MemDis: Predicting Disordered Regions in Transmembrane Proteins
Abstract
1. Introduction
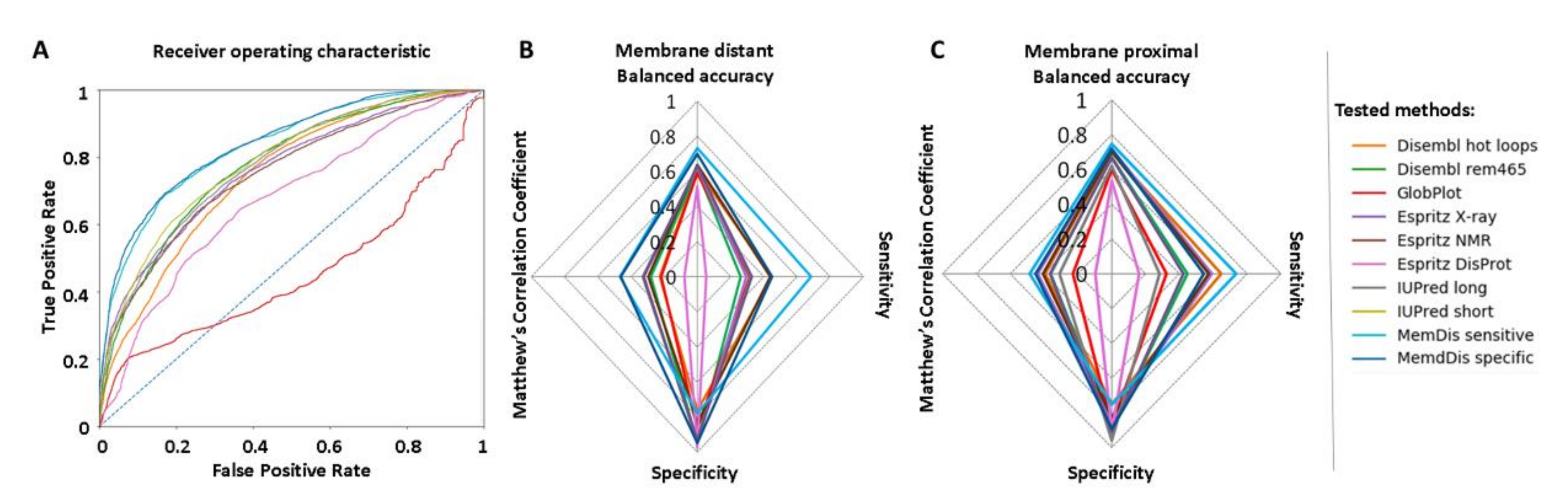
2. Results
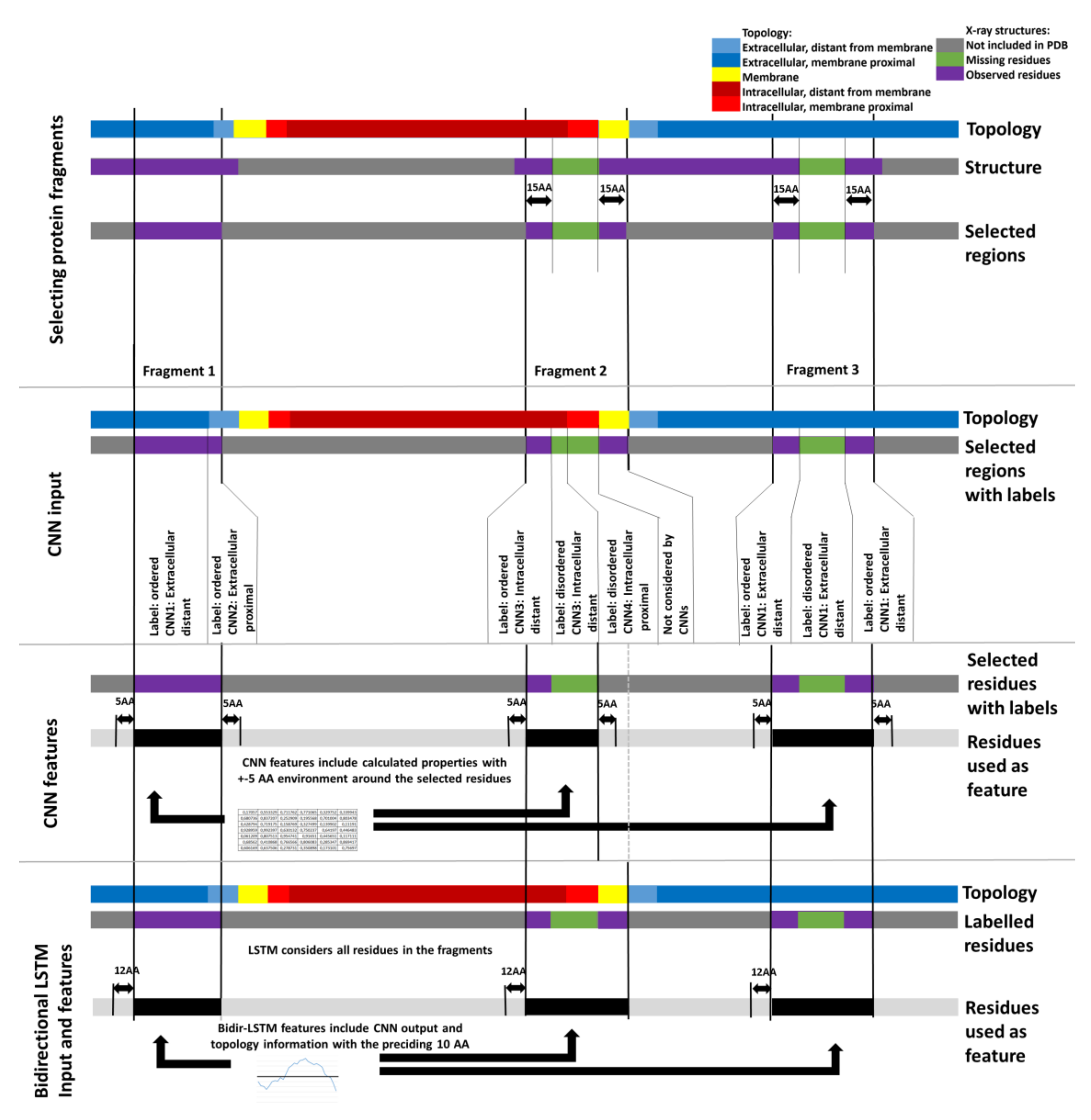
3. Materials and Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dobson, L.; Reményi, I.; Tusnády, G.E. The human transmembrane proteome. Biol. Direct 2015, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjaergaard, M.; Kragelund, B.B. Functions of intrinsic disorder in transmembrane proteins. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 3205–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tusnády, G.E.; Dobson, L.; Tompa, P. Disordered regions in transmembrane proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2015, 1848, 2839–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichmann, D.; Jakob, U. The roles of conditional disorder in redox proteins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2013, 23, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Erdős, G.; Pajkos, M.; Dosztányi, Z. IUPred3: Prediction of protein disorder enhanced with unambiguous experimental annotation and visualization of evolutionary conservation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W297–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linding, R.; Russell, R.B.; Neduva, V.; Gibson, T.J. GlobPlot: Exploring protein sequences for globularity and disorder. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3701–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, I.; Martin, A.J.M.; Di Domenico, T.; Tosatto, S.C.E. ESpritz: Accurate and fast prediction of protein disorder. Bioinformatics 2011, 28, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linding, R.; Jensen, L.J.; Diella, F.; Bork, P.; Gibson, T.J.; Russell, R.B. Protein disorder prediction: Implications for structural proteomics. Structure 2003, 11, 1453–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necci, M.; Piovesan, D.; Tosatto, S.C. Critical assessment of protein intrinsic disorder prediction. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, J.Y.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Song, J.; Gao, E.; Rabinowitz, J.E.; Chan, T.O.; Wang, J. Phospholemman: A Novel Cardiac Stress Protein. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2010, 3, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teriete, P.; Franzin, C.M.; Choi, J.; Marassi, F.M. Structure of the Na, K-ATPase Regulatory Protein FXYD1 in Micelles. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 6774–6783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piovesan, D.; Walsh, I.; Minervini, G.; Tosatto, S.C.E. FELLS: Fast estimator of latent local structure. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 1889–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaglia, F.; Mészáros, B.; Salladini, E.; Hatos, A.; Pancsa, R.; Chemes, B.L.; Pajkos, M.; Lazar, T.; Pena-Diaz, S.; Santos, J.; et al. DisProt in 2022: Improved quality and accessibility of protein intrinsic disorder. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Mészáros, B.; Sámano-Sánchez, H.; Alvarado-Valverde, J.; Čalyševa, J.; Martínez-Pérez, E.; Alves, R.; Shields, D.C.; Kumar, M.; Rippmann, F.; Chemes, L.B.; et al. Short linear motif candidates in the cell entry system used by SARS-CoV-2 and their potential therapeutic implications. Sci. Signal. 2021, 14, eabd0334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmiege, P.; Fine, M.; Blobel, G.; Li, X. Human TRPML1 channel structures in open and closed conformations. Nature 2017, 550, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergarajauregui, S.; Puertollano, R. Two di-leucine motifs regulate trafficking of mucolipin-1 to lysosomes. Traffic 2006, 7, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergarajauregui, S.; Oberdick, R.; Kiselyov, K.; Puertollano, R. Mucolipin 1 channel activity is regulated by protein kinase A-mediated phosphorylation. Biochem. J. 2008, 410, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Michael, S.; Alvarado-Valverde, J.; Mészáros, B.; Sámano-Sánchez, H.; Zeke, A.; Dobson, L.; Lazar, T.; Örd, M.; Nagpal, A.; et al. The Eukaryotic Linear Motif resource: 2022 release. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, gkab975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csizmadia, G.; Erdős, G.; Tordai, H.; Padányi, R.; Tosatto, S.; Dosztányi, Z.; Hegedűs, T. The MemMoRF database for recognizing disordered protein regions interacting with cellular membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 49, D355–D360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katuwawala, A.; Zhao, B.; Kurgan, L. DisoLipPred: Accurate prediction of disordered lipid binding residues in protein sequences with deep recurrent networks and transfer learning. Bioinformatics 2021, 