Magnetoencephalography: Clinical and Research Practices
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. What Is MEG?
1.2. Clinical Uses for MEG
2. MEG at Wake Forest Baptist Health
General MEG Scanning Protocols
3. Illustrative Clinical Cases
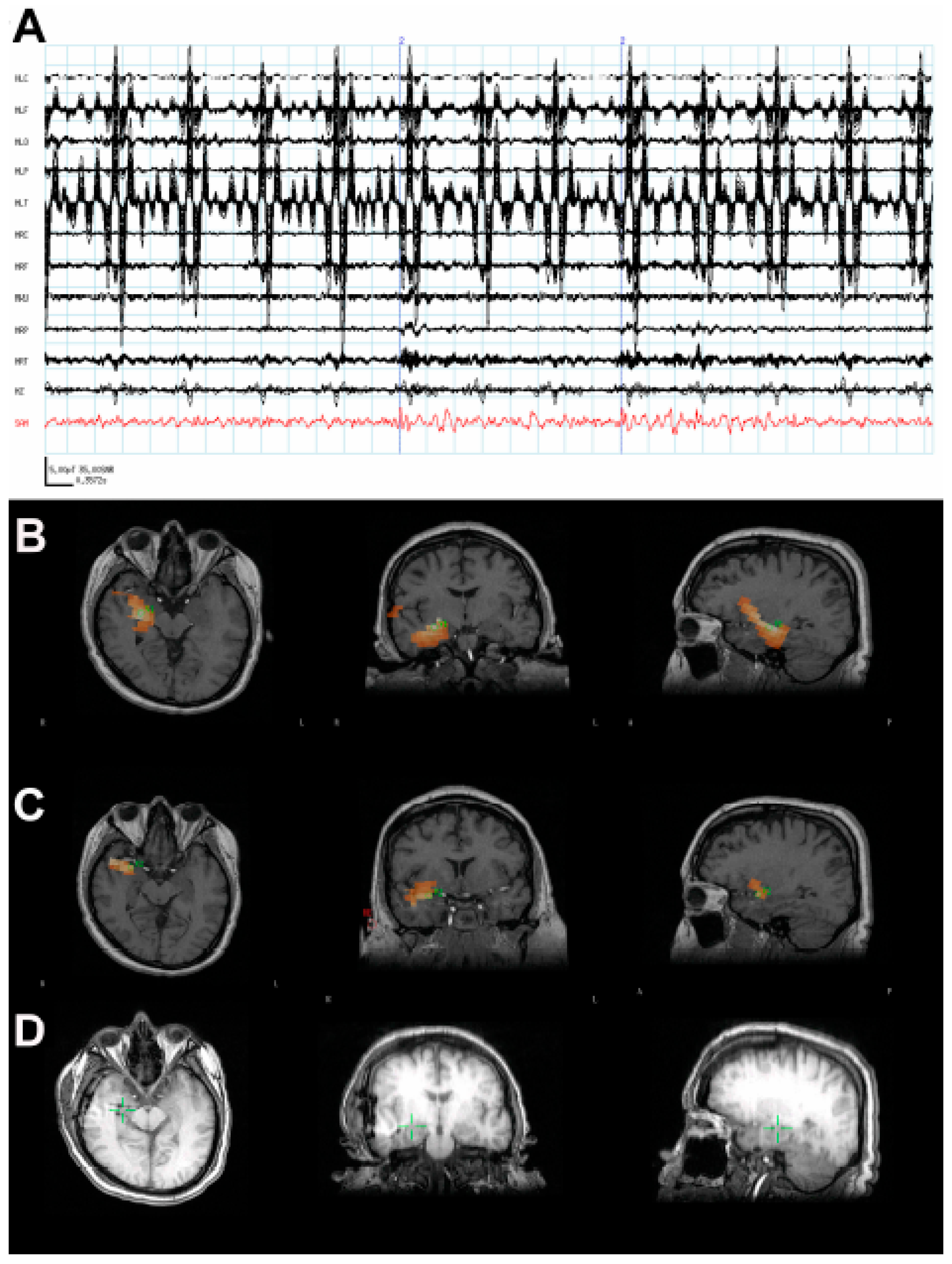
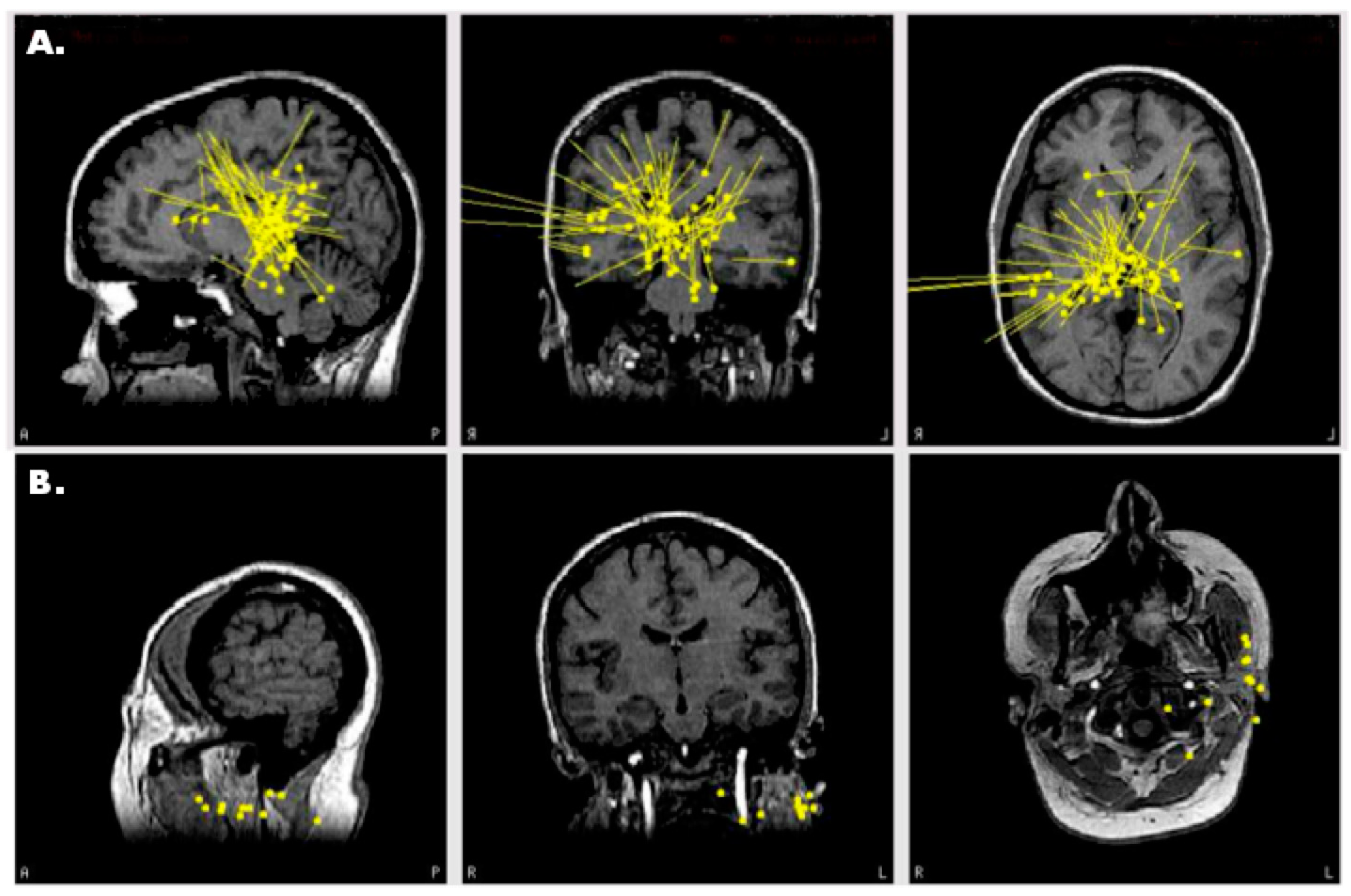
3.1. Case 1: MEG Localization Is Concordant with Multiple Other Modalities
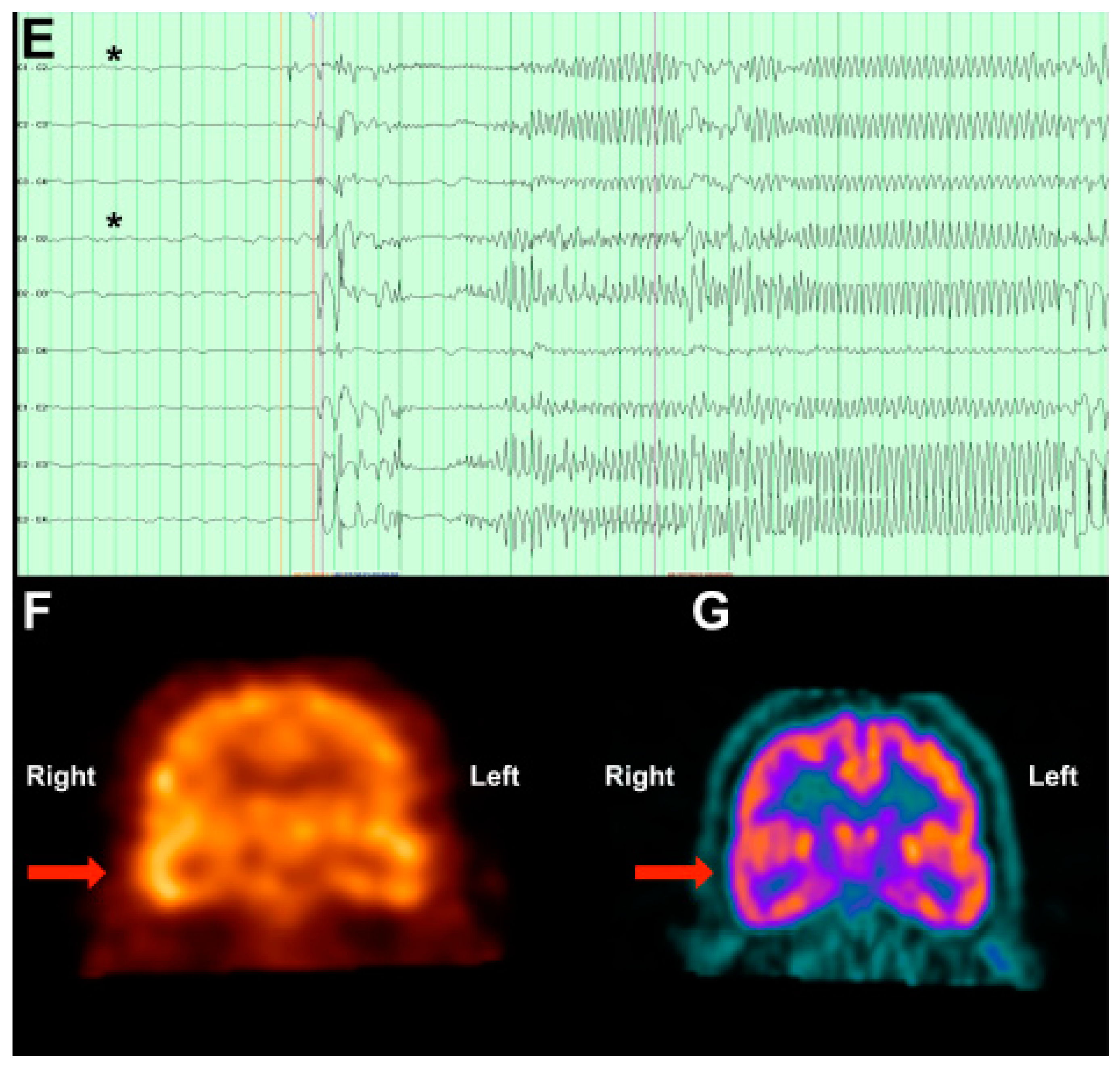
3.2. Case 2: MEG Discrimates among Multiple Seizure Foci
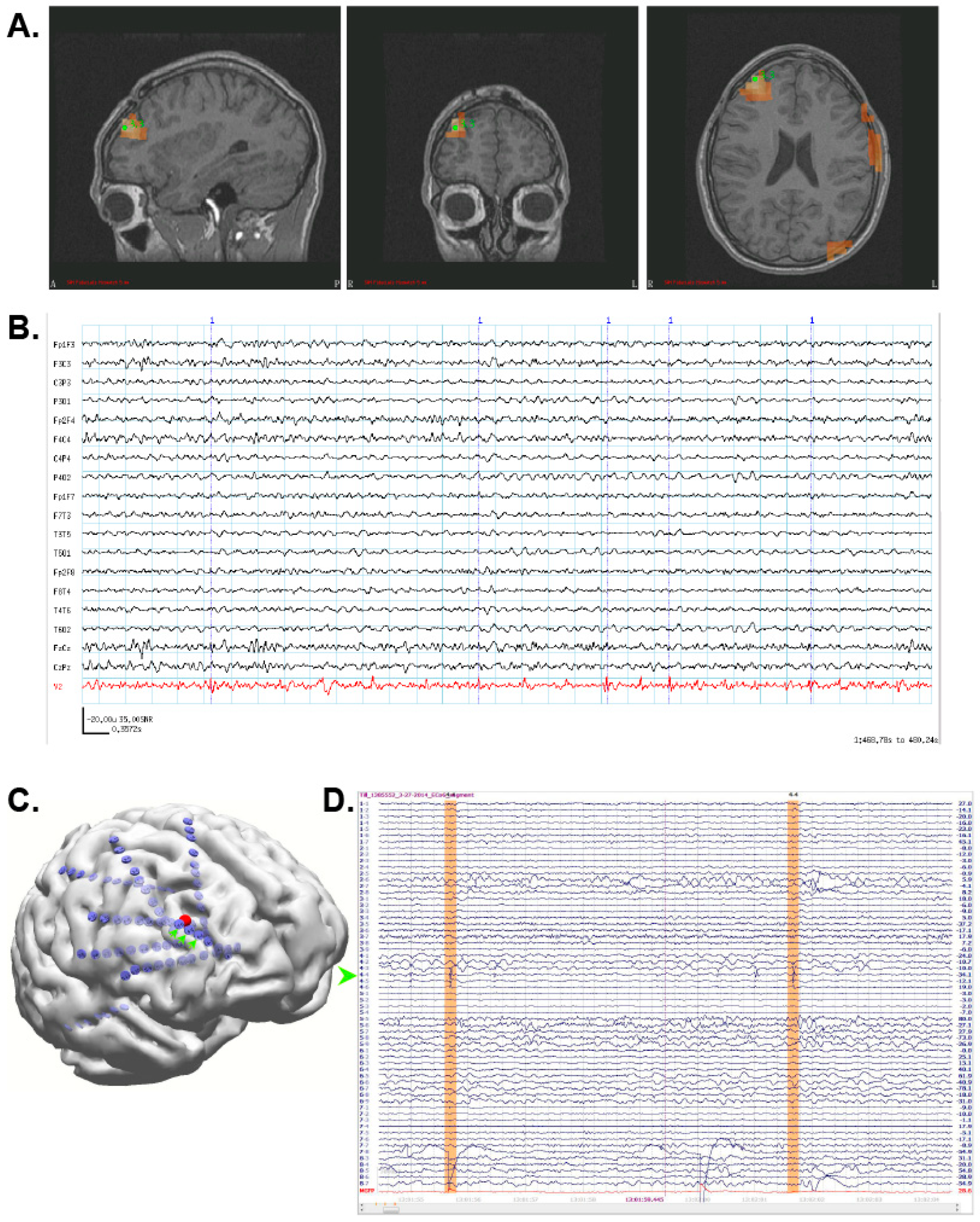
3.3. Case 3: MEG Identifies an Unexpected Seizure Focus
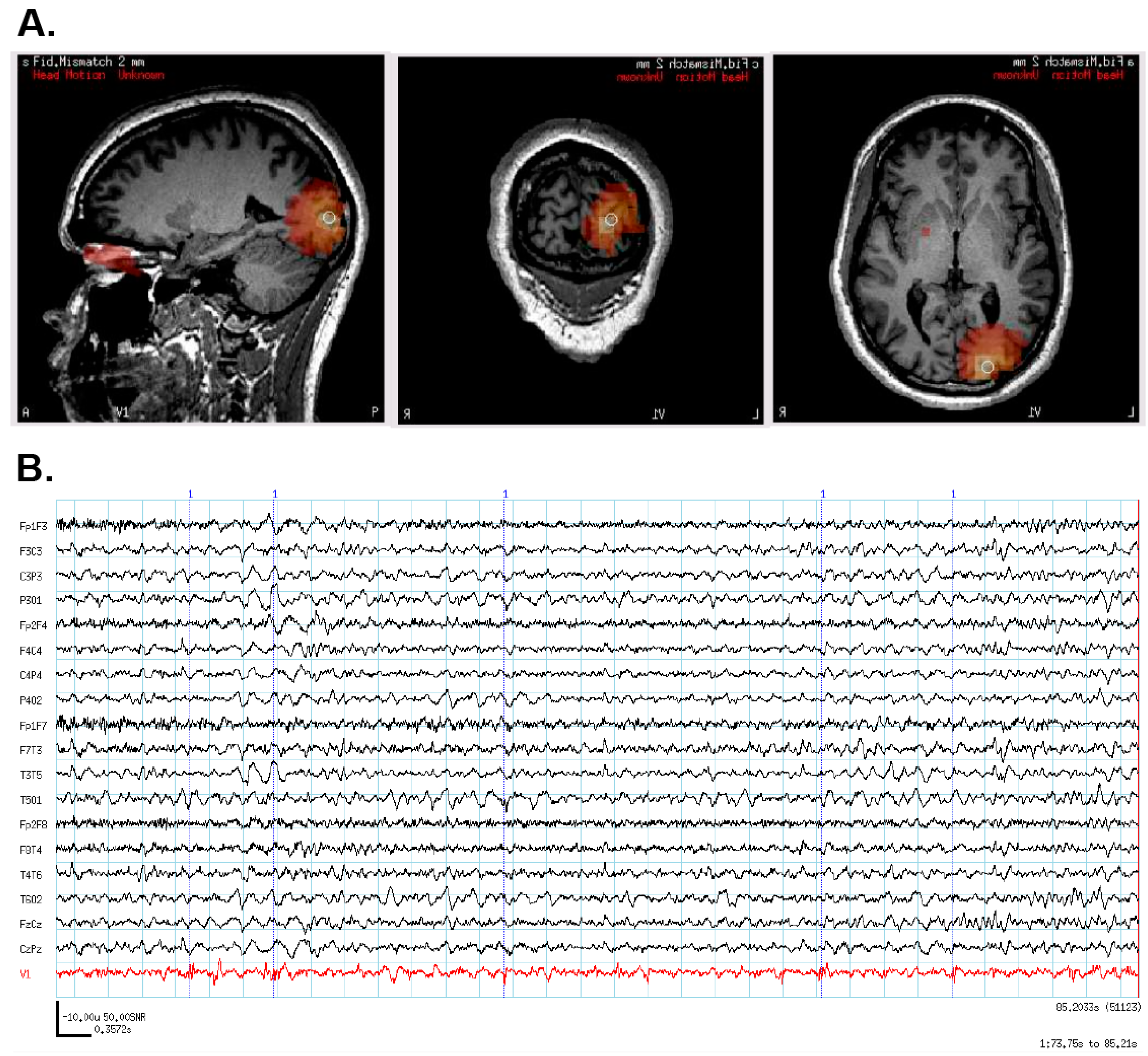
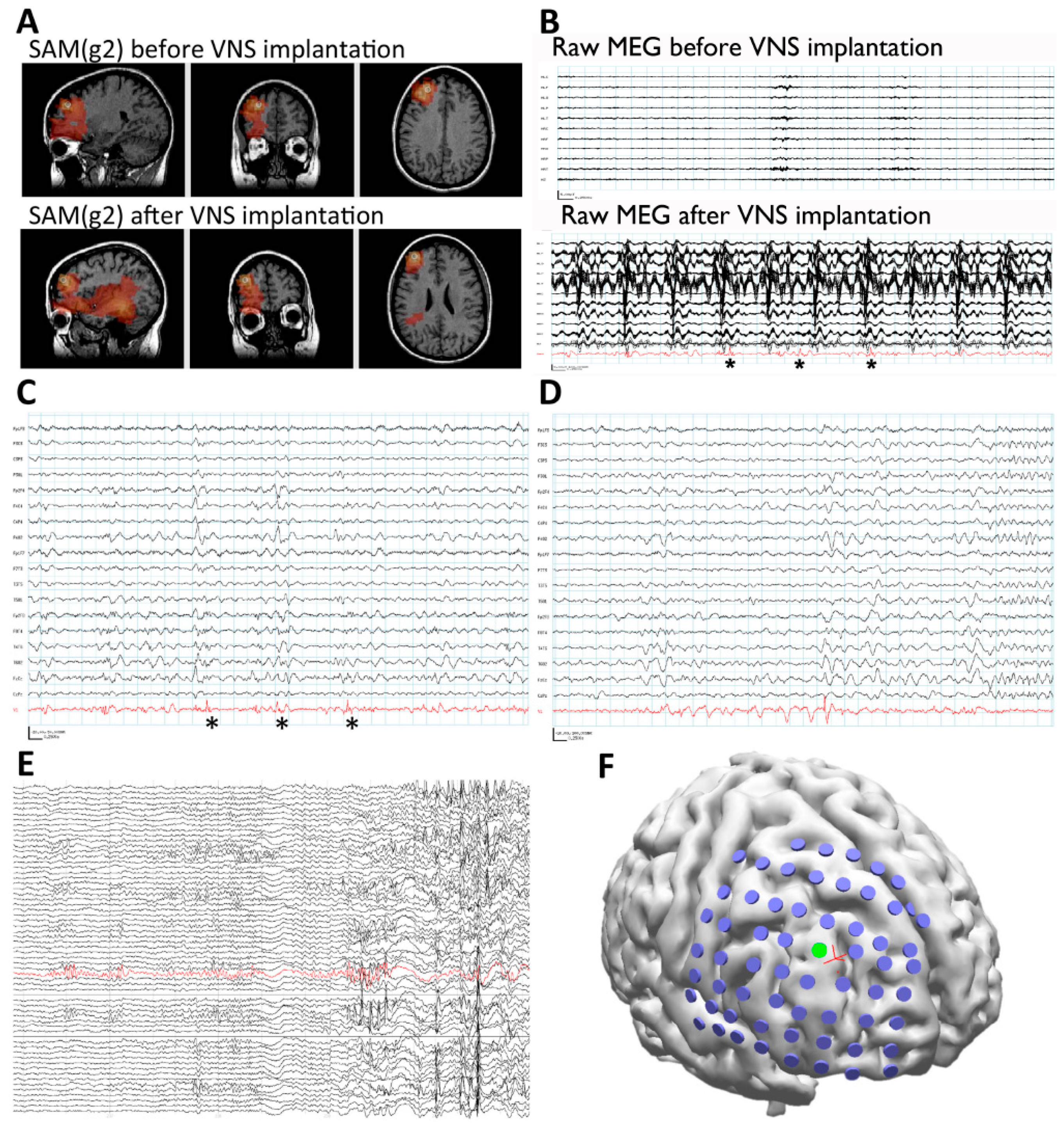
3.4. Case 4: SAM Localization Is Superior to Dipole Analysis
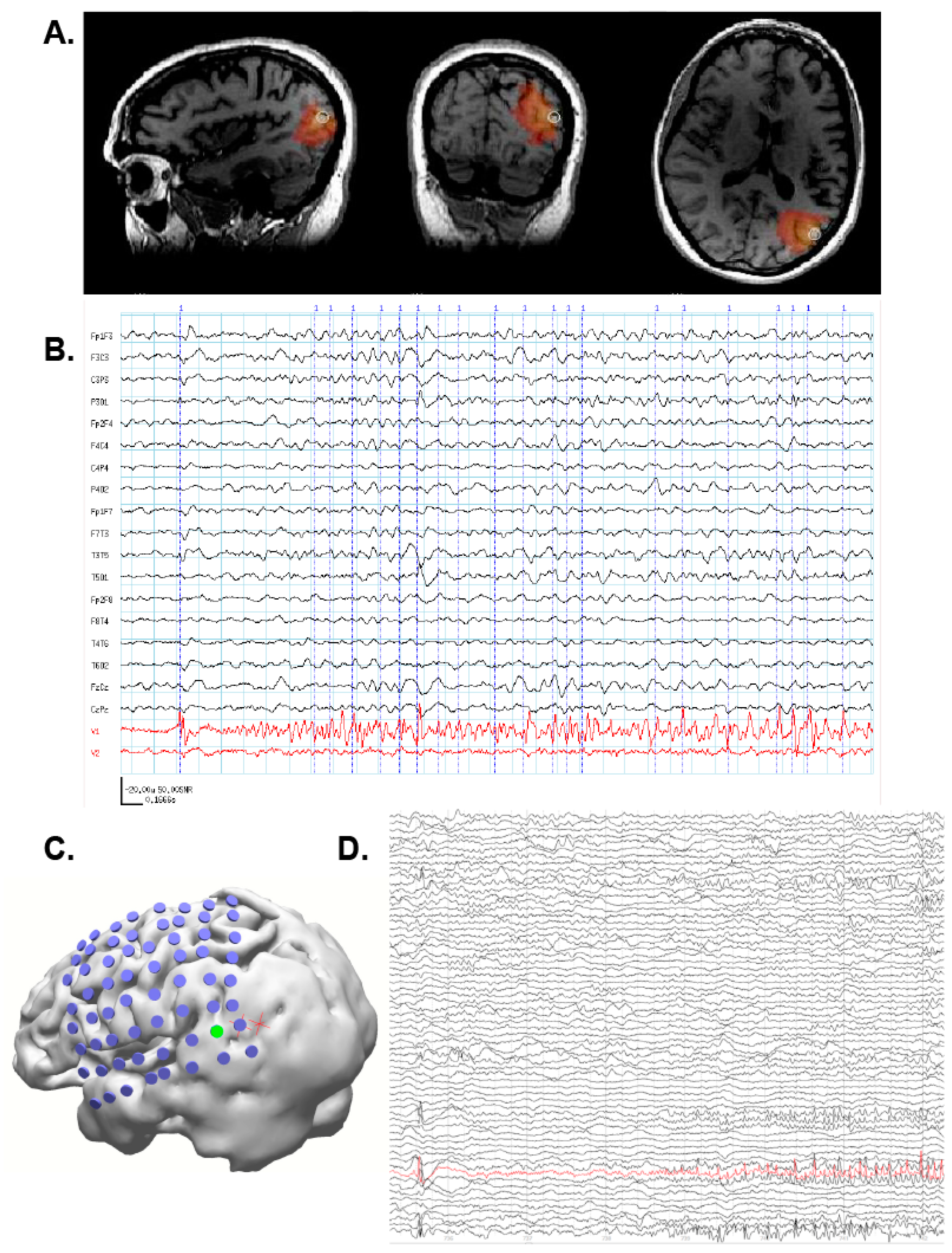
3.5. Case 5: MEG-Only Seizure
4. MEG in Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baillet, S.; Mosher, J.C.; Leahy, R.M. Electromagnetic brain mapping. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2001, 18, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caton, R. The Electric Currents of the Brain. BMJ 1875, 2, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D. Magnetoencephalography: Detection of the brain’s electrical activity with a superconducting magnetometer. Science 1972, 175, 664–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burle, B.; Spieser, L.; Roger, C.; Casini, L.; Hasbroucq, T.; Vidal, F. Spatial and temporal resolutions of EEG: Is it really black and white? A scalp current density view. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2015, 97, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillebrand, A.; Barnes, G.R.; Hubert, P. Beamformer Analysis of MEG Data. In International Review of Neurobiology; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 68, pp. 149–171. ISBN 0074-7742. [Google Scholar]
- Troebinger, L.; Lopez, J.D.; Lutti, A.; Bradbury, D.; Bestmann, S.; Barnes, G. High precision anatomy for MEG. Neuroimage 2014, 86, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, K.; Otsubo, H.; Sell, E.; Mohamed, I.; Ochi, A.; RamachandranNair, R.; Snead, O.C., 3rd. MEG source estimation from mesio-basal temporal areas in a child with a porencephalic cyst. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2007, 116, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quraan, M.A.; Moses, S.N.; Hung, Y.; Mills, T.; Taylor, M.J. Detection and localization of hippocampal activity using beamformers with MEG: A detailed investigation using simulations and empirical data. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2011, 32, 812–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesche, C.D.; Karhu, J. Somatosensory evoked magnetic fields arising from sources in the human cerebellum. Brain Res. 1997, 744, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggs, L.; Moses, S.N.; Bardouille, T.; Herdman, A.T.; Ross, B.; Ryan, J.D. A complementary analytic approach to examining medial temporal lobe sources using magnetoencephalography. Neuroimage 2009, 45, 627–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stapleton-Kotloski, J.R.; Kotloski, R.J.; Boggs, J.A.; Popli, G.; O’Donovan, C.A.; Couture, D.E.; Cornell, C.; Godwin, D. Localization of Interictal Epileptiform Activity Using Magnetoencephalography with Synthetic Aperture Magnetometry in Patients with a Vagus Nerve Stimulator. Front. Neurol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornwell, B.R.; Carver, F.W.; Coppola, R.; Johnson, L.; Alvarez, R.; Grillon, C. Evoked amygdala responses to negative faces revealed by adaptive MEG beamformers. Brain Res 2008, 1244, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, Y.; Smith, M.L.; Bayle, D.J.; Mills, T.; Cheyne, D.; Taylor, M.J. Unattended emotional faces elicit early lateralized amygdala-frontal and fusiform activations. Neuroimage 2010, 50, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannides, A.A.; Corsi-Cabrera, M.; Fenwick, P.B.; del Rio Portilla, Y.; Laskaris, N.A.; Khurshudyan, A.; Theofilou, D.; Shibata, T.; Uchida, S.; Nakabayashi, T.; et al. MEG tomography of human cortex and brainstem activity in waking and REM sleep saccades. Cereb. Cortex 2004, 14, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balderston, N.L.; Schultz, D.H.; Baillet, S.; Helmstetter, F.J. How to Detect Amygdala Activity with Magnetoencephalography using Source Imaging. JoVE 2013, e50212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumas, T.; Dubal, S.; Attal, Y.; Chupin, M.; Jouvent, R.; Morel, S.; George, N. MEG Evidence for Dynamic Amygdala Modulations by Gaze and Facial Emotions. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styliadis, C.; Ioannides, A.A.; Bamidis, P.D.; Papadelis, C. Amygdala responses to valence and its interaction by arousal revealed by MEG. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2014, 93, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, T.; Houck, J.M.; Bish, J.P.; Kičić, D.; Woodruff, C.C.; Moses, S.N.; Lee, D.C.; Tesche, C.D. MEG reveals different contributions of somatomotor cortex and cerebellum to simple reaction time after temporally structured cues. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2005, 27, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Styliadis, C.; Ioannides, A.A.; Bamidis, P.D.; Papadelis, C. Distinct cerebellar lobules process arousal, valence and their interaction in parallel following a temporal hierarchy. Neuroimage 2015, 110, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.E.; Vrba, J. Functional neuroimaging by synthetic aperture magnetometry (SAM). Recent Adv. Biomagn. 1999, 302–305. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, S.E.; Vrba, J.; Otsubo, H.; Ishii, R. Finding epileptic loci by nonlinear parameterization of source waveforms. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Biomagnetism, Jena, Germany, 10–14 August 2002; Nowak, H., Haueisein, J., Giessler, F., Huonker, R., Eds.; VDE Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2002; pp. 220–222. [Google Scholar]
- Ishii, R.; Shinosaki, K.; Ukai, S.; Inouye, T.; Ishihara, T.; Yoshimine, T.; Hirabuki, N.; Asada, H.; Kihara, T.; Robinson, S.E.; et al. Medial prefrontal cortex generates frontal midline theta rhythm. Neuroreport 1999, 10, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.E.; Nagarajan, S.S.; Mantle, M.; Gibbons, V.; Kirsch, H. Localization of interictal spikes using SAM(g2) and dipole fit. Neurol. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004, 2004, 74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.E. Localization of event-related activity by SAM(erf). Neurol. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004, 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bagic, A.; Funke, M.E.; Ebersole, J. American Clinical MEG Society (ACMEGS) position statement: The value of magnetoencephalography (MEG)/magnetic source imaging (MSI) in noninvasive presurgical evaluation of patients with medically intractable localization-related epilepsy. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2009, 26, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oishi, M.; Otsubo, H.; Iida, K.; Suyama, Y.; Ochi, A.; Weiss, S.K.; Xiang, J.; Gaetz, W.; Cheyne, D.; Chuang, S.H.; et al. Preoperative simulation of intracerebral epileptiform discharges: Synthetic aperture magnetometry virtual sensor analysis of interictal magnetoencephalography data. J. Neurosurg. 2006, 105, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, N.; Kringelbach, M.; Jenkinson, N.; Owen, S.; Davies, P.; Wang, S.; De Pennington, N.; Hansen, P.; Stein, J.; Aziz, T. Using magnetoencephalography to investigate brain activity during high frequency deep brain stimulation in a cluster headache patient. Biomed. Imaging Interv. J. 2007, 3, e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, R.S.; Acevedo, C.; Arzimanoglou, A.; Bogacz, A.; Cross, J.H.; Elger, C.E.; Engel, J.; Forsgren, L.; French, J.A.; Glynn, M.; et al. ILAE official report: A practical clinical definition of epilepsy. Epilepsia 2014, 55, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, R.S.; van Emde Boas, W.; Blume, W.; Elger, C.; Genton, P.; Lee, P.; Engel, J. Epileptic seizures and epilepsy: Definitions proposed by the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) and the International Bureau for Epilepsy (IBE). Epilepsia 2005, 46, 470–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesdorffer, D.C.; Begley, C.E. Surveillance of epilepsy and prevention of epilepsy and its sequelae: Lessons from the Institute of Medicine report. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2013, 26, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aaberg, K.M.; Gunnes, N.; Bakken, I.J.; Lund Søraas, C.; Berntsen, A.; Magnus, P.; Lossius, M.I.; Stoltenberg, C.; Chin, R.; Surén, P. Incidence and Prevalence of Childhood Epilepsy: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Pediatrics 2017, 139, e20163908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowan, L.D.; Bodensteiner, J.B.; Leviton, A.; Doherty, L. Prevalence of the Epilepsies in Children and Adolescents. Epilepsia 2018, 30, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, D.; Schachter, S.C. Drug treatment of epilepsy in adults. BMJ 2014, 348, g254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begley, C.E.; Famulari, M.; Annegers, J.F.; Lairson, D.R.; Reynolds, T.F.; Coan, S.; Dubinsky, S.; Newmark, M.E.; Leibson, C.; So, E.L.; et al. The cost of epilepsy in the United States: An estimate from population-based clinical and survey data. Epilepsia 2000, 41, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiebe, S.; Blume, W.T.; Girvin, J.P.; Eliasziw, M. A randomized, controlled trial of surgery for temporal-lobe epilepsy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobst, B.C.; Cascino, G.D. Resective Epilepsy Surgery for Drug-Resistant Focal Epilepsy. JAMA 2015, 313, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, S.; Huh, L. Outcomes of epilepsy surgery in adults and children. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakar, P.; Gaillard, W.D.; Tripathi, M.; Libenson, M.H.; Mathern, G.W.; Cross, J.H. Diagnostic test utilization in evaluation for resective epilepsy surgery in children. Epilepsia 2014, 55, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowlton, R.C.; Razdan, S.N.; Limdi, N.; Elgavish, R.A.; Killen, J.; Blount, J.; Burneo, J.G.; Ver Hoef, L.; Paige, L.; Faught, E.; et al. Effect of epilepsy magnetic source imaging on intracranial electrode placement. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 65, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherling, W.W.; Crandall, P.H.; Cahan, L.D.; Barth, D.S. The magnetic field of epileptic spikes agrees with intracranial localizations in complex partial epilepsy. Neurology 1988, 38, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenberg, H.M.; Papanicolaou, A.C.; Baumann, S.B.; Rogers, R.L.; Brown, L.M. Magnetoencephalographic localization of interictal spike sources. Case report. J. Neurosurg. 1991, 74, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, H.; Schneider, S.; Feistel, H.; Pawlik, G.; Schüler, P.; Abraham-Fuchs, K.; Schlegel, T.; Neubauer, U.; Huk, W.J. Ictal and Interictal Activity in Partial Epilepsy Recorded with Multichannel Magnetoelectroencephalography: Correlation of Electroencephalography/Electrocorticography, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography, and Positron Em. Epilepsia 1992, 33, 874–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, D.S.; Sutherling, W.; Engel, J.; Beatty, J. Neuromagnetic localization of epileptiform spike activity in the human brain. Science 1982, 218, 891–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, H.; Hummel, C.; Scheler, G.; Genow, A.; Druschky, K.; Tilz, C.; Kaltenhauser, M.; Hopfengartner, R.; Buchfelder, M.; Romstock, J. Magnetic brain source imaging of focal epileptic activity: A synopsis of 455 cases. Brain 2003, 126, 2396–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knake, S.; Halgren, E.; Shiraishi, H.; Hara, K.; Hamer, H.M.; Grant, P.E.; Carr, V.A.; Foxe, D.; Camposano, S.; Busa, E.; et al. The value of multichannel MEG and EEG in the presurgical evaluation of 70 epilepsy patients. Epilepsy Res. 2006, 69, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pataraia, E.; Simos, P.G.; Castillo, E.M.; Billingsley, R.L.; Sarkari, S.; Wheless, J.W.; Maggio, V.; Maggio, W.; Baumgartner, J.E.; Swank, P.R.; et al. Does magnetoencephalography add to scalp video-EEG as a diagnostic tool in epilepsy surgery? Neurology 2004, 62, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oishi, M.; Kameyama, S.; Masuda, H.; Tohyama, J.; Kanazawa, O.; Sasagawa, M.; Otsubo, H. Single and multiple clusters of magnetoencephalographic dipoles in neocortical epilepsy: Significance in characterizing the epileptogenic zone. Epilepsia 2006, 47, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamelak, A.N.; Lopez, N.; Akhtari, M.; Sutherling, W.W. Magnetoencephalography-directed surgery in patients with neocortical epilepsy. J. Neurosurg. 