Effects of Magnesium Deficiency on Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes: Focusing on the Processes of Insulin Secretion and Signaling
Abstract
1. Introduction
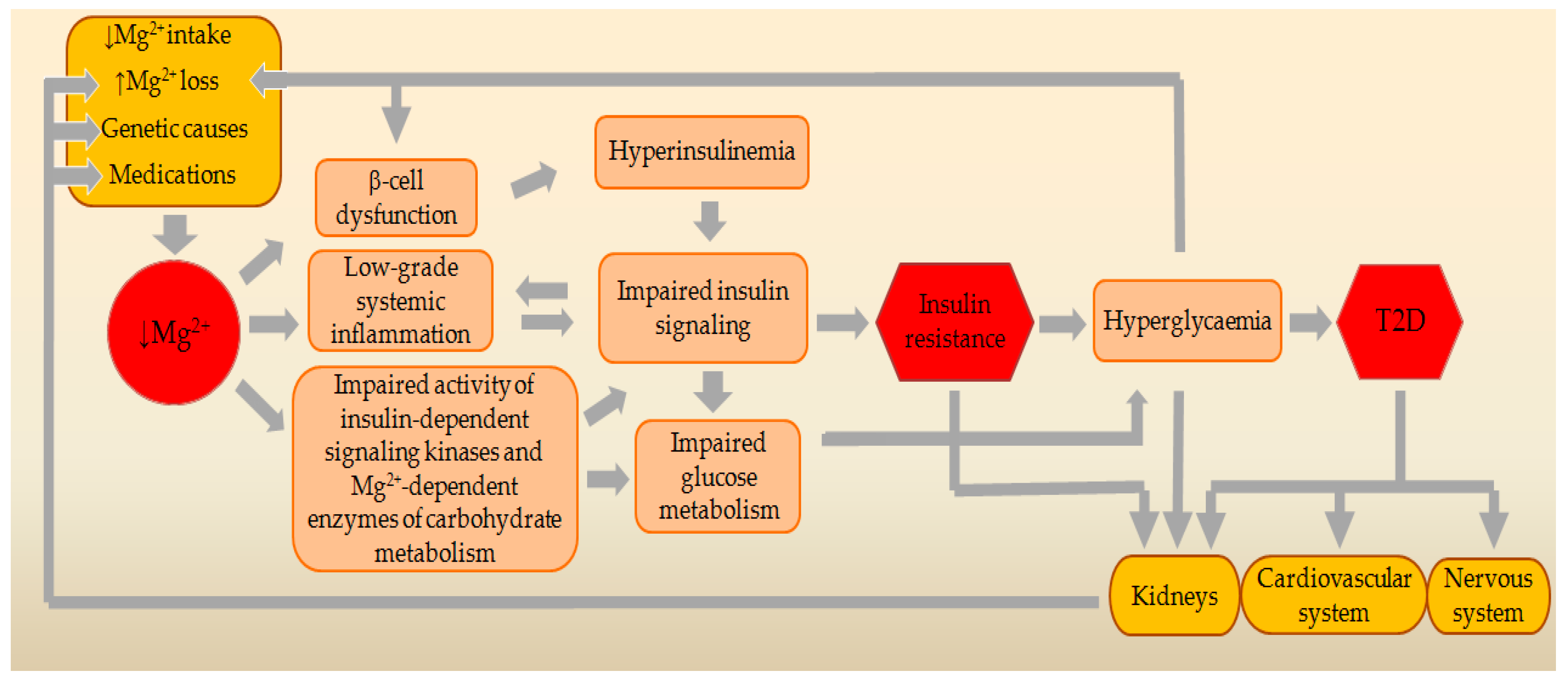
2. Effects of MgD on Molecular Mechanisms of Insulin Action
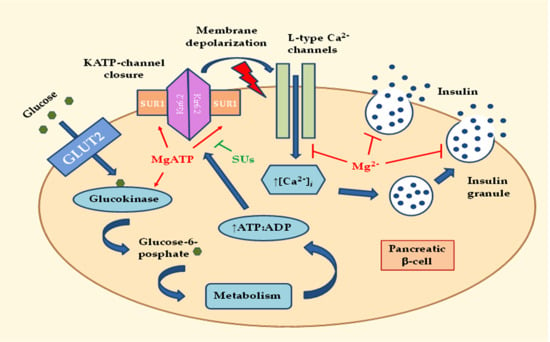
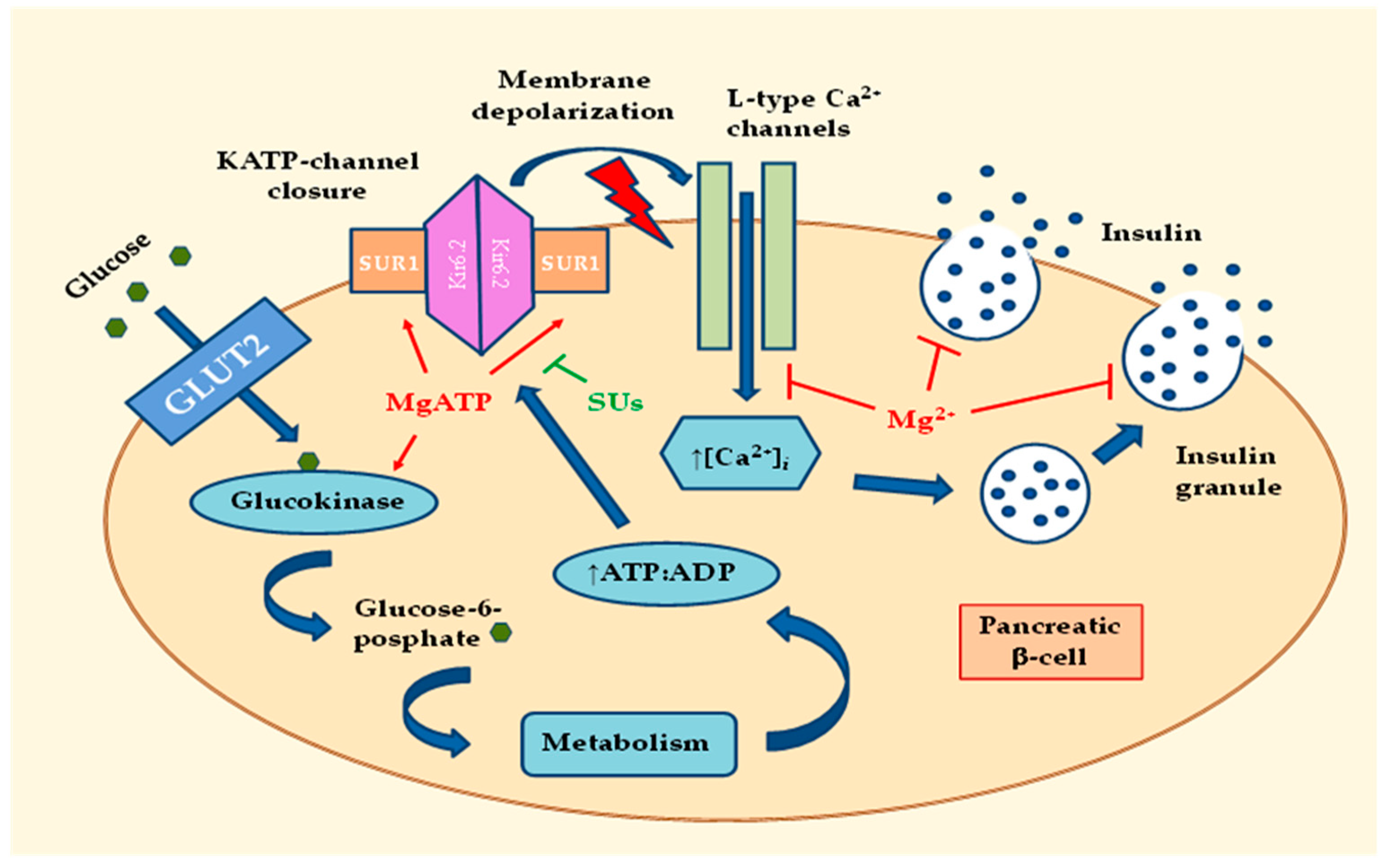
2.1. Effects of MgD on Insulin Secretion
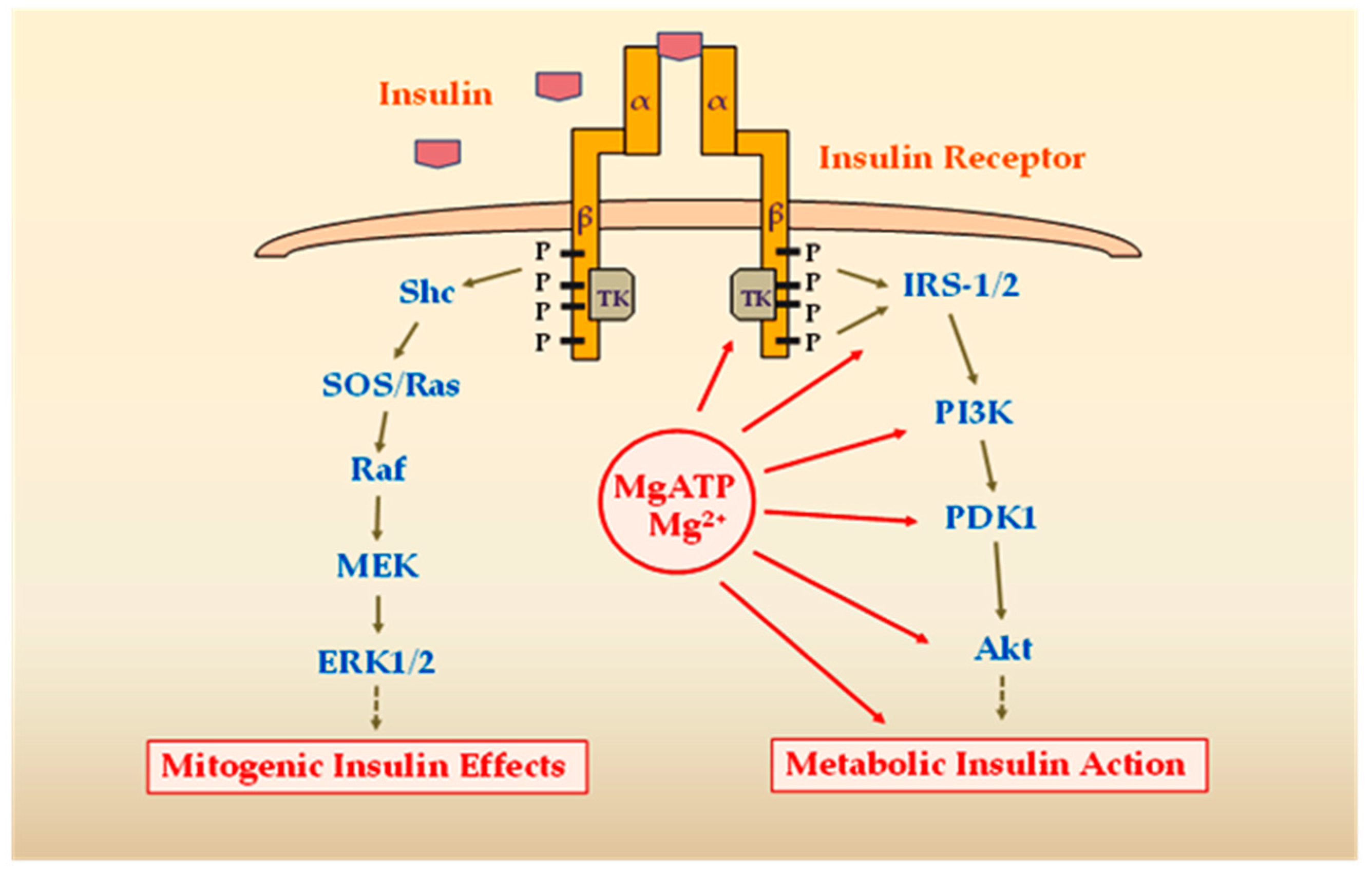
2.2. Effects of MgD on Peripheral Insulin Sensitivity
2.2.1. Effects of MgD-Induced Hyperinsulinemia on Downstream Insulin Signaling
2.2.2. Effects of MgD on Activity of the Insulin-Signaling Kinases
2.3. Effects of MgD on Low-Grade Systemic Inflammation
2.4. Effects of MgD on Key Mg2+-Dependent Enzymes of Carbohydrate and Energy Metabolism
3. Genetic Relationships between MgD and T2D
4. Main Causes and Risk Factors for MgD
4.1. Decreased Intake of Mg2+ from the Food or Drinking Water
4.2. Increased Loss of Mg2+ through the Kidneys
4.3. Impaired Intestinal Absorption of Mg2+
5. Mg2+ Supplementation and Dietary Approaches for Improving Insulin Sensitivity in T2D
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roden, M.; Petersen, K.; Shulman, G. Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes. In Textbook of Diabetes, 5th ed.; Holt, R.I., Cockram, C., Flyvbjerg, A., Goldstein, B.J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York City, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 174–186. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Li, X.; Adams, H.; Kubena, K.; Guo, S. Etiology of Metabolic Syndrome and Dietary Intervention. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salunkhe, V.A.; Veluthakal, R.; Kahn, S.E.; Thurmond, D.C. Novel approaches to restore beta cell function in prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1895–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Bidasee, K.R.; Adeghate, E.; Howarth, C.F.; D’Souza, A.; Singh, R.B. Left ventricle structural remodelling in prediabetes and overt type 2 diabetes mellitus in the Goto-Kakizaki rat. World Heart J. 2017, 9, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Kolte, D.; Vijayaraghavan, K.; Khera, S.; Sica, D.A.; Frishman, W.H. Role of magnesium in cardiovascular diseases. Cardiol. Rev. 2014, 22, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Baaij, J.H.; Hoenderop, J.G.; Bindels, R.J. Magnesium in man: Implications for health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbagallo, M.; Dominguez, L.J. Magnesium and type 2 diabetes. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostov, K.; Halacheva, L. Role of magnesium deficiency in promoting atherosclerosis, endothelial dysfunction, and arterial stiffening as risk factors for hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Sun, S.; Chen, J.; Xu, G.; Wang, H.; Qian, Q. Genetics of magnesium disorders. Kidney Dis. 2017, 3, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNair, P.; Christensen, M.S.; Christiansen, C.; Madsbad, S.; Transbøl, I.B. Renal hypomagnesaemia in human diabetes mellitus: Its relation to glucose homeostasis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1982, 12, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, R. Magnesium metabolism and its disorders. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2003, 24, 47–66. [Google Scholar]
- Vormann, J. Magnesium and Kidney Health-More on the ‘Forgotten Electrolyte’. Am. J. Nephrol. 2016, 44, 379–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florentin, M.; Elisaf, M.S. Proton pump inhibitor-induced hypomagnesemia: A new challenge. World J. Nephrol. 2012, 1, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, K.E.; Chubb, S.P.; Davis, W.A.; Davis, T.M. The relationship between hypomagnesemia, metformin therapy and cardiovascular disease complicating type 2 diabetes: The Fremantle Diabetes Study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbagallo, M.; Dominguez, L.J. Magnesium metabolism in type 2 diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 458, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günther, T. The biochemical function of Mg2+ in insulin secretion, insulin signal transduction and insulin resistance. Magnes. Res. 2010, 23, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barbagallo, M.; Dominguez, L.J. Magnesium and the cardiometabolic syndrome. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2012, 1, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, H.; Wanner, C. Magnesium in disease. Clin. Kidney J. 2012, 5, i25–i38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gommers, L.M.; Hoenderop, J.G.; Bindels, R.J.; de Baaij, J.H. Hypomagnesemia in type 2 diabetes: A vicious circle? Diabetes 2016, 65, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarz, V.L.; MacDonald, P.E.; Klip, A. The cell biology of systemic insulin function. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 2273–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, S.G.; Sharp, G.W. Glucose-stimulated signaling pathways in biphasic insulin secretion. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2002, 18, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepton, S. Beta-Cell Function and Failure; InTech: London, UK, 2013; pp. 115–126. [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft, F.M.; Puljung, M.C.; Vedovato, N. Neonatal diabetes and the KATP channel: From mutation to therapy. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosolova, H.; Mayer, O., Jr.; Reaven, G.M. Insulin-mediated glucose disposal is decreased in normal subjects with relatively low plasma magnesium concentrations. Metabolism 2000, 49, 418–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, C.W.; Lawrence, M.C. Ligand-induced activation of the insulin receptor: A multi-step process involving structural changes in both the ligand and the receptor. Bioessays 2009, 31, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Rodelo, C.; Roura-Guiberna, A.; Olivares-Reyes, J.A. Molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance: An update. Gaceta Médica de México 2017, 153, 214–228. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, C.; Agoramoorthy, G.; Hsu, M.J. Exploring the evolutionary relationship of insulin receptor substrate family using computational biology. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardilovich, K.; Pankratz, S.L.; Shaw, L.M. Expression and function of the insulin receptor substrate proteins in cancer. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2009, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Fluckey, J.D.; Chakraborty, S.; Muthuchamy, M. Hyperglycemia-and hyperinsulinemia-induced insulin resistance causes alterations in cellular bioenergetics and activation of inflammatory signaling in lymphatic muscle. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 2744–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanik, M.H.; Xu, Y.; Škrha, J.; Dankner, R.; Zick, Y.; Roth, J. Insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia: Is hyperinsulinemia the cart or the horse? Diabetes Care 2008, 31, S262–S268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boura-Halfon, S.; Zick, Y. Phosphorylation of IRS proteins, insulin action, and insulin resistance. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 296, E581–E591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, J.; Kleinridders, A.; Kahn, C.R. Insulin receptor signaling in normal and insulin-resistant states. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a009191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbagallo, M.; Gupta, R.K.; Bardicef, O.; Bardicef, M.; Resnick, L.M. Altered ionic effects of insulin in hypertension: Role of basal ion levels in determining cellular responsiveness. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 1761–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, R.; Wang, H.; Liang, F. Mechanisms linking inflammation to insulin resistance. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 2015, 508409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belin, R.J.; He, K. Magnesium physiology and pathogenic mechanisms that contribute to the development of the metabolic syndrome. Magnes. Res. 2007, 20, 107–129. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, K.; Akash, M.S.H. Mechanisms of inflammatory responses and development of insulin resistance: How are they interlinked? J. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 23, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaepfer, D.D.; Hou, S.; Lim, S.T.; Tomar, A.; Yu, H.; Lim, Y.; Hanson, D.A.; Uryu, S.A.; Molina, J.; Mitra, S.K. Tumor necrosis factor-α stimulates focal adhesion kinase activity required for mitogen-activated kinase-associated interleukin 6 expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 17450–17459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodabandehloo, H.; Gorgani-Firuzjaee, S.; Panahi, G.; Meshkani, R. Molecular and cellular mechanisms linking inflammation to insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction. Transl. Res. 2016, 167, 228–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Romero, F.; Bermudez-Peña, C.; Rodríguez-Morán, M. Severe hypomagnesemia and low-grade inflammation in metabolic syndrome. Magnes. Res. 2011, 24, 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, F.H. Magnesium, inflammation, and obesity in chronic disease. Nutr. Rev. 2010, 68, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.E.; Mainous, A.G., III; Geesey, M.E.; Ellis, T. Magnesium intake and serum C-reactive protein levels in children. Magnes. Res. 2007, 20, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- King, D.E.; Mainous, A.G., III; Geesey, M.E.; Woolson, R.F. Dietary magnesium and C-reactive protein levels. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2005, 24, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.J.; Xun, P.; Liu, K.; Loria, C.; Yokota, K.; Jacobs, D.R.; He, K. Magnesium intake in relation to systemic inflammation, insulin resistance, and the incidence of diabetes. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2604–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlavani, M.; Ramalho, T.; Koboziev, I.; Monique, L.J.; Jayarathne, S.; Ramalingam, L.; Filgueiras, L.R.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. Adipose tissue inflammation in insulin resistance: Review of mechanisms mediating anti-inflammatory effects of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. J. Investig. Med. 2017, 65, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, D.P.; Boparai, R.K.; Sharma, R.; Bansal, D.D. Studies on the development of an insulin resistant rat model by chronic feeding of low magnesium high sucrose diet. Magnes. Res. 2004, 17, 293–300. [Google Scholar]
- Voma, C.; Romani, A.M. Role of Magnesium in the Regulation of Hepatic Glucose Homeostasis; InTech: London, UK, 2014; pp. 95–111. [Google Scholar]
- Beurel, E.; Grieco, S.F.; Jope, R.S. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3): Regulation, actions, and diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 148, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, B.; Gary, R.K. The GSK3 kinase inhibitor lithium produces unexpected hyperphosphorylation of β-catenin, a GSK3 substrate, in human glioblastoma cells. Biol. Open 2018, 7, bio030874. [Google Scholar]
