Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Promote the Development and Growth of Human Salivary Stones
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Clinical Interventions
2.2. Chemicals and Biochemicals
2.3. Salivary Stones Storage and Processing
2.4. Micro-Computed Tomography
2.5. Digital Reconstruction of Volumetric µCT Data
2.6. Macrophotography
2.7. Microscopy
2.8. Optical Clearing and Light Sheet Fluorescence Microscopy (LSFM) of Submandibular Sialoliths
2.9. Von Kossa Staining for Mineralized Areas
2.10. DNA Staining
2.11. Immunostaining for Neutrophil Markers
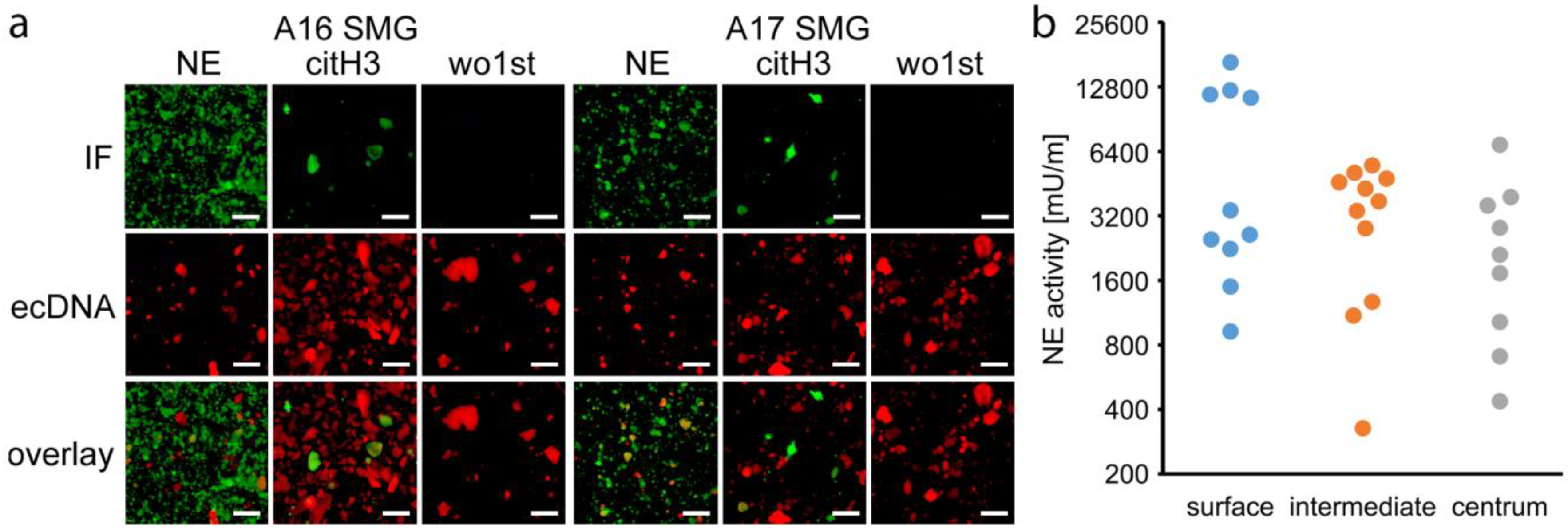
2.12. Neutrophil Elastase Activity in Human Sialoliths
2.13. DNA Extraction, Sequencing, and Microbiome Analysis
2.14. Statistical Analysis
2.15. Study Approval
3. Results
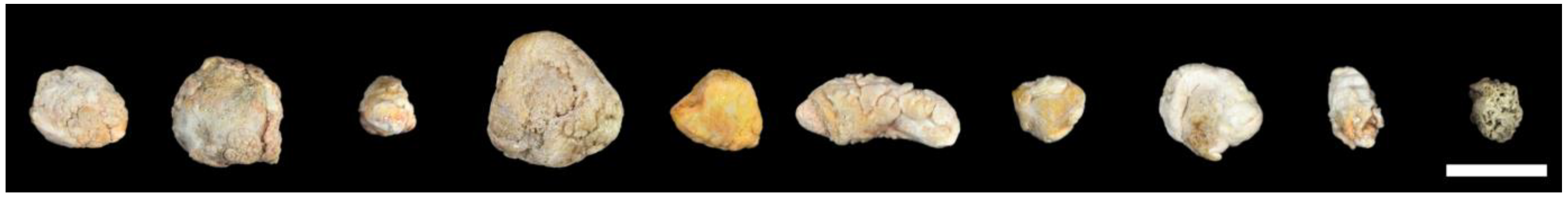
3.1. Human Sialoliths are Macroscopically Polymorphic
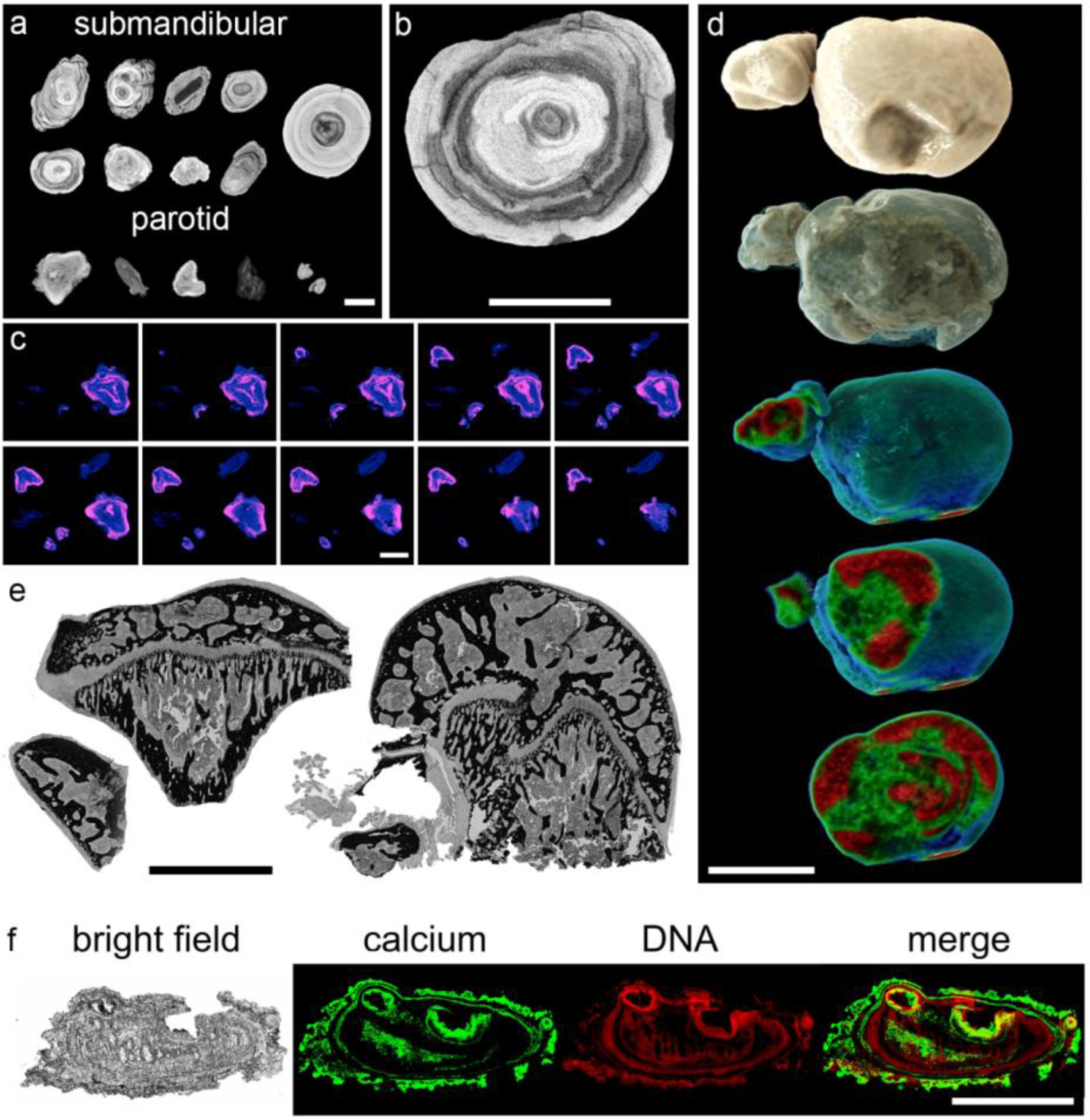
3.2. Sialoliths Consist of an Onion Skin-Like Shell Structure of Extracellular DNA and Calcified Layers
3.3. The Calcium-Containing Layers of Sialoliths are Responsible for their Tightness
3.4. The Majority of Sialoliths Harbor Bacterial DNA
3.5. NETs are Involved in Sialolithogenesis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Termino, P.R. Càlculos salivales salivary calculi anales españoles de odontoestomatologia. Illus 15 Excerpta Med. 1948, 2, 349. [Google Scholar]
- de Termino, P.R. Calculos salivales [Salivary calculi]. Esp. Odontoestomatol. 1948, 7, 661–673. [Google Scholar]
- McGurk, M.C.L. Controversies in the Management of Salivary Gland Disease, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 251–259. [Google Scholar]
- Kraaij, S.; Karagozoglu, K.H.; Forouzanfar, T.; Veerman, E.C.; Brand, H.S. Salivary stones: Symptoms, aetiology, biochemical composition and treatment. Br. Dent. J. 2014, 217, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigismund, P.E.; Zenk, J.; Koch, M.; Schapher, M.; Rudes, M.; Iro, H. Nearly 3000 salivary stones: Some clinical and epidemiologic aspects. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, 1879–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epivatianos, A.; Harrison, J.D. The presence of microcalculi in normal human submandibular and parotid salivary glands. Arch. Oral Biol. 1989, 34, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J. The prevalence of consolidated salivary deposits in the small ducts of human submandibular glands. J. Oral Pathol. 1978, 7, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Lagha, N.; Alantar, A.; Samson, J.; Chapireau, D.; Maman, L. Lithiasis of minor salivary glands: Current data. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2005, 100, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lustmann, J.; Regev, E.; Melamed, Y. Sialolithiasis. A survey on 245 patients and a review of the literature. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1990, 19, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luers, J.C.; Grosheva, M.; Stenner, M.; Beutner, D. Sialoendoscopy: Prognostic factors for endoscopic removal of salivary stones. Arch Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2011, 137, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schapher, M.; Goncalves, M.; Mantsopoulos, K.; Iro, H.; Koch, M. Transoral Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Obstructive Salivary Gland Pathologies. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2019, 45, 2338–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenk, J.; Koch, M.; Klintworth, N.; Konig, B.; Konz, K.; Gillespie, M.B.; Iro, H. Sialendoscopy in the diagnosis and treatment of sialolithiasis: A study on more than 1000 patients. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2012, 147, 858–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iro, H.; Zenk, J.; Koch, M. Modern concepts for the diagnosis and therapy of sialolithiasis. HNO 2010, 58, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves, M.; Mantsopoulos, K.; Schapher, M.; Iro, H.; Koch, M. Ultrasound Supplemented by Sialendoscopy: Diagnostic Value in Sialolithiasis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 159, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, M.; Schapher, M.; Mantsopoulos, K.; Goncalves, M.; Iro, H. Intraductal Pneumatic Lithotripsy after Extended Transoral Duct Surgery in Submandibular Sialolithiasis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Schapher, M.; Mantsopoulos, K.; von Scotti, F.; Goncalves, M.; Iro, H. Multimodal treatment in difficult sialolithiasis: Role of extracorporeal shock-wave lithotripsy and intraductal pneumatic lithotripsy. Laryngoscope 2018, 128, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schapher, M.; Mantsopoulos, K.; Messbacher, M.E.; Iro, H.; Koch, M. Transoral submandibulotomy for deep hilar submandibular gland sialolithiasis. Laryngoscope 2017, 127, 2038–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Iro, H.; Zenk, J. Combined endoscopic-transcutaneous surgery in parotid gland sialolithiasis and other ductal diseases: Reporting medium- to long-term objective and patients’ subjective outcomes. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013, 270, 1933–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Hung, S.H.; Su, C.H.; Lee, K.S.; Iro, H.; Mantsopoulos, K. Intraductal lithotripsy in sialolithiasis with two different Ho:YAG lasers: Presetting parameters, effectiveness, success rates. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 23, 5548–5557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Zenk, J.; Iro, H. Algorithms for treatment of salivary gland obstructions. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 42, 1173–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroder, S.A.; Homoe, P.; Wagner, N.; Bardow, A. Does saliva composition affect the formation of sialolithiasis? J. Laryngol. Otol. 2017, 131, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchal, F.; Kurt, A.M.; Dulguerov, P.; Lehmann, W. Retrograde theory in sialolithiasis formation. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2001, 127, 66–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, J.D. Causes, natural history, and incidence of salivary stones and obstructions. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 42, 927–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, J.D.; Triantafyllou, A.; Baldwin, D.; Schafer, H. Histochemical and biochemical determination of calcium in salivary glands with particular reference to chronic submandibular sialadenitis. Virchows Arch. A Pathol. Anat. Histopathol. 