The E3 Ubiquitin-Protein Ligase Cullin 3 Regulates HIV-1 Transcription
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Isolation of Primary Cells
2.1.1. Immortalized Cell Lines
2.1.2. Primary Cells
2.2. Proviral Constructs and Production of Virus Stocks
2.3. Assays to Quantify Viral Infection
2.4. siRNA and cDNA Transfection
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. NF-κB and NFAT Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.7. Mapping the Antiviral Effect of Cul3 to the HIV-1 Replication Cycle
2.8. CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Knock Out in Primary CD4+ T Cells
2.8.1. Polyclonal Knockouts in Primary CD4+ T-Cells
2.8.2. Virus Production
2.8.3. HIV-1 Infection Quantitation by Flow Cytometry
2.9. Quantification of Cul3 Expression by qRT-PCR
2.10. Flow Cytometry
2.11. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
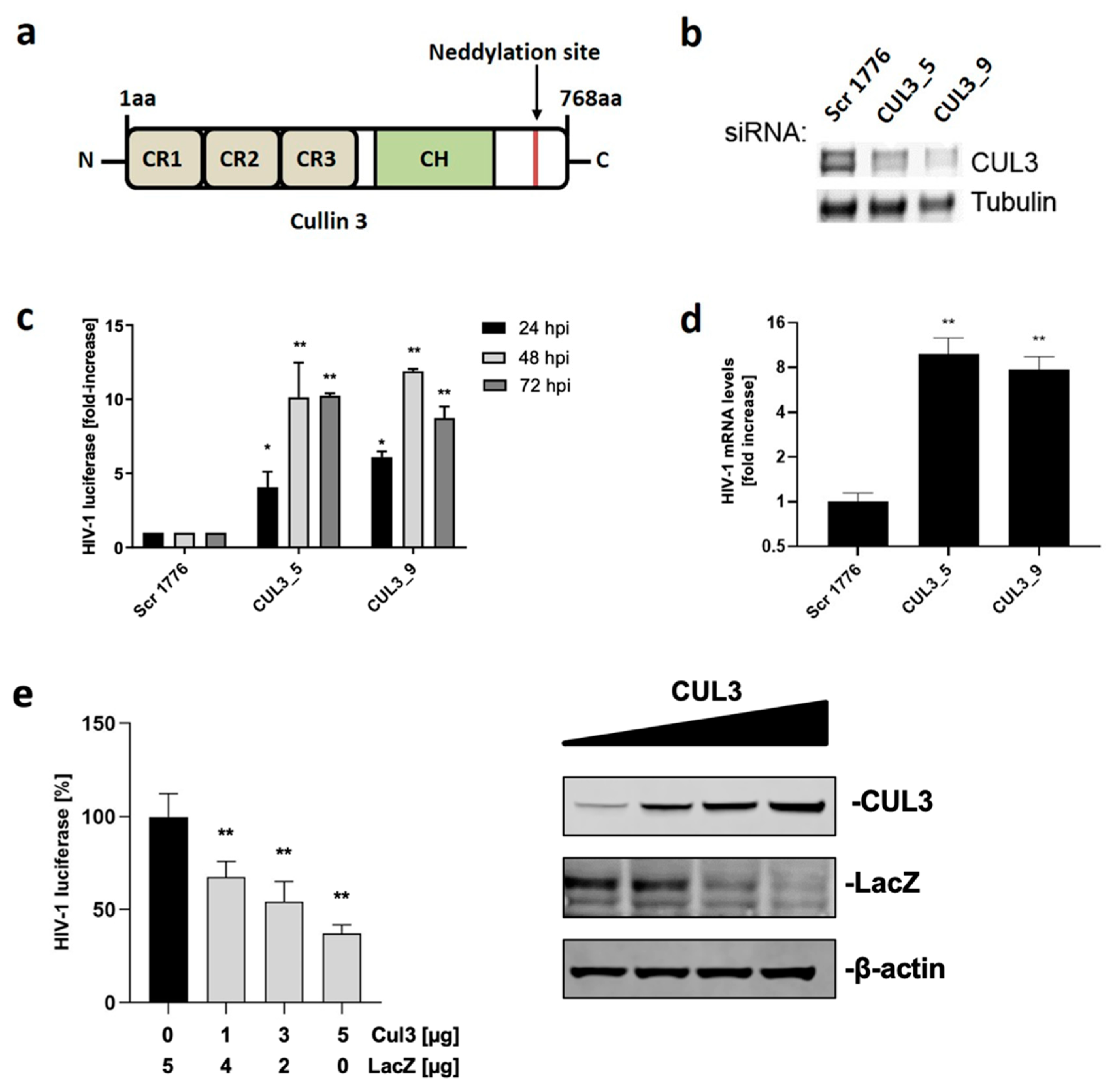
3.1. Cul3 Restricts Viral Replication in Single Cycle Assays
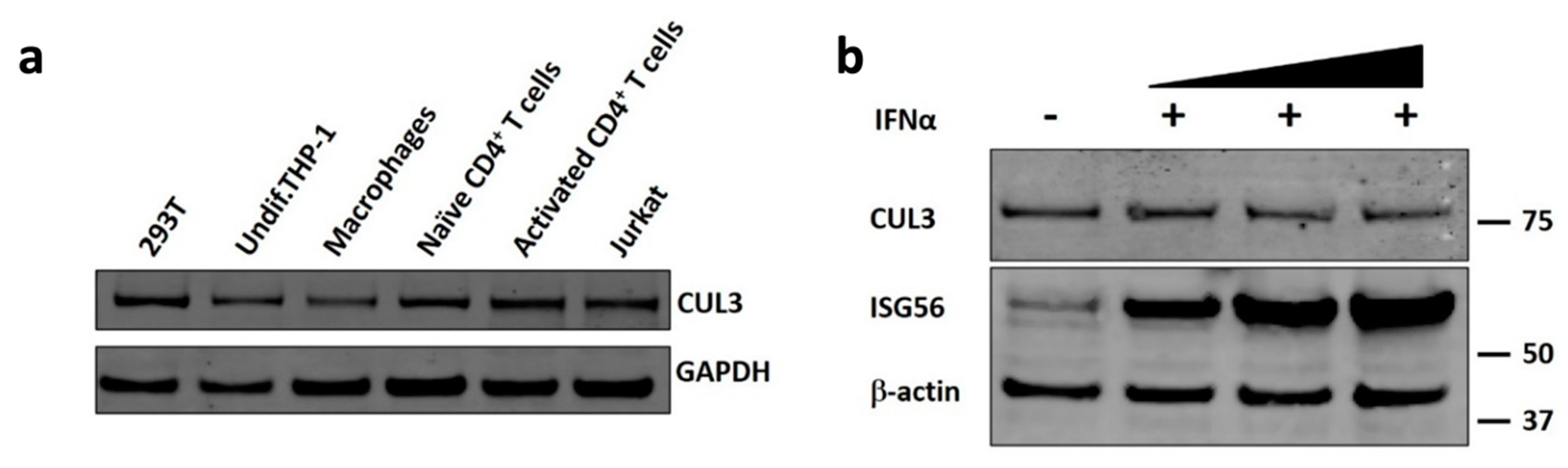
3.2. Cul3 Is Expressed in HIV-1 Target Cells and Is Not Type I IFN Inducible
3.3. Cul3 Restricts Viral Replication in Primary HIV-1 Target Cells
3.4. Cul3 Negatively Regulates HIV-1 Transcript Levels
3.5. NF-κB/NFAT Sites in the HIV-1 LTR Are Important for the Inhibition of HIV-1 Transcription by Cul3
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frankel, A.D.; Young, J.A. HIV-1: Fifteen proteins and an RNA. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brass, A.L.; Dykxhoorn, D.M.; Benita, Y.; Yan, N.; Engelman, A.; Xavier, R.J.; Lieberman, J.; Elledge, S.J. Identification of host proteins required for HIV infection through a functional genomic screen. Science 2008, 319, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchhoff, F. Immune evasion and counteraction of restriction factors by HIV-1 and other primate lentiviruses. Cell Host Microbe 2010, 8, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malim, M.H.; Bieniasz, P.D. HIV Restriction Factors and Mechanisms of Evasion. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a006940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bushman, F.D.; Malani, N.; Fernandes, J.; D’Orso, I.; Cagney, G.; Diamond, T.L.; Zhou, H.; Hazuda, D.J.; Espeseth, A.S.; König, R.; et al. Host cell factors in HIV replication: Meta-analysis of genome-wide studies. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- König, R.; Zhou, Y.; Elleder, D.; Diamond, T.L.; Bonamy, G.M.; Irelan, J.T.; Chiang, C.Y.; Tu, B.P.; De Jesus, P.D.; Lilley, C.E.; et al. Global analysis of host-pathogen interactions that regulate early-stage HIV-1 replication. Cell 2008, 135, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, S.; Cimermancic, P.; Gulbahce, N.; Johnson, J.R.; McGovern, K.E.; Clarke, S.C.; Shales, M.; Mercenne, G.; Pache, L.; Li, K.; et al. Global landscape of HIV-human protein complexes. Nature 2011, 481, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Xu, M.; Huang, Q.; Gates, A.T.; Zhang, X.D.; Castle, J.C.; Stec, E.; Ferrer, M.; Strulovici, B.; Hazuda, D.J.; et al. Genome-scale RNAi screen for host factors required for HIV replication. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 4, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerabkova, K.; Sumara, I. Cullin 3, a cellular scripter of the non-proteolytic ubiquitin code. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 93, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroski, M.D.; Deshaies, R.J. Function and regulation of cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Guo, J.; Wang, Z.; North, B.J.; Tao, K.; Dai, X.; Wei, W. Functional analysis of Cullin 3 E3 ligases in tumorigenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2018, 1869, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Sui, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, C. Cullin family proteins and tumorigenesis: Genetic association and molecular mechanisms. J. Cancer 2015, 6, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarikas, A.; Hartmann, T.; Pan, Z.Q. The cullin protein family. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seissler, T.; Marquet, R.; Paillart, J.C. Hijacking of the Ubiquitin/Proteasome Pathway by the HIV Auxiliary Proteins. Viruses 2017, 9, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, U.; Antón, L.C.; Bacík, I.; Cox, J.H.; Bour, S.; Bennink, J.R.; Orlowski, M.; Strebel, K.; Yewdell, J.W. CD4 glycoprotein degradation induced by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vpu protein requires the function of proteasomes and the ubiquitin-conjugating pathway. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 2280–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margottin, F.; Bour, S.P.; Durand, H.; Selig, L.; Benichou, S.; Richard, V.; Thomas, D.; Strebel, K.; Benarous, R. A novel human WD protein, h-beta TrCp, that interacts with HIV-1 Vpu connects CD4 to the ER degradation pathway through an F-box motif. Mol. Cell 1998, 1, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Baig, T.T.; Love, R.P.; Chelico, L. Suppression of APOBEC3-mediated restriction of HIV-1 by Vif. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, M.E.; Harris, R.S.; Harki, D.A. APOBEC Enzymes as Targets for Virus and Cancer Therapy. Cell Chem. Biol. 2018, 25, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; DeLucia, M.; Hao, C.; Hrecka, K.; Monnie, C.; Skowronski, J.; Ahn, J. HIV-1 Vpr protein directly loads helicase-like transcription factor (HLTF) onto the CRL4-DCAF1 E3 ubiquitin ligase. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 21117–21127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahouassa, H.; Blondot, M.L.; Chauveau, L.; Chougui, G.; Morel, M.; Leduc, M.; Guillonneau, F.; Ramirez, B.C.; Schwartz, O.; Margottin-Goguet, F. HIV-1 Vpr degrades the HLTF DNA translocase in T cells and macrophages. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5311–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrecka, K.; Hao, C.; Shun, M.C.; Kaur, S.; Swanson, S.K.; Florens, L.; Washburn, M.P.; Skowronski, J. HIV-1 and HIV-2 exhibit divergent interactions with HLTF and UNG2 DNA repair proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E3921–E3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahon, C.; Krogan, N.J.; Craik, C.S.; Pick, E. Cullin E3 ligases and their rewiring by viral factors. Biomolecules 2014, 4, 897–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Guo, H.; Han, X.; Liu, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, W.; Yu, X.F. A novel DCAF1-binding motif required for Vpx-mediated degradation of nuclear SAMHD1 and Vpr-induced G2 arrest. Cell Microbiol. 