The Influence of the Degree of Dental Implant Insertion Compression on Primary Stability Measured by Resonance Frequency and Progressive Insertion Torque: In Vitro Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Sample Size
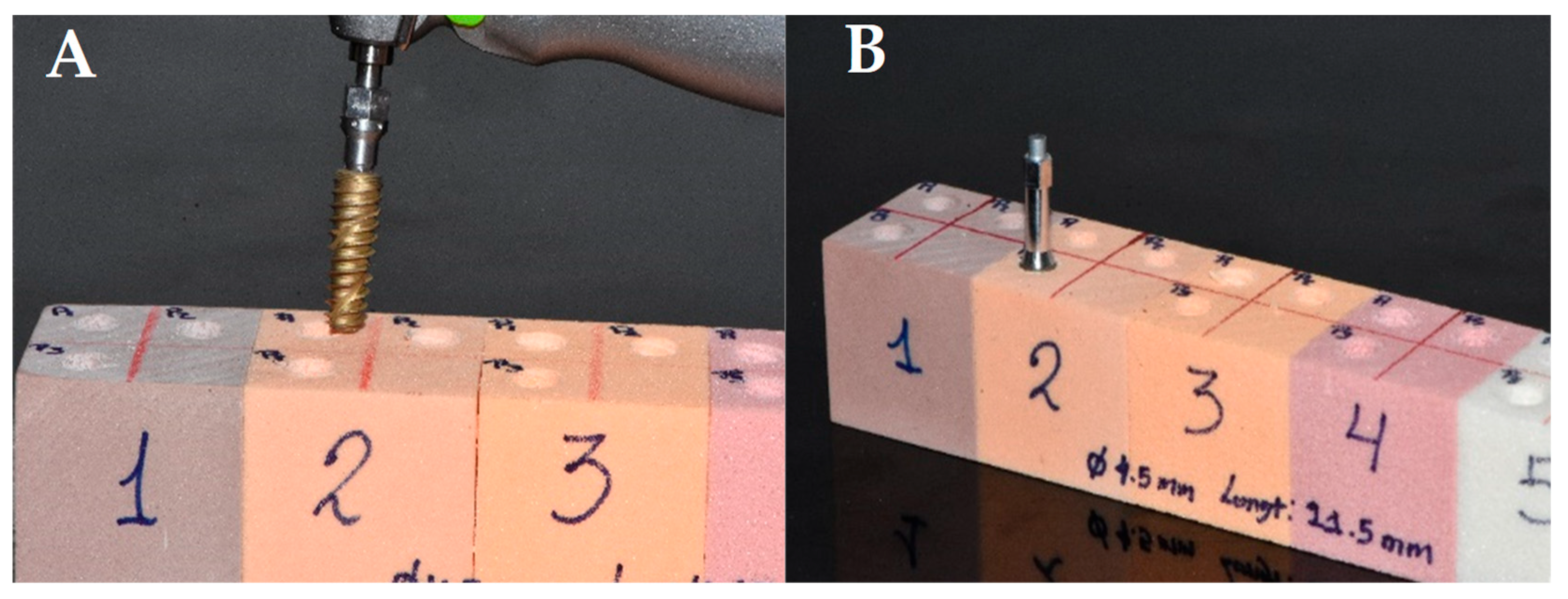
2.3. Standardized Bone Quality Models and Implants
2.4. Surgical Protocols and Measurement of ITV and RFA
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brånemark, P.I.; Hansson, B.O.; Adell, R.; Breine, U.; Lindström, J.; Hallén, O.; Ohman, A. Osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw: Experience from a 10-year period. Scand. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surgery Suppl. 1977, 16, 1–132. [Google Scholar]
- Szmukler-Moncler, S.; Piattelli, A.; Favero, G.A.; Dubruille, J. Considerations preliminary to the application of early and immediate loading protocols in dental implantology. Clin. Oral. Implant. Res. 2000, 11, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosas-Díaz, J.C.; Malpartida-Carrillo, V.; Córdova-Limaylla, N.E.; Guerrero, M.E.; Palomino-Zorrilla, J.J.; Cervantes-Ganoza, L.A.; Cayo-Rojas, C.F. Resonance frequency analysis mapping during implant healing using a nanostructured hydroxyapatite surface. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2022, 13, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiuchi, K.; Uchida, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Sugimura, M. Immediate loading of Brånemark system implants following placement in edentulous patients: A clinical report. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implant. 2001, 15, 824–830. [Google Scholar]
- Mericske-Stern, R.; Zarb, G.A. Overdentures: An alternative implant methodology for edentulous patients. Int. J. Prosthodont. 1993, 6, 203–208. [Google Scholar]
- Palomino-Zorrilla, J.J.; Córdova-Limaylla, N.E.; Rosas-Díaz, J.C.; Cayo-Rojas, C.F.; Cervantes-Ganoza, L.A.; Guerrero, M.E. Jawbone quality classification in dental implant planning and placement studies. A scoping review. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2024, 14, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas-Díaz, J.C.; Córdova-Limaylla, N.E.; Palomino-Zorrilla, J.J.; Guerrero, M.E.; Carreteros, R.; Cervantes-Ganoza, L.A.; Cayo-Rojas, C.F. Repeatability and Reproducibility of a Modified Lekholm and Zarb Bone Quality Classification Based on Cone Beam Computed Tomography: An Observatsion Study. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2022, 14, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambini, F.; Memè, L.; Pellecchia, M.; Sabatucci, A.; Selvaggio, R. Comparative analysis of deformation of two implant/abutment connection systems during implant insertion. An In Vitro study. Minerva Stomatol. 2005, 54, 129–138. [Google Scholar]
- Donati, M.; La Scala, V.; Billi, M.; Di Dino, B.; Torrisi, P.; Berglundh, T. Immediate functional loading of implants in single tooth replacement: A multicenter prospective clinical study. Clin. Oral. Implant. Res. 2008, 19, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barewal, R.M.; Stanford, C.; Weesner, T.C. A randomized controlled clinical trial comparing the effects of three loading protocols on dental implant stability. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 27, 945–956. [Google Scholar]
