Mechanism Analysis of OsbHLH34-OsERF34 Mediated Regulation of Rice Resistance to Sheath Blight
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
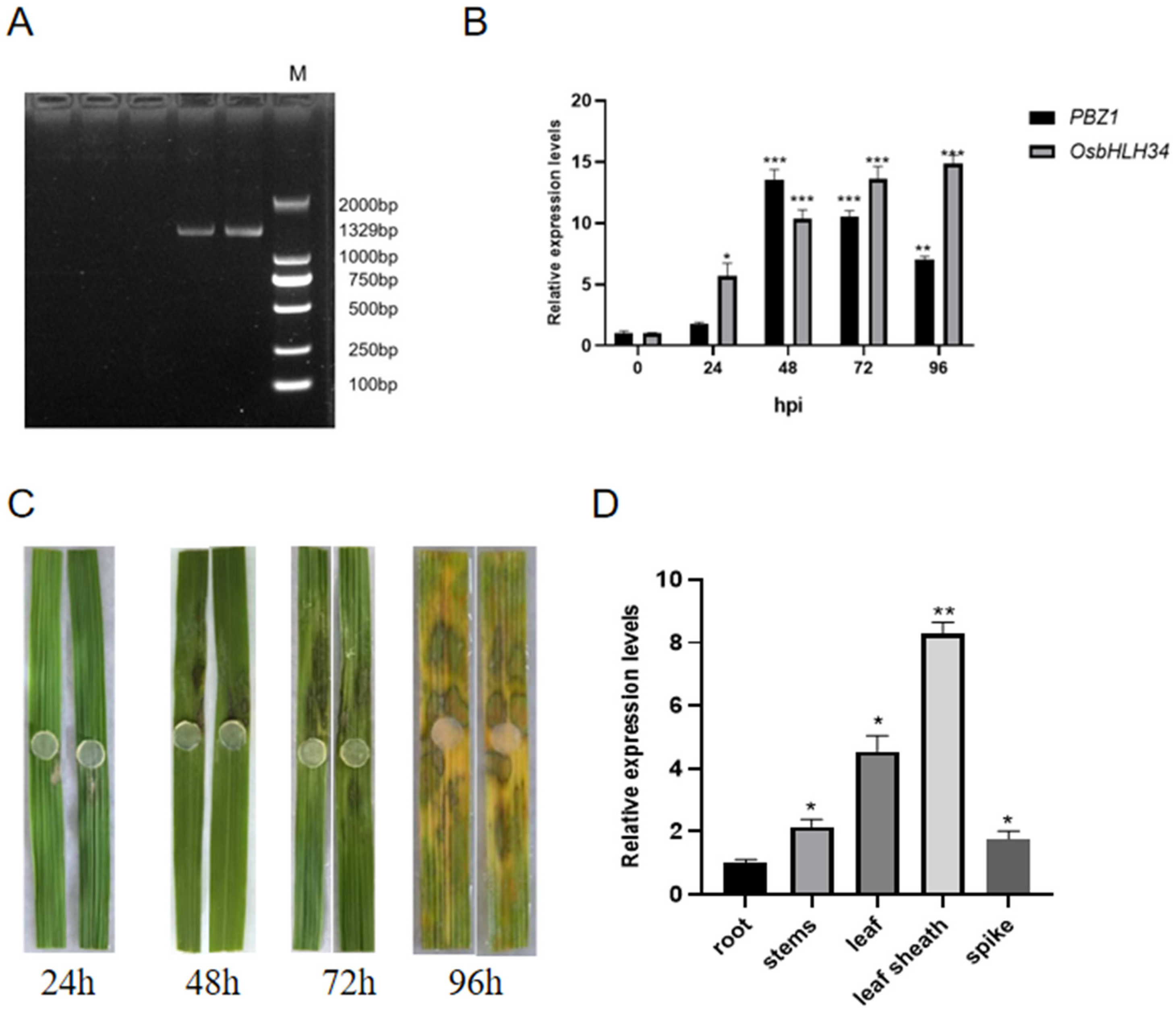
2.1. OsbHLH34 Positively Regulates Rice Resistance to Sheath Blight
2.2. Analysis of Transcriptional Self-Activation Activity
2.3. Subcellular Localization in the Nucleus
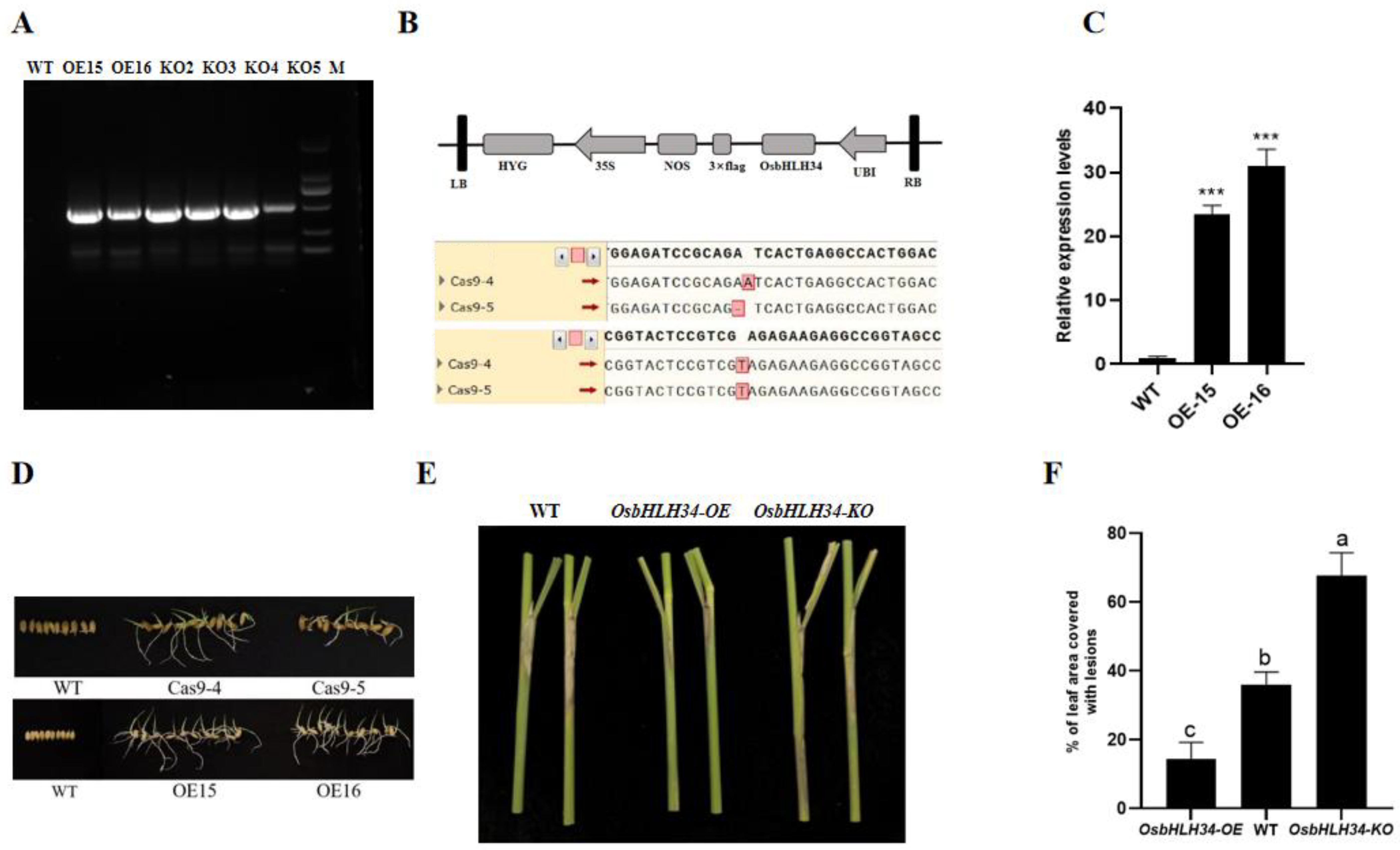
2.4. Construction and Expression Analysis of Mutants and Overexpression Plants
2.5. Knockout and Overexpression of OsbHLH34 Gene Did Not Affect Agronomic Traits
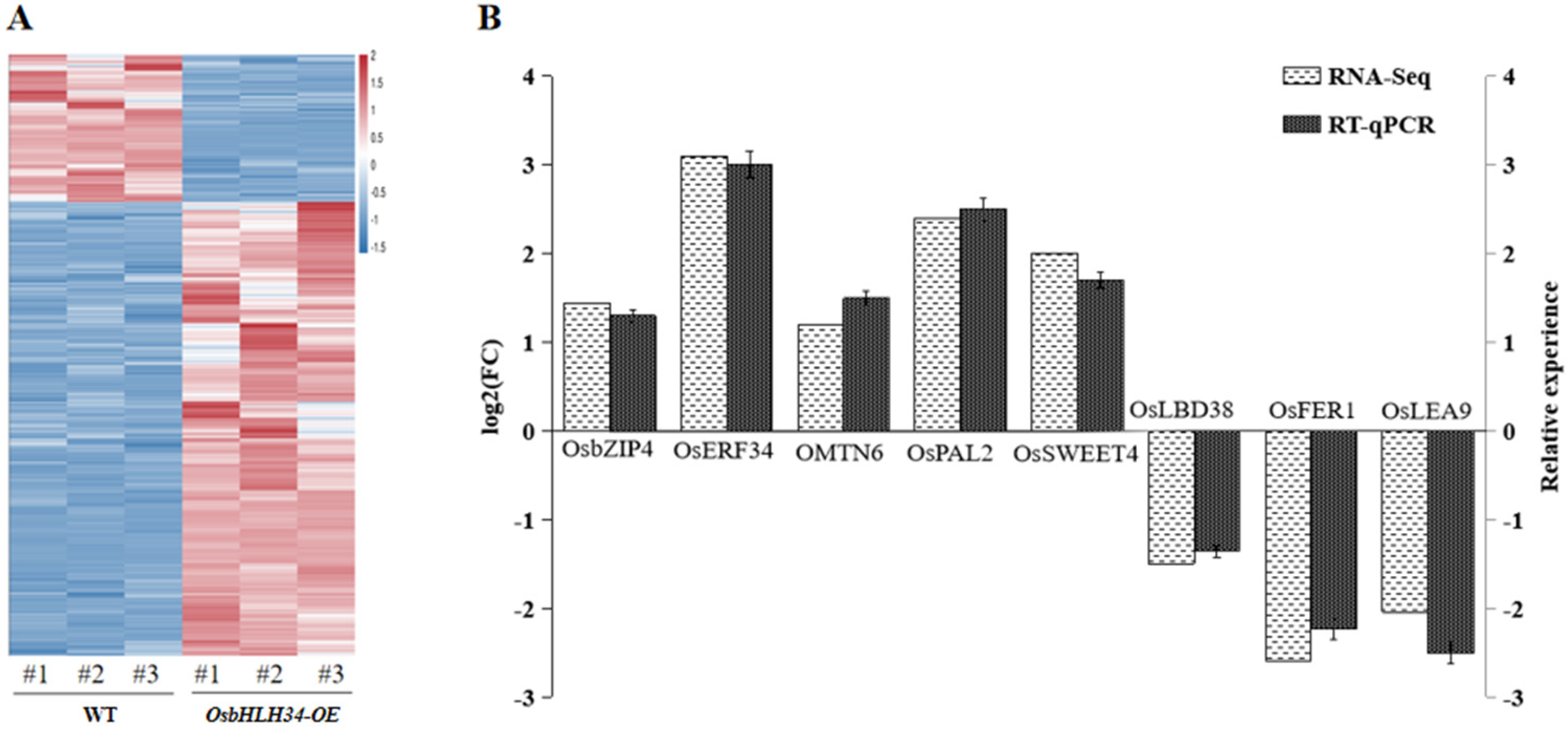
2.6. Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes Regulated by OsbHLH34
2.7. GO and KEGG Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes
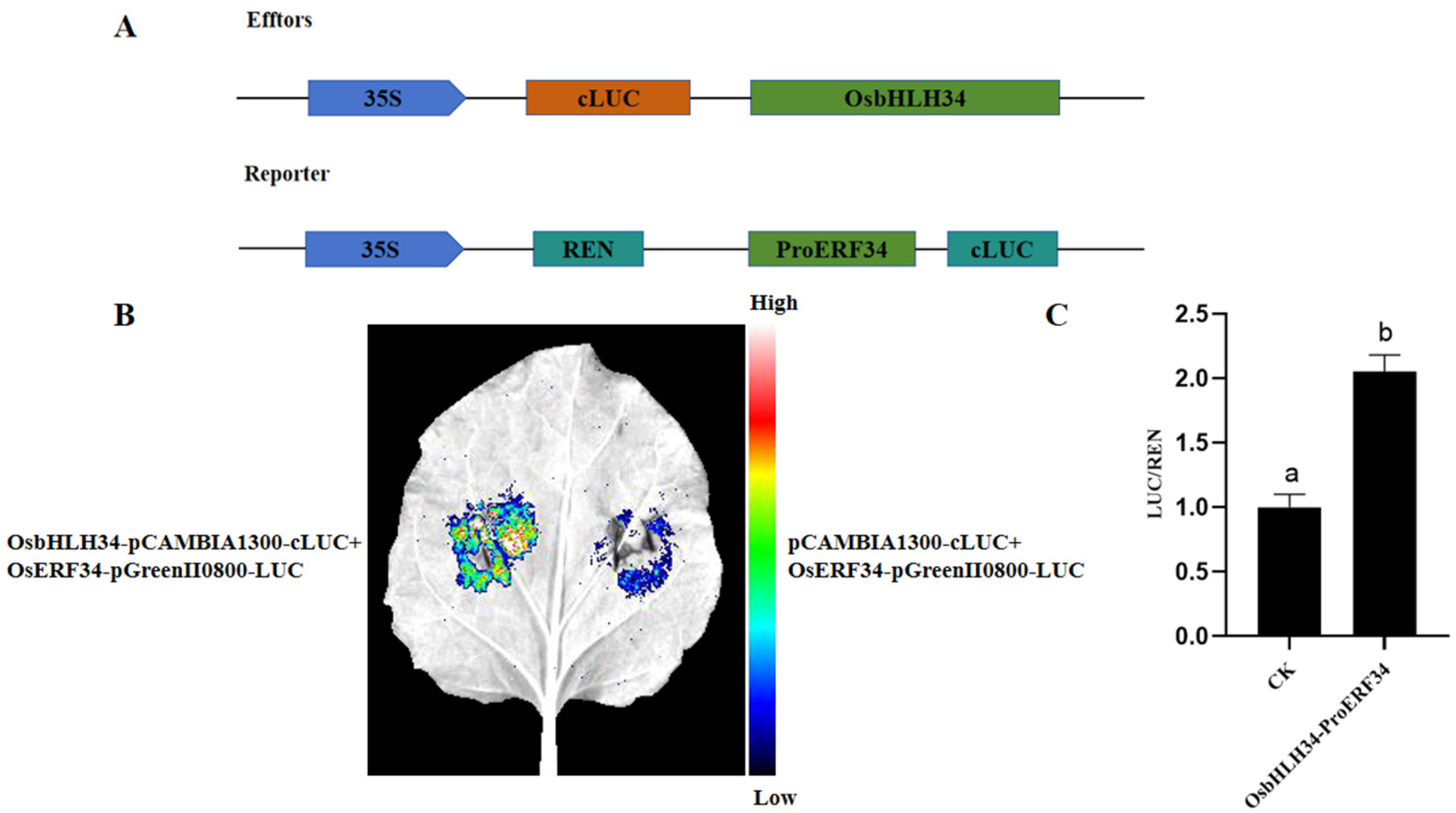
2.8. OsERF34 Interacts with OsbHLH34
2.9. Interaction Between OsbHLH34 and OsERF34 in Vivo
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials, Growth Conditions, and Fungal Inoculation
4.2. Protein Subcellular Localization Analysis
4.3. Quantitative RT-PCR Analysis
4.4. Vector Construction and Transgenic Plant Generation
4.5. Yeast Two-Hybrid (Y2H) and Yeast One-Hybrid (Y1H) Assay
4.6. Agronomic Traits Evaluation
4.7. Transcriptome Sequencing Screened Downstream Genes
4.8. Analysis of Promoter Action Originals
4.9. Transactivation Assay
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, A.; Lin, R.; Zhang, D.; Qin, P.; Xu, L.; Ai, P.; Ding, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. The evolution and pathogenic mechanisms of the rice sheath blight pathogen. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molla, K.A.; Karmakar, S.; Molla, J.; Bajaj, P.; Varshney, R.K.; Datta, S.K.; Datta, K. Understanding sheath blight resistance in rice: The road behind and the road ahead. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 895–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savary, S.; Willocquet, L.; Elazegui, F.A.; Castilla, N.P.; Teng, P.S. Rice Pest Constraints in Tropical Asia: Quantification of Yield Losses Due to Rice Pests in a Range of Production Situations. Plant Dis. 2000, 84, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Wu, K.; Song, W.; Zhong, N.; Wu, Y.; Fu, X. Improving Crop Nitrogen Use Efficiency Toward Sustainable Green Revolution. