Quantifying Intratumoral Heterogeneity and Immunoarchitecture Generated In-Silico by a Spatial Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Model
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
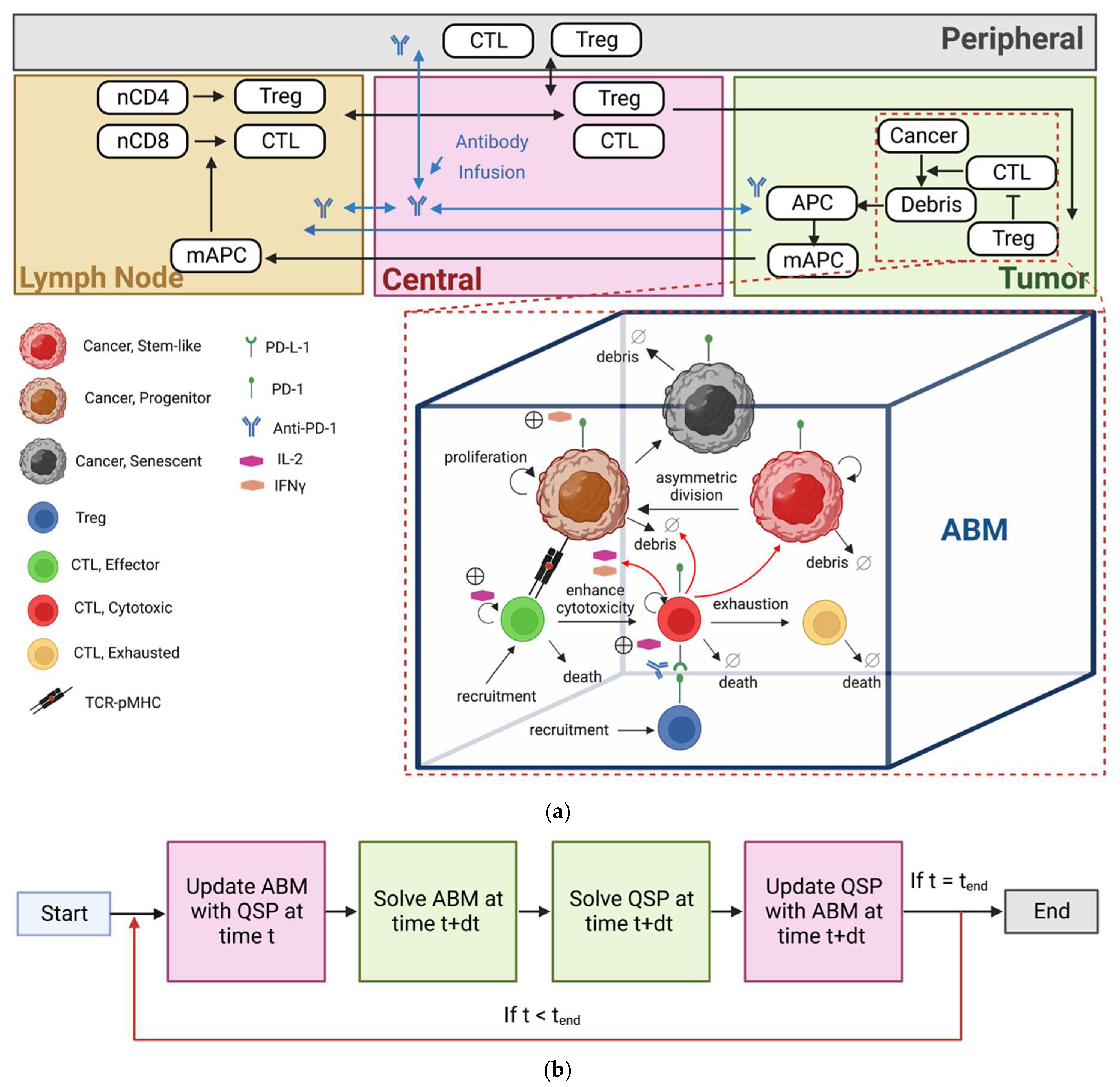
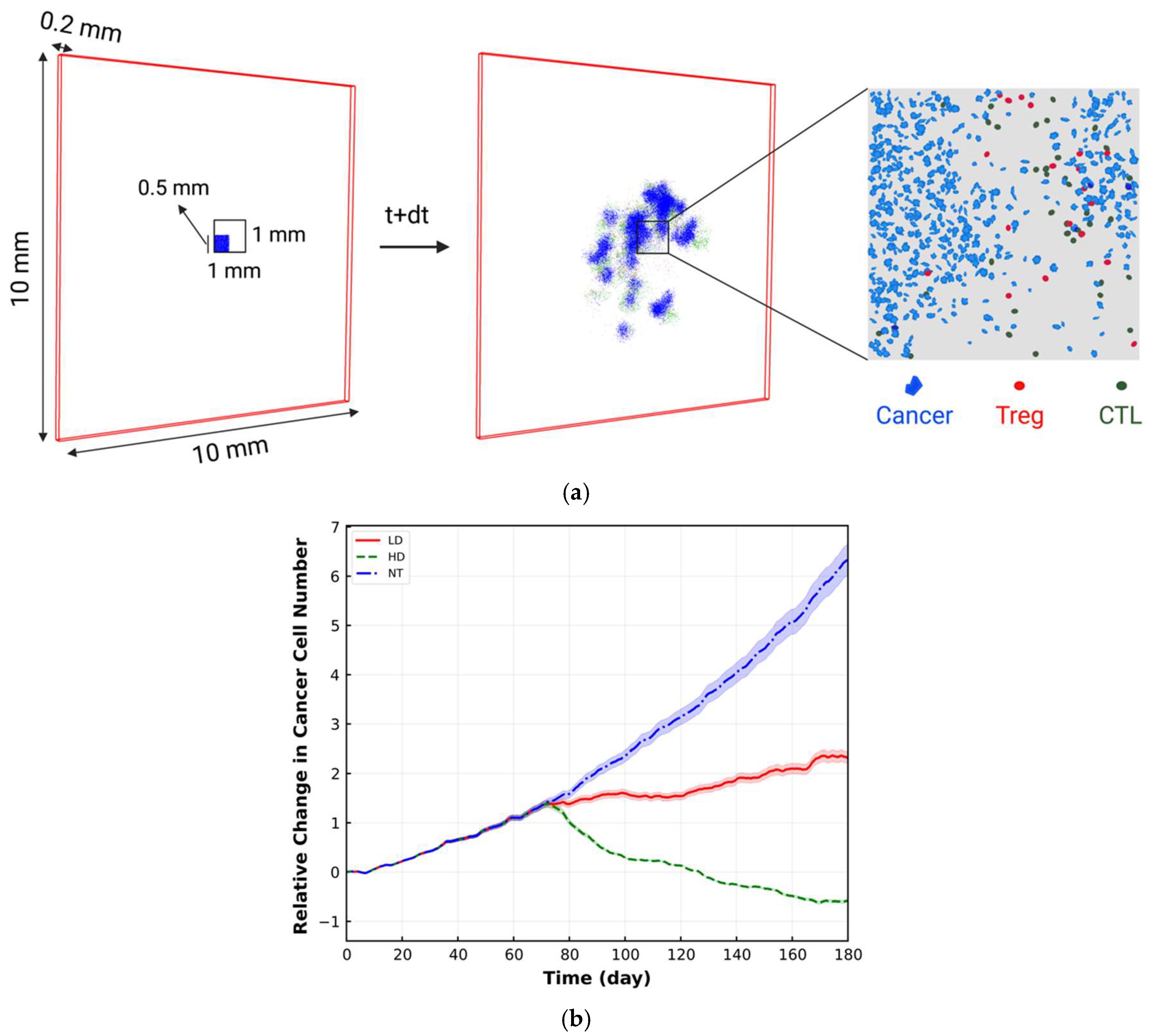
2. Materials and Methods
3. Spatial Metrics
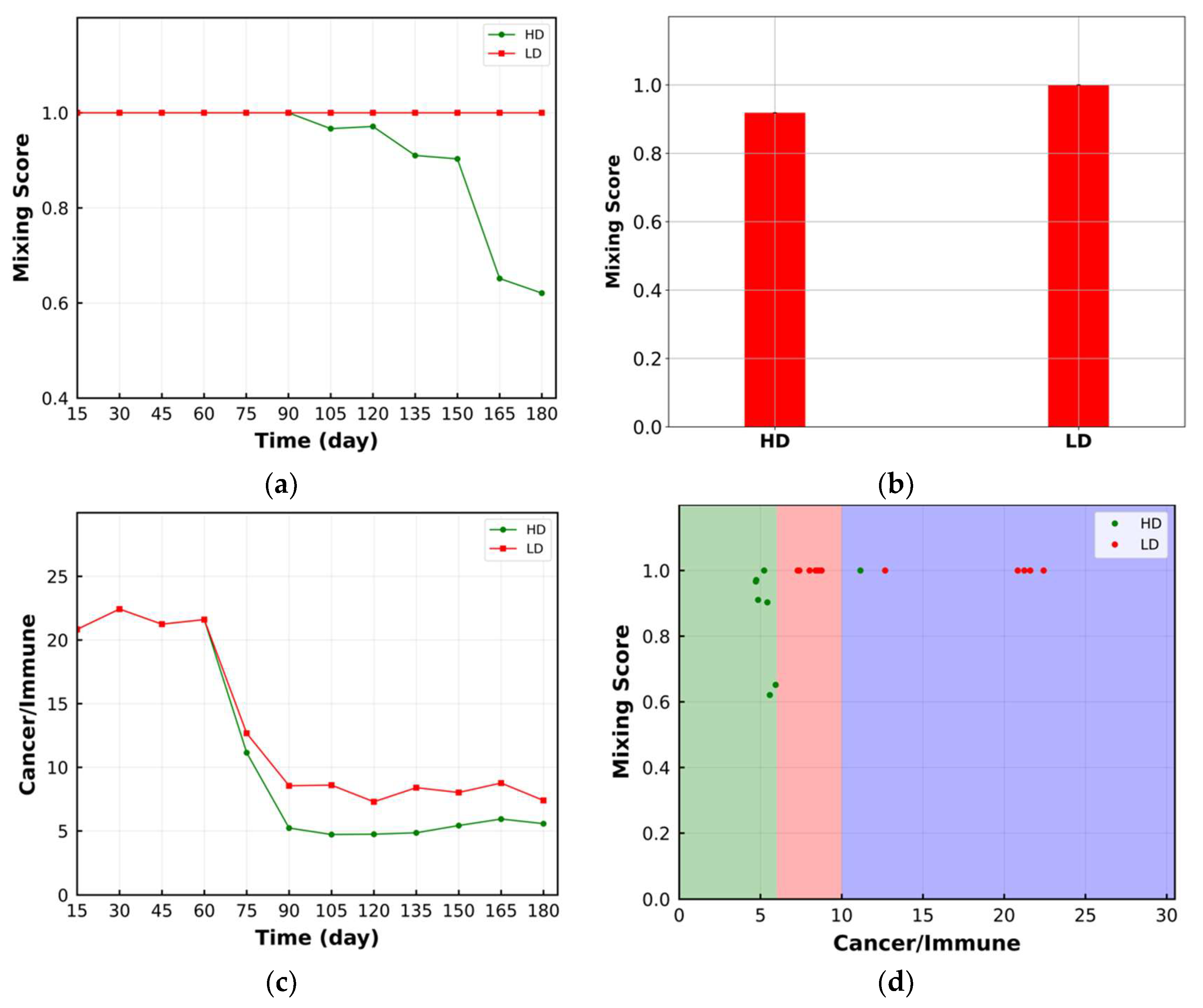
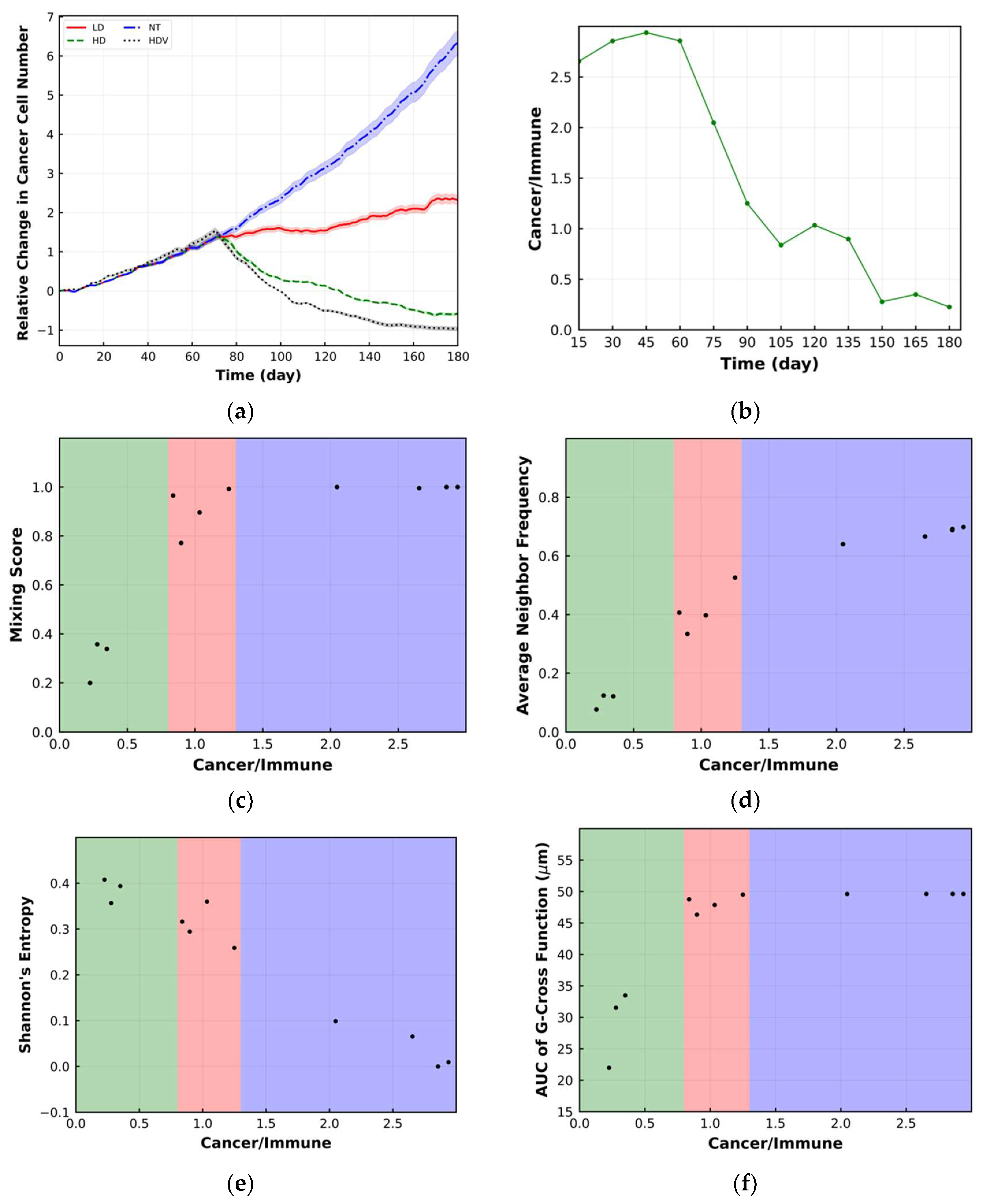
3.1. Mixing Score
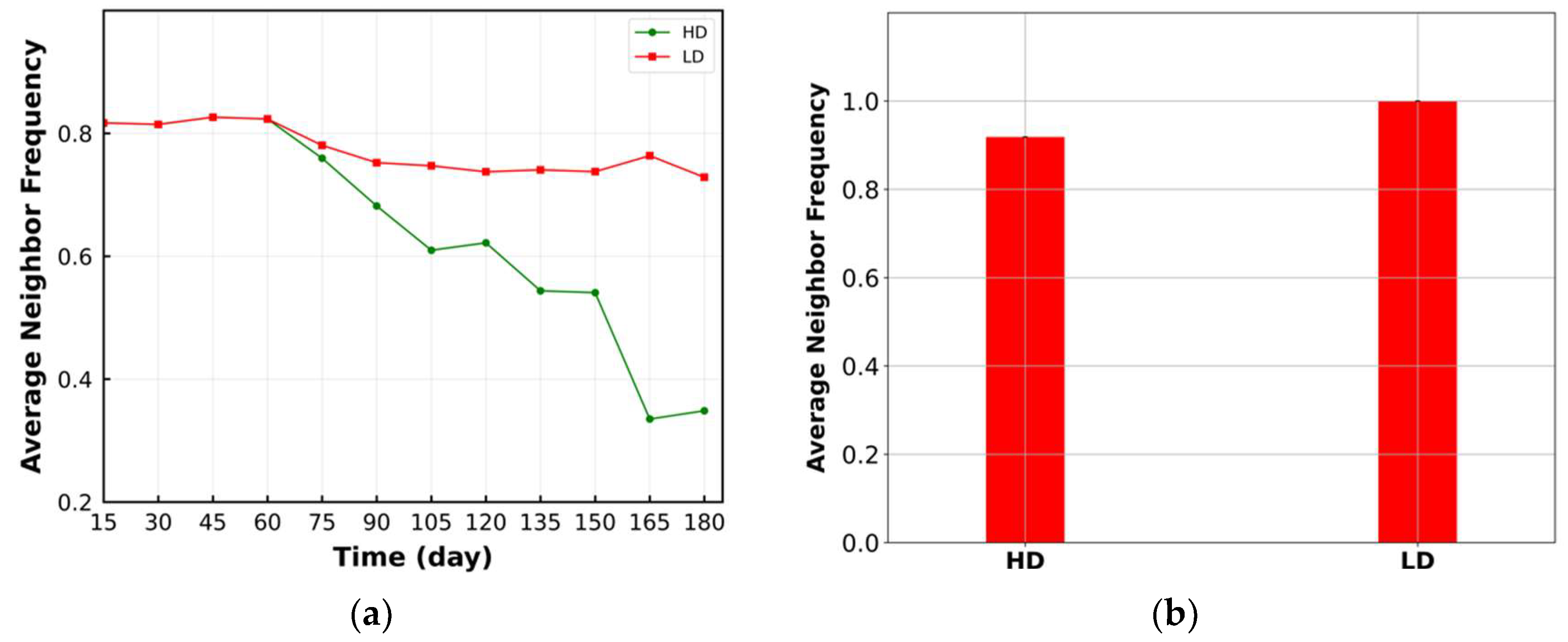
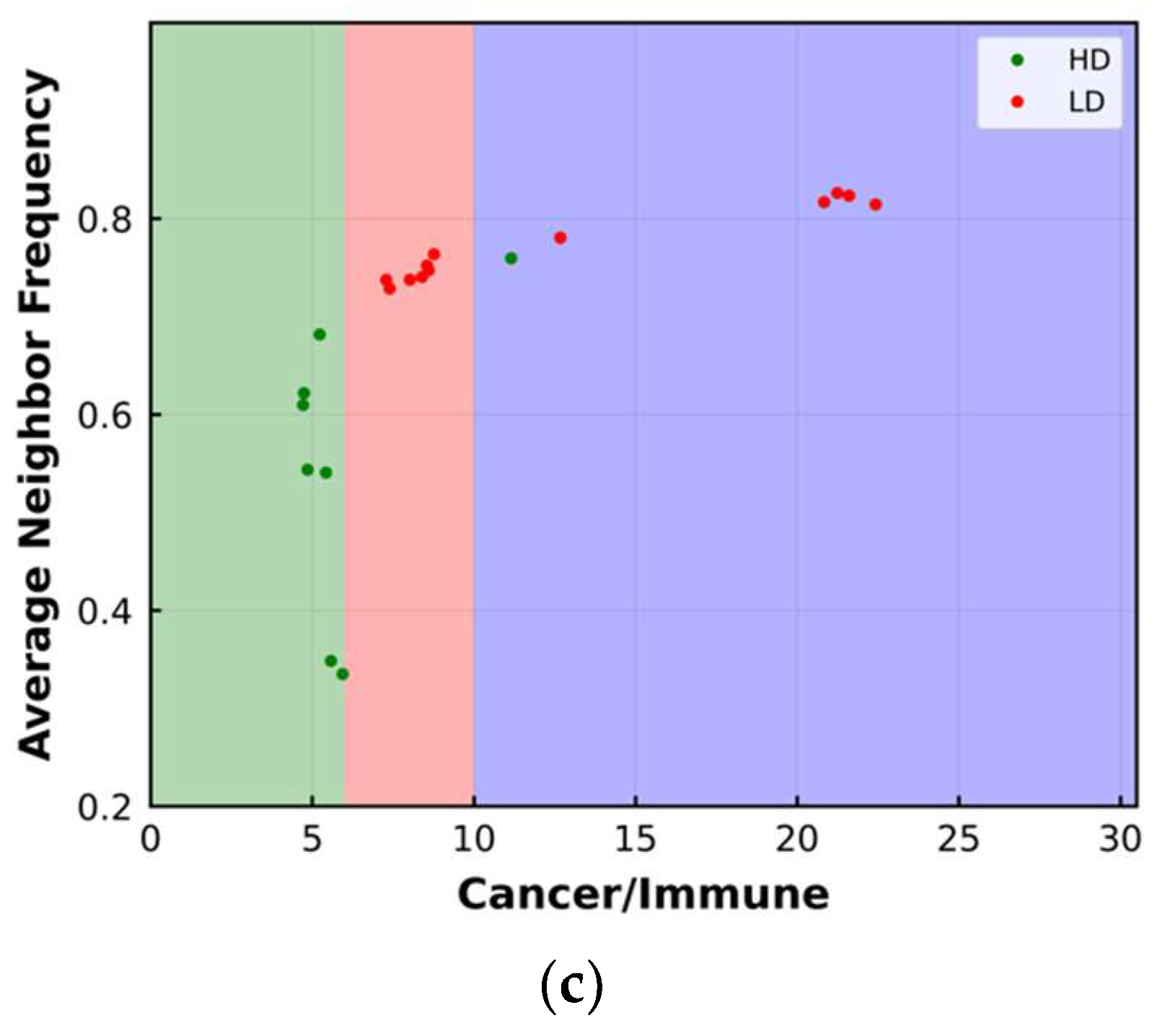
3.2. Average Neighbor Frequency
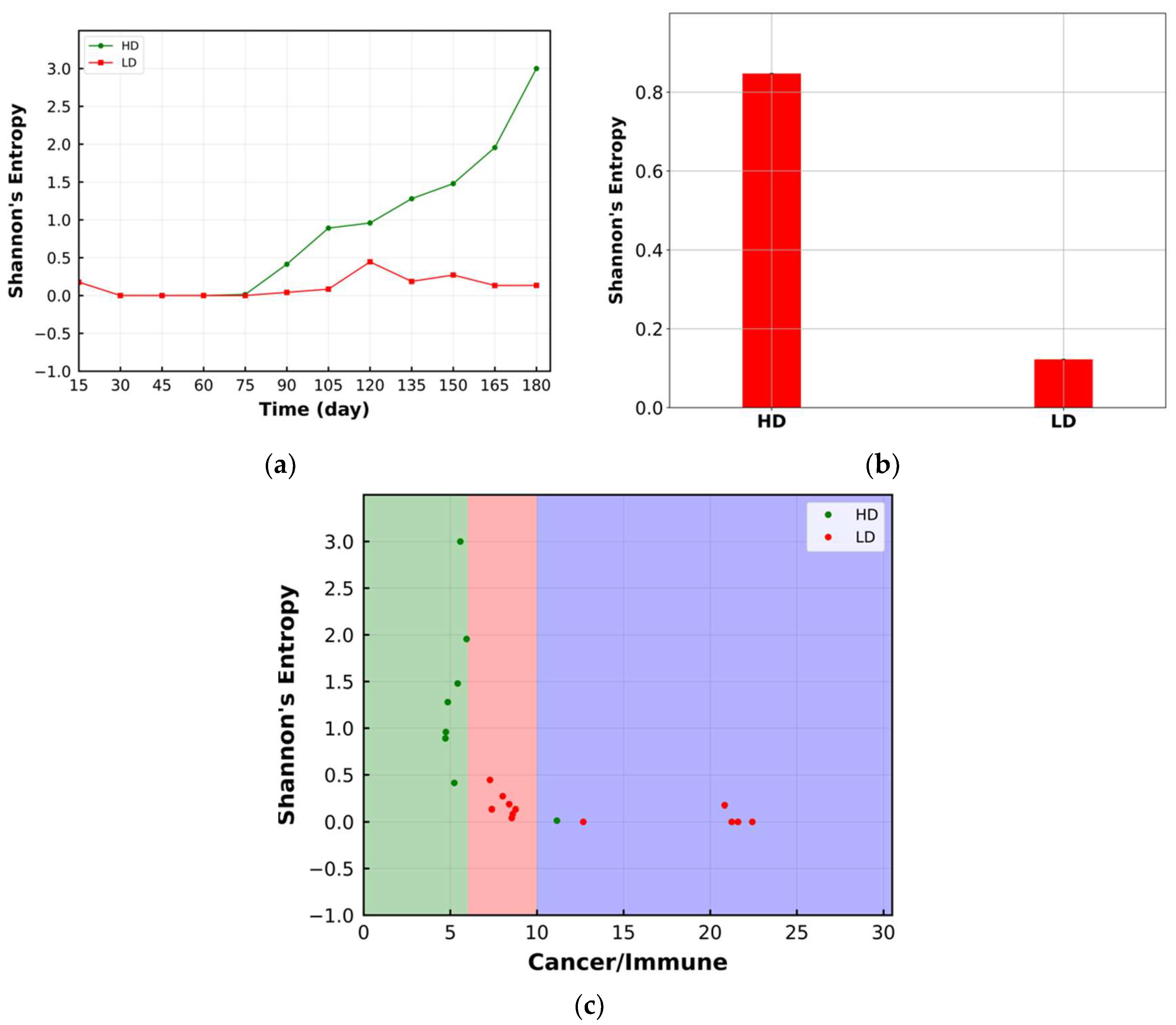
3.3. Shannon’s Entropy
3.4. Area under the Curve of G-Cross Function
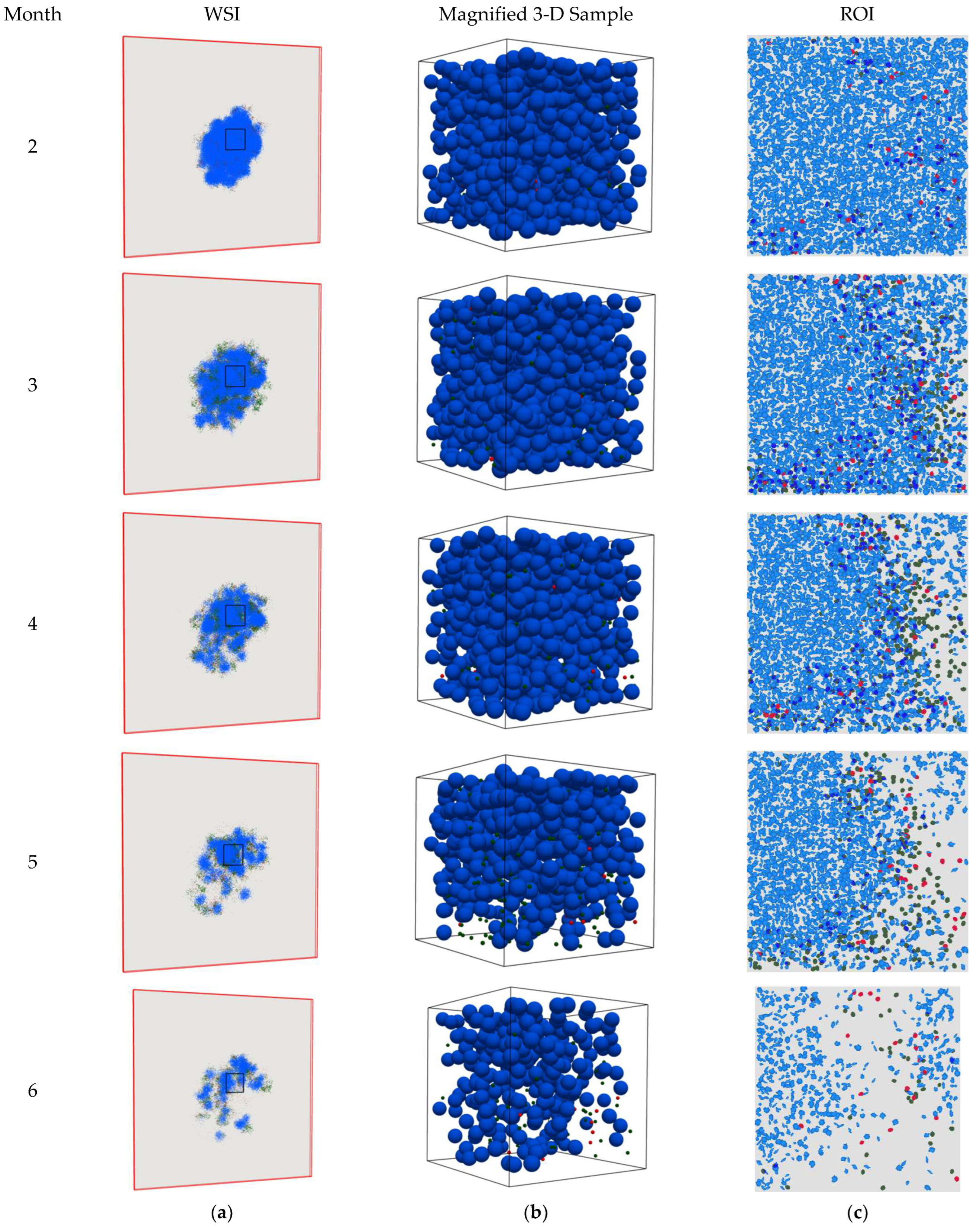
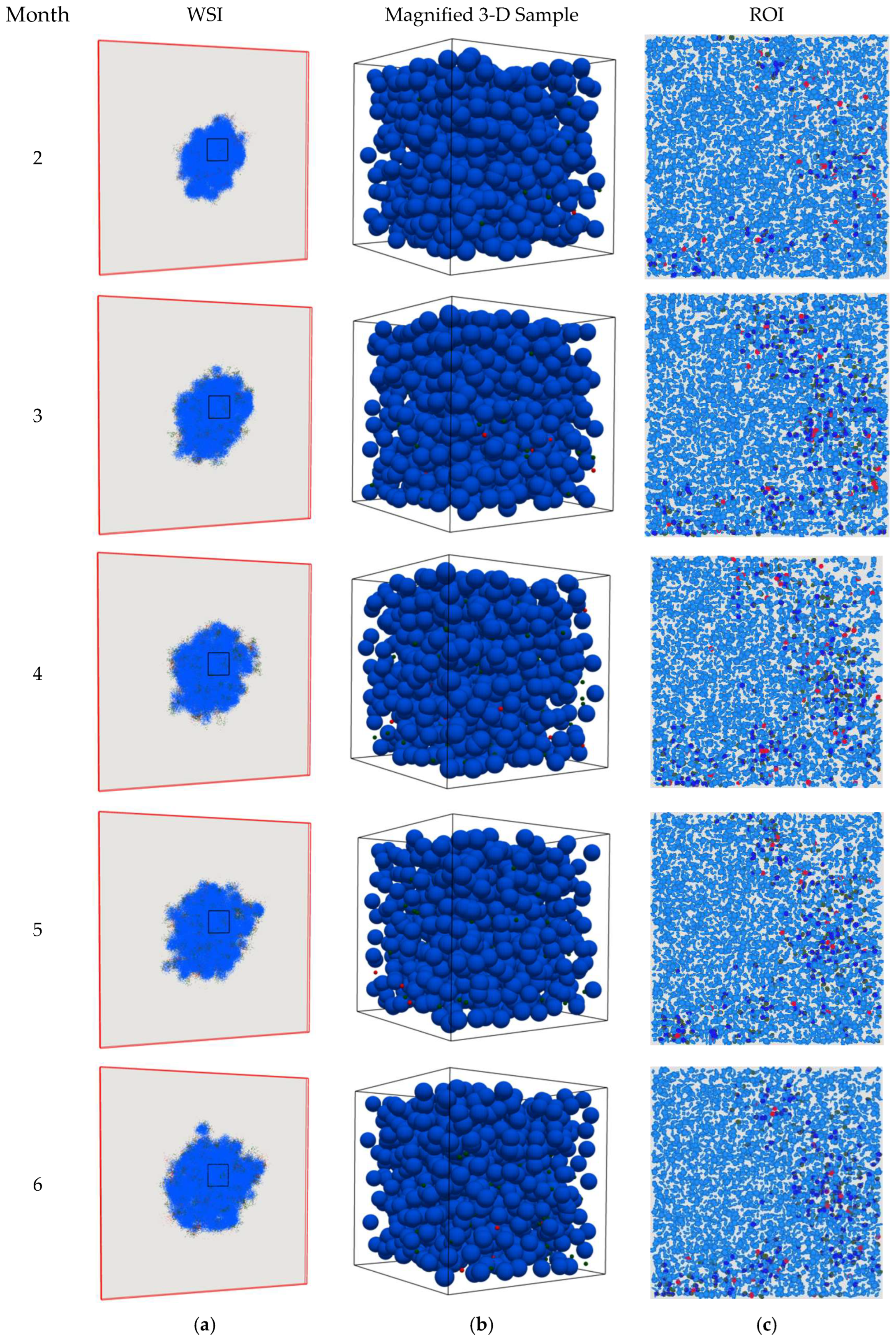
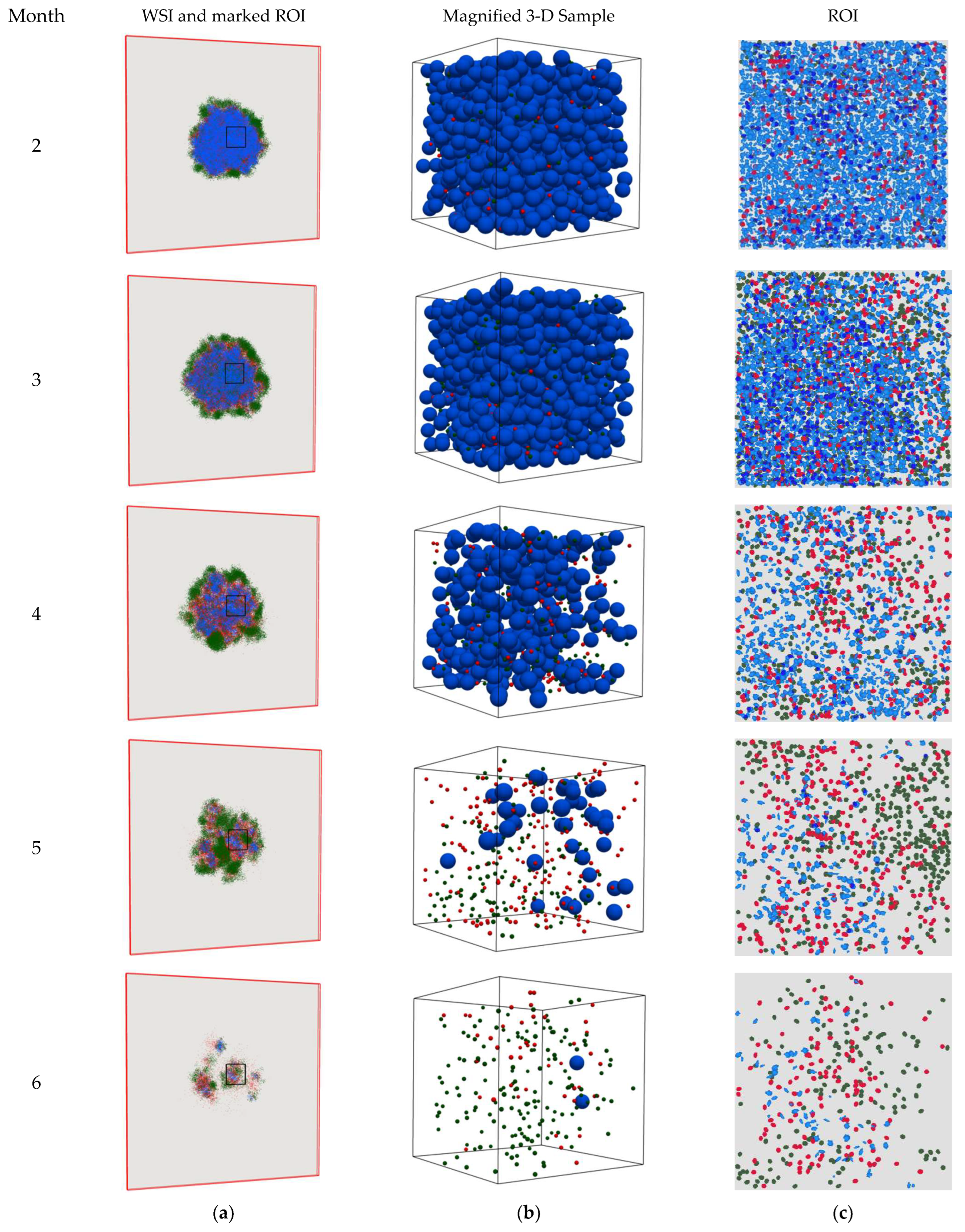
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Shaw, A.T. Tumour heterogeneity and resistance to cancer therapies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Anders, R.A.; Zhu, Q.; Taube, J.M.; Green, B.; Cheng, W.; Bartelink, I.H.; Vicini, P.; Wang, B.; Popel, A.S. Quantitative Characterization of CD8+ T Cell Clustering and Spatial Heterogeneity in Solid Tumors. Front. Oncol. 2019, 8, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, H.; Sivagnanam, S.; Betts, C.B.; Liudahl, S.M.; Jaffee, E.M.; Coussens, L.M.; Popel, A.S. Quantitative Spatial Profiling of Immune Populations in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Reveals Tumor Microenvironment Heterogeneity and Prognostic Biomarkers. Cancer Res 2022, 82, 4359–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Seehawer, M.; Polyak, K. Untangling the web of intratumour heterogeneity. Nat. Cell Biol. 2022, 24, 1192–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marusyk, A.; Janiszewska, M.; Polyak, K. Intratumor Heterogeneity: The Rosetta Stone of Therapy Resistance. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchinson, L.G.; Grimm, O. Integrating digital pathology and mathematical modelling to predict spatial biomarker dynamics in cancer immunotherapy. NPJ Digit. Med. 2022, 5, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, E.R.; Villalobos, P.; Behrens, C.; Jiang, M.; Pataer, A.; Swisher, S.G.; William, W.N., Jr.; Zhang, J.; Lee, J.; Cascone, T.; et al. Effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on the immune microenvironment in non–small cell lung carcinomas as determined by multiplex immunofluorescence and image analysis approaches. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corredor, G.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, C.; Fu, P.; Syrigos, K.N.; Rimm, D.L.; Yang, M.; Romero, E.; Schalper, K.A.; et al. Spatial Architecture and Arrangement of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes for Predicting Likelihood of Recurrence in Early-Stage Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 1526–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brown, J.R.; Wimberly, H.; Lannin, D.R.; Nixon, C.; Rimm, D.L.; Bossuyt, V. Multiplexed Quantitative Analysis of CD3, CD8, and CD20 Predicts Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 5995–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Saltz, J.; Gupta, R.; Hou, L.; Kurc, T.; Singh, P.; Nguyen, V.; Samaras, D.; Shroyer, K.R.; Zhao, T.; Batiste, R.; et al. Spatial Organization and Molecular Correlation of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes Using Deep Learning on Pathology Images. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 181–193.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schwen, L.O.; Andersson, E.; Korski, K.; Weiss, N.; Haase, S.; Gaire, F.; Hahn, H.K.; Homeyer, A.; Grimm, O. Data-Driven Discovery of Immune Contexture Biomarkers. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barua, S.; Fang, P.; Sharma, A.; Fujimoto, J.; Wistuba, I.; Rao, A.U.K.; Lin, S.H. Spatial interaction of tumor cells and regulatory T cells correlates with survival in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2018, 117, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viswanathan, V.S.; Toro, P.; Corredor, G.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Madabhushi, A. The state of the art for artificial intelligence in lung digital pathology. J. Pathol. 2022, 257, 413–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.J.; Lu, M.Y.; Williamson, D.F.K.; Chen, T.Y.; Lipkova, J.; Noor, Z.; Shaban, M.; Shady, M.; Williams, M.; Joo, B.; et al. Pan-cancer integrative histology-genomic analysis via multimodal deep learning. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 865–878.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Ruiz-Martinez, A.; Kimko, H.; Popel, A.S. A Spatial Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Platform spQSP-IO for Simulations of Tumor–Immune Interactions and Effects of Checkpoint Inhibitor Immunotherapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razizadeh, M.; Nikfar, M.; Liu, Y. Small molecule therapeutics to destabilize the ACE2-RBD complex: A molecular dynamics study. Biophys. J. 2021, 120, 2793–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikfar, M.; Razizadeh, M.; Paul, R.; Muzykantov, V.N.; Liu, Y. A numerical study on drug delivery via multiscale synergy of cellular hitchhiking onto red blood cells. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 17359–17372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Martinez, A.; Gong, C.; Wang, H.; Sové, R.J.; Mi, H.; Kimko, H.; Popel, A.S. Simulations of tumor growth and response to immunotherapy by coupling a spatial agent-based model with a whole-patient quantitative systems pharmacology model. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2022, 18, e1010254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Gong, C.; Ruiz-Martinez, A.; Wang, H.; Davis-Marcisak, E.; Deshpande, A.; Popel, A.S.; Fertig, E.J. Integrating single cell sequencing with a spatial quantitative systems pharmacology model spQSP for personalized prediction of triple-negative breast cancer immunotherapy response. Immunoinformatics 2021, 1–2, 100002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, K.-A.; Wallace, T.; Pandey, N.B.; Popel, A.S. An agent-based model of triple-negative breast cancer: The interplay between chemokine receptor CCR5 expression, cancer stem cells, and hypoxia. BMC Syst. Biol. 2017, 11, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jafarnejad, M.; Gong, C.; Gabrielson, E.; Bartelink, I.H.; Vicini, P.; Wang, B.; Narwal, R.; Roskos, L.; Popel, A. A Computational Model of Neoadjuvant PD-1 Inhibition in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. AAPS