2002, 97, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowlton, R.C.; Laxer, K.D.; Aminoff, M.J.; Roberts, T.P.; Wong, S.T.; Rowley, H.A. Magnetoencephalography in partial epilepsy: Clinical yield and localization accuracy. Ann. Neurol. 1997, 42, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iida, K.; Otsubo, H.; Matsumoto, Y.; Ochi, A.; Oishi, M.; Holowka, S.; Pang, E.; Elliott, I.; Weiss, S.K.; Chuang, S.H.; et al. Characterizing magnetic spike sources by using magnetoencephalography-guided neuronavigation in epilepsy surgery in pediatric patients. J. Neurosurg. 2005, 102, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, R.; Canuet, L.; Ochi, A.; Xiang, J.; Imai, K.; Chan, D.; Iwase, M.; Takeda, M.; Snead, O.C., 3rd; Otsubo, H. Spatially filtered magnetoencephalography compared with electrocorticography to identify intrinsically epileptogenic focal cortical dysplasia. Epilepsy Res. 2008, 81, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowlton, R.C.; Elgavish, R.; Howell, J.; Blount, J.; Burneo, J.G.; Faught, E.; Kankirawatana, P.; Riley, K.; Morawetz, R.; Worthington, J.; et al. Magnetic source imaging versus intracranial electroencephalogram in epilepsy surgery: A prospective study. Ann. Neurol. 2006, 59, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.; Xiang, J.; Holowka, S.; Hunjan, A.; Sharma, R.; Otsubo, H.; Chuang, S. Volumetric localization of epileptic activities in tuberous sclerosis using synthetic aperture magnetometry. Pediatr. Radiol. 2006, 36, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canuet, L.; Ishii, R.; Iwase, M.; Kurimoto, R.; Ikezawa, K.; Azechi, M.; Wataya-Kaneda, M.; Takeda, M. Tuberous sclerosis: Localizing the epileptogenic tuber with synthetic aperture magnetometry with excess kurtosis analysis. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2008, 15, 1296–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iida, K.; Otsubo, H.; Mohamed, I.S.; Okuda, C.; Ochi, A.; Weiss, S.K.; Chuang, S.H.; Snead, O.C., 3rd. Characterizing magnetoencephalographic spike sources in children with tuberous sclerosis complex. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 1510–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiyama, I.; Imai, K.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Ochi, A.; Akizuki, Y.; Go, C.; Akiyama, T.; Snead, O.C., 3rd; Rutka, J.T.; Drake, J.M.; et al. Localization of epileptic foci in children with intractable epilepsy secondary to multiple cortical tubers by using synthetic aperture magnetometry kurtosis. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2009, 4, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunold, A.; Haueisen, J.; Ahtam, B.; Doshi, C.; Harini, C.; Camposano, S.; Warfield, S.; Grant, P.E.; Okada, Y.; Papadelis, C. Localization of the Epileptogenic Foci in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex: A Pediatric Case Report. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, F.E.; Huiskamp, G.; van Huffelen, A.C.; Bourez-Swart, M.; Boere, E.; Gebbink, T.; Vincken, K.L.; van Nieuwenhuize, O. Identification of the Epileptogenic Tuber in Patients with Tuberous Sclerosis: A Comparison of High-resolution EEG and MEG. Epilepsia 2006, 47, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.J.; Scheler, G.; Stefan, H. Utilization of magnetoencephalography results to obtain favourable outcomes in epilepsy surgery. Brain 2005, 128, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RamachandranNair, R.; Otsubo, H.; Shroff, M.M.; Ochi, A.; Weiss, S.K.; Rutka, J.T.; Snead, O.C., 3rd. MEG predicts outcome following surgery for intractable epilepsy in children with normal or nonfocal MRI findings. Epilepsia 2007, 48, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiken, K.; Xiang, J.; Zhang, F.; Shi, J.; Tang, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, X. Magnetoencephalography Detection of High-Frequency Oscillations in the Developing Brain. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jirsch, J.D.; Urrestarazu, E.; LeVan, P.; Olivier, A.; Dubeau, F.; Gotman, J. High-frequency oscillations during human focal seizures. Brain 2006, 129, 1593–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, J.; LeVan, P.; Chander, R.; Hall, J.; Dubeau, F.; Gotman, J. Interictal high-frequency oscillations (80-500 Hz) are an indicator of seizure onset areas independent of spikes in the human epileptic brain. Epilepsia 2008, 49, 1893–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zijlmans, M.; Jacobs, J.; Kahn, Y.U.; Zelmann, R.; Dubeau, F.; Gotman, J. Ictal and interictal high frequency oscillations in patients with focal epilepsy. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2011, 122, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamilia, E.; Madsen, J.R.; Grant, P.E.; Pearl, P.L.; Papadelis, C. Current and Emerging Potential of Magnetoencephalography in the Detection and Localization of High-Frequency Oscillations in Epilepsy. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nariai, H.; Nagasawa, T.; Juhasz, C.; Sood, S.; Chugani, H.T.; Asano, E. Statistical mapping of ictal high-frequency oscillations in epileptic spasms. Epilepsia 2011, 52, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, J.; Zijlmans, M.; Zelmann, R.; Chatillon, C.E.; Hall, J.; Olivier, A.; Dubeau, F.; Gotman, J. High-frequency electroencephalographic oscillations correlate with outcome of epilepsy surgery. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 67, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haegelen, C.; Perucca, P.; Chatillon, C.E.; Andrade-Valenca, L.; Zelmann, R.; Jacobs, J.; Collins, D.L.; Dubeau, F.; Olivier, A.; Gotman, J. High-frequency oscillations, extent of surgical resection, and surgical outcome in drug-resistant focal epilepsy. Epilepsia 2013, 54, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Kirtman, E.G.; Kotecha, R.; Chen, Y.; Huo, X.; Fujiwara, H.; Hemasilpin, N.; Lee, K.; et al. Frequency and spatial characteristics of high-frequency neuromagnetic signals in childhood epilepsy. Epileptic Disord. 2009, 11, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Klink, N.; Hillebrand, A.; Zijlmans, M. Identification of epileptic high frequency oscillations in the time domain by using MEG beamformer-based virtual sensors. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadelis, C.; Tamilia, E.; Stufflebeam, S.; Grant, P.E.; Madsen, J.R.; Pearl, P.L.; Tanaka, N. Interictal High Frequency Oscillations Detected with Simultaneous Magnetoencephalography and Electroencephalography as Biomarker of Pediatric Epilepsy. JoVE 2016, e54883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadelis, C.; Poghosyan, V.; Fenwick, P.B.C.; Ioannides, A.A. MEG’s ability to localise accurately weak transient neural sources. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2009, 120, 1958–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, M.; Kato, A.; Taniguchi, M.; Ninomiya, H.; Cheyne, D.; Robinson, S.E.; Maruno, M.; Kumura, E.; Ishii, R.; Hirabuki, N.; et al. Frequency-dependent spatial distribution of human somatosensory evoked neuromagnetic fields. Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 318, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaetz, W.C.; Cheyne, D.O. Localization of human somatosensory cortex using spatially filtered magnetoencephalography. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 340, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadelis, C.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Zilles, K.; Ioannides, A.A. BA3b and BA1 activate in a serial fashion after median nerve stimulation: Direct evidence from combining source analysis of evoked fields and cytoarchitectonic probabilistic maps. Neuroimage 2011, 54, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadelis, C.; Leonardelli, E.; Staudt, M.; Braun, C. Can magnetoencephalography track the afferent information flow along white matter thalamo-cortical fibers? Neuroimage 2012, 60, 1092–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannides, A.A.; Liu, L.; Poghosyan, V.; Saridis, G.A.; Gjedde, A.; Ptito, M.; Kupers, R. MEG reveals a fast pathway from somatosensory cortex to occipital areas via posterior parietal cortex in a blind subject. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adjamian, P.; Worthen, S.F.; Hillebrand, A.; Furlong, P.L.; Chizh, B.A.; Hobson, A.R.; Aziz, Q.; Barnes, G.R. Effective electromagnetic noise cancellation with beamformers and synthetic gradiometry in shielded and partly shielded environments. J. Neurosci. Methods 2009, 178, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaetz, W.; Cheyne, D. Localization of sensorimotor cortical rhythms induced by tactile stimulation using spatially filtered MEG. Neuroimage 2006, 30, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheyne, D.; Bostan, A.C.; Gaetz, W.; Pang, E.W. Event-related beamforming: A robust method for presurgical functional mapping using MEG. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2007, 118, 1691–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevalainen, P.; Pihko, E.; Metsaranta, M.; Sambeth, A.; Wikstrom, H.; Okada, Y.; Autti, T.; Lauronen, L. Evoked magnetic fields from primary and secondary somatosensory cortices: A reliable tool for assessment of cortical processing in the neonatal period. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2011, 123, 2377–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshiyama, M.; Kakigi, R.; Koyama, S.; Watanabe, S.; Shimojo, M. Activity in Posterior Parietal Cortex Following Somatosensory Stimulation in Man: Magnetoencephalographic Study Using Spatio-Temporal Source Analysis. Brain Topogr. 1997, 10, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshiyama, M.; Kakigi, R.; Berg, P.; Koyama, S.; Kitamura, Y.; Shimojo, M.; Watanabe, S.; Nakamura, A. Identification of motor and sensory brain activities during unilateral finger movement: Spatiotemporal source analysis of movement-associated magnetic fields. Exp. Brain Res. 1997, 115, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, A.; Yamada, T.; Goto, A.; Kato, T.; Ito, K.; Abe, Y.; Kachi, T.; Kakigi, R. Somatosensory Homunculus as Drawn by MEG. Neuroimage 1998, 7, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inui, K.; Wang, X.; Tamura, Y.; Kaneoke, Y.; Kakigi, R. Serial processing in the human somatosensory system. Cereb. Cortex 2004, 14, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, E.W.; Drake, M.; Otsubo, H. Intraoperative Confirmation of Hand Motor Area Identified Preoperatively by Magnetoencephalography. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2008, 44, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheyne, D.; Bakhtazad, L.; Gaetz, W. Spatiotemporal mapping of cortical activity accompanying voluntary movements using an event-related beamforming approach. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2006, 27, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheyne, D.; Bells, S.; Ferrari, P.; Gaetz, W.; Bostan, A.C. Self-paced movements induce high-frequency gamma oscillations in primary motor cortex. Neuroimage 2008, 42, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheyne, D.; Ferrari, P. MEG studies of motor cortex gamma oscillations: Evidence for a gamma “fingerprint” in the brain? Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigihara, Y.; Zeki, S. Parallel processing of face and house stimuli by V1 and specialized visual areas: A magnetoencephalographic (MEG) study. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, M.; Kato, A.; Taniguchi, M.; Saitoh, Y.; Ninomiya, H.; Ihara, A.; Kishima, H.; Oshino, S.; Baba, T.; Yorifuji, S.; et al. Determination of language dominance with synthetic aperture magnetometry: Comparison with the Wada test. Neuroimage 2004, 23, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Chung, C.K. Language lateralization using MEG beta frequency desynchronization during auditory oddball stimulation with one-syllable words. Neuroimage 2008, 42, 1499–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, I.S.; Cheyne, D.; Gaetz, W.C.; Otsubo, H.; Logan, W.J.; Carter Snead, O., 3rd; Pang, E.W. Spatiotemporal patterns of oscillatory brain activity during auditory word recognition in children: A synthetic aperture magnetometry study. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2008, 68, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papanicolaou, A.C.; Simos, P.G.; Castillo, E.M.; Breier, J.I.; Sarkari, S.; Pataraia, E.; Billingsley, R.L.; Buchanan, S.; Wheless, J.; Maggio, V.; et al. Magnetocephalography: A noninvasive alternative to the Wada procedure. J. Neurosurg. 