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2022, 73, 523–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savary, S.; Castilla, N.P.; Elazegui, F.A.; McLaren, C.G.; Ynalvez, M.A.; Teng, P.S. Direct and indirect effects of nitrogen supply and disease source structure on rice sheath blight spread. Phytopathology 1995, 85, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Zhang, T.; Zeng, J.; Li, C.; Li, T.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, S. Analysis of the occurrence and control of diseases in five major rice-producing areas in China in recent years. China Plant Prot. 2021, 41, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Richa, K.; Tiwari, I.M.; Kumari, M.; Devanna, B.N.; Sonah, H.; Kumari, A.; Nagar, R.; Sharma, V.; Botella, J.R.; Sharma, T.R. Functional Characterization of Novel Chitinase Genes Present in the Sheath Blight Resistance QTL: qSBR11-1 in Rice Line Tetep. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Cao, Z.X.; Zhang, X.T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.F. Overexpression of OsOSM1 Enhances Resistance to Rice Sheath Blight. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 1634–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helliwell, E.E.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y. Transgenic rice with inducible ethylene production exhibits broad-spectrum disease resistance to the fungal pathogens Magnaporthe oryzae and Rhizoctonia solani. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2012, 11, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Lin, B.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Yang, F.; Ding, X.; Yan, J.; Chu, Z. Natural variation in ZmFBL41 confers banded leaf and sheath blight resistance in maize. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 1540–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushton, D.L.; Tripathi, P.; Rabara, R.C.; Lin, J.; Ringler, P.; Boken, A.K.; Langum, T.J.; Smidt, L.; Boomsma, D.D.; Emme, N.J.; et al. WRKY transcription factors: Key components in abscisic acid signalling. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2011, 10, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eulgem, T.; Rushton, P.J.; Robatzek, S.; Somssich, I.E. The WRKY superfamily of plant transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci. 2000, 5, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, S.P.; Somssich, I.E. The role of WRKY transcription factors in plant immunity. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 1648–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Q.; Hong, X.; Zhu, J.-K.; Gong, Z. ABO3, a WRKY transcription factor, mediates plant responses to abscisic acid and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2010, 63, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Wang, H.; Jang, J.-C.; Xiao, T.; He, H.; Jiang, D.; Tang, X. OsWRKY80-OsWRKY4 Module as a Positive Regulatory Circuit in Rice Resistance Against Rhizoctonia solani. Rice 2016, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, S.; Mori, M.; Sugano, S.; Takatsuji, H. Transcription Factor WRKY62 Plays a Role in Pathogen Defense and Hypoxia-Responsive Gene Expression in Rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2016, 57, 2541–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xue, C.Y.; Liu, J.M.; He, Y.; Mei, Q.; Wei, S.; Xuan, Y.H. Sheath blight resistance in rice is negatively regulated by WRKY53 via SWEET2a activation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 585, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Gao, S.; Li, J.; Song, P.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, J.; Wang, X.; Han, X.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; et al. The bHLH transcription factor regulated gene OsWIH2 is a positive regulator of drought tolerance in rice. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 169, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, C.; Mizutani, E.; Okada, K.; Nakagawa, H.; Fukushima, S.; Tanaka, A.; Maeda, S.; Kamakura, T.; Yamane, H.; Takatsuji, H.; et al. Diterpenoid phytoalexin factor, a bHLH transcription factor, plays a central role in the biosynthesis of diterpenoid phytoalexins in rice. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 84, 1100–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, O.; Chico, J.M.; Saénchez-Serrano, J.J.; Solano, R. JASMONATE-INSENSITIVE1 encodes a MYC transcription factor essential to discriminate between different jasmonate-regulated defense responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 1938–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chini, A.; Gimenez-Ibanez, S.; Goossens, A.; Solano, R. Redundancy and specificity in jasmonate signalling. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2016, 33, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dombrecht, B.; Xue, G.P.; Sprague, S.J.; Kirkegaard, J.A.; Ross, J.J.; Reid, J.B.; Fitt, G.P.; Sewelam, N.; Schenk, P.M.; Manners, J.M.; et al. MYC2 differentially modulates diverse jasmonate-dependent functions in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 2225–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brioudes, F.; Joly, C.; Szécsi, J.; Varaud, E.; Leroux, J.; Bellvert, F.; Bertrand, C.; Bendahmane, M. Jasmonate controls late development stages of petal growth in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2009, 60, 1070–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiribuchi, K.; Jikumaru, Y.; Kaku, H.; Minami, E.; Hasegawa, M.; Kodama, O.; Seto, H.; Okada, K.; Nojiri, H.; Yamane, H. Involvement of the basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor RERJ1 in wounding and drought stress responses in rice plants. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2005, 69, 1042–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Joo, J.; Kim, M.; Kim, Y.; Nahm, B.H.; Song, S.I.; Cheong, J.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.; Choi, Y.D. OsbHLH148, a basic helix-loop-helix protein, interacts with OsJAZ proteins in a jasmonate signaling pathway leading to drought tolerance in rice. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2011, 65, 907–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, D.P.; Li, S.; Kumar, V.; Mei, Q.; Xuan, Y.H. Rhizoctonia solani transcriptional activator interacts with rice WRKY53 and grassy tiller 1 to activate SWEET transporters for nutrition. J. Adv. Res. 2022, 50, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.P.; Yang, S.; Feng, L.; Chu, J.; Dong, H.; Sun, J.; Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Yamamoto, N.; Zheng, A.; et al. Red-light receptor phytochrome B inhibits BZR1-NAC028-CAD8B signaling to negatively regulate rice resistance to sheath blight. Plant Cell Environ. 