Association Between Epstein–Barr Virus Infection and PD-L1 Expression in Gastric Cancer: Prevalence, Clinicopathological Features, and Prognostic Implications
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Procedures
2.2.1. Sample Processing
2.2.2. EBER ISH
2.2.3. PD-L1 IHC
2.3. Outcomes
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. EBV Prevalence and PD-L1 Expression and Their Clinicopathological Features
3.3. Association Between EBV Status and PD-L1 Expression in Gastric Cancer
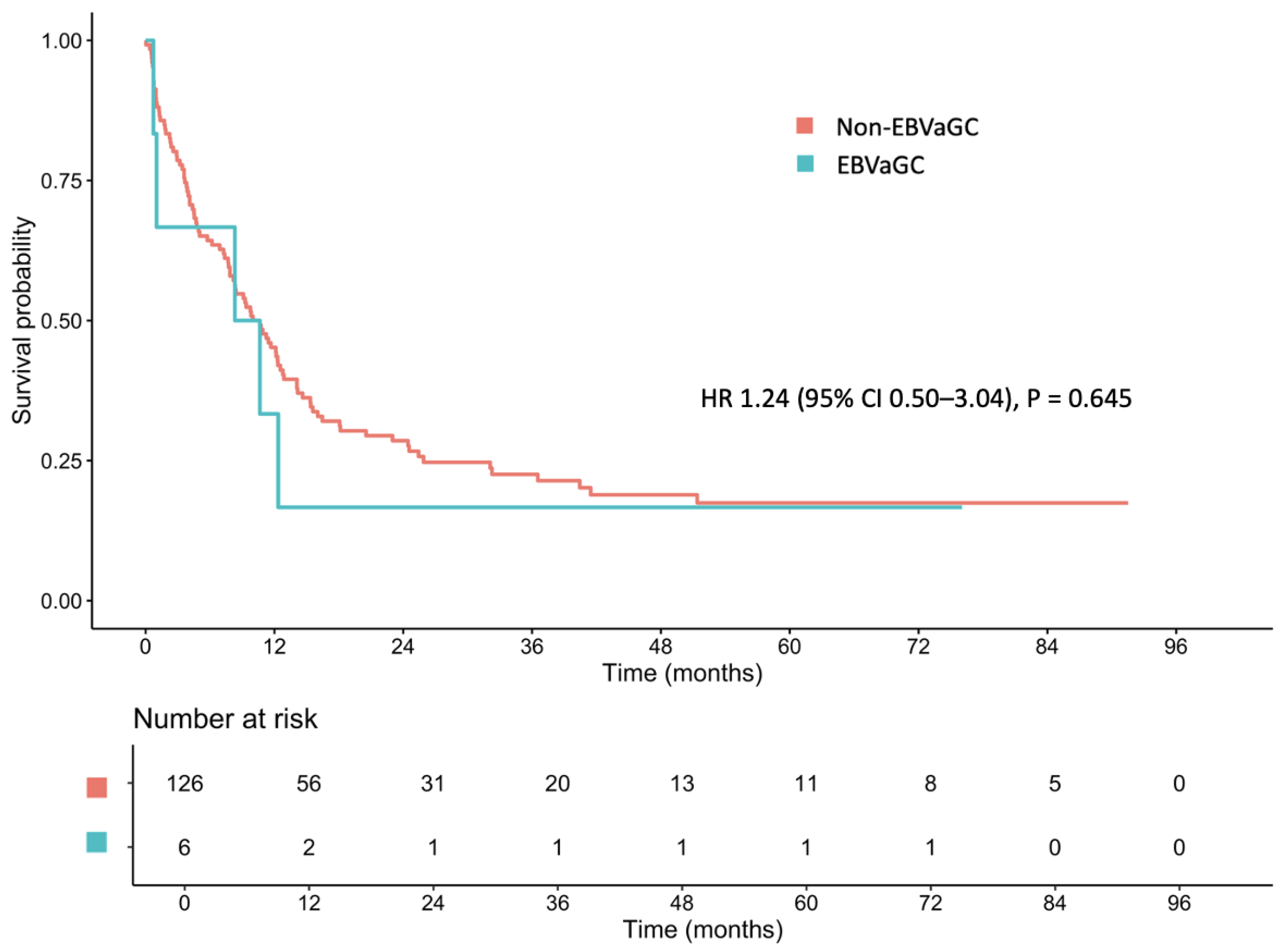
3.4. Survival Outcomes
3.5. Prognostic Implications
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CPS | Combined positive score |
| EBER | Epstein–Barr virus-encoded small RNA |
| EBV | Epstein–Barr virus |
| EBVaGC | Epstein–Barr virus-associated gastric cancer |
| ECOG | Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group |
| FFPE | Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue |
| IHC | Immunohistochemical |
| ISH | In situ hybridization |
| MSI | Microsatellite instability |
| PD-L1 | Programmed death-ligand 1 |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive molecular characterization of gastric adenocarcinoma. Nature 2014, 513, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawazoe, A.; Shitara, K.; Kuboki, Y.; Bando, H.; Kojima, T.; Yoshino, T.; Ohtsu, A.; Ochiai, A.; Togashi, Y.; Nishikawa, H.; et al. Clinicopathological features of 22C3 PD-L1 expression with mismatch repair, Epstein–Barr virus status, and cancer genome alterations in metastatic gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 2019, 22, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, Á.; Sousa, H.; Medeiros, R.; Nobre, A.; Machado, M. PD-L1 expression in EBV associated gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Discov. Oncol. 2022, 13, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, M.A.; Ramos, M.F.K.P.; Faraj, S.F.; Dias, A.R.; Yagi, O.K.; Zilberstein, B.; Cecconello, I.; Alves, V.A.F.; de Mello, E.S.; Ribeiro, U. Clinicopathological and prognostic features of Epstein-Barr virus infection, microsatellite instability, and PD-L1 expression in gastric cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 117, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almhanna, K.; Antonia, S. PD-L1 antibodies for EBV-positive gastric cancer, going beyond PD-L1 expression and microsatellite instability. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 221–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Fátima Aquino Moreira-Nunes, C.; de Souza Almeida Titan Martins, C.N.; Feio, D.; Lima, I.K.; Lamarão, L.M.; de Souza, C.R.; Costa, I.B.; da Silva Maues, J.H.; Soares, P.C.; de Assumpção, P.P.; et al. PD-L1 expression associated with Epstein–Barr virus status and patients’ survival in a large cohort of gastric cancer patients in Northern Brazil. Cancer 2021, 13, 3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Wu, Y.; Jin, M.; Jia, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cao, D.; Qin, L.; Wang, X.; Zheng, M.; Cao, X.; et al. Microsatellite instability and Epstein-Barr virus combined with PD-L1 could serve as a potential strategy for predicting the prognosis and efficacy of postoperative chemotherapy in gastric cancer. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Choi, M.G.; Kim, K.; Kim, K.M.; Kim, S.T.; Park, S.H.; Cristescu, R.; Peter, S.; Lee, J. High PD-L1 expression in gastric cancer (GC) patients and correlation with molecular features. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 152881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Lin, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, D.; Wu, A.; Li, Z. Clinicopathological features of tumor mutation burden, Epstein-Barr virus infection, microsatellite instability and PD-L1 status in Chinese patients with gastric cancer. Diagn. Pathol. 2021, 16, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.L.; Liu, Q.W.; Liu, F.R.; Yuan, S.S.; Li, X.F.; Li, J.N.; Yang, A.L.; Ling, Y.H. The clinicopathological significance and predictive value for immunotherapy of programmed death ligand-1 expression in Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric cancer. Oncoimmunology 2021, 10, 1938381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röcken, C. Predictive biomarkers in gastric cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Peng, Z.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, X.; Li, J.; Shen, L. Current status and future perspective of immunotherapy in gastrointestinal cancers. Innovation 2020, 1, 100041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shitara, K.; Fleitas, T.; Kawakami, H.; Curigliano, G.; Narita, Y.; Wang, F.; Wardhani, S.O.; Basade, M.; Rha, S.Y.; Wan Zamaniah, W.I.; et al. Pan-Asian adapted ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of patients with gastric cancer. ESMO Open 2024, 9, 102226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rha, S.Y.; Oh, D.Y.; Yañez, P.; Bai, Y.; Ryu, M.H.; Lee, J.; Rivera, F.; Alves, G.V.; Garrido, M.; Shiu, K.K.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy versus placebo plus chemotherapy for HER2-negative advanced gastric cancer (KEYNOTE-859): A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 1181–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janjigian, Y.Y.; Shitara, K.; Moehler, M.; Garrido, M.; Salman, P.; Shen, L.; Wyrwicz, L.; Yamaguchi, K.; Skoczylas, T.; Campos Bragagnoli, A.; et al. First-line nivolumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for advanced gastric, gastro-oesophageal junction, and oesophageal adenocarcinoma (CheckMate 649): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjigian, Y.Y.; Kawazoe, A.; Bai, Y.; Xu, J.; Lonardi, S.; Metges, J.P.; Yanez, P.; Wyrwicz, L.S.; Shen, L.; Ostapenko, Y.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus trastuzumab and chemotherapy for HER2-positive gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma: Interim analyses from the phase 3 KEYNOTE-811 randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 2197–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Chen, M.; Guo, D.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, W.; Pan, J.; Zhong, X.; Li, X.; Qian, H.; Wang, X. PD-L1 and gastric cancer prognosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Jia, K.; Lv, H.; Wang, S.Q.; Wu, Y.; Lei, H.; Chen, X. EBV-positive gastric cancer: Current knowledge and future perspectives. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 583463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, J.; Iizasa, H.; Yoshiyama, H.; Shimokuri, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Sasaki, S.; Nakamura, M.; Yanai, H.; Sakai, K.; Suehiro, Y.; et al. Clinical importance of Epstein–Barr virus-associated gastric cancer. Cancer 2018, 10, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, V.D.; Brisotto, G.; Repetto, O.; De Zorzi, M.; Caggiari, L.; Zanussi, S.; Alessandrini, L.; Canzonieri, V.; Miolo, G.; Puglisi, F.; et al. Overview of Epstein–Barr-virus-associated gastric cancer correlated with prognostic classification and development of therapeutic options. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, Y.; Kawazoe, A.; Sasaki, A.; Mishima, S.; Sawada, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Kotani, D.; Kuboki, Y.; Taniguchi, H.; Kojima, T.; et al. The impact of molecular subtype on efficacy of chemotherapy and checkpoint inhibition in advanced gastric cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 3784–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.T.; Cristescu, R.; Bass, A.J.; Kim, K.M.; Odegaard, J.I.; Kim, K.; Liu, X.Q.; Sher, X.; Jung, H.; Lee, M.; et al. Comprehensive molecular characterization of clinical responses to PD-1 inhibition in metastatic gastric cancer. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miliotis, C.N.; Slack, F.J. Multi-layered control of PD-L1 expression in Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric cancer. J. Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, A.; Abe, H.; Kunita, A.; Saito, R.; Kanda, T.; Yamashita, H.; Seto, Y.; Ishikawa, S.; Fukayama, M. Viral loads correlate with upregulation of PD-L1 and worse patient prognosis in Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanek, L.; Gurlich, R.; Musil, Z.; Havluj, L.; Whitley, A. Monitoring EBV infection, MSI, PDL-1 expression, Her-2/neu amplification as a biomarker for PD-1 inhibition in gastric cancer. Bratislavske Lekarske Listy 2022, 123, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Ogura, G.; Tanabe, M.; Hayashi, T.; Ohbayashi, C.; Azuma, M.; Kunisaki, C.; Akazawa, Y.; Ozawa, S.; Matsumoto, S.; et al. Clinicopathological features of PD-L1 protein expression, EBV positivity, and MSI status in patients with advanced gastric and esophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma in Japan. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2022, 23, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinozaki-Ushiku, A.; Kunita, A.; Fukayama, M. Update on Epstein-Barr virus and gastric cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 1421–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, A.; Monavari, S.H.; Solaymani Mohammadi, F.; Kiani, S.J.; Armat, S.; Farahmand, M. Association between Epstein-Barr virus infection and gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, M.C.; Murphy, G.; Koriyama, C.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Kim, W.H.; Herrera-Goepfert, R.; Corvalan, A.H.; Carrascal, E.; Abdirad, A.; Anwar, M.; et al. Determinants of Epstein-Barr virus-positive gastric cancer: An international pooled analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, L.C.; Inam, I.Z.; Saito, Y.; Yoshikawa, T.; Quaas, A.; Hoelscher, A.; Bollschweiler, E.; Fazzi, G.E.; Melotte, V.; Langley, R.E.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus and mismatch repair deficiency status differ between oesophageal and gastric cancer: A large multi-centre study. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 94, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo, M.C.; Kim, W.H.; Chiaravalli, A.M.; Kim, K.M.; Corvalan, A.H.; Matsuo, K.; Yu, J.; Sung, J.J.Y.; Herrera-Goepfert, R.; Meneses-Gonzalez, F.; et al. Improved survival of gastric cancer with tumour Epstein-Barr virus positivity: An international pooled analysis. Gut 2014, 63, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, C.; Mota, M.; Gradiz, R.; Cipriano, M.A.; Caramelo, F.; Cruz, H.; Alarcão, A.; E Sousa, F.C.; Oliveira, F.; Martinho, F.; et al. Prevalence and characteristics of Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinomas in Portugal. Infect. Agent Cancer 2017, 12, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Zhong, M.; Wang, W.; Liao, P.; Yin, X.; Rotroff, D.; Knepper, T.C.; Mcleod, H.L.; Zhou, C.; Xie, S.; et al. EBV infection and MSI status significantly influence the clinical outcomes of gastric cancer patients. Clin. Chim. Acta 2017, 471, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.C.; Ng, K.F.; Chen, K.H.; Hsu, J.T.; Liu, K.H.; Yeh, T.S.; Chen, T.C. Prognostic factors in Epstein-Barr virus-associated stage I–III gastric carcinoma: Implications for a unique type of carcinogenesis. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z. Assessing Epstein–Barr virus in gastric cancer: Clinicopathological features and prognostic implications. Infect. Agent Cancer 2023, 18, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Qiu, H.; Kong, P.; Chen, S.; Li, W.; Zhan, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Prognostic significance of Epstein-Barr virus infection in gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, B.W.; Baek, D.W.; Kang, H.; Baek, J.H.; Kim, J.G. Novel therapeutic approaches for Epstein-Barr virus associated gastric cancer. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 4003–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.; Mehnert, J.M.; Hirshfield, K.M.; Riedlinger, G.; Damare, S.; Saunders, T.; Kane, M.; Sokol, L.; Stein, M.N.; Poplin, E.; et al. Immune activation and benefit from avelumab in EBV-positive gastric cancer. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Gong, J.; Qi, C.; Li, J.; Shen, L.; Peng, Z. Positive status of Epstein-Barr virus as a biomarker for gastric cancer immunotherapy: A prospective observational study. J. Immunother. 2020, 43, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Xie, T.; Wang, Z.; Tong, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, F.; Cai, J.; Wei, X.; Peng, Z.; Shen, L. Efficacy and predictive biomarkers of immunotherapy in Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e004080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, M.S.; Kerr, K.M.; Kockx, M.; Beasley, M.B.; Borczuk, A.C.; Botling, J.; Bubendorf, L.; Chirieac, L.; Chen, G.; Chou, T.Y.; et al. PD-L1 immunohistochemistry comparability study in real-life clinical samples: Results of blueprint Phase 2 project. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1302–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narita, Y.; Sasaki, E.; Masuishi, T.; Taniguchi, H.; Kadowaki, S.; Ito, S.; Yatabe, Y.; Muro, K. PD-L1 immunohistochemistry comparison of 22C3 and 28–8 assays for gastric cancer. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2021, 12, 2696–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitapanarux, T.; Gumrai, P.; Kongkarnka, S.; Wannasai, K.; Lertprasertsuke, N. Programmed death-ligand 1 expression and overall survival in Thai patients with gastric cancer. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crumley, A.B.C.; Stuart, R.C.; McKernan, M.; McMillan, D.C. Is hypoalbuminemia an independent prognostic factor in patients with gastric cancer? World J. Surg. 2010, 34, 2393–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Lis, C.G. Pretreatment serum albumin as a predictor of cancer survival: A systematic review of the epidemiological literature. Nutr. J. 2010, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oñate-Ocaña, L.F.; Aiello-Crocifoglio, V.; Gallardo-Rincón, D.; Herrera-Goepfert, R.; Brom-Valladares, R.; Carrillo, J.F.; Cervera, E.; Mohar-Betancourt, A. Serum albumin as a significant prognostic factor for patients with gastric carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2007, 14, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Wang, P.Y.; Liu, Y.C. Palliative gastrectomy improves the survival of patients with metastatic early-onset gastric cancer: A retrospective cohort study. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 7874–7890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Xu, H.; Jiang, C.; Zheng, J.; Wu, D.; Tou, L.; Que, H.; Sun, Z. The prognostic role of palliative gastrectomy in advanced gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Batran, S.E.; Hartmann, J.T.; Probst, S.; Schmalenberg, H.; Hollerbach, S.; Hofheinz, R.; Rethwisch, V.; Seipelt, G.; Homann, N.; Wilhelm, G.; et al. Phase III trial in metastatic gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma with fluorouracil, leucovorin plus either oxaliplatin or cisplatin: A study of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.M.; Jeung, H.C.; Rha, S.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Jung, I.; Nam, B.H.; Lee, K.H.; Chung, H.C. A randomized phase II trial of S-1-oxaliplatin versus capecitabine-oxaliplatin in advanced gastric cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, Y.J.; Van Cutsem, E.; Feyereislova, A.; Chung, H.C.; Shen, L.; Sawaki, A.; Lordick, F.; Ohtsu, A.; Omuro, Y.; Satoh, T.; et al. Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): A phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Localized Stage (n = 56) | Metastatic Stage (n = 72) | Total # (n = 132) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Median age, years (SD) * | 65.4 (11.5) | 60.9 (12.6) | 63.2 (12.3) |
| Age ≥ 65 years, n (%) | 27 (48.2) | 30 (41.7) | 60 (45.5) |
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Male | 35 (62.5) | 46 (63.9) | 82 (62.1) |
| Female | 21 (37.5) | 26 (36.1) | 50 (37.9) |
| ECOG PS, n (%) * | |||
| 0–1 | 45 (80.4) | 33 (45.8) | 79 (59.8) |
| ≥2 | 11 (19.6) | 39 (54.2) | 53 (40.2) |
| BMI, n (kg/m2; %) | |||
| <18.5 | 11 (19.6) | 30 (41.7) | 41 (31.3) |
| 18.5–22.9 | 22 (39.3) | 23 (31.9) | 47 (35.9) |
| 23.0–24.9 | 13 (23.2) | 10 (13.9) | 24 (18.3) |
| ≥25 | 10 (17.9) | 9 (12.5) | 19 (14.5) |
| Smoking, n (%) | |||
| Current or former | 29 (51.8) | 34 (47.2) | 63 (47.7) |
| Never | 26 (46.4) | 34 (47.2) | 63 (47.7) |
| Unknown | 1 (1.8) | 4 (5.6) | 6 (4.6) |
| Alcohol drinking, n (%) | |||
| Current or former | 25 (44.6) | 29 (40.3) | 54 (40.9) |
| Never | 30 (53.6) | 39 (54.2) | 72 (54.5) |
| Unknown | 1 (1.8) | 4 (5.6) | 6 (4.6) |
| Laboratory at cancer diagnosis | |||
