Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Thalassemia: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Collection and Extraction
3. Results
3.1. Artificial Intelligence in Diagnosing Thalassemia
3.2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Complications of Thalassemia
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Munkongdee, T.; Chen, P.; Winichagoon, P.; Fucharoen, S.; Paiboonsukwong, K. Update in Laboratory Diagnosis of Thalassemia. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sanctis, V.; Kattamis, C.; Canatan, D.; Soliman, A.T.; Elsedfy, H.; Karimi, M.; Daar, S.; Wali, Y.; Yassin, M.; Soliman, N.; et al. β-Thalassemia Distribution in the Old World: An Ancient Disease Seen from a Historical Standpoint. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 9, e2017018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angastiniotis, M.; Modell, B. Global epidemiology of hemoglobin disorders. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 850, 251–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rund, D.; Rachmilewitz, E. β-Thalassemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassebaum, N.J.; Jasrasaria, R.; Naghavi, M.; Wulf, S.K.; Johns, N.; Lozano, R.; Regan, M.; Weatherall, D.; Chou, D.P.; Eisele, T.P.; et al. A systematic analysis of global anemia burden from 1990 to 2010. Blood 2014, 123, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangoul, H.; Altshuler, D.; Cappellini, M.D.; Chen, Y.-S.; Domm, J.; Eustace, B.K.; Foell, J.; de la Fuente, J.; Grupp, S.; Handgretinger, R.; et al. CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Editing for Sickle Cell Disease and β-Thalassemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 384, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, A.; Wong, T.E.; Andrews, J.; Balasa, V.V.; Chung, J.H.; Forester, C.M.; Ikeda, A.K.; Keel, S.B.; Pagano, M.B.; Puthenveetil, G.; et al. Transfusion practices and complications in thalassemia. Transfusion 2018, 58, 2826–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viprakasit, V.; Ekwattanakit, S. Clinical Classification, Screening and Diagnosis for Thalassemia. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 32, 193–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyıldız, H.; Tuncer, S.A. Determination of the effect of red blood cell parameters in the discrimination of iron deficiency anemia and beta thalassemia via Neighborhood Component Analysis Feature Selection-Based machine learning. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2020, 196, 103886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.M.; Al-Sulaiti, A.M.; Younes, S.; Yassin, M.; Zayed, H. The spectrum of beta-thalassemia mutations in the 22 Arab countries: A systematic review. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2021, 14, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentzer, W.C., Jr. Differentiation of iron deficiency from thalassaemia trait. Lancet 1973, 1, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brancaleoni, V.; Di Pierro, E.; Motta, I.; Cappellini, M.D. Laboratory diagnosis of thalassemia. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2016, 38, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, M.M.; Reppun, T.S.; Bhagavan, N.V. Limitations of red blood cell distribution width (RDW) in evaluation of microcytosis. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1986, 85, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- England, J.M.; Fraser, P.M. Differentiation of iron deficiency from thalassaemia trait by routine blood-count. Lancet 1973, 301, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, M.A.; Soliman, A.T.; De Sanctis, V.; Yassin, K.S.; Abdulla, M.A. Final Height and Endocrine Complications in Patients with β-Thalassemia Intermedia: Our Experience in Non-Transfused Versus Infrequently Transfused Patients and Correlations with Liver Iron Content. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 11, e2019026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggio, A.; Vitrano, A.; Capra, M.; Cuccia, L.; Gagliardotto, F.; Filosa, A.; Magnano, C.; Rizzo, M.; Caruso, V.; Gerardi, C.; et al. Improving survival with deferiprone treatment in patients with thalassemia major: A prospective multicenter randomised clinical trial under the auspices of the Italian Society for Thalassemia and Hemoglobinopathies. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2009, 42, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telfer, P.; Coen, P.G.; Christou, S.; Hadjigavriel, M.; Kolnakou, A.; Pangalou, E.; Pavlides, N.; Psiloines, M.; Simamonian, K.; Skordos, G.; et al. Survival of medically treated thalassemia patients in Cyprus. Trends and risk factors over the period 1980–2004. Haematologica 2006, 91, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar]
- Farmaki, K.; Tzoumari, I.; Pappa, C.; Chouliaras, G.; Berdoukas, V. Normalisation of total body iron load with very intensive combined chelation reverses cardiac and endocrine complications of thalassaemia major. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 148, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neufeld, E.J. Oral chelators deferasirox and deferiprone for transfusional iron overload in thalassemia major: New data, new questions. Blood 2006, 107, 3436–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, P.M.; Fisher, S.A.; Madgwick, K.V.; Trivella, M.; Hopewell, S.; Doree, C.; Estcourt, L.J. Interventions for improving adherence to iron chelation therapy in people with sickle cell disease or thalassaemia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 5, Cd012349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, M.A.; Soliman, A.T.; De Sanctis, V.; Hussein, R.M.; Al-Okka, R.; Kassem, N.; Ghasoub, R.; Basha, A.; Nashwan, A.J.; Adel, A.M. Jadenu(®) Substituting Exjade(®) in Iron Overloaded β-Thalassemia Major (BTM) Patients: A Preliminary Report of the Effects on the Tolerability, Serum Ferritin Level, Liver Iron Concentration and Biochemical Profiles. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 10, e2018064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, A.; Yasin, M.; El-Awwa, A.; Osman, M.; de Sanctis, V. Acute effects of blood transfusion on pituitary gonadal axis and sperm parameters in adolescents and young men with thalassemia major: A pilot study. Fertil. Steril. 2012, 98, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, A.T.; Abushahin, A.; Abohezeima, K.; Khalafallah, H.; Adel, A.; Elawwa, A.; Elmulla, N. Age related IGF-I changes and IGF-I generation in thalassemia major. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Rev. 2011, 8 (Suppl. 2), 278–283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- A Yassin, M.; Soliman, A.T.; De Sanctis, V.; Abdula, M.A.; Riaz, L.M.; Ghori, F.F.; Yousaf, A.; Nashwan, A.J.; Abusamaan, S.; Moustafa, A.; et al. Statural Growth and Prevalence of Endocrinopathies in Relation to Liver Iron Content (LIC) in Adult Patients with Beta Thalassemia Major (BTM) and Sickle Cell Disease (SCD). Acta Biomed. Atenei Parm. 2018, 89, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sanctis, V.; Soliman, A.T.; Candini, G.; Yassin, M.; Raiola, G.; Galati, M.C.; Elalaily, R.; Elsedfy, H.; Skordis, N.; Garofalo, P.; et al. Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1): Demographic, Clinical and Laboratory Data in 120 Consecutive Adult Patients with Thalassaemia Major. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 6, e2014074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yassin, M.A.; Soliman, A.T.; De Sanctis, V.; Abdelrahman, M.O.; Aziz Bedair, E.M.; AbdelGawad, M. Effects of the anti-receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand denusomab on beta thalassemia major-induced osteoporosis. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 18, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sanctis, V.; Soliman, A.; Candini, G.; Campisi, S.; Anastasi, S.; Iassin, M. High prevalence of central hypothyroidism in adult patients with β-thalassemia major. Georgian Med. News 2013, 88–94. [Google Scholar]
