Association between Ambient Particulate Matter 2.5 Exposure and Mortality in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Determination of Ambient PM2.5 Concentrations
2.4. Diagnosis of HCC
2.5. Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Staging
Follow-Up
2.6. Statistical Analysis
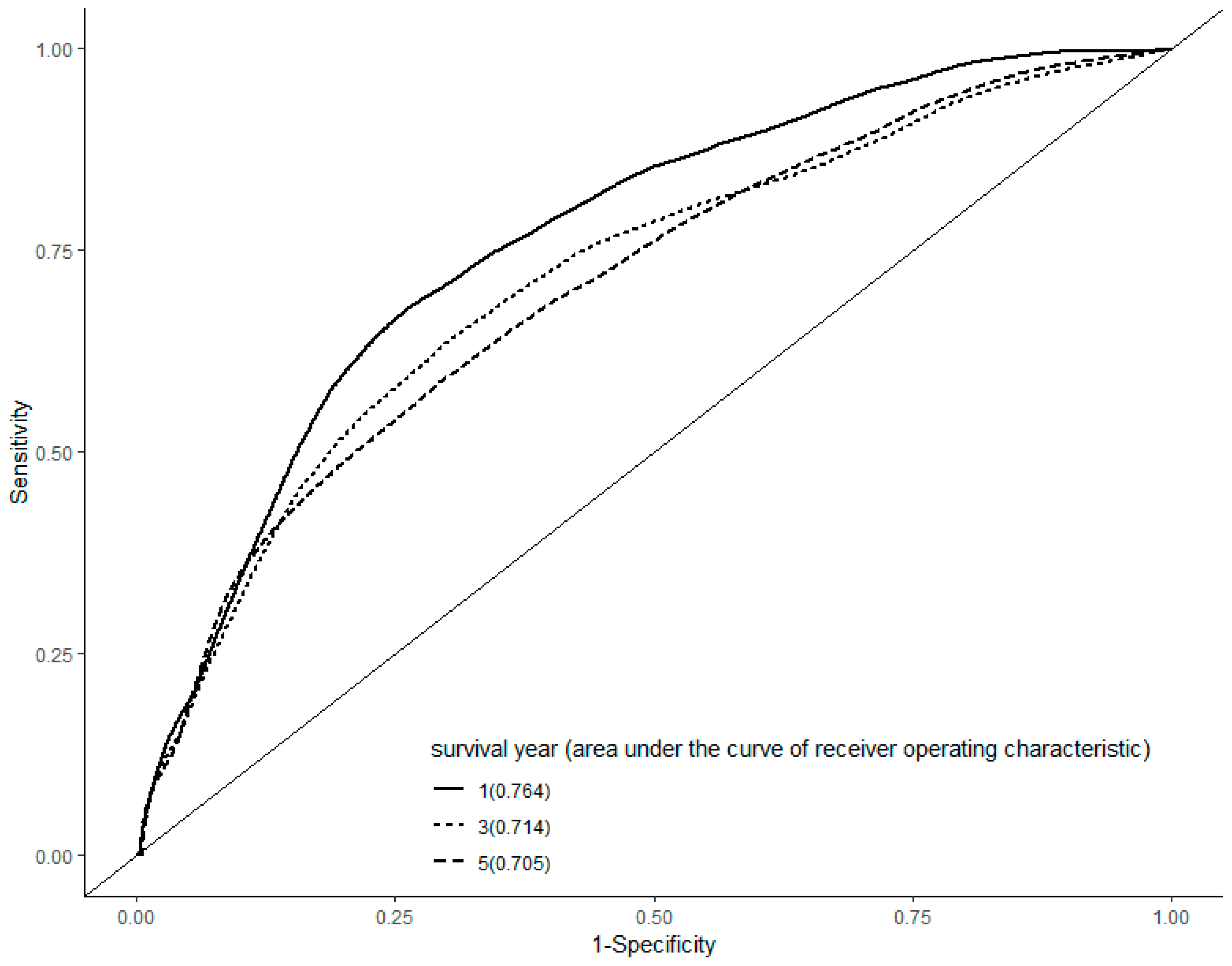
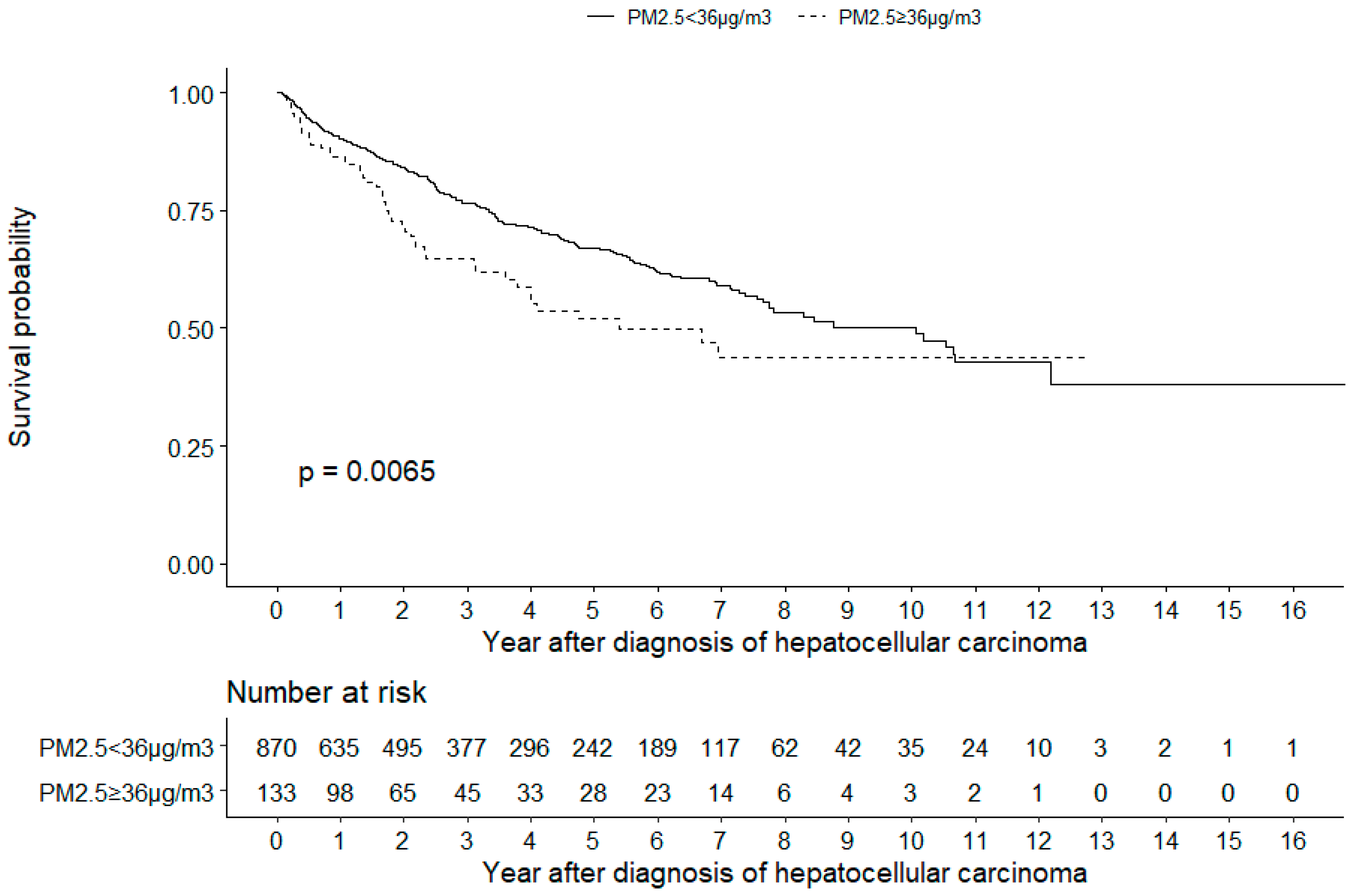
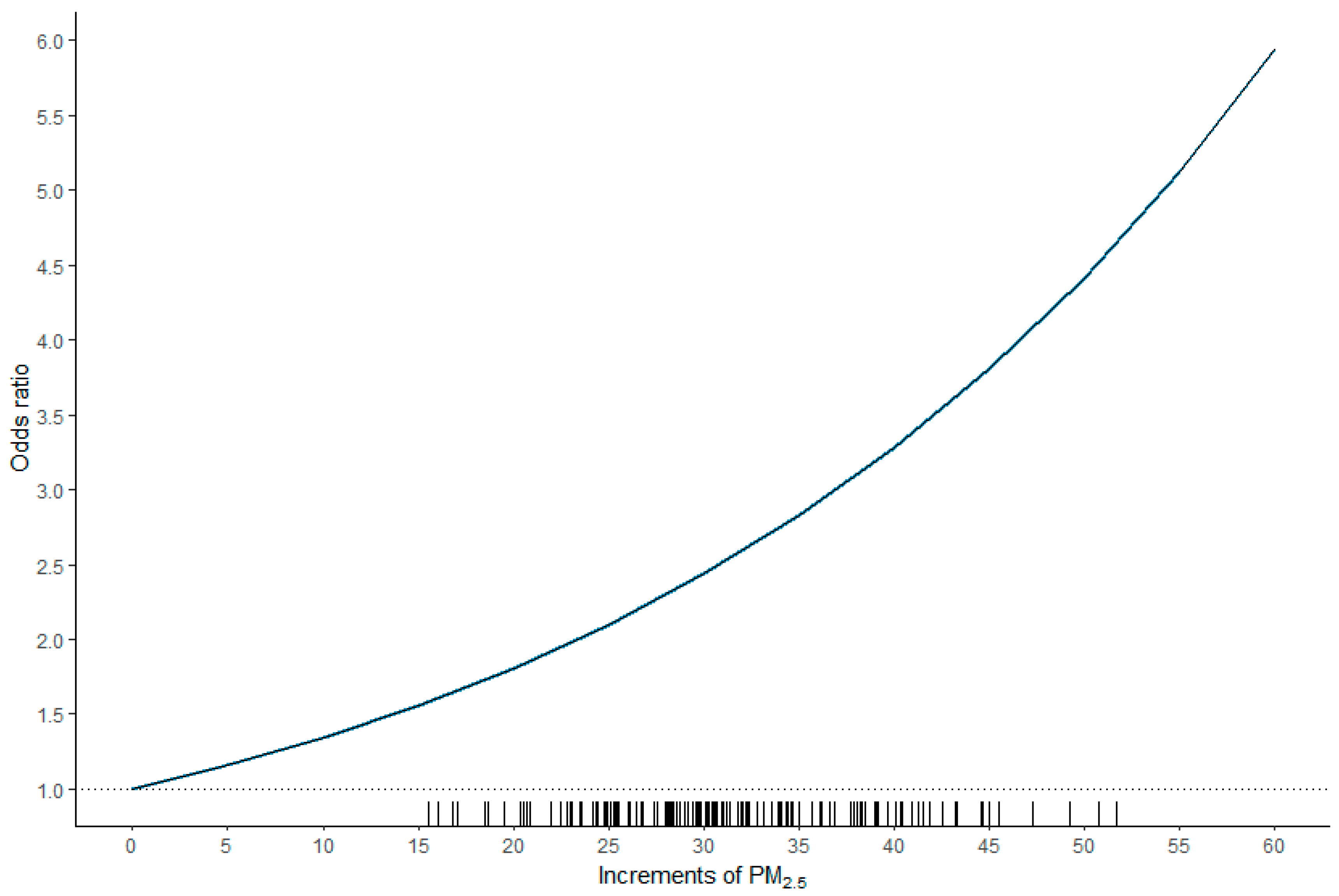
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loomis, D.; Grosse, Y.; Lauby-Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Bouvard, V.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Guha, N.; Baan, R.; Mattock, H.; Straif, K. International Agency for Research on Cancer Monograph Working Group, I., The carcinogenicity of outdoor air pollution. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 1262–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.A., 3rd; Burnett, R.T.; Thun, M.J.; Calle, E.E.; Krewski, D.; Ito, K.; Thurston, G.D. Lung cancer, cardiopulmonary mortality and long-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution. JAMA 2002, 287, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.M.; Tsang, H.; Lai, H.K.; Thomas, G.N.; Lam, K.B.; Chan, K.P.; Zheng, Q.; Ayres, J.G.; Lee, S.Y.; Lam, T.H.; et al. Cancer Mortality Risks from Long-term Exposure to Ambient Fine Particle. Cancer Epidemiol. Prev. Biomark. 2016, 25, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, W.C.; Wu, C.D.; Chen, M.J.; Huang, Y.T.; Chen, C.J.; Su, H.J.; Yang, H.I. Fine Particle Pollution, Alanine Transaminase, and Liver Cancer: A Taiwanese Prospective Cohort Study (REVEAL-HBV). J. Natl. Cancer. Inst. 2016, 108, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, M.; Andersen, Z.J.; Stafoggia, M.; Weinmayr, G.; Galassi, C.; Sorensen, M.; Eriksen, K.T.; Tjonneland, A.; Loft, S.; Jaensch, A.; et al. Ambient air pollution and primary liver cancer incidence in four European cohorts within the ESCAPE project. Environ. Res. 2017, 154, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Eckel, S.P.; Liu, L.; Lurmann, F.W.; Cockburn, M.G.; Gilliland, F.D. Particulate matter air pollution and liver cancer survival. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VoPham, T.; Bertrand, K.A.; Tamimi, R.M.; Laden, F.; Hart, J.E. Ambient PM2.5 air pollution exposure and hepatocellular carcinoma incidence in the United States. Cancer Causes Control. 2018, 29, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Luo, Q.; Yuan, X.; Chai, L.; Li, D.; Liu, J.; Lv, Z. Atmospheric particulate matter2.5 promotes the migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 3445–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mehta, M.; Chen, L.C.; Gordon, T.; Rom, W.; Tang, M.S. Particulate matter inhibits DNA repair and enhances mutagenesis. Mutat. Res. 2008, 657, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Hsieh, S.Y.; Chang, C.C.; Wang, I.K.; Huang, W.H.; Weng, C.H.; Hsu, C.W.; Yen, T.H. Hepatocellular carcinoma in hemodialysis patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 73154–73161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, C.H.; Chang, C.J.; Lin, Y.J.; Yen, C.L.; Shen, C.H.; Cheng, Y.T.; Lin, C.C.; Hsieh, S.Y. Nomogram predicting extrahepatic metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma based on commonly available clinical data. JGH Open 2019, 3, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taiwan Air Quality Monitoring Newwork. Available online: https://taqm.epa.gov.tw/taqm/en/YearlyDataDownload.aspx (accessed on 12 July 2019).
- Shiina, S.; Tateishi, R.; Imamura, M.; Teratani, T.; Koike, Y.; Sato, S.; Obi, S.; Kanai, F.; Kato, N.; Yoshida, H.; et al. Percutaneous ethanol injection for hepatocellular carcinoma: 20-year outcome and prognostic factors. Liver Int. 2012, 32, 1434–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruix, J.; Sherman, M. American Association for the Study of Liver, D., Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1020–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Bru, C.; Bruix, J. Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: The BCLC staging classification. Semin Liver Dis. 1999, 19, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risom, L.; Moller, P.; Loft, S. Oxidative stress-induced DNA damage by particulate air pollution. Mutat. Res. 2005, 592, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Balkwill, F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Qi, X.; Guo, X. Child-Pugh Versus MELD Score for the Assessment of Prognosis in Liver Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Medicine 2016, 95, e2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Wei, M.; Qiu, H.; Wu, J.; Liu, B.; Lyu, A.; Liu, Q.; Li, C.; Leng, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. A scoring system for prediction of early recurrence after liver resection for Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage B hepatocellular carcinoma. Chin. Med. J. (Engl.) 2014, 127, 4171–4176. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.K.; Song, S.K.; Kim, B.W.; Park, S.K.; Chung, C.W.; Wang, H.J. Prognostic significance of microvascular invasion in tumor stage for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 15, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, W.M.; Wu, M.C. Small hepatocellular carcinoma: Current and future approaches. Hepatol. Int. 2013, 7, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.Y.; Xi, T.; Lau, W.Y.; Dong, H.; Xian, Z.H.; Yu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Shen, F.; Wu, M.C.; Cong, W.M. Pathobiological features of small hepatocellular carcinoma: Correlation between tumor size and biological behavior. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 137, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asaoka, Y.; Tateishi, R.; Nakagomi, R.; Kondo, M.; Fujiwara, N.; Minami, T.; Sato, M.; Uchino, K.; Enooku, K.; Nakagawa, H.; et al. Frequency of and predictive factors for vascular invasion after radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montasser, M.F.; Shaker, M.K.; Albreedy, A.M.; Montasser, I.F.; El Dorry, A. Risk factors for early intrahepatic distant recurrence after radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma in Egyptian patients. J. Dig. Dis. 2014, 15, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, W.H.; Cheung, T.T. Bridging and downstaging therapy in patients suffering from hepatocellular carcinoma waiting on the list of liver transplantation. Transl. Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016, 1, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study | Year | Geographic Area | HCC Cases | Air Pollution | Health Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pan et al. [4] | 2016 | Taiwan | 464 | PM2.5 | Increased incidence of HCC |
| Pedersen et al. [5] | 2017 | Denmark, Austria and Italy | 279 | Nitrogen oxides, particulate matters | Increased incidence of HCC |
| Deng H et al. [6] | 2017 | USA | 20,221 | PM2.5 | Increased mortality of HCC |
| VoPham et al. [7] | 2018 | USA | 56,245 | PM2.5 | Increased incidence of HCC |
| Current study | 2019 | Taiwan | 1003 | PM2.5 | Increased mortality of HCC |
| Variable | Total (N = 1003) | PM2.5 < 36 µg/m3 (N = 870) | PM2.5 ≥ 36µg/m3 (N = 133) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 61.05 (12.07) | 61.22 (12.02) | 59.89 (12.36) | 0.235 |
| Male gender | 732 (73.0) | 631 (72.5) | 101 (75.9) | 0.471 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 249 (24.8) | 219 (25.2) | 30 (22.6) | 0.587 |
| Hypertension | 245 (24.4) | 212 (24.4) | 33 (24.8) | 0.998 |
| Hepatitis B virus surface antigen | 565 (56.3) | 483 (55.5) | 82 (61.7) | 0.217 |
| Antibodies to hepatitis C virus | 387 (38.6) | 334 (38.4) | 53 (39.8) | 0.821 |
| Alcoholic consumption | 157 (15.7) | 138 (15.9) | 19 (14.3) | 0.735 |
| Tumor number | 1.94 (1.46) | 1.96 (1.48) | 1.81 (1.33) | 0.245 |
| Tumor size (cm) | 4.41 (3.40) | 4.39 (3.41) | 4.54 (3.33) | 0.637 |
| Tumor, node, metastases staging | 0.253 | |||
| Stage 0 | 136 (13.6) | 124 (14.3) | 12 (9.0) | |
| Stage 1 | 402 (40.1) | 346 (39.8) | 56 (42.1) | |
| Stage 2 | 307 (30.6) | 268 (30.8) | 39 (29.3) | |
| Stage 3 | 143 (14.3) | 118 (13.6) | 25 (18.8) | |
| Stage 4 | 15 (1.5) | 14 (1.6) | 1 (0.8) | |
| Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer staging | 0.492 | |||
| Stage 0 | 140 (14.0) | 123 (14.1) | 17 (12.8) | |
| Stage A | 342 (34.1) | 302 (34.7) | 40 (30.1) | |
| Stage B | 328 (32.7) | 279 (32.1) | 49 (36.8) | |
| Stage C | 147 (14.7) | 129 (14.8) | 18 (13.5) | |
| Stage D | 46 (4.6) | 37 (4.3) | 9 (6.8) | |
| Child-Pugh score | 0.24 | |||
