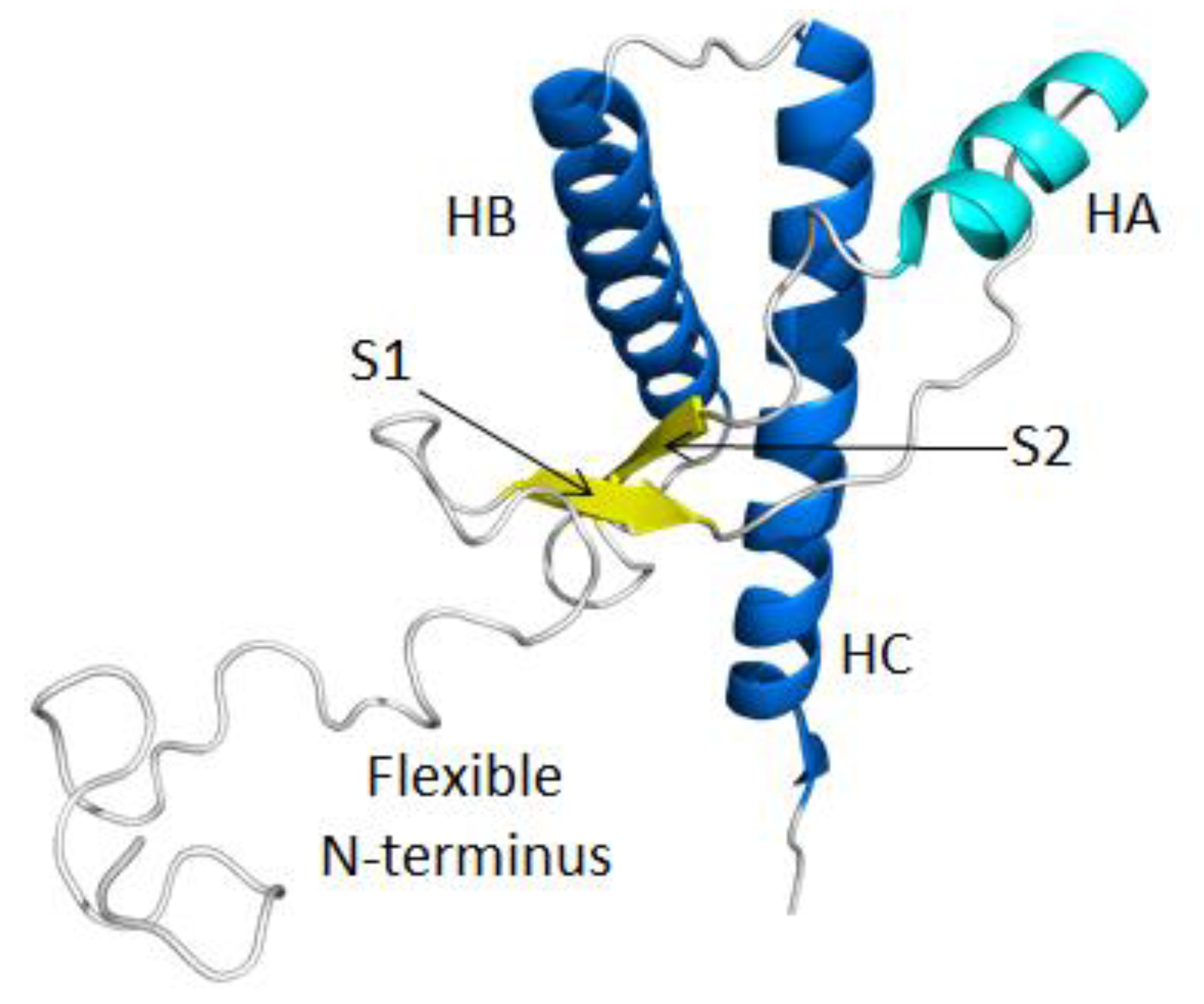
Molecular Dynamics Simulations Capture the Misfolding of the Bovine Prion Protein at Acidic pH
Abstract
:1. Introduction
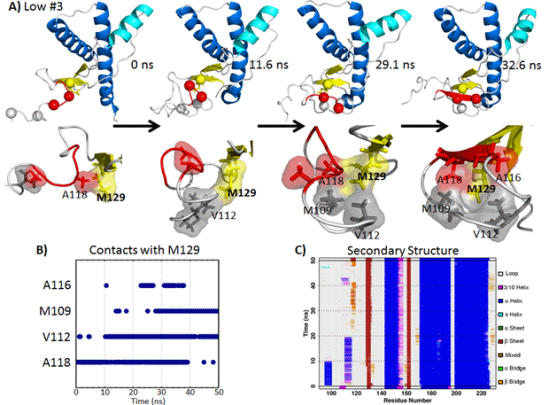
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structural Stability and Deviation from the Native Structure

2.2. HA and Native Sheet Conformational Changes

2.3. Structural Changes and Alterations in Native Polar Contacts
| pH | Simulation | HA relevant contacts | S2 relevant contacts | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y149-D202 | R156-D202 | E146-R208 | K194-E196 | H155-E196 | Y162-T183 | Y162-E186 | Y163-E221 | E186-H187 | ||
| Neutral | Average | 90.7 | 51.4 | 73.7 | 52.8 | 0.0 | 29.7 | 28.1 | 70.9 | 0.0 |
| Mid | 1 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 20.1 | 29.3 | 99.9 | 0.0 |
| Low | 1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 84.4 | 0.0 | 2.9 | 0.0 |
2.3.1. Polar Contacts with HA
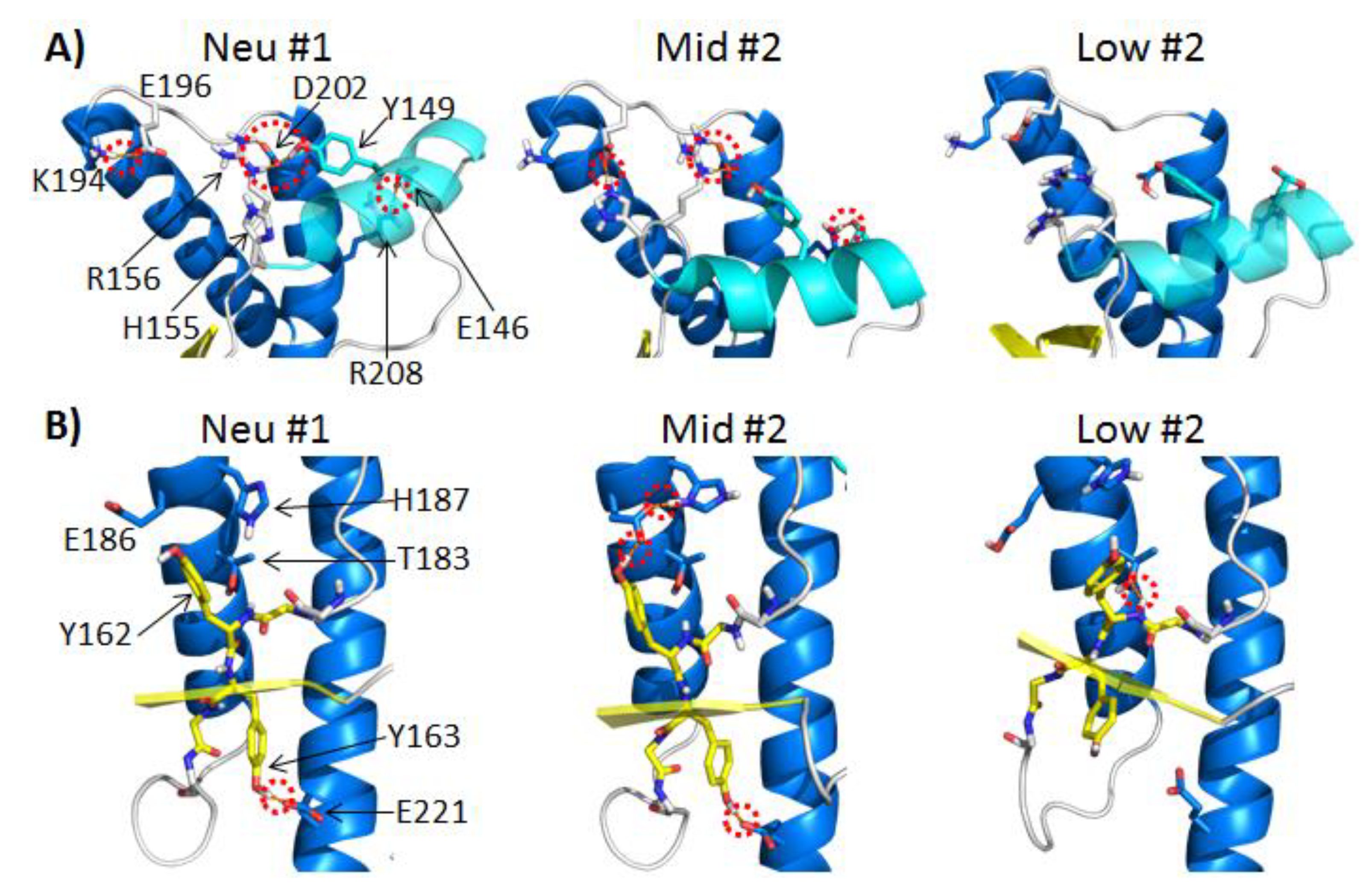
2.3.2. Polar Contacts with S2
2.4. Solvent Exposure of Hydrophobic Regions

2.5. Formation of Nonnative β-Strands
2.5.1. Hydrophobic Contacts at Low pH

2.5.2. Polar Contacts at Mid-pH

3. Experimental Section
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Prusiner, S.B.; Scott, M.R.; DeArmond, S.J.; Cohen, F.E. Prion Protein Biology. Cell 1998, 93, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusiner, S.B. Molecular biology of prion diseases. Science 1991, 252, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almond, J.; Pattison, J. Human BSE. Nature 1997, 389, 437–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collinge, J. Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. The Lancet 1999, 354, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australia lures Japanese beef buyers. Available online: http://www.abc.net.au/news/2003-12-30/australia-lures-japanese-beef-buyers/112748 (accessed on 1 November 2013).
- Hosszu, L.L.P.; Tattum, M.H.; Jones, S.; Trevitt, C.R.; Wells, M.A.; Waltho, J.P.; Collinge, J.; Jackson, G.S.; Clarke, A.R. The H187R Mutation of the Human Prion Protein Induces Conversion of Recombinant Prion Protein to the PrPSc-like Form. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 8729–8738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrover, M.; Pauwels, K.; Prigent, S.; Chiara, C.; Xu, Z.; Chapuis, C.; Pastore, A.; Rezaei, H. Prion Fibrillization Is Mediated by a Native Structural Element That Comprises Helices H2 and H3. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 21004–21012. [Google Scholar]
- Gerber, R.; Tahiri‐Alaoui, A.; Hore, P. Conformational pH dependence of intermediate states during oligomerization of the human prion protein. Protein Sci. 2008, 17, 537–544. [Google Scholar]
- Hornemann, S.; Glockshuber, R. A scrapie-like unfolding intermediate of the prion protein domain PrP(121–231) induced by acidic pH. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1998, 95, 6010–6014. [Google Scholar]
