Plasma Microvesicles May Contribute to Muscle Damage in the mdx Mouse Model of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. MVs from the Plasma of mdx Mice: Quantification, Size, and Morphology Analysis
2.2. Phenotypic Characterization of Plasma MVs from mdx Mice
2.3. Quantification of Plasma MVs from mdx Mice after Spontaneous Physical Activity
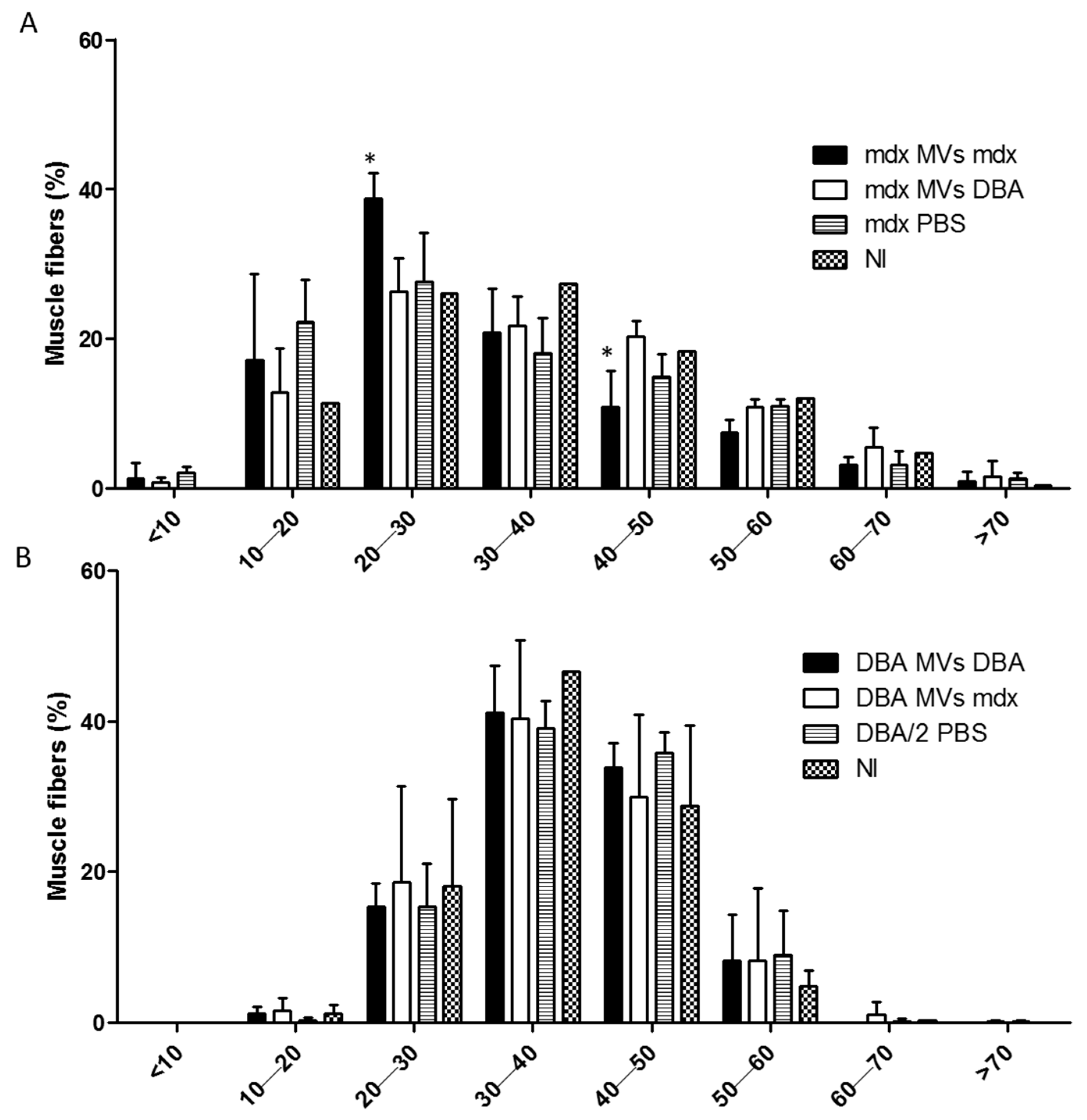
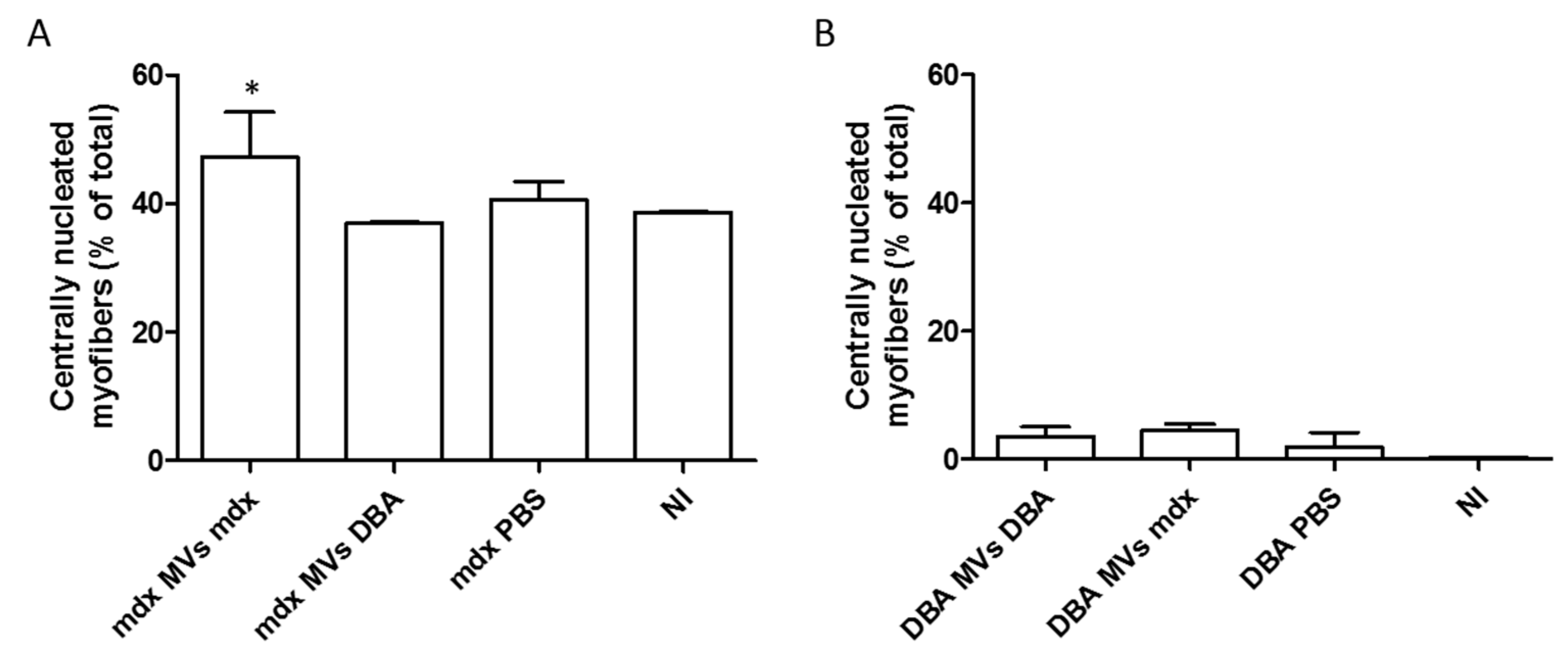
2.4. Analysis of the Fiber Size Distribution and Inflammatory Response after In Vivo Transfer of Plasma MVs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Swimming Protocol
4.3. Blood Collection and MV Isolation through Serial Centrifugation
4.4. Plasma MV Quantification and Phenotyping
4.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
4.6. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) and Electrophoretic Light Scattering (ELS)
4.7. Biochemical Analysis
4.8. Adoptive Transfer of Plasma MVs
4.9. Cytometric Bead Array (CBA)
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stahl, P.D.; Raposo, G. Extracellular Vesicles: Exosomes and Microvesicles, Integrators of Homeostasis. Physiology 2019, 34, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, J.M.; Kroemer, G.; Zitvogel, L. Extracellular vesicles: Masters of intercellular communication and potential clinical interventions. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1139–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatke, B.; Rossi, I.V.; Sana, A.; Bonato, L.B.; Ramirez, M.I. Extracellular vesicles biogenesis and uptake concepts: A comprehensive guide to studying host-pathogen communication. Mol. Microbiol. 2023, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.; Chen, K.K.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, B.; Huang, Z.; Ju, C.; Sun, J.; Zhang, F.; Lv, X.B.; Huang, G. The decade of exosomal long RNA species: An emerging cancer antagonist. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tricarico, C.; Clancy, J.; D’Souza-Schorey, C. Biology and biogenesis of shed microvesicles. Small GTPases 2017, 8, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virla, F.; Turano, E.; Scambi, I.; Schiaffino, L.; Boido, M.; Mariotti, R. Administration of adipose-derived stem cells extracellular vesicles in a murine model of spinal muscular atrophy: Effects of a new potential therapeutic strategy. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2024, 15, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricco, C.; Eldaboush, A.; Liu, M.L.; Werth, V.P. Extracellular Vesicles in the Pathogenesis, Clinical Characterization, and Management of Dermatomyositis: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Shen, Y.; Kim, I.M.; Weintraub, N.L.; Hamrick, M.; Tang, Y. Extracellular Vesicles for Muscle Atrophy Treatment. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2023, 1418, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yedigaryan, L.; Sampaolesi, M. Extracellular vesicles and Duchenne muscular dystrophy pathology: Modulators of disease progression. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1130063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulfield, G.; Siller, W.G.; Wight, P.A.; Moore, K.J. X chromosome-linked muscular dystrophy (mdx) in the mouse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 1189–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacchiarelli, D.; Legnini, I.; Martone, J.; Cazzella, V.; D’Amico, A.; Bertini, E.; Bozzoni, I. miRNAs as serum biomarkers for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. EMBO Mol. Med. 2011, 3, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coenen-Stass, A.M.L.; Wood, M.J.A.; Roberts, T.C. Biomarker Potential of Extracellular miRNAs in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Trends Mol. Med. 2017, 23, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanotti, S.; Gibertini, S.; Blasevich, F.; Bragato, C.; Ruggieri, A.; Saredi, S.; Fabbri, M.; Bernasconi, P.; Maggi, L.; Mantegazza, R.; et al. Exosomes and exosomal miRNAs from muscle-derived fibroblasts promote skeletal muscle fibrosis. Matrix Biol. 2018, 74, 77–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aminzadeh, M.A.; Rogers, R.G.; Fournier, M.; Tobin, R.E.; Guan, X.; Childers, M.K.; Andres, A.M.; Taylor, D.J.; Ibrahim, A.; Ding, X.; et al. Exosome-Mediated Benefits of Cell Therapy in Mouse and Human Models of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Stem Cell Rep. 2018, 10, 942–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, L.; Dong, X.; Gao, X.; Ran, N.; Geng, M.; Zuo, B.; Wu, Y.; Li, W.; Yan, H.; Han, G.; et al. Exosome-mediated improvement in membrane integrity and muscle function in dystrophic mice. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 1459–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaka, Y.; Tanihata, J.; Komaki, H.; Ishiyama, A.; Oya, Y.; Rüegg, U.; Takeda, S.I.; Hashido, K. Characterization and Functional Analysis of Extracellular Vesicles and Muscle-Abundant miRNAs (miR-1, miR-133a, and miR-206) in C2C12 Myocytes and mdx Mice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, S.; Sudo, Y.; Makino, T.; Kimura, S.; Tomita, K.; Noguchi, M.; Sakurai, H.; Shimizu, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Sato, R.; et al. Skeletal muscle releases extracellular vesicles with distinct protein and microRNA signatures that function in the muscle microenvironment. PNAS Nexus 2022, 1, pgac173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, C.P.; Gilligan, K.E.; Dwyer, R.M. Role of Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) in Cell Stress Response and Resistance to Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2019, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisgrill, L.; Lamm, C.; Hartmann, J.; Preißing, F.; Dragosits, K.; Bee, A.; Hell, L.; Thaler, J.; Ay, C.; Pabinger, I.; et al. Peripheral blood microvesicles secretion is influenced by storage time, temperature, and anticoagulants. Cytom. A 2016, 89, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coumans, F.A.W.; Brisson, A.R.; Buzas, E.I.; Dignat-George, F.; Drees, E.E.E.; El-Andaloussi, S.; Emanueli, C.; Gasecka, A.; Hendrix, A.; Hill, A.F.; et al. Methodological Guidelines to Study Extracellular Vesicles. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 1632–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.G.; Leal, A.C.; Vargas, G.; Porto-Carreiro, I.; Monteiro, R.Q. Intercellular transfer of tissue factor via the uptake of tumor-derived microvesicles. Thromb. Res. 2013, 132, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, T.W.; Kappler, M.P.; Hockaden, N.M.; Carpenter, R.L.; Jacobson, S.C. Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles by Resistive-Pulse Sensing on In-Plane Multipore Nanofluidic Devices. