Spatial Statistics and Influencing Factors of the COVID-19 Epidemic at Both Prefecture and County Levels in Hubei Province, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
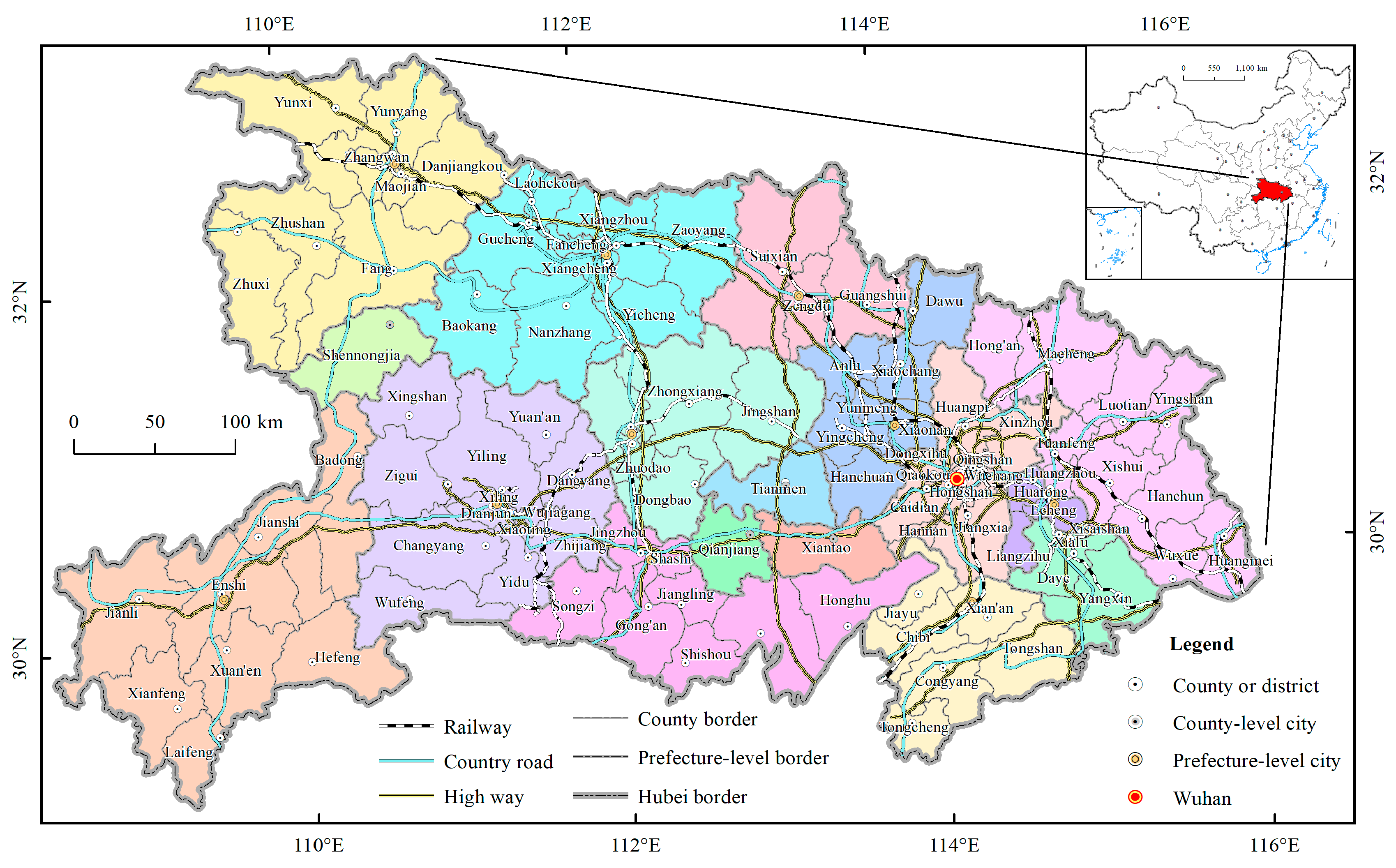
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Research Methods
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Statistics of the COVID-19 Epidemic
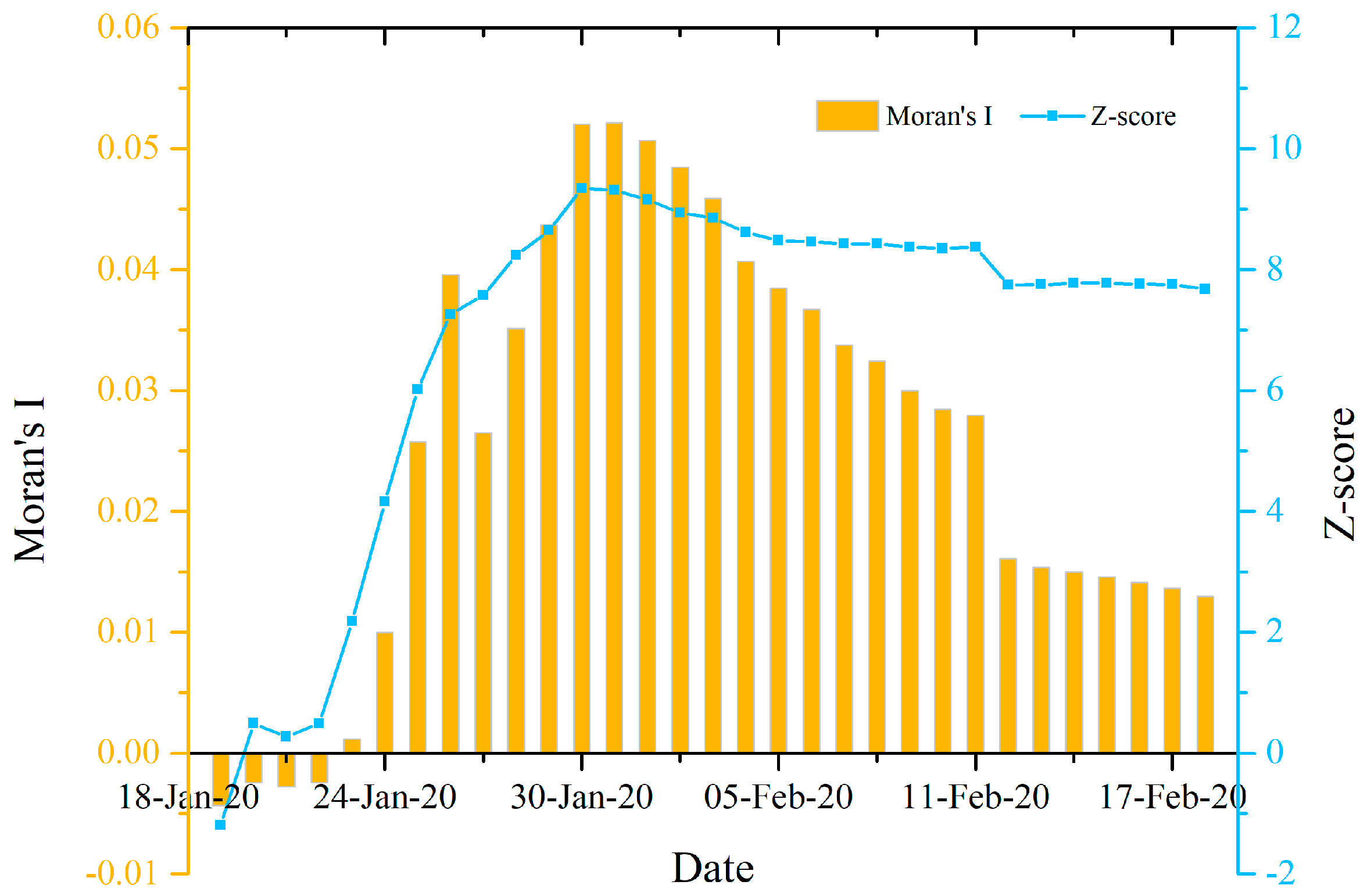
3.1.1. Spatial Autocorrelations of the Provincial COVID-19 Outbreaks Nationwide
3.1.2. Spatial Autocorrelations of the Prefecture Level COVID-19 Outbreaks Nationwide
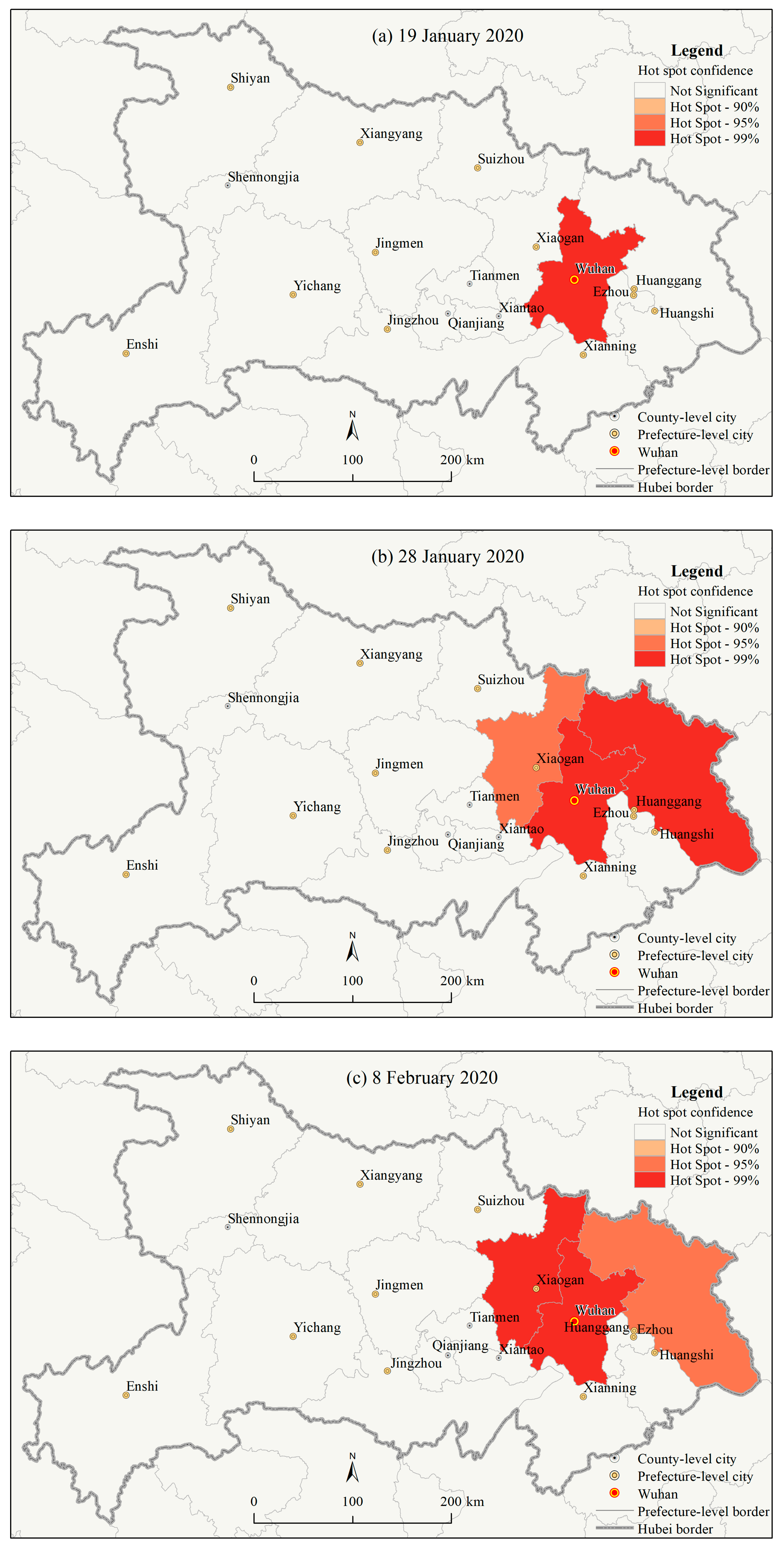
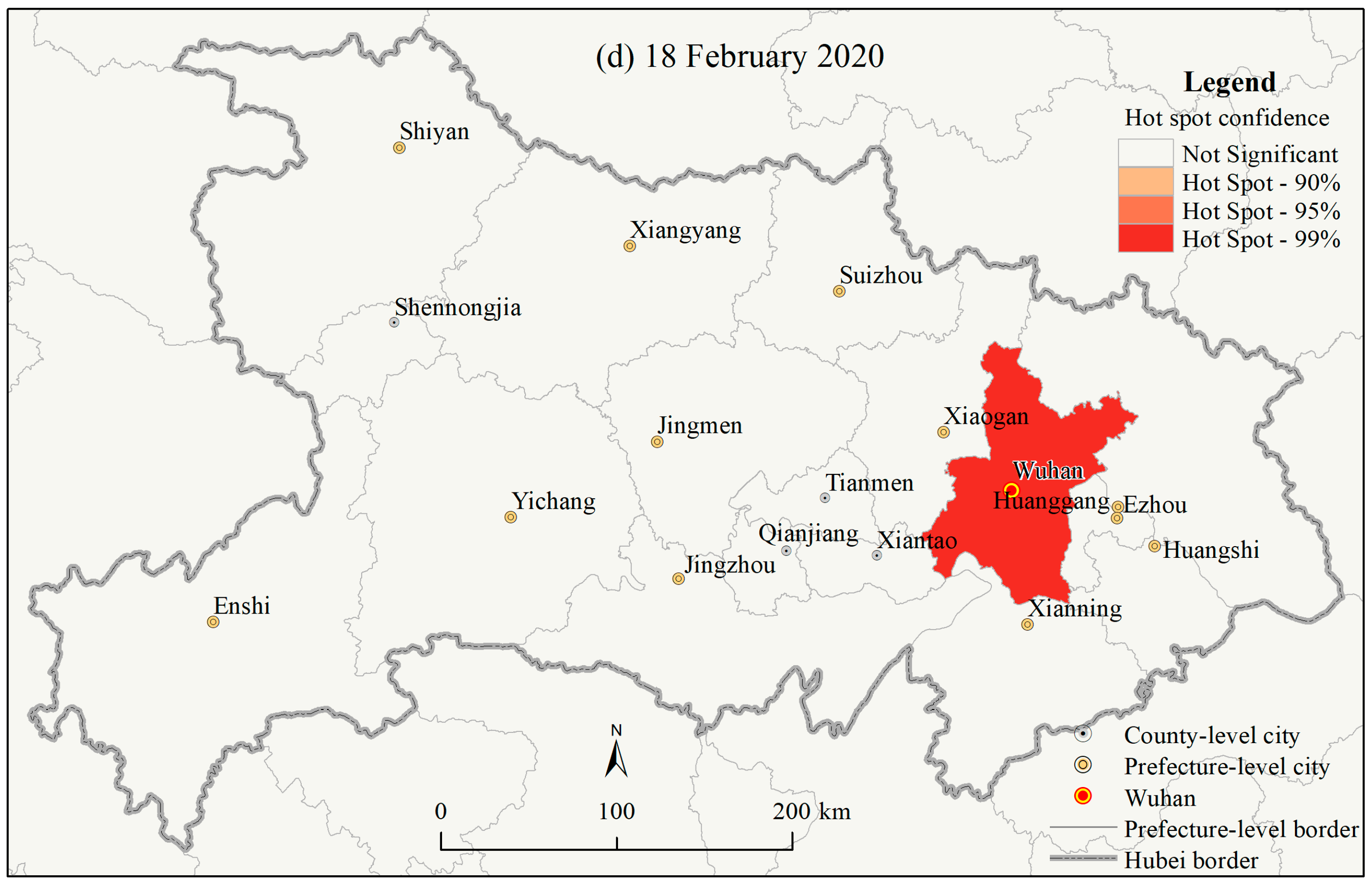
3.1.3. Spatial Autocorrelations of the County Level COVID-19 Outbreaks in Hubei Province
3.2. Influencing Factors of the COVID-19 Epidemic
3.2.1. Influencing Factors of the Prefecture Level COVID-19 Outbreaks in Hubei Province
3.2.2. Influencing Factors of the County Level COVID-19 Outbreaks in Hubei Province
4. Discussion
4.1. Geographic Risk Identification Based on the Spatial Statistics of the COVID-19 Epidemic
4.2. Potential Risk Factors of the COVID-19 Spread
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SARS | severe acute respiratory syndrome |
| SARS-CoV-2 | 2019 novel coronavirus |
| COVID-19 | novel coronavirus pneumonia 2019 (coronavirus disease 2019) |
| CCC | cumulative confirmed COVID-19 cases |
| DCC | daily new confirmed COVID-19 cases |
| LISA | Local Indicators of Spatial Association |
| ALMI | Anselin Local Moran’s I |
| LA | land area |
| PD | population density |
| RGP | registered population |
| RSP | resident population |
| BMI | Baidu migration index |
| GDP | gross domestic production |
| TRS | total retail sales of consumer goods |
| DEM | digital elevation model |
| MAXE | maximum elevation |
| MINE | minimum elevation |
| MNE | mean elevation |
| RAE | range of elevation |
References
- Guan, W.; Ni, Z.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.; Ou, C.; He, J.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Horby, P.W.; Hayden, F.G.; Gao, G.F. A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern. Lancet 2020, 395, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Update on the novel coronavirus pneumonia situation in China as of 24:00 2 April 2020. Available online: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/xcs/yqtb/202004/4786774c1fd84e16b29d872f95241561.shtml (accessed on 3 April 2020).
- Johns Hopkins University. The Johns Hopkins COVID-19 Map Dashboard. Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html (accessed on 3 April 2020).