- Swietnicki, W.; Petersen, R.; Gambetti, P.; Surewicz, W.K. pH-dependent Stability and Conformation of the Recombinant Human Prion Protein PrP(90–231). J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 27517–27520. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, D.A. Trafficking, Turnover and Membrane Topology of PrP Protein Function in Prion Disease. Br. Med. Bull. 2003, 66, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironov, A.; Latawiec, D.; Wille, H.; Bouzamondo-Bernstein, E.; Legname, G.; Williamson, R.A.; Burton, D.; DeArmond, S.J.; Prusiner, S.B.; Peters, P.J. Cytosolic Prion Protein in Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 7183–7193. [Google Scholar]
- Roos, A.; Boron, W.F. Intracellular pH. Physiol. Rev. 1982, 62, 1377–1377. [Google Scholar]
- Aubry, L.; Klein, G.; Martiel, J.L.; Satre, M. Kinetics of endosomal pH evolution in Dictyostelium discoideum amoebae. Study by fluorescence spectroscopy. J. Cell Sci. 1993, 105, 861–866. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, J.E.; Tipler, C.; Laszlo, L.; Hope, J.; Landon, M.; Mayer, R.J. The abnormal isoform of the prion protein accumulates in late-endosome-like organelles in scrapie-infected mouse brain. J. Pathol. 1995, 176, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchelt, D.R.; Taraboulos, A.; Prusiner, S.B. Evidence for synthesis of scrapie prion proteins in the endocytic pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 16188–16199. [Google Scholar]
- Caughey, B.; Raymond, G.J.; Ernst, D.; Race, R.E. N-terminal truncation of the scrapie-associated form of PrP by lysosomal protease(s): implications regarding the site of conversion of PrP to the protease-resistant state. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 6597–6603. [Google Scholar]
- Godsave, S.F.; Wille, H.; Kujala, P.; Latawiec, D.; DeArmond, S.J.; Serban, A.; Prusiner, S.B.; Peters, P.J. Cryo-immunogold electron microscopy for prions: toward identification of a conversion site. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 12489–12499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, Y.; Peretz, D.; Williamson, A.; Burton, D.; Mehlhorn, I.; Groth, D.; Cohen, F.E.; Prusiner, S.B.; Baldwin, M.A. Cryptic epitopes in N-terminally truncated prion protein are exposed in the full-length molecule: dependence of conformation on pH. Proteins 2001, 44, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, T.L.; Liu, H.; Ulyanov, N.B.; Farr-Jones, S.; Zhang, H.; Donne, D.G.; Kaneko, K.; Groth, D.; Mehlhorn, I.; Prusiner, S.B.; Cohen, F.E. Solution structure of a 142-residue recombinant prion protein corresponding to the infectious fragment of the scrapie isoform. