A Computational Study on Renal Artery Anatomy in Patients Treated with Fenestrated or Branched Endovascular Aneurysm Repair
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
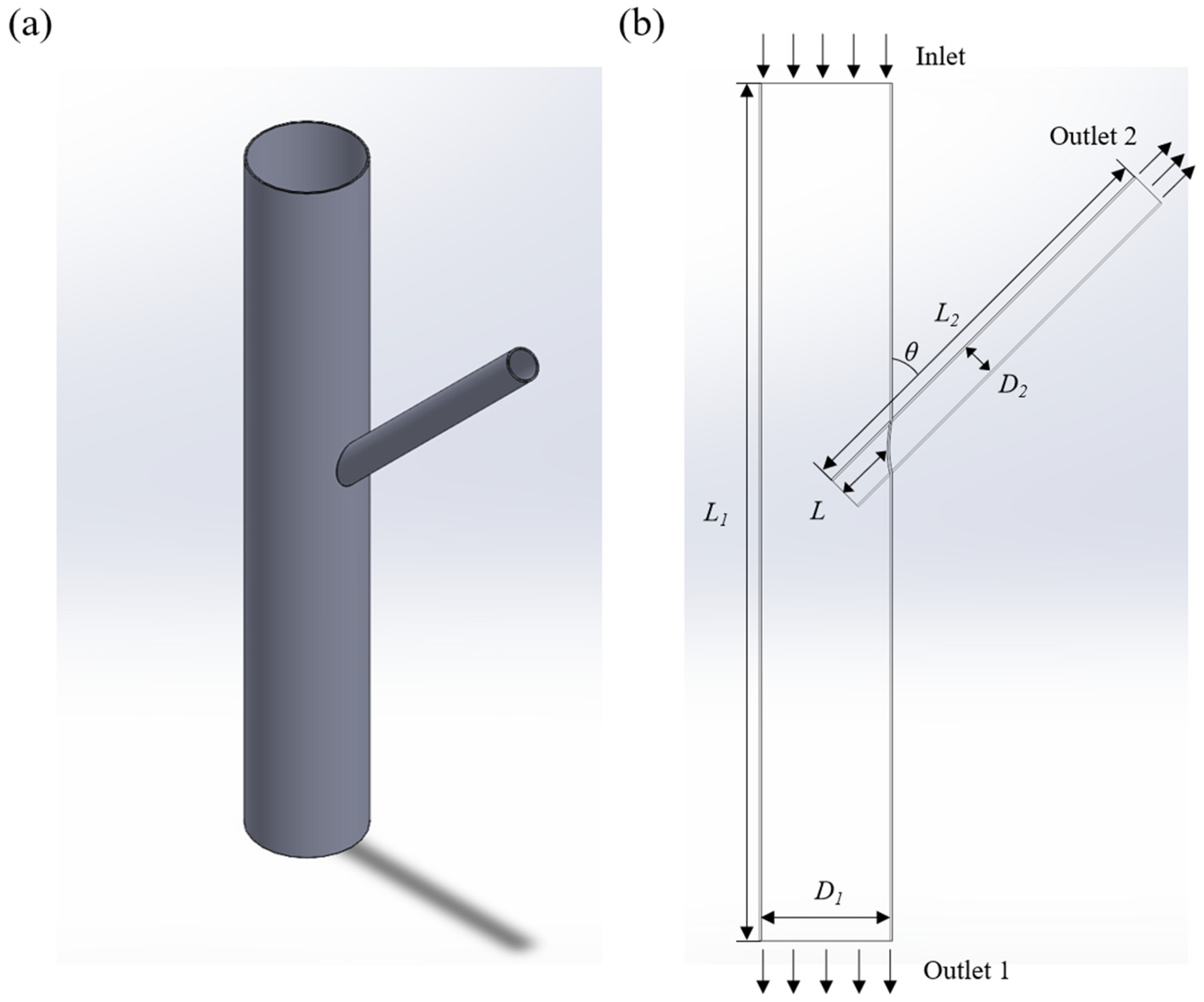
2.1. Scene Setting and Model Building
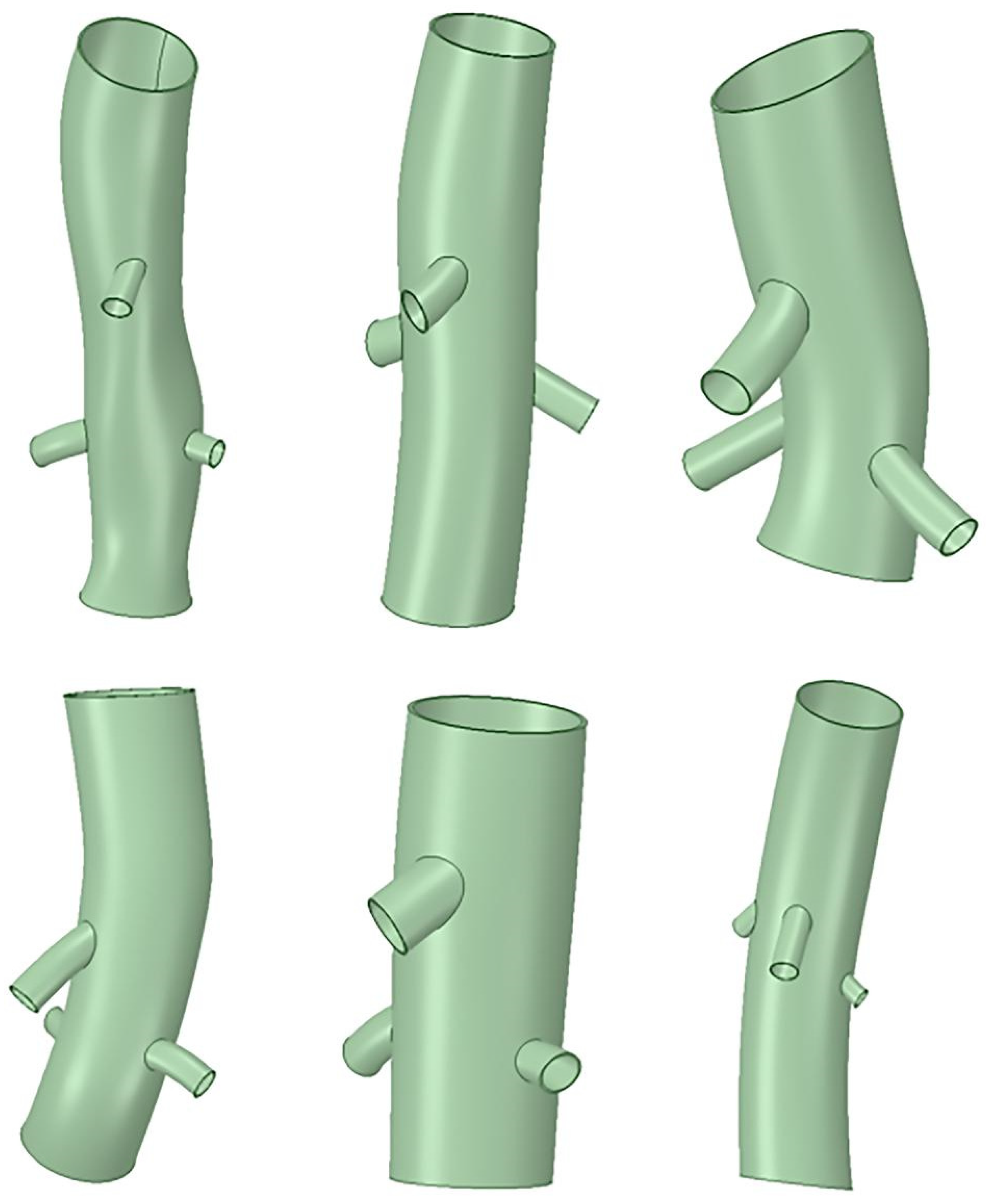
2.2. Clinical Case Selection
2.3. Case Modeling and Analysis
2.4. Boundary Condition Setting
2.5. Numerical Calculation and Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Theoretical Model Simulation Results
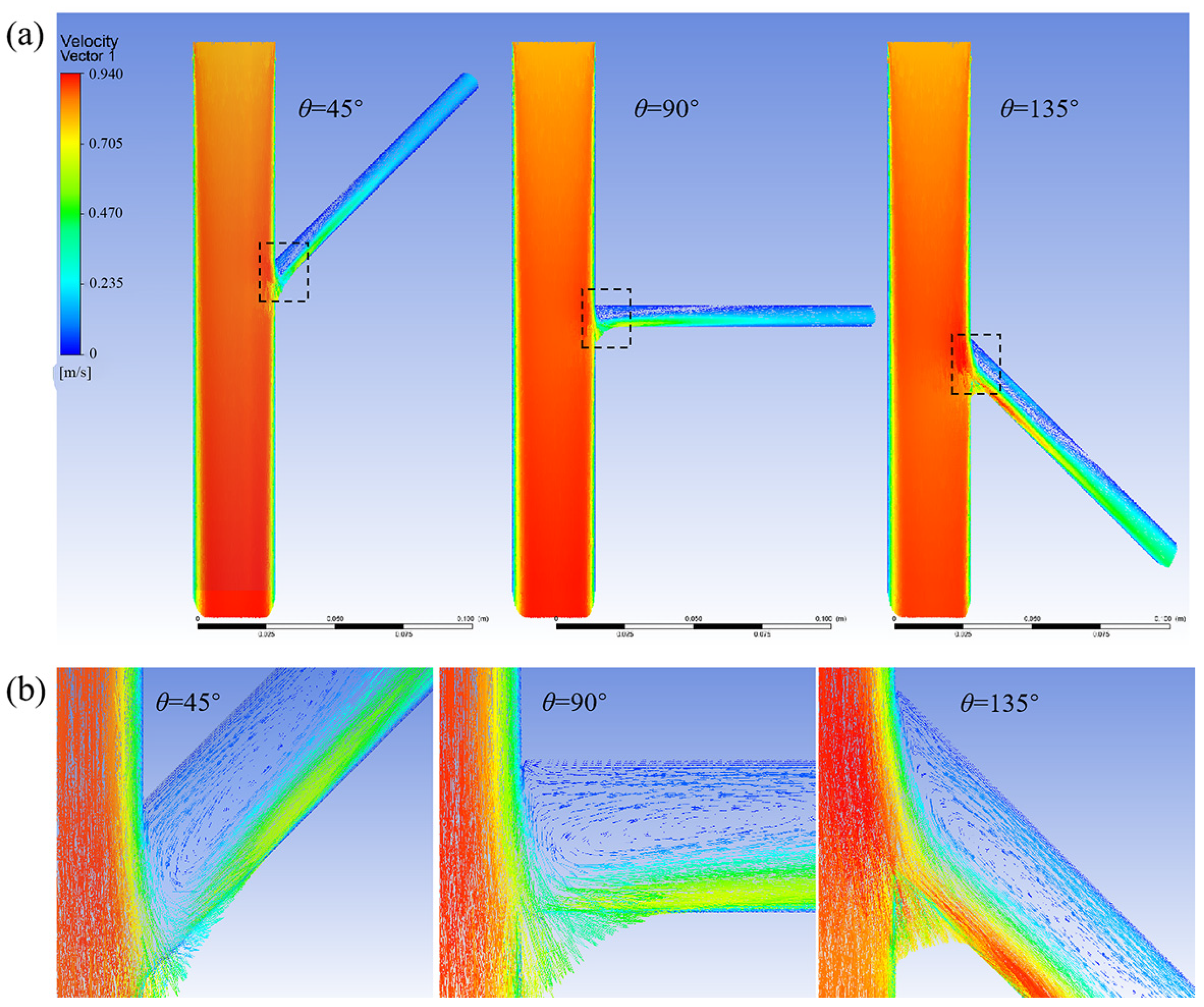
3.1.1. Without the Branch Stent
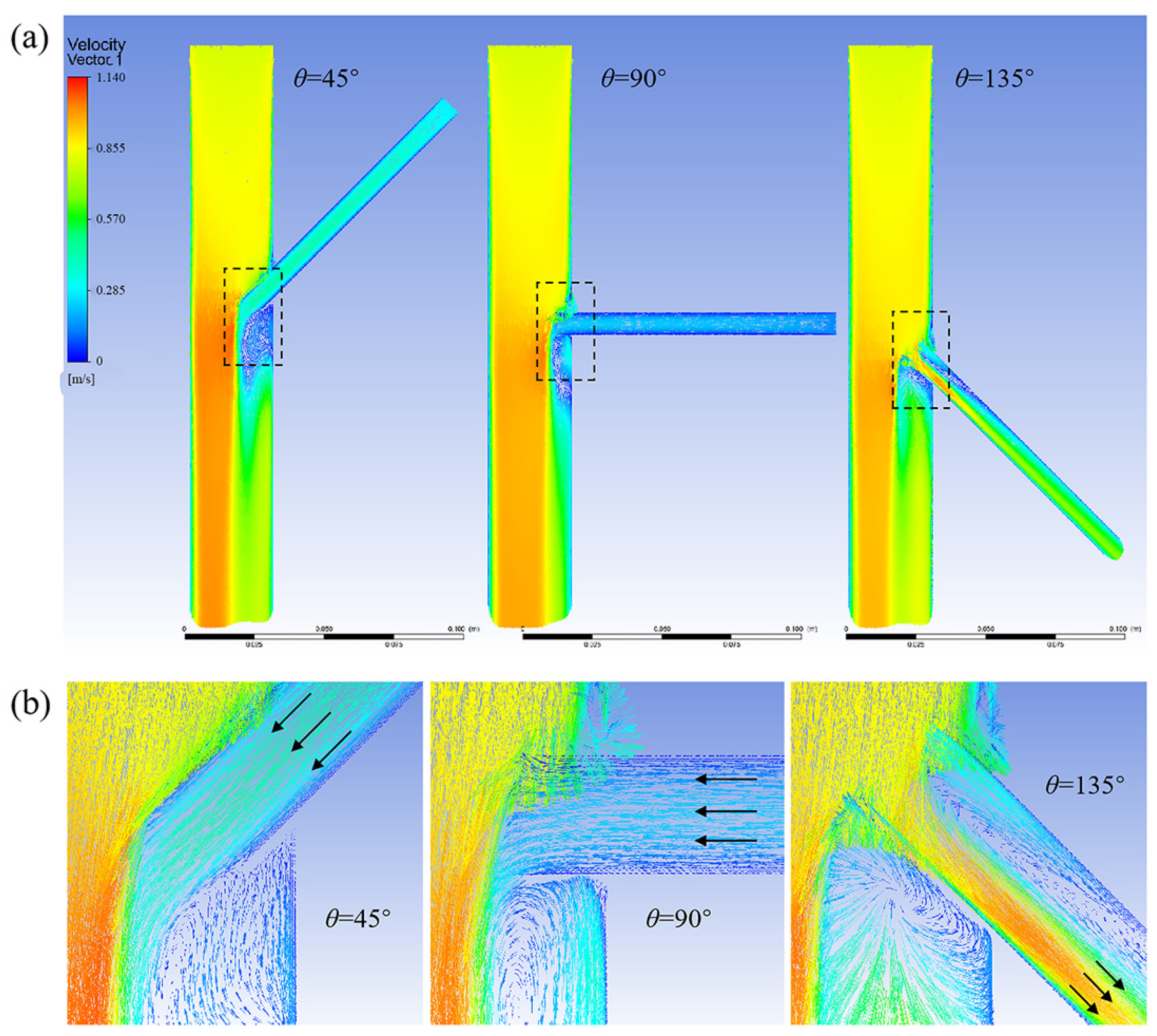
3.1.2. Effect of Different Tilt Angles and Branch Entry Depths on Blood Flow in Branch Arteries
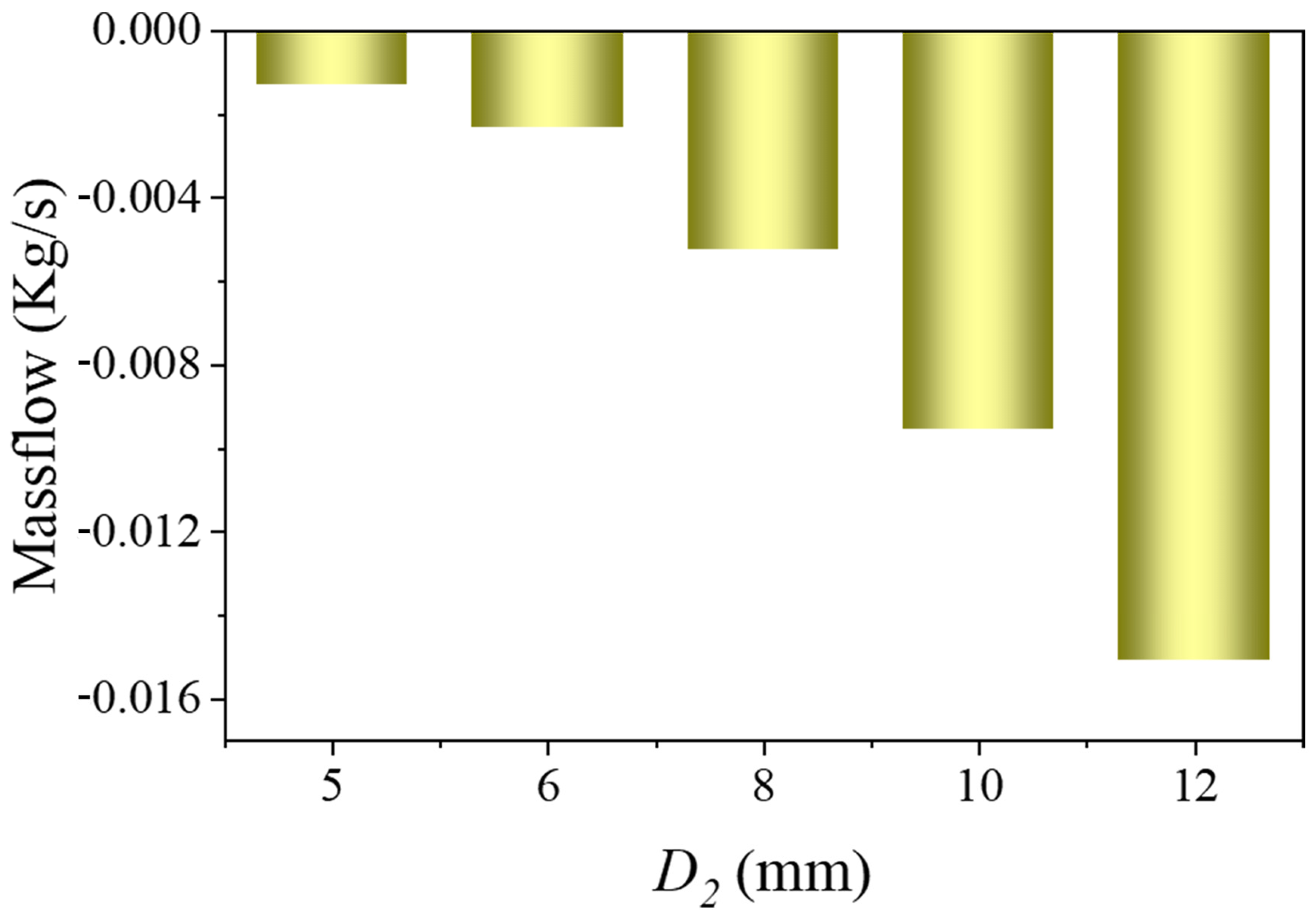
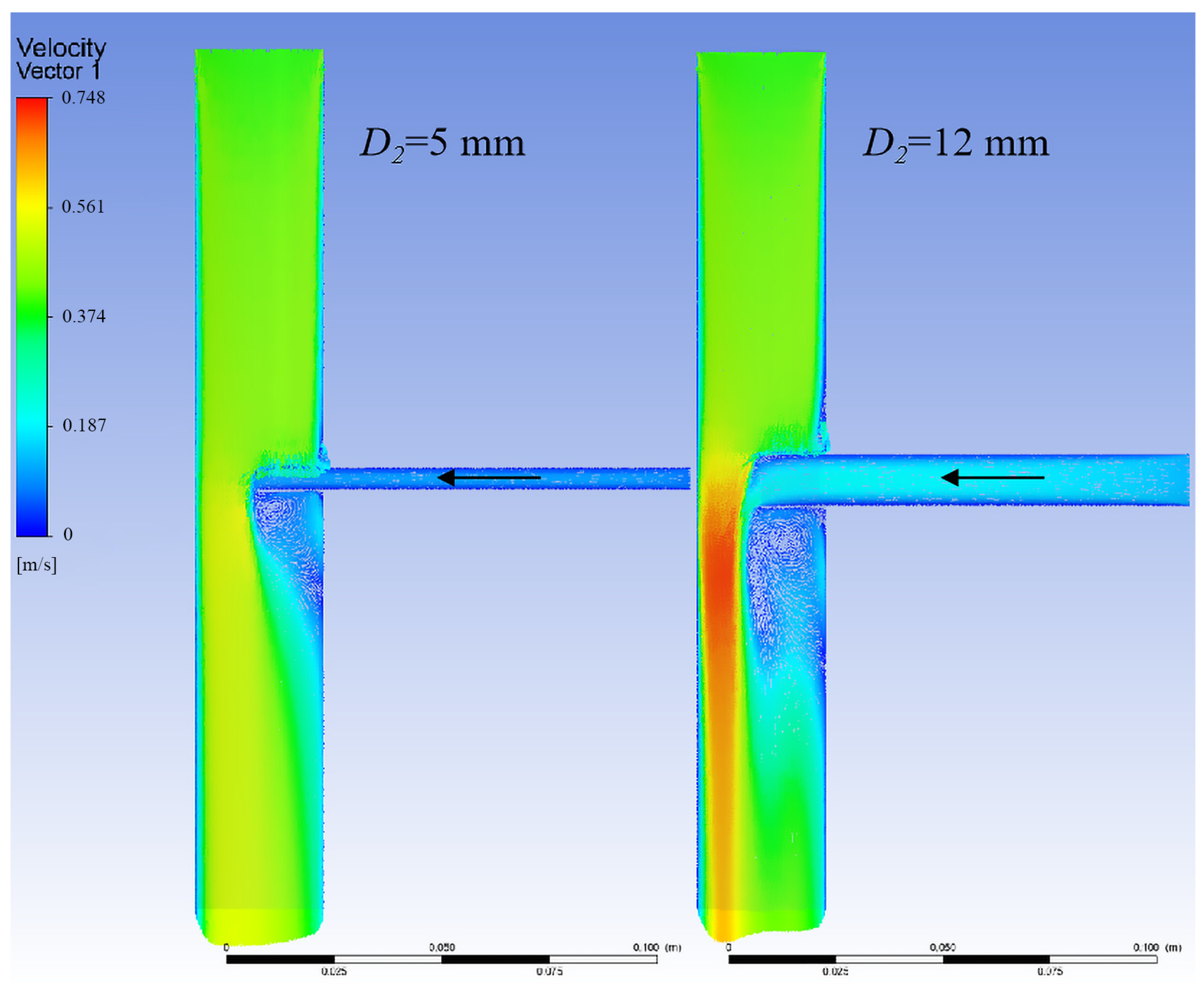
3.1.3. Relationship Between Branch Flow and Branch Stent Diameter
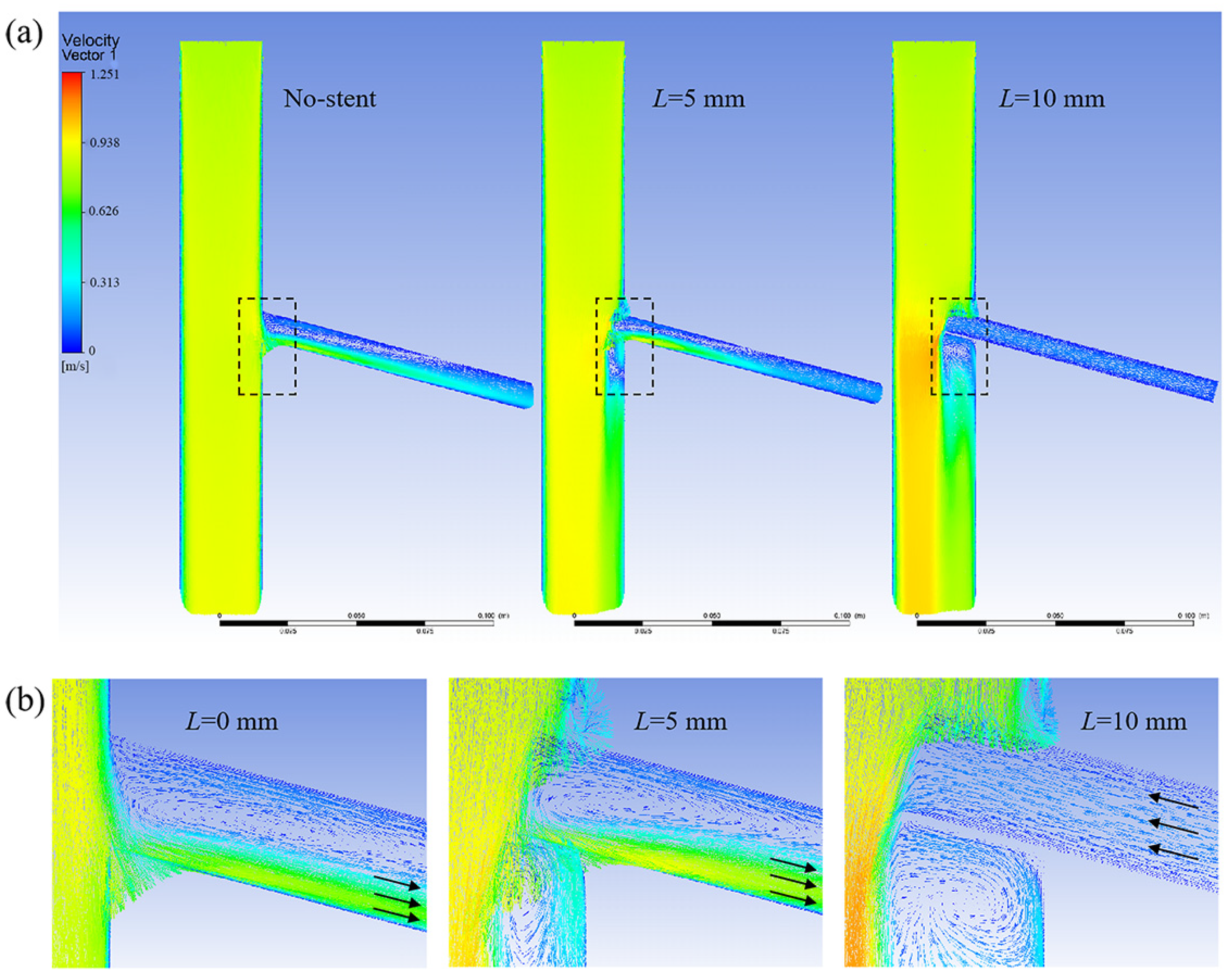
3.1.4. Optimal Design of the Branch Stent
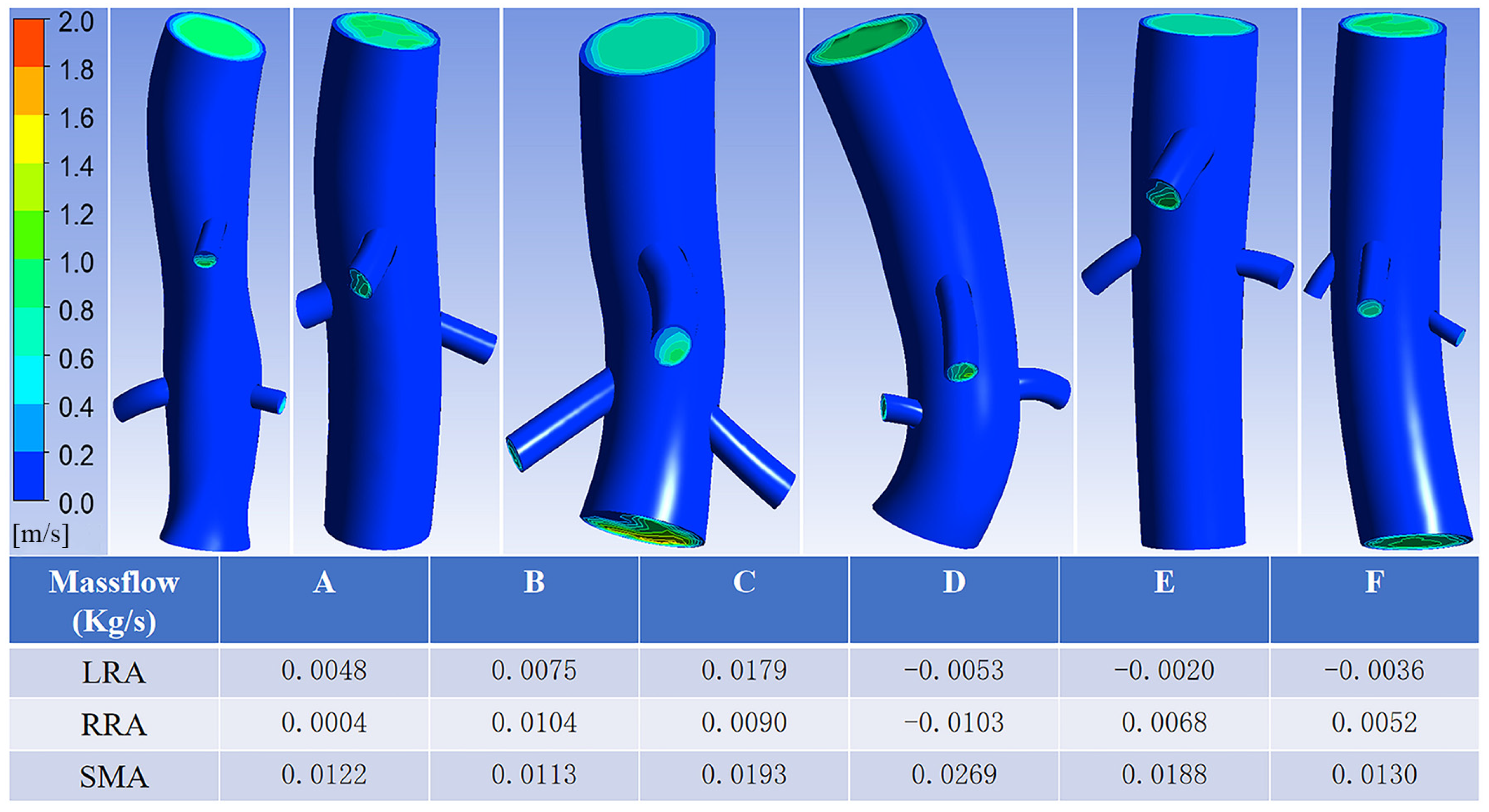
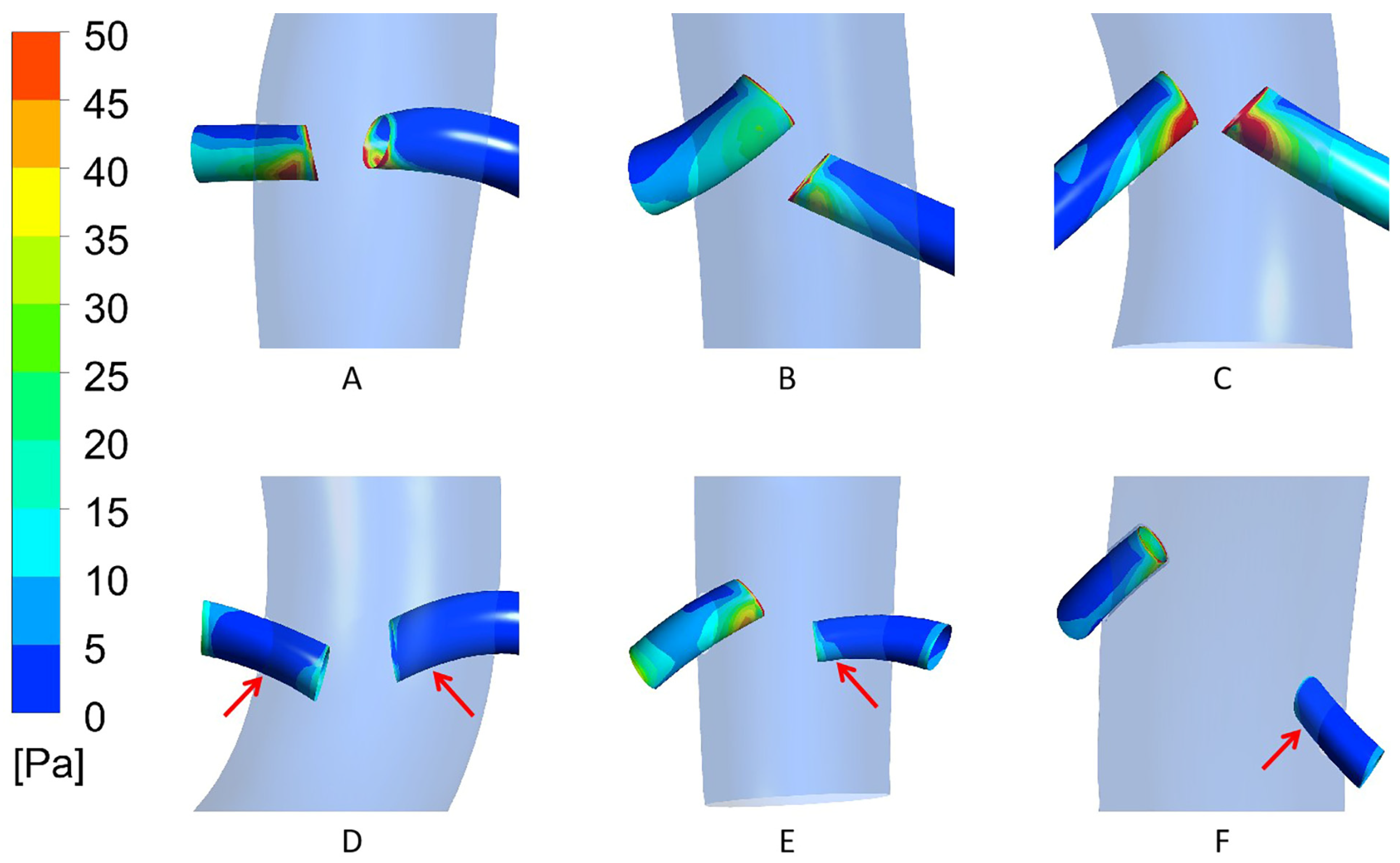
3.2. Case Model Simulation Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parodi, J.C.; Palmaz, J.C.; Barone, H.D. Transfemoral Intraluminal Graft Implantation for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 1991, 5, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, T.F.; Hartley, D.; Purchas, S.; Rosenberg, M.; Van Schie, G.; Lawrence-Brown, M. A Fenestrated Covered Suprarenal Aortic Stent. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 1999, 18, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etheredge, S.; Yee, J.; Smith, J.; Schonberger, S.; Goldman, M. Successful Resection of a Large Aneurysm of the Upper Abdominal Aorta and Replacement with Homograft. Surgery 1955, 38, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar]
- Coselli, J.S.; Amarasekara, H.S.; Green, S.Y.; Price, M.D.; Preventza, O.; de la Cruz, K.I.; Zhang, Q.; LeMaire, S.A. Open Repair of Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysm in Patients 50 Years Old and Younger. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 103, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlberg, A.; Ferrante, A.M.; Miloro, R.; Mascia, D.; Bertoglio, L.; Baccellieri, D.; Melissano, G.; Chiesa, R. Late Patency of Reconstructed Visceral Arteries After Open Repair of Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysm. J. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 67, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, R.B.; Mehaffey, J.H.; Narahari, A.K.; Jain, A.; Ghanta, R.K.; Kron, I.L.; Kern, J.A.; Upchurch, G.R. Improved Outcomes and Value in Staged Hybrid Extent II Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2017, 66, 1357–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, D.; Jordan, W.D., Jr. Hybrid Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair: Current Perspectives. Semin. Vasc. Surg. 2012, 25, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasirajan, K. Branched Grafts for Thoracoabdominal Aneurysms: Off-Label Use of FDA-Approved Devices. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2011, 18, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangialardi, N.; Ronchey, S.; Malaj, A.; Fazzini, S.; Alberti, V.; Ardita, V.; Orrico, M.; Lachat, M. Value and Limitations of Chimney Grafts to Treat Arch Lesions. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015, 56, 503–511. [Google Scholar]
- Kanaoka, Y.; Ohki, T.; Maeda, K.; Baba, T. Analysis of Risk Factors for Early Type I Endoleaks After Thoracic Endovascular Aneurysm Repair. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2017, 24, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usai, M.V.; Torsello, G.; Donas, K.P. Current Evidence Regarding Chimney Graft Occlusions in the Endovascular Treatment of Pararenal Aortic Pathologies: A Systematic Review with Pooled Data Analysis. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2015, 22, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, E.L.; Katsargyris, A.; Bekkema, F.; Oikonomou, K.; Zeebregts, C.; Ritter, W.; Tielliu, I. Editor’s Choice—Ten-Year Experience with Endovascular Repair of Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysms: Results from 166 Consecutive Patients. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2015, 49, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeMaire, S.A.; Price, M.D.; Green, S.Y.; Zarda, S.; Coselli, J.S. Results of Open Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2012, 1, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossabhoy, S.S.; Simons, J.P.; Diamond, K.R.; Flahive, J.M.; Aiello, F.A.; Arous, E.J.; Messina, L.M.; Schanzer, A. Reinterventions After Fenestrated or Branched Endovascular Aortic Aneurysm Repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 68, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, H.M.; Lee, K.-H.; Liao, Y.-C.; Cheng, Y.-C. Hemodynamic Simulation of Intra-Stent Blood Flow. Procedia Eng. 2012, 36, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Yu, Y.; Chen, R.; Liu, X.; Hu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Gao, L.; Jian, W.; Wang, L. Wall Shear Stress and Its Role in Atherosclerosis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1083547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, P.; Shenoy, B.G.; Khader, S.M.A.; Pai, B.R.; Rao, D.S.; Tamagawa, M.; Prabhu, R.; Kumar, N.; Ahmad, K.A. CFD Analysis on Effect of Angulation in a Healthy Abdominal Aorta-Renal Artery Junction. J. Adv. Res. Fluid Mech. Therm. Sci. 2021, 88, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Tang, A.Y.S.; Chiu, T.L.; Chow, K.W.; Chan, Y.C.; Cheng, S.W.K. Haemodynamic Variations of Flow to Renal Arteries in Custom-Made and Pivot Branch Fenestrated Endografting. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2017, 53, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmonik, C.; Diaz, O.; Klucznik, R.; Grossman, R.G.; Zhang, Y.J.; Britz, G.; Lv, N.; Huang, Q. Quantitative Comparison of Hemodynamic Parameters from Steady and Transient CFD Simulations in Cerebral Aneurysms with Focus on the Aneurysm Ostium. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2015, 7, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiastra, C.; Migliavacca, F.; Martínez, M.Á.; Malvè, M. On the Necessity of Modelling Fluid-Structure Interaction for Stented Coronary Arteries. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 34, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockle, J.; Romero, D.A.; Amon, C.H. Optimization of Porous Stents for Endovascular Repair of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Int. J. Numer. Method Biomed. Eng. 2020, 36, e3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, K.; Yang, W.; Marsden, A.; Lee, J.T. Patient-Specific Computational Flow Modelling for Assessing Hemodynamic Changes Following Fenestrated Endovascular Aneurysm Repair. J. Vasc. Sci. 2021, 2, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suess, T.; Anderson, J.; Danielson, L.; Pohlson, K.; Remund, T.; Blears, E.; Gent, S.; Kelly, P. Examination of Near-Wall Hemodynamic Parameters in the Renal Bridging Stent of Various Stent Graft Configurations for Repairing Visceral Branched Aortic Aneurysms. J. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 64, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Looyenga, E.M.; Gent, S.P. Examination of Fluid-Structure Interaction in Stent Grafts and Its Hemodynamic Implications. In Proceedings of the 2018 Design of Medical Devices Conference, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 9–12 April 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Mirsadraee, S.; Rosendahl, U.; Pepper, J.; Xu, X.Y. Fluid-Structure Interaction Simulations of Repaired Type A Aortic Dissection: A Comprehensive Comparison with Rigid Wall Models. Front. Phys. 2022, 13, 913457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Patient | Patient A | Patient B | Patient C | Patient D | Patient E | Patient F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Renal artery | Patent | Patent | Patent | Bilateral occlusion | Left occlusion | Left occlusion |
| Blood pressure | 70/138 mmHg | 72/130 mmHg | 74/133 mmHg | 63/138 mmHg | 71/141 mmHg | 70/135 mmHg |
| Erythrocyte value | 4.66 × 1012/L | 6.24 × 1012/L | 4.34 × 1012/L | 4.56 × 1012/L | 4.44 × 1012/L | 4.51 × 1012/L |
| Leukocyte value | 5.6 × 109/L | 5.4 × 109/L | 5.2 × 109/L | 5.1 × 109/L | 7.5 × 109/L | 4.9 × 109/L |
| Platelet value | 103 × 109/L | 140 × 109/L | 237 × 109/L | 156 × 109/L | 171 × 109/L | 224 × 109/L |
