Whole-Genome Sequencing Reveals the Role of Cis-Regulatory Elements and eQTL/sQTL in the Adaptive Selection of Hubei Indigenous Cattle
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Genomic Sequencing
2.2. Quality Control, Sequence Alignment, and Variant Calling
2.3. Population Structure and Demographic History Analysis
2.4. Theta Pi
2.5. Identification of Adaptive Selections
2.6. Cis-Regulatory Element Annotations and Function QTL
2.7. Definition of Adaptive Regions and Identification of Candidate Adaptive CREs
2.8. Functional Enrichment Analysis of Adaptive CREs
3. Results
3.1. Sequencing and Variation Calling
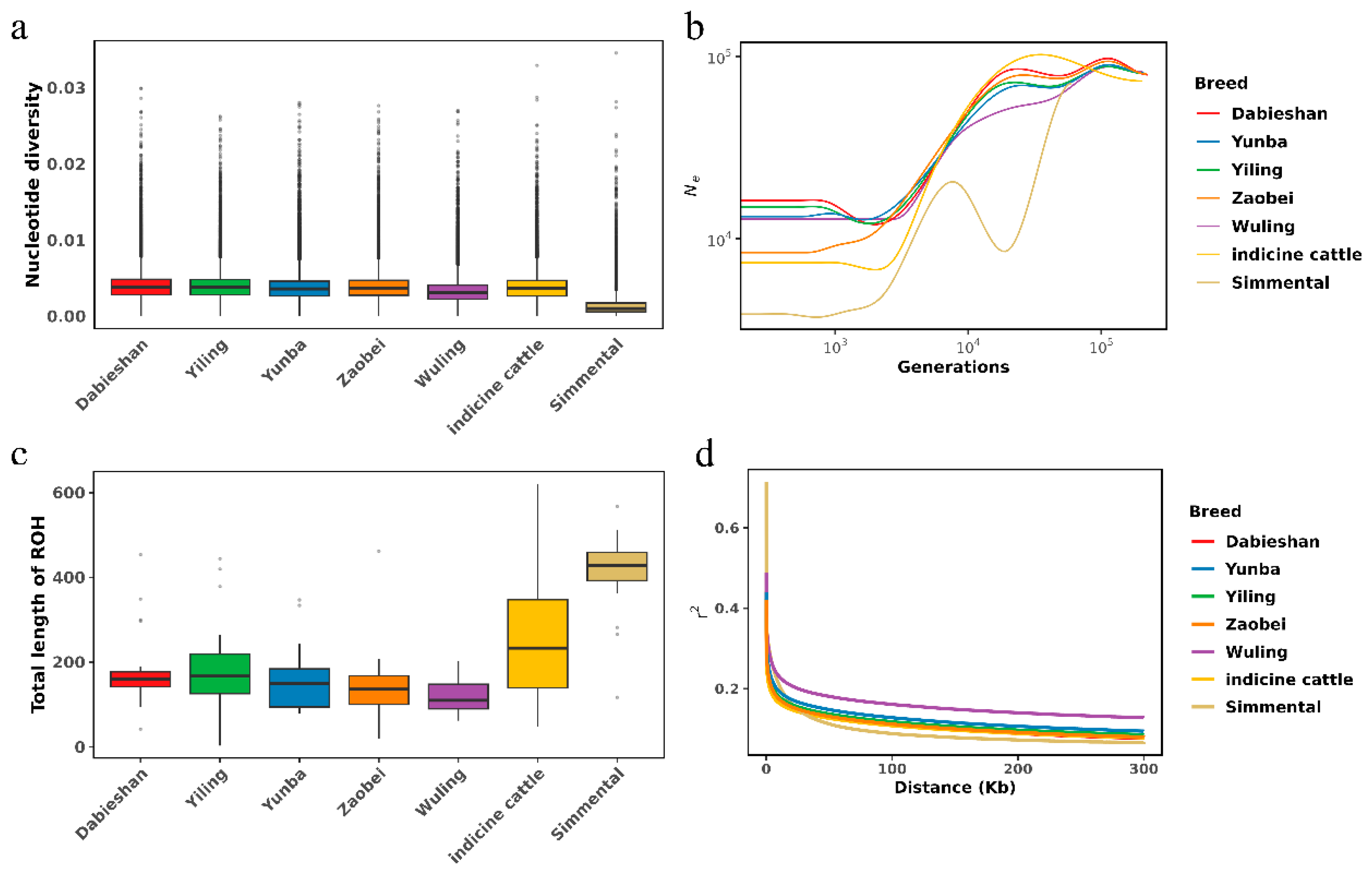
3.2. Population Structure and Genetic Diversity
3.3. Genome-Wide Selective Sweep
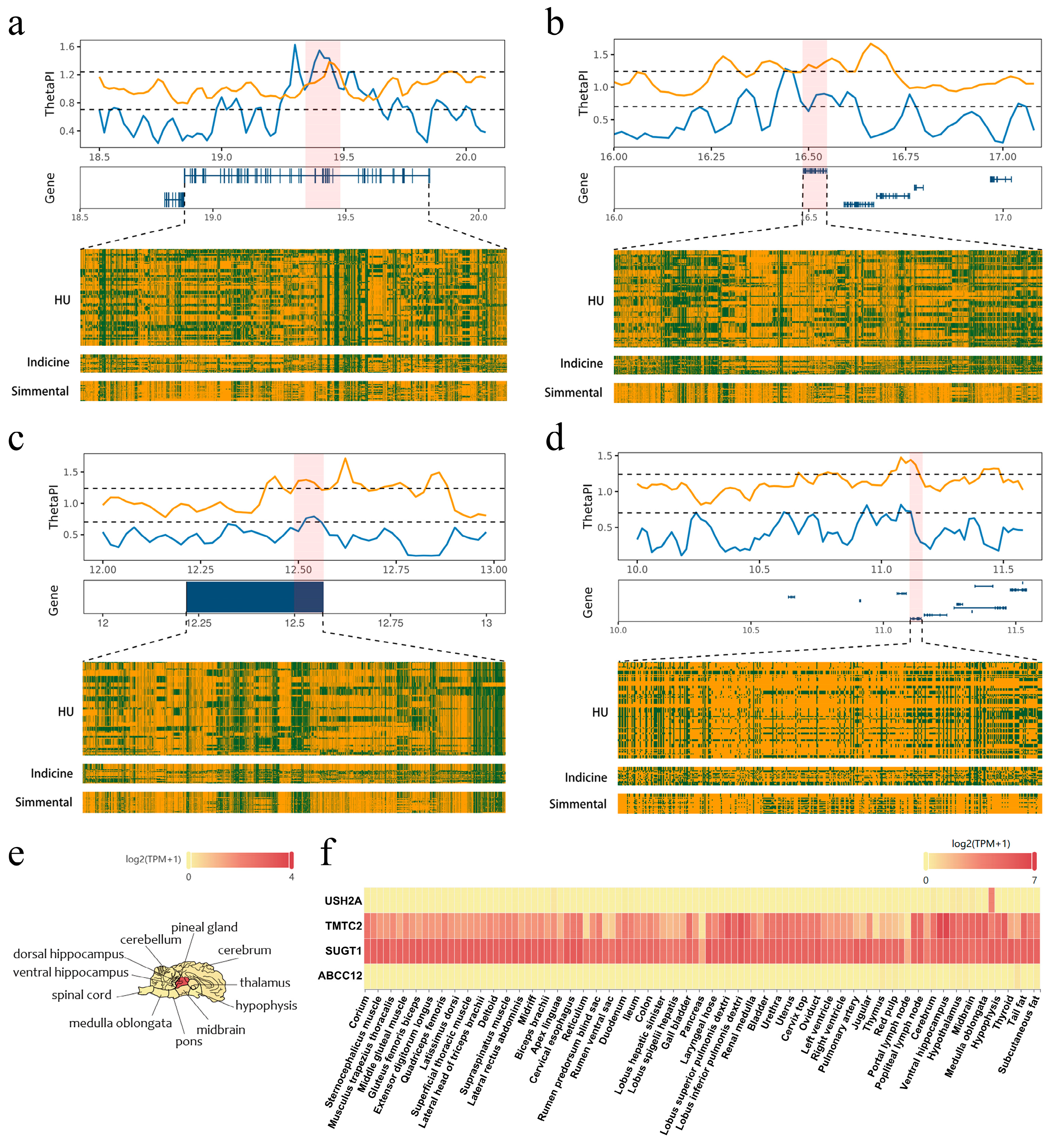
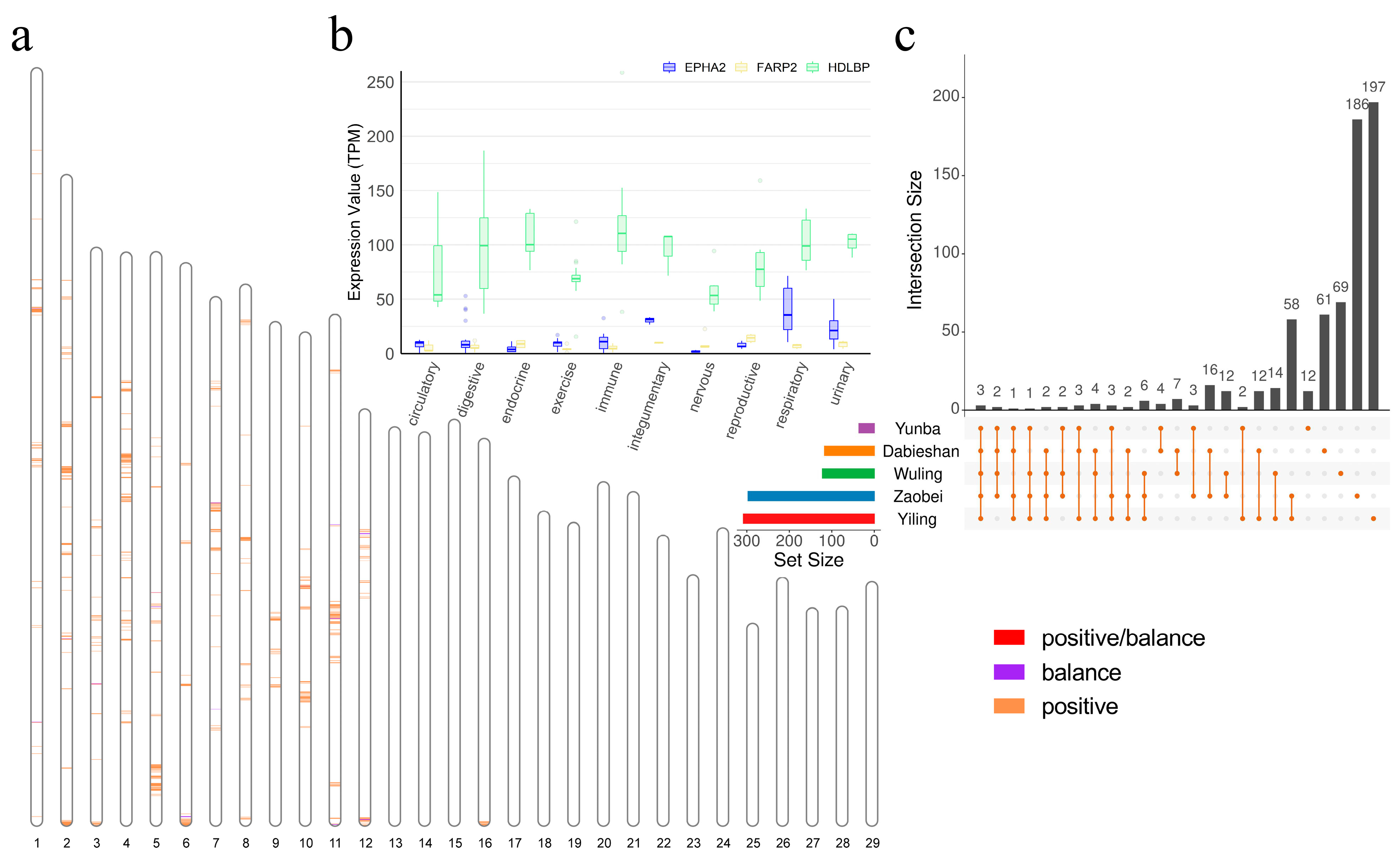
3.4. The Genomic Region Under Adaptive Selection in the Hubei Indigenous Cattle Breeds
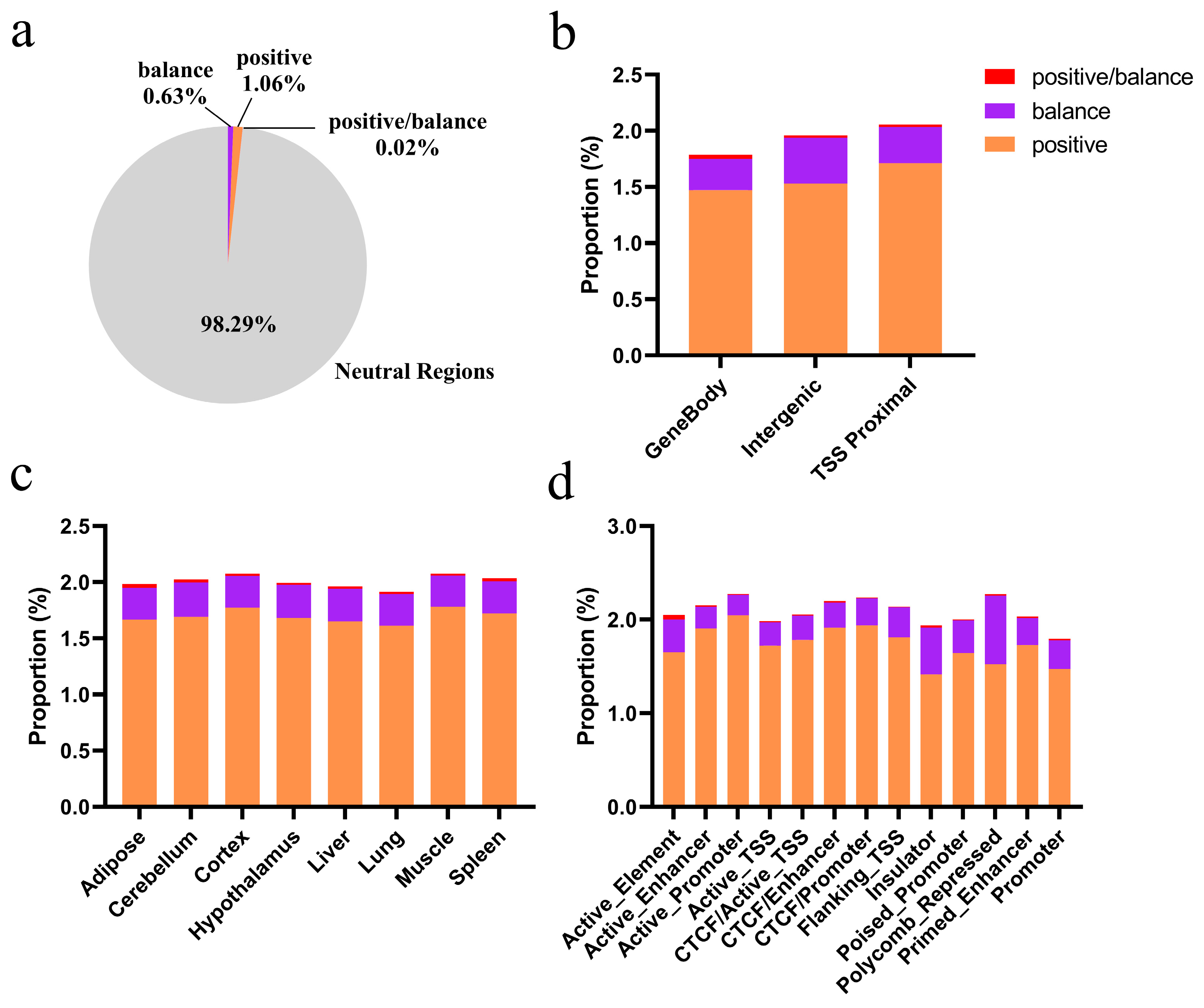
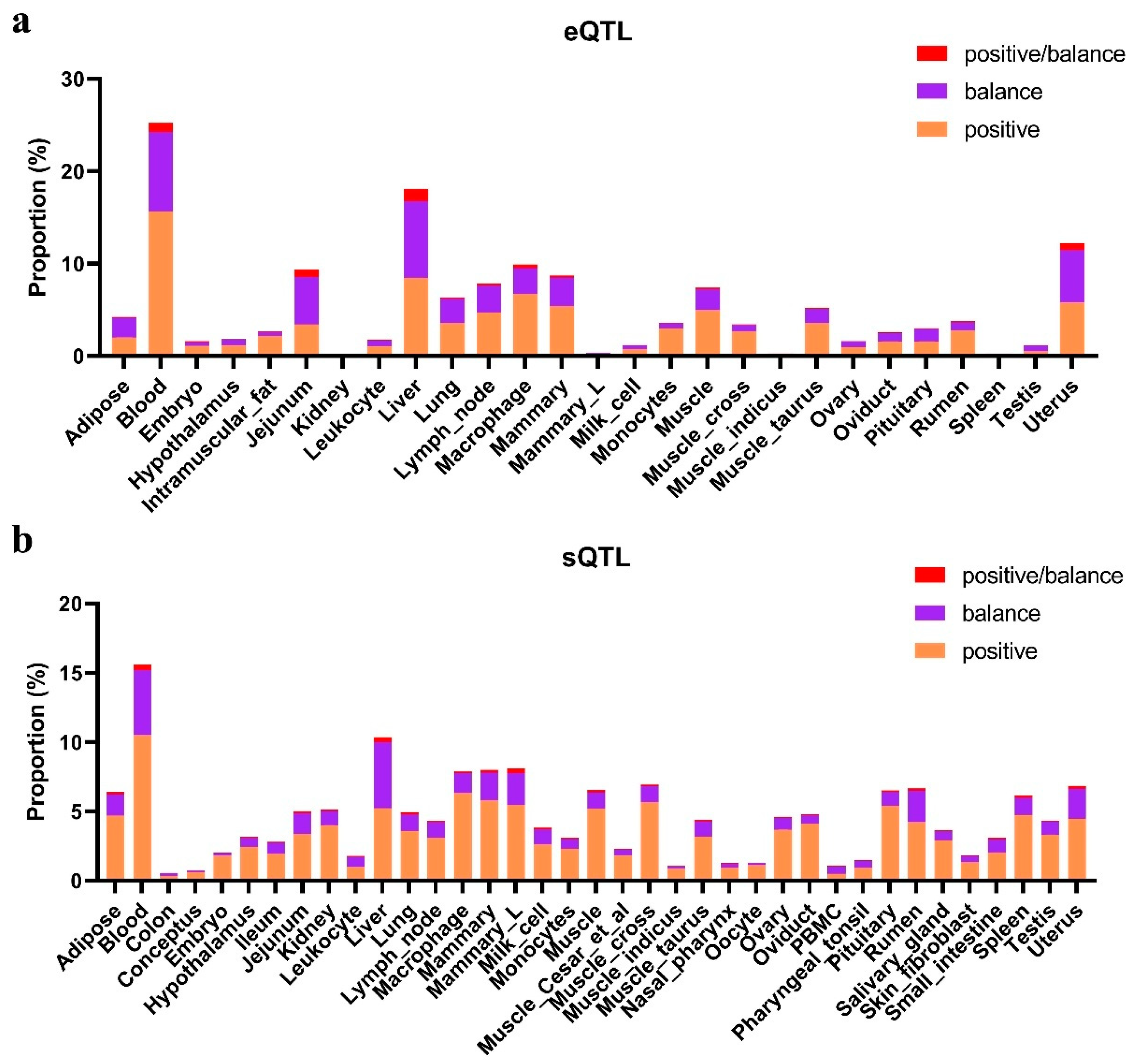
3.5. Candidate Positively Selected CREs in the Hubei Indigenous Cattle Breeds
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, N.; Xia, X.; Hanif, Q.; Zhang, F.; Dang, R.; Huang, B.; Lyu, Y.; Luo, X.; Zhang, H.; Yan, H.; et al. Global genetic diversity, introgression, and evolutionary adaptation of indicine cattle revealed by whole genome sequencing. