Estrogen Receptors and Ubiquitin Proteasome System: Mutual Regulation
Abstract
1. General Introduction
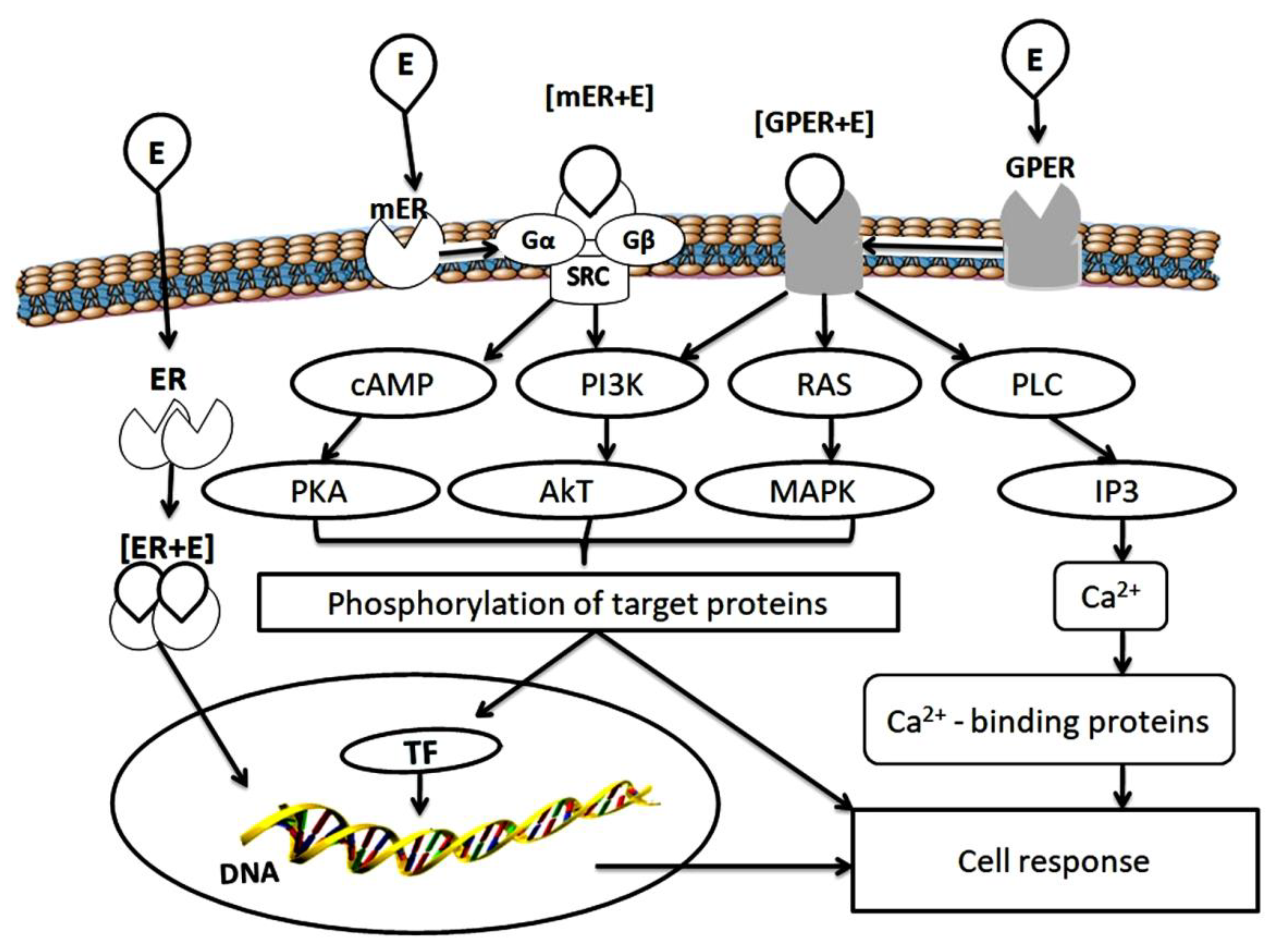
2. Estrogen Receptors
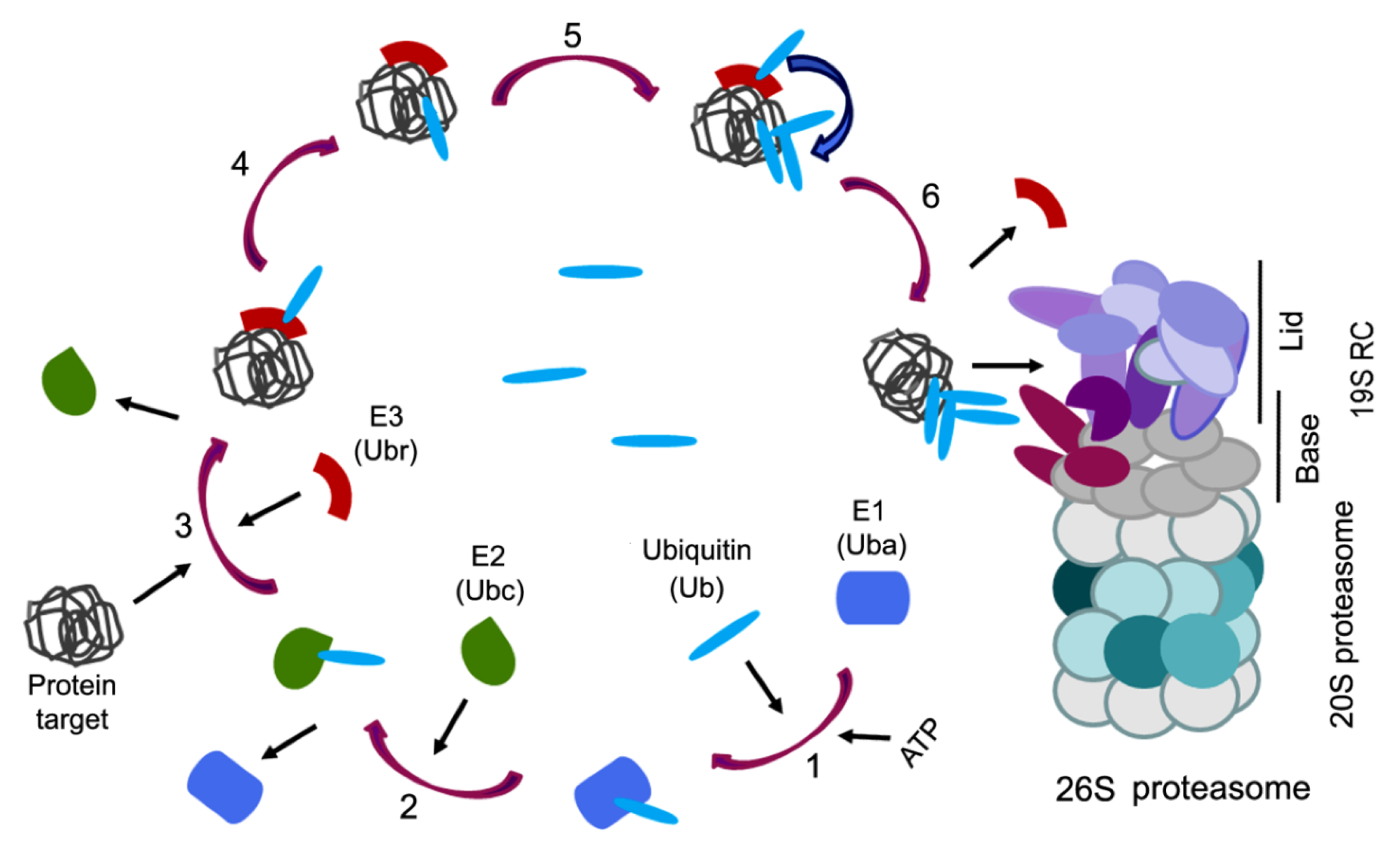
3. Ubiquitin Proteasome System
4. Mutual Regulation of Estrogen Receptors and Ubiquitin Proteasome System
5. Final Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bondesson, M.; Hao, R.; Lin, C.-Y.; Williams, C.; Gustafsson, J.-A. Estrogen receptor signaling during vertebrate development. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1849, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szmyd, M.; Lloyd, V.; Hallman, K.; Aleck, K.; Mladenovik, V.; McKee, C.; Morse, M.; Bedgood, T.; Dinda, S. The effects of black cohosh on the regulation of estrogen receptor (ERα) and progesterone receptor (PR) in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer 2018, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koolschijn, P.C.; Peper, J.S.; Crone, E.A. The influence of sex steroids on structural brain maturation in adolescence. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e83929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jover-Mengual, T.; Castelló-Ruiz, M.; Burguete, M.C.; Jorques, M.; López-Morales, M.A.; Aliena-Valero, A.; Jurado-Rodríguez, A.; Pérez, S.; Centeno, J.M.; Miranda, F.J.; et al. Molecular mechanisms mediating the neuroprotective role of the selective estrogen receptor modulator, bazedoxifene, in acute ischemic stroke: A comparative study with 17β-estradiol. J. Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 171, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, A.; Törnqvist, A.E.; Moverare-Skrtic, S.; Bernardi, A.I.; Farman, H.H.; Chambon, P.; Engdahl, C.; Lagerquist, M.K.; Windahl, S.H.; Carlsten, H.; et al. Roles of activating functions 1 and 2 of estrogen receptor α in lymphopoiesis. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 236, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; Su, S.-C.; Chiang, C.-F.; Chien, C.-Y.; Hsu, C.-C.; Yu, T.-Y.; Huang, S.-M.; Shieh, Y.-S.; Kao, H.-W.; Tsai, C.-S.; et al. Estrogen modulates vascular smooth muscle cell function through downregulation of SIRT1. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 110039–110051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.-I.; Tai, Y.-T.; Chan, W.-P.; Lin, Y.-L.; Liao, M.-H.; Chen, R.-M. Estrogen/ERα signaling axis participates in osteoblast maturation via upregulating chromosomal and mitochondrial complex gene expressions. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 1169–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Yin, J.; Zhang, S.; Guo, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Jia, Z.; Chen, H. Parkin modulates ERRα/eNOS signaling pathway in endothelial cells. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 49, 2022–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valéra, M.-C.; Noirrit-Esclassan, E.; Dupuis, M.; Fontaine, C.; Lenfant, F.; Briaux, A.; Cabou, C.; Garcia, C.; Lairez, O.; Foidart, J.-M.; et al. Effect of estetrol, a selective nuclear estrogen receptor modulator, in mouse models of arterial and venous thrombosis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 477, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalek, R.D.; Gerriets, V.A.; Nichols, A.G.; Inoue, M.; Kazmin, D.; Chang, C.-Y.; Dwyer, M.A.; Nelson, E.R.; Pollizzi, K.N.; Ilkayeva, O.; et al. Estrogen-related receptor-α is a metabolic regulator of effector T-cell activation and differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 18348–18353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-C.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, L.-L.; Li, S.-F.; Jiang, J.-H.; Zhao, Y.; Qian, S.-W.; Tang, Q.-Q.; Li, X.-J. Upregulation of miR-125b by estrogen protects against non-alcoholic fatty liver in female mice. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 1466–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sier, J.H.; Thumser, A.E.; Plant, N.J. Linking physiologically-based pharmacokinetic and genome-scale metabolic networks to understand estradiol biology. BMC Syst. Biol. 2017, 11, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokharel, A.; Kolla, S.; Matouskova, K.; Vandenberg, L.N. Asymmetric development of the male mouse mammary gland and its response to a prenatal or postnatal estrogen challenge. Reprod. Toxicol. 