2012, 14, 1745–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwefel, D.; Boucherit, V.C.; Christodoulou, E.; Walker, P.A.; Stoye, J.P.; Bishop, K.N.; Taylor, I.A. Molecular determinants for recognition of divergent SAMHD1 proteins by the lentiviral accessory protein Vpx. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pache, L.; Dutra, M.S.; Spivak, A.M.; Marlett, J.M.; Murry, J.P.; Hwang, Y.; Maestre, A.M.; Manganaro, L.; Vamos, M.; Teriete, P.; et al. BIRC2/cIAP1 Is a Negative Regulator of HIV-1 Transcription and Can Be Targeted by Smac Mimetics to Promote Reversal of Viral Latency. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 18, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, J.D.; Gurian-West, M.; Clurman, B.; Roberts, J.M. Cullin-3 targets cyclin E for ubiquitination and controls S phase in mammalian cells. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 2375–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghe, S.; Jiang, F.; Miura, Y.; Cerny, R.L.; Tsai, M.-Y.; Furukawa, M. The CUL3-KLHL18 ligase regulates mitotic entry and ubiquitylates Aurora-A. Biol. Open 2012, 1, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.F.; Kuo, H.P.; Liu, M.; Chou, C.K.; Xia, W.; Du, Y.; Shen, J.; Chen, C.T.; Huo, L.; Hsu, M.C.; et al. KEAP1 E3 ligase-mediated downregulation of NF-kappaB signaling by targeting IKKbeta. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, G.E.; Leung, K.; Folks, T.M.; Kunkel, S.; Nabel, G.J. Activation of HIV gene expression during monocyte differentiation by induction of NF-kappa B. Nature 1989, 339, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcamí, J.; Laín de Lera, T.; Folgueira, L.; Pedraza, M.A.; Jacqué, J.M.; Bachelerie, F.; Noriega, A.R.; Hay, R.T.; Harrich, D.; Gaynor, R.B. Absolute dependence on kappa B responsive elements for initiation and Tat-mediated amplification of HIV transcription in blood CD4 T lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 1552–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calman, A.F.; Busch, M.P.; Vyas, G.N.; McHugh, T.M.; Stites, D.P.; Peterlin, B.M. Transcription and replication of human immunodeficiency virus-1 in B lymphocytes in vitro. AIDS 1988, 2, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.K.; Greene, W.C. Dynamic roles for NF-κB in HTLV-I and HIV-1 retroviral pathogenesis. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 246, 286–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, S.; Hammer, C.; Hopfensperger, K.; Klein, L.; Hotter, D.; De Jesus, P.D.; Herbert, K.M.; Pache, L.; Smith, N.; van der Merwe, J.A.; et al. HIV-1 Vpu is a potent transcriptional suppressor of NF-κB-elicited antiviral immune responses. Elife 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanda, S.K.; White, S.; Orth, A.P.; Reisdorph, R.; Miraglia, L.; Thomas, R.S.; DeJesus, P.; Mason, D.E.; Huang, Q.; Vega, R.; et al. Genome-scale functional profiling of the mammalian AP-1 signaling pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 12153–12158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Boso, G.; Langer, S.; Soonthornvacharin, S.; De Jesus, P.D.; Nguyen, Q.; Olivieri, K.C.; Portillo, A.J.; Yoh, S.M.; Pache, L.; et al. Large-Scale Arrayed Analysis of Protein Degradation Reveals Cellular Targets for HIV-1 Vpu. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 2493–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendel, A.; Bak, R.O.; Clark, J.T.; Kennedy, A.B.; Ryan, D.E.; Roy, S.; Steinfeld, I.; Lunstad, B.D.; Kaiser, R.J.; Wilkens, A.B.; et al. Chemically modified guide RNAs enhance CRISPR-Cas genome editing in human primary cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 985–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultquist, J.F.; Schumann, K.; Woo, J.M.; Manganaro, L.; McGregor, M.J.; Doudna, J.; Simon, V.; Krogan, N.J.; Marson, A. A Cas9 Ribonucleoprotein Platform for Functional Genetic Studies of HIV-Host Interactions in Primary Human T Cells. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 1438–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochsenbauer, C.; Edmonds, T.G.; Ding, H.; Keele, B.F.; Decker, J.; Salazar, M.G.; Salazar-Gonzalez, J.F.; Shattock, R.; Haynes, B.F.; Shaw, G.M.; et al. Generation of transmitted/founder HIV-1 infectious molecular clones and characterization of their replication capacity in CD4 T lymphocytes and monocyte-derived macrophages. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 2715–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrish, N.F.; Gao, F.; Li, H.; Giorgi, E.E.; Barbian, H.J.; Parrish, E.H.; Zajic, L.; Iyer, S.S.; Decker, J.M.; Kumar, A.; et al. Phenotypic properties of transmitted founder HIV-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6626–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapham, P.R.; McKnight, A. HIV-1 receptors and cell tropism. Br. Med. Bull. 2001, 58, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Lu, J.; Liu, L.; Bernard, D.; Yang, C.Y.; Fernandez-Salas, E.; Chinnaswamy, K.; Layton, S.; Stuckey, J.; Yu, Q.; et al. A potent small-molecule inhibitor of the DCN1-UBC12 interaction that selectively blocks cullin 3 neddylation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkhout, B.; Silverman, R.H.; Jeang, K.T. Tat trans-activates the human immunodeficiency virus through a nascent RNA target. Cell 1989, 59, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vives, E.; Charneau, P.; van Rietschoten, J.; Rochat, H.; Bahraoui, E. Effects of the Tat basic domain on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transactivation, using chemically synthesized Tat protein and Tat peptides. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 3343–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosque, A.; Planelles, V. Induction of HIV-1 latency and reactivation in primary memory CD4+ T cells. Blood 2009, 113, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesmer, V.M.; Rajadhyaksha, A.; Babin, J.; Bina, M. NF-IL6-mediated transcriptional activation of the long terminal repeat of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 7298–7302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruocco, M.R.; Chen, X.; Ambrosino, C.; Dragonetti, E.; Liu, W.; Mallardo, M.; De Falco, G.; Palmieri, C.; Franzoso, G.; Quinto, I.; et al. Regulation of HIV-1 long terminal repeats by interaction of C/EBP(NF-IL6) and NF-kappaB/Rel transcription factors. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 22479–22486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, N.D.; Agranoff, A.B.; Duckett, C.S.; Nabel, G.J. Transcription factor AP-2 regulates human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gene expression. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 6820–6823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.A.; Kadonaga, J.T.; Luciw, P.A.; Tjian, R. Activation of the AIDS retrovirus promoter by the cellular transcription factor, Sp1. Science 1986, 232, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Adda di Fagagna, F.; Marzio, G.; Gutierrez, M.I.; Kang, L.Y.; Falaschi, A.; Giacca, M. Molecular and functional interactions of transcription factor USF with the long terminal repeat of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 2765–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhnlein, E.; Lowenthal, J.W.; Siekevitz, M.; Ballard, D.W.; Franza, B.R.; Greene, W.C. The same inducible nuclear proteins regulates mitogen activation of both the interleukin-2 receptor-alpha gene and type 1 HIV. Cell 1988, 53, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaka, F.; Saeki, M.; Katayama, S.; Aida, N.; Toh-E, A.; Kominami, K.; Toda, T.; Suzuki, T.; Chiba, T.; Tanaka, K.; et al. Covalent modifier NEDD8 is essential for SCF ubiquitin-ligase in fission yeast. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 3475–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, T.; Osaka, F.; Chiba, T.; Miyamoto, C.; Okabayashi, K.; Shimbara, N.; Kato, S.; Tanaka, K. Covalent modification of all members of human cullin family proteins by NEDD8. Oncogene 1999, 18, 6829–6834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, S.; Su, L.; Amano, M.; Timmerman, L.A.; Kaneshima, H.; Nolan, G.P. The T cell activation factor NF-ATc positively regulates HIV-1 replication and gene expression in T cells. Immunity 1997, 6, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.K.; Greene, W.C. NF-kappaB/Rel: Agonist and antagonist roles in HIV-1 latency. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2011, 6, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.A.; Kwon, H.; Chen, L.-F.; Greene, W.C. Sustained Induction of NF-κB Is Required for Efficient Expression of Latent Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 6043–6056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thu, K.L.; Pikor, L.A.; Chari, R.; Wilson, I.M.; Macaulay, C.E.; English, J.C.; Tsao, M.S.; Gazdar, A.F.; Lam, S.; Lam, W.L.; et al. Genetic disruption of KEAP1/CUL3 E3 ubiquitin ligase complex components is a key mechanism of NF-kappaB pathway activation in lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 1521–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagiya, A.; Suyama, E.; Adachi, H.; Svitkin, Y.V.; Aza-Blanc, P.; Imataka, H.; Mikami, S.; Martineau, Y.; Ronai, Z.A.; Sonenberg, N. Translational homeostasis via the mRNA cap-binding protein, eIF4E. Mol. Cell 2012, 46, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtheoux, T.; Enchev, R.I.; Lampert, F.; Gerez, J.; Beck, J.; Picotti, P.; Sumara, I.; Peter, M. Cortical dynamics during cell motility are regulated by CRL3(KLHL21) E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomer-Lluch, M.; Ruiz, A.; Moris, A.; Prado, J.G. Restriction Factors: From Intrinsic Viral Restriction to Shaping Cellular Immunity Against HIV-1. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmori, Y.; Hamilton, T.A. Cooperative interaction between interferon (IFN) stimulus response element and kappa B sequence motifs controls IFN gamma- and lipopolysaccharide-stimulated transcription from the murine IP-10 promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 6677–6688. [Google Scholar]