- Soliman, A.T.; Yasin, M.; El-Awwa, A.; De Sanctis, V. Detection of glycemic abnormalities in adolescents with beta thalassemia using continuous glucose monitoring and oral glucose tolerance in adolescents and young adults with β-thalassemia major: Pilot study. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 17, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravarotto, V.; Simioni, F.; Pagnin, E.; Davis, P.A.; Calò, L.A. Oxidative stress–chronic kidney disease–cardiovascular disease: A vicious circle. Life Sci. 2018, 210, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravarotto, V.; Bertoldi, G.; Innico, G.; Gobbi, L.; Calò, L.A. The Pivotal Role of Oxidative Stress in the Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular-Renal Remodeling in Kidney Disease. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalesso, F.; Rigato, M.; Cirella, I.; Protti, M.P.; Zanella, R.; Rossi, B.; Putti, M.C.; Martino, F.K.; Calò, L.A. The Assessment of Renal Functional Reserve in β-Thalassemia Major Patients by an Innovative Ultrasound and Doppler Technique: A Pilot Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirdah, M.; Tarazi, I.; Al Najjar, E.; Al Haddad, R. Evaluation of the diagnostic reliability of different RBC indices and formulas in the differentiation of the β-thalassaemia minor from iron deficiency in Palestinian population. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2008, 30, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayabose, S.; Giamelli, J.; LevondogluTugal, O.; Sandoval, C.; Ozkaynak, F.; Visintainer, P. #262 Differentiating iron deficiency anemia from thalassemia minor by using an RDW-based index. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 1999, 21, 314. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, A.; Ottiger, C.; Risch, L.; Regenass, S.; Hergersberg, M.; Herklotz, R. Thalassämie-Syndrome: Klinik und Diagnose. In Swiss Medical Forum; EMH Medi: Muttenz, Switzerland, 2004; pp. 947–952. [Google Scholar]
- Green, R.; King, R. A new red cell discriminant incorporating volume dispersion for differentiating iron deficiency anemia from thalassemia minor. Blood Cells 1989, 15, 481–491; discussion 492. [Google Scholar]
- Ehsani, M.; Shahgholi, E.; Rahiminejad, M.; Seighali, F.; Rashidi, A. A new index for discrimination between iron deficiency anemia and beta-thalassemia minor: Results in 284 patients. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. PJBS 2009, 12, 473–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camaschella, C. Iron-Deficiency Anemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1832–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killip, S.; Bennett, J.M.; Chambers, M.D. Iron deficiency anemia. Am. Fam. Physician 2007, 75, 671–678. [Google Scholar]
