Neuroprotective Effects of Cilomilast and Chlorogenic Acid Against Scopolamine-Induced Memory Deficits via Modulation of the cAMP/PKA–CREB–BDNF Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
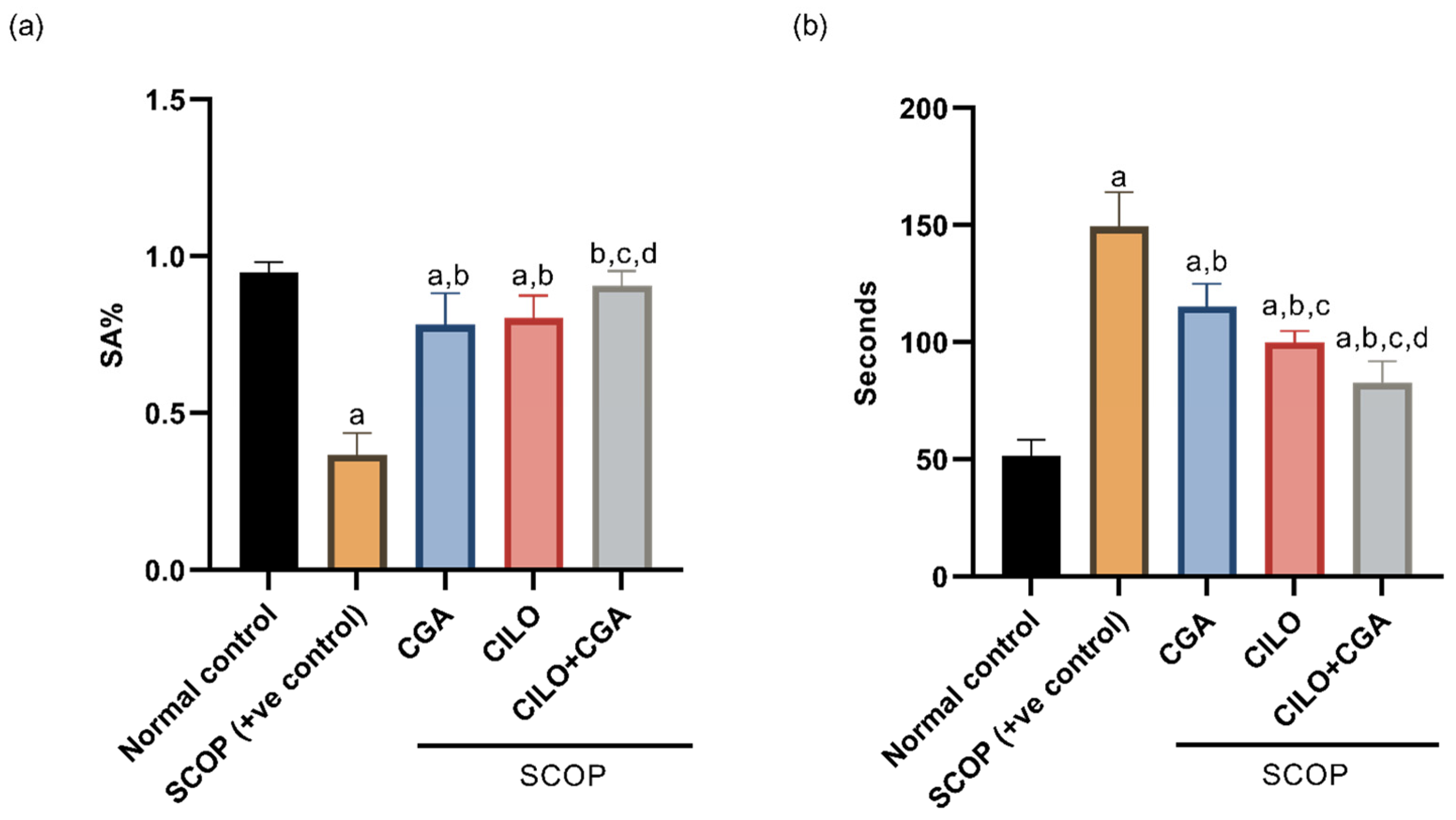