2004, 100, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papanicolaou, A.C.; Pazo-Alvarez, P.; Castillo, E.M.; Billingsley-Marshall, R.L.; Breier, J.I.; Swank, P.R.; Buchanan, S.; McManis, M.; Clear, T.; Passaro, A.D. Functional neuroimaging with MEG: Normative language profiles. Neuroimage 2006, 33, 326–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frye, R.E.; Rezaie, R.; Papanicolaou, A.C. Functional Neuroimaging of Language Using Magnetoencephalography. Phys. Life Rev. 2009, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherling, W.W.; Mamelak, A.N.; Thyerlei, D.; Maleeva, T.; Minazad, Y.; Philpott, L.; Lopez, N. Influence of magnetic source imaging for planning intracranial EEG in epilepsy. Neurology 2008, 71, 990–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowlton, R.C.; Elgavish, R.A.; Limdi, N.; Bartolucci, A.; Ojha, B.; Blount, J.; Burneo, J.G.; Ver Hoef, L.; Paige, L.; Faught, E.; et al. Functional imaging: I. Relative predictive value of intracranial electroencephalography. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 64, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowlton, R.C.; Elgavish, R.A.; Bartolucci, A.; Ojha, B.; Limdi, N.; Blount, J.; Burneo, J.G.; Ver Hoef, L.; Paige, L.; Faught, E.; et al. Functional imaging: II. Prediction of epilepsy surgery outcome. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 64, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, I.S.; Otsubo, H.; Ferrari, P.; Sharma, R.; Ochi, A.; Elliott, I.; Go, C.; Chuang, S.; Rutka, J.; Snead, C., 3rd; Cheyne, D. Source localization of interictal spike-locked neuromagnetic oscillations in pediatric neocortical epilepsy. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2013, 124, 1517–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaetz, W.; Gordon, R.S.; Papadelis, C.; Fujiwara, H.; Rose, D.F.; Edgar, J.C.; Schwartz, E.S.; Roberts, T.P.L. Magnetoencephalography for Clinical Pediatrics: Recent Advances in Hardware, Methods, and Clinical Applications. J. Pediatr. Epilepsy 2015, 4, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadelis, C.; Harini, C.; Ahtam, B.; Doshi, C.; Grant, E.; Okada, Y. Current and emerging potential for magnetoencephalography in pediatric epilepsy. J. Pediatr. Epilepsy 2013, 2, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, Y.; Pratt, K.; Atwood, C.; Mascarenas, A.; Reineman, R.; Nurminen, J.; Paulson, D. BabySQUID: A mobile, high-resolution multichannel magnetoencephalography system for neonatal brain assessment. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2006, 77, 24301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.W.; Crain, S.; Thornton, R.; Tesan, G.; Reid, M. Measurement of brain function in pre-school children using a custom sized whole-head MEG sensor array. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2010, 121, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, M.; Yoshimura, Y.; Shitamichi, K.; Ueno, S.; Hirosawa, T.; Munesue, T.; Ono, Y.; Tsubokawa, T.; Haruta, Y.; Oi, M.; et al. A custom magnetoencephalography device reveals brain connectivity and high reading/decoding ability in children with autism. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, T.; Paulson, D.; Hirschkoff, G.; Pratt, K.; Mascarenas, A.; Miller, P.; Han, M.; Caffrey, J.; Kincade, C.; Power, W.; et al. Artemis 123: Development of a whole-head infant and young child MEG system. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Brock, J.; Johnson, B.W. Face-sensitive brain responses measured from a four-year-old child with a custom-sized child MEG system. J. Neurosci. Methods 2014, 222, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, K.; Lin, F.-H.; Camposano, S.; Foxe, D.M.; Grant, P.E.; Bourgeois, B.F.; Ahlfors, S.P.; Stufflebeam, S.M. Magnetoencephalographic mapping of interictal spike propagation: A technical and clinical report. AJNR. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2007, 28, 1486–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrba, J.; Robinson, S. Signal processing in magnetoencephalography. Methods 2001, 25, 249–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrba, J.; Robinson, S.E. The effect of environmental noise on magnetometer- and gardiometer-based MEG systems. In Proceedings of the Biomag 2000: 12th International Conference on Biomagnetism, Espoo, Finland, 13–17 August 2000; pp. 953–956. [Google Scholar]
