Structural and Social Determinants of Health Factors Associated with County-Level Variation in Non-Adherence to Antihypertensive Medication Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Measurement of County-Level Non-Adherence to AHM
2.3. SDH Variables
2.4. Definition of Social Determinants of Medication Non-Adherence (SDN) Constructs
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Confirmed Social Determinants of Non-Adherence Model
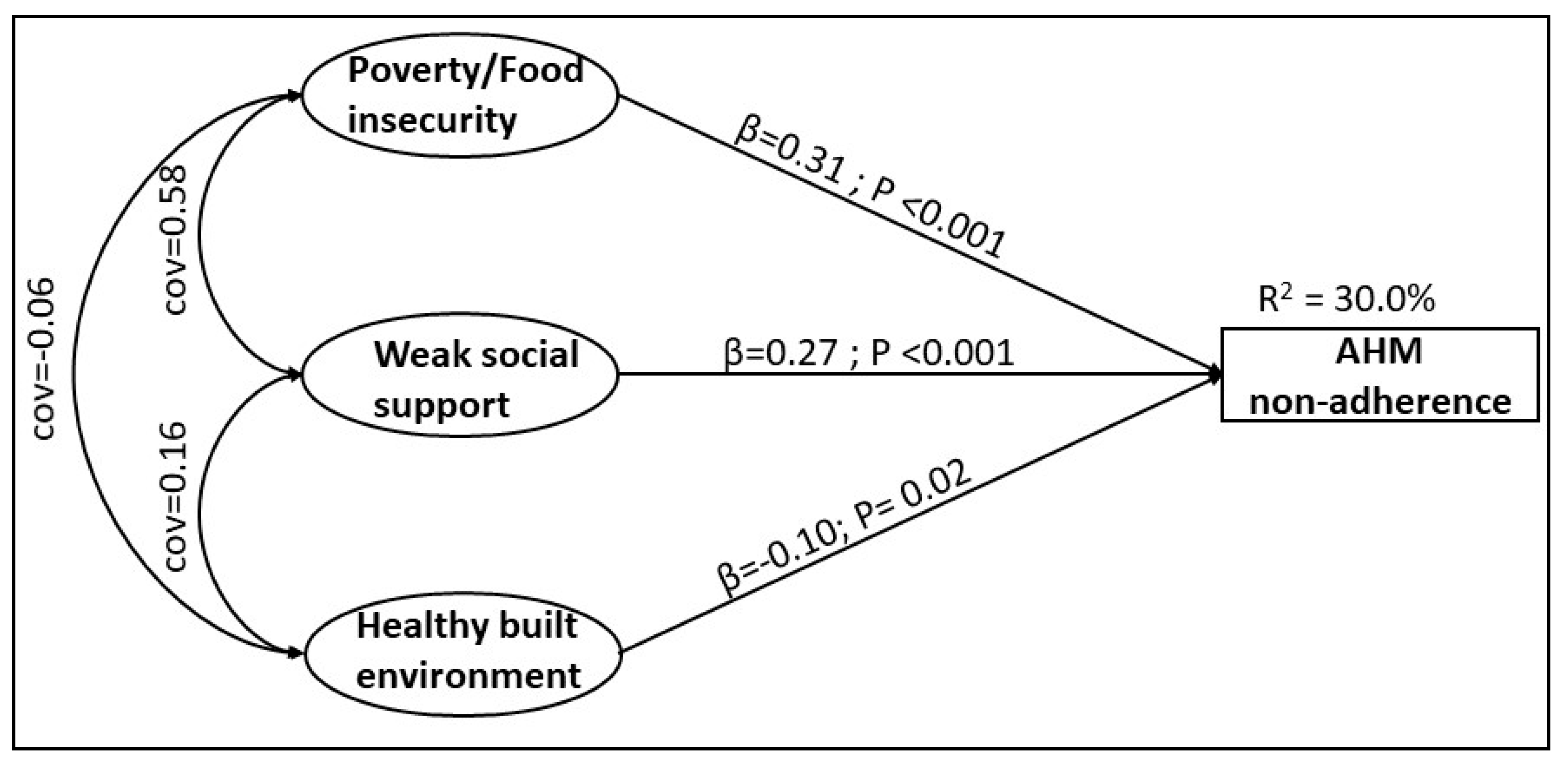
3.2. Structural Relationships between AHM Non-Adherence and SDN
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Strengths
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schulz, M.; Krueger, K.; Schuessel, K.; Friedland, K.; Laufs, U.; Mueller, W.E.; Ude, M. Medication adherence and persistence according to different antihypertensive drug classes: A retrospective cohort study of 255,500 patients. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 220, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abegaz, T.M.; Shehab, A.; Gebreyohannes, E.A.; Bhagavathula, A.S.; Elnour, A.A. Nonadherence to antihypertensive drugs: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2017, 96, e5641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Yu, X.; Ou, S.; Liu, X.; Yuan, J.; Tan, X.; Chen, Y. Adherence to Antihypertensive Medications and Stroke Risk: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Chang, A.; Ritchey, M.D.; Loustalot, F. Antihypertensive medication adherence and risk of cardiovascular disease among older adults: A population-based cohort study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwlaat, R.; Wilczynski, N.; Navarro, T.; Hobson, N.; Jeffery, R.; Keepanasseril, A.; Agoritsas, T.; Mistry, N.; Iorio, A.; Jack, S.; et al. Interventions for enhancing medication adherence. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, CD000011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardas, P.; Lewek, P.; Matyjaszczyk, M. Determinants of patient adherence: A review of systematic reviews. Front. Pharm. 2013, 4, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Laan, D.M.; Elders, P.J.M.; Boons, C.C.L.M.; Beckeringh, J.J.; Nijpels, G.; Hugtenburg, J.G. Factors associated with antihypertensive medication non-adherence: A systematic review. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2017, 31, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdinand, K.C.; Yadav, K.; Nasser, S.A.; Clayton-Jeter, H.D.; Lewin, J.; Cryer, D.R.; Senatore, F.F. Disparities in hypertension and cardiovascular disease in blacks: The critical role of medication adherence. J. Clin. Hypertens. (GreenwichConn.) 2017, 19, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.R.; Piette, J.D.; Resnicow, K.; Kowalski-Dobson, T.; Heisler, M. Social determinants of health, cost-related nonadherence, and cost-reducing behaviors among adults with diabetes: Findings from the national health interview survey. Med. Care 2016, 54, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheurer, D.; Choudhry, N.; Swanton, K.A.; Matlin, O.; Shrank, W. Association between different types of social support and medication adherence. Am. J. Manag. Care 