2.1. Effect on Behavior
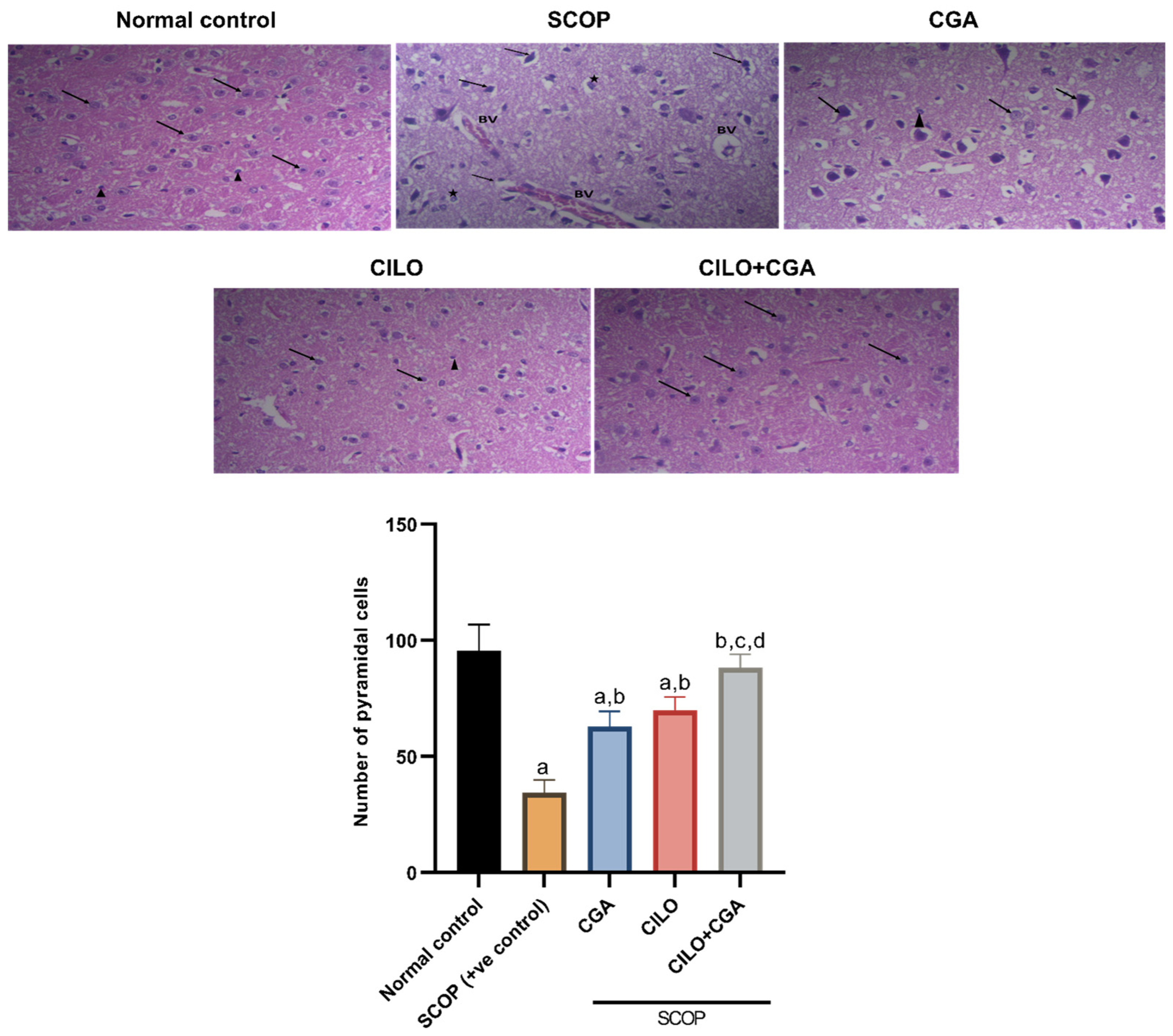
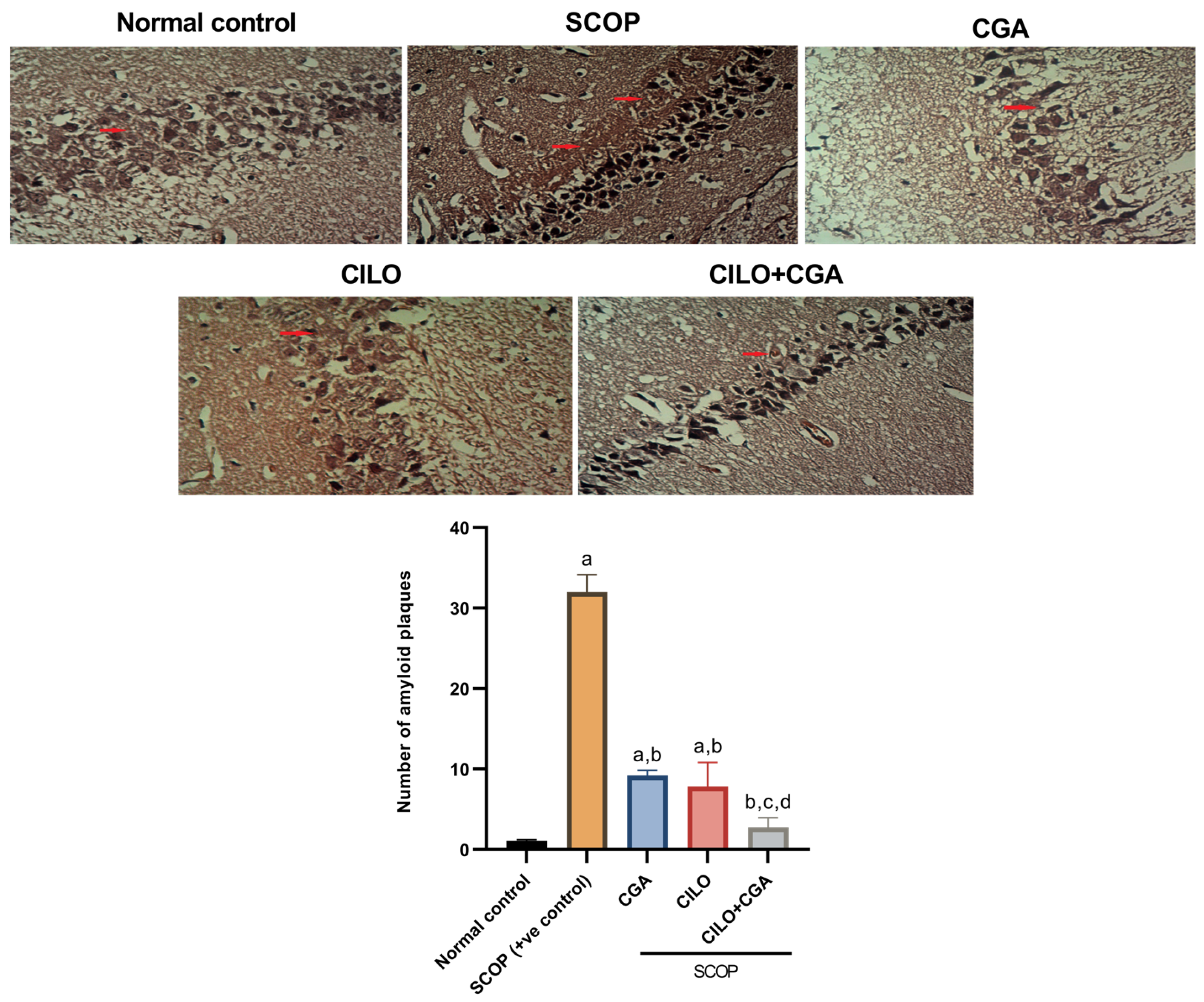
2.2. Histopathological Findings
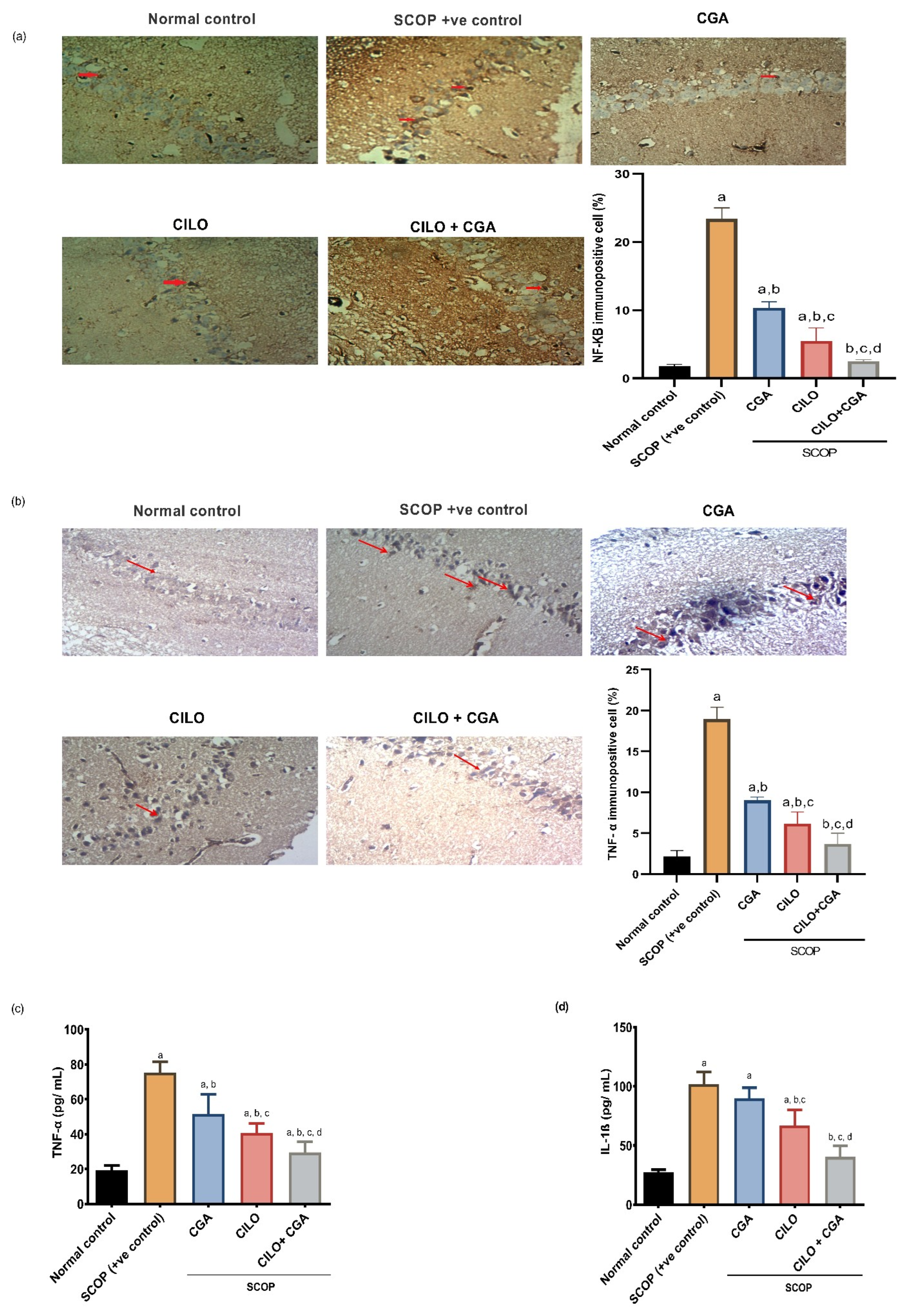
2.3. Effect on Inflammatory Mediators