J. 2019, 21, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, C.; Santa-Maria, C.A.; Emens, L.A.; Popel, A.S. Dynamics of tumor-associated macrophages in a quantitative systems pharmacology model of immunotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. iScience 2022, 25, 104702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ma, H.; Sové, R.J.; Emens, L.A.; Popel, A.S. Quantitative systems pharmacology model predictions for efficacy of atezolizumab and nab-paclitaxel in triple-negative breast cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, A.G.; Osborne, J.M. Seven challenges in the multiscale modeling of multicellular tissues. WIREs Mech. Dis. 2021, 14, e1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaire, V.; Bassen, D.; Reed, M.; Song, R.; Khalili, S.; Lien, Y.T.K.; Huang, L.; Singh, A.P.; Stamatelos, S.; Bottino, D.; et al. From Cold to Hot: Changing Perceptions and Future Opportunities for Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Modeling in Cancer Immunotherapy. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 113, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azer, K.; Kaddi, C.D.; Barrett, J.S.; Bai, J.P.F.; McQuade, S.T.; Merrill, N.J.; Piccoli, B.; Neves-Zaph, S.; Marchetti, L.; Lombardo, R.; et al. History and Future Perspectives on the Discipline of Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Modeling and Its Applications. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 637999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.P.F.; Earp, J.C.; Pillai, V.C. Translational Quantitative Systems Pharmacology in Drug Development: From Current Landscape to Good Practices. AAPS J. 2019, 21, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, J.A.; Byrne, H.M. Quantification of spatial and phenotypic heterogeneity in an agent-based model of tumour-macrophage interactions. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2023, 19, e1010994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, H.V.; Sorribes, I.C.; Handelman, S.K.; Barnaby, J.; Jackson, T.L. Standing Variations Modeling Captures Inter-Individual Heterogeneity in a Deterministic Model of Prostate Cancer Response to Combination Therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radunskaya, A.; Kim, R.; Woods, T., II. Mathematical Modeling of Tumor Immune Interactions: A Closer Look at the Role of a PD-L1 Inhibitor in Cancer Immunotherapy. SPORA J. Biomath. 