2012, 18, e461–e467. [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz, S.A.; Seligman, H.K.; Choudhry, N.K. Treat or eat: Food insecurity, cost-related medication underuse, and unmet needs. Am. J. Med. 2014, 127, 303–310 e303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, D.; Afulani, P.; Coleman-Jensen, A.; Harrison, G.G. Food insecurity and cost-related medication underuse among nonelderly adults in a nationally representative sample. Am. J. Public Health 2015, 105, e48–e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiMatteo, M.R. Social support and patient adherence to medical treatment: A meta-analysis. Health Psychol. 2004, 23, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hensley, C.; Heaton, P.C.; Kahn, R.S.; Luder, H.R.; Frede, S.M.; Beck, A.F. Poverty, transportation access, and medication nonadherence. Pediatrics 2018, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solar, O.; Irwin, A. A Conceptual Framework for Action on the Social Determinants of Health. Social Determinants of Health Discussion Paper 2 (Policy and Practice); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Couto, J.E.; Panchal, J.M.; Lal, L.S.; Bunz, T.J.; Maesner, J.E.; O’Brien, T.; Khan, T. Geographic variation in medication adherence in commercial and Medicare part D populations. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2014, 20, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries McClintock, H.F.; Wiebe, D.J.; O‘Donnell, A.J.; Morales, K.H.; Small, D.S.; Bogner, H.R. Neighborhood social environment and patterns of adherence to oral hypoglycemic agents among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Fam. Community Health 2015, 38, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billimek, J.; August, K.J. Costs and beliefs: Understanding individual- and neighborhood-level correlates of medication nonadherence among Mexican Americans with type 2 diabetes. Health Psychol. Off. J. Div. Health Psychol. Am. Psychol. Assoc. 2014, 33, 1602–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billimek, J.; Sorkin, D.H. Self-reported neighborhood safety and nonadherence to treatment regimens among patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2012, 27, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qato, D.M.; Alexander, G.C.; Chakraborty, A.; Guadamuz, J.S.; Jackson, J.W. Association between pharmacy closures and adherence to cardiovascular medications among older US adults. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e192606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juarez, P.D.; Matthews-Juarez, P.; Hood, D.B.; Im, W.; Levine, R.S.; Kilbourne, B.J.; Langston, M.A.; Al-Hamdan, M.Z.; Crosson, W.L.; Estes, M.G.; et al. The public health exposome: A population-based, exposure science approach to health disparities research. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 12866–12895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Interactive Atlas of Heart Disease and Stroke. Interactive Atlas of Heart Disease and Stroke. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/dhdsp/maps/atlas/index.htm (accessed on 24 October 2019).