93, btab640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piovesan, D.; Tabaro, F.; Paladin, L.; Necci, M.; Mičetić, I.; Camilloni, C.; Davey, N.; Dosztányi, Z.; Mészáros, B.; Monzon, A.M.; et al. MobiDB 3.0: More annotations for intrinsic disorder, conformational diversity and interactions in proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D471–D476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, L.; Reményi, I.; Tusnády, G.E. CCTOP: A consensus constrained topology prediction web server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W408–W412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Niu, B.; Gao, Y.; Fu, L.; Li, W. CD-HIT Suite: A web server for clustering and comparing biological sequences. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 680–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawashima, S. AAindex: Amino acid index database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Duvaud, S.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy Server. In The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, B.; Petersen, T.N.; Andersen, P.; Nielsen, M.; Lundegaard, C. A generic method for assignment of reliability scores applied to solvent accessibility predictions. BMC Struct. Biol. 2009, 9, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarnot, P.; Ziemska-Legięcka, J.; Dobson, L.; Merski, M.; Mier, P.; Andrade-Navarro, M.A.; Hancock, J.M.; Dosztányi, Z.; Paladin, L.; Necci, M.; et al. PlaToLoCo: The first web meta-server for visualization and annotation of low complexity regions in proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W77–W84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dobson, L.; Tusnády, G.E. MemDis: Predicting Disordered Regions in Transmembrane Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212270
Dobson L, Tusnády GE. MemDis: Predicting Disordered Regions in Transmembrane Proteins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(22):12270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212270
Chicago/Turabian StyleDobson, Laszlo, and Gábor E. Tusnády. 2021. "MemDis: Predicting Disordered Regions in Transmembrane Proteins" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 22: 12270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212270
APA StyleDobson, L., & Tusnády, G. E. (2021). MemDis: Predicting Disordered Regions in Transmembrane Proteins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(22), 12270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212270