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1997, 94, 10086–10091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riek, R.; Hornemann, S.; Wider, G.; Billeter, M.; Glockshuber, R.; Wüthrich, K. NMR structure of the mouse prion protein domain PrP(121–231). Nature 1996, 382, 180–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez Garcia, F. NMR structure of the bovine prion protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2000, 97, 8334–8339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahn, R.; Liu, A.; Lührs, T.; Riek, R.; von Schroetter, C.; López García, F.; Billeter, M.; Calzolai, L.; Wider, G.; Wüthrich, K. NMR solution structure of the human prion protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2000, 97, 145–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, K.M.; Baldwin, M.; Nguyen, J.; Gasset, M.; Serban, A.; Groth, D.; Mehlhorn, I.; Huang, Z.; Fletterick, R.J.; Cohen, F.E. Conversion of alpha-helices into beta-sheets features in the formation of the scrapie prion proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1993, 90, 10962–10966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caughey, B.W.; Dong, A.; Bhat, K.S.; Ernst, D.; Hayes, S.F.; Caughey, W.S. Secondary structure analysis of the scrapie-associated protein PrP 27-30 in water by infrared spectroscopy. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 7672–7680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, G.S.; Hill, A.F.; Joseph, C.; Hosszu, L.; Power, A.; Waltho, J.P.; Clarke, A.R.; Collinge, J. Multiple folding pathways for heterologously expressed human prion protein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1431, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Kamp, M.W.; Daggett, V. Influence of pH on the human prion protein: insights into the early steps of misfolding. Biophys. J. 2010, 99, 2289–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMarco, M.L.; Daggett, V. Molecular mechanism for low pH triggered misfolding of the human prion protein. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 3045–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMarco, M.L.; Daggett, V. Characterization of cell-surface prion protein relative to its recombinant analogue: insights from molecular dynamics simulations of diglycosylated, membrane-bound human prion protein. J. Neurochem. 2009, 109, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, D.O.V.; DeArmond, S.J.; Cohen, F.E.; Daggett, V. Mapping the early steps in the pH-induced conformational conversion of the prion protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2001, 98, 2985–2989. [Google Scholar]
- DeMarco, M.L.; Daggett, V. From conversion to aggregation: Protofibril formation of the prion protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2004, 101, 2293–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, D.O.V.; An, C.; Daggett, V. Simulations of biomolecules: Characterization of the early steps in the pH-induced conformational conversion of the hamster, bovine and human forms of the prion protein. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. -Ser. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2002, 360, 1165–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scouras, A.D.; Daggett, V. Species variation in PrPSc protofibril models. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 3625–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Inanami, O.; Horiuchi, M.; Hiraoka, W.; Shimoyama, Y.; Inagaki, F.; Kuwabara, M. Identification of pH-sensitive regions in the mouse prion by the cysteine-scanning spin-labeling ESR technique. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 350, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramithiotis, E.; Pinard, M.; Lawton, T.; LaBoissiere, S.; Leathers, V.L.; Zou, W.-Q.; Estey, L.A.; Lamontagne, J.; Lehto, M.T.; Kondejewski, L.H.; Francoeur, G.P.; Papadopoulos, M.; Haghighat, A.; Spatz, S.J.; Head, M.; Will, R.; Ironside, J.; O’Rourke, K.; Tonelli, Q.; Ledebur, H.C.; Chakrabartty, A.; Cashman, N.R. A prion protein epitope selective for the pathologically misfolded conformation. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzolai, L.; Zahn, R. Influence of pH on NMR structure and stability of the human prion protein globular domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 35592–35596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingenheil, M.; Denschlag, R.; Tavan, P. Highly polar environments catalyze the unfolding of PrPC helix 1. Eur. Biophys. J. 2010, 39, 1177–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; van der Kamp, M.W.; Daggett, V. Diverse effects on the native β-sheet of the human prion protein due to disease-associated mutations. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 9874–9881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haire, L.F.; Whyte, S.M.; Vasisht, N.; Gill, A.C.; Verma, C.; Dodson, E.J.; Dodson, G.G.; Bayley, P.M. The Crystal Structure of the Globular Domain of Sheep Prion Protein. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 336, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Kamp, M.W.; Daggett, V. Pathogenic mutations in the hydrophobic core of the human prion protein can promote structural instability and misfolding. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 404, 732–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, O.; Chatterjee, S.; Thiessen, A.; Graether, S.P.; Sykes, B.D. Differential stability of the bovine prion protein upon urea unfolding. Protein Sci. 2009, 18, 2172–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschberger, T.; Stork, M.; Schropp, B.; Winklhofer, K.F.; Tatzelt, J.; Tavan, P. Structural instability of the prion protein upon M205S/R mutations revealed by molecular dynamics simulations. Biophys. J. 2006, 90, 3908–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafner-Bratkovič, I.; Bester, R.; Pristovšek, P.; Gaedtke, L.; Veranič, P.; Gašperšič, J.; Manček-Keber, M.; Avbelj, M.; Polymenidou, M.; Julius, C.; Aguzzi, A.; Vorberg, I.; Jerala, R. Globular domain of the prion protein needs to be unlocked by domain swapping to support prion protein conversion. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 12149–12156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghiaian, F.; Daubenfeld, T.; Quenet, Y.; Audenhaege, M. van; Bouin, A.