- Medina, M.; Wandosell, F. Deconstructing GSK-3: The fine regulation of its activity. Int. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2011, 2011, 479249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilchova, I.; Klacanova, K.; Tatarkova, Z.; Kaplan, P.; Racay, P. The Involvement of Mg2+ in Regulation of Cellular and Mitochondrial Functions. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfinkel, L.; Garfinkel, D. Magnesium regulation of the glycolytic pathway and the enzymes involved. Magnesium 1985, 4, 60–72. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrè, S.; de Baaij, J.H.; Ferreira, P.; Germann, R.; de Klerk, J.B.; Lavrijsen, M.; van Zeeland, F.; Venselaar, H.; Kluijtmans, L.A.; Hoenderop, J.G.; et al. Mutations in PCBD1 cause hypomagnesemia and renal magnesium wasting. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adalat, S.; Woolf, A.S.; Johnstone, K.A.; Wirsing, A.; Harries, L.W.; Long, D.A.; Hennekam, R.C.; Ledermann, S.E.; Rees, L.; van’t Hoff, W.; et al. HNF1B mutations associate with hypomagnesemia and renal magnesium wasting. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.H.K.; Chacko, S.A.; Song, Y.; Cho, M.; Eaton, C.B.; Wu, W.C.H.; Liu, S. Genetic Variations in Magnesium-Related Ion Channels May Affect Diabetes Risk among African American and Hispanic American Women 1–3. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Baaij, J.H.; Hoenderop, J.G.; Bindels, R.J. Regulation of magnesium balance: Lessons learned from human genetic disease. Clin. Kidney J. 2012, 5, i15–i24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altura, B.M.; Li, W.; Zhang, A.; Zheng, T.; Shah, N.C. Sudden cardiac death in infants, children and young adults: Possible roles of dietary magnesium intake and generation of platelet-activating factor in coronary arteries. J. Heart Health 2016, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Gröber, U.; Schmidt, J.; Kisters, K. Magnesium in prevention and therapy. Nutrients 2015, 7, 8199–8226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, L.; Sullivan, K.R. Low Dietary Magnesium Intake and Hypertension. World J. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 6, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galan, P.; Preziosi, P.; Durlach, V.; Valeix, P.; Ribas, L.; Bouzid, D.; Favier, A.; Hercberg, S. Dietary magnesium intake in a French adult population. Magnes. Res. 1997, 10, 321–328. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, A.A.; Ismail, N.A. Magnesium: A mineral essential for health yet generally underestimated or even ignored. J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2016, 6, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standing Committee on the Scientific Evaluation of Dietary Reference Intakes; Food and Nutrition Board; Institute of Medicine (IOM). Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium, Vitamin D, and Fluoride; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Rosanoff, A. The high heart health value of drinking-water magnesium. Med. Hypotheses 2013, 81, 1063–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Ridaura, R.; Willett, W.C.; Rimm, E.B.; Liu, S.; Stampfer, M.J.; Manson, J.E.; Hu, F.B. Magnesium intake and risk of type 2 diabetes in men and women. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dam, R.M.; Hu, F.B.; Rosenberg, L.; Krishnan, S.; Palmer, J.R. Dietary calcium and magnesium, major food sources, and risk of type 2 diabetes in US black women. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 2238–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausalya, P.J.; Amasheh, S.; Günzel, D.; Wurps, H.; Müller, D.; Fromm, M.; Hunziker, W. Disease-associated mutations affect intracellular traffic and paracellular Mg2+ transport function of Claudin-16. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 878–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, V.; Cohen, R.A. Hypomagnesemia in a patient with an eating disorder. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 71, A12–A14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbagallo, M.; Dominguez, L.J. Magnesium and type 2 diabetes: An Update. Int. J. Diabetes Clin. Res. 2015, 2, 019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuchardt, J.P.; Hahn, A. Intestinal absorption and factors influencing bioavailability of magnesium—An update. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2017, 13, 260–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, R.; Wallace, T.C.; Rosanoff, A. Magnesium. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimke, H.; Hoenderop, J.G.; Bindels, R.J. Molecular basis of epithelial Ca2+ and Mg2+ transport: Insights from the TRP channel family. J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 1535–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Morán, M.; Guerrero-Romero, F. Oral magnesium supplementation improves insulin sensitivity and metabolic control in type 2 diabetic subjects: A randomized double-blind controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Romero, F.; Tamez-Perez, H.E.; González-González, G.E.; Salinas-Martinez, A.M.; Montes-Villarreal, J.; Trevino-Ortiz, J.H.; Rodriguez-Moran, M. Oral magnesium supplementation improves insulin sensitivity in non-diabetic subjects with insulin resistance. A double-blind placebo-controlled randomized trial. Diabetes Metab. 