Matrine Inhibits High-Glucose-Diet-Induced Fat Accumulation and Aβ-Mediated Lipid Metabolic Disorder via AAK-2/NHR-49 Pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Matrine Reduces Fat Accumulation in High-Glucose-Diet C. elegans
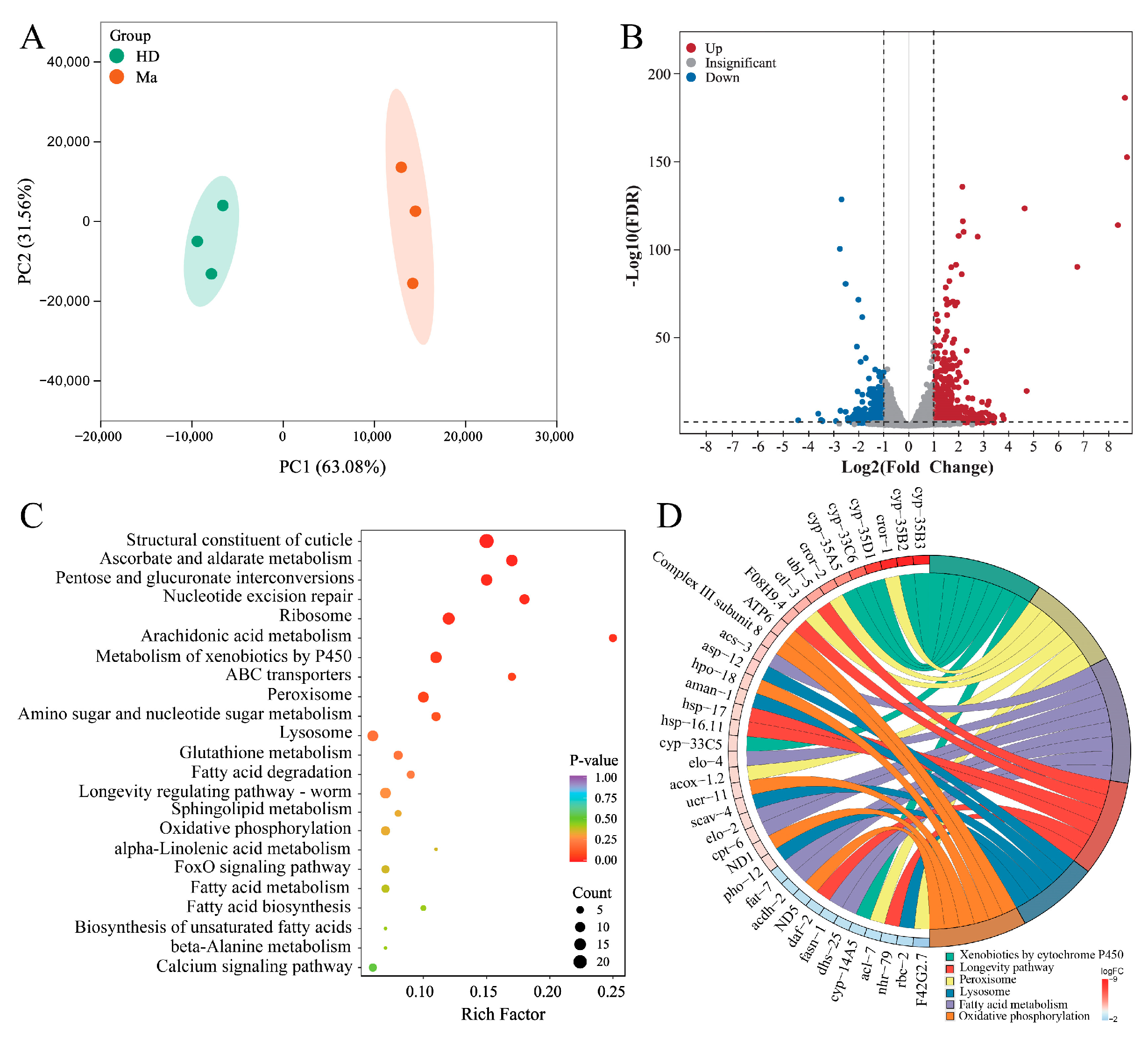
2.2. Transcriptome Analysis of Matrine-Regulated DEGs in High-Glucose Diet C. elegans
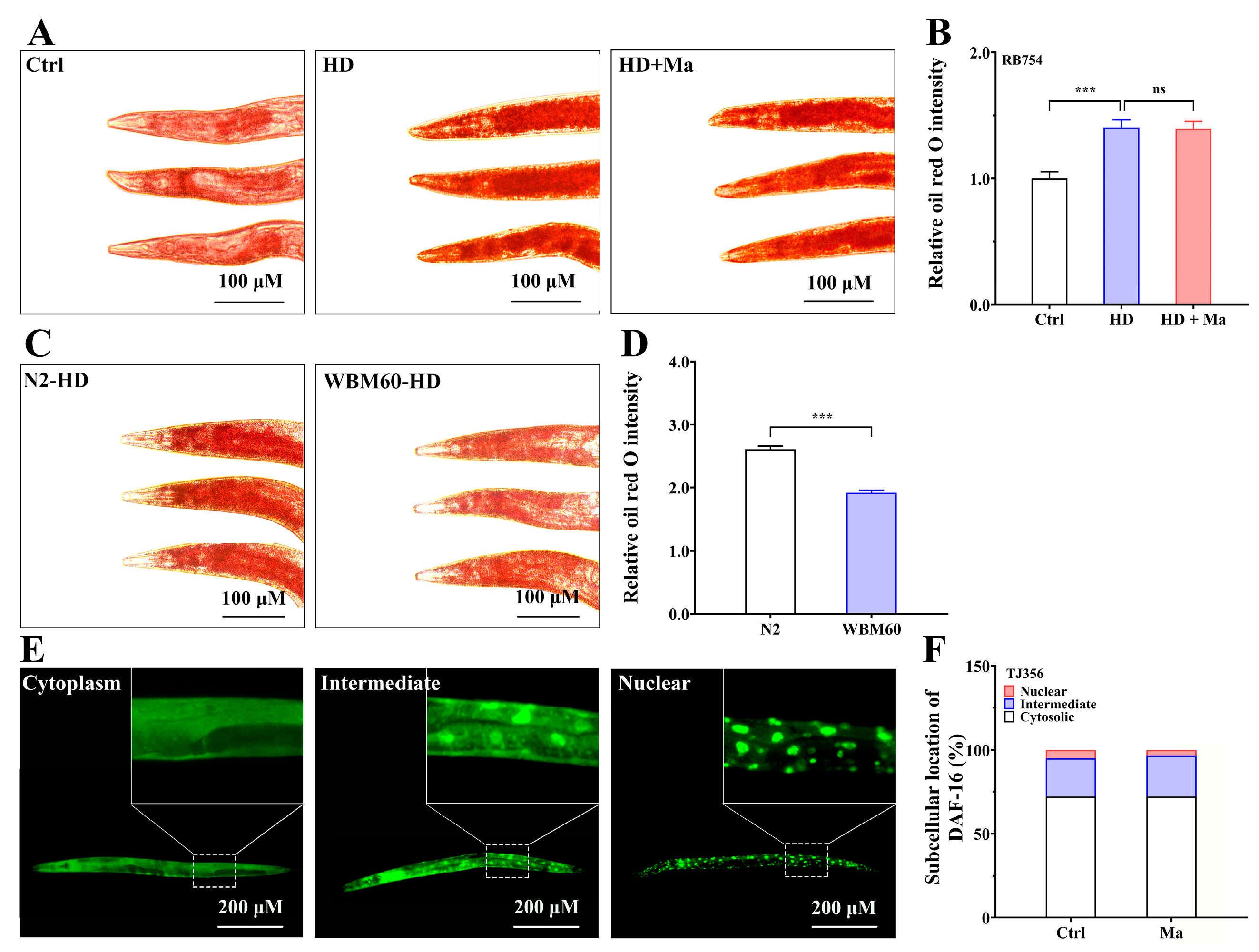
2.3. Matrine-Mediated Fat Lowering Through AAK-2 Pathway but Not DAF-16
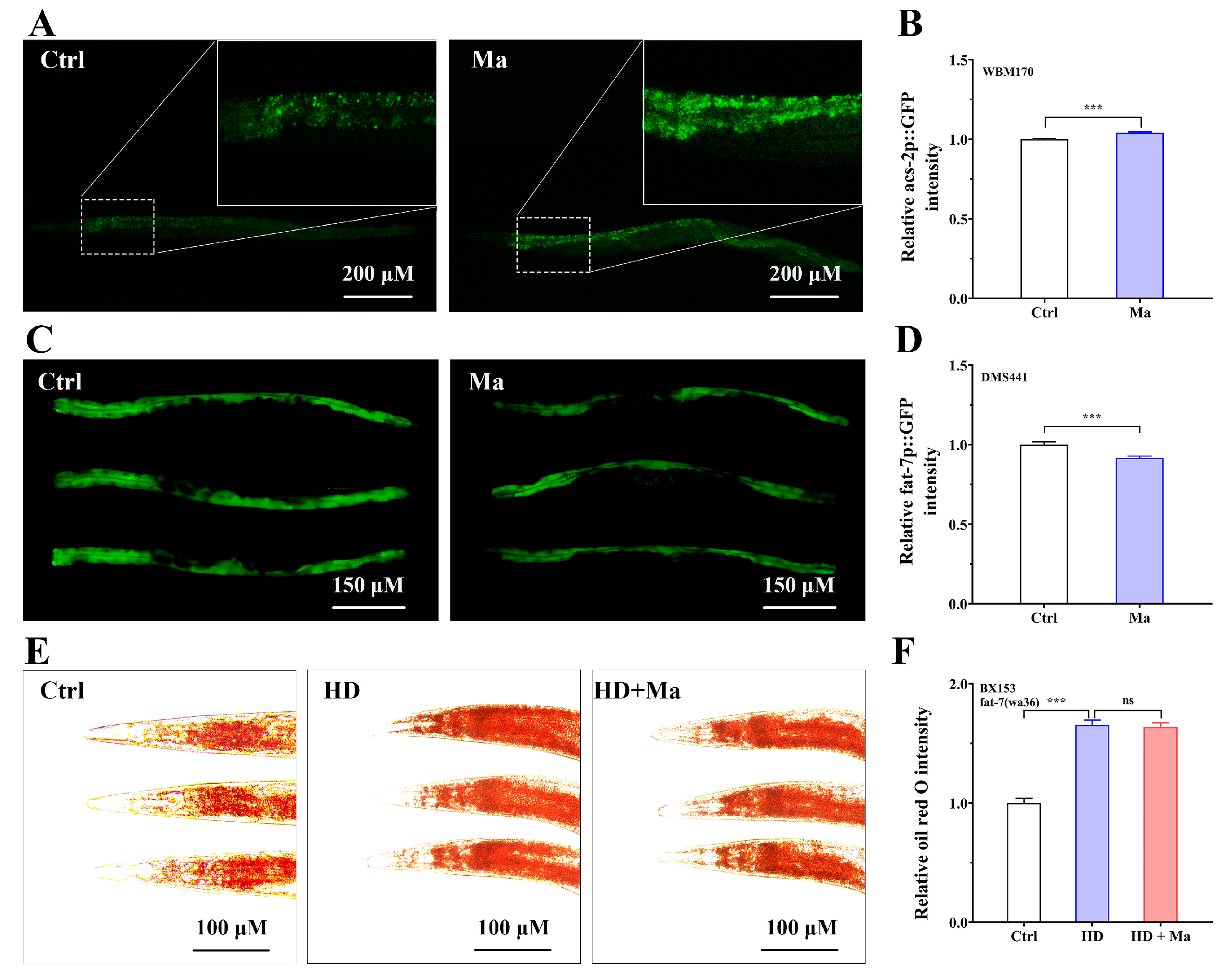
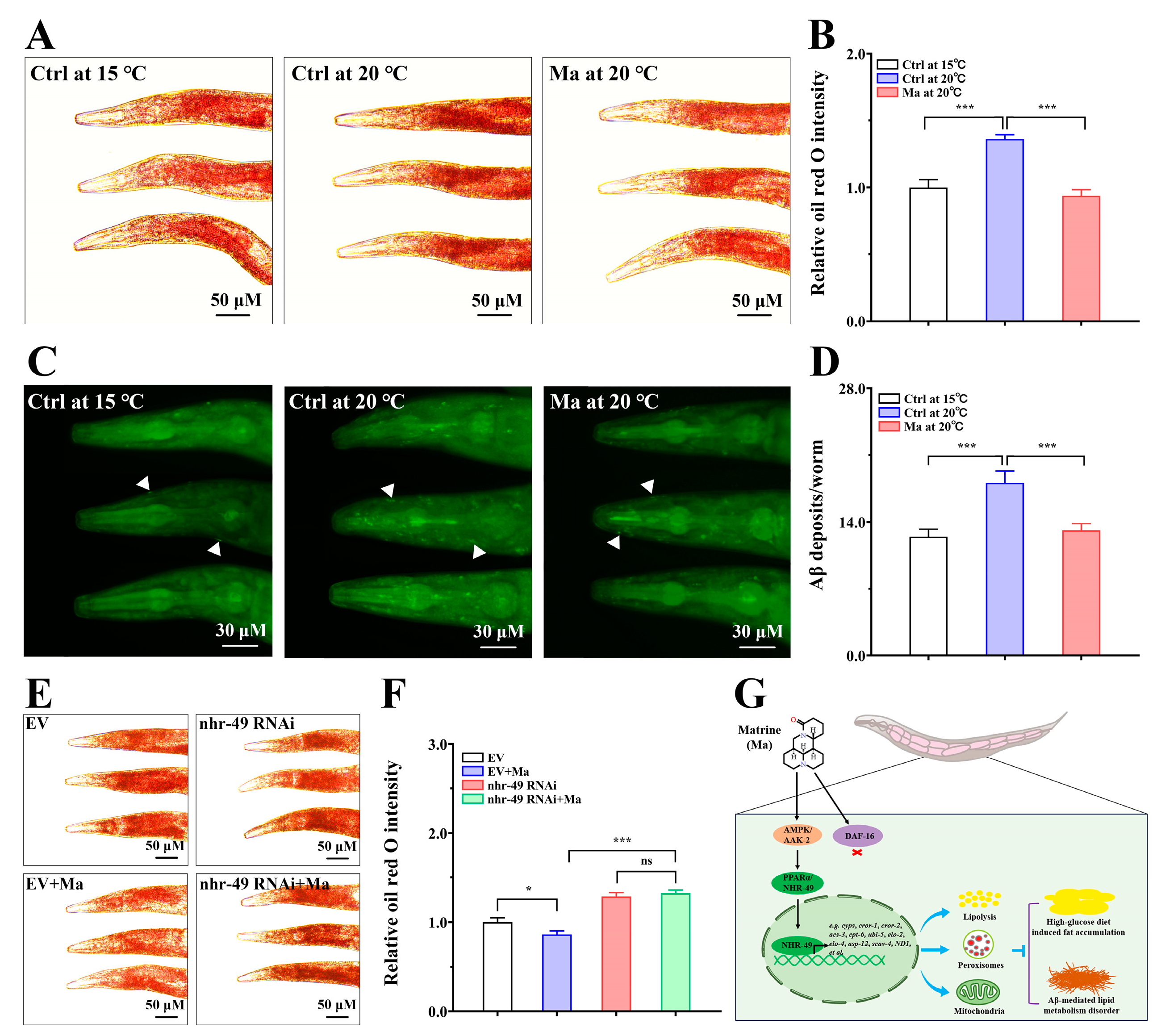
2.4. Involvement of NHR-49 in Matrine-Mediated Fat-Lowering Effect
2.5. Matrine Regulates Lipid Metabolism-Related Gene Expressions
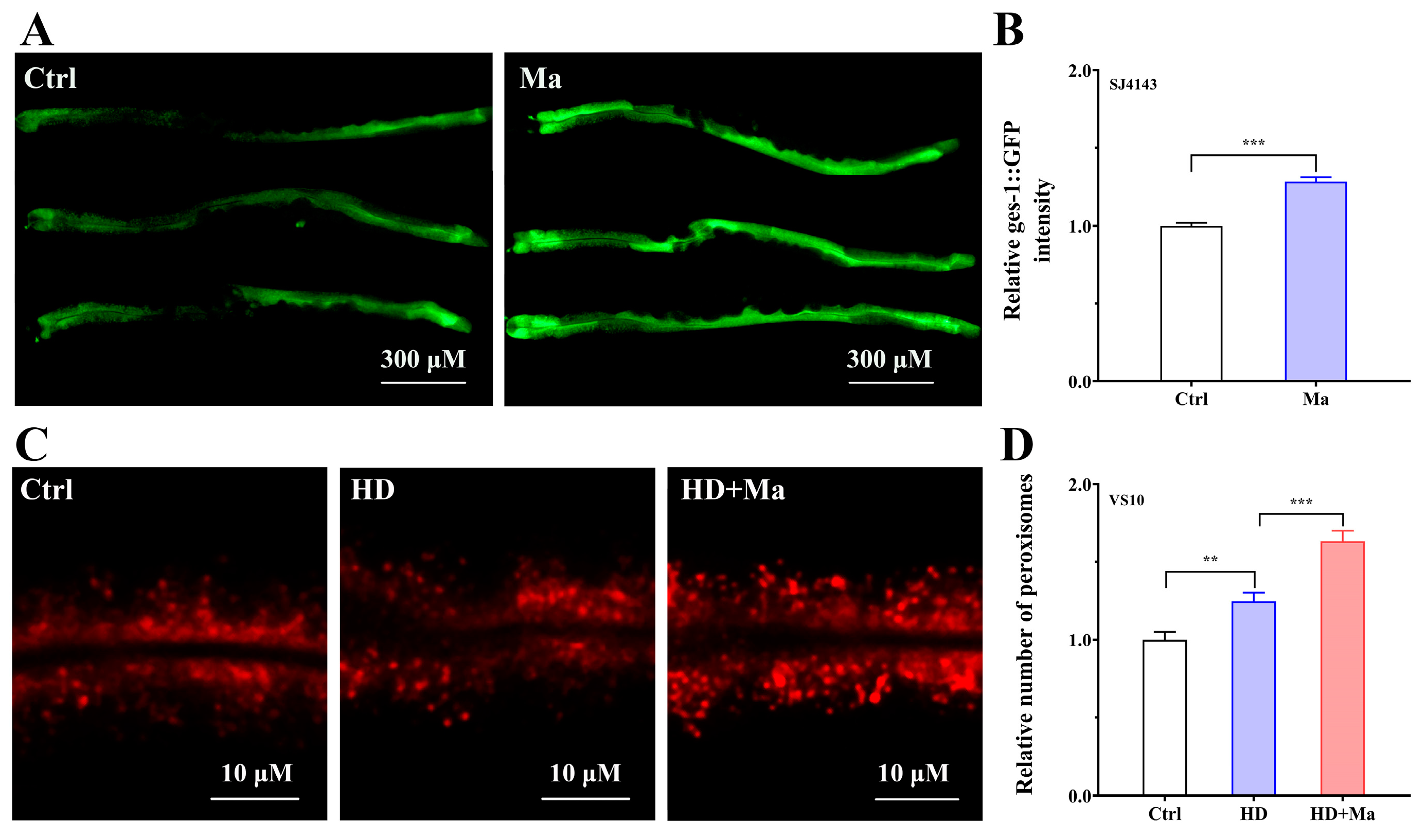
2.6. Matrine Impacts the Functions of Mitochondria and Peroxisomes
2.7. Maintenance of AAK-2/NHR-49-Governed Lipid Homeostasis Increases the Physical Fitness and Lifespan
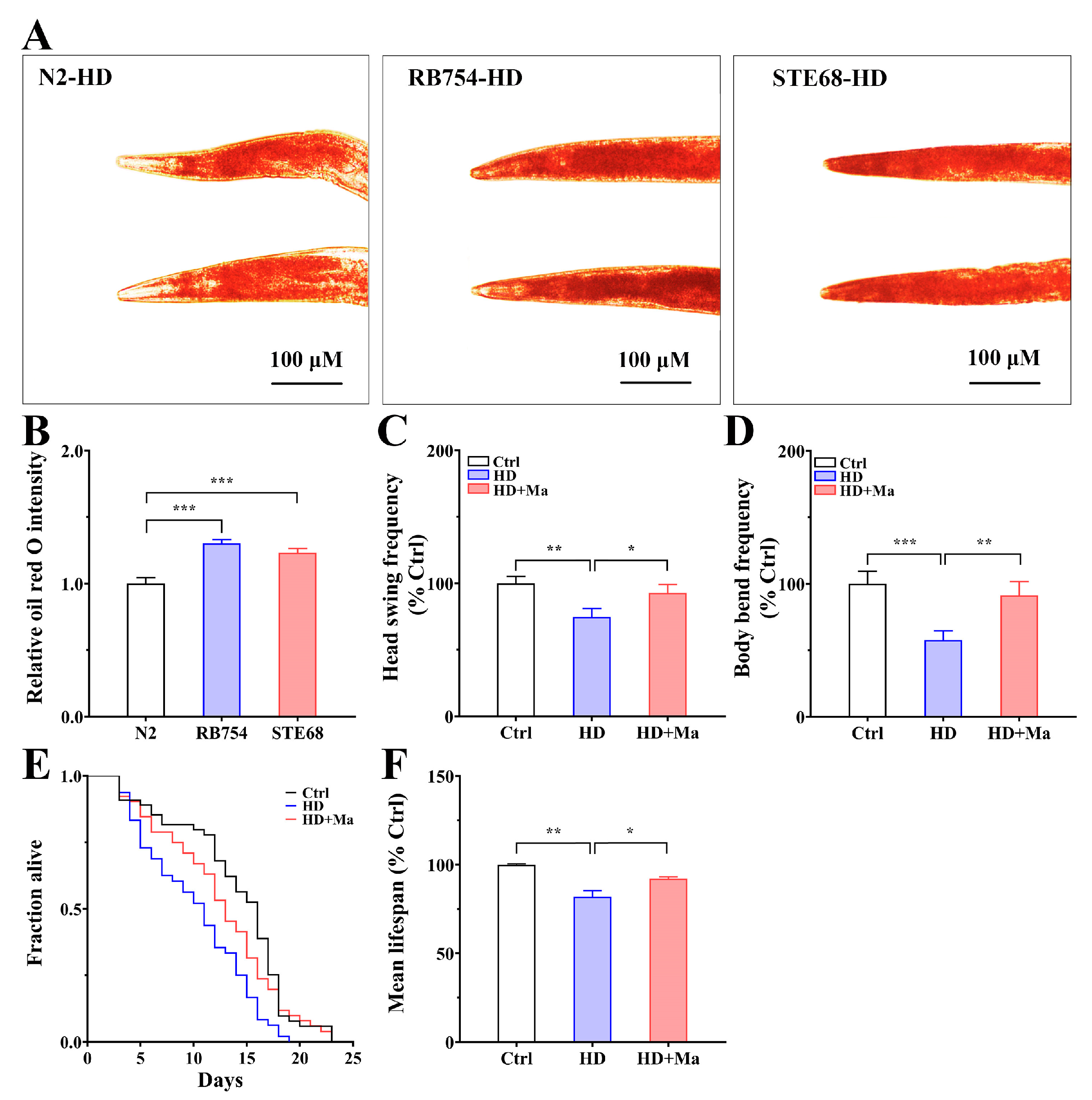
2.8. Matrine Alleviates Aβ-Mediated Lipid Metabolic Disorder
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and C. elegans
4.2. Body Length and Brood Size
4.3. Fat Staining
4.4. Fluorescent Signal Detection
4.5. RNA Sequencing and Transcriptome Analysis
4.6. NHR-49 Nuclear Localization Assay
4.7. DAF-16 Nuclear Localization Assay
4.8. RNA Interference
4.9. Quantification of Mitochondria and Peroxisomes
4.10. Motility Analysis
4.11. Lifespan Assay
4.12. ThS Staining Assay
4.13. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wen, X.; Zhang, B.; Wu, B.; Xiao, H.; Li, Z.; Li, R.; Xu, X.; Li, T. Signaling Pathways in Obesity: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Interventions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 298. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, G.A.; Heisel, W.E.; Afshin, A.; Jensen, M.D.; Dietz, W.H.; Long, M.; Kushner, R.F.; Daniels, S.R.; Wadden, T.A.; Tsai, A.G.; et al. The Science of Obesity Management: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 79–132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jee, W.; Cho, H.-S.; Kim, S.W.; Bae, H.; Chung, W.-S.; Cho, J.-H.; Kim, H.; Song, M.-Y.; Jang, H.-J. Lycium chinense Mill Induces Anti-Obesity and Anti-Diabetic Effects In Vitro and In Vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Wang, D.; Zhuang, X.; Wang, Z.; Ni, Y.; Chen, S.; Sun, F. Berberine Increases Adipose Triglyceride Lipase in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes through the AMPK Pathway. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 214. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Z.-Y.; Hu, Y.-R.; Ma, H.; Wang, Y.-Z.; He, K.; Xia, S.; Wu, H.; Xue, D.-F.; Li, X.-G.; Ye, X.-L. Coptisine Attenuates Obesity-Related Inflammation through LPS/TLR-4-Mediated Signaling Pathway in Syrian Golden Hamsters. Fitoterapia 2015, 105, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sáez-Orellana, F.; Octave, J.-N.; Pierrot, N. Alzheimer’s Disease, a Lipid Story: Involvement of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor α. Cells 2020, 9, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, V.; Sanz-Lamora, H.; Arias, G.; Marrero, P.F.; Haro, D.; Relat, J. Metabolic Impact of Flavonoids Consumption in Obesity: From Central to Peripheral. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.-F.; Yang, C.-J.; Morris-Natschke, S.L.; Li, J.-C.; Yin, X.-D.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Guo, X.; Peng, J.-W.; Goto, M.; Zhang, J.-Y.; et al. Biologically Active Isoquinoline Alkaloids Covering 2014–2018. Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 40, 2212–2289. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Li, J.; Pan, R.; Zhu, Y.; Xiao, X.; Li, Y.; Li, C. Polysaccharides from Volvariella volvacea inhibit fat accumulation in C. elegans via the AAK-2/NHR-49-mediated pathway. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13912. [Google Scholar]
- Warden, A.; Truitt, J.; Merriman, M.; Ponomareva, O.; Jameson, K.; Ferguson, L.B.; Mayfield, R.D.; Harris, R.A. Localization of PPAR Isotypes in the Adult Mouse and Human Brain. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27618. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Teng, F.; Li, J.; Guan, Y.; Xu, J.; Lv, X.; Guan, F.; Zhang, M.; Chen, L. Berberine Improves Cognitive Deficiency and Muscular Dysfunction via Activation of the AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1a Pathway in Skeletal Muscle from Naturally Aging Rats. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 22, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salminen, A.; Kaarniranta, K. AMP-Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) Controls the Aging Process via an Integrated Signaling Network. Ageing Res. Rev. 2012, 11, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Xu, L.; Cai, Q.