1993, 423, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenk, J.; Constantinidis, J.; Kydles, S.; Hornung, J.; Iro, H. Clinical and diagnostic findings of sialolithiasis. HNO 1999, 47, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenk, J.; Iro, H.; Klintworth, N.; Lell, M. Diagnostic imaging in sialadenitis. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 21, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boskey, A.L.; Boyan-Salyers, B.D.; Burstein, L.S.; Mandel, I.D. Lipids associated with mineralization of human submandibular gland sialoliths. Arch. Oral Biol. 1981, 26, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slomiany, B.L.; Murty, V.L.; Aono, M.; Slomiany, A.; Mandel, I.D. Lipid composition of the matrix of human submandibular salivary gland stones. Arch. Oral Biol. 1982, 27, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boskey, A.L.; Burstein, L.S.; Mandel, I.D. Phospholipids associated with human parotid gland sialoliths. Arch. Oral Biol. 1983, 28, 655–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.D.; Triantafyllou, A.; Garrett, J.R. Ultrastructural localization of microliths in salivary glands of cat. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 1993, 22, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllou, A.; Fletcher, D.; Scott, J. Organic secretory products, adaptive responses and innervation in the parotid gland of ferret: A histochemical study. Arch. Oral Biol. 2005, 50, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.D.; Epivatianos, A. Production of microliths and sialadenitis in rats by a short combined course of isoprenaline and calcium gluconate. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1992, 73, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baurmash, H.D. Chronic recurrent parotitis: A closer look at its origin, diagnosis, and management. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2004, 62, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, S. Sialoendoscopic and irrigation findings in chronic obstructive parotitis. Laryngoscope 2005, 115, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Grandi, R.; Capaccio, P.; Bidossi, A.; Bottagisio, M.; Drago, L.; Torretta, S.; Pignataro, L.; De Vecchi, E. Salivary calculi microbiota: New insights into microbial networks and pathogens reservoir. Microbes. Infect. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngu, R.K.; Brown, J.E.; Whaites, E.J.; Drage, N.A.; Ng, S.Y.; Makdissi, J. Salivary duct strictures: Nature and incidence in benign salivary obstruction. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2007, 36, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.I.; Pawar, R.R.; Whitley, S.; Makdissi, J. Incidence of different causes of benign obstruction of the salivary glands: Retrospective analysis of 493 cases using fluoroscopy and digital subtraction sialography. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 53, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, H.M.; Jackson, J.K.; Taylor, D.R.; Crowther, R.S. Activation of human neutrophils by calcium carbonate polymorphs. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1997, 42, 1283–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulay, S.R.; Desai, J.; Kumar, S.V.; Eberhard, J.N.; Thomasova, D.; Romoli, S.; Grigorescu, M.; Kulkarni, O.P.; Popper, B.; Vielhauer, V.; et al. Cytotoxicity of crystals involves RIPK3-MLKL-mediated necroptosis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, L.E.; Boeltz, S.; Bilyy, R.; Schauer, C.; Mahajan, A.; Widulin, N.; Gruneboom, A.; Herrmann, I.; Boada, E.; Rauh, M.; et al. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Initiate Gallstone Formation. Immunity 2019, 51, 443–450.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorn, C.; Janko, C.; Krenn, V.; Zhao, Y.; Munoz, L.E.; Schett, G.; Herrmann, M. Bonding the foe—NETting neutrophils immobilize the pro-inflammatory monosodium urate crystals. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maueroder, C.; Mahajan, A.; Paulus, S.; Gosswein, S.; Hahn, J.; Kienhofer, D.; Biermann, M.H.; Tripal, P.; Friedrich, R.P.; Munoz, L.E.; et al. Menage-a-Trois: The Ratio of Bicarbonate to CO2 and the pH Regulate the Capacity of Neutrophils to Form NETs. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, L.E.; Bilyy, R.; Biermann, M.H.C.; Kienhofer, D.; Maueroder, C.; Hahn, J.; Brauner, J.M.; Weidner, D.; Chen, J.; Scharin-Mehlmann, M.; et al. Nanoparticles size-dependently initiate self-limiting NETosis-driven inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, B. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps and Microcrystals. J. Immunol. Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Biermann, M.H.; Brauner, J.M.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Herrmann, M. New insights into Neutrophil extracellular Traps: Mechanisms of Formation and Role in inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maueroder, C.; Kienhofer, D.; Hahn, J.; Schauer, C.; Manger, B.; Schett, G.; Herrmann, M.; Hoffmann, M.H. How neutrophil extracellular traps orchestrate the local immune response in gout. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 93, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, C.; Janko, C.; Munoz, L.E.; Zhao, Y.; Kienhofer, D.; Frey, B.; Lell, M.; Manger, B.; Rech, J.; Naschberger, E.; et al. Aggregated neutrophil extracellular traps limit inflammation by degrading cytokines and chemokines. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinwald, C.; Schauer, C.; Csepregi, J.Z.; Kienhofer, D.; Weidner, D.; Malissen, M.; Mocsai, A.; Schett, G.; Herrmann, M.; Hoffmann, M. Reply to “Neutrophils are not required for resolution of acute gouty arthritis in mice”. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1384–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppkes, M.; Maueroder, C.; Hirth, S.; Nowecki, S.; Gunther, C.; Billmeier, U.; Paulus, S.; Biermann, M.; Munoz, L.E.; Hoffmann, M.; et al. Externalized decondensed neutrophil chromatin occludes pancreatic ducts and drives pancreatitis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.; Gruneboom, A.; Petru, L.; Podolska, M.J.; Kling, L.; Maueroder, C.; Dahms, F.; Christiansen, S.; Gunter, L.; Krenn, V.; et al. Frontline Science: Aggregated neutrophil extracellular traps prevent inflammation on the neutrophil-rich ocular surface. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2019, 105, 1087–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comaniciu, D.; Engel, K.; Georgescu, B.; Mansi, T. Shaping the future through innovations: From medical imaging to precision medicine. Med. Image Anal. 2016, 33, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.J.; Scholz, M.; Singh, S.; Heichel, J.; Paulsen, F. Etiopathogenesis of lacrimal sac mucopeptide concretions: Insights from cinematic rendering techniques. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingberg, A.; Hasenberg, A.; Ludwig-Portugall, I.; Medyukhina, A.; Mann, L.; Brenzel, A.; Engel, D.R.; Figge, M.T.; Kurts, C.; Gunzer, M. Fully Automated Evaluation of Total Glomerular Number and Capillary Tuft Size in Nephritic Kidneys Using Lightsheet Microscopy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickert, G.; Wirtz, S.; Matzner, J.; Ashfaq-Khan, M.; Heck, R.; Rosigkeit, S.; Thies, D.; Surabattula, R.; Ehmann, D.; Wehkamp, J.; et al. Wheat Consumption Aggravates Colitis in Mice via Amylase Trypsin Inhibitor-mediated Dysbiosis. Gastroenterology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolasco, P.; Anjos, A.J.; Marques, J.M.; Cabrita, F.; da Costa, E.C.; Mauricio, A.; Pereira, M.F.; de Matos, A.P.; Carvalho, P.A. Structure and growth of sialoliths: Computed microtomography and electron microscopy investigation of 30 specimens. Microsc. Microanal. 2013, 19, 1190–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolasco, P.; Coelho, P.V.; Coelho, C.; Angelo, D.F.; Dias, J.R.; Alves, N.M.; Mauricio, A.; Pereira, M.F.C.; Alves de Matos, A.P.; Martins, R.C.; et al. Mineralization of Sialoliths Investigated by Ex Vivo and In Vivo X-ray Computed Tomography. Microsc. Microanal. 2019, 25, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorch, S.K.; Kubes, P. An emerging role for neutrophil extracellular traps in noninfectious disease. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, J.; Foresto-Neto, O.; Honarpisheh, M.; Steiger, S.; Nakazawa, D.; Popper, B.; Buhl, E.M.; Boor, P.; Mulay, S.R.; Anders, H.J. Particles of different sizes and shapes induce neutrophil necroptosis followed by the release of neutrophil extracellular trap-like chromatin. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angarita-Diaz, M.P.; Diaz, J.A.; Tupaz, H.A.; Lopez-Lopez, A.; Forero, D.; Mira, A.; Davila, F.; Ceron, X.A.; Ochoa-Acosta, E.M.; Gomez, O.L.; et al. Presence of Streptococcus dentisani in the dental plaque of children from different Colombian cities. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2019, 5, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiley, R.A.; Beighton, D.; Winstanley, T.G.; Fraser, H.Y.; Hardie, J.M. Streptococcus intermedius, Streptococcus constellatus, and Streptococcus anginosus (the Streptococcus milleri group): Association with different body sites and clinical infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 243–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukic, D.; Karygianni, L.; Flury, M.; Attin, T.; Thurnheer, T. Endodontic-Like Oral Biofilms as Models for Multispecies Interactions in Endodontic Diseases. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriem, L.S.; Wright, K.; Ccahuana-Vasquez, R.A.; Rupp, S. Confocal Raman microscopy to identify bacteria in oral subgingival biofilm models. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morotomi, M.; Nagai, F.; Sakon, H.; Tanaka, R. Dialister succinatiphilus sp. nov. and Barnesiella intestinihominis sp. nov., isolated from human faeces. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 2716–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, J.; Xu, L.; Qian, Y.; Sun, Z.; Yu, D.; Huang, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ren, R.; et al. Evolution of the Gut Microbiome in Early Childhood: A Cross-Sectional Study of Chinese Children. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, J.P.; Antonelli, P.J.; Dirain, C.O. Microbiome Analysis of Cholesteatoma by Gene Sequencing. Otol. Neurotol. 2019, 40, 1186–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triantafyllou, A.; Harrison, J.D.; Garrett, J.R. Analytical ultrastructural investigation of microliths in salivary glands of cat. Histochem. J. 1993, 25, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, W.K.; Chole, R.A.; Ogden, M.A. Evidence of a microbial etiology for sialoliths. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.D. Regarding the Lack of Evidence for a Microbial Etiology of Sialolithiasis. Laryngoscope 2019, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymoortash, A.; Buck, P.; Jepsen, H.; Werner, J.A. Sialolith crystals localized intraglandularly and in the Wharton’s duct of the human submandibular gland: An X-ray diffraction analysis. Arch. Oral Biol. 2003, 48, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christophorou, M.A.; Castelo-Branco, G.; Halley-Stott, R.P.; Oliveira, C.S.; Loos, R.; Radzisheuskaya, A.; Mowen, K.A.; Bertone, P.; Silva, J.C.; Zernicka-Goetz, M.; et al. Citrullination regulates pluripotency and histone H1 binding to chromatin. Nature 2014, 507, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schapher, M.; Koch, M.; Weidner, D.; Scholz, M.; Wirtz, S.; Mahajan, A.; Herrmann, I.; Singh, J.; Knopf, J.; Leppkes, M.; et al. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Promote the Development and Growth of Human Salivary Stones. Cells 2020, 9, 2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092139
Schapher M, Koch M, Weidner D, Scholz M, Wirtz S, Mahajan A, Herrmann I, Singh J, Knopf J, Leppkes M, et al. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Promote the Development and Growth of Human Salivary Stones. Cells. 2020; 9(9):2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092139
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchapher, Mirco, Michael Koch, Daniela Weidner, Michael Scholz, Stefan Wirtz, Aparna Mahajan, Irmgard Herrmann, Jeeshan Singh, Jasmin Knopf, Moritz Leppkes, and et al. 2020. "Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Promote the Development and Growth of Human Salivary Stones" Cells 9, no. 9: 2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092139
APA StyleSchapher, M., Koch, M., Weidner, D., Scholz, M., Wirtz, S., Mahajan, A., Herrmann, I., Singh, J., Knopf, J., Leppkes, M., Schauer, C., Grüneboom, A., Alexiou, C., Schett, G., Iro, H., Muñoz, L. E., & Herrmann, M. (2020). Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Promote the Development and Growth of Human Salivary Stones. Cells, 9(9), 2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092139








