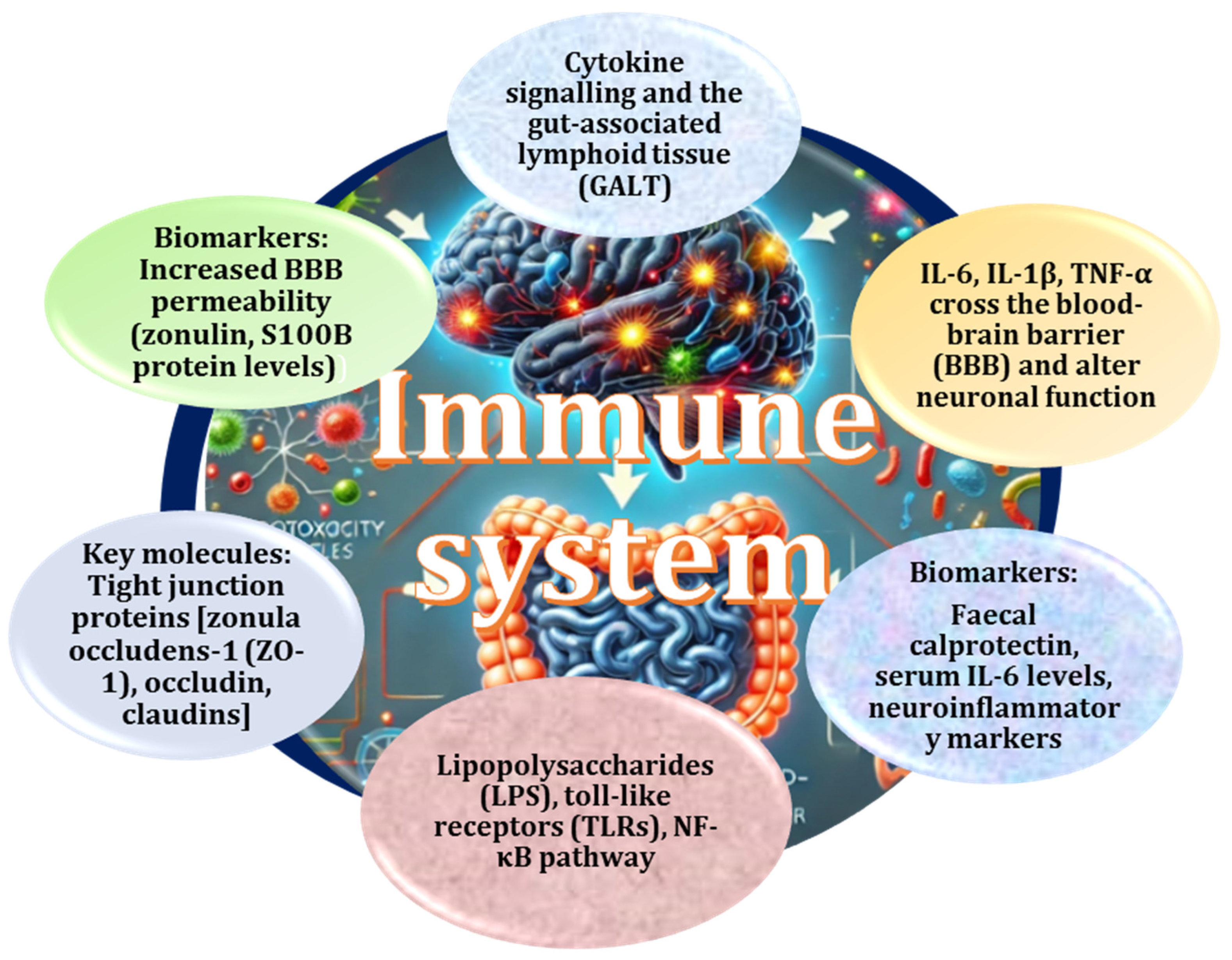
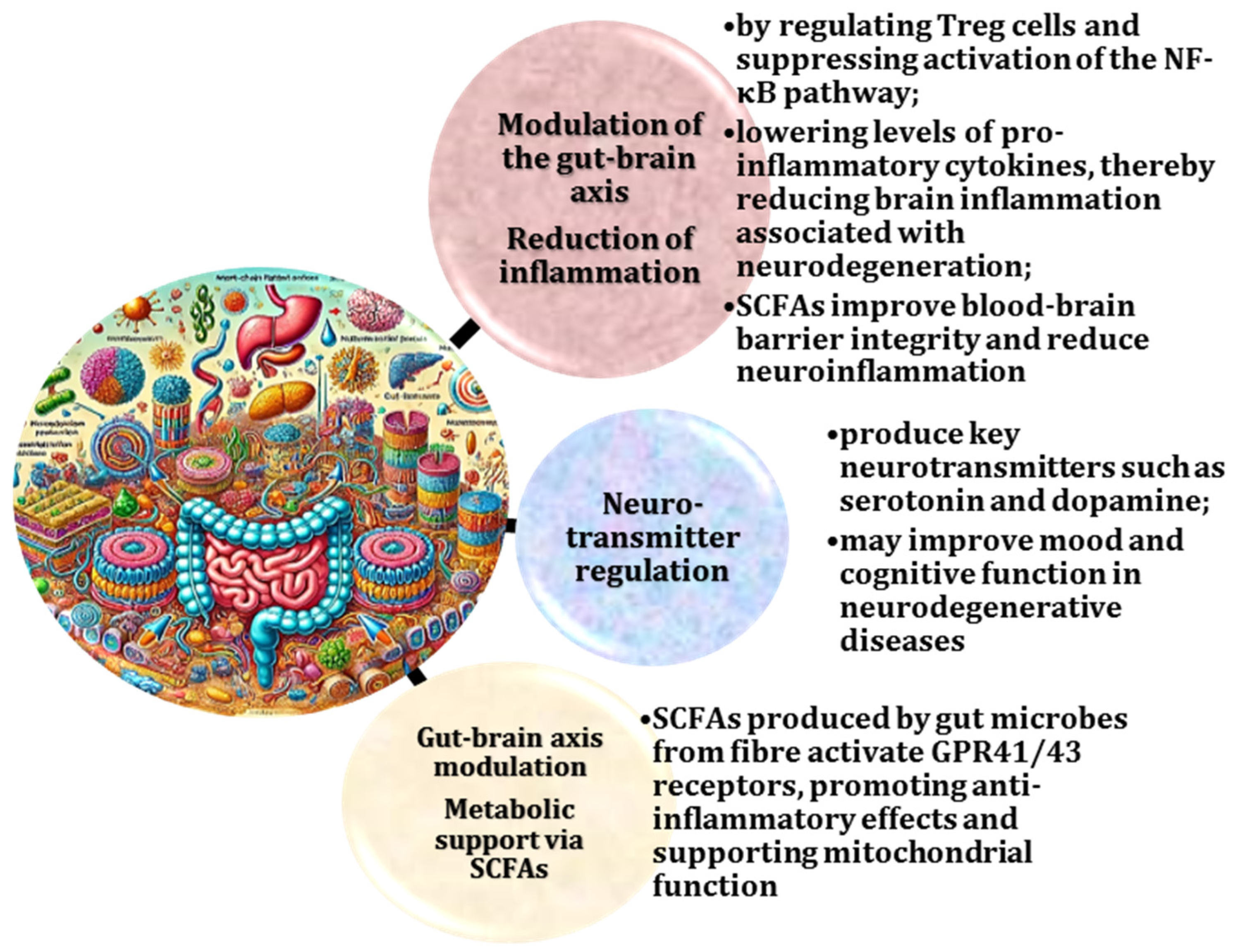
2.3. Critical Role of Gut-Derived Metabolites in Neuroinflammation and Blood–Brain Barrier Integrity
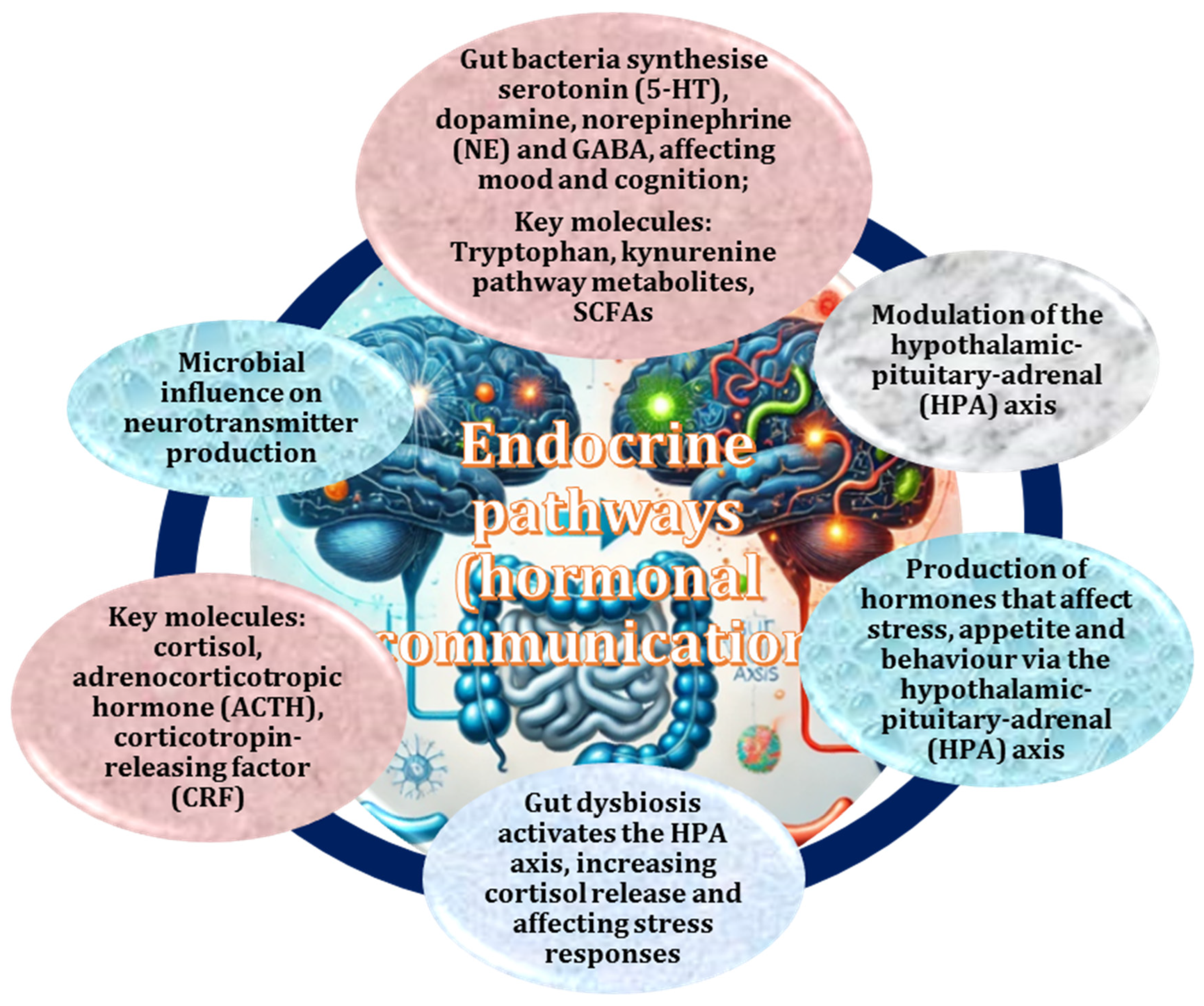
2.4. Gut Microbiota as Mediators of Endocrine Pathways, Hormonal Communication, and Neuroinflammation
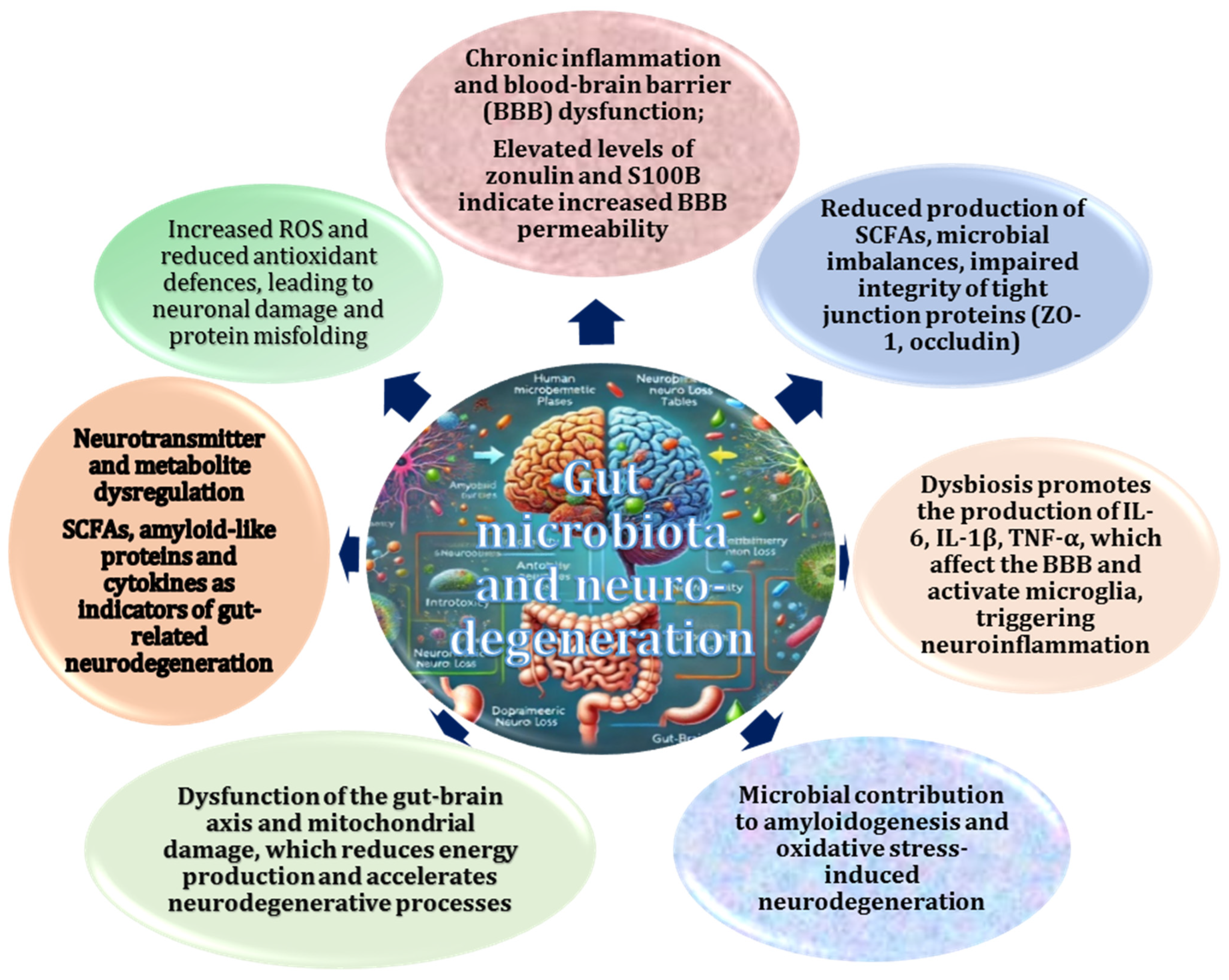
2.5. Impact of Gut Dysbiosis on Neurodegenerative Diseases
2.6. Role of the Gut–Brain Axis, Dysbiosis, and Inflammation in Neurodegeneration
2.7. Role of Microbial Imbalance in Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
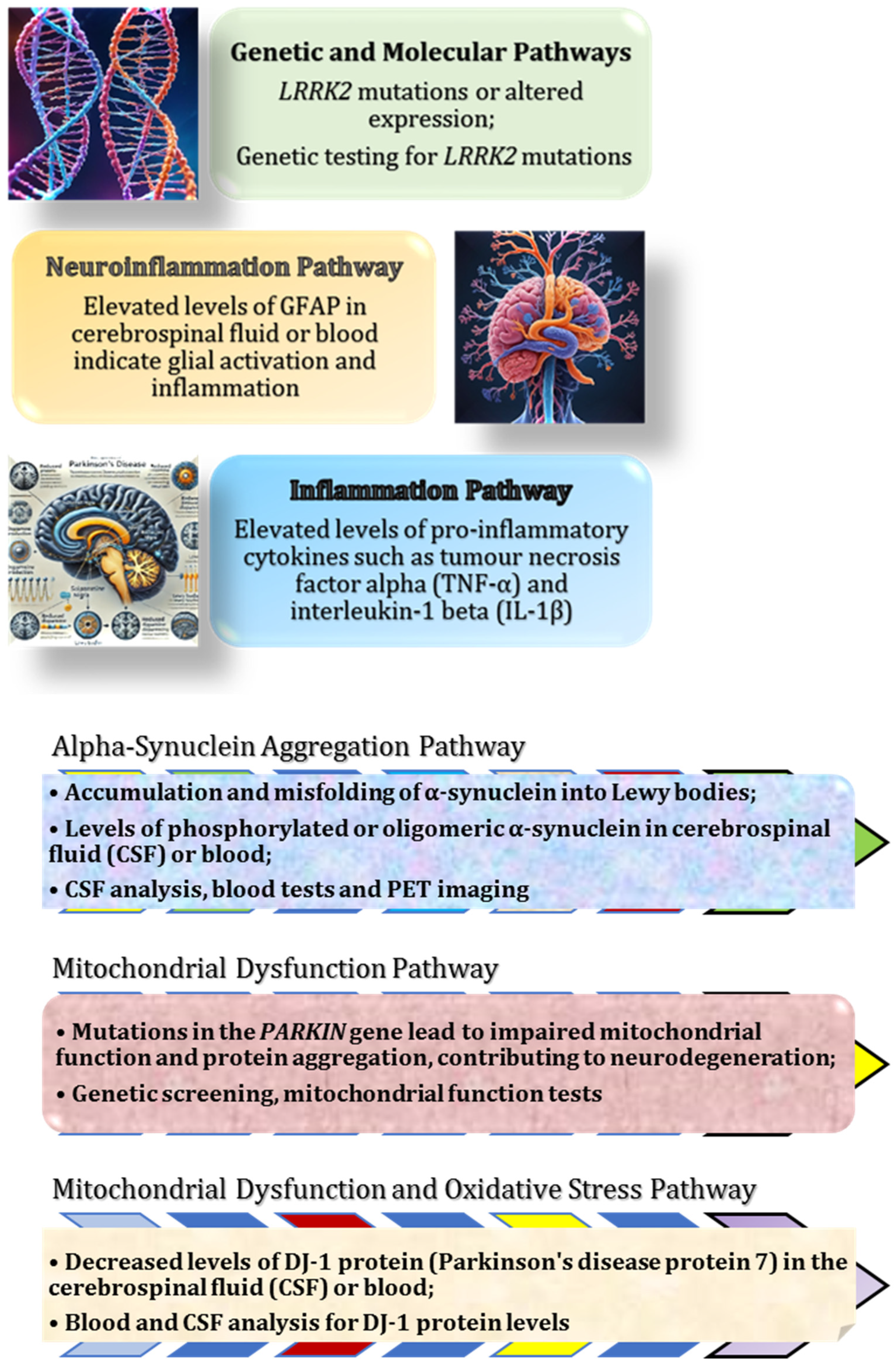
2.8. Role of the Gut–Brain Axis in Parkinson’s Disease
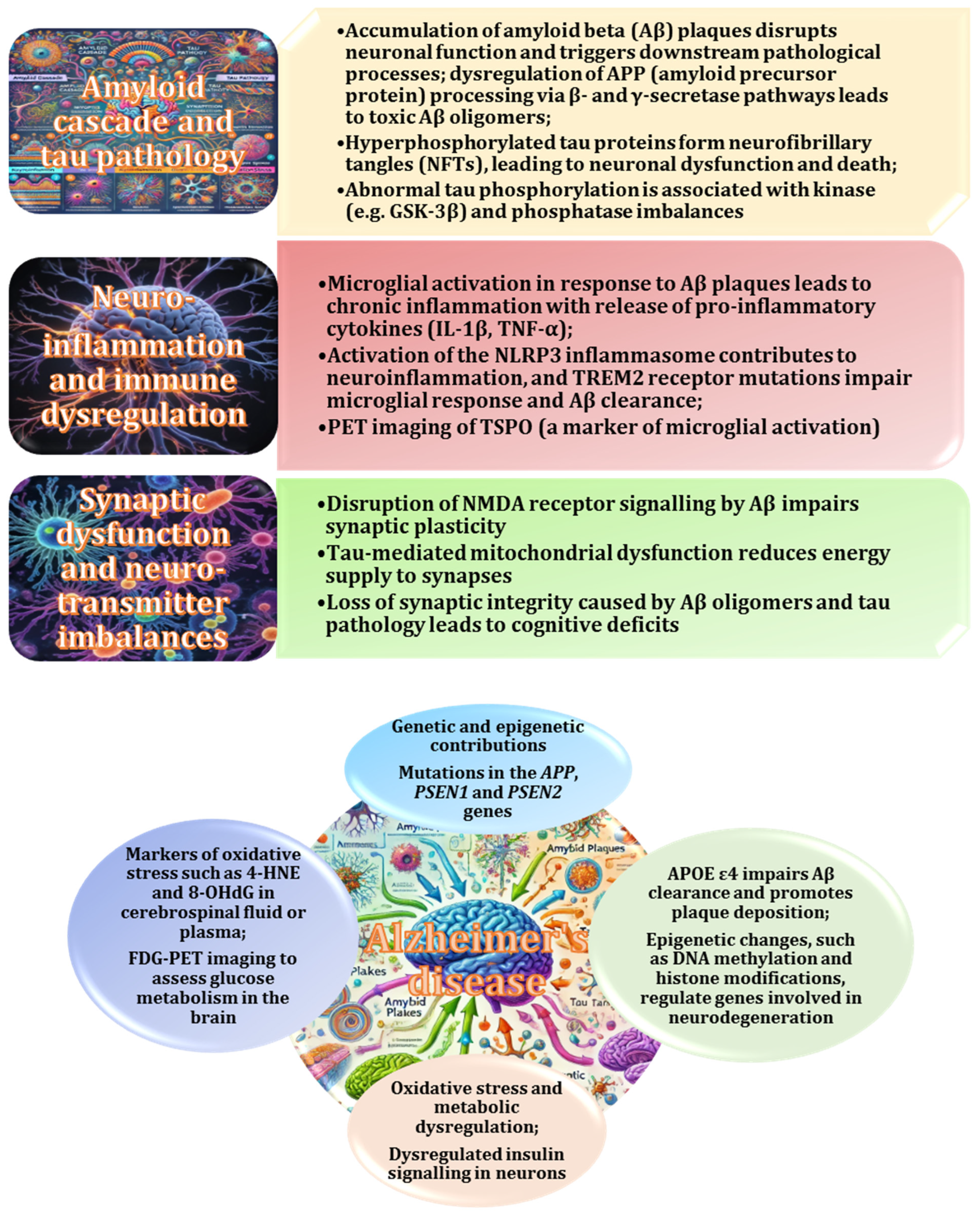
2.9. Role of the Gut Microbiome in Alzheimer’s Disease
2.10. Role of the Gut Microbiome in the Pathogenesis and Progression of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
2.11. Possible Role of Antioxidants in Gut–Brain Axis Homeostasis and Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases
2.12. Role of Antioxidants in Modulating Molecular Pathways to Protect Neuronal Health in Neurodegenerative Diseases
2.13. Antioxidant-Based Therapies and Gut Microbiota Modulation as a Promising Strategy for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases
3. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ursell, L.K.; Metcalf, J.L.; Parfrey, L.W.; Knight, R. Defining the human microbiome. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70 (Suppl. S1), S38–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhang, D.; Qi, S.; Liu, Y. Metabolite interactions between host and microbiota during health and disease: Which feeds the other? Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 160, 114295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, X.; Shi, D.; Khan, J.A.; Liu, H. Gut microbiota-derived short chain fatty acids are potential mediators in gut inflammation. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 8, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Shao, J.H.; Liao, Y.T.; Wang, L.N.; Jia, Y.; Dong, P.J.; Liu, Z.Z.; He, D.D.; Li, C.; Zhang, X. Regulation of short-chain fatty acids in the immune system. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1186892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.Y.; Li, X.; Yu, J.T.; Wang, Y.J. Therapeutics for neurodegenerative diseases by targeting the gut microbiome: From bench to bedside. Transl. Neurodegener. 2024, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Dementia//Official Cite of WHO. 2017. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia (accessed on 31 January 2025).
