Genetic Variant Analyses Identify Novel Candidate Autism Risk Genes from a Highly Consanguineous Cohort of 104 Families from Oman
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cohort Description
2.2. Identification of Candidate ASD Risk Genes in the Omani ASD Cohort
2.3. Refinement and Prioritization of ASD Candidate Genes
2.4. Identification of Copy Number Variants (CNV) in the Omani ASD Cohort
2.5. Identification of 35 Known NDD-Associated Genes
2.6. Identification of 48 Novel ASD-Risk Genes
2.7. Sporadic Variants Identified in Our Novel ASD Candidate Genes
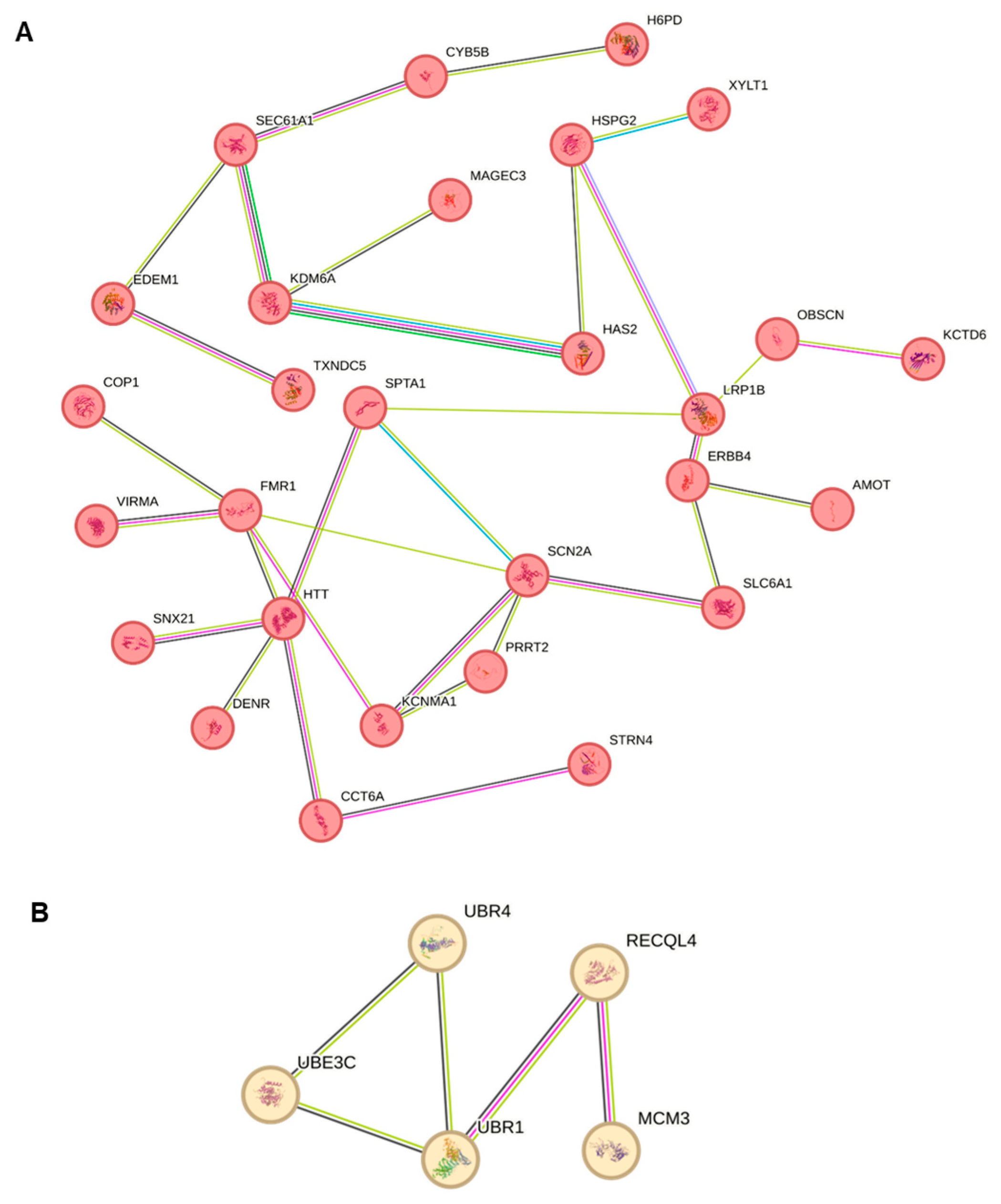
2.8. Protein–Protein Enrichment Analysis of Candidate Genes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sampling Procedures and DNA Isolation
4.2. Library Construction and Genome Sequencing
4.3. Variant Calling Process
4.4. Integrating Genetic Databases to Validate ASD Candidate Genes
4.5. STRING Interaction Enrichment Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
Web Resources
- OMIM, https://www.omim.org/ (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- HGMD, https://my.qiagendigitalinsights.com/bbp/view/hgmd/pro/all.php (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- Genomics England NDD/autism panel genes https://panelapp.genomicsengland.co.uk/panels/285/ (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- SFARI (Simons Foundation Autism Research Initiative) https://gene.sfari.org/database/human-gene/ (accessed on 1 August 2024).
References
- First, M.B. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th edition, and clinical utility. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2013, 201, 727–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, K.J. The genetics of neurodevelopmental disease. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2011, 21, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, S.E.; Mandell, D.S.; Schultz, R.T. Autism. Lancet 2009, 374, 1627–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malachowski, M. Understanding Mental Disorders: Your Guide to DSM-5, by the American Psychiatric Association. Med. Ref. Serv. Q. 2016, 35, 467–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyman, S.L.; Levy, S.E.; Myers, S.M. Council on Children with Disabilities, S.O.D.; Behavioral, P. Identification, Evaluation, and Management of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Pediatrics 2020, 145, e20193447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devnani, P.A.; Hegde, A.U. Autism and sleep disorders. J. Pediatr. Neurosci. 2015, 10, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besag, F.M. Epilepsy in patients with autism: Links, risks and treatment challenges. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2018, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorklund, G.; Pivina, L.; Dadar, M.; Meguid, N.A.; Semenova, Y.; Anwar, M.; Chirumbolo, S. Gastrointestinal alterations in autism spectrum disorder: What do we know? Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 118, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junaid, M.; Slack-Smith, L.; Wong, K.; Bourke, J.; Baynam, G.; Calache, H.; Leonard, H. Association between craniofacial anomalies, intellectual disability and autism spectrum disorder: Western Australian population-based study. Pediatr. Res. 2022, 92, 1795–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razali, R.M.; Rodriguez-Flores, J.; Ghorbani, M.; Naeem, H.; Aamer, W.; Aliyev, E.; Jubran, A.; Qatar Genome Program Research, C.; Clark, A.G.; Fakhro, K.A.; et al. Thousands of Qatari genomes inform human migration history and improve imputation of Arab haplotypes. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Omran, T.; Al Ghanim, K.; Yavarna, T.; El Akoum, M.; Samara, M.; Chandra, P.; Al-Dewik, N. Effects of consanguinity in a cohort of subjects with certain genetic disorders in Qatar. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2020, 8, e1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mouzan, M.I.; Al Salloum, A.A.; Al Herbish, A.S.; Qurachi, M.M.; Al Omar, A.A. Consanguinity and major genetic disorders in Saudi children: A community-based cross-sectional study. Ann. Saudi Med. 2008, 28, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamamy, H.; Antonarakis, S.E.; Cavalli-Sforza, L.L.; Temtamy, S.; Romeo, G.; Kate, L.P.; Bennett, R.L.; Shaw, A.; Megarbane, A.; van Duijn, C.; et al. Consanguineous marriages, pearls and perils: Geneva International Consanguinity Workshop Report. Genet. Med. 2011, 13, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamamy, H.A.; Masri, A.T.; Al-Hadidy, A.M.; Ajlouni, K.M. Consanguinity and genetic disorders. Profile from Jordan. Saudi Med. J. 2007, 28, 1015–1017. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bizzari, S.; Nair, P.; Hana, S.; Deepthi, A.; Al-Ali, M.T.; Al-Gazali, L.; El-Hayek, S. Spectrum of genetic disorders and gene variants in the United Arab Emirates national population: Insights from the CTGA database. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1177204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khayat, A.M.; Alshareef, B.G.; Alharbi, S.F.; AlZahrani, M.M.; Alshangity, B.A.; Tashkandi, N.F. Consanguineous Marriage and Its Association with Genetic Disorders in Saudi Arabia: A Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e53888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilshaw, S.; Al Raisi, T.; Alshaban, F. Arranging marriage; negotiating risk: Genetics and society in Qatar. Anthropol. Med. 2015, 22, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Naofal, M.; Ramaswamy, S.; Alsarhan, A.; Nugud, A.; Sarfraz, F.; Janbaz, H.; Taylor, A.; Jain, R.; Halabi, N.; Yaslam, S.; et al. The genomic landscape of rare disorders in the Middle East. Genome Med. 2023, 15, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatumo, S.; Chikowore, T.; Choudhury, A.; Ayub, M.; Martin, A.R.; Kuchenbaecker, K. A roadmap to increase diversity in genomic studies. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemke, A.A.; Esplin, E.D.; Goldenberg, A.J.; Gonzaga-Jauregui, C.; Hanchard, N.A.; Harris-Wai, J.; Ideozu, J.E.; Isasi, R.; Landstrom, A.P.; Prince, A.E.R.; et al. Addressing underrepresentation in genomics research through community engagement. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2022, 109, 1563–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbarek, H.; Devadoss Gandhi, G.; Selvaraj, S.; Al-Muftah, W.; Badji, R.; Al-Sarraj, Y.; Saad, C.; Darwish, D.; Alvi, M.; Fadl, T.; et al. Qatar genome: Insights on genomics from the Middle East. Hum. Mutat. 2022, 43, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojcik, G.L.; Graff, M.; Nishimura, K.K.; Tao, R.; Haessler, J.; Gignoux, C.R.; Highland, H.M.; Patel, Y.M.; Sorokin, E.P.; Avery, C.L.; et al. Genetic analyses of diverse populations improves discovery for complex traits. Nature 2019, 570, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshaban, F.; Aldosari, M.; Al-Shammari, H.; El-Hag, S.; Ghazal, I.; Tolefat, M.; Ali, M.; Kamal, M.; Abdel Aati, N.; Abeidah, M.; et al. Prevalence and correlates of autism spectrum disorder in Qatar: A national study. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2019, 60, 1254–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, M.; Aliyev, E.; Trost, B.; Kohailan, M.; Aamer, W.; Syed, N.; Shaath, R.; Gandhi, G.D.; Engchuan, W.; Howe, J.; et al. Genomic architecture of autism spectrum disorder in Qatar: The BARAKA-Qatar Study. Genome Med. 2023, 15, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sarraj, Y.; Taha, R.Z.; Al-Dous, E.; Ahram, D.; Abbasi, S.; Abuazab, E.; Shaath, H.; Habbab, W.; Errafii, K.; Bejaoui, Y.; et al. The genetic landscape of autism spectrum disorder in the Middle Eastern population. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1363849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Mahmoud, A.; Gupta, V.; Abdelaleem, A.; Thompson, R.; Aden, A.; Mbarek, H.; Saad, C.; Tolefat, M.; Alshaban, F.; Stanton, L.W.; et al. Genome Sequencing Identifies 13 Novel Candidate Risk Genes for Autism Spectrum Disorder in a Qatari Cohort. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.; Ben-Mahmoud, A.; Ku, B.; Velayutham, D.; Jan, Z.; Yousef Aden, A.; Kubbar, A.; Alshaban, F.; Stanton, L.W.; Jithesh, P.V.; et al. Identification of two novel autism genes, TRPC4 and SCFD2, in Qatar simplex families through exome sequencing. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1251884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mamri, W.; Idris, A.B.; Dakak, S.; Al-Shekaili, M.; Al-Harthi, Z.; Alnaamani, A.M.; Alhinai, F.I.; Jalees, S.; Al Hatmi, M.; El-Naggari, M.A.; et al. Revisiting the Prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder among Omani Children: A multicentre study. Sultan Qaboos Univ. Med. J. 2019, 19, e305–e309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satterstrom, F.K.; Kosmicki, J.A.; Wang, J.; Breen, M.S.; De Rubeis, S.; An, J.Y.; Peng, M.; Collins, R.; Grove, J.; Klei, L.; et al. Large-Scale Exome Sequencing Study Implicates Both Developmental and Functional Changes in the Neurobiology of Autism. Cell 2020, 180, 568–584 e523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.M.; Satterstrom, F.K.; Peng, M.; Brand, H.; Collins, R.L.; Dong, S.; Wamsley, B.; Klei, L.; Wang, L.; Hao, S.P.; et al. Rare coding variation provides insight into the genetic architecture and phenotypic context of autism. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 1320–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Feliciano, P.; Shu, C.; Wang, T.; Astrovskaya, I.; Hall, J.B.; Obiajulu, J.U.; Wright, J.R.; Murali, S.C.; Xu, S.X.; et al. Integrating de novo and inherited variants in 42,607 autism cases identifies mutations in new moderate-risk genes. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 1305–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rubeis, S.; He, X.; Goldberg, A.P.; Poultney, C.S.; Samocha, K.; Cicek, A.E.; Kou, Y.; Liu, L.; Fromer, M.; Walker, S.; et al. Synaptic, transcriptional and chromatin genes disrupted in autism. Nature 2014, 515, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huguet, G.; Ey, E.; Bourgeron, T. The genetic landscapes of autism spectrum disorders. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2013, 14, 191–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postorino, V.; Fatta, L.M.; Sanges, V.; Giovagnoli, G.; De Peppo, L.; Vicari, S.; Mazzone, L. Intellectual disability in Autism Spectrum Disorder: Investigation of prevalence in an Italian sample of children and adolescents. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2016, 48, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, S.J.; He, X.; Willsey, A.J.; Ercan-Sencicek, A.G.; Samocha, K.E.; Cicek, A.E.; Murtha, M.T.; Bal, V.H.; Bishop, S.L.; Dong, S.; et al. Insights into Autism Spectrum Disorder Genomic Architecture and Biology from 71 Risk Loci. Neuron 2015, 87, 1215–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandin, S.; Lichtenstein, P.; Kuja-Halkola, R.; Hultman, C.; Larsson, H.; Reichenberg, A. The Heritability of Autism Spectrum Disorder. JAMA 2017, 318, 1182–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hnoonual, A.; Thammachote, W.; Tim-Aroon, T.; Rojnueangnit, K.; Hansakunachai, T.; Sombuntham, T.; Roongpraiwan, R.; Worachotekamjorn, J.; Chuthapisith, J.; Fucharoen, S.; et al. Chromosomal microarray analysis in a cohort of underrepresented population identifies SERINC2 as a novel candidate gene for autism spectrum disorder. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, T.N.; Wilfert, A.B.; Bakken, T.E.; Bernier, R.A.; Pepper, M.R.; Zhang, Z.; Torene, R.I.; Retterer, K.; Eichler, E.E. Sex-Based Analysis of De Novo Variants in Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 105, 1274–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grove, J.; Ripke, S.; Als, T.D.; Mattheisen, M.; Walters, R.K.; Won, H.; Pallesen, J.; Agerbo, E.; Andreassen, O.A.; Anney, R.; et al. Identification of common genetic risk variants for autism spectrum disorder. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Duyzend, M.H.; Coe, B.P.; Baker, C.; Hoekzema, K.; Gerdts, J.; Turner, T.N.; Zody, M.C.; Beighley, J.S.; Murali, S.C.; et al. Genome sequencing identifies multiple deleterious variants in autism patients with more severe phenotypes. Genet. Med. 2019, 21, 1611–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Wang, T.; Wu, H.; Long, M.; Coe, B.P.; Li, H.; Xun, G.; Ou, J.; Chen, B.; Duan, G.; et al. Inherited and multiple de novo mutations in autism/developmental delay risk genes suggest a multifactorial model. Mol. Autism 2018, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, G.; Severson, E.A.; Cai, L.; Hoffmann, H.M.; Holden, K.A.; Fitzgerald, K.; Kenyon, A.; Zeng, Q.; Mooney, M.; Gardner, S.; et al. Clinical characterization of the mutational landscape of 24,639 real-world samples from patients with myeloid malignancies. Cancer Genet. 2023, 278–279, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iossifov, I.; O’Roak, B.J.; Sanders, S.J.; Ronemus, M.; Krumm, N.; Levy, D.; Stessman, H.A.; Witherspoon, K.T.; Vives, L.; Patterson, K.E.; et al. The contribution of de novo coding mutations to autism spectrum disorder. Nature 2014, 515, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, M.; Kazuno, A.A.; Nakamura, T.; Sakai, N.; Hayama, T.; Fujii, K.; Matsuo, K.; Komori, A.; Ishiwata, M.; Watanabe, Y.; et al. Systematic analysis of exonic germline and postzygotic de novo mutations in bipolar disorder. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Roak, B.J.; Deriziotis, P.; Lee, C.; Vives, L.; Schwartz, J.J.; Girirajan, S.; Karakoc, E.; Mackenzie, A.P.; Ng, S.B.; Baker, C.; et al. Exome sequencing in sporadic autism spectrum disorders identifies severe de novo mutations. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Roak, B.J.; Stessman, H.A.; Boyle, E.A.; Witherspoon, K.T.; Martin, B.; Lee, C.; Vives, L.; Baker, C.; Hiatt, J.B.; Nickerson, D.A.; et al. Recurrent de novo mutations implicate novel genes underlying simplex autism risk. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, S.J.; Murtha, M.T.; Gupta, A.R.; Murdoch, J.D.; Raubeson, M.J.; Willsey, A.J.; Ercan-Sencicek, A.G.; DiLullo, N.M.; Parikshak, N.N.; Stein, J.L.; et al. De novo mutations revealed by whole-exome sequencing are strongly associated with autism. Nature 2012, 485, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, A.; Miyake, N.; Tsurusaki, Y.; Fukai, R.; Miyatake, S.; Koshimizu, E.; Kushima, I.; Okada, T.; Morikawa, M.; Uno, Y.; et al. Integrative Analyses of De Novo Mutations Provide Deeper Biological Insights into Autism Spectrum Disorder. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 734–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, A.; Nakashima, M.; Saitsu, H.; Mizuguchi, T.; Mitsuhashi, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Okamoto, N.; Osaka, H.; Nakamura, K.; Tohyama, J.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of coding variants highlights genetic complexity in developmental and epileptic encephalopathy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentino, F.; Bruno, L.P.; Doddato, G.; Giliberti, A.; Tita, R.; Resciniti, S.; Fallerini, C.; Bruttini, M.; Lo Rizzo, C.; Mencarelli, M.A.; et al. Exome Sequencing in 200 Intellectual Disability/Autistic Patients: New Candidates and Atypical Presentations. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrier, V.; Zhang, X.; Reed, P.; Havdahl, A.; Moore, T.M.; Cliquet, F.; Leblond, C.S.; Rolland, T.; Rosengren, A.; Eu-Aims, L.; et al. Genetic correlates of phenotypic heterogeneity in autism. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 1293–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilfert, A.B.; Turner, T.N.; Murali, S.C.; Hsieh, P.; Sulovari, A.; Wang, T.; Coe, B.P.; Guo, H.; Hoekzema, K.; Bakken, T.E.; et al. Recent ultra-rare inherited variants implicate new autism candidate risk genes. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trost, B.; Thiruvahindrapuram, B.; Chan, A.J.S.; Engchuan, W.; Higginbotham, E.J.; Howe, J.L.; Loureiro, L.O.; Reuter, M.S.; Roshandel, D.; Whitney, J.; et al. Genomic architecture of autism from comprehensive whole-genome sequence annotation. Cell 2022, 185, 4409–4427.e4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaugler, T.; Klei, L.; Sanders, S.J.; Bodea, C.A.; Goldberg, A.P.; Lee, A.B.; Mahajan, M.; Manaa, D.; Pawitan, Y.; Reichert, J.; et al. Most genetic risk for autism resides with common variation. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, E.T.; Raychaudhuri, S.; Sanders, S.J.; Stevens, C.; Sabo, A.; MacArthur, D.G.; Neale, B.M.; Kirby, A.; Ruderfer, D.M.; Fromer, M.; et al. Rare complete knockouts in humans: Population distribution and significant role in autism spectrum disorders. Neuron 2013, 77, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncay, I.O.; Parmalee, N.L.; Khalil, R.; Kaur, K.; Kumar, A.; Jimale, M.; Howe, J.L.; Goodspeed, K.; Evans, P.; Alzghoul, L.; et al. Analysis of recent shared ancestry in a familial cohort identifies coding and noncoding autism spectrum disorder variants. NPJ Genom. Med. 2022, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, L.; An, J.Y. Genetic architecture of autism spectrum disorder: Lessons from large-scale genomic studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 128, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doan, R.N.; Lim, E.T.; De Rubeis, S.; Betancur, C.; Cutler, D.J.; Chiocchetti, A.G.; Overman, L.M.; Soucy, A.; Goetze, S.; Autism Sequencing, C.; et al. Recessive gene disruptions in autism spectrum disorder. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 1092–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, S.; Catreux, S.; Rossi, M.; Truong, S.; Huang, Z.; Ruehle, M.; Visvanath, A.; Parnaby, G.; Roddey, C.; Onuchic, V.; et al. Comprehensive genome analysis and variant detection at scale using DRAGEN. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, N.D.; Wagner, J.; McDaniel, J.; Stephens, S.H.; Westreich, S.T.; Prasanna, A.G.; Johanson, E.; Boja, E.; Maier, E.J.; Serang, O.; et al. PrecisionFDA Truth Challenge V2: Calling variants from short and long reads in difficult-to-map regions. Cell. Genom. 2022, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostic, M.; Raymond, J.J.; Freyre, C.A.C.; Henry, B.; Tumkaya, T.; Khlghatyan, J.; Dvornik, J.; Li, J.; Hsiao, J.S.; Cheon, S.H.; et al. Patient Brain Organoids Identify a Link between the 16p11.2 Copy Number Variant and the RBFOX1 Gene. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2023, 14, 3993–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Leary, A.; Fernandez-Castillo, N.; Gan, G.; Yang, Y.; Yotova, A.Y.; Kranz, T.M.; Grunewald, L.; Freudenberg, F.; Anton-Galindo, E.; Cabana-Dominguez, J.; et al. Behavioural and functional evidence revealing the role of RBFOX1 variation in multiple psychiatric disorders and traits. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 4464–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Castillo, N.; Gan, G.; van Donkelaar, M.M.J.; Vaht, M.; Weber, H.; Retz, W.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A.; Franke, B.; Harro, J.; Reif, A.; et al. RBFOX1, encoding a splicing regulator, is a candidate gene for aggressive behavior. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020, 30, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, N.; Ito, H.; Nishijo, T.; Iwamoto, I.; Morishita, R.; Tabata, H.; Momiyama, T.; Nagata, K. Essential role of the nuclear isoform of RBFOX1, a candidate gene for autism spectrum disorders, in the brain development. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altintas, M.; Yildirim, M.; Bektas, O.; Teber, S. Progressive Myoclonus Epilepsy and Beyond: Systematic Review of SEMA6B-Related Disorders. Neuropediatrics 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiffert, S.; Pendziwiat, M.; Bierhals, T.; Goel, H.; Schwarz, N.; van der Ven, A.; Bosselmann, C.M.; Lemke, J.; Syrbe, S.; Willemsen, M.H.; et al. Modulating effects of FGF12 variants on Na(V)1.2 and Na(V)1.6 being associated with developmental and epileptic encephalopathy and Autism spectrum disorder: A case series. EBioMedicine 2022, 83, 104234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamanaka, K.; Imagawa, E.; Koshimizu, E.; Miyatake, S.; Tohyama, J.; Yamagata, T.; Miyauchi, A.; Ekhilevitch, N.; Nakamura, F.; Kawashima, T.; et al. De Novo Truncating Variants in the Last Exon of SEMA6B Cause Progressive Myoclonic Epilepsy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 106, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torene, R.I.; Guillen Sacoto, M.J.; Millan, F.; Zhang, Z.; McGee, S.; Oetjens, M.; Heise, E.; Chong, K.; Sidlow, R.; O’Grady, L.; et al. Systematic analysis of variants escaping nonsense-mediated decay uncovers candidate Mendelian diseases. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2024, 111, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.Y.; Chang, K.C.; Chen, P.L.; Yeung, C.Y.; Liou, B.Y.; Chen, H.L. SLCO1B1 and SLCO1B3 genetic mutations in Taiwanese patients with Rotor syndrome. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2023, 122, 648–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobs, P.M.; Hess, J.F.; FitzGerald, P.G.; Kramer, P.; Weleber, R.G.; Litt, M. Autosomal-dominant congenital cataract associated with a deletion mutation in the human beaded filament protein gene BFSP2. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2000, 66, 1432–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, D.; Inami, C.; Ikeda, R.; Sawahata, M.; Urata, S.; Yamaguchi, S.T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Fujita, K.; Arioka, Y.; Okumura, H.; et al. Mice with deficiency in Pcdh15, a gene associated with bipolar disorders, exhibit significantly elevated diurnal amplitudes of locomotion and body temperature. Transl. Psychiatry 2024, 14, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardecchia, F.; De Giorgi, A.; Palombo, F.; Fiorini, C.; De Negri, A.M.; Carelli, V.; Caporali, L.; Leuzzi, V. Missense PDSS1 mutations in CoenzymeQ10 synthesis cause optic atrophy and sensorineural deafness. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2021, 8, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, P.S.; Sajuthi, S.; Langefeld, C.D.; Walker, S.J. Immune function genes CD99L2, JARID2 and TPO show association with autism spectrum disorder. Mol. Autism 2012, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roelens, R.; Peigneur, A.N.F.; Voets, T.; Vriens, J. Neurodevelopmental disorders caused by variants in TRPM3. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2024, 1871, 119709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima Caldeira, G.; Peca, J.; Carvalho, A.L. New insights on synaptic dysfunction in neuropsychiatric disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2019, 57, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris-Rosendahl, D.J.; Crocq, M.A. Neurodevelopmental disorders-the history and future of a diagnostic concept. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 22, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talkowski, M.E.; Sanders, S. Diverse mutations in autism-related genes and their expression in the developing brain. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 1263–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antaki, D.; Guevara, J.; Maihofer, A.X.; Klein, M.; Gujral, M.; Grove, J.; Carey, C.E.; Hong, O.; Arranz, M.J.; Hervas, A.; et al. A phenotypic spectrum of autism is attributable to the combined effects of rare variants, polygenic risk and sex. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, Y.; Niihori, T.; Kawame, H.; Kurosawa, K.; Ohashi, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Filocamo, M.; Kato, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Kure, S.; et al. Germline mutations in HRAS proto-oncogene cause Costello syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 1038–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeron, T. From the genetic architecture to synaptic plasticity in autism spectrum disorder. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandler, W.M.; Antaki, D.; Gujral, M.; Kleiber, M.L.; Whitney, J.; Maile, M.S.; Hong, O.; Chapman, T.R.; Tan, S.; Tandon, P.; et al. Paternally inherited cis-regulatory structural variants are associated with autism. Science 2018, 360, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castel, S.E.; Cervera, A.; Mohammadi, P.; Aguet, F.; Reverter, F.; Wolman, A.; Guigo, R.; Iossifov, I.; Vasileva, A.; Lappalainen, T. Modified penetrance of coding variants by cis-regulatory variation contributes to disease risk. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Fragoza, R.; Klei, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Roeder, K.; Devlin, B.; Yu, H. An interactome perturbation framework prioritizes damaging missense mutations for developmental disorders. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coe, B.P.; Stessman, H.A.F.; Sulovari, A.; Geisheker, M.R.; Bakken, T.E.; Lake, A.M.; Dougherty, J.D.; Lein, E.S.; Hormozdiari, F.; Bernier, R.A.; et al. Neurodevelopmental disease genes implicated by de novo mutation and copy number variation morbidity. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, B.B.; Karczewski, K.J.; Kosmicki, J.A.; Seaby, E.G.; Watts, N.A.; Singer-Berk, M.; Mudge, J.M.; Karjalainen, J.; Satterstrom, F.K.; O’Donnell-Luria, A.H.; et al. Transcript expression-aware annotation improves rare variant interpretation. Nature 2020, 581, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faial, T. Perturbing autism risk genes. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neale, B.M.; Kou, Y.; Liu, L.; Ma’ayan, A.; Samocha, K.E.; Sabo, A.; Lin, C.F.; Stevens, C.; Wang, L.S.; Makarov, V.; et al. Patterns and rates of exonic de novo mutations in autism spectrum disorders. Nature 2012, 485, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Roak, B.J.; Vives, L.; Girirajan, S.; Karakoc, E.; Krumm, N.; Coe, B.P.; Levy, R.; Ko, A.; Lee, C.; Smith, J.D.; et al. Sporadic autism exomes reveal a highly interconnected protein network of de novo mutations. Nature 2012, 485, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenson, P.D.; Mort, M.; Ball, E.V.; Chapman, M.; Evans, K.; Azevedo, L.; Hayden, M.; Heywood, S.; Millar, D.S.; Phillips, A.D.; et al. The Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD((R))): Optimizing its use in a clinical diagnostic or research setting. Hum. Genet. 2020, 139, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, X.Y.; Lim, Y.T.; Chae, W.R.; Park, C.; Park, H.; Jung, S. Alterations of presynaptic proteins in autism spectrum disorder. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 1062878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovedi, S.; Corradi, A.; Fassio, A.; Benfenati, F. Involvement of synaptic genes in the pathogenesis of autism spectrum disorders: The case of synapsins. Front. Pediatr. 2014, 2, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trobiani, L.; Meringolo, M.; Diamanti, T.; Bourne, Y.; Marchot, P.; Martella, G.; Dini, L.; Pisani, A.; De Jaco, A.; Bonsi, P. The neuroligins and the synaptic pathway in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 119, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, A.J.; Hoffiz, Y.C.; Charles, A.J.; Zhu, Y.; Mabb, A.M. A Comprehensive Atlas of E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Mutations in Neurological Disorders. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasherman, M.A.; Premarathne, S.; Burne, T.H.J.; Wood, S.A.; Piper, M. The Ubiquitin System: A Regulatory Hub for Intellectual Disability and Autism Spectrum Disorder. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 2179–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louros, S.R.; Osterweil, E.K. Perturbed proteostasis in autism spectrum disorders. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139, 1081–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, M.R.; Sadeghi, H.; Hashemi-Gorji, F.; Mirfakhraie, R.; Gupta, V.; Ben-Mahmoud, A.; Bagheri, S.; Razjouyan, K.; Salehpour, S.; Tonekaboni, S.H.; et al. Exome sequencing reveals neurodevelopmental genes in simplex consanguineous Iranian families with syndromic autism. BMC Med. Genom. 2024, 17, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Yu, S.; Zhang, W. The Molecular Basis of Multiple Morphological Abnormalities of Sperm Flagella and Its Impact on Clinical Practice. Genes 2024, 15, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitfield, M.; Thomas, L.; Bequignon, E.; Schmitt, A.; Stouvenel, L.; Montantin, G.; Tissier, S.; Duquesnoy, P.; Copin, B.; Chantot, S.; et al. Mutations in DNAH17, Encoding a Sperm-Specific Axonemal Outer Dynein Arm Heavy Chain, Cause Isolated Male Infertility Due to Asthenozoospermia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 105, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Yuan, L.; Deng, S.; Xia, H.; Tu, X.; Deng, X.; Huang, X.; Cao, X.; Deng, H. Identification of DNAH17 Variants in Han-Chinese Patients with Left-Right Asymmetry Disorders. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 862292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, E.T.; Uddin, M.; De Rubeis, S.; Chan, Y.; Kamumbu, A.S.; Zhang, X.; D’Gama, A.M.; Kim, S.N.; Hill, R.S.; Goldberg, A.P.; et al. Rates, distribution and implications of postzygotic mosaic mutations in autism spectrum disorder. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarathinam, I.; Chong, S.S.; Thelma, B.K.; Justin Margret, J.; Venkataraman, V.; Natarajan Padmavathy, K.; Srisailapathy, C.R.S. FMR1 gene CGG repeat distribution among the three individual cohorts with intellectual disability, autism, and primary ovarian insufficiency from Tamil Nadu, Southern India. Adv. Genet. 2021, 2, e10048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handt, M.; Epplen, A.; Hoffjan, S.; Mese, K.; Epplen, J.T.; Dekomien, G. Point mutation frequency in the FMR1 gene as revealed by fragile X syndrome screening. Mol. Cell Probes 2014, 28, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santa Maria, L.; Aliaga, S.; Faundes, V.; Morales, P.; Pugin, A.; Curotto, B.; Soto, P.; Pena, M.I.; Salas, I.; Alliende, M.A. FMR1 gene mutations in patients with fragile X syndrome and obligate carriers: 30 years of experience in Chile. Genet. Res. 2016, 98, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidorov, M.S.; Auerbach, B.D.; Bear, M.F. Fragile X mental retardation protein and synaptic plasticity. Mol. Brain 2013, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mila, M.; Alvarez-Mora, M.I.; Madrigal, I.; Rodriguez-Revenga, L. Fragile X syndrome: An overview and update of the FMR1 gene. Clin. Genet. 2018, 93, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, H.G.; Wu, W.C.; Nip, K.; Gould, E.; Kim, J.H. Scn2a deletion disrupts oligodendroglia function: Implication for myelination, neural circuitry, and auditory hypersensitivity in ASD. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.O.; Uy, J.A.; Murtaza, N.; Rosa, E.; Alfonso, A.; Dave, B.M.; Kilpatrick, S.; Cheng, A.A.; White, S.H.; Scherer, S.W.; et al. Disruption of the autism-associated gene SCN2A alters synaptic development and neuronal signaling in patient iPSC-glutamatergic neurons. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1239069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Bae, H.G.; Wu, W.C.; Nip, K.; Gould, E. SCN2A-linked myelination deficits and synaptic plasticity alterations drive auditory processing disorders in ASD. Res. Sq. 2024, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.H.; Potet, F.; Abramova, T.V.; DeKeyser, J.M.; Ghabra, N.F.; Vanoye, C.G.; Millichap, J.J.; George, A.L. Epilepsy-associated SCN2A (NaV1.2) variants exhibit diverse and complex functional properties. J. Gen. Physiol. 2023, 155, e202313375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortin, J.P.; Schroeder, J.C.; Zhu, Y.; Beinborn, M.; Kopin, A.S. Pharmacological characterization of human incretin receptor missense variants. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 332, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, R.; Hivert, M.F.; Langenberg, C.; Tanaka, T.; Pankow, J.S.; Vollenweider, P.; Lyssenko, V.; Bouatia-Naji, N.; Dupuis, J.; Jackson, A.U.; et al. Genetic variation in GIPR influences the glucose and insulin responses to an oral glucose challenge. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Kaneko, K.; Lin, H.Y.; Mo, Q.; Xu, Y.; Suganami, T.; Ravn, P.; Fukuda, M. Gut Hormone GIP Induces Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in the Hypothalamus. Endocrinology 2020, 161, bqaa102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekpen, C.; Kunzel, S.; Xie, C.; Eaaswarkhanth, M.; Lin, Y.L.; Gokcumen, O.; Akdis, C.A.; Tautz, D. Segmental duplications and evolutionary acquisition of UV damage response in the SPATA31 gene family of primates and humans. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekpen, C.; Xie, C.; Nebel, A.; Tautz, D. Involvement of SPATA31 copy number variable genes in human lifespan. Aging 2018, 10, 674–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljabban, J.; Syed, S.; Syed, S.; Rohr, M.; Weisleder, N.; McElhanon, K.E.; Hasan, L.; Safeer, L.; Hoffman, K.; Aljabban, N.; et al. Investigating genetic drivers of dermatomyositis pathogenesis using meta-analysis. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, Z.; Lu, S.; Kang, Y.; Jin, G.; Tian, J. Genome-Wide Analysis of Cell-Free DNA Methylation Profiling for the Early Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 596078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micale, L.; Fusco, C.; Augello, B.; Napolitano, L.M.; Dermitzakis, E.T.; Meroni, G.; Merla, G.; Reymond, A. Williams-Beuren syndrome TRIM50 encodes an E3 ubiquitin ligase. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 16, 1038–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, W.; Zhou, S.; Chang, S.; Chang, J.; Tian, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Che, G. The genomic and transcriptome characteristics of lung adenocarcinoma patients with previous breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Number of Individuals (%) | |
|---|---|
| Sex | Male—66% |
| Female—34% | |
| Consanguinity (parents) | 56% |
| Ethnicity | 100% |
| Autism | 100% |
| Language/speech delay | 78% |
| Behavioural problems | 60% |
| Developmental Delays | 42% |
| Intellectual disability | 13% |
| Epilepsy/seizures/spasms | 12% |
| Subject | Gender | Consanguinity | Genes | Accession Number | Chr. | Nucleotide Change | Protein Change | Type of Variant | Inheritance (GENOTYPE) | gnomAD (AF) | QGP (AF) | CADD | ACMG Interpretation | Z Score | pLI Score | Previously Linked with ASD/NDDs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | + | HNRNPCL4 | NM_001302551.2 | 1 | c.830C>T | p.A277V | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0 | 21.2 | LP | NA | NA | Novel |
| 2 | M | - | PNCK | NM_001366977.1 | X | c.932G>A | p.R311Q | missense | x-linked | 0 | 0.000238598 | 21.1 | LP | NA | NA | Novel |
| 3 | M | - | COP1 | NM_022457.7 | 1 | c.1291C>T | p.R431W | missense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 25.8 | P | −0.36 | 0.92 | Novel |
| TRIM73 | NM_198924.4 | 7 | c.487C>T | p.R163* | nonsense | homoz. | 0 | 0 | 35 | P | 3.23 | 0.93 | Novel | |||
| 4 | M | + | TSKU | NM_015516.4 | 11 | c.979C>T | p.R327W | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0 | 25 | LP | 1.22 | 0.17 | Novel |
| 5 | F | - | SLC6A1 | NM_003042.4 | 3 | c.1328G>T | p.G443V | missense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 27.9 | P | 4.92 | 1 | Known |
| CAPN8 | NM_001143962.2 | 1 | c.730-2A>G | splicing | splicing | de novo | 0 | 0 | 25.9 | P | −0.19 | 0 | Novel | |||
| MYO7A | NM_000260.4 | 11 | c.2489G>A | p.R830H | missense | homoz. | 0.0114, European | 0.00214739 | 32 | VUS | 0.06 | 0 | Known | |||