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 16710–16716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corona, M.L.; Hurbain, I.; Raposo, G.; van Niel, G. Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles by Transmission Electron Microscopy and Immunolabeling Electron Microscopy. Methods Mol. Biol. 2023, 2668, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanou, A.; Crespo, M.; Flohr, P.; De Bono, J.S.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Scanning Electron Microscopy of Circulating Tumor Cells and Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. Cancers 2018, 10, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.; Anand, S.; Deshmukh, S.K.; Singh, S.; Singh, A.P. Determining the Size Distribution and Integrity of Extracellular Vesicles by Dynamic Light Scattering. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2413, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepsha, O.S.; Burmenskaya, O.V.; Akhmedova, Z.F.; Romanov, E.A.; Sysoeva, A.P.; Goryunov, K.V.; Shevtsova, Y.A.; Silachev, D.N.; Makarova, N.P.; Kalinina, E.A. Changes in the Transcription of Proliferation- and Apoptosis-Related Genes in Embryos in Women of Different Ages under the Influence of Extracellular Vesicles from Donor Follicular Fluid In Vitro. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2024, 176, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, B.; Syed, F.; Khan, S.; Iqbal, A.; Ahmad, I. Characterization of extracellular vesicles by flow cytometry: Challenges and promises. Micron 2022, 161, 103341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Pol, E.; Welsh, J.A.; Nieuwland, R. Minimum information to report about a flow cytometry experiment on extracellular vesicles: Communication from the ISTH SSC subcommittee on vascular biology. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 20, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, V.F.A.; Chometon, T.Q.; de Castro, K.K.G.; Ponte, M.S.G.; Pimentel, M.I.F.; Lyra, M.R.; Bertho, A.L. Platelet-Derived Microvesicles Contribute to the Pathophysiogenesis of Human Cutaneous Leishmaniasis: A Nano-Flow Cytometric Approach in Plasma Samples from Patients before and under Antimonial Treatment. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brittain, G.C.; Chen, Y.Q.; Martinez, E.; Tang, V.A.; Renner, T.M.; Langlois, M.A.; Gulnik, S. A Novel Semiconductor-Based Flow Cytometer with Enhanced Light-Scatter Sensitivity for the Analysis of Biological Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.; Jin, H. Extracellular vesicles from keratinocytes and other skin-related cells in psoriasis: A review. Exp. Dermatol. 2024, 33, e15001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorling, D.C.; Müller, C.K.; Pechmann, A.; Borell, S.; Rosenfelder, S.; Kölbel, H.; Schara, U.; Zieger, B.; Kirschner, J. Impaired secretion of platelet granules in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy—Results of a prospective diagnostic study. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2021, 31, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñol-Jurado, P.; Gallardo, E.; de Luna, N.; Suárez-Calvet, X.; Sánchez-Riera, C.; Fernández-Simón, E.; Gomis, C.; Illa, I.; Díaz-Manera, J. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor BB Influences Muscle Regeneration in Duchenne Muscle Dystrophy. Am. J. Pathol. 