| Child 0 | 287 (28.6) | 249 (28.6) | 38 (28.6) | |
| Child A | 496 (49.5) | 437 (50.2) | 59 (44.4) | |
| Child B | 169 (16.8) | 144 (16.6) | 25 (18.8) | |
| Child C | 51 (5.1) | 40 (4.6) | 11 (8.3) | |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (IU/L) | 76.78 (91.83) | 75.23 (87.67) | 86.93 (115.30) | 0.171 |
| Alanine aminotransferase (IU/L) | 68.64 (94.19) | 68.13 (86.50) | 71.98 (134.46) | 0.66 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 1.51 (2.25) | 1.50 (2.22) | 1.58 (2.44) | 0.702 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.70 (3.08) | 3.61 (0.64) | 4.30 (8.30) | 0.017 * |
| Alkaline phosphatase (U/L) | 121.21 (89.32) | 120.74 (91.72) | 124.28 (71.87) | 0.671 |
| Blood urea nitrogen (mg/dL) | 18.60 (16.23) | 18.65 (16.96) | 18.33 (10.36) | 0.834 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.36 (1.64) | 1.37 (1.69) | 1.31 (1.24) | 0.703 |
| Sodium (meq/L) | 140.57 (42.22) | 140.67 (45.13) | 139.92 (10.97) | 0.849 |
| White Blood Cell (1000/μL) | 4.65 (2.39) | 4.65 (2.39) | 4.65 (2.39) | 0.394 |
| Hemogloblin (mg/dL) | 12.19 (2.44) | 12.18 (2.48) | 12.26 (2.18) | 0.718 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 36.38 (7.03) | 36.35 (7.14) | 36.61 (6.27) | 0.687 |
| Platelet (103/μL) | 144.31 (85.00) | 142.18 (80.07) | 158.19 (111.41) | 0.043 * |
| Prolong prothrombin time (second) | 2.23 (4.87) | 2.17 (4.01) | 2.63 (8.57) | 0.31 |
| Alpha fetoprotein (ng/mL) | 8332.45 (82,445.91) | 9452.76 (88,468.89) | 1004.17 (3072.30) | 0.271 |
| First treatment method | 0.604 | |||
| Transarterial chemoembolization | 444 (44.3) | 378 (43.4) | 66 (49.6) | |
| Radiofrequency ablation | 152 (15.2) | 136 (15.6) | 16 (12.0) | |
| Resection | 260 (25.9) | 225 (25.9) | 35 (26.3) | |
| Supportive | 108 (10.8) | 96 (11.0) | 12 (9.0) | |
| Radiotherapy or Chemotherapy | 39 (3.9) | 35 (4.0) | 4 (3.0) | |
| Macrovascular invasion | 135 (13.5) | 118 (13.6) | 17 (12.8) | 0.913 |
| Follow-up duration (year) | 3.32 (2.97) | 3.38 (3.01) | 2.91 (2.69) | 0.086 |
| Mortality | 288 (28.7) | 239 (27.5) | 49 (36.8) | 0.034 * |