- Gale, S.A.; Acar, D.; Daffner, K.R. Dementia. Am. J. Med. 2018, 131, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabotti, M.; Scirocco, A.; Maselli, M.A.; Severi, C. The gut-brain axis: Interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Bonfili, L.; Wei, T.; Eleuteri, A.M. Understanding the Gut-Brain Axis and Its Therapeutic Implications for Neurodegenerative Disorders. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Zhao, Q.; Guan, Y.; Sun, Z.; Li, W.; Guo, S.; Zhang, A. The communication mechanism of the gut-brain axis and its effect on central nervous system diseases: A systematic review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 178, 117207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, Y. Regulation of Neurotransmitters by the Gut Microbiota and Effects on Cognition in Neurological Disorders. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicks, L.M.T. Gut Bacteria and Neurotransmitters. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mhanna, A.; Martini, N.; Hmaydoosh, G.; Hamwi, G.; Jarjanazi, M.; Zaifah, G.; Kazzazo, R.; Haji Mohamad, A.; Alshehabi, Z. The correlation between gut microbiota and both neurotransmitters and mental disorders: A narrative review. Medicine 2024, 103, e37114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, S.; Arachchige, A.S.P.M. Depletion of dopamine in Parkinson’s disease and relevant therapeutic options: A review of the literature. AIMS Neurosci. 2023, 10, 200–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Gut instincts: Microbiota as a key regulator of brain development, ageing and neurodegeneration. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzino, G.; Irrera, N.; Cucinotta, M.; Pallio, G.; Mannino, F.; Arcoraci, V.; Squadrito, F.; Altavilla, D.; Bitto, A. Oxidative Stress: Harms and Benefits for Human Health. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 8416763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olufunmilayo, E.O.; Gerke-Duncan, M.B.; Holsinger, R.M.D. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicknell, B.; Liebert, A.; Borody, T.; Herkes, G.; McLachlan, C.; Kiat, H. Neurodegenerative and Neurodevelopmental Diseases and the Gut-Brain Axis: The Potential of Therapeutic Targeting of the Microbiome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.J.; Gao, Y. Gut-brain axis and neurodegeneration: Mechanisms and therapeutic potentials. Front. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1481390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.H.; Kim, J.E.; Rhie, S.J.; Yoon, S. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Exp. Neurobiol. 2015, 24, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2024 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2024, 20, 3708–3821. [CrossRef]
- Kouli, A.; Torsney, K.M.; Kuan, W.L. Parkinson’s Disease: Etiology, Neuropathology, and Pathogenesis. In Parkinson’s Disease: Pathogenesis and Clinical Aspects; Stoker, T.B., Greenland, J.C., Eds.; Codon Publication: Brisbane, Australia, 2018; Chapter 1. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536722/ (accessed on 31 January 2025).
- Ou, Z.; Pan, J.; Tang, S.; Duan, D.; Yu, D.; Nong, H.; Wang, Z. Global Trends in the Incidence, Prevalence, and Years Lived With Disability of Parkinson’s Disease in 204 Countries/Territories from 1990 to 2019. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 776847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondi, M.W.; Edmonds, E.C.; Salmon, D.P. Alzheimer’s Disease: Past, Present, and Future. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2017, 23, 818–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeTure, M.A.; Dickson, D.W. The neuropathological diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Guo, J.; Ye, X.Y.; Xie, Y.; Xie, T. Oxidative stress: The core pathogenesis and mechanism of Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 77, 101619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trist, B.G.; Hare, D.J.; Double, K.L. Oxidative stress in the aging substantia nigra and the etiology of Parkinson’s disease. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e13031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Ratan, R.R. Oxidative Stress and Huntington’s Disease: The Good, The Bad, and The Ugly. J. Huntingtons Dis. 2016, 5, 217–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motataianu, A.; Serban, G.; Barcutean, L.; Balasa, R. Oxidative Stress in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Synergy of Genetic and Environmental Factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, T.; Deore, S.L.; Kide, A.A.; Shende, B.A.; Sharma, R.; Dadarao Chakole, R.; Nemade, L.S.; Kishor Kale, N.; Borah, S.; Shrikant Deokar, S.; et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis—An updated review. Mitochondrion 2023, 71, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T. Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction-linked neurodegenerative disorders. Neurol. Res. 2017, 39, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teleanu, D.M.; Niculescu, A.G.; Lungu, I.I.; Radu, C.I.; Vladâcenco, O.; Roza, E.; Costăchescu, B.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Teleanu, R.I. An Overview of Oxidative Stress, Neuroinflammation, and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.Y.; Yeo, X.Y.; Bae, H.G.; Lee, D.P.S.; Ho, R.C.; Kim, J.E.; Jo, D.G.; Jung, S. Association of Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis with Neurodegeneration: Can Gut Microbe-Modifying Diet Prevent or Alleviate the Symptoms of Neurodegenerative Diseases? Life 2021, 11, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, L.S.; Anderton, R.S. The role of the microbiota-gut-brain axis in long-term neurodegenerative processes following traumatic brain injury. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2023, 57, 400–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buga, A.M.; Padureanu, V.; Riza, A.L.; Oancea, C.N.; Albu, C.V.; Nica, A.D. The Gut-Brain Axis as a Therapeutic Target in Multiple Sclerosis. Cells 2023, 12, 1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.H.; Cha, M.; Lee, B.H. Neuroprotective Effect of Antioxidants in the Brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyży, A.; Rozenek, H.; Gondek, E.; Jaworski, M. Effect of Antioxidants on the Gut Microbiome Profile and Brain Functions: A Review of Randomized Controlled Trial Studies. Foods 2025, 14, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morén, C.; deSouza, R.M.; Giraldo, D.M.; Uff, C. Antioxidant Therapeutic Strategies in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, U.R.; Danish, S.M.; Ahmad, S.; Ikram, M.; Nadaf, A.; Hasan, N.; Kesharwani, P.; Ahmad, F.J. New opportunities for antioxidants in amelioration of neurodegenerative diseases. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2024, 221, 111961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleton, J. The Gut-Brain Axis: Influence of Microbiota on Mood and Mental Health. Integr. Med. 2018, 17, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Sittipo, P.; Choi, J.; Lee, S.; Lee, Y.K. The function of gut microbiota in immune-related neurological disorders: A review. J. Neuroinflammation 2022, 19, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Liu, Q.; Luo, M.; Xiong, L. Gut Microbiota-Derived Metabolites in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 729346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Wei, Y.; Hashimoto, K. Brain-gut-microbiota axis in depression: A historical overview and future directions. Brain Res. Bull. 2022, 182, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xie, P. Gut microbiota and its metabolites in depression: From pathogenesis to treatment. EBioMedicine 2023, 90, 104527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangiola, F.; Ianiro, G.; Franceschi, F.; Fagiuoli, S.; Gasbarrini, G.; Gasbarrini, A. Gut microbiota in autism and mood disorders. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattorusso, A.; Di Genova, L.; Dell’Isola, G.B.; Mencaroni, E.; Esposito, S. Autism Spectrum Disorders and the Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2019, 11, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, E.M.M. Microbiota-Brain-Gut Axis and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2017, 17, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, B.; Gao, H.; He, C.; Hua, R.; Liang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Xin, S.; Xu, J. Vagus Nerve and Underlying Impact on the Gut Microbiota-Brain Axis in Behavior and Neurodegenerative Diseases. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 6213–6230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, Y.P.; Bernardi, A.; Frozza, R.L. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids from Gut Microbiota in Gut-Brain Communication. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Mu, C.L.; Farzi, A.; Zhu, W.Y. Tryptophan Metabolism: A Link Between the Gut Microbiota and Brain. Adv. Nutr. 2020, 11, 709–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusch, J.A.; Layden, B.T.; Dugas, L.R. Signalling cognition: The gut microbiota and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1130689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossad, O.; Erny, D. The microbiota-microglia axis in central nervous system disorders. Brain Pathol. 2020, 30, 1159–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Jiang, J.; Tan, Y.; Chen, S. Microglia in neurodegenerative diseases: Mechanism and potential therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzio, L.; Viotti, A.; Martino, G. Microglia in Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration: From Understanding to Therapy. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 742065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostick, J.W.; Schonhoff, A.M.; Mazmanian, S.K. Gut microbiome-mediated regulation of neuroinflammation. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2022, 76, 102177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camberos-Barraza, J.; Guadrón-Llanos, A.M.; De la Herrán-Arita, A.K. The Gut Microbiome-Neuroglia Axis: Implications for Brain Health, Inflammation, and Disease. Neuroglia 2024, 5, 254–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.; Sun, M.; Yang, H. Microglia in the Neuroinflammatory Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Therapeutic Targets. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 856376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Zhu, H.; Feng, Y.; Guo, R.; Wan, D. The Impact of Gut Microbiota Disorders on the Blood-Brain Barrier. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 3351–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvey, P.M.; Hendey, B.; Monahan, A.J. The blood-brain barrier in neurodegenerative disease: A rhetorical perspective. J. Neurochem. 2009, 111, 291–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veres-Székely, A.; Szász, C.; Pap, D.; Szebeni, B.; Bokrossy, P.; Vannay, Á. Zonulin as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis Disorders: Encouraging Results and Emerging Questions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yue, J.; Hu, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Lin, X.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, H.; et al. Gut Microbiota Interact With the Brain Through Systemic Chronic Inflammation: Implications on Neuroinflammation, Neurodegeneration, and Aging. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 796288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, L.; Gonzalez-Paramás, A.M.; Heleno, S.A.; Calhelha, R.C. Gut Microbiota as an Endocrine Organ: Unveiling Its Role in Human Physiology and Health. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 9383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, N.; Faisal, Z.; Irfan, R.; Shah, Y.A.; Batool, S.A.; Zahid, T.; Zulfiqar, A.; Fatima, A.; Jahan, Q.; Tariq, H.; et al. Exploring the serotonin-probiotics-gut health axis: A review of current evidence and potential mechanisms. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 12, 694–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Pramanik, J.; Goyal, N.; Chauhan, D.; Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Prajapati, B.G.; Chaiyasut, C. Gut Microbiota in Anxiety and Depression: Unveiling the Relationships and Management Options. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamamah, S.; Aghazarian, A.; Nazaryan, A.; Hajnal, A.; Covasa, M. Role of Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Regulating Dopaminergic Signaling. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suganya, K.; Koo, B.S. Gut-Brain Axis: Role of Gut Microbiota on Neurological Disorders and How Probiotics/Prebiotics Beneficially Modulate Microbial and Immune Pathways to Improve Brain Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haney, M.M.; Ericsson, A.C.; Lever, T.E. Effects of Intraoperative Vagal Nerve Stimulation on the Gastrointestinal Microbiome in a Mouse Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Comp. Med. 2018, 68, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaz, B.; Sinniger, V.; Pellissier, S. The Vagus Nerve in the Neuro-Immune Axis: Implications in the Pathology of the Gastrointestinal Tract. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raskov, H.; Burcharth, J.; Pommergaard, H.C.; Rosenberg, J. Irritable bowel syndrome, the microbiota and the gut-brain axis. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 365–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Liu, S.; Li, S.; Yang, J.; Hu, G.; Xu, C.; Song, W. Psychological stress in inflammatory bowel disease: Psychoneuroimmunological insights into bidirectional gut-brain communications. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1016578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.F.; Albusoda, A.; Farmer, A.D.; Aziz, Q. The anatomical basis for transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation. J. Anat. 2020, 236, 588–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaz, B.; Bazin, T.; Pellissier, S. The Vagus Nerve at the Interface of the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesampour, F.; Bernstein, C.N.; Ghia, J.E. Brain-Gut Axis: Invasive and Noninvasive Vagus Nerve Stimulation, Limitations, and Potential Therapeutic Approaches. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2024, 30, 482–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirillo, G.; Negrete-Diaz, F.; Yucuma, D.; Virtuoso, A.; Korai, S.A.; De Luca, C.; Kaniusas, E.; Papa, M.; Panetsos, F. Vagus Nerve Stimulation: A Personalized Therapeutic Approach for Crohn’s and Other Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Cells 2022, 11, 4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaz, B. Anti-inflammatory effects of vagal nerve stimulation with a special attention to intestinal barrier dysfunction. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2022, 34, e14456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaz, B.; Picq, C.; Sinniger, V.; Mayol, J.F.; Clarençon, D. Vagus nerve stimulation: From epilepsy to the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 25, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breit, S.; Kupferberg, A.; Rogler, G.; Hasler, G. Vagus Nerve as Modulator of the Brain-Gut Axis in Psychiatric and Inflammatory Disorders. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.J.; Wu, J.; Gong, L.J.; Yang, H.S.; Chen, H. Non-invasive vagus nerve stimulation in anti-inflammatory therapy: Mechanistic insights and future perspectives. Front. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1490300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraji, N.; Payami, B.; Ebadpour, N.; Gorji, A. Vagus nerve stimulation and gut microbiota interactions: A novel therapeutic avenue for neuropsychiatric disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2025, 169, 105990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woźniak, D.; Cichy, W.; Przysławski, J.; Drzymała-Czyż, S. The role of microbiota and enteroendocrine cells in maintaining homeostasis in the human digestive tract. Adv. Med. Sci. 2021, 66, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Singh, R.; Ghoshal, U.C. Enterochromaffin Cells-Gut Microbiota Crosstalk: Underpinning the Symptoms, Pathogenesis, and Pharmacotherapy in Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2022, 28, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falvey, A. Vagus nerve stimulation and inflammation: Expanding the scope beyond cytokines. Bioelectron. Med. 2022, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, V.A.; Tracey, K.J. The vagus nerve and the inflammatory reflex—Linking immunity and metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaro, R.; Actis, G.C.; Caviglia, G.P.; Pitoni, D.; Ribaldone, D.G. Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Role of Vagus Nerve Stimulation. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, W.A.; Kastin, A.J.; Broadwell, R.D. Passage of cytokines across the blood-brain barrier. Neuroimmunomodulation 1995, 2, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillisch, K. The effects of gut microbiota on CNS function in humans. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulluwishewa, D.; Anderson, R.C.; McNabb, W.C.; Moughan, P.J.; Wells, J.M.; Roy, N.C. Regulation of tight junction permeability by intestinal bacteria and dietary components. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, B.; He, B.; Li, L.; Nice, E.C.; Zhang, W.; Xu, J. New Insights into the Gut Microbiota in Neurodegenerative Diseases from the Perspective of Redox Homeostasis. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wang, H.B.; Hashimoto, K. The vagus nerve: An old but new player in brain-body communication. Brain Behav. Immun. 2025, 124, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiefels, M.D.; Furar, E.; Eshraghi, R.S.; Mittal, J.; Memis, I.; Moosa, M.; Mittal, R.; Eshraghi, A.A. Targeting Gut Dysbiosis and Microbiome Metabolites for the Development of Therapeutic Modalities for Neurological Disorders. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2024, 22, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Riordan, K.J.; Collins, M.K.; Moloney, G.M.; Knox, E.G.; Aburto, M.R.; Fülling, C.; Morley, S.J.; Clarke, G.; Schellekens, H.; Cryan, J.F. Short chain fatty acids: Microbial metabolites for gut-brain axis signalling. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2022, 546, 111572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayazid, A.B.; Kim, J.G.; Azam, S.; Jeong, S.A.; Kim, D.H.; Park, C.W.; Lim, B.O. Sodium butyrate ameliorates neurotoxicity and exerts anti-inflammatory effects in high fat diet-fed mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 159, 112743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiuolo, J.; Bulotta, R.M.; Ruga, S.; Nucera, S.; Macrì, R.; Scarano, F.; Oppedisano, F.; Carresi, C.; Gliozzi, M.; Musolino, V.; et al. The Postbiotic Properties of Butyrate in the Modulation of the Gut Microbiota: The Potential of Its Combination with Polyphenols and Dietary Fibers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moțățăianu, A.; Șerban, G.; Andone, S. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Microbiota-Gut-Brain Cross-Talk with a Focus on Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, Z.; Tang, X.; Lu, M.; Hu, Z.; Tang, Z. The role of short-chain fatty acids in central nervous system diseases: A bibliometric and visualized analysis with future directions. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Hu, H.; Ju, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Y. Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids and depression: Deep insight into biological mechanisms and potential applications. Gen. Psychiatr. 2024, 37, e101374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, R.; Karande, A.; Ranganathan, P. Emerging role of gut microbiota dysbiosis in neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1149618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Gao, J.; Zhu, M.; Liu, K.; Zhang, H.L. Gut Microbiota and Dysbiosis in Alzheimer’s Disease: Implications for Pathogenesis and Treatment. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 5026–5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, M.; Ohno, K. Parkinson’s Disease and Gut Microbiota. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 77 (Suppl. S2), 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairamian, D.; Sha, S.; Rolhion, N.; Sokol, H.; Dorothée, G.; Lemere, C.A.; Krantic, S. Microbiota in neuroinflammation and synaptic dysfunction: A focus on Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2022, 17, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Ding, N.; Feng, X.; Liao, W. The gut microbiome, immune modulation, and cognitive decline: Insights on the gut-brain axis. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1529958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.J.; Wu, E. The role of gut microbiota in immune homeostasis and autoimmunity. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.P.; Huang, J.; Chan, K.W.Y.; Leung, W.K.; Goto, T.; Ho, Y.S.; Chang, R.C. IL-1β and TNF-α play an important role in modulating the risk of periodontitis and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflammation 2023, 20, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Balachandran, Y.L.; Chong, W.P.; Chan, K.W.Y. Roles of Cytokines in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ghosh, S. Toll-like receptor-mediated NF-kappaB activation: A phylogenetically conserved paradigm in innate immunity. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciesielska, A.; Matyjek, M.; Kwiatkowska, K. TLR4 and CD14 trafficking and its influence on LPS-induced pro-inflammatory signaling. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 1233–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerton, C.B.; Longlands, M.G.; Wiener, K.; Shreeve, D.R. Faecal calprotectin: A marker of inflammation throughout the intestinal tract. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2002, 14, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatek-Majkusiak, J.; Geremek, M.; Koziorowski, D.; Tomasiuk, R.; Szlufik, S.; Friedman, A. Serum levels of hepcidin and interleukin 6 in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2020, 80, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langeh, U.; Singh, S. Targeting S100B Protein as a Surrogate Biomarker and its Role in Various Neurological Disorders. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2021, 19, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michetti, F.; Clementi, M.E.; Di Liddo, R.; Valeriani, F.; Ria, F.; Rende, M.; Di Sante, G.; Romano Spica, V. The S100B Protein: A Multifaceted Pathogenic Factor More Than a Biomarker. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, S. Regulation of Physiological Barrier Function by the Commensal Microbiota. Life 2023, 13, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.; Fonseca, S.; Carding, S.R. Gut microbes and metabolites as modulators of blood-brain barrier integrity and brain health. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 135–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, R.; Bouzari, B.; Hosseini-Fard, S.R.; Mazaheri, M.; Ahmadyousefi, Y.; Abdi, M.; Jalalifar, S.; Karimitabar, Z.; Teimoori, A.; Keyvani, H.; et al. Role of microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids in nervous system disorders. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 139, 111661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, A. All disease begins in the (leaky) gut: Role of zonulin-mediated gut permeability in the pathogenesis of some chronic inflammatory diseases. F1000Research 2020, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, T.; Du, Y.; Xing, C.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, R.F. Toll-Like Receptor Signaling and Its Role in Cell-Mediated Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 812774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, C.R.; Balachandran, Y.; Aulakh, G.K.; Singh, B. TLR10: An Intriguing Toll-Like Receptor with Many Unanswered Questions. J. Innate Immun. 2024, 16, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Bayardo, T.I.; Román-Rojas, D.; García-Sánchez, A.; Cardona-Muñoz, E.G.; Sánchez-Lozano, D.I.; Totsuka-Sutto, S.; Gómez-Hermosillo, L.F.; Casillas-Moreno, J.; Andrade-Sierra, J.; Pazarín-Villaseñor, L.; et al. The Role of TLRs in Obesity and Its Related Metabolic Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, A.; Nyavor, Y.; Zarabian, N.; Mahoney, A.; Frame, L.A. The microbiota-gut-brain-immune interface in the pathogenesis of neuroinflammatory diseases: A narrative review of the emerging literature. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1365673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Hua, H.; Liu, L.; Mao, Y.; Wang, R. Interactions between toll-like receptors signaling pathway and gut microbiota in host homeostasis. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2024, 12, e1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolzer, I.; Scherer, E.; Süß, P.; Rothhammer, V.; Winner, B.; Neurath, M.F.; Günther, C. Impact of Microbiome-Brain Communication on Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Knauf, C. How gut microbes talk to organs: The role of endocrine and nervous routes. Mol. Metab. 2016, 5, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandpal, M.; Indari, O.; Baral, B.; Jakhmola, S.; Tiwari, D.; Bhandari, V.; Pandey, R.K.; Bala, K.; Sonawane, A.; Jha, H.C. Dysbiosis of Gut Microbiota from the Perspective of the Gut-Brain Axis: Role in the Provocation of Neurological Disorders. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symons, F.J.; Wolff, J.J.; Stone, L.S.; Lim, T.K.; Bodfish, J.W. Salivary biomarkers of HPA axis and autonomic activity in adults with intellectual disability with and without stereotyped and self-injurious behavior disorders. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2011, 3, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, J.P.; McKlveen, J.M.; Ghosal, S.; Kopp, B.; Wulsin, A.; Makinson, R.; Scheimann, J.; Myers, B. Regulation of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenocortical Stress Response. Compr. Physiol. 2016, 6, 603–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirmer, M.; Smeekens, S.P.; Vlamakis, H.; Jaeger, M.; Oosting, M.; Franzosa, E.A.; Ter Horst, R.; Jansen, T.; Jacobs, L.; Bonder, M.J.; et al. Linking the Human Gut Microbiome to Inflammatory Cytokine Production Capacity. Cell 2016, 167, 1125–1136.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, K.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. The microbiome: A key regulator of stress and neuroinflammation. Neurobiol. Stress 2016, 4, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intili, G.; Paladino, L.; Rappa, F.; Alberti, G.; Plicato, A.; Calabrò, F.; Fucarino, A.; Cappello, F.; Bucchieri, F.; Tomasello, G.; et al. From Dysbiosis to Neurodegenerative Diseases through Different Communication Pathways: An Overview. Biology 2023, 12, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Sun, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, D. Oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage and neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen. Res. 2013, 8, 2003–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Meenatchi, R.; Ahmed, Z.H.T.; Thacharodi, A.; Rohinth, M.; Kumar, R.R.S.; Varthan, H.M.K.; Hassan, S. Implications of the gut microbiome in cardiovascular diseases: Association of gut microbiome with cardiovascular diseases, therapeutic interventions and multi-omics approach for precision medicine. Med. Microecol. 2024, 19, 100096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Bosch, C.; Boorman, E.; Zunszain, P.A.; Mann, G.E. Short-chain fatty acids as modulators of redox signaling in health and disease. Redox Biol. 2021, 47, 102165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukiw, W.J.; Cong, L.; Jaber, V.; Zhao, Y. Microbiome-Derived Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Selectively Inhibits Neurofilament Light Chain (NF-L) Gene Expression in Human Neuronal-Glial (HNG) Cells in Primary Culture. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vincenzo, F.; Del Gaudio, A.; Petito, V.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Scaldaferri, F. Gut microbiota, intestinal permeability, and systemic inflammation: A narrative review. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2024, 19, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Cong, L.; Lukiw, W.J. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Accumulates in Neocortical Neurons of Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Brain and Impairs Transcription in Human Neuronal-Glial Primary Co-cultures. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogue, A.I.; Jaber, V.R.; Sharfman, N.M.; Zhao, Y.; Lukiw, W.J. Downregulation of Neurofilament Light Chain Expression in Human Neuronal-Glial Cell Co-Cultures by a Microbiome-Derived Lipopolysaccharide-Induced miRNA-30b-5p. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 900048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, S.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; Jia, M.; Chen, T.; Zhang, X. Gut microbiota modulates neurotransmitter and gut-brain signaling. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 287, 127858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teleanu, R.I.; Niculescu, A.G.; Roza, E.; Vladâcenco, O.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Teleanu, D.M. Neurotransmitters-Key Factors in Neurological and Neurodegenerative Disorders of the Central Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agus, A.; Planchais, J.; Sokol, H. Gut Microbiota Regulation of Tryptophan Metabolism in Health and Disease. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Li, J.; Ying, S. Tryptophan Metabolism and Gut Microbiota: A Novel Regulatory Axis Integrating the Microbiome, Immunity, and Cancer. Metabolites 2023, 13, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, S.; Nadar, R.; Kim, S.; Liu, K.; Govindarajulu, M.; Cook, P.; Watts Alexander, C.S.; Dhanasekaran, M.; Moore, T. The Influence of Kynurenine Metabolites on Neurodegenerative Pathologies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; He, H.; Peng, M.; Zeng, M.; Sun, H. The role of the indoles in microbiota-gut-brain axis and potential therapeutic targets: A focus on human neurological and neuropsychiatric diseases. Neuropharmacology 2023, 239, 109690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Li, H.; Anjum, K.; Zhong, X.; Miao, S.; Zheng, G.; Liu, W.; Li, L. Dual Role of Indoles Derived from Intestinal Microbiota on Human Health. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 903526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.C. Neurodegenerative disorders of aging: The down side of rising longevity. Mo. Med. 2013, 110, 393–394. [Google Scholar]
- Dorsey, E.R.; Sherer, T.; Okun, M.S.; Bloem, B.R. The Emerging Evidence of the Parkinson Pandemic. J. Parkinsons Dis. 2018, 8, S3–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinger, K.A. Recent advances in our understanding of neurodegeneration. J. Neural Transm. 2009, 116, 1111–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jellinger, K.A. Basic mechanisms of neurodegeneration: A critical update. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 457–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Sanchez, M.; Licitra, F.; Underwood, B.R.; Rubinsztein, D.C. Huntington’s Disease: Mechanisms of Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Strategies. Cold Spring Harb. Perspec. Med. 2017, 7, a024240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.H.; Al-Chalabi, A. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollah, S.A.; Nayak, A.; Barhai, S.; Maity, U. A comprehensive review on frontotemporal dementia: Its impact on language, speech and behavior. Dement. Neuropsychol. 2024, 18, e20230072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wootla, B.; Eriguchi, M.; Rodriguez, M. Is multiple sclerosis an autoimmune disease? Autoimmune Dis. 2012, 2012, 969657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soong, B.W.; Morrison, P.J. Spinocerebellar ataxias. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 155, 143–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, C.; Satani, N. The intricate mechanisms of neurodegeneration in prion diseases. Trends Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulisano, W.; Maugeri, D.; Baltrons, M.A.; Fà, M.; Amato, A.; Palmeri, A.; D’Adamio, L.; Grassi, C.; Devanand, D.P.; Honig, L.S.; et al. Role of Amyloid-β and Tau Proteins in Alzheimer’s Disease: Confuting the Amyloid Cascade. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 64, S611–S631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Benito, M.; Granado, N.; García-Sanz, P.; Michel, A.; Dumoulin, M.; Moratalla, R. Modeling Parkinson’s Disease With the Alpha-Synuclein Protein. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Diamond, M.I. Huntington disease and the huntingtin protein. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2012, 107, 189–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picca, A.; Calvani, R.; Coelho-Junior, H.J.; Landi, F.; Bernabei, R.; Marzetti, E. Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress, and Neuroinflammation: Intertwined Roads to Neurodegeneration. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koszła, O.; Sołek, P. Misfolding and aggregation in neurodegenerative diseases: Protein quality control machinery as potential therapeutic clearance pathways. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, P.J.; Herman, A.M.; Moussa, C.E. Inflammation in the early stages of neurodegenerative pathology. J. Neuroimmunol. 2011, 238, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinney, J.W.; Bemiller, S.M.; Murtishaw, A.S.; Leisgang, A.M.; Salazar, A.M.; Lamb, B.T. Inflammation as a central mechanism in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 4, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansey, M.G.; Wallings, R.L.; Houser, M.C.; Herrick, M.K.; Keating, C.E.; Joers, V. Inflammation and immune dysfunction in Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 657–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.A.; Das, A.; Ray, S.K.; Banik, N.L. Role of pro-inflammatory cytokines released from microglia in neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res. Bull. 2012, 87, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinashi, Y.; Hase, K. Partners in Leaky Gut Syndrome: Intestinal Dysbiosis and Autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 673708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyan, M.; Tousif, A.H.; Sonali, S.; Vichitra, C.; Sunanda, T.; Praveenraj, S.S.; Ray, B.; Gorantla, V.R.; Rungratanawanich, W.; Mahalakshmi, A.M.; et al. Role of Endogenous Lipopolysaccharides in Neurological Disorders. Cells 2022, 11, 4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Ullah, N.; Zha, L.; Bai, Y.; Khan, A.; Zhao, T.; Che, T.; Zhang, C. Alteration of Gut Microbiota in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Cause or Consequence? IBD Treatment Targeting the Gut Microbiome. Pathogens 2019, 8, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, S.D.; Sun, N.; Canakis, A.; Park, W.Y.; Weber, H.C. Irritable Bowel Syndrome and the Gut Microbiome: A Comprehensive Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrncir, T. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis: Triggers, Consequences, Diagnostic and Therapeutic Options. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, N.; Luthra, N.S.; Corcos, D.M.; Fantuzzi, G. C-reactive protein as the biomarker of choice to monitor the effects of exercise on inflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1178448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Molin, G.; Davidson, S.; Roth, B.; Sjöberg, K.; Håkansson, Å. CRP in Outpatients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease Is Linked to the Blood Microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Chu, J.; Feng, S.; Guo, C.; Xue, B.; He, K.; Li, L. Immunological mechanisms of inflammatory diseases caused by gut microbiota dysbiosis: A review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 164, 114985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kukreti, R.; Saso, L.; Kukreti, S. Oxidative Stress: A Key Modulator in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Molecules 2019, 24, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamagno, E.; Guglielmotto, M.; Vasciaveo, V.; Tabaton, M. Oxidative Stress and Beta Amyloid in Alzheimer’s Disease. Which Comes First: The Chicken or the Egg? Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rademacher, K.; Nakamura, K. Role of dopamine neuron activity in Parkinson’s disease pathophysiology. Exp. Neurol. 