- AlAgha, A.S.; Faris, H.; Hammo, B.H.; Al-Zoubi, A.M. Identifying β-thalassemia carriers using a data mining approach: The case of the Gaza Strip, Palestine. Artif. Intell. Med. 2018, 88, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, J.F.; Dusse, L.M.S.; Borges, K.B.G.; de Castro, R.L.V.; Coura-Vital, W.; Carvalho, M.d.G. A new index to discriminate between iron deficiency anemia and thalassemia trait. Rev. Bras. Hematol. Hemoter. 2016, 38, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabootarizadeh, L.; Jamshidnezhad, A.; Koohmareh, Z. Differential Diagnosis of Iron-Deficiency Anemia from β-Thalassemia Trait Using an Intelligent Model in Comparison with Discriminant Indexes. Acta Inf. Med 2019, 27, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellinger, C.; Amid, A.; Japkowicz, N.; Victor, H. Multi-label classification of anemia patients. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 14th International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Miami, FL, USA, 9–11 December 205; pp. 825–830.
- Jamei, M.K.; Talarposhti, K.M. Discrimination between Iron Deficiency Anaemia (IDA) and β-Thalassemia Trait (β-TT) Based on Pattern-Based Input Selection Artificial Neural Network (PBIS- ANN). J. Adv. Comput. Res. 2016, 7, 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, Z.; Khattak, A.A.; Ali, S.A.; Hussain, J.; Noor, B.; Bano, R.; Jan Mahsud, M.A. Evaluation of five discriminating indexes to distinguish Beta-Thalassemia Trait from Iron Deficiency Anaemia. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2016, 66, 1627–1631. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.-K.; Liu, H.-M.; Lee, L.-H.; Chen, Y.-J.; Chien, S.-H.; Lin, J.-S.; Chen, W.-C.; Cheng, M.-H.; Lin, P.-H.; Lai, J.-Y.; et al. The TVGH-NYCU Thal-Classifier: Development of a Machine-Learning Classifier for Differentiating Thalassemia and Non-Thalassemia Patients. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amendolia, S.R.; Cossu, G.; Ganadu, M.L.; Golosio, B.; Masala, G.; Mura, G.M. A comparative study of K-Nearest Neighbour, Support Vector Machine and Multi-Layer Perceptron for Thalassemia screening. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2003, 69, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongseree, W.; Chaiyaratana, N.; Vichittumaros, K.; Winichagoon, P.; Fucharoen, S. Thalassemia classification by neural networks and genetic programming. Inf. Sci. 2007, 177, 771–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.; Habib, M.A. Comparison of Different Classification Techniques Using WEKA for Hematological Data. Am. J. Eng. Res. 2015, 4, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Saikia Borah, M.; Bhuyan, B.; Pathak, D.; Bhattacharya, P. Machine learning in predicting hemoglobin variants. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Comput. 2018, 8, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Datta, S.; Kaviraj, A.; Sanyal, S.N.; Nielsen, P.; Nielsen, I.; Sharma, P.; Sanyal, T.; Dey, K.; Saha, S. A decision support scheme for beta thalassemia and HbE carrier screening. J. Adv. Res. 2020, 24, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.C.; Bevington, J.M. Iron deficiency and-or thalassaemia trait. Lancet 1973, 1, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shine, I.; Lal, S. A strategy to detect beta-thalassaemia minor. Lancet 1977, 1, 692–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çil, B.; Ayyıldız, H.; Tuncer, T. Discrimination of β-thalassemia and iron deficiency anemia through extreme learning machine and regularized extreme learning machine based decision support system. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 138, 109611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purwar, S.; Tripathi, R.K.; Ranjan, R.; Saxena, R. Detection of microcytic hypochromia using cbc and blood film features extracted from convolution neural network by different classifiers. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 4573–4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St Pierre, T.; Aydinok, Y.; El-Beshlawy, A.; Bayraktaroglu, S.; Ibrahim, A.; Hamdy, M.; Pang, W.; Khorshid, S.; Bangma, S.; House, M. P1505: Using Artificial Intelligence Neural Networks to Obtain Automated Liver Iron Concentration Measurements Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging—A Multi-Scanner Validation Study. Hemasphere 2022, 6, 1386–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Positano, V.; Meloni, A.; Santarelli, M.F.; Pistoia, L.; Spasiano, A.; Cuccia, L.; Casini, T.; Gamberini, M.R.; Allò, M.; Bitti, P.P.; et al. Deep Learning Staging of Liver Iron Content From Multiecho MR Images. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 57, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
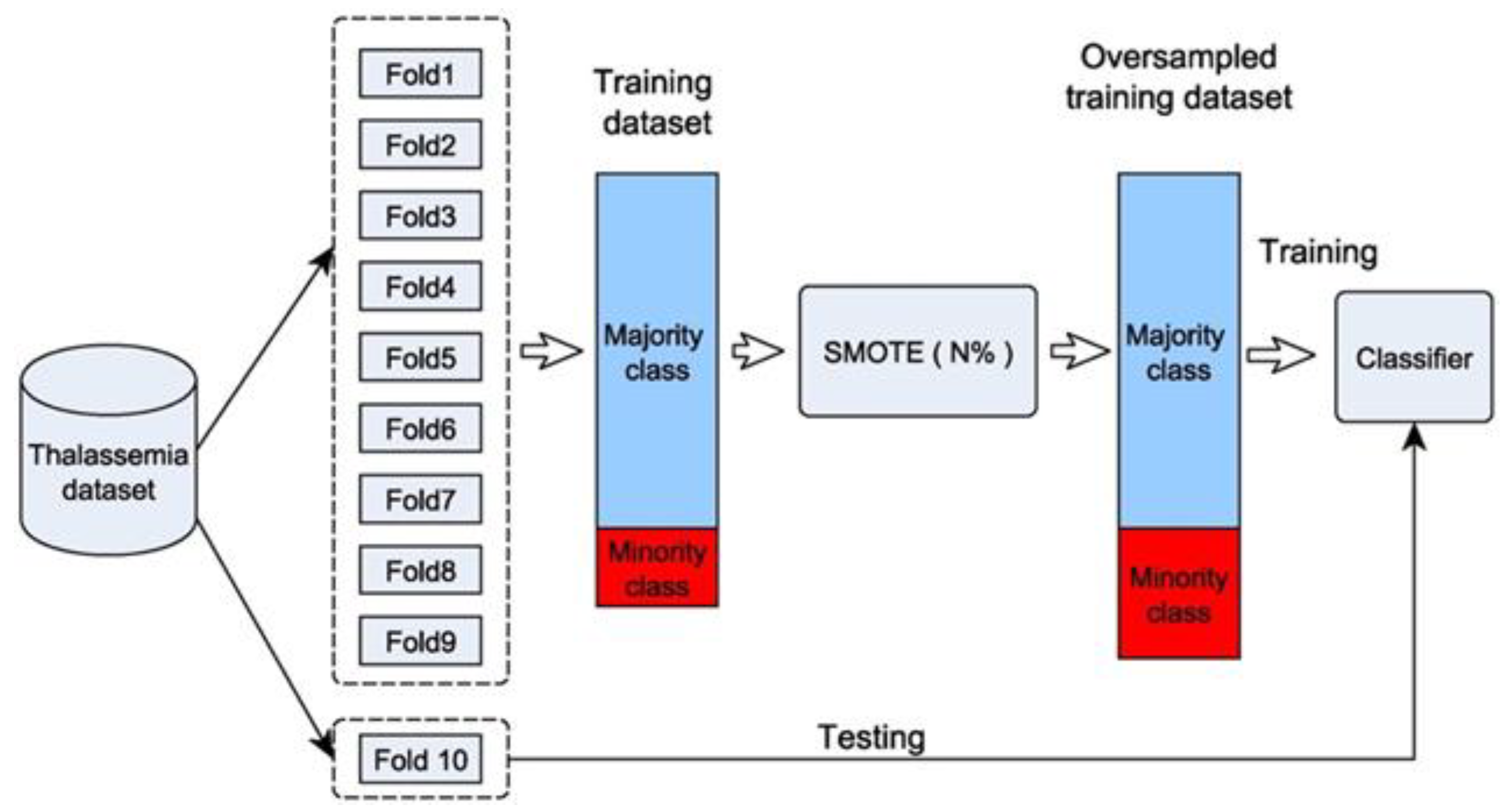

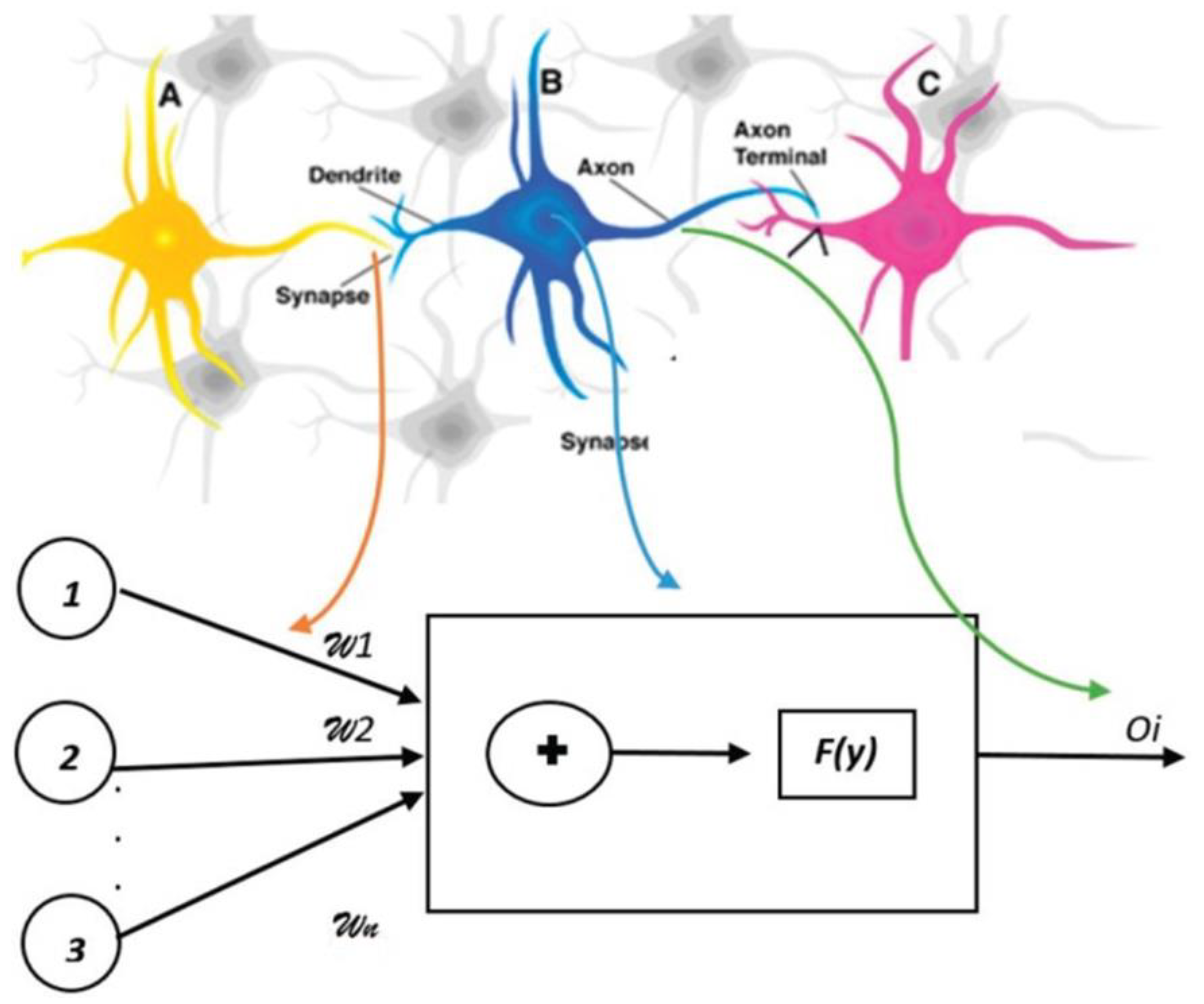

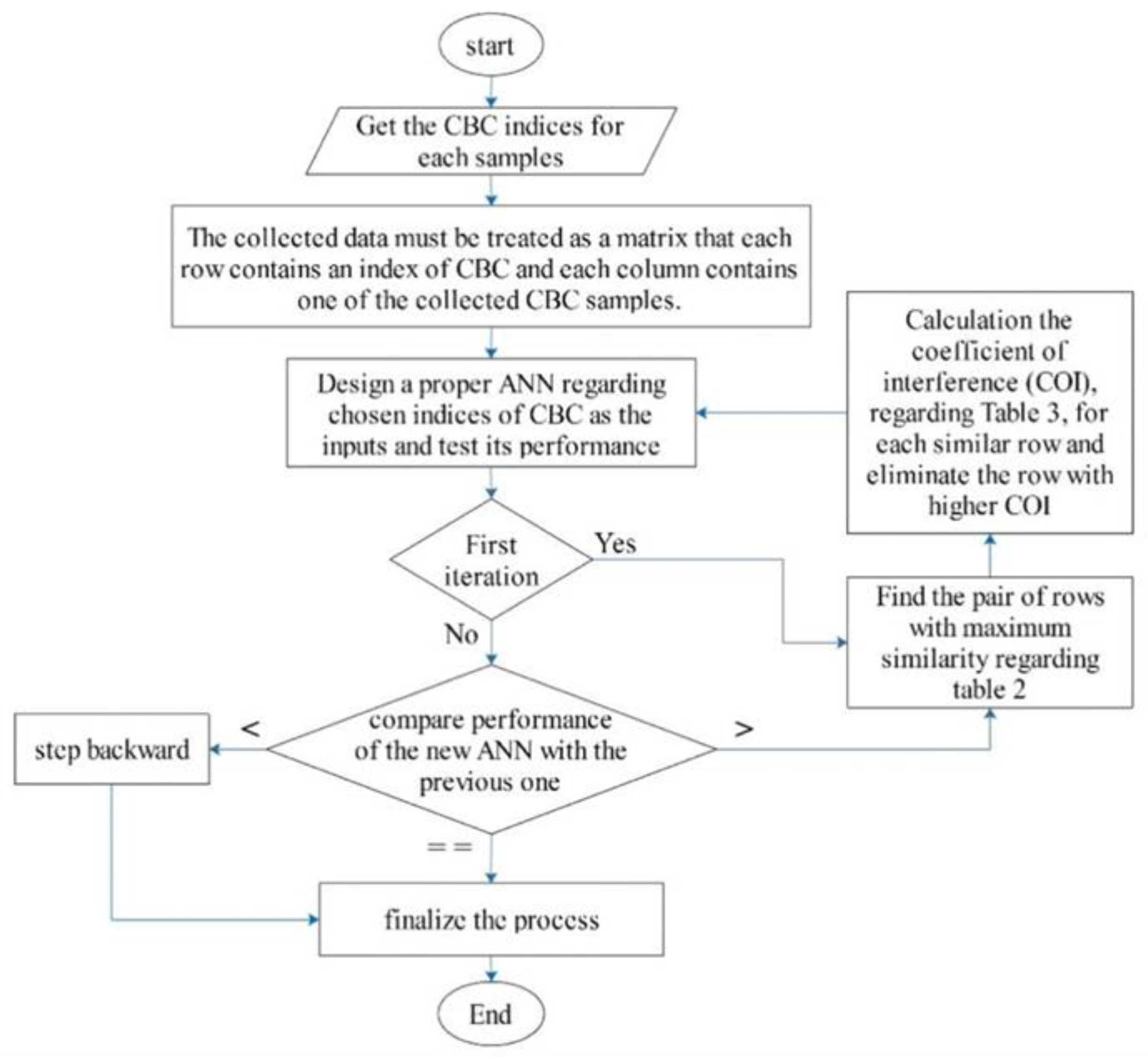
| Method | Feature Ranking Order |
|---|---|
| cfsSubsetEval | RBC, RDW |
| Attribute Correlation | RBC, age, RDW. Hb, Hct |
| Gain Ratio | RBC. RDW. Hb. age, Hct, gender |
| Symmetrical Uncertainty | RBC. RDW. Hb, age, Hct, gender |