- Remington, P.L.; Catlin, B.B.; Gennuso, K.P. The County Health Rankings: Rationale and methods. Popul. Health Metr. 2015, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, J.F.; Koepsell, T.D.; Fihn, S.D.; Inui, T.S. A general method of compliance assessment using centralized pharmacy records. Description and validation. Med. Care 1988, 26, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, J.F.; Prochazka, A.V. The assessment of refill compliance using pharmacy records: Methods, validity, and applications. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1997, 50, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterberg, L.; Blaschke, T. Adherence to medication. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kindig, D.; Stoddart, G. What is population health? Am. J. Public Health 2003, 93, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zullig, L.L.; Blalock, D.V.; Dougherty, S.; Henderson, R.; Ha, C.C.; Oakes, M.M.; Bosworth, H.B. The new landscape of medication adherence improvement: Where population health science meets precision medicine. Patient Prefer Adherence 2018, 12, 1225–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumme, A.A.; Glynn, R.J.; Schneeweiss, S.; Gagne, J.J.; Dougherty, J.S.; Brill, G.; Choudhry, N.K. Medication synchronization programs improve adherence to cardiovascular medications and health care use. Health Aff. (Millwood) 2018, 37, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seabury, S.A.; Dougherty, J.S.; Sullivan, J. Medication adherence as a measure of the quality of care provided by physicians. Am. J. Manag. Care 2019, 25, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Part C & D Star Ratings Technical Notes; Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rankings, C.H. 2016 Measures & Data Sources. Available online: https://www.countyhealthrankings.org/sites/default/files/media/document/2016_Measures_DataSourcesYears.pdf (accessed on 7 June 2020).
- Booske, B.C.; Athens, J.K.; Kindig, D.A.; Park, H.; Remington, P.L. Different Perspectives for Assigning Weights to Determinants of Health; University of Wisconsin: Madison, WI, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb, L.M.; Francis, D.E.; Beck, A.F. Uses and Misuses of Patient- and Neighborhood-level Social Determinants of Health Data. Perm. J. 2018, 22, 18–078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crystal, S.; Akincigil, A.; Bilder, S.; Walkup, J.T. Studying prescription drug use and outcomes with medicaid claims data: Strengths, limitations, and strategies. Med. Care 2007, 45, S58–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