| 6 | M | - | RAB11FIP3 | NM_014700.4 | 16 | c.1396-2A>G | splicing | splicing | de novo | 0 | 0 | 35 | P | −0.86 | 1 | Novel |
| 7 | M | + | XYLT1 | NM_022166.4 | 16 | c.1129C>G | p.Q377E | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0.0144863 | 22.3 | LP | 0.75 | 0.99 | Known |
| 8 | F | - | SYTL1 | NM_001193308.2 | 1 | c.1317_1323delAGGATCC | p.G440fs*? | frameshift | de novo | 0 | 0 | P | −0.52 | 0 | Novel | |
| 9 | M | - | LAS1L | NM_031206.7 | X | c.1082C>G | p.P361R | missense | X-linked | 0 | 0.00572636 | 22.1 | LP | NA | NA | Known |
| 10 | M | - | RIBC1 | NM_001031745.5 | X | c.106C>G | p.R36G | missense | X-linked | 0 | 0 | 23.9 | LP | NA | NA | Novel |
| 11 | F | + | KIAA1755 | NM_001029864.2 | 20 | c.2052+1G>A | splicing | splicing | homoz. | 0.0024, African | 0.00105665 | 33 | P | −0.24 | 0 | Novel |
| 12 | M | - | EDEM1 | NM_014674.3 | 3 | c.1301G>A | p.W434* | nonsense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 45 | P | −1.39 | 0 | Novel |
| SLC12A9 | NM_020246.4 | 7 | c.764A>C | p.Y255S | missense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 28.5 | LP | 1.96 | 0 | Novel | |||
| 13 | M | - | AMOT | NM_001113490.2 | X | c.514C>T | p.R172C | missense | X-linked | 0 | 0 | 29 | LP | NA | NA | Novel |
| 14 | F | + | VWA8 | NM_015058.2 | 13 | c.5093G>A | p.R1698Q | missense | homoz. | 0.0038, European | 3.40855 × 10−5 | 29.9 | VUS | 0.51 | 0 | Novel |
| H6PD | NM_004285.4 | 1 | c.127T>C | p.W43R | missense | homoz. | 0.0013, European | 3.40855 × 10−5 | 29.6 | VUS | 0.11 | 0 | Novel | |||
| KIAA1755 | NM_001029864.2 | 20 | c.19G>A | p.D7N | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0.000340855 | 25.3 | LP | −0.24 | 0 | Novel | |||
| 15 | M | + | TTC36 | NM_001080441.4 | 11 | c.284G>C | p.R95P | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0 | 23.6 | LP | −1.92 | 0 | Novel |
| 16 | M | - | LILRB3 | NM_006864.4 | 19 | c.1050T>G | p.Y350* | nonsense | homoz. | 0 | 0 | 23.2 | P | 1.45 | 0 | Novel |
| TMEM31 | NM_182541.2 | X | c.142C>A | p.Q48K | missense | X-linked | 0.0094, Latino | 0.000443111 | 21.7 | VUS | NA | NA | Novel | |||
| 17 | M | + | PRRT2 | NM_145239.3 | 16 | c.649dupC | p.R217fs*8 | frameshift | de novo | 0 | 0 | 31 | P | −0.26 | 0.65 | Known |
| 18 | F | + | TRIM15 | NM_033229.3 | 6 | c.608A>G | p.D203G | missense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 23.5 | LP | −0.18 | 0 | Novel |
| LTBP1 | NM_206943.4 | 2 | c.3616T>C | p.C1206R | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0 | 29.8 | LP | −0.7 | 0 | Novel | |||
| 19 | M | - | CNV identified | |||||||||||||
| 20 | M | + | ATP13A5 | NM_198505.4 | 3 | c.632A>G | p.Q211R | missense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 26.1 | LP | 1.24 | 0 | Novel |
| COL6A6 | NM_001102608.3 | 3 | c.5002G>T | p.G1668* | nonsense | homoz. | 0 | 0.000340855 | 47 | P | 0.53 | 0 | Novel | |||
| 21 | M | - | RORC | NM_005060.4 | 1 | c.253C>T | p.H85Y | missense | homoz. | 0.0654 | 0.0116572 | 26.9 | VUS | 2.89 | 1 | Novel |
| 22 | M | + | ERBB4 | NM_005235.3 | 2 | c.2900T>G | p.F967C | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0.000204513 | 31 | LP | 2.82 | 1 | Known |
| FMR1 | NM_002024.6 | X | c.716C>T | p.A239V | missense | X-linked | 0 | 0 | 25.3 | LP | NA | NA | Known | |||
| 23 | M | + | ECH1 | NM_001398.3 | 19 | c.284A>G | p.K95R | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0 | 26 | LP | −0.17 | 0 | Novel |
| 24 | M | + | ZNF250 | NM_001109689.4 | 8 | c.593A>T | p.E198V | missense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 23.4 | LP | 3.41 | 0.93 | Novel |
| AGTR2 | NM_000686.5 | X | c.411C>A | p.C137* | nonsense | X-linked | 0 | 3.40855 × 10−5 | 31 | P | NA | NA | Known | |||
| 25 | F | - | CNV identified | |||||||||||||
| 26 | F | _ | DENND2A | NM_015689.5 | 7 | c.2971G>A | p.G991S | missense | homoz. | 0.0024, African | 0.000204513 | 25.8 | LP | 1.84 | 0 | Novel |
| 27 | M | _ | HTT | NM_001388492.1 | 4 | c.102_110dupGCAGCAGCA | p.Q36_Q38dup | in-frame Insertion | de novo | 0 | 0 | NA | LP | 3.7 | 1 | Known |
| 28 | F | _ | HIVEP3 | NM_024503.5 | 1 | c.3316C>T | p.Q1106* | nonsense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 35 | P | NA | NA | Novel |
| 29 | M | PLIN4 | NM_001367868.2 | 19 | c.2246_2247insG | p.G750fs*14 | frameshift | de novo | 0.0151, Latino | 0 | 23.9 | P | −1.44 | 0 | Novel | |
| RAB3B | NM_002867.4 | 1 | c.8C>T | p.S3L | missense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 23.7 | LP | NA | NA | Novel | |||
| PGAP3 | NM_033419.5 | 17 | c.717G>C | p.W239C | missense | homoz. | 0.0048, African | 0 | 31 | VUS | -0.47 | 0 | Novel | |||
| 30 | M | + | LMF1 | NM_022773.4 | 16 | c.529C>T | p.L177F | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0.00146568 | 28.2 | LP | −2.56 | 0 | Known |
| 31 | M | _ | DNAH17 | NM_173628.4 | 17 | c.12650T>C | p.I4217T | missense | comp. het. | 0 | 0 | 26.9 | LP | −2.01 | 0 | Known |
| 17 | c.2121C>A | p.N707K | missense | 0 | 3.40855 × 10−5 | 10 | LP | |||||||||
| 32 | M | _ | AGAP9 | NM_001190810.1 | 10 | c.1930_1931insTCTGGTA | p.T644fs*? | frameshift | homoz. | 0 | 0 | NA | P | 4.15 | 0 | Novel |
| 33 | M | + | OBSCN | NM_001386125.1 | 1 | c.2186A>C | p.E729A | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0.00654441 | 25 | LP | −0.82 | 0 | Known |
| HAS2 | NM_005328.3 | 8 | c.221C>G | p.S74C | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0 | 23.4 | LP | 4.42 | 1 | Novel | |||
| ZNF81 | NM_007137.5 | X | c.980A>G | p.E327G | missense | X-linked | 0.0188, Latino | 0.000579493 | 24.2 | VUS | NA | NA | Known | |||
| 34 | M | - | MAP3K9 | NM_001284230.2 | 14 | c.1790G>A | p.R597Q | missense | de novo | 0 | 3.40855 × 10−5 | 23.8 | LP | 1.6 | 0 | Novel |
| MAGEC3 | NM_138702.1 | X | c.212C>A | p.S71* | nonsense | X-linked | 0.0017 European | 0 | 26.3 | P | NA | NA | Novel | |||
| 35 | F | - | ABCA13 | NM_152701.5 | 7 | c.633-2A>G | splicing | splicing | de novo | 0 | 0 | 33 | P | −0.12 | 0 | Known |
| CLEC18C | NM_173619.4 | 16 | c.994G>A | p.G332R | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0 | 29 | LP | 3.26 | 0.94 | Novel | |||
| 36 | M | + | ZNF483 | NM_133464.5 | 9 | c.2047C>T | p.R683* | nonsense | homoz. | 0 | 0 | 35 | P | 3 | 0.97 | Novel |
| PREP | NM_002726.5 | 6 | c.1213+1G>A | splicing | splicing | homoz. | 0.0013 European | 3.40855 × 10−5 | 34 | P | 2.65 | 1 | Novel | |||
| 37 | M | + | ZNF207 | NM_001098507.2 | 17 | c.637G>C | p.G213R | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0 | 25 | LP | 2.69 | 0.12 | Novel |
| CARMIL1 | NM_017640.6 | 6 | c.3149A>T | p.H1050L | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0.00132933 | 20.7 | LP | 2.03 | 0 | Novel | |||
| 38 | F | NA | KCNMA1 | NM_001161352.2 | 10 | c.2725C>T | p.R909W | missense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 32 | LP | 6.52 | 1 | Known |
| TMEM184A | NM_001097620.2 | 7 | c.365C>T | p.S122F | missense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 22.8 | LP | −0.75 | 0 | Novel | |||
| 39 | M | - | CRYBG1 | NM_001371242.2 | 6 | c.4916A>T | p.K1639I | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0 | 22.5 | LP | 0.93 | 0 | Novel |
| - | NUS1 | NM_138459.5 | 6 | c.684T>A | p.S228R | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0 | 22 | LP | 1.03 | 1 | Known | ||