- Fife, A.A.; Vrba, J.; Robinson, S.E.; Anderson, G.; Betts, K.; Burbank, M.B.; Cheyne, D.; Cheung, T.; Govorkov, S.; Haid, G.; et al. Synthetic gradiometer systems for MEG. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 1999, 9, 4063–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsch, H.E.; Robinson, S.E.; Mantle, M.; Nagarajan, S. Automated localization of magnetoencephalographic interictal spikes by adaptive spatial filtering. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2006, 117, 2264–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ukai, S.; Kawaguchi, S.; Ishii, R.; Yamamoto, M.; Ogawa, A.; Mizuno-Matsumoto, Y.; Robinson, S.E.; Fujita, N.; Yoshimine, T.; Shinosaki, K.; et al. SAM(g2) analysis for detecting spike localization: A comparison with clinical symptoms and ECD analysis in an epileptic patient. Neurol. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004, 2004, 57. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Wu, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zou, Y.; Liu, W.; Xiang, J.; Xiao, C.; Yang, L.; Fu, Z. Interictal magnetoencephalographic findings related with surgical outcomes in lesional and nonlesional neocortical epilepsy. Seizure 2011, 20, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Negrillo, A. Influence of Sleep and Sleep Deprivation on Ictal and Interictal Epileptiform Activity. Epilepsy Res. Treat. 2013, 2013, 492524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.X.; Mosher, J.C.; Leahy, R.M. A sensor-weighted overlapping-sphere head model and exhaustive head model comparison for MEG. Phys. Med. Biol. 1999, 44, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowland, J.A.; Stapleton-Kotloski, J.R.; Dobbins, D.L.; Rogers, E.; Godwin, D.W.; Taber, K.H. Increased Small-World Network Topology Following Deployment-Acquired Traumatic Brain Injury Associated with the Development of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. Brain Connect. 2018, 8, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowland, J.A.; Stapleton-Kotloski, J.R.; Alberto, G.E.; Rawley, J.A.; Kotloski, R.J.; Taber, K.H.; Godwin, D.W. Contrasting Effects of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder and Mild Traumatic Brain Injury on the Whole-Brain Resting-State Network: A Magnetoencephalography Study. Brain Connect. 2017, 7, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowland, J.A.; Stapleton-Kotloski, J.R.; Alberto, G.E.; Davenport, A.T.; Kotloski, R.J.; Friedman, D.P.; Godwin, D.W.; Daunais, J.B. Changes in nonhuman primate brain function following chronic alcohol consumption in previously naïve animals. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017, 177, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taulu, S.; Hari, R. Removal of magnetoencephalographic artifacts with temporal signal-space separation: Demonstration with single-trial auditory-evoked responses. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2009, 30, 1524–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, T.W.; Godwin, D.W.; Czoty, P.W.; Nader, M.A.; Kraft, R.A.; Buchheimer, N.C.; Daunais, J.B. A MEG investigation of somatosensory processing in the rhesus monkey. Neuroimage 2009, 46, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stapleton-Kotloski, J.R.; Kotloski, R.J.; Popli, G.; Godwin, D.W. Magnetoencephalography: Clinical and Research Practices. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8080157
Stapleton-Kotloski JR, Kotloski RJ, Popli G, Godwin DW. Magnetoencephalography: Clinical and Research Practices. Brain Sciences. 2018; 8(8):157. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8080157
Chicago/Turabian StyleStapleton-Kotloski, Jennifer R., Robert J. Kotloski, Gautam Popli, and Dwayne W. Godwin. 2018. "Magnetoencephalography: Clinical and Research Practices" Brain Sciences 8, no. 8: 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8080157
APA StyleStapleton-Kotloski, J. R., Kotloski, R. J., Popli, G., & Godwin, D. W. (2018). Magnetoencephalography: Clinical and Research Practices. Brain Sciences, 8(8), 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8080157