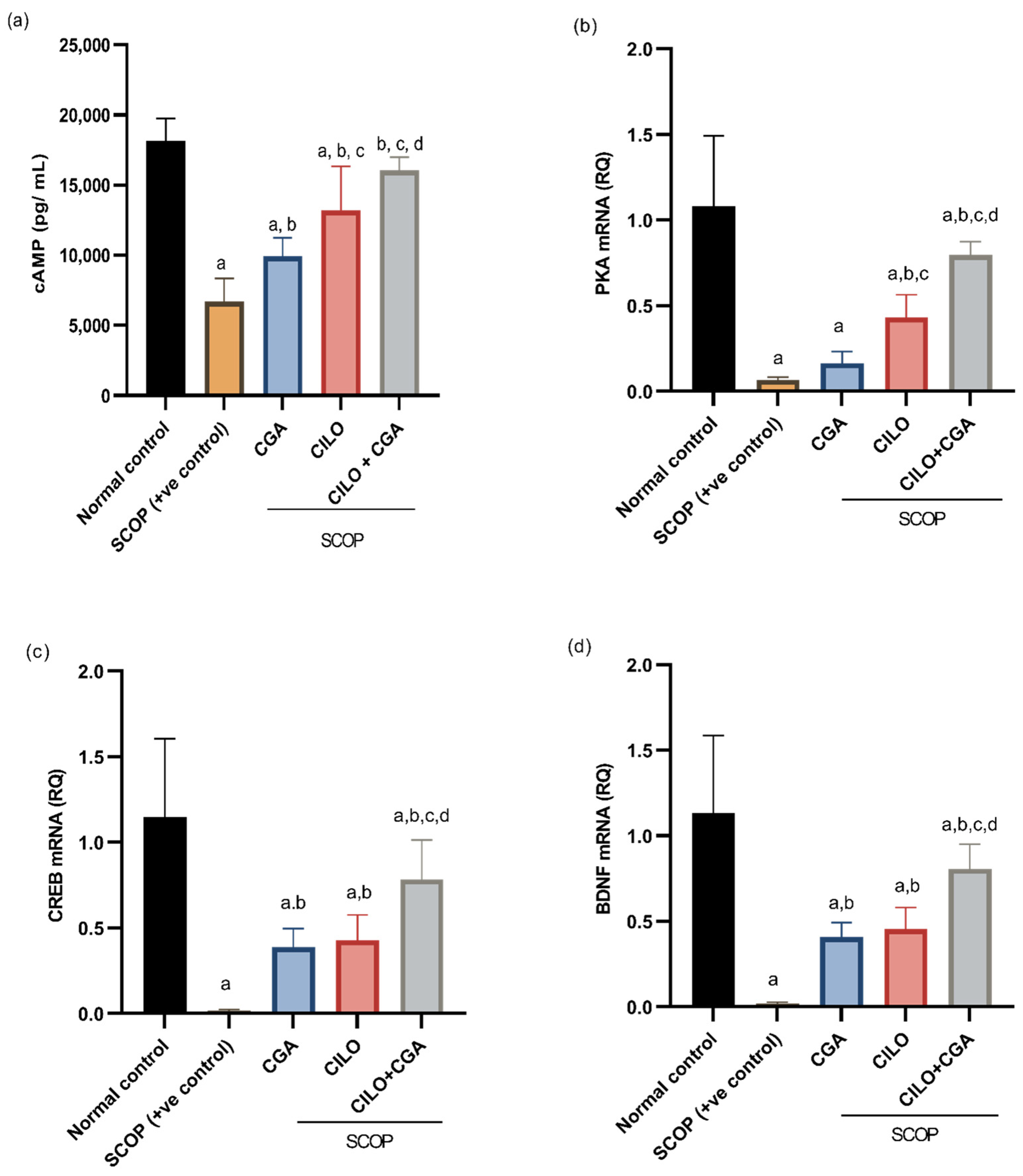
2.4. Effect on cAMP, PKA, CREB, and BDNF
2.5. Effect on PDE4
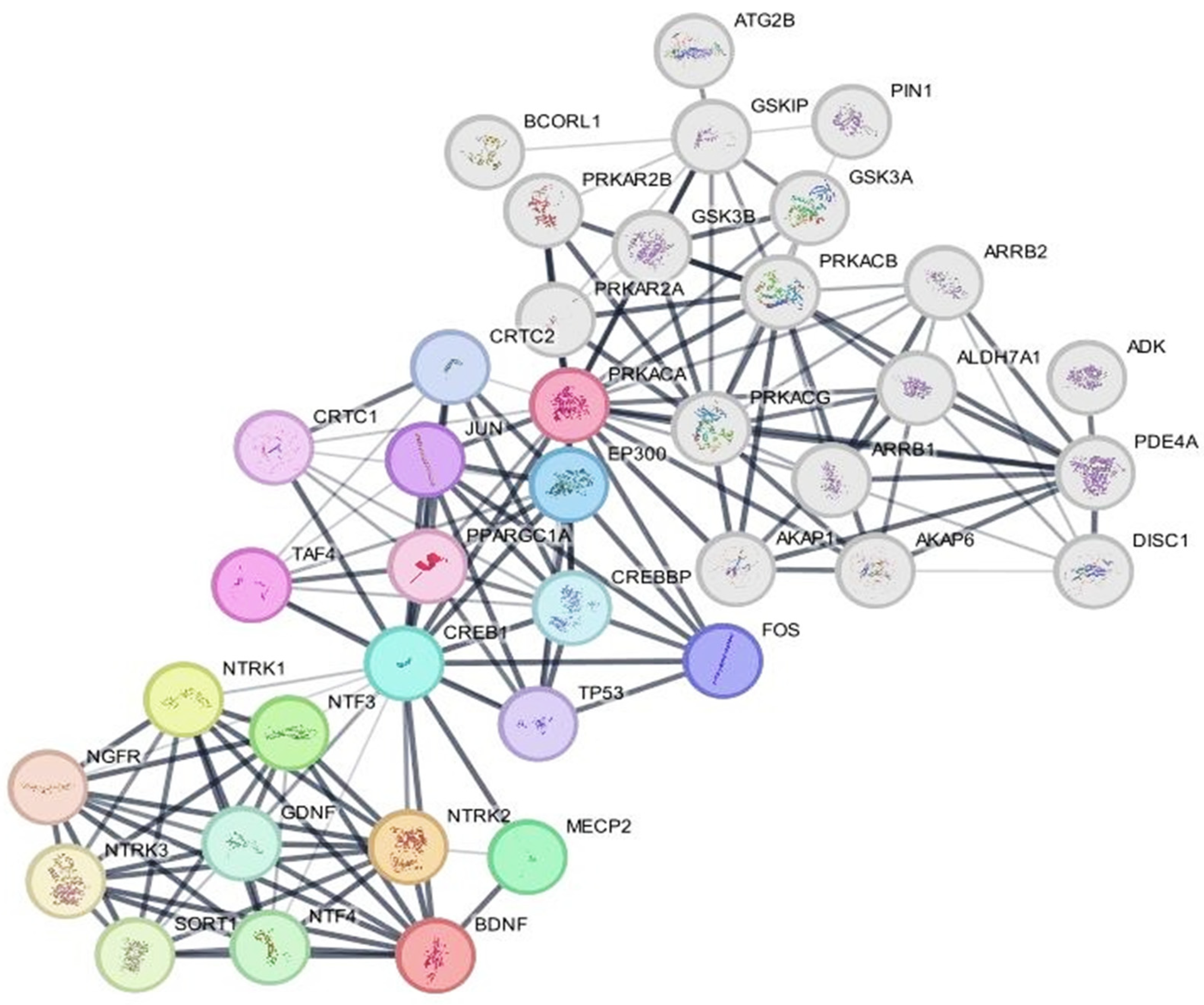
2.6. Protein–Protein Network Analysis
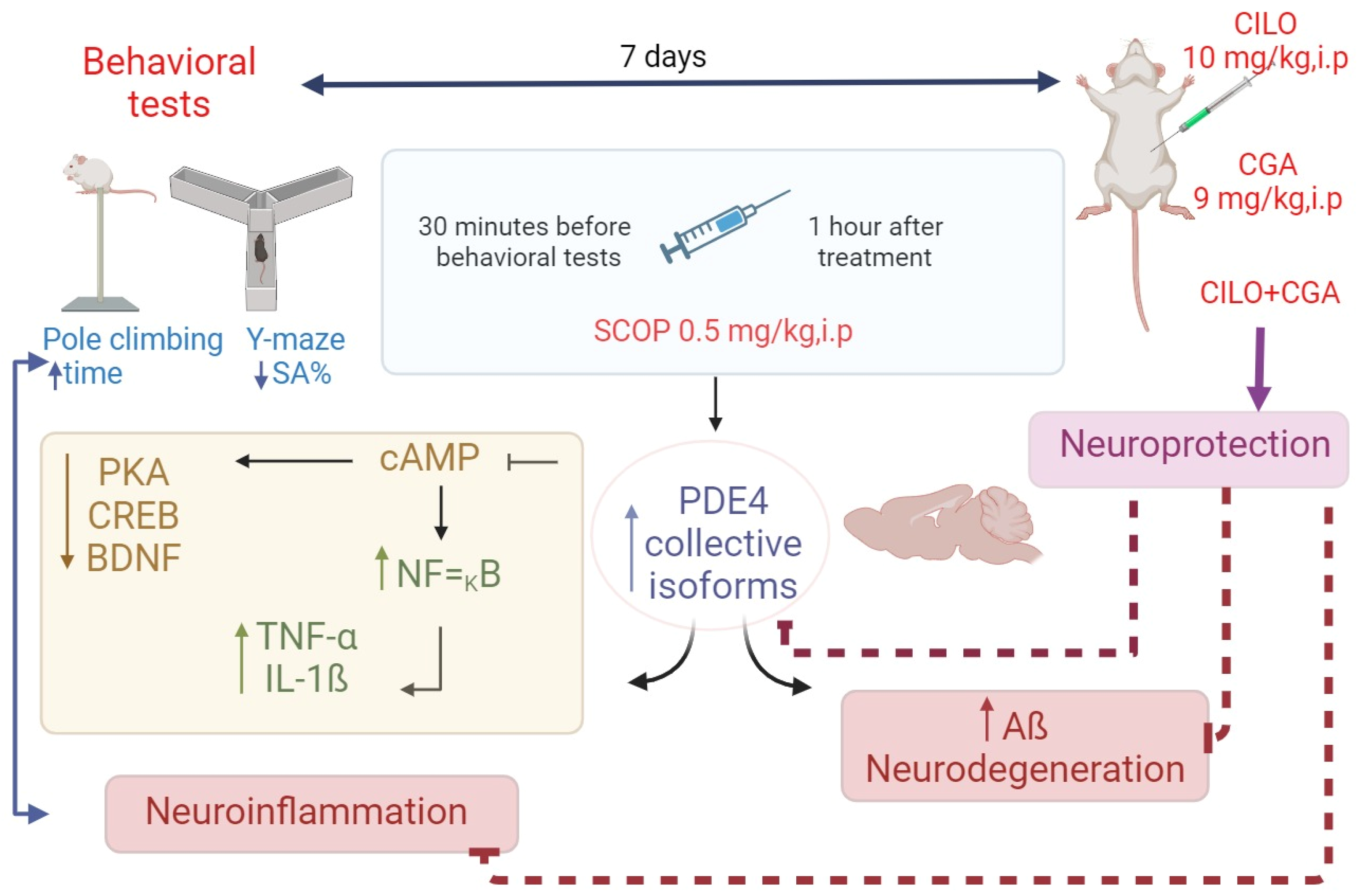
