Transcription Factor ETS-1 and Reactive Oxygen Species: Role in Vascular and Renal Injury
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Regulation
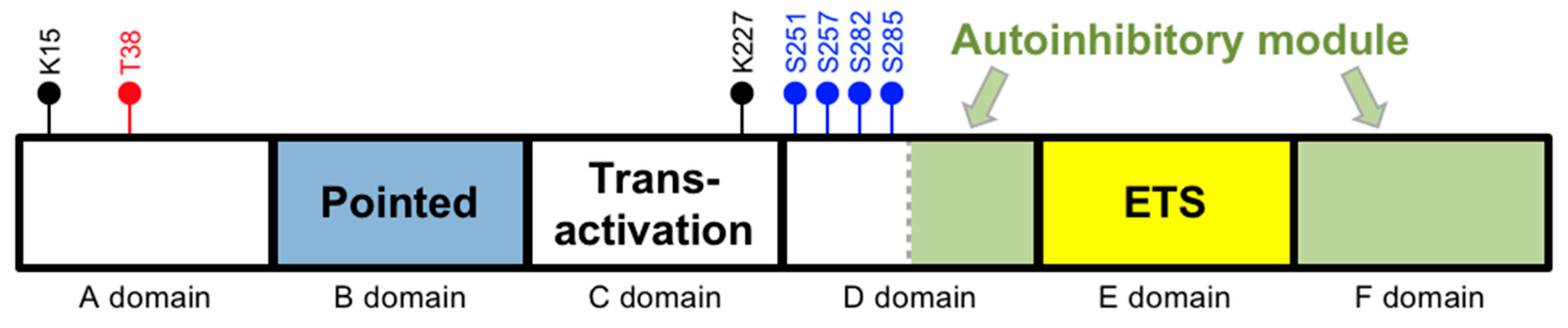
2.1. Posttranslational Modifications
2.2. By Transcription Factors
2.3. By Nuclear Transport
2.4. Regulation of Its Expression
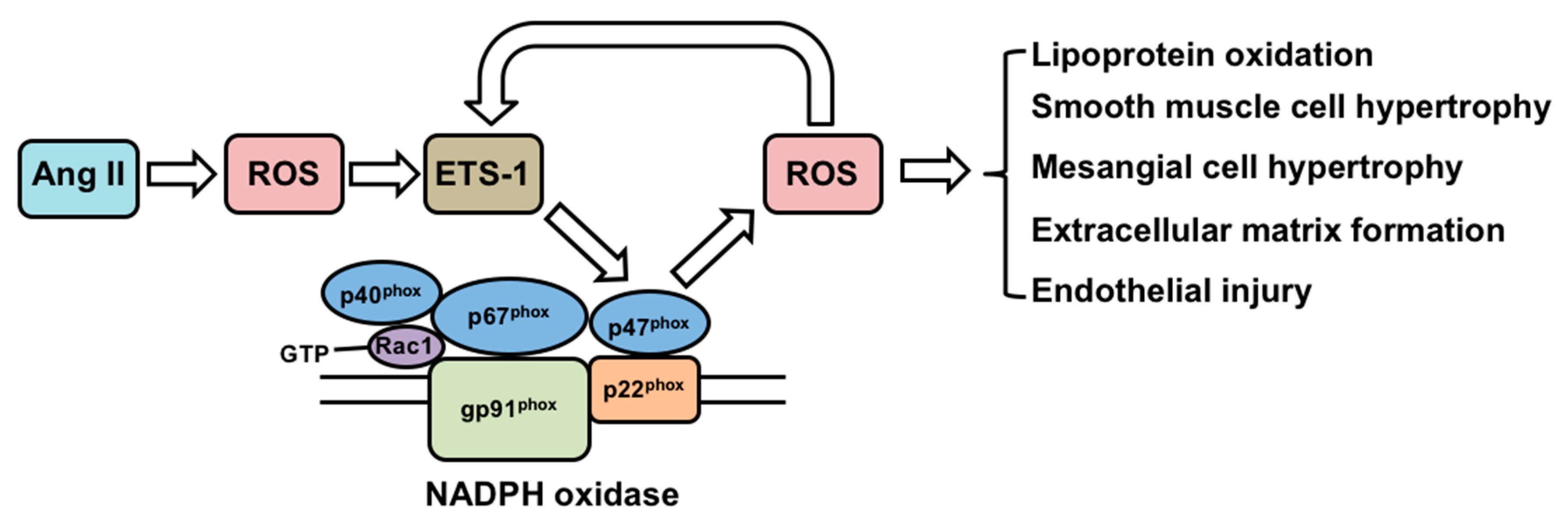
3. Effects of Angiotensin II on ETS-1 Expression and the Functional Consequences in the Vasculature and Kidney
3.1. In Vitro Studies
3.2. In Vivo Studies
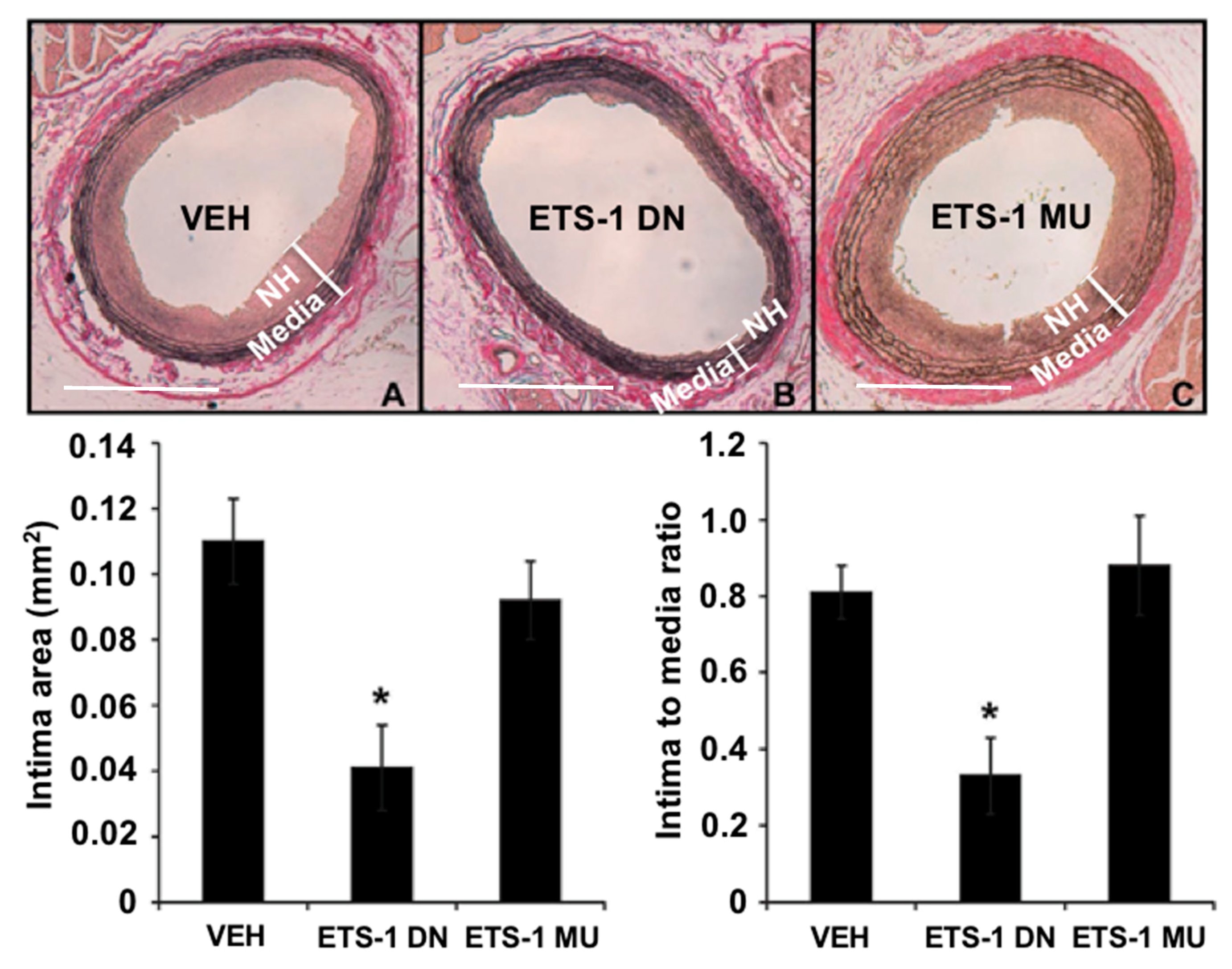
4. ETS-1 in Neointima Formation
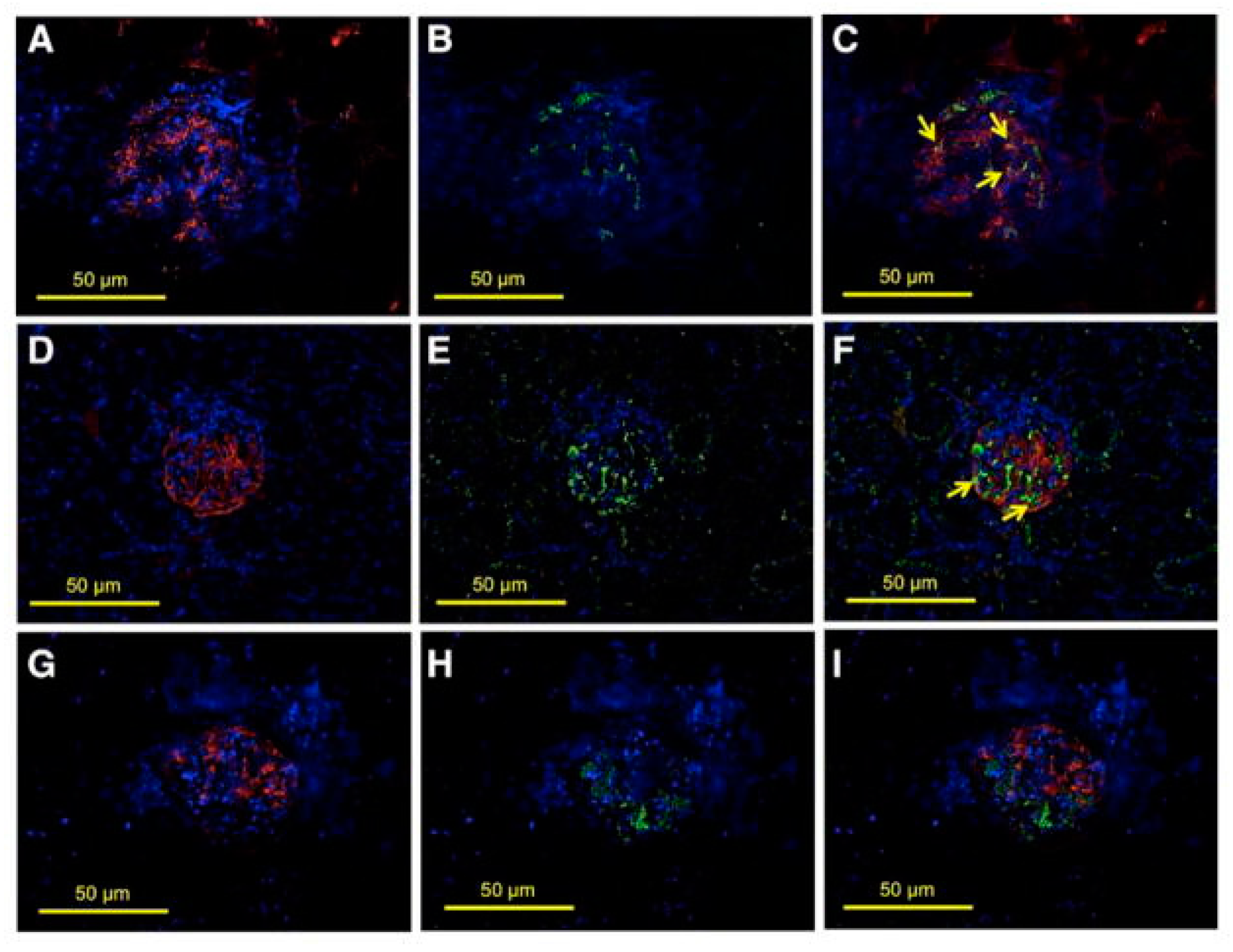
5. ETS-1 in Salt-Sensitive Hypertension
6. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leprince, D.; Gegonne, A.; Coll, J.; de Taisne, C.; Schneeberger, A.; Lagrou, C.; Stehelin, D. A putative second cell-derived oncogene of the avian leukaemia retrovirus E26. Nature 1983, 306, 395–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunn, M.F.; Seeburg, P.H.; Moscovici, C.; Duesberg, P.H. Tripartite structure of the avian erythroblastosis virus E26 transforming gene. Nature 1983, 306, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, D.K.; McWilliams-Smith, M.J.; Nunn, M.F.; Duesberg, P.H.; O’Brien, S.J.; Papas, T.S. The ets sequence from the transforming gene of avian erythroblastosis virus, E26, has unique domains on human chromosomes 11 and 21: Both loci are transcriptionally active. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 7294–7298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollenhorst, P.C.; McIntosh, L.P.; Graves, B.J. Genomic and biochemical insights into the specificity of ETS transcription factors. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 2011, 80, 437–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Findlay, V.J.; LaRue, A.C.; Turner, D.P.; Watson, P.M.; Watson, D.K. Understanding the role of ETS-mediated gene regulation in complex biological processes. Adv. Cancer Res. 2013, 119, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iotsova, V.; Crepieux, P.; Montpellier, C.; Laudet, V.; Stehelin, D. TATA-less promoters of some Ets-family genes are efficiently repressed by wild-type p53. Oncogene 1996, 13, 2331–2337. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garrett-Sinha, L.A. Review of Ets1 structure, function, and roles in immunity. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 3375–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmer, J. The biology of the Ets1 proto-oncogene. Mol. Cancer 2003, 2, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.S.; Hauser, C.A.; Henkel, G.; Colman, M.S.; Van Beveren, C.; Stacey, K.J.; Hume, D.A.; Maki, R.A.; Ostrowski, M.C. Ras-mediated phosphorylation of a conserved threonine residue enhances the transactivation activities of c-Ets1 and c-Ets2. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slupsky, C.M.; Gentile, L.N.; Donaldson, L.W.; Mackereth, C.D.; Seidel, J.J.; Graves, B.J.; McIntosh, L.P. Structure of the Ets-1 pointed domain and mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation site. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 12129–12134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasylyk, B.; Hagman, J.; Gutierrez-Hartmann, A. Ets transcription factors: Nuclear effectors of the Ras-MAP-kinase signaling pathway. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1998, 23, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulds, C.E.; Nelson, M.L.; Blaszczak, A.G.; Graves, B.J. Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling activates Ets-1 and Ets-2 by CBP/p300 recruitment. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 10954–10964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, M.L.; Kang, H.S.; Lee, G.M.; Blaszczak, A.G.; Lau, D.K.; McIntosh, L.P.; Graves, B.J. Ras signaling requires dynamic properties of Ets1 for phosphorylation-enhanced binding to coactivator CBP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 10026–10031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czuwara-Ladykowska, J.; Sementchenko, V.I.; Watson, D.K.; Trojanowska, M. Ets1 is an effector of the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) signaling pathway and an antagonist of the profibrotic effects of TGF-beta. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 20399–20408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowley, D.O.; Graves, B.J. Phosphorylation represses Ets-1 DNA binding by reinforcing autoinhibition. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nishida, T.; Terashima, M.; Fukami, K.; Yamada, Y. PIASy controls ubiquitination-dependent proteasomal degradation of Ets-1. Biochem. J. 2007, 405, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.; Degerny, C.; Vintonenko, N.; Deheuninck, J.; Foveau, B.; Leroy, C.; Coll, J.; Tulasne, D.; Baert, J.L.; Fafeur, V. Regulation of the Ets-1 transcription factor by sumoylation and ubiquitinylation. Oncogene 2007, 26, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, T.; Terashima, M.; Fukami, K. PIASy-mediated repression of the Ets-1 is independent of its sumoylation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 345, 1536–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieweke, M.H.; Tekotte, H.; Jarosch, U.; Graf, T. Cooperative interaction of Ets-1 with USF-1 required for HIV-1 enhancer activity in T cells. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 1728–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvie, C.W.; Hagman, J.; Wolberger, C. Structural studies of Ets-1/Pax5 complex formation on DNA. Mol. Cell. 2001, 8, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Erman, B.; Ishii, H.; Gangopadhyay, S.S.; Sen, R. Transcriptional activation by ETS and leucine zipper-containing basic helix-loop-helix proteins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 2946–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.Y.; Sieweke, M.; Ogawa, E.; Wee, H.J.; Englmeier, U.; Graf, T.; Ito, Y. Mutual activation of Ets-1 and AML1 DNA binding by direct interaction of their autoinhibitory domains. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 1609–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetz, T.L.; Gu, T.L.; Speck, N.A.; Graves, B.J. Auto-inhibition of Ets-1 is counteracted by DNA binding cooperativity with core-binding factor alpha2. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzsimmons, D.; Lukin, K.; Lutz, R.; Garvie, C.W.; Wolberger, C.; Hagman, J. Highly cooperative recruitment of Ets-1 and release of autoinhibition by Pax5. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 392, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baillat, D.; Begue, A.; Stehelin, D.; Aumercier, M. ETS-1 transcription factor binds cooperatively to the palindromic head to head ETS-binding sites of the stromelysin-1 promoter by counteracting autoinhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 29386–29398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulukos, K.E.; Pognonec, P.; Rabault, B.; Begue, A.; Ghysdael, J. Definition of an Ets1 protein domain required for nuclear localization in cells and DNA-binding activity in vitro. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1989, 9, 5718–5721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearse, D.D.; Tian, R.X.; Nigro, J.; Iorgulescu, J.B.; Puzis, L.; Jaimes, E.A. Angiotensin II increases the expression of the transcription factor ETS-1 in mesangial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2008, 294, F1094–F1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, K.; Nakashima, H.; Ishida, M.; Miho, N.; Sawano, M.; Soe, N.N.; Kurabayashi, M.; Chayama, K.; Yoshizumi, M.; Ishida, T. Angiotensin II-induced osteopontin expression in vascular smooth muscle cells involves Gq/11, Ras, ERK, Src and Ets-1. Hypertens. Res. 2008, 31, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzau, V.J. Theodore Cooper Lecture: Tissue angiotensin and pathobiology of vascular disease: A unifying hypothesis. Hypertension 2001, 37, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniyama, Y.; Hitomi, H.; Shah, A.; Alexander, R.W.; Griendling, K.K. Mechanisms of reactive oxygen species-dependent downregulation of insulin receptor substrate-1 by angiotensin II. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 1142–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedeljkovic, Z.S.; Gokce, N.; Loscalzo, J. Mechanisms of oxidative stress and vascular dysfunction. Postgrad. Med. J. 2003, 79, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaimes, E.A.; Galceran, J.M.; Raij, L. Angiotensin II induces superoxide anion production by mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 1998, 54, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetze, S.; Kintscher, U.; Kaneshiro, K.; Meehan, W.P.; Collins, A.; Fleck, E.; Hsueh, W.A.; Law, R.E. TNFalpha induces expression of transcription factors c-fos, Egr-1, and Ets-1 in vascular lesions through extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2. Atherosclerosis 2001, 159, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultgardh-Nilsson, A.; Cercek, B.; Wang, J.W.; Naito, S.; Lovdahl, C.; Sharifi, B.; Forrester, J.S.; Fagin, J.A. Regulated expression of the ETS-1 transcription factor in vascular smooth muscle cells in vivo and in vitro. Circ. Res. 1996, 78, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naito, S.; Shimizu, S.; Maeda, S.; Wang, J.; Paul, R.; Fagin, J.A. Ets-1 is an early response gene activated by ET-1 and PDGF-BB in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 274, C472–C480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Y.; Brown, C.; Maynard, E.; Anshelevich, A.; Ni, W.; Ho, I.C.; Oettgen, P. Ets-1 is a critical regulator of Ang II-mediated vascular inflammation and remodeling. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 2508–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, P.; Feng, W.; Rezonzew, G.; Chumley, P.; Jaimes, E.A. The transcription factor ETS-1 regulates angiotensin II-stimulated fibronectin production in mesangial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2012, 302, F1418–F1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, L.A.; Gemin, A.; Espiritu, R.; Singh, G. ETS-1 is transcriptionally up-regulated by H2O2 via an antioxidant response element. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 2085–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, K.K.; Subbaram, S.; Connor, K.M.; Dasgupta, J.; Ha, X.F.; Meng, T.C.; Tonks, N.K.; Melendez, J.A. Redox-dependent matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression is regulated by JNK through Ets and AP-1 promoter motifs. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 14100–14110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landmesser, U.; Cai, H.; Dikalov, S.; McCann, L.; Hwang, J.; Jo, H.; Holland, S.M.; Harrison, D.G. Role of p47(phox) in vascular oxidative stress and hypertension caused by angiotensin II. Hypertension 2002, 40, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaimes, E.A.; Tian, R.X.; Pearse, D.; Raij, L. Up-regulation of glomerular COX-2 by angiotensin II: Role of reactive oxygen species. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 2143–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.S.; Jaimes, E.A.; Raij, L. Vascular but not cardiac remodeling is associated with superoxide production in angiotensin II hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2005, 23, 1737–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffetseder, U.; Wernert, N.; Ostendorf, T.; van Roeyen, C.; Rauen, T.; Behrens, P.; Floege, J.; Mertens, P.R. Mesangial cell expression of proto-oncogene Ets-1 during progression of mesangioproliferative glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 2004, 66, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Terada, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Okado, T.; Inoshita, S.; Kuwahara, M.; Seth, A.; Sato, Y.; Sasaki, S. Expression and function of Ets-1 during experimental acute renal failure in rats. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 3083–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naito, T.; Razzaque, M.S.; Nazneen, A.; Liu, D.; Nihei, H.; Koji, T.; Taguchi, T. Renal expression of the Ets-1 proto-oncogene during progression of rat crescentic glomerulonephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2000, 11, 2243–2255. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Chumley, P.; Hua, P.; Rezonzew, G.; Jaimes, D.; Duckworth, M.W.; Xing, D.; Jaimes, E.A. Role of the transcription factor erythroblastosis virus E26 oncogen homolog-1 (ETS-1) as mediator of the renal proinflammatory and profibrotic effects of angiotensin II. Hypertension 2012, 60, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, W.; Zhan, Y.; He, H.; Maynard, E.; Balschi, J.A.; Oettgen, P. Ets-1 is a critical transcriptional regulator of reactive oxygen species and p47(phox) gene expression in response to angiotensin II. Circ. Res. 2007, 101, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Xing, D.; Hua, P.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.F.; Oparil, S.; Jaimes, E.A. The transcription factor ETS-1 mediates proinflammatory responses and neointima formation in carotid artery endoluminal vascular injury. Hypertension 2010, 55, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Chumley, P.; Allon, M.; George, J.; Scott, D.W.; Patel, R.P.; Litovsky, S.; Jaimes, E.A. The transcription factor E26 transformation-specific sequence-1 mediates neointima formation in arteriovenous fistula. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberger, M.H.; Miller, J.Z.; Luft, F.C.; Grim, C.E.; Fineberg, N.S. Definitions and characteristics of sodium sensitivity and blood pressure resistance. Hypertension 1986, 8, II127–II134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.S.; Adam, A.G.; Jaimes, E.A.; Raij, L. In salt-sensitive hypertension, increased superoxide production is linked to functional upregulation of angiotensin II. Hypertension 2003, 42, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navar, L.G.; Harrison-Bernard, L.M.; Nishiyama, A.; Kobori, H. Regulation of intrarenal angiotensin II in hypertension. Hypertension 2002, 39, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Re, R.N. Intracellular renin and the nature of intracrine enzymes. Hypertension 2003, 42, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobori, H.; Ozawa, Y.; Suzaki, Y.; Prieto-Carrasquero, M.C.; Nishiyama, A.; Shoji, T.; Cohen, E.P.; Navar, L.G. Young Scholars Award Lecture: Intratubular angiotensinogen in hypertension and kidney diseases. Am. J. Hypertens. 