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Ni, Z. Research Progress on the Pharmacological Effects of Matrine. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 977374. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; He, F.; Wu, L.; Xu, Y.; Du, Q. Matrine Exerts Pharmacological Effects Through Multiple Signaling Pathways: A Comprehensive Review. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2022, 16, 533–569. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, X.-Y.; Wang, H.; Bai, F.; Zhou, X.; Li, S.-P.; Ren, L.-P.; Sun, R.-Q.; Xue, C.C.L.; Jiang, H.-L.; Hu, L.-H.; et al. Identification of Matrine as a Promising Novel Drug for Hepatic Steatosis and Glucose Intolerance with HSP72 as an Upstream Target. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 4303–4318. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, H.; Liu, G.; Li, L.; Ren, X.; Jiang, Y.; Hou, W.; Liu, R.; Liu, K.; Liu, H.; Huang, H. Quantitative Proteomics Reveal the Role of Matrine in Regulating Lipid Metabolism. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 24308–24320. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, L.; Cai, Y.; Cheng, W.; Liu, G.; Zhao, J.; Cao, H.; Tao, H.; Wang, Y.; Yin, M.; Liu, T.; et al. A Novel, Multi-Target Natural Drug Candidate, Matrine, Improves Cognitive Deficits in Alzheimer’s Disease Transgenic Mice by Inhibiting Aβ Aggregation and Blocking the RAGE/Aβ Axis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 1939–1952. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, P.; Wang, P.; Liu, L.; Wang, P.; Lin, G.; Qu, Z.; Yu, Z.; Liu, N. Naringin Alleviates Glucose-Induced Aging by Reducing Fat Accumulation and Promoting Autophagy in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nutrients 2023, 15, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavorov-Dayliev, D.; Milagro, F.I.; Ayo, J.; Oneca, M.; Goyache, I.; López-Yoldi, M.; Aranaz, P. Glucose-Lowering Effects of a Synbiotic Combination Containing Pediococcus acidilactici in C. elegans and Mice. Diabetologia 2023, 66, 2117–2138. [Google Scholar]