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Drugs and Chemicals
4.2. Animals
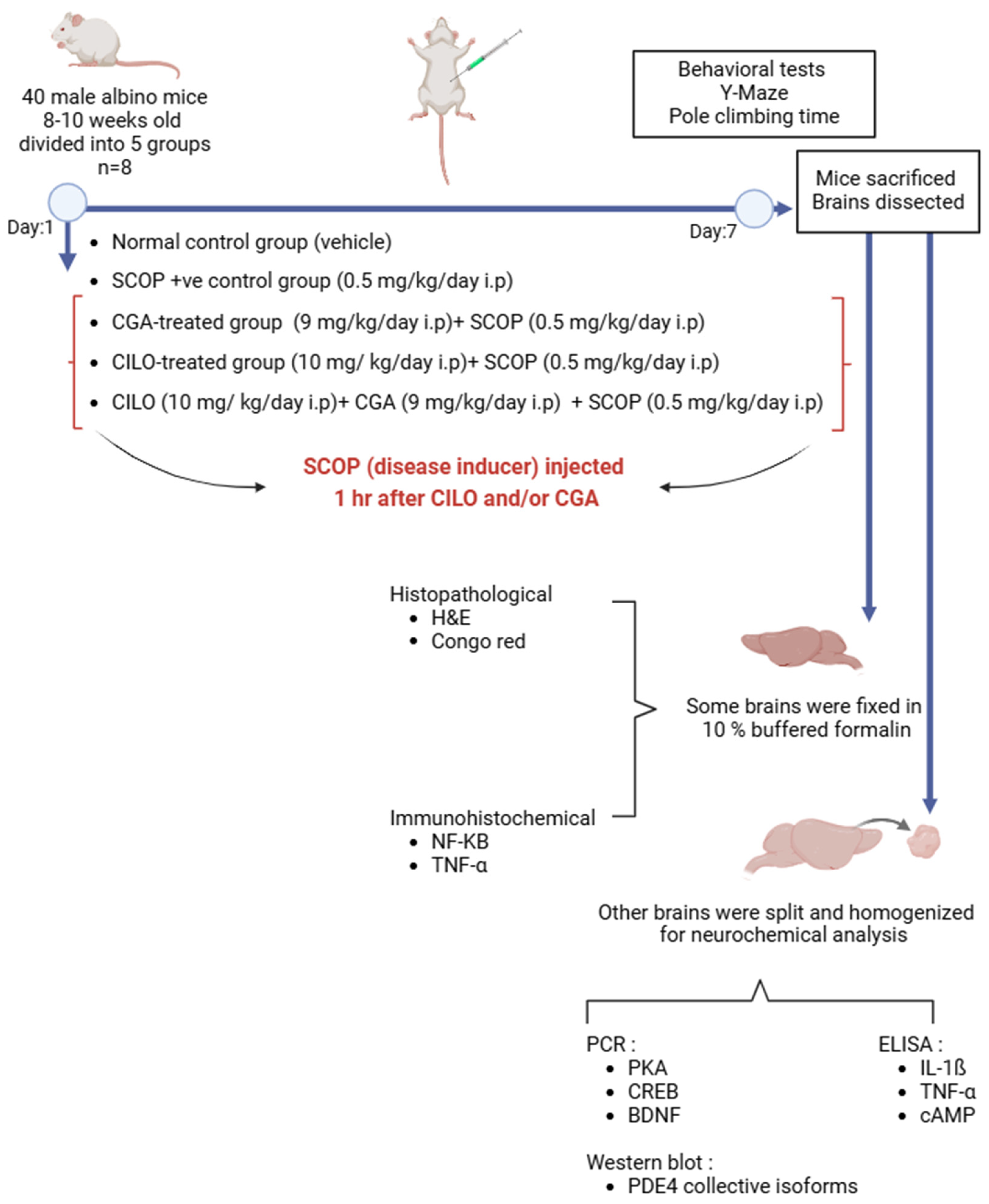
4.3. Study Design and Disease Induction
- Normal control group received the vehicle;
- Positive control group was injected only SCOP (0.5 mg/kg, i.p.) [31];
- CILO-treated group (10 mg/kg i.p.) [58] + SCOP (0.5 mg/kg, i.p.);
- CGA-treated group (9 mg/kg i.p.) [59] + SCOP (0.5 mg/kg, i.p.);
- Combination group: CILO (10 mg/kg i.p.) + CGA (9 mg/kg i.p.) + SCOP (0.5 mg/kg, i.p.).
