Decellularization of Human Digits: A Step Towards Off-the-Shelf Composite Allograft Transplantation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Digit Procurement
2.2. Perfusion Decellularization
2.3. Digit X-Ray with Contrast
2.4. DNA Quantification Assay
2.5. Biochemical Assays for Quantification of ECM Components
2.5.1. Collagen Assay
2.5.2. Glycosaminoglycan (GAG) Assay
2.5.3. Elastin Assay
2.5.4. Histology
2.5.5. Mechanical Testing of Tendons
2.5.6. Dynamics Function
2.5.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
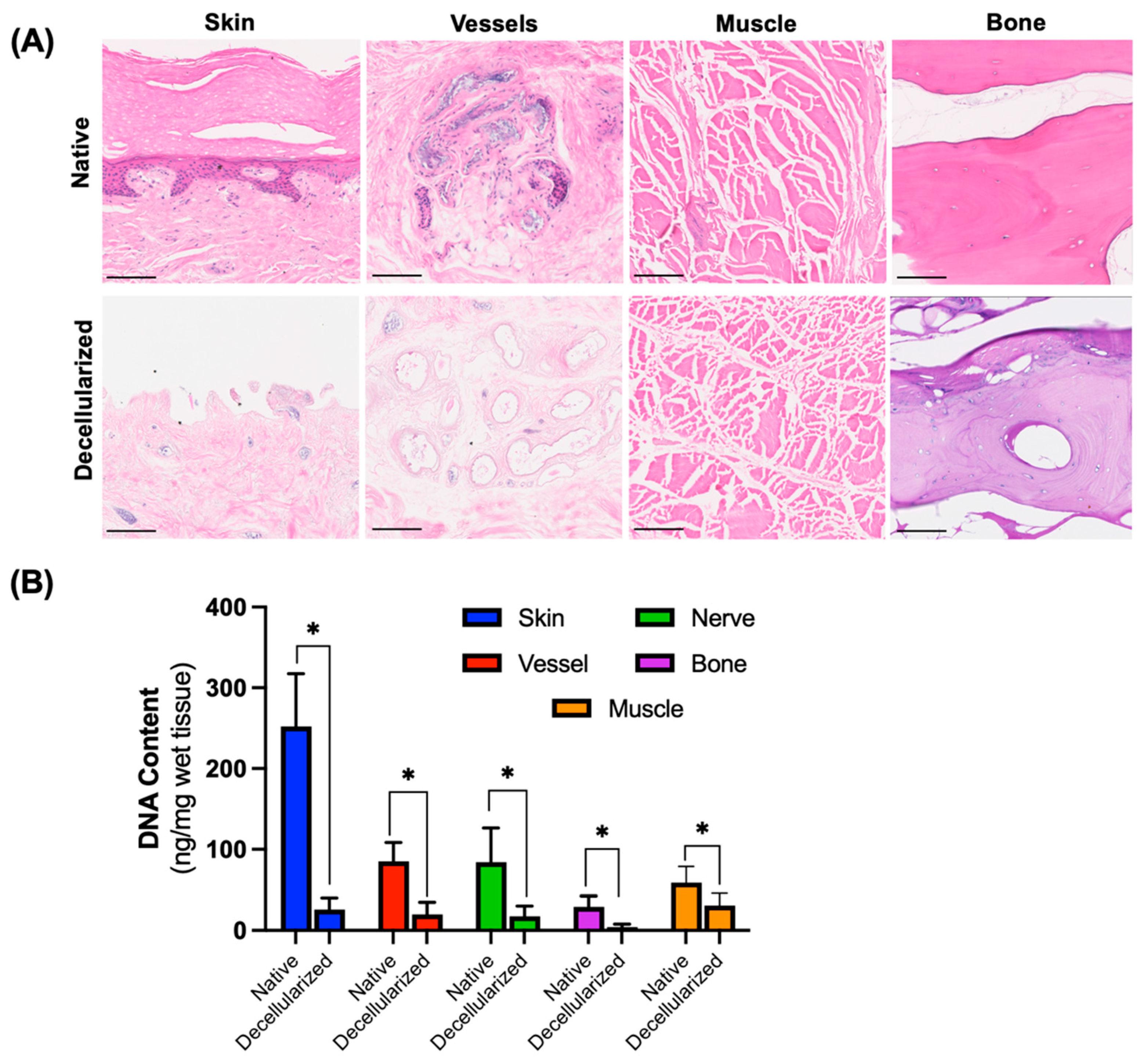
3.1. Removal of Cells from Digits After Decellularization
3.2. Preservation of Extracellular Matrix Components
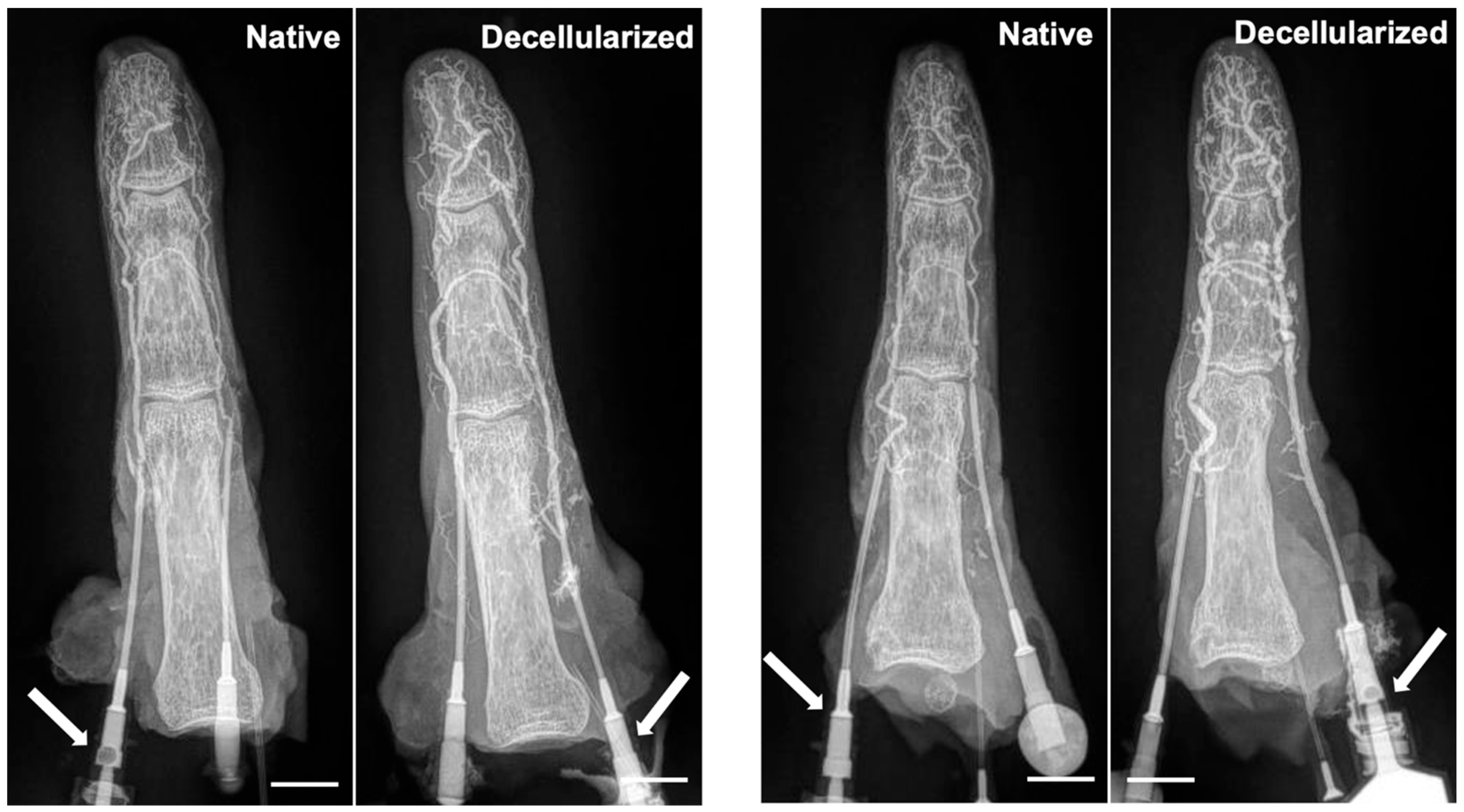
3.3. Maintenance of Vascular Network
3.4. Mechanical Testing of Tendons
3.5. Dynamic Function
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crowe, C.S.; Massenburg, B.B.; Morrison, S.D.; Chang, J.; Friedrich, J.B.; Abady, G.G.; Alahdab, F.; Alipour, V.; Arabloo, J.; Asaad, M.; et al. Global trends of hand and wrist trauma: A systematic analysis of fracture and digit amputation using the Global Burden of Disease 2017 Study. Inj. Prev. 2020, 26, i115–i124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giwa, S.; Lewis, J.K.; Alvarez, L.; Langer, R.; Roth, A.E.; Church, G.M.; Markmann, J.F.; Sachs, D.H.; Chandraker, A.; Wertheim, J.A.; et al. The promise of organ and tissue preservation to transform medicine. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milek, D.; Reed, L.T.; Echternacht, S.R.; Shanmugarajah, K.; Cetrulo, C.L., Jr.; Lellouch, A.G.; Langstein, H.N.; Leckenby, J.I. A Systematic Review of the Reported Complications Related to Facial and Upper Extremity Vascularized Composite Allotransplantation. J. Surg. Res. 2023, 281, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruzzo, P.; Sardu, C.; Lanzetta, M.; Dubernard, J.M. Report (2017) of the International Registry on Hand and Composite Tissue Allotransplantation (IRHCTT). Curr. Transplant. Rep. 2017, 4, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uluer, M.C.; Brazio, P.S.; Woodall, J.D.; Nam, A.J.; Bartlett, S.T.; Barth, R.N. Vascularized Composite Allotransplantation: Medical Complications. Curr. Transplant. Rep. 2016, 3, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badylak, S.F.; Taylor, D.; Uygun, K. Whole-organ tissue engineering: Decellularization and recellularization of three-dimensional matrix scaffolds. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 13, 27–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uygun, B.E.; Yarmush, M.L.; Uygun, K. Application of whole-organ tissue engineering in hepatology. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uygun, B.E.; Yarmush, M.L. Engineered liver for transplantation. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uygun, B.E.; Soto-Gutierrez, A.; Yagi, H.; Izamis, M.L.; Guzzardi, M.A.; Shulman, C.; Milwid, J.; Kobayashi, N.; Tilles, A.; Berthiaume, F.; et al. Organ reengineering through development of a transplantable recellularized liver graft using decellularized liver matrix. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uygun, B.E.; Price, G.; Saedi, N.; Izamis, M.L.; Berendsen, T.; Yarmush, M.; Uygun, K. Decellularization and recellularization of whole livers. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 48, e2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruinsma, B.G.; Kim, Y.; Berendsen, T.A.; Ozer, S.; Yarmush, M.L.; Uygun, B.E. Layer-by-layer heparinization of decellularized liver matrices to reduce thrombogenicity of tissue engineered grafts. J. Clin. Transl. Res. 2015, 1, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupon, E.; Lellouch, A.G.; Acun, A.; Andrews, A.R.; Oganesyan, R.; Goutard, M.; Taveau, C.B.; Lantieri, L.A.; Cetrulo, C.L.; Uygun, B.E. Engineering Vascularized Composite Allografts Using Natural Scaffolds: A Systematic Review. Tissue Eng. Part. B Rev. 2022, 28, 677–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupon, E.; Acun, A.; Taveau, C.B.; Oganesyan, R.; Lancia, H.H.; Andrews, A.R.; Randolph, M.A.; Cetrulo, C.L., Jr.; Lellouch, A.G.; Uygun, B.E. Optimized Decellularization of a Porcine Fasciocutaneaous Flap. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duisit, J.; Maistriaux, L.; Taddeo, A.; Orlando, G.; Joris, V.; Coche, E.; Behets, C.; Lerut, J.; Dessy, C.; Cossu, G.; et al. Bioengineering a Human Face Graft: The Matrix of Identity. Ann. Surg. 2017, 266, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duisit, J.; Amiel, H.; Orlando, G.; Dedriche, A.; Behets, C.; Gianello, P.; Lengelé, B. Face Graft Scaffold Production in a Rat Model. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 141, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duisit, J.; Amiel, H.; Wüthrich, T.; Taddeo, A.; Dedriche, A.; Destoop, V.; Pardoen, T.; Bouzin, C.; Joris, V.; Magee, D.; et al. Perfusion-decellularization of human ear grafts enables ECM-based scaffolds for auricular vascularized composite tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2018, 73, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duisit, J.; Orlando, G.; Debluts, D.; Maistriaux, L.; Xhema, D.; de Bisthoven, Y.J.; Galli, C.; Peloso, A.; Behets, C.; Lengelé, B.; et al. Decellularization of the Porcine Ear Generates a Biocompatible, Nonimmunogenic Extracellular Matrix Platform for Face Subunit Bioengineering. Ann. Surg. 2018, 267, 1191–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Landford, W.N.; Garza, M.; Suarez, A.; Zhou, Z.; Coon, D. Complete Human Penile Scaffold for Composite Tissue Engineering: Organ Decellularization and Characterization. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerli, M.F.M.; Guyette, J.P.; Evangelista-Leite, D.; Ghoshhajra, B.B.; Ott, H.C. Perfusion decellularization of a human limb: A novel platform for composite tissue engineering and reconstructive surgery. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jank, B.J.; Xiong, L.; Moser, P.T.; Guyette, J.P.; Ren, X.; Cetrulo, C.L.; Leonard, D.A.; Fernandez, L.; Fagan, S.P.; Ott, H.C. Engineered composite tissue as a bioartificial limb graft. Biomaterials 2015, 61, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jank, B.J.; Goverman, J.; Guyette, J.P.; Charest, J.M.; Randolph, M.; Gaudette, G.R.; Gershlak, J.R.; Purschke, M.; Javorsky, E.; Nazarian, R.M.; et al. Creation of a Bioengineered Skin Flap Scaffold with a Perfusable Vascular Pedicle. Tissue Eng. Part A 2017, 23, 696–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozzo, V.; Romano, G.; Goutard, M.; Lupon, E.; Tawa, P.; Acun, A.; Andrews, A.R.; Taveau, C.B.; Uygun, B.E.; Randolph, M.A.; et al. A Reliable Porcine Fascio-Cutaneous Flap Model for Vascularized Composite Allografts Bioengineering Studies. J. Vis. Exp. 2022, 181, e63557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Van Hogezand, R.M.; Zhao, C.; Kuo, B.J.; Carlsen, B.T. Decellularization of a Fasciocutaneous Flap for Use as a Perfusable Scaffold. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2015, 75, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Johnson, J.A.; Dunne, L.W.; Chen, Y.; Iyyanki, T.; Wu, Y.; Chang, E.I.; Branch-Brooks, C.D.; Robb, G.L.; Butler, C.E. Decellularized skin/adipose tissue flap matrix for engineering vascularized composite soft tissue flaps. Acta Biomater. 