| 40 | M | + | KCTD6 | NM_001128214.2 | 3 | c.538G>A | p.G180R | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0 | 23.1 | LP | 2.86 | 0.38 | Novel |
| 41 | F | + | PDE2A | NM_002599.5 | 11 | c.229C>T | p.R77* | nonsense | homoz. | 0 | 0 | 34 | P | 3.86 | 0.02 | Known |
| 42 | M | _ | ARHGAP33 | NM_001366178.1 | 19 | c.3691C>T | p.P1231S | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0.000272684 | 21.4 | LP | 1.78 | 0 | Novel |
| 43 | F | + | UBE2Q2 | NM_173469.4 | 15 | c.1031A>T | p.N344I | missense | homoz. | 0.0065 | 0.000715795 | 25 | VUS | 0.38 | 0 | Novel |
| 44 | M | + | SPATA31A3 | NM_001083124.1 | 9 | c.1879C>T | p.Q627* | nonsense | homoz. | 0 | 0 | 25.9 | P | 5.51 | 0.65 | Novel |
| 45 | M | + | SORCS2 | NM_020777.3 | 4 | c.1662G>A | p.W554* | nonsense | homoz. | 0 | 0 | 47 | P | −1.75 | 0 | Novel |
| 46 | M | + | CWF19L2 | NM_152434.3 | 11 | c.270G>T | p.K90N | missense | de novo | 0 | 3.40994 × 10−5 | 23 | LP | −0.65 | 0 | Novel |
| 47 | F | + | CYB5B | NM_030579.3 | 16 | c.212G>A | p.G71D | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0 | 28.5 | LP | 0.81 | 0.01 | Novel |
| HSPG2 | NM_005529.7 | 1 | c.1369A>G | p.S457G | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0 | 27.9 | LP | 3.4 | 0 | Known | |||
| 48 | M | + | SPTA1 | NM_003126.4 | 1 | c.2195T>A | p.L732Q | missense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 25.4 | LP | −0.8 | 0 | Known |
| 49 | F | - | SCN2A | NM_001040142.2 | 2 | c.3932T>G | p.L1311R | missense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 29.3 | LP | 8.71 | 1 | Known |
| 50 | F | + | NOTCH4 | NM_004557.4 | 6 | c.1522C>T | p.Q508* | nonsense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 38 | P | 2.17 | 0 | Novel |
| MTUS1 | NM_001363059.2 | 8 | c.1165C>T | p.Q389* | nonsense | de novo | 0 | 0.00149976 | 36 | P | −5.75 | 0 | Novel | |||
| 51 | M | + | NHLRC1 | NM_198586.3 | 6 | c.946T>A | p.F316I | missense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 22.4 | LP | −0.09 | 0 | Known |
| 52 | F | - | CNV identified | |||||||||||||
| 53 | M | + | SEC61A1 | NM_013336.4 | 3 | c.331C>G | p.L111V | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0 | 23.4 | LP | 4.94 | 1 | Novel |
| 54 | F | + | CNV identified | |||||||||||||
| 55 | M | + | RNF113A | NM_006978.3 | X | c.76G>A | p.G26R | missense | X-linked | 0 | 0.00037494 | 21.7 | LP | NA | NA | Novel |
| 56 | M | - | TNRC18 | NM_001080495.3 | 7 | c.487+126delT | Intronic | intronic | de novo | 0 | 0 | NA | LP | −7.54 | 0 | Novel |
| 57 | M | - | PHF14 | NM_001007157.2 | 7 | c.73A>C | p.S25R | missense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 29.9 | LP | 0.87 | 0.03 | Known |
| 58 | M | - | SPATA31A3 | NM_001083124.1 | 9 | c.1879C>T | p.Q627* | nonsense | homoz. | 0 | 0 | 25.9 | LP | 5.51 | 0.65 | Novel |
| 59 | M | + | CCT6A | NM_001762.4 | 7 | c.336+1G>A | Splicing | splicing | de novo | 0 | 3.40855 × 10−5 | 34 | P | 1.42 | 1 | Novel |
| 60 | F | - | ESYT3 | NM_031913.5 | 3 | c.2468+1G>T | Splicing | splicing | homoz. | 0 | 0.00528325 | 34 | P | 0.17 | 0 | Novel |
| 61 | M | + | UBE3C | NM_014671.3 | 7 | c.916_917delAG | p.S306* | frameshift | homoz. | 0 | 0 | NA | P | 3.04 | 1 | Novel |
| 62 | F | + | MANSC1 | NM_018050.4 | 12 | c.250T>G | p.F84V | missense | comp. het. | 0 | 0 | 27.3 | LP | 0.82 | 0 | Novel |
| 12 | c.38T>A | p.L13* | nonsense | 0.00037494 | 34 | P | 0.82 | 0 | ||||||||
| 63 | F | + | SLC19A1 | NM_194255.4 | 21 | c.1514A>G | p.E505G | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0.00109074 | 22.9 | LP | −0.71 | 0 | Novel |
| 64 | M | - | LRP1B | NM_018557.3 | 2 | c.1560G>T | p.K520N | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0 | 26.3 | LP | 3.33 | 1 | Known |
| 65 | M | - | VIRMA | NM_015496.5 | 8 | c.1069A>T | p.T357S | missense | de novo | 0 | 3.40855 × 10−5 | 25.2 | LP | 3.68 | 1 | Novel |
| GRAMD1B | NM_001387025.1 | 11 | c.973T>C | p.F325L | missense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 24.2 | LP | 1.13 | 0.01 | Novel | |||
| 66 | M | + | DNAH17 | NM_173628.4 | 17 | c.12389C>T | p.P4130L | missense | comp. het | 0 | 0.000102256 | 27.5 | LP | −2.01 | 0 | Known |
| 17 | c.11825G>A | p.R3942Q | missense | 1.4 | 0.00453337 | 23.5 | LP | −2.01 | 0 | |||||||
| 67 | M | + | RNF175 | NM_173662.4 | 4 | c.247-1G>A | splicing | splicing | homoz. | 0 | 3.40855 × 10−5 | 33 | P | 0.45 | 0 | Novel |
| 68 | M | - | PLBD2 | NM_173542.4 | 12 | c.1576C>T | p.R526C | missense | comp. het. | 0.05 | 0.000920308 | 25.8 | VUS | −0.17 | 0 | Novel |
| 12 | c.1012C>T | p.R338W | missense | 0.07 | 0.000272684 | 24.6 | VUS | −0.17 | 0 | |||||||
| 69 | F | + | DNAH3 | NM_001347886.2 | 16 | c.2023G>T | p.V675F | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0.0058627 | 23 | LP | 2.47 | 0 | Known |
| 70 | M | - | RECQL4 | NM_004260.4 | 8 | c.2386G>A | p.E796K | missense | comp. het | 0.01 | 3.40855 × 10−5 | 25.6 | VUS | −6.29 | 0 | Known |
| 8 | c.3501C>T | p.I1167I | missense | 0.01 | 6.8171 × 10−5 | NA | VUS | −6.29 | 0 | |||||||
| 71 | M | - | UBR4 | NM_020765.3 | 1 | c.2551G>A | p.V851M | missense | comp. het | 0.02 | 0.000852137 | 23 | VUS | 8.42 | 1 | Known |
| 1 | c.3137G>A | p.R1046Q | missense | 0.0024 | 0.000136342 | 23.5 | VUS | 8.42 | 1 | |||||||
| 72 | F | + | SNX21 | NM_033421.4 | 20 | c.287C>T | p.A96V | missense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 26 | LP | −0.17 | 0 | Novel |
| 73 | M | - | FNDC1 | NM_032532.3 | 6 | c.5047C>T | p.P1683S | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0.000988479 | 25.2 | LP | −0.57 | 0 | Known |
| 74 | M | - | CNV identified | |||||||||||||
| 75 | M | - | CNV identified | |||||||||||||
| 76 | M | + | TXNDC5 | NM_030810.5 | 6 | c.625T>G | p.F209V | missense | homoz. | 0 | 3.40855 × 10−5 | 29.6 | LP | −1.09 | 0 | Known |
| 77 | F | + | TRIM73 | NM_198924.4 | 7 | c.487C>T | p.R163* | nonsense | homoz. | 0 | 0 | 35 | P | 3.23 | 0.93 | Novel |
| MCM3 | NM_002388.6 | 6 | c.2282A>G | p.Q761R | missense | homoz. | 0 | 3.40855 × 10−5 | 24.6 | LP | 1.92 | 0 | Novel | |||
| 78 | F | + | ASGR2 | NM_001201352.2 | 17 | c.532G>T | p.E178* | nonsense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 36 | P | 0.28 | 0 | Novel |
| 79 | M | + | ATP13A5 | NM_198505.4 | 3 | c.632A>G | p.Q211R | missense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 26.1 | LP | 1.24 | 0 | Novel |
| 80 | F | + | TRIM15 | NM_033229.3 | 6 | c.608A>G | p.D203G | missense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 23.5 | LP | −0.18 | 0 | Novel |
| 81 | M | + | ALG11 | NM_001004127.3 | 13 | c.1184T>C | p.M395T | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0 | 26 | LP | 1.11 | 0 | Known |
| UBR1 | NM_174916.3 | 15 | c.850G>C | p.E284Q | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0.00190879 | 23.9 | LP | 3.29 | 0.96 | Known | |||
| 82 | F | + | RAP1GAP | NM_002885.4 | 1 | c.1429-864C>T | Intronic | intronic | homoz. | 0 | 0 | 23.8 | VUS | 1.36 | 0.01 | Novel |
| 83 | F | + | CEP135 | NM_025009.5 | 4 | c.3130G>C | p.E1044Q | missense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 28 | LP | −0.03 | 0 | Known |
| APOL2 | NM_030882.4 | 22 | c.943C>T | p.Q315* | nonsense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 33 | P | −0.6 | 0 | Novel | |||