2006, 19, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobori, H.; Nangaku, M.; Navar, L.G.; Nishiyama, A. The intrarenal renin-angiotensin system: From physiology to the pathobiology of hypertension and kidney disease. Pharmacol. Rev. 2007, 59, 251–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingert, C.; Grima, M.; Coquard, C.; Barthelmebs, M.; Imbs, J.L. Contribution of angiotensin II internalization to intrarenal angiotensin II levels in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2002, 283, F1003–F1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, J.; Dahl, L.K.; Knudsen, K.D. Genetic influence on the renin-angiotensin system: Low renin activities in hypertension-prone rats. Circ. Res. 1973, 32, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, H.; Coffee, K.; Raij, L. Endothelial dysfunction and cardiorenal injury in experimental salt-sensitive hypertension: Effects of antihypertensive therapy. Circulation 1997, 96, 2407–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, K.; Adachi, H.; Sonoda, J. Beneficial effects of long-term enalapril treatment and low-salt intake on survival rate of dahl salt-sensitive rats with established hypertension. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997, 283, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Otsuka, F.; Yamauchi, T.; Kataoka, H.; Mimura, Y.; Ogura, T.; Makino, H. Effects of chronic inhibition of ACE and AT1 receptors on glomerular injury in dahl salt-sensitive rats. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 274, R1797–R1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashida, W.; Kihara, Y.; Yasaka, A.; Inagaki, K.; Iwanaga, Y.; Sasayama, S. Stage-specific differential activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases in hypertrophied and failing rat hearts. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2001, 33, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakata, Y.; Masuyama, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Doi, R.; Mano, T.; Kuzuya, T.; Miwa, T.; Takeda, H.; Hori, M. Renin angiotensin system-dependent hypertrophy as a contributor to heart failure in hypertensive rats: Different characteristics from renin angiotensin system-independent hypertrophy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2001, 37, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikimi, T.; Mori, Y.; Kobayashi, N.; Tadokoro, K.; Wang, X.; Akimoto, K.; Yoshihara, F.; Kangawa, K.; Matsuoka, H. Renoprotective effect of chronic adrenomedullin infusion in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Hypertension 2002, 39, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobori, H.; Nishiyama, A.; Abe, Y.; Navar, L.G. Enhancement of intrarenal angiotensinogen in Dahl salt-sensitive rats on high salt