| Variable | Univariate Analysis Odds Ratio (95% Confidence Interval) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 ≥ 36 µg/m3 | 1.528 (1.123–2.079) | 0.007 ** |
| Age (year) | 1.001 (0.991–1.011) | 0.873 |
| Gender, male | 1.154 (0.882–1.511) | 0.296 |
| Diabetes mellitus, yes | 1.059 (0.808–1.387) | 0.68 |
| Hypertension, yes | 0.904 (0.689–1.186) | 0.47 |
| Hepatitis B virus surface antigen, yes | 1.126 (0.89–1.425) | 0.325 |
| Antibodies to hepatitis C virus, yes | 0.866 (0.682–1.101) | 0.239 |
| Alcoholic Consumption, yes | 1.398 (1.031–1.895) | 0.03 * |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (IU/L) | 1.002 (1.002–1.002) | <0.001 *** |
| Alanine aminotransferase (IU/L) | 1 (0.998–1.002) | 0.661 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 1.071 (1.031–1.111) | <0.001 *** |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 0.578 (0.483–0.69) | <0.001 *** |
| Alkaline phosphatase (U/L) | 1.003 (1.003–1.003) | <0.001 *** |
| Blood urea nitrogen (mg/dL) | 1.008 (1–1.016) | 0.027 * |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.019 (0.958–1.082) | 0.553 |
| Sodium (meq/L) | 0.989 (0.975–1.003) | 0.087 |
| White Blood Cell (1000/μL) | 1.002 (0.996–1.008) | 0.367 |
| Hemogloblin (mg/dL) | 0.932 (0.89–0.974) | 0.002 ** |
| Hematocrit (%) | 0.976 (0.961–0.992) | 0.002 ** |
| Platelet (103/μL) | 1 (0.998–1.002) | 0.601 |
| Prolong prothrombin time (second) | 1.013 (0.993–1.034) | 0.19 |
| Alpha fetoprotein (ng/mL) | 1 (1–1) | 0.284 |
| Tumor number | 1.227 (1.143–1.318) | <0.001 *** |
| Tumor size (cm) | 1.102 (1.07–1.134) | <0.001 *** |
| Macrovascular invasion | 1.956 (1.461–2.62) | <0.001 *** |
| Tumor, node, metastases stage (0 as reference) | <0.001 *** | |
| Stage 1 | 1.109 (0.74–1.66) | 0.616 |
| Stage 2 | 1.558 (1.031–2.351) | 0.034 * |
| Stage 3 | 2.584 (1.639–4.071) | <0.001 *** |
| Stage 4 | 6.088 (2.34–15.831) | <0.001 *** |
| Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage (0 as reference) | <0.001 *** | |
| Stage A | 1.096 (0.734–1.634) | 0.654 |
| Stage B | 1.772 (1.2–2.617) | 0.004 ** |
| Stage C | 3.247 (2.094–5.038) | <0.001 *** |
| Stage D | 3.256 (1.87–5.675) | <0.001 *** |
| Child-Pugh score (0 as reference) | <0.001 *** | |
| Child A | 0.89 (0.668–1.184) | 0.424 |