-P.; Rest, G. van der; Grosclaude, J.; Rezaei, H. Diversity in prion protein oligomerization pathways results from domain expansion as revealed by hydrogen/deuterium exchange and disulfide linkage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2007, 104, 7414–7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.; McLoughlin, V.; Connolly, J.G.; Farquhar, C.F.; MacGregor, I.R.; Head, M.W. Production and characterization of a panel of monoclonal antibodies against native human cellular prion protein. Hybridoma 2009, 28, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanik, D.L.; Surewicz, W.K. Disease-associated F198S mutation increases the propensity of the recombinant prion protein for conformational conversion to scrapie-like form. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 49065–49070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liemann, S.; Glockshuber, R. Influence of amino acid substitutions related to inherited human prion diseases on the thermodynamic stability of the cellular prion protein. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 3258–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.S.; Dryden, A.J.; Hughes, J.T.; Collinge, J. Homozygous prion protein genotype predisposes to sporadic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease. Nature 1991, 352, 340–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schätzl, H.M.; Wopfner, F.; Gilch, S.; von Brunn, A.; Jäger, G. Is codon 129 of prion protein polymorphic in human beings but not in animals? The Lancet 1997, 349, 1603–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, K.M.; Browning, S.R.; Seward, T.S.; Jewell, J.E.; Ross, D.L.; Green, M.A.; Williams, E.S.; Hoover, E.A.; Telling, G.C. The elk PRNP codon 132 polymorphism controls cervid and scrapie prion propagation. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 598–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Van der Kamp, M.W.; Daggett, V. Structural and dynamic properties of the human prion protein. Biophys. J. 2014, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Forloni, G.; Angeretti, N.; Chiesa, R.; Monzani, E.; Salmona, M.; Bugiani, O.; Tagliavini, F. Neurotoxicity of a prion protein fragment. Nature 1993, 362, 543–546. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaggini, C.; Degioia, L.; Cantu, L.; Ghibaudi, E.; Diomede, L.; Passerini, F.; Forloni, G.; Bugiani, O.; Tagliavini, F.; Salmona, M. Molecular Characteristics of a Protease-Resistant, Amyloidogenic and Neurotoxic Peptide Homologous to Residues 106-126 of the Prion Protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 194, 1380–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gioia, L.; Selvaggini, C.; Ghibaudi, E.; Diomede, L.; Bugiani, O.; Forloni, G.; Tagliavini, F.; Salmona, M. Conformational polymorphism of the amyloidogenic and neurotoxic peptide homologous to residues 106-126 of the prion protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 7859–7862. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, D.R.; Schmidt, B.; Kretzschmar, H.A. Role of microglia and host prion protein in neurotoxicity of a prion protein fragment. Nature 1996, 380, 345–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armen, R.S.; Bernard, B.M.; Day, R.; Alonso, D.O.V.; Daggett, V. Characterization of a possible amyloidogenic precursor in glutamine-repeat neurodegenerative diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2005, 102, 13433–13438. [Google Scholar]
- Daggett, V. Alpha-sheet: The toxic conformer in amyloid diseases? Acc. Chem. Res. 2006, 39, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baylis, M.; Goldmann, W. The Genetics of Scrapie in Sheep and Goats. Curr. Mol. Med. 2004, 4, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambetti, P.; Parchi, P.; Petersen, R.B.; Chen, S.G.; Lugaresi, E. Fatal familial insomnia and familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: clinical, pathological and molecular features. Brain Pathol. 1995, 5, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gsponer, J.; Ferrara, P.; Caflisch, A. Flexibility of the murine prion protein and its Asp178Asn mutant investigated by molecular dynamics simulations. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2001, 20, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, K.; Zulianello, L.; Scott, M.; Cooper, C.M.; Wallace, A.C.; James, T.L.; Cohen, F.E.; Prusiner, S.B. Evidence for protein X binding to a discontinuous epitope on the cellular prion protein during scrapie prion propagation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1997, 94, 10069–10074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmus, J.J.; Surewicz, K.; Nadaud, P.S.; Surewicz, W.K.; Jaroniec, C.P. Molecular conformation and dynamics of the Y145Stop variant of human prion protein in amyloid fibrils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2008, 105, 6284–6289. [Google Scholar]
- Abalos, G.C.; Cruite, J.T.; Bellon, A.; Hemmers, S.; Akagi, J.; Mastrianni, J.A.; Williamson, R.A.; Solforosi, L. Identifying key components of the PrPC-PrPSc replicative interface. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 34021–34028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norstrom, E.M.; Mastrianni, J.A. The AGAAAAGA palindrome in PrP is required to generate a productive PrPSc-PrPC complex that leads to prion propagation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 27236–27243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muramoto, T.; Scott, M.; Cohen, F.E.; Prusiner, S.B. Recombinant scrapie-like prion protein of 106 amino acids is soluble. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1996, 93, 15457–15462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langella, E.; Improta, R.; Crescenzi, O.; Barone, V. Assessing the acid–base and conformational properties of histidine residues in human prion protein (125–228) by means of pKa calculations and molecular dynamics simulations. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinforma. 2006, 64, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, D.A.C.; McCully, M.E.; Alonso, D.O.V.; Daggett, V. in lucem Molecular Mechanics(ilmm). 2000-2014. [Google Scholar]