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barendse, W. Climate Adaptation of Tropical Cattle. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2017, 5, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoreishifar, S.M.; Eriksson, S.; Johansson, A.M.; Khansefid, M.; Moghaddaszadeh-Ahrabi, S.; Parna, N.; Davoudi, P.; Javanmard, A. Signatures of selection reveal candidate genes involved in economic traits and cold acclimation in five Swedish cattle breeds. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2020, 52, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buggiotti, L.; Yurchenko, A.A.; Yudin, N.S.; Vander Jagt, C.J.; Vorobieva, N.V.; Kusliy, M.A.; Vasiliev, S.K.; Rodionov, A.N.; Boronetskaya, O.I.; Zinovieva, N.A.; et al. Demographic History, Adaptation, and NRAP Convergent Evolution at Amino Acid Residue 100 in the World Northernmost Cattle from Siberia. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3093–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaler, J.; Addo, S.; Thaller, G.; Hinrichs, D. Exploration of conservation and development strategies with a limited stakeholder approach for local cattle breeds. Animal 2019, 13, 2922–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, J.; Talenti, A.; Fisch, A.; Hemmink, J.D.; Paxton, E.; Toye, P.; Santos, I.; Ferreira, B.R.; Connelley, T.K.; Morrison, L.J.; et al. Profiling the immune epigenome across global cattle breeds. Genome Biol. 2023, 24, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somenzi, E.; Partel, E.; Barbato, M.; Chero Osorio, A.M.; Colli, L.; Franceschi, N.; Mantovani, R.; Pilla, F.; Komjanc, M.; Achilli, A.; et al. Genetic legacy and adaptive signatures: Investigating the history, diversity, and selection signatures in Rendena cattle resilient to eighteenth century rinderpest epidemics. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2024, 56, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, D.A.; Elyashiv, E.; Amster, G.; Sella, G. Broad-scale variation in human genetic diversity levels is predicted by purifying selection on coding and non-coding elements. Elife 2023, 12, e76065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Xiao, L.; Fu, R.; Nie, Q.; Zhang, X.; Luo, W. Genetic characteristics and selection signatures between Southern Chinese local and commercial chickens. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Wang, F.; Cheng, H.; Han, J.; Dang, R.; Xia, X.; Wang, H.; Zhong, J.; Lenstra, J.A.; Zhang, H.; et al. Recent selection and introgression facilitated high-altitude adaptation