2024, 373, 114645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieryńska, M.; Szulc-Dąbrowska, L.; Struzik, J.; Mielcarska, M.B.; Gregorczyk-Zboroch, K.P. Integrity of the Intestinal Barrier: The Involvement of Epithelial Cells and Microbiota—A Mutual Relationship. Animals 2022, 12, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takiishi, T.; Fenero, C.I.M.; Câmara, N.O.S. Intestinal barrier and gut microbiota: Shaping our immune responses throughout life. Tissue Barriers 2017, 5, e1373208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolfi, C.; Maresca, C.; Monteleone, G.; Laudisi, F. Implication of Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction in Gut Dysbiosis and Diseases. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xiao, D.; Mao, Q.; Xia, H. Role of neuroinflammation in neurodegeneration development. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Jung, U.J.; Kim, S.R. The Crucial Role of the Blood–Brain Barrier in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Mechanisms of Disruption and Therapeutic Implications. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, J.S.; Mak, W.Q.; Tan, L.K.S.; Ng, C.X.; Chan, H.H.; Yeow, S.H.; Foo, J.B.; Ong, Y.S.; How, C.W.; Khaw, K.Y. Microbiota-gut-brain axis and its therapeutic applications in neurodegenerative diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qi, Y.; Zheng, H. Dietary Polyphenol, Gut Microbiota, and Health Benefits. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaranta, G.; Guarnaccia, A.; Fancello, G.; Agrillo, C.; Iannarelli, F.; Sanguinetti, M.; Masucci, L. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation and Other Gut Microbiota Manipulation Strategies. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liang, J.; Hu, N.; He, N.; Liu, B.; Liu, G.; Qin, Y. The Gut Microbiota Modulates Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s Disease: Elucidating Crucial Factors and Mechanistic Underpinnings. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2024, 30, e70091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, E.; Chandrasekhar, G.; Chandrasekar, P.; Anbarasu, K.; Vickram, A.S.; Karunakaran, R.; Rajasekaran, R.; Srikumar, P.S. Alpha-Synuclein Aggregation in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 736978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogers, J.S.; Bloem, B.R.; Den Heijer, J.M. The Etiology of Parkinson’s Disease: New Perspectives from Gene-Environment Interactions. J. Park. Dis. 2023, 13, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caradonna, E.; Nemni, R.; Bifone, A.; Gandolfo, P.; Costantino, L.; Giordano, L.; Mormone, E.; Macula, A.; Cuomo, M.; Difruscolo, R.; et al. The Brain–Gut Axis, an Important Player in Alzheimer and Parkinson Disease: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, B.; Caridade-Silva, R.; Soares-Guedes, C.; Martins-Macedo, J.; Gomes, E.D.; Monteiro, S.; Teixeira, F.G. Neuroinflammation and Parkinson’s Disease-From Neurodegeneration to Therapeutic Opportunities. Cells 2022, 11, 2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Liu, X.; Ye, Y.; Yan, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, L.; Chen, F.; Ling, Z. Gut Microbiota: A Novel Therapeutic Target for Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 937555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashique, S.; Mohanto, S.; Ahmed, M.G.; Mishra, N.; Garg, A.; Chellappan, D.K.; Omara, T.; Iqbal, S.; Kahwa, I. Gut-brain axis: A cutting-edge approach to target neurological disorders and potential synbiotic application. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Cui, L.; Gao, J.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.L. Gut Microbial Metabolites in Parkinson’s Disease: Implications of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in the Pathogenesis and Treatment. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 3745–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghammer, P.; Van Den Berge, N. Brain-First versus Gut-First Parkinson’s Disease: A Hypothesis. J. Park. Dis. 2019, 9, S281–S295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Mor, D.E. Gut-to-Brain α-Synuclein Transmission in Parkinson’s Disease: Evidence for Prion-like Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaz, B. The gut-brain axis in Parkinson’s disease. Rev. Neurol. 2024, 180, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, K.N.; Verheijden, S.; Boeckxstaens, G.E. The Vagus Nerve in Appetite Regulation, Mood, and Intestinal Inflammation. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 730–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claudino Dos Santos, J.C.; Oliveira, L.F.; Noleto, F.M.; Gusmão, C.T.P.; Brito, G.A.C.; Viana, G.S.B. Gut-microbiome-brain axis: The crosstalk between the vagus nerve, alpha-synuclein and the brain in Parkinson’s disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 18, 2611–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klann, E.M.; Dissanayake, U.; Gurrala, A.; Farrer, M.; Shukla, A.W.; Ramirez-Zamora, A.; Mai, V.; Vedam-Mai, V. The Gut-Brain Axis and Its Relation to Parkinson’s Disease: A Review. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 13, 782082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrand, A.Q.; Helke, K.L.; Gregory, R.A.; Gooz, M.; Hinson, V.K.; Boger, H.A. Vagus nerve stimulation improves locomotion and neuronal populations in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Stimul. 2017, 10, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrand, A.Q.; Verner, R.S.; McGuire, R.M.; Helke, K.L.; Hinson, V.K.; Boger, H.A. Differential effects of vagus nerve stimulation paradigms guide clinical development for Parkinson’s disease. Brain Stimul. 2020, 13, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionnet, A.; Leclair-Visonneau, L.; Neunlist, M.; Murayama, S.; Takao, M.; Adler, C.H.; Derkinderen, P.; Beach, T.G. Does Parkinson’s disease start in the gut? Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 135, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Gao, G.; Yang, H. The Pathological Mechanism Between the Intestine and Brain in the Early Stage of Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 861035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riederer, P.; Nagatsu, T.; Youdim, M.B.H.; Wulf, M.; Dijkstra, J.M.; Sian-Huelsmann, J. Lewy bodies, iron, inflammation and neuromelanin: Pathological aspects underlying Parkinson’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 2023, 130, 627–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho-Alonso, M.; Sarriés-Serrano, U.; Miquel-Rio, L.; Yanes Castilla, C.; Paz, V.; Meana, J.J.; Perello, M.; Bortolozzi, A. New insights into the effects of serotonin on Parkinson’s disease and depression through its role in the gastrointestinal tract. Span. J. Psychiatry Ment. Health 2024, 9, S2950-2853(24)00039-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, M.; Ding, J.Y. The interplay between gut microbiota and the brain-gut axis in Parkinson’s disease treatment. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1415463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Karaman, R. Comprehensive Review on Alzheimer’s Disease: Causes and Treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, 5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Geng, R.; Tu, Q. Gut microbial involvement in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. Aging 2021, 13, 13359–13371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.O.; Holtzman, D.M. Current understanding of the Alzheimer’s disease-associated microbiome and therapeutic strategies. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhaar, B.J.H.; Hendriksen, H.M.A.; de Leeuw, F.A.; Doorduijn, A.S.; van Leeuwenstijn, M.; Teunissen, C.E.; Barkhof, F.; Scheltens, P.; Kraaij, R.; van Duijn, C.M.; et al. Gut Microbiota Composition Is Related to AD Pathology. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 794519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, S.; Sisodia, S.S.; Vassar, R.J. The gut microbiome in Alzheimer’s disease: What we know and what remains to be explored. Mol. Neurodegener. 2023, 18, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloom, G.S. Amyloid-β and tau: The trigger and bullet in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, X.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liang, X.; Wu, J.; Yang, Y.; et al. Gut-derived β-amyloid: Likely a centerpiece of the gut-brain axis contributing to Alzheimer’s pathogenesis. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2167172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mroke, P.; Goit, R.; Rizwan, M.; Tariq, S.; Rizwan, A.W.; Umer, M.; Nassar, F.F.; Torijano Sarria, A.J.; Singh, D.; Baig, I. Implications of the Gut Microbiome in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Narrative Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e73681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, N.M.; Kerby, R.L.; Dill-McFarland, K.A.; Harding, S.J.; Merluzzi, A.P.; Johnson, S.C.; Carlsson, C.M.; Asthana, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; et al. Gut microbiome alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Bander, Z.; Nitert, M.D.; Mousa, A.; Naderpoor, N. The Gut Microbiota and Inflammation: An Overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roveta, F.; Bonino, L.; Piella, E.M.; Rainero, I.; Rubino, E. Neuroinflammatory Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearns, R. Gut-Brain Axis and Neuroinflammation: The Role of Gut Permeability and the Kynurenine Pathway in Neurological Disorders. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2024, 44, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhalifa, A.E.; Al-Ghraiybah, N.F.; Odum, J.; Shunnarah, J.G.; Austin, N.; Kaddoumi, A. Blood-Brain Barrier Breakdown in Alzheimer’s Disease: Mechanisms and Targeted Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenaro, E.; Piacentino, G.; Constantin, G. The blood-brain barrier in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2017, 107, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, M.D.; Sagare, A.P.; Zlokovic, B.V. Blood-brain barrier breakdown in Alzheimer disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, F.; Ma, X.; Perry, G.; Zhu, X. Mitochondria dysfunction in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Recent advances. Mol. Neurodegener. 2020, 15, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernocchi, P.; Del Chierico, F.; Putignani, L. Gut Microbiota Metabolism and Interaction with Food Components. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.N.; Theiss, A.L. Gut bacteria signaling to mitochondria in intestinal inflammation and cancer. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakhar, D.; Sarin, S.K.; Kaur, S. Gut microbiota and dynamics of ammonia metabolism in liver disease. npj Gut Liver 2024, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Lu, M.H.; Yuan, D.J.; Xu, D.E.; Yao, P.P.; Ji, W.L.; Chen, H.; Liu, W.L.; Yan, C.X.; Xia, Y.Y.; et al. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Neural Injury. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S.M.; Barnes, K.; De Marco, M.; Shaw, P.J.; Ferraiuolo, L.; Blackburn, D.J.; Venneri, A.; Mortiboys, H. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Biomarker of the Future? Biomedicines 2021, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenova, N.; Garashchenko, N.; Kolesnikov, S.; Darenskaya, M.; Kolesnikova, L. Gut Microbiome Interactions with Oxidative Stress: Mechanisms and Consequences for Health. Pathophysiology 2024, 31, 309–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, U.C.; Bhol, N.K.; Swain, S.K.; Samal, R.R.; Nayak, P.K.; Raina, V.; Panda, S.K.; Kerry, R.G.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Jena, A.B. Oxidative stress and inflammation in the pathogenesis of neurological disorders: Mechanisms and implications. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2025, 15, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, K.F.; Al-Mubarak, B.; Martel, M.A.; McKay, S.; Wheelan, N.; Hasel, P.; Márkus, N.M.; Baxter, P.; Deighton, R.F.; Serio, A.; et al. Neuronal development is promoted by weakened intrinsic antioxidant defences due to epigenetic repression of Nrf2. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyanaraman, B.; Cheng, G.; Hardy, M. Gut microbiome, short-chain fatty acids, alpha-synuclein, neuroinflammation, and ROS/RNS: Relevance to Parkinson’s disease and therapeutic implications. Redox Biol. 2024, 71, 103092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, W.X.; Wang, F.; Liu, J.Y.; Liu, C.F. Relationship Between Short-chain Fatty Acids and Parkinson’s Disease: A Review from Pathology to Clinic. Neurosci. Bull. 2024, 40, 500–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, A.; Nixon, R.A. Neurofilament Proteins as Biomarkers to Monitor Neurological Diseases and the Efficacy of Therapies. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 689938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buawangpong, N.; Pinyopornpanish, K.; Siri-Angkul, N.; Chattipakorn, N.; Chattipakorn, S.C. The role of trimethylamine-N-Oxide in the development of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Cell. Physiol. 2022, 237, 1661–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrona Cardoza, P.; Spillane, M.B.; Morales Marroquin, E. Alzheimer’s disease and gut microbiota: Does trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) play a role? Nutr. Rev. 2022, 80, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatarek, P.; Kaluzna-Czaplinska, J. Trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) in human health. EXCLI J. 2021, 20, 301–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudimela, S.; Vishwanath, N.K.; Pillai, A.; Morales, R.; Marrelli, S.P.; Barichello, T.; Giridharan, V.V. Clinical significance and potential role of trimethylamine N-oxide in neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 103334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, N.M.; Romano, K.A.; Darst, B.F.; Engelman, C.D.; Johnson, S.C.; Carlsson, C.M.; Asthana, S.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Bendlin, B.B.; et al. The gut microbiota-derived metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide is elevated in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2018, 10, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.D.; Cohen, L.S.; Corbo, C.; Morozova, V.; ElIdrissi, A.; Phillips, G.; Kleiman, F.E. Hyperphosphorylation of Tau Associates With Changes in Its Function Beyond Microtubule Stability. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggiore, A.; Latina, V.; D’Erme, M.; Amadoro, G.; Coccurello, R. Non-canonical pathways associated to Amyloid beta and tau protein dyshomeostasis in Alzheimer’s disease: A narrative review. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 102, 102578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, S.K.; Shah, R.; Alford, N.; Mishra, S.P.; Jain, S.; Hansen, B.; Sanberg, P.; Molina, A.J.A.; Yadav, H. The Triple Alliance: Microbiome, Mitochondria, and Metabolites in the Context of Age-Related Cognitive Decline and Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2023, 78, 2187–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Es, M.A.; Hardiman, O.; Chio, A.; Al-Chalabi, A.; Pasterkamp, R.J.; Veldink, J.H.; van den Berg, L.H. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Lancet 2017, 390, 2084–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duranti, E.; Villa, C. Molecular Investigations of Protein Aggregation in the Pathogenesis of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peggion, C.; Scalcon, V.; Massimino, M.L.; Nies, K.; Lopreiato, R.; Rigobello, M.P.; Bertoli, A. SOD1 in ALS: Taking Stock in Pathogenic Mechanisms and the Role of Glial and Muscle Cells. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksoy, Y.A.; Deng, W.; Stoddart, J.; Chung, R.; Guillemin, G.; Cole, N.J.; Neely, G.G.; Hesselson, D. “STRESSED OUT”: The role of FUS and TDP-43 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2020, 126, 105821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.L.; Manley, J.L. Multiple ways to a dead end: Diverse mechanisms by which ALS mutant genes induce cell death. Cell Cycle 2021, 20, 631–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Huo, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Meng, F.; Su, Q.; Bao, W.; Zhang, L.; et al. The Impact of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Cells 2022, 11, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.J. Mitochondrial and Cell Death Mechanisms in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 839–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Ma, Z.; Chen, X.; Shu, S. Microglia activation in central nervous system disorders: A review of recent mechanistic investigations and development efforts. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1103416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mead, R.J.; Shan, N.; Reiser, H.J.; Marshall, F.; Shaw, P.J. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A neurodegenerative disorder poised for successful therapeutic translation. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2023, 22, 185–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boddy, S.L.; Giovannelli, I.; Sassani, M.; Cooper-Knock, J.; Snyder, M.P.; Segal, E.; Elinav, E.; Barker, L.A.; Shaw, P.J.; McDermott, C.J. The gut microbiome: A key player in the complexity of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). BMC Med. 2021, 19, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertzberg, V.S.; Singh, H.; Fournier, C.N.; Moustafa, A.; Polak, M.; Kuelbs, C.A.; Torralba, M.G.; Tansey, M.G.; Nelson, K.E.; Glass, J.D. Gut microbiome differences between amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients and spouse controls. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2022, 23, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaul, M.; Mukherjee, D.; Weiner, H.L.; Cox, L.M. Gut microbiota immune cross-talk in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurotherapeutics 2024, 21, e00469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiller, K.J.; Restrepo, C.R.; Khan, T.; Dominique, M.A.; Fang, T.C.; Canter, R.G.; Roberts, C.J.; Miller, K.R.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; et al. Microglia-mediated recovery from ALS-relevant motor neuron degeneration in a mouse model of TDP-43 proteinopathy. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoforidou, E.; Joilin, G.; Hafezparast, M. Potential of activated microglia as a source of dysregulated extracellular microRNAs contributing to neurodegeneration in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Youssef, M.M.M.; Santos, J.R.; Lee, J.; Park, J. Microglia and Astrocytes in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Disease-Associated States, Pathological Roles, and Therapeutic Potential. Biology 2023, 12, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Henderson, R.; Aylward, J.; McCombe, P. Gut Symptoms, Gut Dysbiosis and Gut-Derived Toxins in ALS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, V.; Fontdevila, L.; Rico-Rios, S.; Povedano, M.; Andrés-Benito, P.; Torres, P.; Serrano, J.C.E.; Pamplona, R.; Portero-Otin, M. Microbial Influences on Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: The Gut–Brain Axis and Therapeutic Potential of Microbiota Modulation. Sclerosis 2025, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemerková, P.; Vališ, M. Role of Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Antioxidant Metalloenzymes and Therapeutic Strategies. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mincic, A.M.; Antal, M.; Filip, L.; Miere, D. Modulation of gut microbiome in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases: A systematic review. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 43, 1832–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadigh-Eteghad, S.; Sabermarouf, B.; Majdi, A.; Talebi, M.; Farhoudi, M.; Mahmoudi, J. Amyloid-beta: A crucial factor in Alzheimer’s disease. Med. Princ. Pract. 2015, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, T.; Li, P.; Wei, N.; Zhao, Z.; Liang, H.; Ji, X.; Chen, W.; Xue, M.; Wei, J. The Ambiguous Relationship of Oxidative Stress, Tau Hyperphosphorylation, and Autophagy Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 352723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Jung, U.J.; Kim, S.R. Role of Oxidative Stress in Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, V.; Junn, E.; Mouradian, M.M. The role of oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. J. Park. Dis. 2013, 3, 461–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, J.G.; Montine, K.S.; Zhang, J.; Montine, T.J. Mitochondrial therapeutics in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2011, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golpich, M.; Amini, E.; Mohamed, Z.; Azman Ali, R.; Mohamed Ibrahim, N.; Ahmadiani, A. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Biogenesis in Neurodegenerative diseases: Pathogenesis and Treatment. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2017, 23, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, P.; Sun, Y.; Li, L. Mitochondrial dysfunction in chronic neuroinflammatory diseases (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2024, 53, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houldsworth, A. Role of oxidative stress in neurodegenerative disorders: A review of reactive oxygen species and prevention by antioxidants. Brain Commun. 2024, 6, fcad356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, A.; Monteiro, L.; Lima, R.M.; Oliveira, D.M.; Cerqueira, M.D.; El-Bachá, R.S. Oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases: Mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2011, 2011, 467180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuzzo, D. Role of Natural Antioxidants on Neuroprotection and Neuroinflammation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riaz Rajoka, M.S.; Thirumdas, R.; Mehwish, H.M.; Umair, M.; Khurshid, M.; Hayat, H.F.; Phimolsiripol, Y.; Pallarés, N.; Martí-Quijal, F.J.; Barba, F.J. Role of Food Antioxidants in Modulating Gut Microbial Communities: Novel Understandings in Intestinal Oxidative Stress Damage and Their Impact on Host Health. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowiak-Kopeć, P.; Śliżewska, K. The Effect of Probiotics on the Production of Short-Chain Fatty Acids by Human Intestinal Microbiome. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; He, C.; An, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Fu, W.; Wang, M.; Shan, Z.; Xie, J.; Yang, Y.; et al. The Role of Short Chain Fatty Acids in Inflammation and Body Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ney, L.M.; Wipplinger, M.; Grossmann, M.; Engert, N.; Wegner, V.D.; Mosig, A.S. Short chain fatty acids: Key regulators of the local and systemic immune response in inflammatory diseases and infections. Open Biol. 2023, 13, 230014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagov, A.V.; Summerhill, V.I.; Sukhorukov, V.N.; Zhigmitova, E.B.; Postnov, A.Y.; Orekhov, A.N. Potential use of antioxidants for the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1378335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, D.K.; Heilmann, R.M.; Paital, B.; Patel, A.; Yadav, V.K.; Wong, D.; Jergens, A.E. Oxidative stress, hormones, and effects of natural antioxidants on intestinal inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1217165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabska-Kobyłecka, I.; Szpakowski, P.; Król, A.; Książek-Winiarek, D.; Kobyłecki, A.; Głąbiński, A.; Nowak, D. Polyphenols and Their Impact on the Prevention of Neurodegenerative Diseases and Development. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, M.; Swierczynski, M.; Fichna, J.; Piechota-Polanczyk, A. The Nrf2 in the pathophysiology of the intestine: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications for inflammatory bowel diseases. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 163, 105243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, V.; Duennwald, M.L. Nrf2 and Oxidative Stress: A General Overview of Mechanisms and Implications in Human Disease. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkaczenko, H.; Kurhaluk, N. Antioxidant-Rich Functional Foods and Exercise: Unlocking Metabolic Health Through Nrf2 and Related Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Mansilla, M.J.; Rodríguez Sojo, M.J.; Lista, A.R.; Ayala Mosqueda, C.V.; Ruiz Malagón, A.J.; Ho Plagaro, A.; Gálvez, J.; Rodríguez Nogales, A.; Rodríguez Sánchez, M.J. Microbial-Derived Antioxidants in Intestinal Inflammation: A Systematic Review of Their Therapeutic Potential. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasarello, K.; Cudnoch-Jedrzejewska, A.; Czarzasta, K. Communication of gut microbiota and brain via immune and neuroendocrine signaling. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1118529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhol, N.K.; Bhanjadeo, M.M.; Singh, A.K.; Dash, U.C.; Ojha, R.R.; Majhi, S.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Jena, A.B. The interplay between cytokines, inflammation, and antioxidants: Mechanistic insights and therapeutic potentials of various antioxidants and anti-cytokine compounds. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 178, 117177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villavicencio Tejo, F.; Quintanilla, R.A. Contribution of the Nrf2 Pathway on Oxidative Damage and Mitochondrial Failure in Parkinson and Alzheimer’s Disease. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.S.; Rai, S.N.; Birla, H.; Zahra, W.; Rathore, A.S.; Singh, S.P. NF-κB-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s Disease and Potential Therapeutic Effect of Polyphenols. Neurotox. Res. 2020, 37, 491–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, E.; Motolani, A.; Campos, L.; Lu, T. The Pivotal Role of NF-kB in the Pathogenesis and Therapeutics of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, A.A.; Shao, C.; Geng, P.; Wang, S.; Xiao, J. Polyphenols Targeting NF-κB Pathway in Neurological Disorders: What We Know So Far? Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2024, 20, 1332–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.Z.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, Z.W.; Luo, H.Y.; Wen, D.D.; Gao, L.C. PI3K/AKT Signal Pathway: A Target of Natural Products in the Prevention and Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 648636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Lin, Q.; Liang, Y. Plant-Derived Antioxidants Protect the Nervous System from Aging by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, A.; Agrawal, A.; Verma, A.; Dubey, N. The PI3K-AKT pathway: A plausible therapeutic target in Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2023, 129, 104846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.J.; Pan, W.W.; Liu, S.B.; Shen, Z.F.; Xu, Y.; Hu, L.L. ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert-Gascó, H.; Ros-Bernal, F.; Castillo-Gómez, E.; Olucha-Bordonau, F.E. MAP/ERK Signaling in Developing Cognitive and Emotional Function and Its Effect on Pathological and Neurodegenerative Processes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulselvan, P.; Fard, M.T.; Tan, W.S.; Gothai, S.; Fakurazi, S.; Norhaizan, M.E.; Kumar, S.S. Role of Antioxidants and Natural Products in Inflammation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 5276130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Zulfiqar, A.; Arguelles, S.; Rasekhian, M.; Nabavi, S.F.; Silva, A.S.; Nabavi, S.M. Map kinase signaling as therapeutic target for neurodegeneration. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 160, 105090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardyn, J.D.; Ponsford, A.H.; Sanderson, C.M. Dissecting molecular cross-talk between Nrf2 and NF-κB response pathways. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2015, 43, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; An, C.; Gao, Y.; Leak, R.K.; Chen, J.; Zhang, F. Emerging roles of Nrf2 and phase II antioxidant enzymes in neuroprotection. Prog. Neurobiol. 2013, 100, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, F.; Neshat, M.; Pourjafar, H.; Jafari, S.M.; Samakkhah, S.A.; Mirzakhani, E. The role of probiotics and prebiotics in modulating of the gut-brain axis. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1173660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Dey, S.; Kumar, Y.; Malviya, R.; Prajapati, B.G.; Chaiyasut, C. Probiotics as modulators of gut-brain axis for cognitive development. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1348297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnik, W.; Fularski, P.; Gajewska, A.; Jakubowska, P.; Uszok, Z.; Młynarska, E.; Rysz, J.; Franczyk, B. The Role of Intestinal Microbiota and Diet as Modulating Factors in the Course of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases. Nutrients 2024, 16, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazziotta, C.; Tognon, M.; Martini, F.; Torreggiani, E.; Rotondo, J.C. Probiotics Mechanism of Action on Immune Cells and Beneficial Effects on Human Health. Cells 2023, 12, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azad, M.A.K.; Sarker, M.; Wan, D. Immunomodulatory Effects of Probiotics on Cytokine Profiles. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8063647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X. Probiotics Regulate Gut Microbiota: An Effective Method to Improve Immunity. Molecules 2021, 26, 6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Agarwal, N.; Verma, P. Probiotics: The Emissaries of Health from Microbial World. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 2, 138–143. [Google Scholar]
- Plaza-Diaz, J.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Gil-Campos, M.; Gil, A. Mechanisms of Action of Probiotics. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10 (Suppl. S1), S49–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayamohan, P.; Joseph, D.; Viju, L.S.; Baskaran, S.A.; Venkitanarayanan, K. Efficacy of Probiotics in Reducing Pathogenic Potential of Infectious Agents. Fermentation 2024, 10, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannitti, T.; Palmieri, B. Therapeutical use of probiotic formulations in clinical practice. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 29, 701–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-González, P.F.; Liceaga, A.M.; Aguilar-Toalá, J.E. Postbiotics and paraprobiotics: From concepts to applications. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarita, B.; Samadhan, D.; Hassan, M.Z.; Kovaleva, E.G. A comprehensive review of probiotics and human health-current prospective and applications. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 15, 1487641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.K.; Pradhan, S.; Chakrabarti, S.; Mondal, K.C.; Ghosh, K. Current status of probiotic and related health benefits. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabetafika, H.N.; Razafindralambo, A.; Ebenso, B.; Razafindralambo, H.L. Probiotics as Antibiotic Alternatives for Human and Animal Applications. Encyclopedia 2023, 3, 561–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, R.; Takeda, K. The role of the mucosal barrier system in maintaining gut symbiosis to prevent intestinal inflammation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2024, 47, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaberi, K.R.; Alamdari-Palangi, V.; Savardashtaki, A.; Vatankhah, P.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Tajbakhsh, A.; Sahebkar, A. Modulatory Effects of Phytochemicals on Gut-Brain Axis: Therapeutic Implication. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2024, 8, 103785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Jin, W.; Liu, S.J.; Jiao, Z.; Li, X. Probiotics, prebiotics, and postbiotics in health and disease. MedComm (2020) 2023, 4, e420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.; Ma, Y.; Yan, B.; Pei, W.; Wu, Q.; Ding, C.; Huang, C. The promotion mechanism of prebiotics for probiotics: A review. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1000517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunst, C.; Schmid, S.; Michalski, M.; Tümen, D.; Buttenschön, J.; Müller, M.; Gülow, K. The Influence of Gut Microbiota on Oxidative Stress and the Immune System. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayek, N. Chocolate, gut microbiota, and human health. Front. Pharmacol. 2013, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavefve, L.; Howard, L.R.; Carbonero, F. Berry polyphenols metabolism and impact on human gut microbiota and health. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Burillo, S.; Navajas-Porras, B.; López-Maldonado, A.; Hinojosa-Nogueira, D.; Pastoriza, S.; Rufián-Henares, J.Á. Green Tea and Its Relation to Human Gut Microbiome. Molecules 2021, 26, 3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemzer, B.V.; Al-Taher, F.; Kalita, D.; Yashin, A.Y.; Yashin, Y.I. Health-Improving Effects of Polyphenols on the Human Intestinal Microbiota: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bear, T.L.K.; Dalziel, J.E.; Coad, J.; Roy, N.C.; Butts, C.A.; Gopal, P.K. The Role of the Gut Microbiota in Dietary Interventions for Depression and Anxiety. Adv. Nutr. 2020, 11, 890–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Dhaneshwar, S. Role of prebiotics, probiotics, and synbiotics in management of inflammatory bowel disease: Current perspectives. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 2078–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantri, A.; Klümpen, L.; Seel, W.; Krawitz, P.; Stehle, P.; Weber, B.; Koban, L.; Plassmann, H.; Simon, M.C. Beneficial Effects of Synbiotics on the Gut Microbiome in Individuals with Low Fiber Intake: Secondary Analysis of a Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khursheed, R.; Gulati, M.; Wadhwa, S.; Vishwas, S.; Sharma, D.S.; Corrie, L.; Alam, A.; Alnasser, S.M.; Aba Alkhayl, F.F.; Parveen, Z.; et al. Multifaceted role of synbiotics as nutraceuticals, therapeutics and carrier for drug delivery. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 368, 110223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scazzocchio, B.; Minghetti, L.; D’Archivio, M. Interaction between Gut Microbiota and Curcumin: A New Key of Understanding for the Health Effects of Curcumin. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Meng, L.; Shen, L.; Ji, H.F. Regulation of gut microbiota by vitamin C, vitamin E and β-carotene. Food Res. Int. 2023, 169, 112749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, V.; Bose, C.; Sunilkumar, D.; Cherian, R.M.; Thomas, S.S.; Nair, B.G. Resveratrol as a Promising Nutraceutical: Implications in Gut Microbiota Modulation, Inflammatory Disorders, and Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchetti, G.; De Maio, F.; Abeltino, A.; Serantoni, C.; Riente, A.; Santarelli, G.; Sanguinetti, M.; Delogu, G.; Martinoli, R.; Barbaresi, S.; et al. Unraveling the Gut Microbiome-Diet Connection: Exploring the Impact of Digital Precision and Personalized Nutrition on Microbiota Composition and Host Physiology. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeltino, A.; Hatem, D.; Serantoni, C.; Riente, A.; De Giulio, M.M.; De Spirito, M.; De Maio, F.; Maulucci, G. Unraveling the Gut Microbiota: Implications for Precision Nutrition and Personalized Medicine. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kurhaluk, N.; Kamiński, P.; Bilski, R.; Kołodziejska, R.; Woźniak, A.; Tkaczenko, H. Role of Antioxidants in Modulating the Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis and Their Impact on Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3658. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083658
Kurhaluk N, Kamiński P, Bilski R, Kołodziejska R, Woźniak A, Tkaczenko H. Role of Antioxidants in Modulating the Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis and Their Impact on Neurodegenerative Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3658. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083658
Chicago/Turabian StyleKurhaluk, Natalia, Piotr Kamiński, Rafał Bilski, Renata Kołodziejska, Alina Woźniak, and Halina Tkaczenko. 2025. "Role of Antioxidants in Modulating the Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis and Their Impact on Neurodegenerative Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3658. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083658
APA StyleKurhaluk, N., Kamiński, P., Bilski, R., Kołodziejska, R., Woźniak, A., & Tkaczenko, H. (2025). Role of Antioxidants in Modulating the Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis and Their Impact on Neurodegenerative Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3658. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083658