- Maló, P.; Rangert, B.; Dvarsater, L. Immediate function of Brånemark implants in the aesthetic zone: A retrospective clinical study with 6 months to 4 years of follow-up. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2000, 2, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gapski, R.; Wang, H.; Mascarenhas, P.; Lang, N.P. Critical review of immediate implant loading. Clin. Oral. Implant. Res. 2003, 14, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ericsson, I.; Nilson, H.; Lindh, T.; Nilner, K.; Randow, K. Immediate functional loading of Brånemark unidental implants. Clin. Oral. Implant. Res. 2000, 11, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, N.; Alleyne, D.; Cawley, P. Quantitative determination of implant-tissue interface stability using resonance frequency analysis. Clin. Oral. Implant. Res. 1996, 7, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, N.; Libro, K.; Friberg, B.; Jemt, T.; Sennerby, L. Resonance frequency measurements of implant stability In Vivo: A cross-sectional and longitudinal study of implant resonance frequency measurements in the edentulous and partially dentate maxilla. Clin. Oral. Implant. Res. 1997, 8, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atsumi, M.; Park, S.; Wang, H. Methods used to evaluate implant stability: Current status. Implant. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. 2007, 22, 743–754. [Google Scholar]
- Friberg, B.; Sennerby, L.; Roos, J.; Johansson, P.; Strid, C.; Lekholm, U. Evaluation of bone density by shear strength measurements and microradiography: An in vitro study in pork ribs. Clin. Oral. Implant. Res. 1995, 6, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barewal, R.; Oates, T.; Meredith, N.; Cochran, D. Resonance frequency analysis of in vivo implant stability in implants with a sandblasted and acid-etched surface. Implant. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. 2003, 18, 641–651. [Google Scholar]
- Ottoni, J.; Olivieri, Z.; Mansini, R.; Cabral, A. Correlation between placement torque and survival of unidental implants. Implant. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. 2005, 20, 769–776. [Google Scholar]
- Lages, F.S.; Douglas-de Oliveira, D.W.; Costa, F.O. Relationship between implant stability measurements obtained by insertion torque and resonance frequency analysis: A systematic review. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2018, 20, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krithikadatta, J.; Datta, M.; Gopikrishna, V. CRIS Guidelines (Checklist for Reporting In-vitro Studies): A concept note on the need for standardized guidelines for improving quality and transparency in reporting in-vitro studies in experimental dental research. J. Conserv. Dent. 2014, 17, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, H.; Davarpanah, M.; Missika, P.; Celletti, R.; Lazzara, R. Optimal implant stabilization in low density bone. Clin. Oral. Implant. Res. 2001, 12, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Marshood, M.M.; Junker, R.; Al-Rasheed, A.; Al Farraj Aldosari, A.; Jansen, J.A.; Anil, S. Study of the osseointegration of dental implants placed with an adapted surgical technique. Clin. Oral. Implant. Res. 2011, 22, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabassum, A.; Meijer, G.J.; Walboomers, X.F.; Jansen, J.A. Biological limits of the undersized surgical technique: A study in goats. Clin. Oral. Implant. Res. 2011, 22, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degidi, M.; Daprile, G.; Piattelli, A. Influence of underpreparation on primary stability of implantsinserted in poor quality bone sites: An in vitro study. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 73, 1084–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekholm, U.; Zarb, G.; Albrektsson, T. Patient Selection and Preparation: Tissue Integrated Prostheses; Quintessence Publishing Co., Inc.: Chicago, IL, USA, 1985; pp. 199–209. [Google Scholar]