in cattle. Sci. Bull. 2024, 69, 3415–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.L.; Lin, J.; Huang, Y.Y.; Gao, Q.S.; Piao, Z.Y.; Yuan, S.L.; Chen, L.; Ren, X.; Ye, R.C.; Dong, M.; et al. Population genomics reveals that natural variation in PRDM16 contributes to cold tolerance in domestic cattle. Zool. Res. 2022, 43, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.D.; Ding, X.D.; Wang, S.; Wojcik, J.M.; Zhang, Y.; Tokarska, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.S.; Faruque, O.; Nielsen, R.; et al. Pervasive introgression facilitated domestication and adaptation in the Bos species complex. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Liu, Y.; Niu, Q.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhu, B.; Gao, X.; Zhang, L.; et al. Runs of homozygosity analysis reveals consensus homozygous regions affecting production traits in Chinese Simmental beef cattle. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Yang, L.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, X.; Gao, H.; Liu, G.E.; et al. Genome-wide scan reveals genetic divergence and diverse adaptive selection in Chinese local cattle. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Cole, J.B.; Tenesa, A.; Wang, T.; McDaneld, T.G.; Ma, L.; Liu, G.E.; Fang, L. Epigenomics and genotype-phenotype association analyses reveal conserved genetic architecture of complex traits in cattle and human. BMC Biol. 2020, 18, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Liu, S.; Shi, S.; Jiang, Y.; Cao, M.; Tang, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, J.; Fang, L.; Yu, Y.; et al. Comparative epigenomics reveals the impact of ruminant-specific regulatory elements on complex traits. BMC Biol. 2022, 20, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senczuk, G.; Mastrangelo, S.; Ciani, E.; Battaglini, L.; Cendron, F.; Ciampolini, R.; Crepaldi, P.; Mantovani, R.; Bongioni, G.; Pagnacco, G.; et al. The genetic heritage of Alpine local cattle breeds using genomic SNP data. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2020, 52, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akasaka, H.; Sano, F.K.; Shihoya, W.; Nureki, O. Structural mechanisms of potent lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 activation by nonlipid basic agonists. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assembly contigs with BWA-MEM. arXiv 2013, arXiv:13033997. [Google Scholar]