| Hemoglobin, g/dL (IQR) | 11.1 (9.6, 12.7) | 10.6 (9.2, 12.0) | 11.0 (9.3, 12.2) |
| Creatinine, mg/dL (IQR) | 0.9 (0.7, 1.0) | 0.8 (0.7, 1.0) | 0.8 (0.7, 1.0) |
| CrCl < 60 mL/min, n (%) | 21 (37.5) | 26 (37.1) | 49 (38.0) |
| Total bilirubin, mg/dL (IQR) | 0.4 (0.3, 0.7) | 0.4 (0.2, 0.7) | 0.4 (0.3, 0.7) |
| Albumin, g/dL (SD) * | 3.8 (0.6) | 3.4 (0.6) | 3.6 (0.7) |
| Tumor location, n (%) | |||
| Proximal stomach | 23 (41.1) | 22 (30.6) | 45 (34.1) |
| Middle stomach | 18 (32.1) | 17 (23.6) | 36 (27.3) |
| Distal stomach | 13 (23.2) | 25 (34.7) | 41 (31.1) |
| Diffuse/linitis plastica | 2 (3.6) | 8 (11.1) | 10 (7.5) |
| T stage, n (%) * | |||
| T1 | 3 (5.4) | 0 (0) | 3 (2.3) |
| T2 | 5 (8.9) | 1 (1.4) | 6 (4.5) |
| T3 | 21 (37.5) | 13 (18.1) | 34 (25.8) |
| T4 | 24 (42.9) | 15 (20.8) | 39 (29.5) |
| Tx | 3 (5.4) | 43 (59.7) | 50 (37.9) |
| N stage, n (%) * | |||
| N0 | 17 (30.4) | 1 (1.4) | 18 (13.6) |
| N1 | 15 (26.8) | 14 (19.4) | 29 (22.0) |
| N2 | 13 (23.2) | 17 (23.6) | 30 (22.7) |
| N3 | 11 (19.6) | 11 (15.3) | 22 (16.7) |
| Nx | 0 (0) | 29 (40.3) | 33 (25.0) |
| Tumor differentiation, n (%) | |||
| Well | 8 (14.3) | 6 (8.3) | 16 (12.1) |
| Moderate | 17 (30.4) | 15 (20.8) | 33 (25.0) |
| Poor | 31 (55.4) | 51 (70.8) | 83 (62.9) |
| Signet ring cell feature, n (%) | 13 (23.2) | 20 (27.8) | 34 (25.8) |
| Lauren classification, n (%) * | |||
| Diffuse | 20 (35.7) | 47 (65.3) | 69 (52.3) |
| Intestinal | 26 (46.4) | 14 (19.4) | 41 (31.1) |
| Mixed | 7 (12.5) | 11 (15.3) | 19 (14.1) |
| Unknown | 3 (5.4) | (0) | 3 (2.3) |
| Lymphovascular invasion, n (%) * | |||
| Yes | 29 (51.8) | 12 (16.7) | 41 (31.1) |
| No | 18 (32.1) | 0 (0) | 18 (13.6) |
| Unknown | 9 (16.1) | 60 (83.3) | 73 (55.3) |
| Perineural invasion, n (%) * | |||
| Yes | 22 (39.3) | 9 (12.5) | 31 (23.5) |
| No | 25 (44.6) | 3 (4.2) | 28 (21.2) |
| Unknown | 9 (16.1) | 60 (83.3) | 73 (55.3) |
| Helicobacter pylori infection, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 10 (17.9) | 8 (11.1) | 19 (14.4) |
| No | 22 (39.3) | 20 (27.8) | 43 (32.6) |
| Unknown | 24 (42.9) | 44 (61.1) | 70 (53.0) |
| HER2 overexpression, n (%) * | |||
| Yes | 1 (1.8) | 0 (0) | 1 (0.8) |
| No | 4 (7.1) | 21 (29.2) | 25 (18.9) |
| Unknown | 51 (91.1) | 51 (70.8) | 106 (80.3) |
| EBV Status | PD-L1 Status | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive (n = 6) | Negative (n = 126) | p-Value | Positive (CPS ≥ 1) (n = 12) | Negative (CPS < 1) (n = 120) | p-Value | |
| Median age, years (SD) | 70.6 (10.7) | 62.8 (12.3) | 0.133 | 67.7 (10.9) | 62.7 (12.4) | 0.186 |
| Age ≥ 65 years, n (%) | 4 (66.7) | 56 (44.4) | 0.410 | 7 (58.3) | 53 (44.2) | 0.525 |
| Sex, n (%) | 0.082 | 1.000 | ||||
| Male | 6 (100) | 76 (60.3) | 8 (66.7) | 74 (61.7) | ||
| Female | 0 (0) | 50 (39.7) | 4 (33.3) | 46 (38.2) | ||
| Smoking, n (%) | 0.058 | 0.730 | ||||
| Current or former | 6 (100) | 57 (45.2) | 6 (50.0) | 57 (47.5) | ||
| Never | 0 (0) | 63 (50.0) | 6 (50.0) | 57 (47.5) | ||
| Unknown | 0 (0) | 6 (4.8) | 0 (0) | 6 (5.0) | ||
| Tumor Location, n (%) | 0.152 | 0.512 | ||||
| Proximal | 2 (33.3) | 43 (34.1) | 3 (25.0) | 42 (35.0) | ||
| Middle | 3 (50.0) | 33 (26.2) | 2 (16.7) | 34 (28.3) | ||
| Distal | 1 (16.7) | 40 (31.8) | 5 (41.6) | 36 (30.0) | ||
| Diffuse | 0 (0) | 10 (7.9) | 2 (16.7) | 8 (66.7) | ||
| T stage, n (%) | 0.370 | 0.741 | ||||
| T1 | 0 (0) | 3 (2.4) | 0 (0) | 3 (2.5) | ||