| Information Gain | RBC. RDW. Hb. age, Hct, gender |
| Index | Formula | BTT | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | Efficiency | Youden’s Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mentzer [11] | MCVRBC | <13 | 70.31 | 96.28 | 86.54 | 90.50 | 89.68 | 66.59 |
| Srivastava [51] | MCHRBC | <3.8 | 62.50 | 97.34 | 88.89 | 88.40 | 88.49 | 59.84 |
| Shine and Lal [52] | MCV2 × MCH100 | <1530 | 95.31 | 79.79 | 61.62 | 98.04 | 83.73 | 75.10 |
| Jayabose, et al. [33] | MCV × RDWRBC | <220 | 64.06 | 90.96 | 70.69 | 88.14 | 84.13 | 55.02 |
| Sirdah, et al. [32] | MCV − RBC − 3Hb | <27 | 64.06 | 97.34 | 89.13 | 88.83 | 88.89 | 61.40 |
| Ehsani, et al. [35] | MCV − 10RBC | <15 | 68.75 | 96.81 | 88 | 90.10 | 89.68 | 65.56 |
| Study | Outcomes | AUC | ACC | SE | SP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlAgha, et al. [39] | Identification of thalassemia | 99.8% | 99.8% | 99.5% | 99.5% |
| Matos, et al. [40] | Identification of thalassemia | 95.7% | 95% | 76.7% | 99.3% |
| Kabootarizadeh L., et al. [41] | Identification of thalassemia | -- | 92.5% | 93.1% | 92.3% |
| Jamei, M.K. [43] | Identification of thalassemia | -- | 98% | 97.7% | 98.4% |
| Purwar, S., et al. [52] | Identification of thalassemia | -- | 99% | 100% | 98% |
| Ullah, Z., et al. [44] | Identification of thalassemia | -- | -- | 100% | 93% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferih, K.; Elsayed, B.; Elshoeibi, A.M.; Elsabagh, A.A.; Elhadary, M.; Soliman, A.; Abdalgayoom, M.; Yassin, M. Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Thalassemia: A Comprehensive Review. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13091551
Ferih K, Elsayed B, Elshoeibi AM, Elsabagh AA, Elhadary M, Soliman A, Abdalgayoom M, Yassin M. Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Thalassemia: A Comprehensive Review. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(9):1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13091551
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerih, Khaled, Basel Elsayed, Amgad M. Elshoeibi, Ahmed A. Elsabagh, Mohamed Elhadary, Ashraf Soliman, Mohammed Abdalgayoom, and Mohamed Yassin. 2023. "Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Thalassemia: A Comprehensive Review" Diagnostics 13, no. 9: 1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13091551
APA StyleFerih, K., Elsayed, B., Elshoeibi, A. M., Elsabagh, A. A., Elhadary, M., Soliman, A., Abdalgayoom, M., & Yassin, M. (2023). Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Thalassemia: A Comprehensive Review. Diagnostics, 13(9), 1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13091551