2018, 82, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, L.; Meldrum, K.K.; Wang, M.-J.; Sankula, R.; Vanam, R.; Raiesdana, A.; Tsai, B.; Hile, K.; Brown, J.W.; Meldrum, D.R. The role of estrogen in cardiovascular disease. J. Surg. Res. 2003, 115, 325–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, D.; Hevener, A.L.; Moreau, K.L.; Morselli, E.; Criollo, A.; Van Pelt, R.E.; Vieira-Potter, V.J. Sex Hormones and cardiometabolic health: Role of estrogen and estrogen receptors. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farahmand, M.; Ramezani Tehrani, F.; Khalili, D.; Cheraghi, L.; BahriKhomami, M.; Azizi, F. Association between duration of endogenous estrogen exposure and cardiovascular outcomes: A population—Based cohort study. Life Sci. 2019, 221, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Gong, X.; Yang, X.; Shang, X.; Du, Q.; Liao, Q.; Xie, R.; Chen, Y.; Xu, J. The roles of estrogen and estrogen receptors in gastrointestinal disease. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 5673–5680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozasa, K.; Mabuchi, S.; Matsumoto, Y.; Kuroda, H.; Yokoi, E.; Komura, N.; Kawano, M.; Takahashi, R.; Sasano, T.; Shimura, K.; et al. Estrogen stimulates female cancer progression by inducing myeloid-derived suppressive cells: Investigations on pregnant and non-pregnant experimental models. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 1887–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milette, S.; Hashimoto, M.; Perrino, S.; Qi, S.; Chen, M.; Ham, B.; Wang, N.; Istomine, R.; Lowy, A.M.; Piccirillo, C.A.; et al. Sexual dimorphism and the role of estrogen in the immune microenvironment of liver metastases. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, E.; Xu, W. Intermolecular interactions identify ligand-selective activity of estrogen receptor alpha/beta dimers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19012–19017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaşar, P.; Ayaz, G.; User, S.D.; Güpür, G.; Muyan, M. Molecular mechanism of estrogen-estrogenreceptor signaling. Reprod. Med. Biol. 2016, 16, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madak-Erdogan, Z.; Charn, T.H.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, E.T.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S. Integrative genomics of gene and metabolic regulation by estrogen receptors alpha and beta and their coregulators. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2013, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.C.; Weng, Y.J.; Shibu, M.A.; Han, C.K.; Chen, Y.S.; Shen, C.Y.; Lin, Y.M.; Viswanadha, V.P.; Liang, H.Y.; Huang, C.Y. Estrogen and/or estrogen receptor α inhibits BNIP3-induced apoptosis and autophagy in H9c2 cardiomyoblast cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Yu, W.; Liu, B.; Yang, M.; Tao, H. Estrogen receptor β induces autophagy of osteosarcoma through the mTOR signaling pathway. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2020, 15, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, S.; Eng, V.; Taylor, J.; Lubahn, D.B.; Korach, K.S.; Pfaff, D.W. Roles of estrogen receptor-α gene expression in reproduction-related behaviors in female mice. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 5070–5081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, M.; Ågmo, A.; Sagoshi, S.; Ogawa, S. The role of estrogen receptor β (ERβ) in the establishment of hierarchical social relationships in male mice. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.R. Integration of the extranuclear and nuclear actions of estrogen. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 19, 1951–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, K.J.; Arao, Y.; Korach, K.S. Estrogen hormone physiology: Reproductive findings from estrogen receptor mutant mice. Reprod. Biol. 2014, 14, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grober, O.M.; Mutarelli, M.; Giurato, G.; Ravo, M.; Cicatiello, L.; De Filippo, M.R.; Ferraro, L.; Nassa, G.; Papa, M.F.; Paris, O.; et al. Global analysis of estrogen receptor beta binding to breast cancer cell genome reveals an extensive interplay with estrogen receptor alpha for target gene regulation. BMC Genomics 2011, 2, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Klein, K.; Sugathan, A.; Nassery, N.; Dombkowski, A.; Zanger, U.M.; Waxman, D.J. Transcriptional profiling of human liver identifies sex-biased genes associated with polygenic dyslipidemia and coronary artery disease. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Gu, Y.; Pang, X.; Wu, J.; Gobin, R.; Yu, J. Oestrogen receptor α regulates the odonto/osteogenic differentiation of stem cells from apical papilla via ERK and JNK MAPK pathways. Cell Prolif. 2018, 51, e12485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tecalco-Cruz, A.C.; Pérez-Alvarado, I.A.; Ramírez-Jarquín, J.O.; Rocha-Zavaleta, L. Nucleo-cytoplasmic transport of estrogen receptor alpha in breast cancer cells. Cell Signal. 2017, 34, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, H.; Russell, I.A.; Stark, R.; Rueda, O.M.; Hickey, T.E.; Tarulli, G.A.; Serandour, A.A.; Birrell, S.N.; Bruna, A.; Saadi, A.; et al. Corrigendum: Progesterone receptor modulates ERα action in breast cancer. Nature 2015, 526, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rettberg, J.R.; Yao, J.; Brinton, R.D. Estrogen: A master regulator of bioenergetic systems in the brain and body. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2014, 35, 8–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpkins, J.W.; Yang, S.H.; Sarkar, S.N.; Pearce, V. Estrogen actions on mitochondria-physiological and pathological implications. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2008, 290, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, E.R.; Hammes, S.R. Nuclear receptors outside the nucleus: Extranuclear signalling by steroid receptors. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2016, 17, 783–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, P.; Nadig, N.; Nambiar, S. Non-canonical Estrogen Signaling in Endocrine Resistance. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggiolini, M.; Picard, D. The unfolding stories of GPR30, a new membrane-bound estrogen receptor. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 204, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.; Pang, Y.; Filardo, E.J.; Dong, J. Identity of an estrogen membrane receptor coupled to a G protein in human breast cancer cells. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prossnitz, E.R.; Barton, M. Estrogen biology: New insights into GPER function and clinical opportunities. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2014, 389, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenti, A.; Tedesco, S.; Boscaro, C.; Trevisi, L.; Bolego, C.; Cignarella, A. Estrogen, Angiogenesis, Immunity and Cell Metabolism: Solving the Puzzle. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, D.P.; Lappano, R.; Albanito, L.; Madeo, A.; Maggiolini, M.; Picard, D. Estrogenic GPR30 signalling induces proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells through CTGF. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, A.M.; Flamini, M.I.; Baldacci, C.; Goglia, L.; Genazzani, A.R.; Simoncini, T. Estrogen receptor-alpha promotes breast cancer cell motility and invasion via focal adhesion kinase and N-WASP. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 24, 2114–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, G.; Prossnitz, E.R. G-Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor (GPER) and Sex-Specific Metabolic Homeostasis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1043, 427–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.B.; O’Malley, B.W. Steroid receptor coactivators 1, 2, and 3: Critical regulators of nuclear receptor activity and steroid receptor modulator (SRM)-based cancer therapy. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011, 348, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.E.; Martin-Hirsch, P.L.; Martin, F.L. Oestrogen receptor splice variants in the pathogenesis of disease. Cancer Lett. 2010, 288, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinge, C.M. miRNAs and estrogen action. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 23, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wu, H.