| Triglyceride value | 1.66 mmol/L | 0.98 mmol/L | 0.68 mmol/L | 0.83 mmol/L | 1.27 mmol/L | 0.88 mmol/L |
| Total cholesterol | 3.82 mmol/L | 4.03 mmol/L | 4.40 mmol/L | 3.77 mmol/L | 3.64 mmol/L | 4.62 mmol/L |
| Patient Conditions | Patient A | Patient B | Patient C | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LRA | RRA | LRA | RRA | LRA | RRA | |
| Tilt Angle | 103.5° | 105.6° | 131.8° | 126.7° | 139.8° | 106.7° |
| Entry Depth | 5.04 mm | 10.06 mm | 8.59 mm | 7.88 mm | 9.55 mm | 6.16 mm |
| Branch Diameter | 5.21 mm | 5.10 mm | 4.95 mm | 5.72 mm | 5.50 mm | 5.50 mm |
| Aortic Diameter | 23.21 mm | 19.14 mm | 21.77 mm | |||
| Patient Conditions | Patient D | Patient E | Patient F | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LRA | RRA | LRA | RRA | LRA | RRA | |
| Tilt Angle | 81.1° | 77.5° | 91.9° | 118.8° | 80.5° | 127.1° |
| Entry Depth | 6.34 mm | 10.13 mm | 6.75 mm | 4.59 mm | 5.67 mm | 4.80 mm |
| Branch Diameter | 5.80 mm | 5.47 mm | 3.88 mm | 3.67 mm | 3.92 mm | 4.20 mm |
| Aortic Diameter | 34.93 mm | 18.06 mm | 21.88 mm | |||
| High Mass Flow (n = 6) | Low Mass Flow (n = 6) | Cohen’s d | 95%CI | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tilt Angle (°) | 126.9 (115.8, 133.8) | 86.5 (79.8, 104.0) | 1.32 | 0.89–1.75 | 0.004 |
| Entry Depth (mm) | 7.02 (4.75, 8.83) | 6.55 (5.51, 10.03) | 0.18 | −0.35–0.71 | 0.522 |