- Editorial. Communication, collaboration, and cooperation can stop the 2019 coronavirus. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, X.; Wang, B.; Kang, Y. Novel coronavirus infection during the 2019–2020 epidemic: Preparing intensive care units—the experience in Sichuan Province, China. Intens. Care Med. 2020, 46, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Lin, Q.; Ran, J.; Musa, S.S.; Yang, G.; Wang, W.; Lou, Y.; Gao, D.; Yang, L.; He, D.; et al. Preliminary estimation of the basic reproduction number of novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in China, from 2019 to 2020: A data-driven analysis in the early phase of the outbreak. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 92, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forna, A.; Dorigatti, I.; Nouvellet, P.; Donnelly, C.A. Spatiotemporal variability in case fatality ratios for 2013–2016 Ebola epidemic in West Africa. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 93, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.W.; Tambyah, P.A.; Hui, D.S.C. Emergence of a novel coronavirus causing respiratory illness from Wuhan, China. J. Infection 2020, 80, 350–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Pathogenicity and transmissibility of 2019-nCoV—A quick overview and comparison with other emerging viruses. Microbes Infect. 2020, 22, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 549, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, P.; Wang, J.; Feng, J.; Zhou, H.; Li, X.; Zhong, W.; Hao, P. Evolution of the novel coronavirus from the ongoing Wuhan outbreak and modeling of its spike protein for risk of human transmission. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhou, M.; Dong, X.; Qu, J.; Gong, F.; Han, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet 2020, 395, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.F.; Yuan, S.; Kok, K.; To, K.K.; Chu, H.; Yang, J.; Xing, F.; Liu, J.; Yip, C.C.; Poon, R.W.; et al. A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: A study of a family cluster. Lancet 2020, 395, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, P.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhu, N.; et al. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 2020, 395, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Guo, D. Emerging coronaviruses: Genome structure, replication, and pathogenesis. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Huang, F.; Wang, F.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Feng, C.; et al. Clinical and biochemical indexes from 2019-nCoV infected patients linked to viral loads and lung injury. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wu, K.; Chen, M.; Shia, B.; Wu, S. Prediction of Number of Cases of 2019 Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) Using Social Media Search Index. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.T.; Leung, K.; Leung, G.M. Nowcasting and forecasting the potential domestic and international spread of the 2019-nCoV outbreak originating in Wuhan, China: A modelling study. Lancet 2020, 395, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollalo, A.; Vahedi, B.; Rivera, K.M. GIS-based spatial modeling of COVID-19 incidence rate in the continental United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinazzi, M.; Davis, J.T.; Ajelli, M.; Gioannini, C.; Litvinova, M.; Merler, S.; Pastore Y Piontti, A.; Mu, K.; Rossi, L.; Sun, K.; et al. The effect of travel restrictions on the spread of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak. Science 2020, 368, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Gong, J.; Sun, J.; Zhou, J. Exploring the epidemic transmission network of SARS in-out flow in mainland China. China Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Meng, B.; Liu, X. Spatial association analysis on epidemic of SARS in Beijing, 2003. J. Zhejiang Univ. (Agric. Life Sci.) 2005, 31, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Ying, L. An exploratory spatial data analysis of SARS epidemic in China. Adv. Earth Sci. 2005, 20, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Han, W.; Feng, X.; Zeng, G. Risk factors and autocorrelation characteristics on severe acute respiratory syndrome in Guangzhou. Acta Geogr. Sinica 2008, 63, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Chen, W.; Zheng, S.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Cao, W. Analysis of Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Pandemic SARS Spread in Mainland China. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Zeng, D.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. Spatio-temporal evolution of Beijing 2003 SARS epidemic. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2010, 40, 776–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Choi, H.; Kim, J.; Choi, J. Spatial epidemic dynamics of the COVID-19 outbreak in China. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Gong, J.; Zhou, J.; Sun, J.; Yang, L.; Xia, Y.; Ibrahim, A.N. Spatial-temporal characteristics of epidemic spread in-out flow—Using SARS epidemic in Beijing as a case study. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2013, 56, 1380–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Thilakavathy, K.; Kumar, S.S.; He, G.; Liu, S.V. Potential Factors Influencing Repeated SARS Outbreaks in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirouz, B.; Haghshenas, S.S.; Haghshenas, S.S.; Piro, P. Investigating a Serious Challenge in the Sustainable Development Process: Analysis of Confirmed cases of COVID-19 (New Type of Coronavirus) Through a Binary Classification Using Artificial Intelligence and Regression Analysis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, J.; Yao, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Xu, X.; He, X.; Wang, B.; Fu, S.; Niu, T.; et al. Impact of meteorological factors on the COVID-19 transmission: A multi-city study in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosepu, R.; Gunawan, J.; Effendy, D.S.; Ahmad, L.O.A.I.; Lestari, H.; Bahar, H.; Asfian, P. Correlation between weather and Covid-19 pandemic in Jakarta, Indonesia. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, H.; Wu, X.; Guo, X. Distribution of COVID-19 Morbidity Rate in Association with Social and Economic Factors in Wuhan, China: Implications for Urban Development. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Sha, D.; Liu, W.; Houser, P.; Zhang, L.; Hou, R.; Lan, H.; Flynn, C.; Lu, M.; Hu, T.; et al. Spatiotemporal Patterns of COVID-19 Impact on Human Activities and Environment in Mainland China Using Nighttime Light and Air Quality Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Shi, R. Spatial Distribution of the Population in Shandong Province at Multi-Scales. Prog. Geogr. 2012, 31, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, D. The spatial sprawl and driving mechanism of the floating population in Beijing metropolitan areas. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2019, 39, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, N.; Wu, W.; Wu, J. Evolution of spatial-temporal pattern of county economic development in China during 1982–2010. Prog. Geogr. 2014, 33, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Lin, N.H.; Lin, C.; King, C.; Su, M. Spatial mapping of temporal risk characteristics to improve environmental health risk identification: A case study of a dengue epidemic in Taiwan. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 367, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Huang, H. Analysis on the characteristics of gathering and spreading of major infectious diseases. Chinese J. Public Health 2010, 26, 1186–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, K.; Mu, X.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, N.; Fan, H.; Guo, L.; Huo, X. Spatio-Temporal Pattern and Influencing Factors of Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome (HFRS) in Hubei Province (China) between 2005 and 2014. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, R.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Tian, G.; Feng, Y. Impacts of urbanization on the urban thermal environment in Beijing. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 6040–6049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, P.A.P. Notes on Continuous Stochastic Phenomena. Biometrika 1950, 37, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anselin, L. Local Indicators of Spatial Association—LISA. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ord, K.; Getis, A. Local spatial autocorrelation statistics: Distributional issues and an application. Geogr. Anal. 2010, 27, 286–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, C.; Rosentreter, J.; Voltersen, M.; Baumgart, C.; Schmullius, C.; Hese, S. Spatio-temporal analysis of the relationship between 2D/3D urban site characteristics and land surface temperature. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 193, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lv, J.; Tan, Y.; Guo, M.; Gu, Y.; Xu, S.; Zhou, Y. Temporospatial variations and Spearman correlation analysis of ozone concentrations to nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, particulate matters and carbon monoxide in ambient air, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, S.; Amin, M.; Munir, B.A. Spatial mapping of temporal risk to improve prevention measures: A case study of dengue epidemic in Lahore. Spat. Spat. Temp. Epidemiol. 2017, 21, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Bi, J. Epidemic transition of environmental health risk during China’s urbanization. Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; Atkinson, P.M. Identifying the spatio-temporal risk variability of avian influenza A H7N9 in China. Ecol. Model. 2019, 414, 108807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Tong, Y.; Hu, S.; Ke, Y. Measurement of Intercity Interaction among Wuhan urban clusters. Urban Probl. 2017, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Chen, M. Study on Urban Economic Relations and Regional Economic Development in Hubei Province. Stat. Decis. 2018, 34, 127–130. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, H.; Huang, J. Dynamic development of Wuhan metropolitan area based on urban connection. Planners 2017, 33, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Heymann, D.L. Data sharing and outbreaks: Best practice exemplified. Lancet 2020, 395, 469–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Kraemer, M.U.G.; Xu, B.; Gutierrez, B.; Mekaru, S.; Sewalk, K.; Loskill, A.; Wang, L.; Cohn, E.; Hill, S.; et al. Open access epidemiological data from the COVID-19 outbreak. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

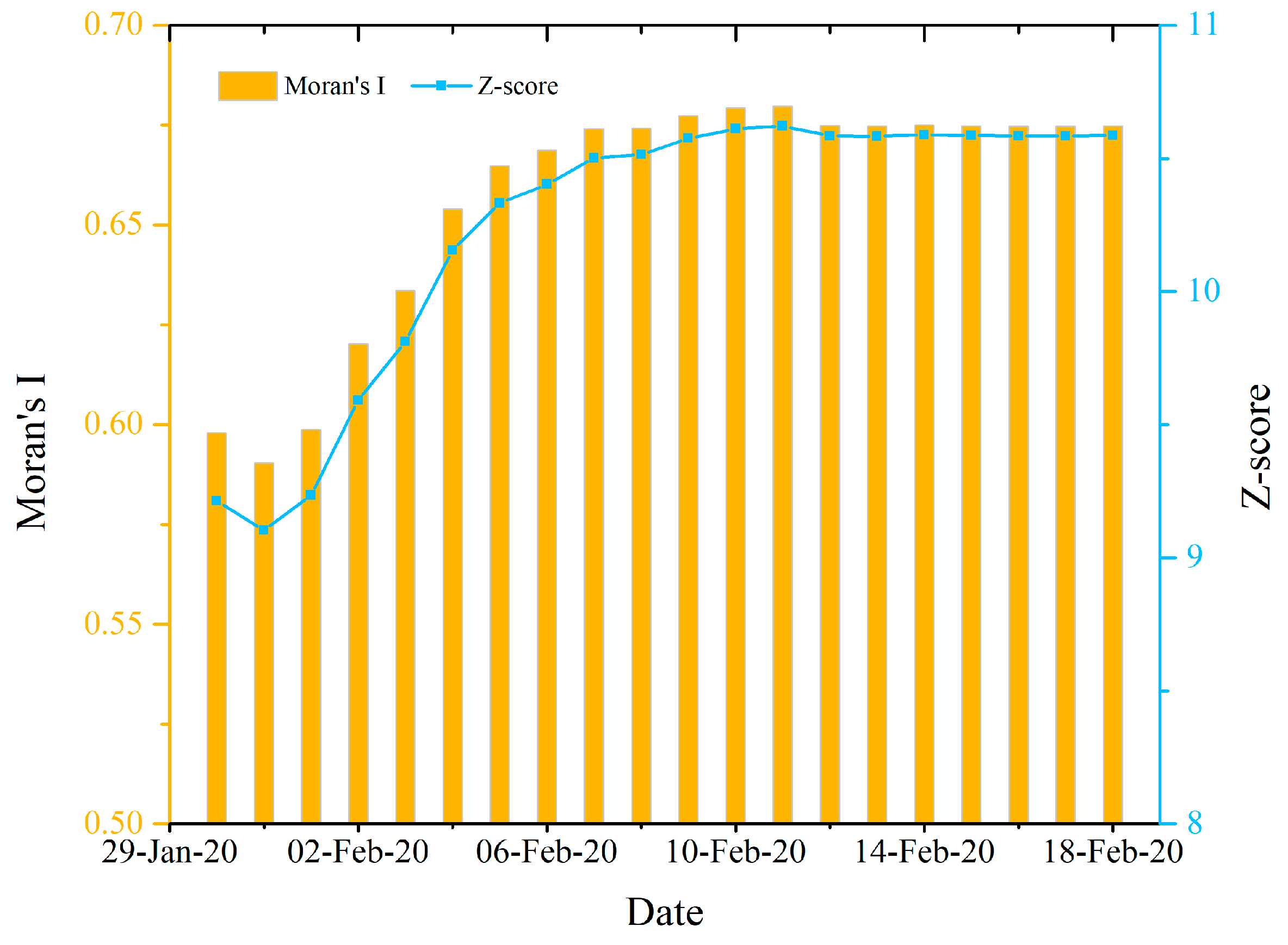
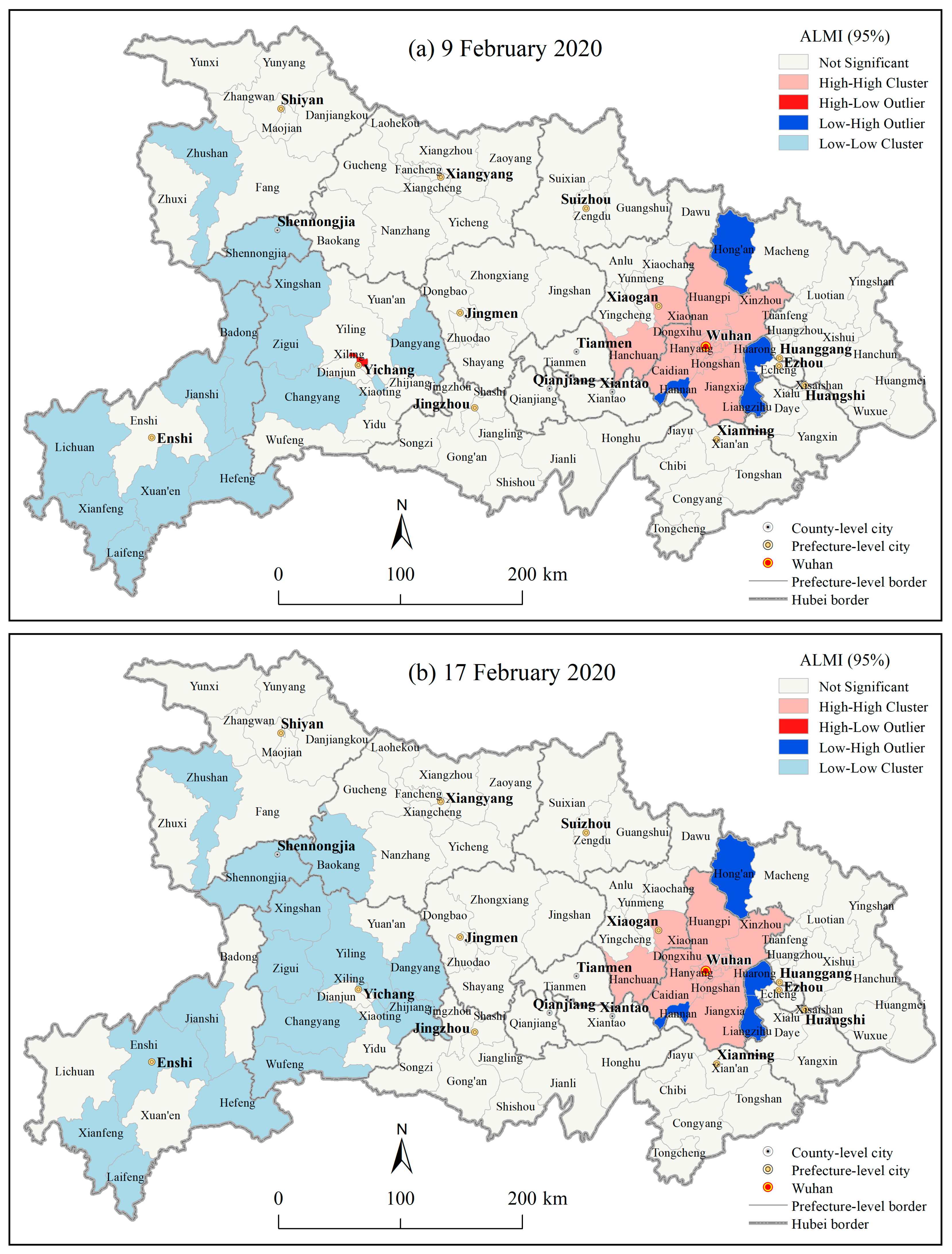
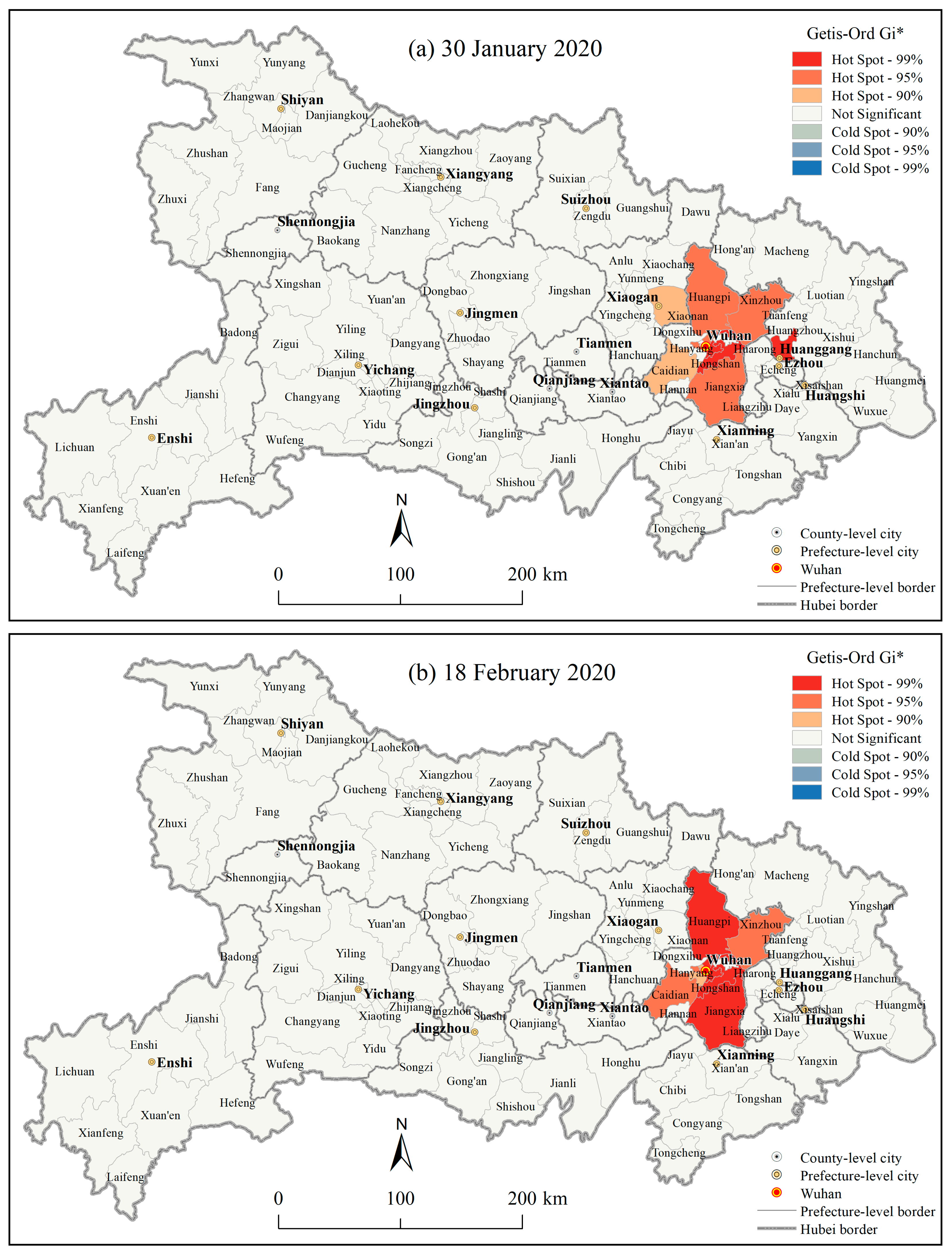
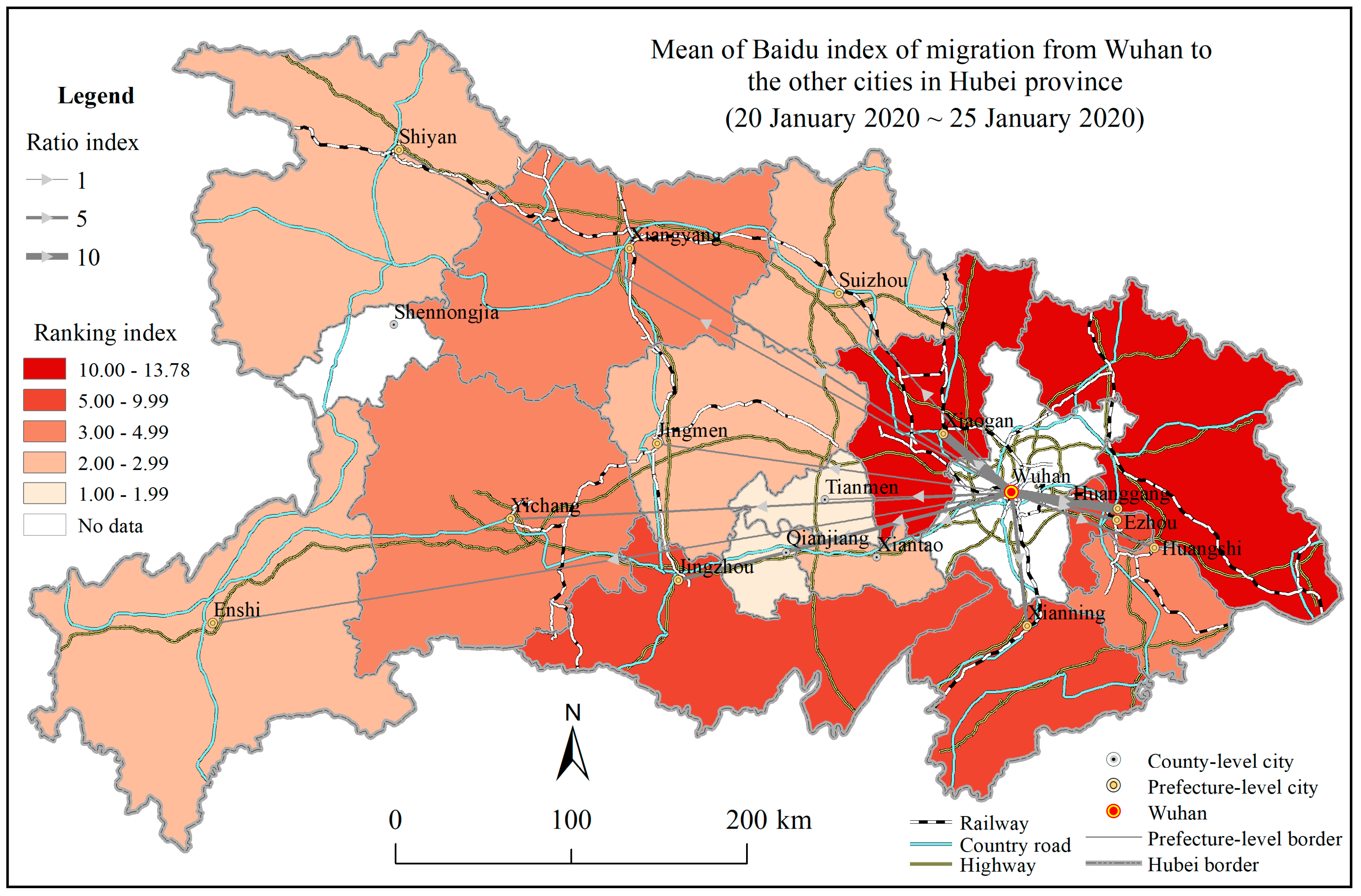
| Indicator | MINE | MAXE | MNE | RAE | LA | PD | RGP | RSP | TRS | GDP | BMI | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCC0123 | −0.508 * | −0.084 | −0.185 | −0.097 | 0.218 | 0.231 | 0.640 ** | 0.647 ** | 0.555 * | 0.608 ** | 0.579 * | |||||||||
| CCC0124 | −0.321 | 0.021 | −0.067 | 0.018 | 0.328 | 0.123 | 0.650 ** | 0.605 * | 0.411 | 0.418 | 0.460 | |||||||||
| CCC0125 | −0.568 * | 0.082 | 0.039 | 0.076 | 0.375 | 0.158 | 0.712 ** | 0.702 ** | 0.622 ** | 0.654 ** | 0.586 * | |||||||||
| CCC0126 | −0.515 * | 0.113 | 0.075 | 0.104 | 0.417 | 0.169 | 0.757 ** | 0.765 ** | 0.689 ** | 0.737 ** | 0.602 * | |||||||||