2022, 46, 1249–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.; Xue, C.Y.; Song, H.D.; Gao, Y.; Feng, L.; Li, Y.; Xuan, Y.H. Tissue-specific activation of DOF11 promotes rice resistance to sheath blight disease and increases grain weight via activation of SWEET14. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 19, 409–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Li, T.Y.; Li, D.D.; Wang, Z.Y.; Li, S.; Li, D.P.; Han, X.; Liu, J.M.; Xuan, Y.H. Overexpression of Loose Plant Architecture 1 increases planting density and resistance to sheath blight disease via activation of PIN-FORMED 1a in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 855–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, T.; Suzuki, K.; Fujimura, T.; Shinshi, H. Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 411–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liao, J.; Ling, Q.; Xi, Y.; Qian, Y. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling analysis of maize AP2/ERF superfamily genes reveal essential roles in abiotic stress tolerance. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Han, D.; Jia, W.; Ma, X.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Z. Molecular characterization and systematic analysis of NtAP2/ERF in tobacco and functional determination of NtRAV-4 under drought stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 156, 420–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Duan, X.; Jiang, H.; Sun, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Guo, J.; Liang, W.; Chen, L.; Yin, J.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family in rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onohata, T.; Gomi, K. Overexpression of jasmonate-responsive OsbHLH034 in rice results in the induction of bacterial blight resistance via an increase in lignin biosynthesis. Plant Cell Rep. 2020, 39, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Liang, W.; Yuan, Z.; Hu, J.; Ren, H.; Zhang, D. RICE MORPHOLOGY DETERMINANT encodes the type II formin FH5 and regulates rice morphogenesis. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 681–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liang, W.; Zhang, X.; Ren, H.; Hu, J.; Bennett, M.J.; Zhang, D. Rice actin-binding protein RMD is a key link in the auxin-actin regulatory loop that controls cell growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10377–10382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liang, W.; Sturrock, C.J.; Pandey, B.K.; Giri, J.; Mairhofer, S.; Wang, D.; Muller, L.; Tan, H.; York, L.M.; et al. Rice actin binding protein RMD controls crown root angle in response to external phosphate. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, G.; Nowak, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, D.; Yang, X.; Huang, G.; Liang, W.; Yang, L.; Wang, C.; et al. The Rice Actin-Binding Protein RMD Regulates Light-Dependent Shoot Gravitropism. Plant Physiol. 2019, 181, 630–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, J.; Mertens, J.; Goossens, A. Role and functioning of bHLH transcription factors in jasmonate signalling. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 1333–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Lu, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Yuan, L.; Guan, H.; Wang, G.; et al. Suppressing chlorophyll degradation by silencing OsNYC3 improves rice resistance to Rhizoctonia solani, the causal agent of sheath blight. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 20, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuhara, I.; Ugaki, M.; Hirochika, H.; Ohshima, M.; Murakami, T. Efficient promoter cassettes for enhanced expression of foreign genes in dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 1996, 37, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, Y.H.; Priatama, R.A.; Huang, J.; Je, B.I.; Liu, J.M.; Park, S.J.; Piao, H.L.; Son, D.Y.; Lee, J.J.; Park, S.H.; et al. Indeterminate domain 10 regulates ammonium-mediated gene expression in rice roots. New Phytol. 2012, 197, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiei, Y.; Ohta, S.; Komari, T.; Kumashiro, T. Efficient transformation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) mediated by Agrobacterium and sequence analysis of the boundaries of the T-DNA. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 1994, 6, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, S.; Park, S.; Jeong, D.