- Papsdorf, K.; Miklas, J.W.; Hosseini, A.; Cabruja, M.; Morrow, C.S.; Savini, M.; Yu, Y.; Silva-García, C.G.; Haseley, N.R.; Murphy, L.M.; et al. Lipid Droplets and Peroxisomes Are Co-Regulated to Drive Lifespan Extension in Response to Mono-Unsaturated Fatty Acids. Nat. Cell Biol. 2023, 25, 672–684. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, T.; Bonni, A.; Zhao, G. Robust Principal Component Analysis for Accurate Outlier Sample Detection in RNA-Seq Data. BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Sun, J.; Liu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y. The New Role of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase in Regulating Fat Metabolism and Energy Expenditure in Adipose Tissue. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zečić, A.; Braeckman, B.P. DAF-16/FoxO in Caenorhabditis elegans and Its Role in Metabolic Remodeling. Cells 2020, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farias-Pereira, R.; Savarese, J.; Yue, Y.; Lee, S.-H.; Park, Y. Fat-Lowering Effects of Isorhamnetin Are via NHR-49-Dependent Pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2019, 2, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, J.L. Fat Synthesis and Adiposity Regulation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 20, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savova, M.S.; Todorova, M.N.; Apostolov, A.G.; Yahubyan, G.T.; Georgiev, M.I. Betulinic Acid Counteracts the Lipid Accumulation in Caenorhabditis elegans by Modulation of nhr-49 Expression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 156, 113862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doering, K.R.S.; Ermakova, G.; Taubert, S. Nuclear Hormone Receptor NHR-49 Is an Essential Regulator of Stress Resilience and Healthy Aging in Caenorhabditis elegans. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1241591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzig, S.; Shaw, R.J. AMPK: Guardian of Metabolism and Mitochondrial Homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, B.A.; Petersen, D.A.; Gaeta, A.L.; Stanley, S.P.; Caldwell, G.A.; Caldwell, K.A. Dysregulation of the Mitochondrial Unfolded Protein Response Induces Non-Apoptotic Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration in C. elegans Models of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 11085–11100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodhi, I.J.; Semenkovich, C.F. Peroxisomes: A Nexus for Lipid Metabolism and Cellular Signaling. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman, M.; Peter, Q.; Seinstra, R.I.; Perni, M.; Vendruscolo, M.; Dobson, C.M.; Knowles, T.P.J.; Nollen, E.A.A. Assessing Motor-Related Phenotypes of Caenorhabditis elegans with the Wide Field-of-View Nematode Tracking Platform. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 2071–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheltens, P.; Strooper, B.D.; Kivipelto, M.; Holstege, H.; Chételat, G.; Teunissen, C.E.; Cummings, J.; van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s Disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Di Paolo, G.; Kim, T.-W. Linking Lipids to Alzheimer’s Disease: Cholesterol and Beyond. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teitsdottir, U.D.; Halldorsson, S.; Rolfsson, O.; Lund, S.H.; Jonsdottir, M.K.; Snaedal, J.; Petersen, P.H. Cerebrospinal Fluid C18 Ceramide Associates with Markers of Alzheimer’s Disease and Inflammation at the Pre- and Early Stages of Dementia. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021, 81, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Querfurth, H.W.; LaFerla, F.M. Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Müller-Schiffmann, A.; Herring, A.; Abdel-Hafiz, L.; Chepkova, A.N.; Schäble, S.; Wedel, D.; Horn, A.H.C.; Sticht, H.; de Souza Silva, M.A.; Gottmann, K.; et al. Amyloid-β Dimers in the Absence of Plaque Pathology Impair Learning and Synaptic Plasticity. Brain 2016, 139, 509–525. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, W.; Su, Q.; Cheng, Q.; Peng, Q.; Qiao, A.; Luo, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y. Neuroprotective Effects of Palmatine via the Enhancement of Antioxidant Defense and Small Heat Shock Protein Expression in Aβ-Transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 9966223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójtowicz, S.; Strosznajder, A.K.; Jeżyna, M.; Strosznajder, J.B. The Novel Role of PPAR Alpha in the Brain: Promising Target in Therapy of Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Neurodegenerative Disorders. Neurochem. Res. 2020, 45, 972–988. [Google Scholar]