4.4. Behavioral Tests
4.4.1. Y-Maze Test
4.4.2. Pole Climbing Test
4.5. Biochemical Assay
4.5.1. Brain Tissue Preparation
4.5.2. Histopathological Examination
4.5.3. Immunohistochemistry Examination
4.5.4. Determination of Inflammatory Cytokines and cAMP in Brain Tissue by ELISA
4.5.5. Determination of PKA, CREB and BDNF Gene Expression by qRT-PCR
4.5.6. Determination of PDE4 Isoforms Expression by Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Protein–Protein Network Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Aβ | Amyloid beta |
| PRKACA | Protein kinase A subunit alpha |
| CREBBP | CREB-binding protein |
| FOS | Fos proto-oncogene, AP-1 transcription factor subunit |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| BCA | Bicinchoninic Acid |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| BV | Blood vessels |
| cAMP | Cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| cDNA | Complementary DNA |
| CGA | Chlorogenic acid |
| CILO | Cilomilast |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase-2 |
| CREB | cAMP response element-binding protein |
| DAB | Diaminobenzidine |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| EPAC1 | Exchange Protein Activated by Cyclic-AMP1/2 |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| H & E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| HRP | Horseradish peroxidase |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-γ |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| IL-17 | Interleukin-17 |
| IL-1β | Interleukin 1 beta |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| LTP | Long-term potentiation |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa B |
| NFTs | Neurofibrillary tangles |
| PBS | Phosphate buffered saline |
| PDE4 | Phosphodiesterase-4 |
| PKA | Protein kinase A |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene fluoride |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction |
| RIPA | Radioimmunoprecipitation assay |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SA% | The percent of Spontaneous Alteration |
| SCOP | Scopolamine |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
References
- Mosalam, E.M.; Abdel-Bar, H.M.; Elberri, A.I.; Abdallah, M.S.; Zidan, A.-A.A.; Batakoushy, H.A.; Abo Mansour, H.E. Enhanced Neuroprotective Effect of Verapamil-Loaded Hyaluronic Acid Modified Carbon Quantum Dots in an in-Vitro Model of Amyloid-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 275, 133742. [Google Scholar]
- Gustavsson, A.; Norton, N.; Fast, T.; Frölich, L.; Georges, J.; Holzapfel, D.; Kirabali, T.; Krolak-Salmon, P.; Rossini, P.M.; Ferretti, M.T. Global Estimates on the Number of Persons across the Alzheimer’s Disease Continuum. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023, 19, 658–670. [Google Scholar]
- Soto, C.; Mollenhauer, B.; Hansson, O.; Kang, U.J.; Alcalay, R.N.; Standaert, D.; Trenkwalder, C.; Marek, K.; Galasko, D.; Poston, K. Toward a Biological Definition of Neuronal and Glial Synucleinopathies. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 396–408. [Google Scholar]
- Petkova-Kirova, P.; Anastassova, N.; Minchev, B.; Uzunova, D.; Grigorova, V.; Tsvetanova, E.; Georgieva, A.; Alexandrova, A.; Stefanova, M.; Yancheva, D.; et al. Behavioral and Biochemical Effects of an Arylhydrazone Derivative of 5-Methoxyindole-2-Carboxylic Acid in a Scopolamine-Induced Model of Alzheimer’s Type Dementia in Rats. Molecules 2024, 29, 5711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosalam, E.M.; Elberri, A.I.; Sallam, A.S.; Salem, H.R.; Metwally, E.M.; Abdallah, M.S.; Shaldam, M.A.; Mansour, H.E.A. Chronotherapeutic Neuroprotective Effect of Verapamil against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Neuroinflammation in Mice through Modulation of Calcium-Dependent Genes. Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 139. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez-Rodelo, C.; Martínez-Tolibia, S.E.; Morales-Figueroa, G.E.; Velázquez-Moyado, J.A.; Olivares-Reyes, J.A.; Navarrete-Castro, A. Modulating Cyclic Nucleotides Pathways by Bioactive Compounds in Combatting Anxiety and Depression Disorders. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 7797–7814. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, V.K.; Singh, T.G.; Singh, S. Cyclic Nucleotides Signaling and Phosphodiesterase Inhibition: Defying Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Drug Targets 2020, 21, 1371–1384. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bonato, J.M.; Meyer, E.; de Mendonça, P.S.B.; Milani, H.; Prickaerts, J.; Weffort de Oliveira, R.M. Roflumilast Protects against Spatial Memory Impairments and Exerts Anti-inflammatory Effects after Transient Global Cerebral Ischemia. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2021, 53, 1171–1188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bhat, A.; Ray, B.; Mahalakshmi, A.M.; Tuladhar, S.; Nandakumar, D.N.; Srinivasan, M.; Essa, M.M.; Chidambaram, S.B.; Guillemin, G.J.; Sakharkar, M.K. Phosphodiesterase-4 Enzyme as a Therapeutic Target in Neurological Disorders. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 160, 105078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Wang, C.; He, W.; Wu, X.; Li, S.; Zeng, Z.; Wei, M.; He, B. Roflumilast Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment in APP/PS1 Mice via CAMP/CREB/BDNF Signaling and Anti-Neuroinflammatory Effects. Metab. Brain Dis. 2019, 34, 583–591. [Google Scholar]
- Khakha, N.; Khan, H.; Kaur, A.; Singh, T.G. Therapeutic Implications of Phosphorylation- and Dephosphorylation-Dependent Factors of CAMP-Response Element-Binding Protein (CREB) in Neurodegeneration. Pharmacol. Rep. 2023, 75, 1152–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amidfar, M.; de Oliveira, J.; Kucharska, E.; Budni, J.; Kim, Y.-K. The Role of CREB and BDNF in Neurobiology and Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Life Sci. 2020, 257, 118020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.; Sun, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, G.; Wang, G. Effects of Selective Phosphodiesterases-4 Inhibitors on Learning and Memory: A Review of Recent Research. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 70, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhu, G. CAMP-PKA Cascade: An Outdated Topic for Depression? Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 150, 113030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugin, L.J.S.; Murugesan, A.; Bindu, M.; Sunil, K.N. Roflumilast: A Potential Drug for the Treatment of Cognitive Impairment? Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 736, 135281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondarev, A.D.; Attwood, M.M.; Jonsson, J.; Chubarev, V.N.; Tarasov, V.V.; Liu, W.; Schioth, H.B. Recent Developments of Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors: Clinical Trials, Emerging Indications and Novel Molecules. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1057083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Mukherjee, S.; Paliwal, P.; Singh, S.S.; Birla, H.; Singh, S.P.