| CCC0127 | −0.531 * | 0.045 | −0.006 | 0.037 | 0.347 | 0.254 | 0.753 ** | 0.764 ** | 0.699 ** | 0.766 ** | 0.704 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0128 | −0.451 | 0.088 | 0.049 | 0.074 | 0.373 | 0.238 | 0.755 ** | 0.782 ** | 0.725 ** | 0.784 ** | 0.607 * | |||||||||
| CCC0129 | −0.468 | 0.047 | −0.005 | 0.034 | 0.355 | 0.267 | 0.772 ** | 0.797 ** | 0.750 ** | 0.819 ** | 0.679 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0130 | −0.473 | −0.025 | −0.061 | −0.044 | 0.248 | 0.368 | 0.711 ** | 0.745 ** | 0.748 ** | 0.811 ** | 0.654 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0131 | −0.468 | 0.022 | −0.017 | −0.002 | 0.316 | 0.319 | 0.765 ** | 0.799 ** | 0.811 ** | 0.865 ** | 0.668 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0201 | −0.456 | 0.042 | 0.002 | 0.015 | 0.324 | 0.304 | 0.755 ** | 0.794 ** | 0.814 ** | 0.868 ** | 0.650 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0202 | −0.527 * | −0.012 | −0.054 | −0.032 | 0.304 | 0.350 | 0.779 ** | 0.816 ** | 0.831 ** | 0.882 ** | 0.682 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0203 | −0.505 * | 0.034 | 0.005 | 0.010 | 0.326 | 0.304 | 0.767 ** | 0.794 ** | 0.806 ** | 0.850 ** | 0.661 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0204 | −0.551 * | 0.015 | −0.022 | 0.000 | 0.324 | 0.348 | 0.799 ** | 0.824 ** | 0.838 ** | 0.875 ** | 0.725 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0205 | −0.522 * | −0.027 | −0.051 | −0.051 | 0.265 | 0.370 | 0.738 ** | 0.760 ** | 0.782 ** | 0.824 ** | 0.675 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0206 | −0.534 * | −0.059 | −0.083 | −0.086 | 0.233 | 0.395 | 0.721 ** | 0.748 ** | 0.770 ** | 0.816 ** | 0.657 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0207 | −0.534 * | −0.059 | −0.083 | −0.086 | 0.233 | 0.395 | 0.721 ** | 0.748 ** | 0.770 ** | 0.816 ** | 0.657 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0208 | −0.561 * | −0.074 | −0.108 | −0.096 | 0.228 | 0.439 | 0.750 ** | 0.775 ** | 0.804 ** | 0.843 ** | 0.732 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0209 | −0.529 * | −0.071 | −0.096 | −0.100 | 0.208 | 0.419 | 0.708 ** | 0.733 ** | 0.760 ** | 0.804 ** | 0.675 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0210 | −0.527 * | −0.096 | −0.120 | −0.125 | 0.174 | 0.449 | 0.689 ** | 0.711 ** | 0.735 ** | 0.782 ** | 0.686 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0211 | −0.498 * | −0.086 | −0.110 | −0.115 | 0.189 | 0.436 | 0.691 ** | 0.718 ** | 0.745 ** | 0.787 ** | 0.657 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0212 | −0.529 * | −0.120 | −0.154 | −0.145 | 0.172 | 0.451 | 0.696 ** | 0.718 ** | 0.725 ** | 0.787 ** | 0.704 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0213 | −0.554 * | −0.147 | −0.179 | −0.172 | 0.127 | 0.490 * | 0.667 ** | 0.684 ** | 0.701 ** | 0.757 ** | 0.725 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0214 | −0.551 * | −0.135 | −0.167 | −0.162 | 0.137 | 0.485 * | 0.674 ** | 0.691 ** | 0.716 ** | 0.767 ** | 0.732 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0215 | −0.554 * | −0.147 | −0.179 | −0.172 | 0.127 | 0.490 * | 0.667 ** | 0.684 ** | 0.701 ** | 0.757 ** | 0.725 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0216 | −0.569 * | −0.162 | −0.199 | −0.184 | 0.108 | 0.517 * | 0.659 ** | 0.676 ** | 0.699 ** | 0.755 ** | 0.754 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0217 | −0.566 * | −0.150 | −0.186 | −0.174 | 0.118 | 0.512 * | 0.667 ** | 0.684 ** | 0.713 ** | 0.765 ** | 0.761 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0218 | −0.566 * | −0.150 | −0.186 | −0.174 | 0.118 | 0.512 * | 0.667 ** | 0.684 ** | 0.713 ** | 0.765 ** | 0.761 ** | |||||||||
| tMean | −0.539 * | −0.113 | −0.145 | −0.140 | 0.169 | 0.466 | 0.701 ** | 0.721 ** | 0.743 ** | 0.792 ** | 0.725 ** | |||||||||
| N5 | NES | NS | NM | NW | None | PW | PM | PS | PES | P5 | ||||||||||
| p < 0.05 | −1~−0.8 | −0.8~−0.6 | −0.6~−0.4 | −0.4~−0.2 | −0.2~0.2 | 0.2~0.4 | 0.4~0.6 | 0.6~0.8 | 0.8~1 | p < 0.05 | ||||||||||
| Indicator | MINE | MAXE | MNE | RAE | LA | PD | RGP | RSP | TRS | GDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCC0126 | −0.314 * | −0.477 ** | −0.513 ** | −0.478 ** | −0.289 * | 0.482 ** | 0.257 * | 0.286 * | 0.449 ** | 0.290 * |
| CCC0127 | −0.287 * | −0.537 ** | −0.523 ** | −0.529 ** | −0.150 | 0.424 ** | 0.344 ** | 0.386 ** | 0.470 ** | 0.331 ** |
| CCC0128 | −0.321 ** | −0.483 ** | −0.484 ** | −0.482 ** | −0.179 | 0.499 ** | 0.466 ** | 0.508 ** | 0.591 ** | 0.488 ** |
| CCC0129 | −0.326 ** | −0.491 ** | −0.494 ** | −0.489 ** | −0.145 | 0.526 ** | 0.529 ** | 0.575 ** | 0.648 ** | 0.538 ** |
| CCC0130 | −0.354 ** | −0.537 ** | −0.534 ** | −0.535 ** | −0.221 * | 0.583 ** | 0.499 ** | 0.583 ** | 0.705 ** | 0.633 ** |
| CCC0131 | −0.372 ** | −0.557 ** | −0.544 ** | −0.556 ** | −0.266 * | 0.613 ** | 0.465 ** | 0.552 ** | 0.704 ** | 0.622 ** |
| CCC0201 | −0.406 ** | −0.532 ** | −0.552 ** | −0.526 ** | −0.254 * | 0.618 ** | 0.494 ** | 0.578 ** | 0.705 ** | 0.609 ** |
| CCC0202 | −0.456 ** | −0.570 ** | −0.601 ** | −0.561 ** | −0.276 ** | 0.657 ** | 0.530 ** | 0.613 ** | 0.706 ** | 0.597 ** |
| CCC0203 | −0.488 ** | −0.589 ** | −0.628 ** | −0.577 ** | −0.277 ** | 0.664 ** | 0.547 ** | 0.630 ** | 0.712 ** | 0.606 ** |
| CCC0204 | −0.502 ** | −0.603 ** | −0.640 ** | −0.590 ** | −0.305 ** | 0.691 ** | 0.545 ** | 0.626 ** | 0.699 ** | 0.586 ** |
| CCC0205 | −0.509 ** | −0.611 ** | −0.649 ** | −0.598 ** | −0.311 ** | 0.695 ** | 0.543 ** | 0.624 ** | 0.696 ** | 0.589 ** |
| CCC0206 | −0.511 ** | −0.614 ** | −0.651 ** | −0.600 ** | −0.293 ** | 0.689 ** | 0.553 ** | 0.634 ** | 0.694 ** | 0.584 ** |
| CCC0207 | −0.517 ** | −0.624 ** | −0.665 ** | −0.610 ** | −0.297 ** | 0.696 ** | 0.553 ** | 0.635 ** | 0.703 ** | 0.584 ** |
| CCC0208 | −0.519 ** | −0.631 ** | −0.669 ** | −0.617 ** | −0.299 ** | 0.700 ** | 0.554 ** | 0.638 ** | 0.705 ** | 0.584 ** |