diet. Hypertension 2003, 41, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, A.; Yoshizumi, M.; Rahman, M.; Kobori, H.; Seth, D.M.; Miyatake, A.; Zhang, G.X.; Yao, L.; Hitomi, H.; Shokoji, T.; et al. Effects of AT1 receptor blockade on renal injury and mitogen-activated protein activity in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 972–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onozato, M.L.; Tojo, A.; Kobayashi, N.; Goto, A.; Matsuoka, H.; Fujita, T. Dual blockade of aldosterone and angiotensin II additively suppresses TGF-beta and NADPH oxidase in the hypertensive kidney. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2007, 22, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Chumley, P.; Prieto, M.C.; Miyada, K.; Seth, D.M.; Fatima, H.; Hua, P.; Rezonzew, G.; Sanders, P.W.; Jaimes, E.A. Transcription factor avian erythroblastosis virus E26 oncogen homolog-1 is a novel mediator of renal injury in salt-sensitive hypertension. Hypertension 2015, 65, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.S.; Hernandez Schulman, I.; Pagano, P.J.; Jaimes, E.A.; Raij, L. Reduced NAD(P)H oxidase in low renin hypertension: Link among angiotensin II, atherogenesis, and blood pressure. Hypertension 2006, 47, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbashir, S.M.; Harborth, J.; Weber, K.; Tuschl, T. Analysis of gene function in somatic mammalian cells using small interfering RNAs. Methods 2002, 26, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Roberts, L.J., 2nd; Cason, G.W.; Curry, T.S.; Manning, R.D., Jr. Superoxide dismutase and oxidative stress in Dahl salt-sensitive and -resistant rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2002, 283, R732–R738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Chen, B.; Xing, D.; Li, X.; Fatima, H.; Jaimes, E.A.; Sanders, P.W. Haploinsufficiency of the Transcription Factor Ets-1 Is Renoprotective in Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rats. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 3239–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shiu, Y.-T.; Jaimes, E.A. Transcription Factor ETS-1 and Reactive Oxygen Species: Role in Vascular and Renal Injury. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7070084
Shiu Y-T, Jaimes EA. Transcription Factor ETS-1 and Reactive Oxygen Species: Role in Vascular and Renal Injury. Antioxidants. 2018; 7(7):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7070084
Chicago/Turabian StyleShiu, Yan-Ting, and Edgar A. Jaimes. 2018. "Transcription Factor ETS-1 and Reactive Oxygen Species: Role in Vascular and Renal Injury" Antioxidants 7, no. 7: 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7070084
APA StyleShiu, Y.-T., & Jaimes, E. A. (2018). Transcription Factor ETS-1 and Reactive Oxygen Species: Role in Vascular and Renal Injury. Antioxidants, 7(7), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7070084