2018, 4, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, J.; Robertson-Tessi, M.; Anderson, A.R. Agent-based methods facilitate integrative science in cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 2022, 33, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keren, L.; Bosse, M.; Marquez, D.; Angoshtari, R.; Jain, S.; Varma, S.; Yang, S.-R.; Kurian, A.; Van Valen, D.; West, R.; et al. A Structured Tumor-Immune Microenvironment in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Revealed by Multiplexed Ion Beam Imaging. Cell 2018, 174, 1373–1387.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mi, H.; Gong, C.; Sulam, J.; Fertig, E.J.; Szalay, A.S.; Jaffee, E.M.; Stearns, V.; Emens, L.A.; Cimino-Mathews, A.M.; Popel, A.S. Digital Pathology Analysis Quantifies Spatial Heterogeneity of CD3, CD4, CD8, CD20, and FoxP3 Immune Markers in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 583333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enfield, K.S.S.; Martin, S.D.; Marshall, E.A.; Kung, S.H.Y.; Gallagher, P.; Milne, K.; Chen, Z.; Nelson, B.H.; Lam, S.; English, J.C.; et al. Hyperspectral cell sociology reveals spatial tumor-immune cell interactions associated with lung cancer recurrence. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mi, H.; Ho, W.J.; Yarchoan, M.; Popel, A.S. Multi-Scale Spatial Analysis of the Tumor Microenvironment Reveals Features of Cabozantinib and Nivolumab Efficacy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 892250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, A.; Ghaddar, B.; Riedlinger, G.; De, S. Inference on spatial heterogeneity in tumor microenvironment using spatial transcriptomics data. Comput. Syst. Oncol. 2022, 2, e21043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topalian, S.L.; Taube, J.M.; Pardoll, D.M. Neoadjuvant checkpoint blockade for cancer immunotherapy. Science 2020, 367, eaax0182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, K.