2004, 30, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; He, K.; Levitan, E.B.; Manson, J.E.; Liu, S. Effects of oral magnesium supplementation on glycaemic control in Type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized double-blind controlled trials. Diabet. Med. 2006, 23, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacko, S.A.; Sul, J.; Song, Y.; Li, X.; LeBlanc, J.; You, Y.; Butch, A.; Liu, S. Magnesium supplementation, metabolic and inflammatory markers, and global genomic and proteomic profiling: A randomized, double-blind, controlled, crossover trial in overweight individuals. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooren, F.C.; Krüger, K.; Völker, K.; Golf, S.W.; Wadepuhl, M.; Kraus, A. Oral magnesium supplementation reduces insulin resistance in non-diabetic subjects—A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2011, 13, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solati, M.; Ouspid, E.; Hosseini, S.; Soltani, N.; Keshavarz, M.; Dehghani, M. Oral magnesium supplementation in type II diabetic patients. Med. J. Islam. Repub. Iran 2014, 28, 67. [Google Scholar]
- ELDerawi, W.; Naser, I.; Taleb, M.; Abutair, A. The Effects of Oral Magnesium Supplementation on Glycemic Response among Type 2 Diabetes Patients. Nutrients 2019, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosique-Esteban, N.; Guasch-Ferré, M.; Hernández-Alonso, P.; Salas-Salvadó, J. Dietary Magnesium and Cardiovascular Disease: A Review with Emphasis in Epidemiological Studies. Nutrients 2018, 10, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, M.; Schindler, C. Clinically and pharmacologically relevant interactions of antidiabetic drugs. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 7, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forouhi, N.G.; Misra, A.; Mohan, V.; Taylor, R.; Yancy, W. Dietary and nutritional approaches for prevention and management of type 2 diabetes. Br. Med. J. 2018, 361, k2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.M.; Steck, S.E.; Fung, T.T.; Zhang, J.; Hazlett, L.J.; Han, K.; Lee, S.H.; Kwon, H.S.; Merchant, A.T. Mediterranean diet, Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) style diet, and metabolic health in US adults. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, A.P. DASH eating plan: An eating pattern for diabetes management. Diabetes Spectr. 2017, 30, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, F.M.; Svetkey, L.P.; Vollmer, W.M.; Appel, L.J.; Bray, G.A.; Harsha, D.; Obarzanek, E.; Conlin, P.R.; Miller, E.R., 3rd; Simons-Morton, D.G.; et al. Effects on blood pressure of reduced dietary sodium and the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| General: Anxiety, agitation, irritability, headache, loss of appetite, and nausea. |
| Musculature: Muscle spasm and tetany. |
| CNS/Nerves: Nervousness, migraine, depression, poor memory, low stress tolerance, paraesthesia, tremor, and seizures. |
| Metabolism: Pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction, IR, decreased glucose tolerance, increased risk of MetS and T2D, dyslipoproteinemia, disorders of vitamin D metabolism, resistance to PTH, and osteoporosis. |