| T2 | 0 (0) | 6 (4.7) | 0 (0) | 6 (5.0) | ||
| T3 | 3 (50.0) | 31 (24.6) | 4 (33.3) | 30 (25.0) | ||
| T4 | 0 (0) | 39 (31.0) | 2 (16.7) | 37 (30.8) | ||
| Tx | 3 (50.0) | 47 (37.3) | 6 (50.0) | 44 (36.7) | ||
| N stage, n (%) | 0.561 | 0.428 | ||||
| N0 | 1 (16.7) | 17 (13.5) | 2 (16.7) | 16 (13.3) | ||
| N1 | 0 (0) | 29 (23.0) | 2 (16.7) | 27 (22.5) | ||
| N2 | 1 (16.7) | 29 (23.0) | 5 (41.7) | 25 (20.8) | ||
| N3 | 1 (16.7) | 21 (16.7) | 2 (16.7) | 20 (16.7) | ||
| Nx | 3 (50.0) | 30 (23.8) | 1 (8.3) | 32 (26.7) | ||
| M stage, n (%) | 0.747 | 0.091 | ||||
| M0 | 2 (33.3) | 55 (43.6) | 7 (58.3) | 49 (40.8) | ||
| M1 | 4 (66.7) | 68 (54.0) | 5 (41.7) | 67 (55.9) | ||
| Mx | 0 (0) | 3 (2.4) | 0 (0) | 4 (3.3) | ||
| Tumor differentiation, n (%) | 0.704 | 0.822 | ||||
| Well | 0 (0) | 16 (12.7) | 1 (8.3) | 15 (12.5) | ||
| Moderate | 1 (16.7) | 32 (25.4) | 4 (33.3) | 29 (24.2) | ||
| Poor | 5 (83.3) | 78 (61.9) | 7 (58.3) | 76 (63.3) | ||
| Signet ring cell feature, n (%) | 0 (0) | 34 (27.0) | 0.338 | 4 (33.3) | 30 (25.0) | 0.505 |
| Lauren classification, n (%) | 0.261 | 0.617 | ||||
| Diffuse | 4 (66.7) | 65 (51.6) | 5 (41.7) | 64 (53.3) | ||
| Intestinal | 0 (0) | 41 (32.5) | 4 (33.3) | 37 (30.8) | ||
| Mixed | 2 (33.3) | 17 (13.5) | 3 (25.0) | 16 (13.4) | ||
| Unknown | 0 (0) | 3 (2.4) | 0 (0) | 3 (2.5) | ||
| Lymphovascular invasion, n (%) | 0.860 | 0.483 | ||||
| Yes | 2 (33.3) | 39 (30.9) | 2 (16.7) | 39 (32.5) | ||
| No | 0 (0) | 18 (14.3) | 1 (8.3) | 17 (14.2) | ||
| Unknown | 4 (66.7) | 69 (54.8) | 9 (75.0) | 64 (53.3) | ||
| Perineural invasion, n (%) | 1.000 | 0.393 | ||||
| Yes | 1 (16.7) | 30 (23.8) | 2 (16.7) | 29 (24.2) | ||
| No | 1 (16.7) | 27 (21.4) | 1 (8.3) | 27 (22.5) | ||
| Unknown | 4 (66.7) | 69 (54.8) | 9 (75.0) | 64 (53.3) | ||
| Helicobacter pylori infection, n (%) | 1.000 | 0.070 | ||||
| Yes | 1 (16.7) | 18 (14.3) | 3 (25.0) | 16 (13.3) | ||
| No | 2 (33.3) | 41 (32.5) | 6 (50.0) | 37 (30.9) | ||
| Unknown | 3 (50.0) | 67 (53.2) | 3 (25.0) | 67 (55.8) | ||
| HER2 overexpression, n (%) | 0.613 | 0.073 | ||||
| Yes | 0 (0) | 1 (0.8) | 1 (8.3) | 0 (0) | ||
| No | 0 (0) | 25 (19.8) | 1 (8.3) | 24 (20.0) | ||
| Unknown | 6 (100) | 100 (79.4) | 10 (83.4) | 96 (80.0) | ||
| All Patient Cohort | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| PD-L1 Expression | EBV Positive (n = 6) | EBV Negative (n = 126) | p-Value |
| CPS < 1 | 4 (66.7) | 116 (92.1) | 0.093 |
| CPS ≥ 1 | 2 (33.3) | 10 (7.9) | |
| CPS < 5 | 4 (66.7) | 119 (94.4) | 0.054 |
| CPS ≥ 5 | 2 (33.3) | 7 (5.6) | |
| CPS < 10 | 6 (100) | 119 (94.4) | 1.0 |
| CPS ≥ 10 | 0 (0) | 7 (5.6) | |
| Localized-stage cohort | |||
| PD-L1 expression | EBV positive (n = 2) | EBV negative (n = 54) | p-value |
| CPS < 1 | 1 (50.0) | 48 (88.9) | 0.236 |
| CPS ≥ 1 | 1 (50.0) | 6 (11.1) | |
| CPS < 5 | 1 (50.0) | 48 (88.9) | 0.236 |
| CPS ≥ 5 | 1 (50.0) | 6 (11.1) | |
| CPS < 10 | 2 (100) | 48 (88.9) | 1.0 |
| CPS ≥ 10 | 0 (0) | 6 (11.1) | |
| Metastatic-stage cohort | |||
| PD-L1 expression | EBV positive (n = 4) | EBV negative (n = 68) | p-value |
| CPS < 1 | 3 (75.0) | 64 (94.1) | 0.255 |
| CPS ≥ 1 | 1 (25.0) | 4 (5.9) | |
| CPS < 5 | 3 (75.0) | 67 (98.5) | 0.109 |
| CPS ≥ 5 | 1 (25.0) | 1 (1.5) | |
| CPS < 10 | 4 (100) | 67 (98.5) | 1.0 |
| CPS ≥ 10 | 0 (0) | 1 (1.5) | |