-A.; Popel, A.S. An agent-based model of cancer stem cell initiated avascular tumour growth and metastasis: The effect of seeding frequency and location. J. R. Soc. Interface 2014, 11, 20140640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ghaffarizadeh, A.; Friedman, S.H.; Macklin, P. BioFVM: An efficient, parallelized diffusive transport solver for 3-D biological simulations. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 1256–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ahrens, J.; Geveci, B.; Law, C. ParaView: An end-user tool for large data visualization. In Visualization Handbook; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 717–731. [Google Scholar]
- Kather, J.N.; Suarez-Carmona, M.; Charoentong, P.; Weis, C.-A.; Hirsch, D.; Bankhead, P.; Horning, M.; Ferber, D.; Kel, I.; Herpel, E.; et al. Topography of cancer-associated immune cells in human solid tumors. Elife 2018, 7, e36967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coudray, N.; Ocampo, P.S.; Sakellaropoulos, T.; Narula, N.; Snuderl, M.; Fenyö, D.; Moreira, A.L.; Razavian, N.; Tsirigos, A. Classification and mutation prediction from non–small cell lung cancer histopathology images using deep learning. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1559–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy-Jurgenson, A.; Tekpli, X.; Kristensen, V.N.; Yakhini, Z. Spatial transcriptomics inferred from pathology whole-slide images links tumor heterogeneity to survival in breast and lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy-Jurgenson, A.; Tekpli, X.; Yakhini, Z. Assessing heterogeneity in spatial data using the HTA index with applications to spatial transcriptomics and imaging. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 3796–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, C.; Milberg, O.; Wang, B.; Vicini, P.; Narwal, R.; Roskos, L.; Popel, A.S. A computational multiscale agent-based model for simulating spatio-temporal tumour immune response to PD1 and PDL1 inhibition. J. R. Soc. Interface 2017, 14, 20170320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mi, H.; Ho, W.J.; Yarchoan, M.; Popel, A.S. 825 High-dimensional image cytometry