- Hiscott, J.; Alper, D.; Cohen, L.; Leblanc, J.F.; Sportza, L.; Wong, A.; Xanthoudakis, S. Induction of human interferon gene expression is associated with a nuclear factor that interacts with the NF-kappa B site of the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 2557–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeffer, L.M.; Kim, J.G.; Pfeffer, S.R.; Carrigan, D.J.; Baker, D.P.; Wei, L.; Homayouni, R. Role of nuclear factor-kappaB in the antiviral action of interferon and interferon-regulated gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 31304–31311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libermann, T.A.; Baltimore, D. Activation of interleukin-6 gene expression through the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Mol. Cell Biol. 1990, 10, 2327–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauter, D.; Hotter, D.; Van Driessche, B.; Stürzel, C.M.; Kluge, S.F.; Wildum, S.; Yu, H.; Baumann, B.; Wirth, T.; Plantier, J.C.; et al. Differential regulation of NF-κB-mediated proviral and antiviral host gene expression by primate lentiviral Nef and Vpu proteins. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 586–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siliciano, J.D.; Kajdas, J.; Finzi, D.; Quinn, T.C.; Chadwick, K.; Margolick, J.B.; Kovacs, C.; Gange, S.J.; Siliciano, R.F. Long-term follow-up studies confirm the stability of the latent reservoir for HIV-1 in resting CD4+ T cells. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 727–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Anderson, J.L.; Lewin, S.R. Getting the “Kill” into “Shock and Kill”: Strategies to Eliminate Latent HIV. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, G.; Dandekar, S. Targeting NF-κB signaling with protein kinase C agonists as an emerging strategy for combating HIV latency. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2015, 31, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Langer, S.; Yin, X.; Diaz, A.; Portillo, A.J.; Gordon, D.E.; Rogers, U.H.; Marlett, J.M.; Krogan, N.J.; Young, J.A.T.; Pache, L.; et al. The E3 Ubiquitin-Protein Ligase Cullin 3 Regulates HIV-1 Transcription. Cells 2020, 9, 2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092010
Langer S, Yin X, Diaz A, Portillo AJ, Gordon DE, Rogers UH, Marlett JM, Krogan NJ, Young JAT, Pache L, et al. The E3 Ubiquitin-Protein Ligase Cullin 3 Regulates HIV-1 Transcription. Cells. 2020; 9(9):2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092010
Chicago/Turabian StyleLanger, Simon, Xin Yin, Arturo Diaz, Alex J. Portillo, David E. Gordon, Umu H. Rogers, John M. Marlett, Nevan J. Krogan, John A. T. Young, Lars Pache, and et al. 2020. "The E3 Ubiquitin-Protein Ligase Cullin 3 Regulates HIV-1 Transcription" Cells 9, no. 9: 2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092010
APA StyleLanger, S., Yin, X., Diaz, A., Portillo, A. J., Gordon, D. E., Rogers, U. H., Marlett, J. M., Krogan, N. J., Young, J. A. T., Pache, L., & Chanda, S. K. (2020). The E3 Ubiquitin-Protein Ligase Cullin 3 Regulates HIV-1 Transcription. Cells, 9(9), 2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092010