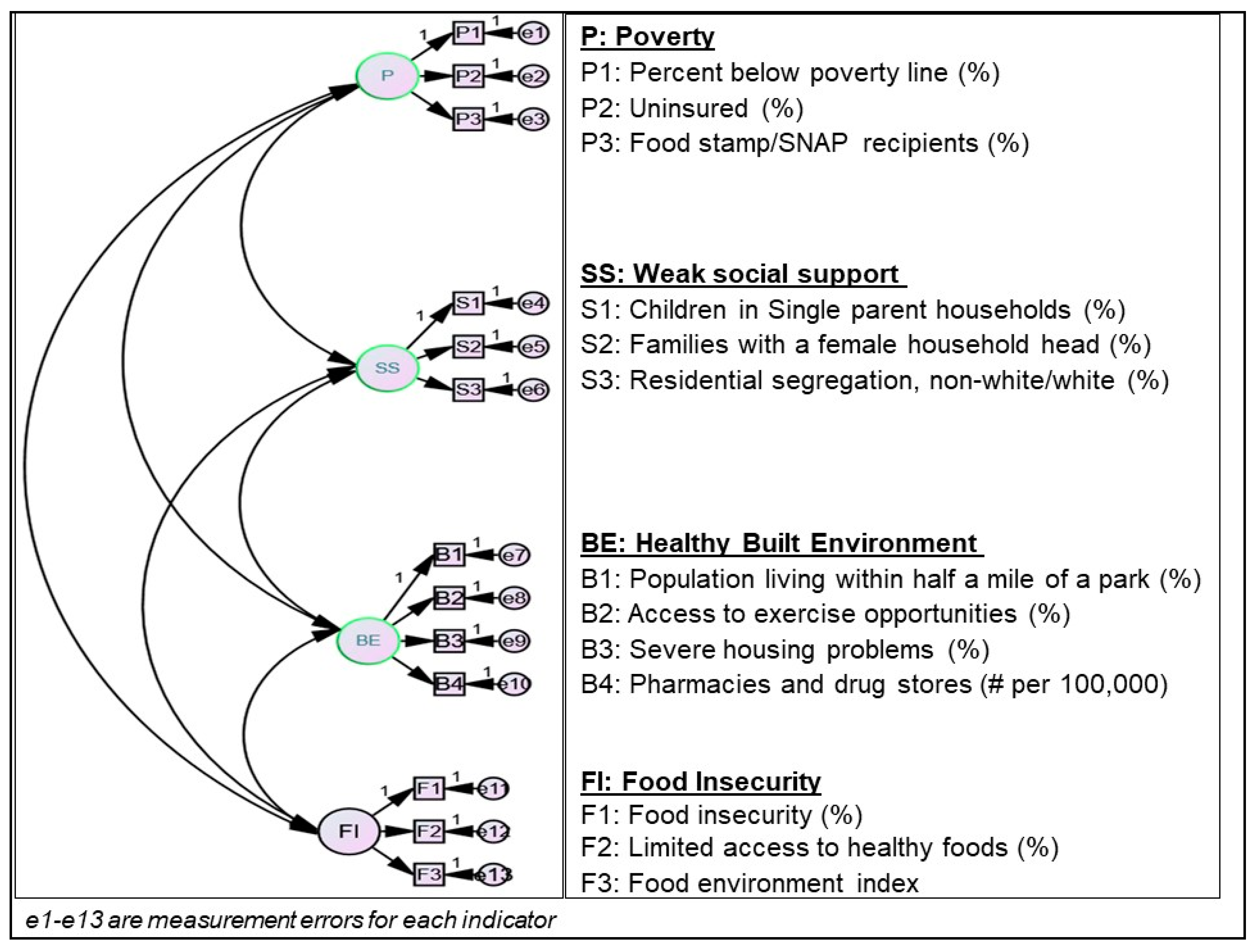

| Constructs of SDH | Geographic Region, Mean (Standard Deviation) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Midwest (n = 621) | Northeast (n = 197) | South (n = 1044) | West (n = 205) | P-Value | |
| Poverty | |||||
| Percent below poverty line (%) | 13.2 (4.3) | 12.8 (3.8) | 18.6 (6.2) | 15.7 (5.2) | <0.01 |
| Uninsured (%) | 12.9 (3.2) | 11.4 (3.1) | 19.7 (4.4) | 18.9 (3.7) | <0.01 |
| Food stamp/SNAP recipient (%) | 12.6 (5.0) | 13.0 (4.7) | 18.3 (6.8) | 15.0 (7.8) | <0.01 |
| Weak Social Network | |||||
| Children in single-parent household (%) | 29.8 (6.9) | 31.5 (7.1) | 36.4 (9.3) | 31.4 (8.0) | <0.01 |
| Families with female household head (%) | 9.7 (2.3) | 11.0 (2.8) | 13.5 (3.8) | 10.7 (3.0) | <0.01 |
| Residential segregation, non-white/white (%) | 35.0 (11.9) | 39.6 (10.9) | 31.1 (12.3) | 27.8 (10.3) | <0.01 |
| Built Environment | |||||
| Population living within half a mile of a park (%) | 27.7 (18.6) | 24.8 (20.1) | 12.2 (14.4) | 32.7 (22.3) | <0.01 |
| Access to exercise opportunities (%) | 66.3 (17.1) | 76.3 (16.3) | 59.9 (22.2) | 73.9 (18.0) | <0.01 |
| Severe housing problems (%) | 13.0 (3.0) | 16.5 (4.7) | 15.2 (3.7) | 18.6 (5.5) | <0.01 |
| Pharmacies (# per 100,000) | 27.7 (18.6) | 24.8 (20.1) | 12.2 (14.4) | 32.7 (22.3) | <0.01 |
| Food insecurity | |||||
| Food insecurity (%) | 13.3 (2.8) | 12.6 (2.2) | 16.8 (3.8) | 14.8 (2.5) | <0.01 |
| Limited access to healthy foods (%) | 5.7 (3.6) | 4.2 (2.6) | 7.0 (4.8) | 8.0 (5.0) | <0.01 |
| Food environment index | 7.6 (0.7) | 7.9 (0.5) | 6.7 (1.1) | 7.1 (0.8) | <0.01 |
| Demographic Variables | |||||
| Age above 65 (%) | 17.1 (3.5) | 17.2 (2.7) | 16.7 (4.3) | 16.6 (5.3) | 0.10 |
| African American (%) | 3.3 (5.2) | 5.2 (6.5) | 16.3 (16.6) | 1.7 (2.1) | <0.01 |
| Asian American (%) | 1.3 (1.6) | 2.8 (3.8) | 1.3 (1.8) | 3.4 (5.4) | <0.01 |
| Pacific Islander (%) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.3 (0.3) | <0.01 |
| Hispanic (%) | 4.4 (4.6) | 6.7 (6.1) | 9.4 (14.0) | 21.3 (18.4) | <0.01 |
| Female (%) | 50.0 (1.3) | 51.0 (1.3) | 50.4 (2.1) | 49.7 (1.2) | <0.01 |
| Rural (%) | 49.8 (25.1) | 42.3 (28.8) | 53.1 (28.7) | 33.1 (23.3) | <0.01 |