reveals spatially organized tumor-immune microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. ImmunoTherapy Cancer 2021, 9, A863–A864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armani, G.; Madeddu, D.; Mazzaschi, G.; Bocchialini, G.; Sogni, F.; Frati, C.; Lorusso, B.; Falco, A.; Lagrasta, C.A.; Cavalli, S.; et al. Blood and lymphatic vessels contribute to the impact of the immune microenvironment on clinical outcome in non-small-cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2018, 53, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatelos, S.K.; Kim, E.; Pathak, A.P.; Popel, A.S. A bioimage informatics based reconstruction of breast tumor microvasculature with computational blood flow predictions. Microvasc. Res. 2014, 91, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Stamatelos, S.K.; Bhargava, A.; Kim, E.; Popel, A.S.; Pathak, A.P. Tumor Ensemble-Based Modeling and Visualization of Emergent Angiogenic Heterogeneity in Breast Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bačić, I.; Karlo, R.; Zadro, A.; Zadro, Z.; Skitarelić, N.; Antabak, A. Tumor angiogenesis as an important prognostic factor in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (Stage IIIA). Oncol. Lett. 2017, 15, 2335–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combes, A.J.; Samad, B.; Tsui, J.; Chew, N.W.; Yan, P.; Reeder, G.C.; Kushnoor, D.; Shen, A.; Davidson, B.; Barczak, A.J.; et al. Discovering dominant tumor immune archetypes in a pan-cancer census. Cell 2022, 185, 184–203.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Umbach, D.M.; Bingham, A.; Li, Q.-J.; Zhuang, Y.; Li, L. Putative biomarkers for predicting tumor sample purity based on gene expression data. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popel, A.S. Immunoactivating the tumor microenvironment enhances immunotherapy as predicted by integrative computational model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 4447–4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cess, C.G.; Finley, S.D. Multi-scale modeling of macrophage—T cell interactions within the tumor microenvironment. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1008519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