2016, 35, 166–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pring, D.J.; Amis, A.A.; Coombs, R.R. The mechanical properties of human flexor tendons in relation to artificial tendons. J. Hand Surg. Br. 1985, 10, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, K.; Traylor, K.; Lee, S.W.; Ellis, B.; Weiss, J.; Kamper, D. Mechanical properties vary for different regions of the finger extensor apparatus. J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 3094–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDiarmid, S.V.; Azari, K.K. Donor-related issues in hand transplantation. Hand Clin. 2011, 27, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu Kwan, W.; Partanen, A.; Narayanan, U.; Waspe, A.C.; Drake, J.M. Biomechanical testing of ex vivo porcine tendons following high intensity focused ultrasound thermal ablation. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0302778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavert, P.; Kempf, J.F.; Bonnomet, F.; Boutemy, P.; Marcelin, L.; Kahn, J.L. Effects of freezing/thawing on the biomechanical properties of human tendons. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2001, 23, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motulsky, H.J.; Brown, R.E. Detecting outliers when fitting data with nonlinear regression—A new method based on robust nonlinear regression and the false discovery rate. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adil, A.; Xu, M.; Haykal, S. Recellularization of Bioengineered Scaffolds for Vascular Composite Allotransplantation. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 843677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendibil, U.; Ruiz-Hernandez, R.; Retegi-Carrion, S.; Garcia-Urquia, N.; Olalde-Graells, B.; Abarrategi, A. Tissue-Specific Decellularization Methods: Rationale and Strategies to Achieve Regenerative Compounds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopera Higuita, M.; Griffiths, L.G. Antigen removal process preserves function of small diameter venous valved conduits, whereas SDS-decellularization results in significant valvular insufficiency. Acta Biomater. 2020, 107, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crapo, P.M.; Gilbert, T.W.; Badylak, S.F. An overview of tissue and whole organ decellularization processes. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 3233–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopera Higuita, M.; Lopera Giraldo, J.F.; Sarrafian, T.L.; Griffiths, L.G. Tissue engineered bovine saphenous vein extracellular matrix scaffolds produced via antigen removal achieve high in vivo patency rates. Acta Biomater. 2021, 134, 144–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.; Nürnberger, S. Decellularization of Articular Cartilage: A Hydrochloric Acid-Based Strategy. Methods Mol. Biol. 2023, 2598, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Berning, K.; Tang, S.W.; Lam, Y.W. Rapid and Detergent-Free Decellularization of Cartilage. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2020, 26, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, U.; Evrard, R.; Lengelé, B.; Schubert, T.; Kadlub, N.; Boisson, J. Decellularized vascularized bone grafts as therapeutic solution for bone reconstruction: A mechanical evaluation. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0280193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McCarthy, M.E.; Filz von Reiterdank, I.; Parfitt van Pallandt, O.H.; Taggart, M.S.; Charlès, L.; Uygun, K.; Lellouch, A.G.; Cetrulo, C.L., Jr.; Uygun, B.E. Decellularization of Human Digits: A Step Towards Off-the-Shelf Composite Allograft Transplantation. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040383
McCarthy ME, Filz von Reiterdank I, Parfitt van Pallandt OH, Taggart MS, Charlès L, Uygun K, Lellouch AG, Cetrulo CL Jr., Uygun BE. Decellularization of Human Digits: A Step Towards Off-the-Shelf Composite Allograft Transplantation. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(4):383. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040383
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcCarthy, Michelle E., Irina Filz von Reiterdank, Oliver H. Parfitt van Pallandt, McLean S. Taggart, Laura Charlès, Korkut Uygun, Alexandre G. Lellouch, Curtis L. Cetrulo, Jr., and Basak E. Uygun. 2025. "Decellularization of Human Digits: A Step Towards Off-the-Shelf Composite Allograft Transplantation" Bioengineering 12, no. 4: 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040383
APA StyleMcCarthy, M. E., Filz von Reiterdank, I., Parfitt van Pallandt, O. H., Taggart, M. S., Charlès, L., Uygun, K., Lellouch, A. G., Cetrulo, C. L., Jr., & Uygun, B. E. (2025). Decellularization of Human Digits: A Step Towards Off-the-Shelf Composite Allograft Transplantation. Bioengineering, 12(4), 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040383