| Model 1 (Unadjusted) | Model 2 (Adjusted) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standardized Regression Coefficient | P-Value | Standardized Regression Coefficient | P-Value | |
| SDH Constructs | ||||
| Poverty/food insecurity | 0.31 | <0.001 | 0.38 | <0.01 |
| Weak social support | 0.27 | <0.001 | 0.12 | 0.05 |
| Healthy built environments | −0.12 | <0.01 | −0.13 | <0.01 |
| Demographic Factors | ||||
| % African American | 0.12 | <0.01 | ||
| % Female | −0.02 | 0.36 | ||
| % Rural | −0.02 | 0.36 | ||
| R2 | 0.30 | 0.28 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Donneyong, M.M.; Chang, T.-J.; Jackson, J.W.; Langston, M.A.; Juarez, P.D.; Sealy-Jefferson, S.; Lu, B.; Im, W.; Valdez, R.B.; Way, B.M.; et al. Structural and Social Determinants of Health Factors Associated with County-Level Variation in Non-Adherence to Antihypertensive Medication Treatment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6684. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17186684
Donneyong MM, Chang T-J, Jackson JW, Langston MA, Juarez PD, Sealy-Jefferson S, Lu B, Im W, Valdez RB, Way BM, et al. Structural and Social Determinants of Health Factors Associated with County-Level Variation in Non-Adherence to Antihypertensive Medication Treatment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(18):6684. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17186684
Chicago/Turabian StyleDonneyong, Macarius M., Teng-Jen Chang, John W. Jackson, Michael A. Langston, Paul D. Juarez, Shawnita Sealy-Jefferson, Bo Lu, Wansoo Im, R. Burciaga Valdez, Baldwin M. Way, and et al. 2020. "Structural and Social Determinants of Health Factors Associated with County-Level Variation in Non-Adherence to Antihypertensive Medication Treatment" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 18: 6684. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17186684
APA StyleDonneyong, M. M., Chang, T.-J., Jackson, J. W., Langston, M. A., Juarez, P. D., Sealy-Jefferson, S., Lu, B., Im, W., Valdez, R. B., Way, B. M., Colen, C., Fischer, M. A., Salsberry, P., Bridges, J. F. P., & Hood, D. B. (2020). Structural and Social Determinants of Health Factors Associated with County-Level Variation in Non-Adherence to Antihypertensive Medication Treatment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(18), 6684. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17186684