| Variables | Univariate | Multivariate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age ≥ 65 years | 1.18 (0.80, 1.74) | 0.410 | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | ||||
| <18.5 | Ref | |||
| 18.5–22.9 | 0.64 (0.40, 1.02) | 0.059 | ||
| 23.0–24.9 | 0.82 (0.44, 1.54) | 0.544 | ||
| ≥25.0 | 0.60 (0.32, 1.13) | 0.113 | ||
| ECOG PS | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| 0–1 | 0.30 (0.20, 0.46) | 0.37 (0.23, 0.61) | ||
| ≥2 | Ref | Ref | ||
| Lauren classification | ||||
| Diffuse | Ref | |||
| Intestinal | 0.66 (0.41, 1.06) | 0.086 | ||
| Mixed | 0.92 (0.53, 1.60) | 0.769 | ||
| Tumor location | ||||
| Proximal | Ref | Ref | ||
| Middle | 1.31 (0.77, 2.24) | 0.315 | 0.87 (0.46, 1.63) | 0.665 |
| Distal | 1.15 (0.72, 1.84) | 0.549 | 0.92 (0.54, 1.57) | 0.758 |
| Diffuse | 2.23 (1.09, 4.57) | 0.029 | 1.32 (0.60, 2.92) | 0.486 |
| Differentiation | ||||
| Well | Ref | |||
| Moderate | 0.85 (0.42, 1.70) | 0.638 | ||
| Poor | 0.96 (0.53, 1.74) | 0.896 | ||
| Signet ring cell feature | 0.82 (0.52, 1.29) | 0.393 | ||
| Stage | <0.001 | 0.007 | ||
| Localized stage | 0.31 (0.18, 0.50) | 0.22 (0.07, 0.66) | ||
| Metastatic stage | Ref | Ref | ||
| EBV positive | 1.48 (0.60, 3.66) | 0.400 | 0.78 (0.28, 2.19) | 0.643 |
| PD-L1-positive (CPS ≥ 1) | 1.02 (0.49, 2.11) | 0.953 | 0.99 (0.43, 2.29) | 0.981 |
| Hemoglobin < 10 g/dL | 1.07 (0.70, 1.62) | 0.758 | ||
| Albumin < 3.5 g/dL | 1.78 (1.19, 2.67) | 0.005 | 1.71 (1.05, 2.79) | 0.032 |
| Gastrectomy | ||||
| No | Ref | Ref | ||
| Subtotal | 0.32 (0.17, 0.59) | <0.001 | 1.07 (0.32, 3.59) | 0.909 |
| Total | 0.33 (0.17, 0.65) | 0.001 | 1.8 (0.52, 6.19) | 0.354 |
| Palliative | 0.53 (0.28, 1.00) | 0.051 | 0.51 (0.25, 1.04) | 0.064 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wonglhow, J.; Tantipisit, J.; Wetwittayakhlang, P.; Sunpaweravong, P.; Sathitruangsak, C.; Kanjanapradit, K.; Thongwatchara, P.; Dechaphunkul, A. Association Between Epstein–Barr Virus Infection and PD-L1 Expression in Gastric Cancer: Prevalence, Clinicopathological Features, and Prognostic Implications. Cancers 2025, 17, 1492. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091492
Wonglhow J, Tantipisit J, Wetwittayakhlang P, Sunpaweravong P, Sathitruangsak C, Kanjanapradit K, Thongwatchara P, Dechaphunkul A. Association Between Epstein–Barr Virus Infection and PD-L1 Expression in Gastric Cancer: Prevalence, Clinicopathological Features, and Prognostic Implications. Cancers. 2025; 17(9):1492. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091492
Chicago/Turabian StyleWonglhow, Jirapat, Jarukit Tantipisit, Panu Wetwittayakhlang, Patrapim Sunpaweravong, Chirawadee Sathitruangsak, Kanet Kanjanapradit, Phatcharaporn Thongwatchara, and Arunee Dechaphunkul. 2025. "Association Between Epstein–Barr Virus Infection and PD-L1 Expression in Gastric Cancer: Prevalence, Clinicopathological Features, and Prognostic Implications" Cancers 17, no. 9: 1492. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091492
APA StyleWonglhow, J., Tantipisit, J., Wetwittayakhlang, P., Sunpaweravong, P., Sathitruangsak, C., Kanjanapradit, K., Thongwatchara, P., & Dechaphunkul, A. (2025). Association Between Epstein–Barr Virus Infection and PD-L1 Expression in Gastric Cancer: Prevalence, Clinicopathological Features, and Prognostic Implications. Cancers, 17(9), 1492. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091492