- Leiteritz, A.; Baumanns, S.; Wenzel, U. Amyloid-Beta (Aβ1–42)-Induced Paralysis in Caenorhabditis elegans Is Reduced through NHR-49/PPARalpha. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 730, 135042. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.; Yang, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Sun, Q. The Cellular and Molecular Targets of Natural Products against Metabolic Disorders: A Translational Approach to Reach the Bedside. MedComm 2024, 5, e664. [Google Scholar]
- Pyo, I.S.; Yun, S.; Yoon, Y.E.; Choi, J.-W.; Lee, S.-J. Mechanisms of Aging and the Preventive Effects of Resveratrol on Age-Related Diseases. Molecules 2020, 25, 4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurindo, L.F.; Rodrigues, V.D.; Laurindo, L.F.; Cherain, L.M.A.; de Lima, E.P.; Boaro, B.L.; da Silva Camarinha Oliveira, J.; Chagas, E.F.B.; Catharin, V.C.S.; Dos Santos Haber, J.F.; et al. Targeting AMPK with Irisin: Implications for metabolic disorders, cardiovascular health, and inflammatory conditions—A systematic review. Life Sci. 2025, 360, 123230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Sun, Q.; Gao, R.; Park, Y. AAK-2 and SKN-1 are involved in chicoric acid-induced lifespan extension in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 9178–9186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadagurski, M.; White, M.F. Integrating Metabolism and Longevity through Insulin and IGF1 Signaling. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 42, 127–148. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, L.; Li, X.; Preusch, C.B.; He, G.J.; Xu, N.; Cheung, T.H.; Qu, J.; Mak, H.Y. Nuclear Receptors NHR-49 and NHR-79 Promote Peroxisome Proliferation to Compensate for Aldehyde Dehydrogenase Deficiency in C. elegans. PLoS Genet. 2021, 17, e1009635. [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta, M.; Shashikanth, M.; Gupta, A.; Sandhu, A.; De, A.; Javed, S.; Singh, V. NHR-49 Transcription Factor Regulates Immunometabolic Response and Survival of Caenorhabditis elegans during Enterococcus faecalis Infection. Infect. Immun. 2020, 88, e00130-20. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrzyn, A.; Ntambi, J.M. Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase as a New Drug Target for Obesity Treatment. Obes. Rev. 2005, 6, 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, A.S.; Zhuang, L.; Gan, B. Spatial Control of AMPK Signaling at Subcellular Compartments. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 55, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumoto, K.; Tamura, S.; Honsho, M.; Fujiki, Y. Peroxisome: Metabolic Functions and Biogenesis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1299, 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Weir, H.J.; Yao, P.; Huynh, F.K.; Escoubas, C.C.; Goncalves, R.L.; Burkewitz, K.; Laboy, R.; Hirschey, M.D.; Mair, W.B. Dietary Restriction and AMPK Increase Lifespan via Mitochondrial Network and Peroxisome Remodeling. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 884–896.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, J.C.; Marchesi Bozi, L.H.; Krum, B.; Grassmann Bechara, L.R.; Ferreira, N.D.; Arini, G.S.; Albuquerque, R.P.; Traa, A.; Ogawa, T.; van der Bliek, A.M.; et al. Exercise Preserves Physical Fitness during Aging through AMPK and Mitochondrial Dynamics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2204750120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Geiss, C.; Zarse, K.; Madreiter-Sokolowski, C.T.; Ristow, M. Green Tea Catechins EGCG and ECG Enhance the Fitness and Lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans by Complex I Inhibition. Aging 2021, 13, 22629–22648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F. Lipid Metabolism and Alzheimer’s Disease: Clinical Evidence, Mechanistic Link and Therapeutic Promise. FEBS J. 2023, 290, 1420–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, B.; Yang, G.; Kim, J.U. Natural Products as the Potential to Improve Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, E.P.; Laurindo, L.F.; Catharin, V.C.S.; Direito, R.; Tanaka, M.; Jasmin Santos German, I.; Lamas, C.B.; Guiguer, E.L.; Araújo, A.C.; Fiorini, A.M.R.; et al. Polyphenols, Alkaloids, and Terpenoids Against Neurodegeneration: Evaluating the Neuroprotective Effects of Phytocompounds Through a Comprehensive Review of the Current Evidence. Metabolites 2025, 15, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Huang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, M.; Liu, H.; Yu, Y.; Liang, M.; Luo, N.; Li, K.; et al. Abalone Peptide Increases Stress Resilience and Cost-Free Longevity via SKN-1-Governed Transcriptional Metabolic Reprogramming in C. elegans. Aging Cell 2024, 23, e14046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, K.