2017, 187, 1814–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagiotti, S.; Abbas, F.; Montanari, M.; Barattini, C.; Rossi, L.; Magnani, M.; Papa, S.; Canonico, B. Extracellular Vesicles as New Players in Drug Delivery: A Focus on Red Blood Cells-Derived EVs. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.R.; Xia, H.F.; Gong, P.; Yu, Z.L. Red Blood Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: An Overview of Current Research Progress, Challenges, and Opportunities. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danesh, A.; Inglis, H.C.; Jackman, R.P.; Wu, S.; Deng, X.; Muench, M.O.; Heitman, J.W.; Norris, P.J. Exosomes from red blood cell units bind to monocytes and induce proinflammatory cytokines, boosting T-cell responses in vitro. Blood 2014, 123, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangaraju, K.; Neerukonda, S.N.; Katneni, U.; Buehler, P.W. Extracellular Vesicles from Red Blood Cells and Their Evolving Roles in Health, Coagulopathy and Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzas, E.I. The roles of extracellular vesicles in the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 236–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshtkar, S.; Soleimanian, S.; Kaviani, M.; Sarvestani, F.S.; Azarpira, N.; Asvar, Z.; Pakbaz, S. Immune Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in the Face of Pathogenic Infections. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 906078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, W.; Wu, X.; Zhang, B.; Liu, L.; Yin, L. Immune cell-derived extracellular vesicles for precision therapy of inflammatory-related diseases. J. Control. Release 2024, 368, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Vayalil, J.; Lee, G.; Wang, Y.; Peng, G. Emerging role of tumor-derived extracellular vesicles in T cell suppression and dysfunction in the tumor microenvironment. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e003217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.C.; Song, S.J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Autoimmune Pathogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 579043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madaro, L.; Bouché, M. From Innate to Adaptive Immune Response in Muscular Dystrophies and Skeletal Muscle Regeneration: The Role of Lymphocytes. BioMed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 438675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frühbeis, C.; Helmig, S.; Tug, S.; Simon, P.; Krämer-Albers, E.M. Physical exercise induces rapid release of small extracellular vesicles into the circulation. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 28239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, M.; Chen, Z.; Xu, L.; Chang, M.; Wang, K.; Deng, C.; Gu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Shen, Y.; et al. Biogenesis and function of extracellular vesicles in pathophysiological processes of skeletal muscle atrophy. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 198, 114954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estébanez, B.; Jiménez-Pavón, D.; Huang, C.J.; Cuevas, M.J.; González-Gallego, J. Effects of exercise on exosome release and cargo in in vivo and ex vivo models: A systematic review. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 3336–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, A.; Clemens, Z.J.; Shinde, S.N.; Sivakumar, S.; Pius, A.; Bhatia, A.; Picciolini, S.; Carlomagno, C.; Gualerzi, A.; Bedoni, M.; et al. Regulation of aged skeletal muscle regeneration by circulating extracellular vesicles. Nat. Aging 2021, 1, 1148–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, X.; Gong, W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, P.; Shi, T.; Mahmut, A.; Qin, J.; Yao, Y.; Yan, W.; Chen, D.; et al. Atrophic skeletal muscle fibre-derived small extracellular vesicle miR-690 inhibits satellite cell differentiation during ageing. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 3163–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.S.; Yoon, H.I.; Lee, K.S.; Choi, Y.C.; Yang, S.H.; Kim, I.S.; Cho, Y.W. Exosomes from differentiating human skeletal muscle cells trigger myogenesis of stem cells and provide biochemical cues for skeletal muscle regeneration. J. Control. Release 2016, 222, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guescini, M.; Maggio, S.; Ceccaroli, P.; Battistelli, M.; Annibalini, G.; Piccoli, G.; Sestili, P.; Stocchi, V. Extracellular Vesicles Released by Oxidatively Injured or Intact C2C12 Myotubes Promote Distinct Responses Converging toward Myogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, E.; Tanihata, J.; Iwamura, A.; Takeda, S.; Hayashi, Y.K.; Matsuda, R. Treatment with the anti-IL-6 receptor antibody attenuates muscular dystrophy via promoting skeletal muscle regeneration in dystrophin-/utrophin-deficient mice. Skelet. Muscle 2017, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelosi, L.; Berardinelli, M.G.; Forcina, L.; Spelta, E.; Rizzuto, E.; Nicoletti, C.; Camilli, C.; Testa, E.; Catizone, A.; De Benedetti, F.; et al. Increased levels of interleukin-6 exacerbate the dystrophic phenotype in mdx mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 6041–6053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, J.A.; Goberdhan, D.C.I.; O’Driscoll, L.; Buzas, E.I.; Blenkiron, C.; Bussolati, B.; Cai, H.; Di Vizio, D.; Driedonks, T.A.P.; Erdbrügger, U.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cascabulho, C.M.; Horita, S.I.M.; Beghini, D.G.; Menna-Barreto, R.F.S.; Monsores, A.C.H.M.G.; Bertho, A.L.; Henriques-Pons, A. Plasma Microvesicles May Contribute to Muscle Damage in the mdx Mouse Model of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083499
Cascabulho CM, Horita SIM, Beghini DG, Menna-Barreto RFS, Monsores ACHMG, Bertho AL, Henriques-Pons A. Plasma Microvesicles May Contribute to Muscle Damage in the mdx Mouse Model of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083499
Chicago/Turabian StyleCascabulho, Cynthia Machado, Samuel Iwao Maia Horita, Daniela Gois Beghini, Rubem Figueiredo Sadok Menna-Barreto, Ana Carolina Heber Max Guimarães Monsores, Alvaro Luiz Bertho, and Andrea Henriques-Pons. 2025. "Plasma Microvesicles May Contribute to Muscle Damage in the mdx Mouse Model of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083499
APA StyleCascabulho, C. M., Horita, S. I. M., Beghini, D. G., Menna-Barreto, R. F. S., Monsores, A. C. H. M. G., Bertho, A. L., & Henriques-Pons, A. (2025). Plasma Microvesicles May Contribute to Muscle Damage in the mdx Mouse Model of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083499