-T.; Zhu, N.; Shi, Y.-N.; Liu, Z.; Ao, B.-X.; Liao, D.-F.; Zheng, X.-L.; Qin, L. Steroid receptor RNA activator: Biologic function and role in disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 459, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Romancer, M.; Poulard, C.; Cohen, P.; Sentis, S.; Renoir, J.M.; Corbo, L. Cracking the estrogen receptor’s posttranslational code in breast tumors. Endocr. Rev. 2011, 32, 597–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ye, Z.-W.; Chen, W.; Manevich, Y.; Mehrotra, S.; Ball, L.E.; Janssen-Heininger, Y.M.; Tew, K.D.; Townsend, D.M. S-Glutathionylation of estrogen receptor alpha affects dendritic cell function. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 4366–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickart, C.M.; Cohen, R. Proteasomes and their kin: Proteases in the machine age. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 5, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K. The proteasome: Overiew of structure and function. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 2009, 85, 12–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadre-Bazzaz, K.; Whitby, F.G.; Robinson, H.; Formosa, T. Structure of a Blm10 complex reveals common mechanisms for proteasome binding and gate opening. Mol. Cell. 2010, 37, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, T.; Grune, T. Structure of the proteasome. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2012, 109, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raynes, R.; Pomatto, L.C.; Davies, K.J. Degradation of oxidized proteins by the proteasome: Distinguishing between the 20S, 26S, and immunoproteasome proteolytic pathways. Mol. Aspects Med. 2016, 50, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciechanover, A.; Heller, H.; Katz-Etzion, R.; Hershko, A. Activation of the heat-stable polypeptide of the ATP-dependent proteolytic system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershko, A.; Heller, H.; Elias, S.; Ciechanover, A. Components of ubiquitin-protein ligase system. Resolution, affinity purification, and role in protein breakdown. J. Biol. Chem. 1983, 258, 8206–8214. [Google Scholar]
- Hershko, A.; Ciechanover, A. The ubiquitin system. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 425–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiss, Y.; Heller, H.; Hershko, A. Binding sites of ubiquitin-protein ligase. Binding of ubiquitin-protein conjugates and of ubiquitin-carrier protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 10378–10383. [Google Scholar]
- Dohmen, R.J.; Madura, K.; Bartel, B.; Varshavsky, A. The N-end rule is mediated by the UBC2 (RAD6) ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 7351–7355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechsteiner, M.; Rogers, S.W. PEST sequences and regulation by proteolysis. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1996, 21, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, R.W.; Glotzer, M.; Kirschner, M.W. Mutagenic analysis of the destruction signal of mitotic cyclins and structural characterization of ubiquitinated intermediates. Mol. Biol. Cell 1996, 7, 1343–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshavsky, A. The N-end rule: Functions, mysteries, uses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 12142–12149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.K.; Maniatis, T. Regulation of interferon-gamma-activated STAT1 by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Science 1996, 273, 1717–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storey, A.; Thomas, M.; Kalita, A.; Harwood, C.; Gardiol, D.; Mantovani, F.; Breuer, J.; Leigh, I.M.; Matlashewski, G.; Banks, L. Role of a p53 polymorphism in the development of human papillomavirus-associated cancer. Nature 1998, 393, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, V.; Tobias, J.W.; Bachmair, A.; Marriott, D.; Ecker, D.J.; Gonda, D.K.; Varshavsky, A. Multiubiquitin chain is confined to specific lysine in a targeted short-lived protein. Science 1989, 243, 1576–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammer, E.B.; Na, C.H.; Xu, P.; Seyfried, N.T.; Duong, D.M.; Cheng, D.; Gearing, M.; Rees, H.; Lah, J.J.; Levey, A.I.; et al. Polyubiquitin linkage profiles in three models of proteolytic stress suggest the etiology of Alzheimer disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 10457–10465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciechanover, A.; Stanhill, A. The complexity of recognition of ubiquitinated substrates by the 26S proteasome. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, J.; Sadis, S.; Haas, A.L.; Finley, D. A ubiquitin mutant with specific defects in DNA repair and multiubiquitination. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1995, 15, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtake, F.; Tsuchiya, H.; Saeki, Y.; Tanaka, K. K63 ubiquitylation triggers proteasomal degradation by seeding branched ubiquitin chains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1401–E1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, H.-J.; Rape, M. Enhanced protein degradation by branched ubiquitin chains. Cell 2014, 157, 910–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, R.G.; Doerner, K.; Castellanos, E.R.; Haakonsen, D.L.; Werner, A.; Wang, N.; Yang, X.W.; Martinez-Martin, N.; Matsumoto, M.L.; Dixit, V.M.; et al. Assembly and Function of Heterotypic Ubiquitin Chains in Cell-Cycle and Protein Quality Control. Cell 2017, 171, 918–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glickman, M.H.; Rubin, D.M.; Fried, V.A.; Finley, D. The regulatory particle of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae proteasome. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 3149–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, J.; Finley, D. A proteasome for all occasions. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 2854–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, R.; Aravind, L.; Oania, R.; McDonald, W.H.; Yates, J.R., 3rd; Koonin, E.V.; Deshaies, R.J. Role of Rpn11 metalloprotease in deubiquitination and degradation by the 26S proteasome. Science 2002, 298, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Li, P.; Song, L.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Chenova, T.A.; Wilkinson, K.D.; Cohen, R.E.; Shi, Y. Structure and mechanisms of the proteasome-associated deubiquitinating enzyme USP14. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 3747–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamazaki, J.; Iemura, S.; Natsume, T.; Yashiroda, H.; Tanaka, K.; Murata, S. A novel proteasome interacting protein recruits the deubiquitinating enzyme UCH37 to 26S proteasomes. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 4524–4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Song, L.; Xu, W.; DeMartino, G.N.; Florens, L.; Swanson, S.K.; Washburn, M.P.; Conaway, R.C.; Conaway, J.W.; Cohen, R.E. Proteasome recruitment and activation of the Uch37 deubiquitinating enzyme by Adrm1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, P.; Chen, X.; Husnjak, K.; Randles, L.; Zhang, N.; Elsasser, S.; Finley, D.; Dikic, I.; Walters, K.J.; Groll, M. Ubiquitin docking at the proteasome through a novel pleckstrin-homology domain interaction. Nature 2008, 453, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husnjak, K.; Elsasser, S.; Zhang, N.; Chen, X.; Randles, L.; Shi, Y.; Hofmann, K.; Walters, K.J.; Finley, D.; Dikic, I. Proteasome subunit Rpn13 is a novel ubiquitin receptor. Nature 2008, 453, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, B.C.; Glickman, M.; Kraft, R.; Dahlmann, B.; Kloetzel, P.M.; Finley, D.; Schmidt, M. The base of the proteasome regulatory particle exhibits chaperone-like activity. Nat. Cell Biol. 1999, 1, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strickland, E.; Hakala, K.; Thomas, P.J.; DeMartino, G.N. Recognition of misfolding proteins by PA700, the regulatory subcomplex of the 26 S proteasome. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 5565–5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Kasahara, M. The MHC class I ligand-generating system: Roles of immunoproteasomes and the interferon-gamma-inducible proteasome activator PA28. Immunol. Rev. 1998, 163, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strehl, B.; Seifert, U.; Kruger, E.; Heink, S.; Kuckelkorn, U.; Kloetzel, P.M. Interferon-gamma, the functional plasticity of the ubiquitin-proteasome system, and MHC class I antigen processing. Immunol. Rev. 2005, 207, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unno, M.; Mizushima, T.; Morimoto, Y.; Tomisugi, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Yasuoka, N.; Tsukihara, T. The structure of the mammalian 20S proteasome at 2.75 A resolution. Structure 2002, 10, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisselev, A.F.; Akopian, T.N.; Woo, K.M.; Goldberg, A.L. The sizes of peptides generated from protein by mammalian 26 and 20 S proteasomes. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 3363–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astakhova, T.M.; Bozhok, G.A.; Alabedal’karim, N.M.; Karpova, Y.D.; Lyupina, Y.V.; Ushakova, E.M.; Legach, E.I.; Bondarenko, T.P.; Sharova, N.P. Proteasome expression in ovarian heterotopic allografts of Wistar and August rats under induction of donor specific tolerance. Russ. J. Dev. Biol. 2019, 50, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spirina, L.V.; Yunusova, N.V.; Kondakova, I.V. Association of growth factors, HIF-1 and NF-kappa B expression with proteasomes in endometrial cancer. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 8655–8662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldin, J.; O’Callaghan, P.; Hernández Vera, R.; Fuchs, P.F.; Gerwins, P.; Kreuger, J. FGD5 sustains vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) signaling through inhibition of proteasome-mediated VEGF receptor 2 degradation. Cell Signal. 2017, 40, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Slingerland, J.M. Links between oestrogen receptor activation and proteolysis: Relevance to hormone-regulated cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, M.; Susa, T.; Tamamori Adachi, M.; Okinaga, H.; Okazaki, T. Intrinsic ubiquitin E3 ligase activity of histone acetyltransferase Hbo1 for estrogen receptor α. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B. Phys. Biol. Sci. 2017, 93, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helzer, K.T.; Hooper, C.; Miyamoto, S.; Alarid, E.T. Ubiquitylation of nuclear receptors: New linkages and therapeutic implications. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 54, R151–R167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, M.; Park, A.; Nephew, K.P. CHIP (carboxyl terminus of Hsc70-interacting protein) promotes basal and geldanamycin-induced degradation of estrogen receptor-alpha. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 19, 2901–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, V.; Boulle, N.; Daujat, S.; Chauvet, J.; Bonnet, S.; Neel, H.; Cavaillès, V. Differential regulation of estrogen receptor alpha turnover and transactivation by Mdm2 and stress-inducing agents. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 5513–5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, M.; Picard, N.; Sauvé, K.; Tremblay, A. Coordinate regulation of estrogen receptor β degradation by Mdm2 and CREB-binding protein in response to growth signals. Oncogene 2013, 32, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajbhandari, P.; Schalper, K.A.; Solodin, N.M.; Ellison-Zelski, S.J.; Ping Lu, K.; Rimm, D.L.; Alarid, E.T. Pin1 modulates ERα levels in breast cancer through inhibition of phosphorylation-dependent ubiquitination and degradation. Oncogene 2014, 33, 1438–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhou, W.; Kaliappan, K.; Nawaz, Z.; Slingerland, J.M. ERα phosphorylation at Y537 by Src triggers E6-AP-ERα binding, ERα ubiquitylation, promoter occupancy, and target gene expression. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 26, 1567–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, S.; Xiao, Z.; Meng, Z.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S. Phosphorylation by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase promotes estrogen receptor α turnover and functional activity via the SCF (Skp2) proteasomal complex. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 1928–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, G.L.; Ellison-Zelski, S.J.; Casa, A.J.; Lee, A.V.; Alarid, E.T. Proteasome inhibition represses ERα gene expression in ER+ cells—A new link between proteasome activity and estrogen signaling in breast cancer. Oncogene 2010, 29, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amita, M.; Takahashi, T.; Igarashi, H.; Nagase, S. Clomiphene citrate down-regulates estrogenreceptor-α through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in a human endometrial cancer cell line. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 428, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Sharma, V.; Verma, V.; Pandey, D.; Yadav, S.K.; Maikhuri, J.P.; Gupta, G. Apigenin manipulates the ubiquitin-proteasome system to rescue estrogen receptor-β from degradation and induce apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Eur. J. Nutr. 2015, 54, 1255–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijayaratne, A.L.; McDonnell, D.P. The human estrogen receptor alpha is a ubiquitinated protein whose stability is affected differentially by agonists, antagonists, and selective estrogen receptor modulators. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 35684–35692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohoka, N.; Morita, Y.; Nagai, K.; Shimokawa, K.; Ujikawa, O.; Fujimori, I.; Ito, M.; Hayase, Y.; Okuhira, K.; Shibata, N.; et al. Derivatization of inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP) ligands yields improved inducers of estrogen receptor α degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 6776–6790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Liao, Y.; Huang, C.; Liu, Y.; He, J.; Shao, Z.; Jiang, L.; Dou, Q.P.; Liu, J.; Huang, H. Deubiquitination and stabilization of estrogen receptor α by ubiquitin-specific protease 7 promotes breast tumorigenesis. Cancer Lett. 2019, 465, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kos, M.; Reid, G.; Denger, S.; Gannon, F. Minireview: Genomic organization of the human ERalpha gene promoter region. Mol. Endocrinol. 2001, 15, 2057–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, G.L.; Rajbhandari, P.; Solodin, N.M.; Bickford, B.; Alarid, E.T. The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib induces an inhibitory chromatin environment at a distal enhancer of the estrogen receptor-α gene. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, L.; Liang, J.; Yu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, R.; Sun, X.; Shang, Y. The catalytic subunit of the proteasome is engaged in the entire process of estrogen receptor-regulated transcription. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 4223–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prenzel, T.; Begus-Nahrmann, Y.; Kramer, F.; Hennion, M.; Hsu, C.; Gorsler, T.; Hintermair, C.; Eick, D.; Kremmer, E.; Simons, M.; et al. Estrogen-dependent gene transcription in human breast cancer cells relies upon proteasome-dependent monoubiquitination of histone H2B. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 5739–5753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.B.; Quinn, J.A.; Graeber, C.T.; Filardo, E.J. Down-modulation of the G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor, GPER, from the cell surface occurs via a trans-Golgi-proteasome pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 22441–22455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portbury, A.L.; Ronnebaum, S.M.; Zungu, M.; Patterson, C.; Willis, M.S. Back to your heart: Ubiquitin proteasome system-regulated signal transduction. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2012, 52, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heino, T.J.; Chagin, A.S.; Sävendahl, L. The novel estrogen receptor G-protein-coupled receptor 30 is expressed in human bone. J. Endocrinol. 2008, 197, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shashova, E.E.; Lyupina, Y.V.; Glushchenko, S.A.; Slonimskaya, E.M.; Savenkova, O.V.; Kulikov, A.M.; Gornostaev, N.G.; Kondakova, I.V.; Sharova, N.P. Proteasome functioning in breast cancer: Connection with clinical-pathological factors. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassin, W. Zu den Grenzen menschlicher Erkenntnis. Beacon J. Stud. Ideol. Ment. Dimens. 2018, 1, 010310202. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net//20.500.12656/thebeacon.1.010310202 (accessed on 1 December 2019).