| Child B | 2.262 (1.624–3.149) | <0.001 *** |
| Child C | 2.683 (1.68–4.284) | <0.001 *** |
| First treatment method (supportive as reference) | <0.001 *** | |
| Transarterial chemoembolization | 0.418 (0.289–0.605) | <0.001 *** |
| Radiofrequency ablation | 0.278 (0.176–0.439) | <0.001 *** |
| Resection | 0.229 (0.152–0.347) | <0.001 *** |
| Radiotherapy or Chemotherapy | 0.927 (0.507–1.695) | 0.806 |
| Variable | Odds Ratio (95% Confidence Interval) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 ≥ 36 µg/m3 | 1.584 (1.162–2.160) | 0.004 ** |
| Child-Pugh score (0 as reference) | <0.001 *** | |
| Child A | 0.97 (0.723–1.302) | 0.84 |
| Child B | 2.075 (1.458–2.954) | <0.001 *** |
| Child C | 2.741 (1.652–4.545) | <0.001 *** |
| Albumin | 0.679 (0.558–0.826) | <0.001 *** |
| Macrovascular invasion | 2.323 (1.655–3.261) | <0.001 *** |
| Tumor number | 1.195 (1.111–1.285) | <0.001 *** |
| Tumor size (cm) | 1.085 (1.048–1.124) | <0.001 *** |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, C.-H.; Hsieh, S.-Y.; Huang, W.-H.; Wang, I.-K.; Yen, T.-H. Association between Ambient Particulate Matter 2.5 Exposure and Mortality in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2490. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16142490
Lee C-H, Hsieh S-Y, Huang W-H, Wang I-K, Yen T-H. Association between Ambient Particulate Matter 2.5 Exposure and Mortality in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(14):2490. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16142490
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Chern-Horng, Sen-Yung Hsieh, Wen-Hung Huang, I-Kuan Wang, and Tzung-Hai Yen. 2019. "Association between Ambient Particulate Matter 2.5 Exposure and Mortality in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 14: 2490. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16142490
APA StyleLee, C.-H., Hsieh, S.-Y., Huang, W.-H., Wang, I.-K., & Yen, T.-H. (2019). Association between Ambient Particulate Matter 2.5 Exposure and Mortality in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(14), 2490. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16142490