- Levitt, M.; Hirshberg, M.; Sharon, R.; Daggett, V. Potential energy function and parameters for simulations of the molecular dynamics of proteins and nucleic acids in solution. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1995, 91, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, D.A.C.; Daggett, V. Methods for molecular dynamics simulations of protein folding/unfolding in solution. Methods 2004, 34, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kell, G.S. Precise representation of volume properties of water at one atmosphere. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1967, 12, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitt, M.; Hirshberg, M.; Sharon, R.; Laidig, K.E.; Daggett, V. Calibration and testing of a water model for simulation of the molecular dynamics of proteins and nucleic acids in solution. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 5051–5061. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, D.A.C.; Armen, R.S.; Daggett, V. Cutoff size does strongly influence molecular dynamics results on solvated polypeptides. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 5856–5860. [Google Scholar]
- Kabsch, W.; Sander, C. Dictionary of protein secondary structure: pattern recognition of hydrogen-bonded and geometrical features. Biopolymers 1983, 22, 2577–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Richards, F.M. The interpretation of protein structures: Estimation of static accessibility. J. Mol. Biol. 1971, 55, 379–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD – Visual Molecular Dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMarco, M.L.; Silveira, J.; Caughey, B.; Daggett, V. Structural properties of prion protein protofibrils and fibrils: An experimental assessment of atomic models. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 15573–15582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, C.J.; Daggett, V. Molecular Dynamics Simulations Capture the Misfolding of the Bovine Prion Protein at Acidic pH. Biomolecules 2014, 4, 181-201. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom4010181
Cheng CJ, Daggett V. Molecular Dynamics Simulations Capture the Misfolding of the Bovine Prion Protein at Acidic pH. Biomolecules. 2014; 4(1):181-201. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom4010181
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Chin Jung, and Valerie Daggett. 2014. "Molecular Dynamics Simulations Capture the Misfolding of the Bovine Prion Protein at Acidic pH" Biomolecules 4, no. 1: 181-201. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom4010181
APA StyleCheng, C. J., & Daggett, V. (2014). Molecular Dynamics Simulations Capture the Misfolding of the Bovine Prion Protein at Acidic pH. Biomolecules, 4(1), 181-201. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom4010181