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Li, G.; Lian, X.; Fan, J.; Song, C.; Jian, Y. IDO1-Mediated M2 Macrophage Polarization Alleviates the Progression of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Autoimmunity 2025, 58, 2441134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Watterson, A.; Arneaud, S.L.B.; Wajahat, N.; Wall, J.M.; Tatge, L.; Beheshti, S.T.; Mihelakis, M.; Cheatwood, N.Y.; McClendon, J.; Ghorashi, A.; et al. Loss of Heat Shock Factor Initiates Intracellular Lipid Surveillance by Actin Destabilization. Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 111493. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, N.; Ma, Y.-C.; Gong, X.-Q.; Zhao, P.-J.; Jia, Y.-J.; Zhao, Q.; Duan, J.-H.; Zou, C.-G. The Metabolite Alpha-Ketobutyrate Extends Lifespan by Promoting Peroxisomal Function in C. elegans. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 240. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiao, A.; Pan, M.; Zeng, Y.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lan, X.; Tang, L.; Jia, W. Matrine Inhibits High-Glucose-Diet-Induced Fat Accumulation and Aβ-Mediated Lipid Metabolic Disorder via AAK-2/NHR-49 Pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3048. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073048
Qiao A, Pan M, Zeng Y, Gong Y, Zhang Y, Lan X, Tang L, Jia W. Matrine Inhibits High-Glucose-Diet-Induced Fat Accumulation and Aβ-Mediated Lipid Metabolic Disorder via AAK-2/NHR-49 Pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3048. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073048
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiao, Aimin, Meiqing Pan, Yue Zeng, Ying Gong, Yunfeng Zhang, Xiucai Lan, Lei Tang, and Weizhang Jia. 2025. "Matrine Inhibits High-Glucose-Diet-Induced Fat Accumulation and Aβ-Mediated Lipid Metabolic Disorder via AAK-2/NHR-49 Pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3048. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073048
APA StyleQiao, A., Pan, M., Zeng, Y., Gong, Y., Zhang, Y., Lan, X., Tang, L., & Jia, W. (2025). Matrine Inhibits High-Glucose-Diet-Induced Fat Accumulation and Aβ-Mediated Lipid Metabolic Disorder via AAK-2/NHR-49 Pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3048. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073048