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Patnaik, R. Neuroprotective Effect of Chlorogenic Acid in Global Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Rat Model. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs. Arch. Pharmacol. 2019, 392, 1293–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.S.; Rai, S.N.; Birla, H.; Zahra, W.; Rathore, A.S.; Dilnashin, H.; Singh, R.; Singh, S.P. Neuroprotective Effect of Chlorogenic Acid on Mitochondrial Dysfunction-Mediated Apoptotic Death of DA Neurons in a Parkinsonian Mouse Model. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 6571484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Protective Effects of Chlorogenic Acid on Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Rats by Regulating Oxidative Stress-Related Nrf2 Pathway. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2020, 14, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosalam, E.M.; Elberri, A.I.; Abdallah, M.S.; Abdel-Bar, H.M.; Zidan, A.-A.A.; Batakoushy, H.A.; Abo Mansour, H.E. Mechanistic Insights of Neuroprotective Efficacy of Verapamil-Loaded Carbon Quantum Dots against LPS-Induced Neurotoxicity in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.; Kim, S.; Nam, Y.; Jung, U.J.; Kim, S.R. Mitochondrial Dysfunction as a Driver of Cognitive Impairment in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, K.; Singh, M.K.; Kohat, K.; SriVarshini, T.; Chenchula, S.; Padmavathi, R.; Amerneni, L.S.; VishnuVardhan, K.; MythiliBai, K.; Chavan, M.R.; et al. Recent Insights into the Neurobiology of Alzheimer’s Disease and Advanced Treatment Strategies. Mol. Neurobiol. 2025, 62, 2314–2332. [Google Scholar]
- Khesmakhi, M.V.; Salimi, Z.; Pourmotabbed, A.; Moradpour, F.; Rezayof, A.; Nedaei, S.E. The Role of Glutamate NMDA Receptors of the Mediodorsal Thalamus in Scopolamine-Induced Amnesia in Rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2023, 137595. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, I.-S.; Choi, G.-Y.; Sreelatha, I.; Yoon, J.-W.; Youn, S.-H.; Maeng, S.; Park, J.-H. Effect of Sinapic Acid on Scopolamine-Induced Learning and Memory Impairment in SD Rats. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Rahman, M.U.; Balakrishnan, R.; Kim, J.-M.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, D.-K. The Novel Peptide DBCH Reduces LPS-Stimulated NF-ΚB/MAPK Signaling in BV-2 Microglia and Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment in Scopolamine-Treated Mice by Modulating BDNF/CREB. Neurochem. Int. 2025, 185, 105946. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kazmi, I.; Al-Abbasi, F.A.; Afzal, M.; Nadeem, M.S.; Altayb, H.N. Sterubin Protects against Chemically-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease by Reducing Biomarkers of Inflammation-IL-6/IL-β/TNF-α and Oxidative Stress-SOD/MDA in Rats. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 30, 103560. [Google Scholar]
- Sandhu, M.; Irfan, H.M.; Shah, S.A.; Ahmed, M.; Naz, I.; Akram, M.; Fatima, H.; Farooq, A.S. Friedelin Attenuates Neuronal Dysfunction and Memory Impairment by Inhibition of the Activated JNK/NF-ΚB Signalling Pathway in Scopolamine-Induced Mice Model of Neurodegeneration. Molecules 2022, 27, 4513. [Google Scholar]
- Cheon, S.Y.; Koo, B.-N.; Kim, S.Y.; Kam, E.H.; Nam, J.; Kim, E.J. Scopolamine Promotes Neuroinflammation and Delirium-like Neuropsychiatric Disorder in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8376. [Google Scholar]
- Olayinka, J.; Eduviere, A.; Adeoluwa, O.; Fafure, A.; Adebanjo, A.; Ozolua, R. Quercetin Mitigates Memory Deficits in Scopolamine Mice Model via Protection against Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration. Life Sci. 2022, 292, 120326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Liu, M.; Cao, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yi, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, P.; Du, Q.; et al. Sinomenine Regulates the Cholinergic Anti-Inflammatory Pathway to Inhibit TLR4/NF-ΚB Pathway and Protect the Homeostasis in Brain and Gut in Scopolamine-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease Mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 171, 116190. [Google Scholar]
- Abo Mansour, H.E.; Elberri, A.I.; Ghoneim, M.E.-S.; Samman, W.A.; Alhaddad, A.A.; Abdallah, M.S.; El-Berri, E.I.; Salem, M.A.; Mosalam, E.M. The Potential Neuroprotective Effect of Thymoquinone on Scopolamine-Induced In Vivo Alzheimer’s Disease-like Condition: Mechanistic Insights. Molecules 2023, 28, 6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankowska, A.; Pawłowski, M.; Chłoń-Rzepa, G. Diabetic Theory in Anti-Alzheimer’s Drug Research and Development. Part 2: Therapeutic Potential of CAMP-Specific Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 3535–3553. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Z.-Q.; Chen, J.-J.; Feng, H.-F.; Cheng, Y.-F.; Wang, H.-T.; Zhou, Z.-Z.; Guo, H.-B.; Zheng, W.; Xu, J.-P. Novel Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibitor FCPR03 Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Neuroinflammation by Regulation of the CAMP/PKA/CREB Signaling Pathway and NF- κ B Inhibition. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2017, 362, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, N.; Lesa, K.N.; Sudarmanto, A.; Fakhrudin, N.; Ikawati, Z. The Role of Phosphodiesterase-1 and Its Natural Product Inhibitors in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1070677. [Google Scholar]
- Koga, Y.; Tsurumaki, H.; Aoki-Saito, H.; Sato, M.; Yatomi, M.; Takehara, K.; Hisada, T. Roles of Cyclic AMP Response Element Binding Activation in the ERK1/2 and P38 MAPK Signalling Pathway in Central Nervous System, Cardiovascular System, Osteoclast Differentiation and Mucin and Cytokine Production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.K.; Singh, T.G. CREB: A Multifaceted Target for Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2020, 17, 1280–1293. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Teng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Geng, F.; Chen, X.; Jiang, H.; Yang, J.; Zheng, M.; Wang, Z.; Yang, L. Molecular Mechanism of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor (PDGF)-BB-Mediated Protection against MPP+ Toxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 71, 1131–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Hu, Y.; Tong, L.; Bi, X. High-Intensity Training on CREB Activation for Improving Brain Health: A Narrative Review of Possible Molecular Talks. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 15, 1498495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schick, M.A.; Schlegel, N. Clinical Implication of Phosphodiesterase-4-Inhibition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Cao, J.; Zhu, G. CAMP-PKA Signaling Pathway and Anxiety: Where Do We Go Next? Cell. Signal. 2024, 111311. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, N.; Zameer, S.; Najmi, A.K.; Parvez, S.; Akhtar, M. Roflumilast Reduces Pathological Symptoms of Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease in Rats Produced by Intracerebroventricular Streptozotocin by Inhibiting NF-ΚB/BACE-1 Mediated Aβ Production in the Hippocampus and Activating the CAMP/BDNF Signalling Pathway. Neurotox. Res. 2022, 40, 432–448. [Google Scholar]