- Nagpal, N.; Ahmad, H.M.; Molparia, B.; Kulshreshtha, R. MicroRNA-191, an estrogen responsive microRNA, functions as an oncogenic regulator in human breast cancer. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 1889–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leva, G.; Piovan, C.; Gasparini, P.; Ngankeu, A.; Taccioli, C.; Briskin, D.; Cheung, D.G.; Bolon, B.; Anderlucci, L.; Alder, H.; et al. Estrogen mediated-activation of miR-191/425 cluster modulates tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells depending on estrogen receptor status. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aue, G.; Du, Y.; Cleveland, S.M.; Smith, S.B.; Dave, U.P.; Liu, D.; Weniger, M.A.; Metais, J.Y.; Jenkins, N.A.; Copeland, N.G.; et al. Sox4 cooperates with PU.1 haploinsufficiency in murine myeloid leukemia. Blood 2011, 118, 4674–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.W.; Wang, P.; Liu, J.Q.; Zhang, H.; Xi, W.D.; Jia, X.H.; Wang, K.K. Coordinated regulation of the immunoproteasome subunits by PML/RARα and PU.1 in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Oncogene 2014, 33, 2700–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astakhova, T.M.; Morozov, A.V.; Erokhov, P.A.; Mikhailovskaya, M.I.; Akopov, S.B.; Chupikova, N.I.; Safarov, R.R.; Sharova, N.P. Combined Effect of Bortezomib and Menadione Sodium Bisulfite on Proteasomes of Tumor Cells: The Dramatic Decrease of Bortezomib Toxicity in a Preclinical Trial. Cancers 2018, 10, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donskikh, O.A. Horror Zivilisationis, oder Horror der Subjektivität. Beacon J. Stud. Ideol. Ment. Dimens. 2019, 2, 020110205. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net//20.500.12656/thebeacon.2.020110205 (accessed on 23 January 2020).
- Thaler, S.; Thiede, G.; Hengstler, J.G.; Schad, A.; Schmidt, M.; Sleeman, J.P. The proteasome inhibitor Bortezomib (Velcade) as potential inhibitor of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 686–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, F.; Liang, Y.; Bi, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, F.; Cui, Y.; Jiang, J. REGγ regulates ERα degradation via ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in breast cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 456, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shashova, E.E.; Astakhova, T.M.; Plekhanova, A.S.; Bogomyagkova, Y.V.; Lyupina, Y.V.; Sumedi, I.R.; Slonimskaya, E.M.; Erokhov, P.A.; Abramova, E.B.; Rodoman, G.V.; et al. Changes in proteasome chymotrypsin-like activity during the development of human mammary and thyroid carcinomas. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2013, 156, 242–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondakova, I.V.; Spirina, L.V.; Shashova, E.E.; Koval, V.D.; Kolomiets, L.A.; Chernyshova, A.L.; Slonimskaya, E.M. Proteasome activity in tumors of the female reproductive system. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2012, 38, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondakova, I.V.; Spirina, L.V.; Koval, V.D.; Shashova, E.E.; Choinzonov, E.L.; Ivanova, E.V.; Kolomiets, L.A.; Chernyshova, A.L.; Slonimskaya, E.M.; Usynin, E.A.; et al. Chymotrypsin-like activity and subunit composition of proteasomes in human cancers. Mol. Biol. 2014, 48, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynadier, M.; Basile, I.; Gallud, A.; Gary-Bobo, M.; Garcia, M. Combination treatment with proteasome inhibitors and antiestrogens has a synergistic effect mediated by p21WAF1 in estrogenreceptor-positive breast cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Liao, Y.; Guo, Z.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, F.; Huang, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, N.; et al. Targeting proteasome-associated deubiquitinases as a novel strategy for the treatment of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Oncogenesis 2018, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kondakova, I.V.; Shashova, E.E.; Sidenko, E.A.; Astakhova, T.M.; Zakharova, L.A.; Sharova, N.P. Estrogen Receptors and Ubiquitin Proteasome System: Mutual Regulation. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040500
Kondakova IV, Shashova EE, Sidenko EA, Astakhova TM, Zakharova LA, Sharova NP. Estrogen Receptors and Ubiquitin Proteasome System: Mutual Regulation. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(4):500. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040500
Chicago/Turabian StyleKondakova, Irina V., Elena E. Shashova, Evgenia A. Sidenko, Tatiana M. Astakhova, Liudmila A. Zakharova, and Natalia P. Sharova. 2020. "Estrogen Receptors and Ubiquitin Proteasome System: Mutual Regulation" Biomolecules 10, no. 4: 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040500
APA StyleKondakova, I. V., Shashova, E. E., Sidenko, E. A., Astakhova, T. M., Zakharova, L. A., & Sharova, N. P. (2020). Estrogen Receptors and Ubiquitin Proteasome System: Mutual Regulation. Biomolecules, 10(4), 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040500