-H.; Lee, D.-Y.; Kang, H.-G.; Yu, J.-H.; Hur, J.; Kim, S.-R.; Kim, Y.-H.; Lee, M.; et al. Generation and analysis of end sequence database for T-DNA tagging lines in rice. Plant Physiol. 2003, 133, 2040–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wei, S.; Wang, L. Mechanism Analysis of OsZF8-Mediated Regulation of Rice Resistance to Sheath Blight. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 11, 5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, A.K.; Stoos, L.; Crosby, P.; Eggers, N.; Nie, X.Y.; Makasheva, K.; Minnich, M.; Healy, K.L.; Weiss, J.; Kempf, G.; et al. Cooperation between bHLH transcription factors and histones for DNA access. Nature 2023, 619, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.P.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Li, S.; Xuan, Y.H.; Ma, D. bZIP23 interacts with NAC028 to modulate rice resistance to sheath blight disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 672, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhai, H.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Wei, S.; Li, T. Mechanism Analysis of OsbHLH34-OsERF34 Mediated Regulation of Rice Resistance to Sheath Blight. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052249
Zhai H, Zhou C, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Wang M, Wei S, Li T. Mechanism Analysis of OsbHLH34-OsERF34 Mediated Regulation of Rice Resistance to Sheath Blight. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(5):2249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052249
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhai, Hongyang, Chang Zhou, Yating Zhang, Yiming Wang, Mengyu Wang, Songhong Wei, and Tianya Li. 2025. "Mechanism Analysis of OsbHLH34-OsERF34 Mediated Regulation of Rice Resistance to Sheath Blight" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 5: 2249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052249
APA StyleZhai, H., Zhou, C., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Wang, M., Wei, S., & Li, T. (2025). Mechanism Analysis of OsbHLH34-OsERF34 Mediated Regulation of Rice Resistance to Sheath Blight. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(5), 2249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052249