- Lazarova, M.; Tsvetanova, E.; Georgieva, A.; Stefanova, M.; Uzunova, D.; Denev, P.; Vassileva, V.; Tasheva, K. Extracts of Sideritis Scardica and Clinopodium Vulgare Alleviate Cognitive Impairments in Scopolamine-Induced Rat Dementia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhang, S.; Sun, N.; Zhu, B.; Lin, S. Neuroprotective Function of a Novel Hexapeptide QMDDQ from Shrimp via Activation of the PKA/CREB/BNDF Signaling Pathway and Its Structure–Activity Relationship. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 6759–6769. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.; Mazzacuva, F.; Crocetti, L.; Giovannoni, M.P.; Cilibrizzi, A. PDE4 Inhibitors: Profiling Hits through the Multitude of Structural Classes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paes, D.; Schepers, M.; Rombaut, B.; van den Hove, D.; Vanmierlo, T.; Prickaerts, J. The Molecular Biology of Phosphodiesterase 4 Enzymes as Pharmacological Targets: An Interplay of Isoforms, Conformational States, and Inhibitors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2021, 73, 1016–1049. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Pan, T.; An, B.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Huang, L. Synthesis and Evaluation of Clioquinol-Rolipram/Roflumilast Hybrids as Multitarget-Directed Ligands for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 163, 512–526. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, S.; Zheng, V.; Chen, L.; Ma, M.; Shen, S.; Qu, J.; Zhang, H.; Gurney, M.E.; O’Donnell, J.M. A Novel PDE4D Inhibitor BPN14770 Reverses Scopolamine-Induced Cognitive Deficits via CAMP/SIRT1/Akt/Bcl-2 Pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 599389. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Yu, G.; Shen, H.; Luo, Y.; Shang, T.; Shen, R.; Xi, M.; Sun, H. Targeting Phosphodiesterase 4 as a Therapeutic Strategy for Cognitive Improvement. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 130, 106278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Han, W.; Lee, S.G.; Shin, J.H. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Chlorogenic Acid on Macrophages: A Simplified Simulation of Pharmacokinetics Following Ingestion Using a Windup Syringe Pump. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebai, O.; Belkhir, M.; Sanchez-Gomez, M.V.; Matute, C.; Fattouch, S.; Amri, M. Differential Molecular Targets for Neuroprotective Effect of Chlorogenic Acid and Its Related Compounds against Glutamate Induced Excitotoxicity and Oxidative Stress in Rat Cortical Neurons. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 3559–3572. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuyama, K.; Kakio, S.; Nakazawa, Y.; Kobata, K.; Funakoshi-Tago, M.; Suzuki, T.; Tamura, H. Roasted Coffee Reduces Β-Amyloid Production by Increasing Proteasomal Β-Secretase Degradation in Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1800238. [Google Scholar]
- Ishida, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Misawa, K.; Nishimura, H.; Misawa, K.; Ota, N.; Shimotoyodome, A. Coffee Polyphenols Prevent Cognitive Dysfunction and Suppress Amyloid β Plaques in APP/PS2 Transgenic Mouse. Neurosci. Res. 2020, 154, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Choi, S.-Y.; Lee, P.; Hur, J. Neochlorogenic Acid Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Activation and pro-Inflammatory Responses in BV2 Microglial Cells. Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 1792–1798. [Google Scholar]
- Murai, T.; Matsuda, S. The Chemopreventive Effects of Chlorogenic Acids, Phenolic Compounds in Coffee, against Inflammation, Cancer, and Neurological Diseases. Molecules 2023, 28, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, A.; El Sayed, N.; Nafea, H.; Gad, M. Rolipram Rescues Memory Consolidation Deficits Caused by Sleep Deprivation: Implication of the CAMP/PKA and CAMP/Epac Pathways. CNS Neurol. Disord. Targets Formerly Curr. Drug Targets-CNS Neurol. Disord. 2022, 21, 631–639. [Google Scholar]
- Bouayed, J.; Rammal, H.; Dicko, A.; Younos, C.; Soulimani, R. Chlorogenic Acid, a Polyphenol from Prunus Domestica (Mirabelle), with Coupled Anxiolytic and Antioxidant Effects. J. Neurol. Sci. 2007, 262, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Shim, J.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, J.; Jang, Y.J.; Yang, H.; Park, J.; Choi, S.H.; Yoon, J.H. Caffeinated Coffee, Decaffeinated Coffee, and the Phenolic Phytochemical Chlorogenic Acid up-Regulate NQO1 Expression and Prevent H2O2-Induced Apoptosis in Primary Cortical Neurons. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 60, 466–474. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Elzoghby, A.O.; Alalaiwe, A.; Hwang, T.-L.; Fang, J.-Y. Oleic Acid as the Active Agent and Lipid Matrix in Cilomilast-Loaded Nanocarriers to Assist PDE4 Inhibition of Activated Neutrophils for Mitigating Psoriasis-like Lesions. Acta Biomater. 2019, 90, 350–361. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, S.-H.; Lee, H.-K.; Kim, J.-A.; Hong, S.-I.; Kim, H.-C.; Jo, T.-H.; Park, Y.-I.; Lee, C.-K.; Kim, Y.-B.; Lee, S.-Y. Neuroprotective Effects of Chlorogenic Acid on Scopolamine-Induced Amnesia via Anti-Acetylcholinesterase and Anti-Oxidative Activities in Mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 649, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponne, S.; Kumar, C.R.; Boopathy, R. Verapamil Attenuates Scopolamine Induced Cognitive Deficits by Averting Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Injury–A Potential Therapeutic Agent for Alzheimer’s Disease. Metab. Brain Dis. 2020, 35, 503–515. [Google Scholar]
- Latif, K.; Saneela, S.; Khan, A. Ameliorative Effect of Carveol on Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment in Rats. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2022, 25, 1504. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mosalam, E.M.; Atya, S.M.; Mesbah, N.M.; Allam, S.; Mehanna, E.T. Neuroprotective Effects of Cilomilast and Chlorogenic Acid Against Scopolamine-Induced Memory Deficits via Modulation of the cAMP/PKA–CREB–BDNF Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073108
Mosalam EM, Atya SM, Mesbah NM, Allam S, Mehanna ET. Neuroprotective Effects of Cilomilast and Chlorogenic Acid Against Scopolamine-Induced Memory Deficits via Modulation of the cAMP/PKA–CREB–BDNF Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073108
Chicago/Turabian StyleMosalam, Esraa M., Soha M. Atya, Noha M. Mesbah, Shady Allam, and Eman T. Mehanna. 2025. "Neuroprotective Effects of Cilomilast and Chlorogenic Acid Against Scopolamine-Induced Memory Deficits via Modulation of the cAMP/PKA–CREB–BDNF Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073108
APA StyleMosalam, E. M., Atya, S. M., Mesbah, N. M., Allam, S., & Mehanna, E. T. (2025). Neuroprotective Effects of Cilomilast and Chlorogenic Acid Against Scopolamine-Induced Memory Deficits via Modulation of the cAMP/PKA–CREB–BDNF Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073108