| HERC3 | NM_014606.3 | 4 | c.38G>A | p.G13D | missense | de novo | 0 | 0.000170427 | 27.1 | LP | 4.35 | 1 | Novel | |||
| 84 | M | - | DNAH17 | NM_173628.4 | 17 | c.2121C>A | p.N707K | missense | comp. het. | 0 | 3.40855 × 10−5 | NA | LP | −2.01 | 0 | Known |
| 17 | c.12650T>C | p.I4217T | missense | 0 | 0 | 26.9 | LP | −2.01 | 0 | |||||||
| 85 | M | - | DDR2 | NM_006182.4 | 1 | c.473C>T | p.P158L | missense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 25.8 | LP | 3.82 | 1 | Known |
| 86 | F | + | STRN4 | NM_013403.3 | 19 | c.1610G>C | p.S537T | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0.000272684 | 23.8 | LP | 2.14 | 0.84 | Novel |
| 87 | M | + | COL5A2 | NM_000393.5 | 2 | c.4088G>T | p.G1363V | missense | homoz. | 0 | 3.40901 × 10−5 | 32 | LP | 3.35 | 1 | Known |
| 88 | M | + | SPOUT1 | NM_016390.4 | 9 | c.836T>C | p.F279S | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0.000102256 | 27.5 | LP | 0.88 | 0 | Novel |
| BNC1 | NM_001717.4 | 2 | c.1697A>G | p.D566G | missense | homoz. | 0 | 0.000579453 | 23.5 | LP | 2.25 | 1 | Novel | |||
| 89 | F | + | CNV identified | |||||||||||||
| 90 | F | + | SCN2A | NM_001040142.2 | 2 | c.532G>T | p.G178C | missense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 28.3 | LP | 8.71 | 1 | Known |
| 91 | M | + | FMR1 | NM_002024.6 | X | c.716C>T | p.A239V | missense | X-linked | 0 | 0 | 25.3 | LP | NA | NA | Known |
| 92 | M | + | KDM6A | NM_001291415.2 | X | c.182G>C | p.R61T | missense | X-linked | 0 | 0 | 22.6 | LP | NA | NA | Known |
| 93 | - | No SNV/CNV identified | ||||||||||||||
| 94 | M | + | TMEM259 | NM_001033026.2 | 19 | c.380A>G | p.Q127R | missense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 25 | LP | −2.09 | 0 | Novel |
| 95 | M | - | INTS6L | NM_001351601.3 | X | c.2584G>A | p.A862T | missense | X-linked | 0 | 6.8171 × 10−5 | 22.2 | LP | NA | NA | Novel |
| 96 | F | - | GIPR | NM_000164.4 | 19 | c.1152G>T | p.Q384H | missense | comp. het. | 0 | 0.000409026 | 36 | LP | −1.18 | 0 | Novel |
| 19 | c.302G>A | p.R101H | missense | 1.46 | 0.000647624 | 25.6 | VUS | −1.18 | 0 | |||||||
| 97 | F | + | SLC16A5 | NM_004695.4 | 17 | c.380C>G | p.T127R | missense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 23.9 | LP | 1.33 | 0 | Novel |
| 98 | F | + | CNV identified | |||||||||||||
| 99 | M | + | ARHGAP4 | NM_001666.5 | X | c.1339T>C | p.Y447H | missense | X-linked | 0 | 6.8171 × 10−5 | 24.9 | LP | NA | NA | Novel |
| 100 | M | - | GIPR | NM_000164.4 | 19 | c.1264C>T | p.Q422* | nonsense | de novo | 0 | 0.000749932 | 36 | P | −1.18 | 0 | Novel |
| MAP3K5 | NM_005923.4 | 6 | c.439T>C | p.Y147H | missense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 32 | LP | 3.26 | 1 | Novel | |||
| 101 | M | + | CIP2A | NM_020890.3 | 3 | c.2303C>G | p.S768* | nonsense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 41 | P | −0.62 | 0 | Novel |
| CLCNKA | NM_004070.4 | 1 | c.781+1G>A | splicing | splicing | de novo | 0 | 3.40855 × 10−5 | 34 | P | 1.05 | 0 | Known | |||
| 102 | M | + | SAFB2 | NM_014649.3 | 19 | c.1798G>A | p.D600N | missense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 28.5 | LP | −0.14 | 0.99 | Novel |
| 103 | F | - | ZNF827 | NM_001306215.2 | 4 | c.1892A>T | p.D631V | missense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 23.1 | LP | 2.95 | 1 | Novel |
| 104 | F | + | DENR | NM_003677.5 | 12 | c.434A>G | p.Q145R | missense | de novo | 0 | 0 | 22.7 | LP | 1.6 | 0.92 | Novel |
| Subject ID | Subject 19 | Subject 25 | Subject 52 | Subject 54 | Subject 74 | Subject 75 | Subject 89 | Subject 98 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | M | F | F | F | M | M | F | F | ||
| CNV and genomic coordinates (hg38) | Chr16:6864585-6865758 | Chr3:192671334-192672351 | Chr19:4559368-4562532 | Chr3:133414146-133418344 | Chr10:54921983-54925066 | Chr9:71289426-71290609 | Chr17:45440911-45508556 | Chr2:1521403-1522564 | Chr10:26709200-26711140 | Chr12:21165423-21166430 |
| Type of CNV | heterozygous microdeletion | heterozygous microdeletion | heterozygous microdeletion | heterozygous microdeletion | heterozygous microdeletion | heterozygous microduplication | heterozygous microdeletion | heterozygous microdeletion | heterozygous microdeletion | heterozygous microdeletion |
| Size of CNV (bp) | 1173 | 1017 | 3164 | −4198 | 3083 | 1183 | 67645 | 1161 | 1940 | 1007 |
| Cytoband | 16p13.3 | 3q29 | 19p13.3 | 3q22.1 | 10q21.1 | 9q21.12 | 17q21.31 | 2p25.3 | 10p12.1 | 12p12.1 |
| Genes involved | RBFOX1 (NM_001142333) | FGF12 (NM_001377292) | SEMA6B (NM_032108) | BFSP2 (NM_003571) | PCDH15 (NM_001354404) | TRPM3 (NM_001366141) | PLEKHM1 (NM_014798) | TPO (NM_000547) | PDSS1 (NM_001321978) | SLCO1B1 (NM_006446) |
| Location | intron 3 | intron 2 | exon 1 and intron 1 | intron 1 | intron 3 | intron 1 | exon 6 (LRRC37A4P) exon 1-intron9 (PLEKHM1) | Intron 15 | Intron 4, exon 5, intron 5 | intron 2 |
| Inheritance | de novo | de novo | de novo | de novo | de novo | de novo | de novo | de novo | ||
| Disease linked | autism susceptibility 1; epilepsy, HGMD-71 | developmental and epileptic encephalopathy, MIM 601513, HGMD-26 | epilepsy, progressive myoclonic, MIM- 608873, HGMD-43 | Cataract, MIM 603212, HGMD-13 | Usher syndrome type 1; nonsyndromic genetic hearing loss, MIM 605514, HGMD-225 | autosomal dominant non-syndromic intellectual disability, HGMD-24 | osteopetrosis, MIM- 611466, PLEKHM1 HGMD-15 | familial thyroid dyshormonogenesis, MIM 600044, HGMD-264 | deafness–encephaloneuropathy–obesity-valvulopathy syndrome, MIM 607429, HGMD-19 | rotor syndrome, MIM 604843, HGMD-51 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gupta, V.; Ben-Mahmoud, A.; Idris, A.B.; Hottenga, J.-J.; Habbab, W.; Alsayegh, A.; Kim, H.-G.; AL-Mamari, W.; Stanton, L.W. Genetic Variant Analyses Identify Novel Candidate Autism Risk Genes from a Highly Consanguineous Cohort of 104 Families from Oman. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13700. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413700
Gupta V, Ben-Mahmoud A, Idris AB, Hottenga J-J, Habbab W, Alsayegh A, Kim H-G, AL-Mamari W, Stanton LW. Genetic Variant Analyses Identify Novel Candidate Autism Risk Genes from a Highly Consanguineous Cohort of 104 Families from Oman. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(24):13700. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413700
Chicago/Turabian StyleGupta, Vijay, Afif Ben-Mahmoud, Ahmed B. Idris, Jouke-Jan Hottenga, Wesal Habbab, Abeer Alsayegh, Hyung-Goo Kim, Watfa AL-Mamari, and Lawrence W. Stanton. 2024. "Genetic Variant Analyses Identify Novel Candidate Autism Risk Genes from a Highly Consanguineous Cohort of 104 Families from Oman" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 24: 13700. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413700
APA StyleGupta, V., Ben-Mahmoud, A., Idris, A. B., Hottenga, J.-J., Habbab, W., Alsayegh, A., Kim, H.-G., AL-Mamari, W., & Stanton, L. W. (2024). Genetic Variant Analyses Identify Novel Candidate Autism Risk Genes from a Highly Consanguineous Cohort of 104 Families from Oman. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(24), 13700. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413700