- Tabassum, A.; Meijer, G.J.; Wolke, J.G.C.; Jansen, J.A. Influence of the surgical technique and surface roughness on the primary stability of an implant in artificial bone with a density equivalent to maxillary bone: A laboratory study. Clin. Oral. Implant. Res. 2009, 20, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.-J.; Leesungbok, R.; Lee, S.-W.; Heo, Y.-K.; Kang, K.L. Differences in implant stability associated with various methods of preparation of the implant bed: An in vitro study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2012, 107, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, B.F.; Lopez-Jarana, P.; Falcao, C.; Ríos-Carrasco, B.; Gil, J.; Ríos-Santos, J.V.; Herrero-Climent, M. Effects of Different Undersizing Site Preparations on Implant Stability. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farronato, D.; Manfredini, M.; Stocchero, M.; Caccia, M.; Azzi, L.; Farronato, M. Influence of Bone Quality, Drilling Protocol, Implant Diameter/Length on Primary Stability: An In Vitro Comparative Study on Insertion Torque and Resonance Frequency Analysis. J. Oral. Implant. 2020, 46, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Dependent Variable | Protocol | n | Mean | SD | SE | 95% CI | * p | Protocol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LL | UL | 0.5 | 0.8 | |||||||
| ITV (Ncm) | 0.2 | 40 | 25.05 | 8.34 | 1.32 | 22.38 | 27.72 | <0.001 * | ** p < 0.001 | ** p < 0.001 |
| 0.5 | 40 | 47.33 | 14.22 | 2.25 | 42.78 | 51.87 | ** p < 0.001 | |||
| 0.8 | 40 | 63.23 | 14.90 | 2.36 | 58.46 | 67.99 | ||||
| RFA (ISQ) | 0.2 | 40 | 67.55 | 5.39 | 0.85 | 65.83 | 69.27 | 0.166 | ||
| 0.5 | 40 | 65.78 | 3.37 | 0.53 | 64.70 | 66.85 | ||||
| 0.8 | 40 | 65.68 | 4.02 | 0.64 | 64.39 | 66.96 | ||||
| Cause | Dependent Variable | Significance and Effect Size | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||||
| p * | ηp2 | Value | p ** | ηp2 | ||
| Protocol | ITV (Ncm) | <0.001 * | 0.762 | 0.130 | <0.001 ** | 0.639 |
| ISQ | 0.166 | 0.088 | ||||
| Diameter | ITV | <0.001 * | 0.327 | 0.532 | <0.001 ** | 0.270 |
| ISQ | <0.001 * | 0.417 | ||||
| Length | ITV | 0.030 * | 0.161 | 0.773 | 0.048 ** | 0.121 |
| ISQ | 0.103 | 0.119 | ||||
| Protocol × Diameter | ITV | 0.470 | 0.086 | 0.768 | 0.182 | 0.124 |
| ISQ | 0.915 | 0.033 | ||||
| Protocol × Length | ITV | 0.975 | 0.034 | 0.755 | 0.353 | 0.131 |
| ISQ | 0.560 | 0.102 | ||||
| Diameter × Length | ITV | 0.528 | 0.156 | 0.613 | 0.140 | 0.217 |
| ISQ | 0.528 | 0.156 | ||||
| Protocol × Diameter × Length | ITV | 1000 | 0.091 | 0.636 | 0.967 | 0.203 |
| ISQ | 0.959 | 0.173 | ||||
| Corrected model | ITV (a) | <0.001 * | 0.811 | |||
| ISQ (b) | 0.056 | 0.598 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rosas-Díaz, J.; Guerrero, M.E.; Córdova-Limaylla, N.; Galindo-Gómez, M.; García-Luna, M.; Cayo-Rojas, C. The Influence of the Degree of Dental Implant Insertion Compression on Primary Stability Measured by Resonance Frequency and Progressive Insertion Torque: In Vitro Study. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2878. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122878
Rosas-Díaz J, Guerrero ME, Córdova-Limaylla N, Galindo-Gómez M, García-Luna M, Cayo-Rojas C. The Influence of the Degree of Dental Implant Insertion Compression on Primary Stability Measured by Resonance Frequency and Progressive Insertion Torque: In Vitro Study. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(12):2878. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122878
Chicago/Turabian StyleRosas-Díaz, José, Maria Eugenia Guerrero, Nancy Córdova-Limaylla, Maisely Galindo-Gómez, Marco García-Luna, and César Cayo-Rojas. 2024. "The Influence of the Degree of Dental Implant Insertion Compression on Primary Stability Measured by Resonance Frequency and Progressive Insertion Torque: In Vitro Study" Biomedicines 12, no. 12: 2878. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122878
APA StyleRosas-Díaz, J., Guerrero, M. E., Córdova-Limaylla, N., Galindo-Gómez, M., García-Luna, M., & Cayo-Rojas, C. (2024). The Influence of the Degree of Dental Implant Insertion Compression on Primary Stability Measured by Resonance Frequency and Progressive Insertion Torque: In Vitro Study. Biomedicines, 12(12), 2878. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122878