| Branch Diameter (mm) | 5.23 (4.07, 5.56) | 5.16 (3.91, 5.56) | 0.05 | −0.48–0.58 | 0.873 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Sang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, Y.; He, X.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Liu, Z. A Computational Study on Renal Artery Anatomy in Patients Treated with Fenestrated or Branched Endovascular Aneurysm Repair. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050482
Wang Y, Sang Y, Li W, Zhou M, Zhao Y, He X, Wang C, Li X, Liu Z. A Computational Study on Renal Artery Anatomy in Patients Treated with Fenestrated or Branched Endovascular Aneurysm Repair. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(5):482. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050482
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yuzhu, Yuna Sang, Wendong Li, Minjie Zhou, Yushun Zhao, Xiaodong He, Chao Wang, Xiaoqiang Li, and Zhao Liu. 2025. "A Computational Study on Renal Artery Anatomy in Patients Treated with Fenestrated or Branched Endovascular Aneurysm Repair" Bioengineering 12, no. 5: 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050482
APA StyleWang, Y., Sang, Y., Li, W., Zhou, M., Zhao, Y., He, X., Wang, C., Li, X., & Liu, Z. (2025). A Computational Study on Renal Artery Anatomy in Patients Treated with Fenestrated or Branched Endovascular Aneurysm Repair. Bioengineering, 12(5), 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050482