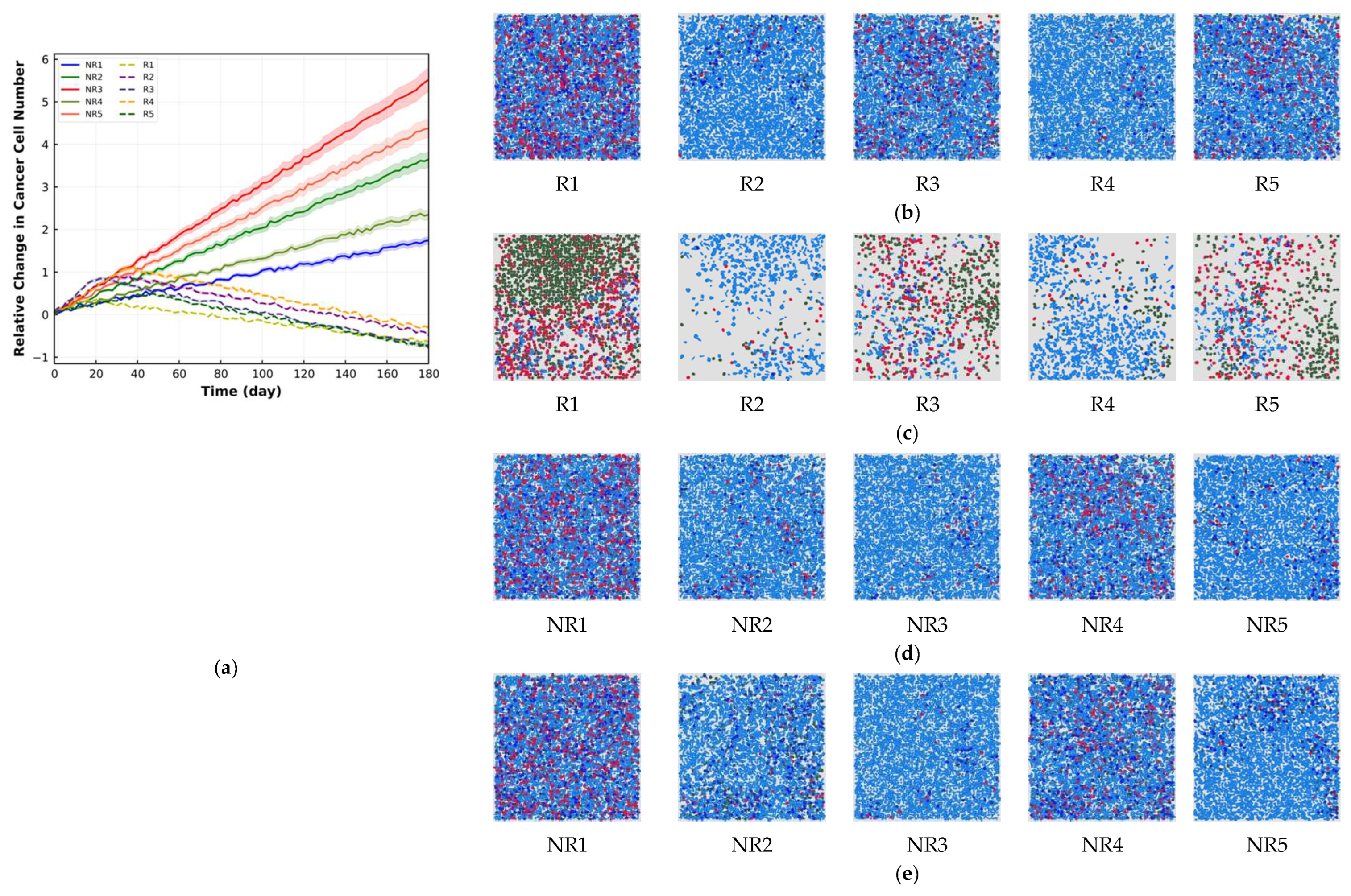

| Cell Ratio | Mixing Score | Average Neighbor Frequency | AUC of G-Cross Function | Shannon’s Entropy | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BT | AT | Reduction (%) | Reduction (%) | Reduction (%) | Reduction (%) | Increase (%) | |
| R1 | 2.86 | 0.43 | 84.96 | 64.03 | 67.25 | 34.71 | 310.13 |
| R2 | 15.41 | 5.71 | 67.94 | 47.98 | 49.87 | 14.53 | 421.13 |
| R3 | 3.67 | 0.57 | 84.46 | 63.35 | 64.92 | 30.81 | 300.76 |
| R4 | 17.36 | 6.91 | 65.19 | 44.15 | 46.26 | 12.06 | 433.78 |
| R5 | 3.45 | 0.49 | 85.79 | 64.69 | 67.38 | 34.67 | 347.19 |
| NR1 | 3.19 | 2.84 | 10.97 | 2.82 | 3.28 | 2.91 | 4.24 |
| NR2 | 16.92 | 13.46 | 20.45 | 0.78 | 1.71 | 0.81 | 2.31 |
| NR3 | 19.64 | 15.41 | 21.53 | 0.0 | 0.86 | 0.0 | 0.93 |
| NR4 | 6.94 | 5.81 | 16.28 | 2.68 | 2.87 | 1.71 | 3.92 |
| NR5 | 18.49 | 14.56 | 21.25 | 0.68 | 1.21 | 0.67 | 2.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nikfar, M.; Mi, H.; Gong, C.; Kimko, H.; Popel, A.S. Quantifying Intratumoral Heterogeneity and Immunoarchitecture Generated In-Silico by a Spatial Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Model. Cancers 2023, 15, 2750. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102750
Nikfar M, Mi H, Gong C, Kimko H, Popel AS. Quantifying Intratumoral Heterogeneity and Immunoarchitecture Generated In-Silico by a Spatial Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Model. Cancers. 2023; 15(10):2750. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102750
Chicago/Turabian StyleNikfar, Mehdi, Haoyang Mi, Chang Gong, Holly Kimko, and Aleksander S. Popel. 2023. "Quantifying Intratumoral Heterogeneity and Immunoarchitecture Generated In-Silico by a Spatial Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Model" Cancers 15, no. 10: 2750. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102750
APA StyleNikfar, M., Mi, H., Gong, C., Kimko, H., & Popel, A. S. (2023). Quantifying Intratumoral Heterogeneity and Immunoarchitecture Generated In-Silico by a Spatial Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Model. Cancers, 15(10), 2750. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102750