| CCC0209 | −0.520 ** | −0.632 ** | −0.668 ** | −0.619 ** | −0.299 ** | 0.703 ** | 0.554 ** | 0.636 ** | 0.696 ** | 0.571 ** |
| CCC0210 | −0.518 ** | −0.633 ** | −0.668 ** | −0.619 ** | −0.295 ** | 0.700 ** | 0.551 ** | 0.632 ** | 0.697 ** | 0.566 ** |
| CCC0211 | −0.522 ** | −0.642 ** | −0.679 ** | −0.629 ** | −0.292 ** | 0.706 ** | 0.561 ** | 0.642 ** | 0.705 ** | 0.570 ** |
| CCC0212 | −0.525 ** | −0.646 ** | −0.680 ** | −0.634 ** | −0.269 * | 0.689 ** | 0.570 ** | 0.650 ** | 0.705 ** | 0.577 ** |
| CCC0213 | −0.528 ** | −0.632 ** | −0.677 ** | −0.620 ** | −0.284 ** | 0.694 ** | 0.575 ** | 0.648 ** | 0.694 ** | 0.560 ** |
| CCC0214 | −0.533 ** | −0.635 ** | −0.683 ** | −0.622 ** | −0.283 ** | 0.690 ** | 0.570 ** | 0.642 ** | 0.696 ** | 0.559 ** |
| CCC0215 | −0.534 ** | −0.640 ** | −0.687 ** | −0.627 ** | −0.277 ** | 0.689 ** | 0.580 ** | 0.653 ** | 0.704 ** | 0.567 ** |
| CCC0216 | −0.532 ** | −0.646 ** | −0.690 ** | −0.632 ** | −0.277 ** | 0.690 ** | 0.579 ** | 0.651 ** | 0.704 ** | 0.569 ** |
| CCC0217 | −0.530 ** | −0.650 ** | −0.693 ** | −0.636 ** | −0.276 ** | 0.690 ** | 0.580 ** | 0.652 ** | 0.710 ** | 0.574 ** |
| CCC0218 | −0.525 ** | −0.650 ** | −0.690 ** | −0.638 ** | −0.275 ** | 0.688 ** | 0.574 ** | 0.649 ** | 0.708 ** | 0.572 ** |
| tMean | −0.515 ** | −0.638 ** | −0.677 ** | −0.626 ** | −0.290 ** | 0.702 ** | 0.562 ** | 0.645 ** | 0.720 ** | 0.587 ** |
| N5 | NES | NS | NM | NW | None | PW | PM | PS | PES | P5 |
| p < 0.05 | −1~−0.8 | −0.8~−0.6 | −0.6~−0.4 | −0.4~−0.2 | −0.2~0.2 | 0.2~0.4 | 0.4~0.6 | 0.6~0.8 | 0.8~1 | p < 0.05 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhu, M. Spatial Statistics and Influencing Factors of the COVID-19 Epidemic at Both Prefecture and County Levels in Hubei Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3903. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17113903
Xiong Y, Wang Y, Chen F, Zhu M. Spatial Statistics and Influencing Factors of the COVID-19 Epidemic at Both Prefecture and County Levels in Hubei Province, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(11):3903. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17113903
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Yongzhu, Yunpeng Wang, Feng Chen, and Mingyong Zhu. 2020. "Spatial Statistics and Influencing Factors of the COVID-19 Epidemic at Both Prefecture and County Levels in Hubei Province, China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 11: 3903. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17113903
APA StyleXiong, Y., Wang, Y., Chen, F., & Zhu, M. (2020). Spatial Statistics and Influencing Factors of the COVID-19 Epidemic at Both Prefecture and County Levels in Hubei Province, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(11), 3903. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17113903