| Cardiovascular system: Arrhythmias, coronary spasm, atherosclerosis, hypertension, arterial stiffness, endothelial dysfunction, and increased platelet aggregation. |
| Electrolytes: Sodium retention, hypokalemia, and hypocalcemia. |
| Study | Mg2+ Intake (mg/day) | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Rodrguez-Moran et al., 2003 [71] | 50 mL MgCl2 solution (50 g MgCl2 per 1000 mL solution) daily for 16 weeks. | Oral supplementation with MgCl2 solution restores serum Mg2+ levels, improving insulin sensitivity and metabolic control in T2D patients with decreased serum Mg2+ levels |
| Guerrero-Romero et al., 2004 [72] | MgCl2 2.5 g daily for 3 months | Oral Mg2+ supplementation improves insulin sensitivity in hypomagnesemic non-diabetic subjects |
| Song et al., 2006 [73] | 360 mg/day for 4–16 weeks | Oral Mg2+ supplementation reduces plasma fasting glucose levels and increases HDL cholesterol in patients with T2D |
| Chacko et al., 2011 [74] | 500 mg/day for 4 weeks | Mg2+ treatment significantly improves fasting C-peptide concentrations and fasting insulin concentrations |
| Mooren et al., 2011 [75] | 365 mg/day for 6 months | Mg2+ supplementation resulted in a significant improvement in fasting plasma glucose and insulin sensitivity in normomagnesemic, overweight non-diabetic subjects |
| Solati et al., 2014 [76] | 300 mg/day for 3 months | Oral Mg2+ supplementation has beneficial effects on blood glucose, lipid profile, and blood pressure in patients with T2D |
| ELDerawi et al., 2019 [77] | 250 mg/day for 3 months | Oral Mg2+ supplementation reduces IR and improves glycemic control in T2D patients |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kostov, K. Effects of Magnesium Deficiency on Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes: Focusing on the Processes of Insulin Secretion and Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061351
Kostov K. Effects of Magnesium Deficiency on Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes: Focusing on the Processes of Insulin Secretion and Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(6):1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061351
Chicago/Turabian StyleKostov, Krasimir. 2019. "Effects of Magnesium Deficiency on Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes: Focusing on the Processes of Insulin Secretion and Signaling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 6: 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061351
APA StyleKostov, K. (2019). Effects of Magnesium Deficiency on Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes: Focusing on the Processes of Insulin Secretion and Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(6), 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061351