- Danecek, P.; Bonfield, J.K.; Liddle, J.; Marshall, J.; Ohan, V.; Pollard, M.O.; Whitwham, A.; Keane, T.; McCarthy, S.A.; Davies, R.M.; et al. Twelve years of SAMtools and BCFtools. Gigascience 2021, 10, giab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budnik, L.T.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K. Lysophosphatidic acid and its role in reproduction. Biol. Reprod. 2002, 66, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Auwera, G.A.; O’Connor, B.D. Genomics in the Cloud: Using Docker, GATK, and WDL in Terra; O’Reilly Media: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Poplin, R.; Ruano-Rubio, V.; DePristo, M.A.; Fennell, T.J.; Carneiro, M.O.; Van der Auwera, G.A.; Kling, D.E.; Gauthier, L.D.; Levy-Moonshine, A.; Roazen, D. Scaling accurate genetic variant discovery to tens of thousands of samples. BioRxiv 2017. BioRxiv:201178. [Google Scholar]
- Browning, B.L.; Tian, X.; Zhou, Y.; Browning, S.R. Fast two-stage phasing of large-scale sequence data. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 108, 1880–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, D.H.; Novembre, J.; Lange, K. Fast model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickrell, J.K.; Pritchard, J.K. Inference of population splits and mixtures from genome-wide allele frequency data. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terhorst, J.; Kamm, J.A.; Song, Y.S. Robust and scalable inference of population history from hundreds of unphased whole genomes. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Xie, R.; Fang, L.; Xiang, R.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L. Analysis of 206 whole-genome resequencing reveals selection signatures associated with breed-specific traits in Hu sheep. Evol. Appl. 2024, 17, e13697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Dong, S.S.; Xu, J.Y.; He, W.M.; Yang, T.L. PopLDdecay: A fast and effective tool for linkage disequilibrium decay analysis based on variant call format files. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1786–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.S.; He, W.M.; Ji, J.J.; Zhang, C.; Guo, Y.; Yang, T.L. LDBlockShow: A fast and convenient tool for visualizing linkage disequilibrium and haplotype blocks based on variant call format files. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danecek, P.; Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.; Albers, C.A.; Banks, E.; DePristo, M.A.; Handsaker, R.E.; Lunter, G.; Marth, G.T.; Sherry, S.T.; et al. The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2156–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nei, M.; Li, W.H. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 5269–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Luo, C.; Wu, F.; Huang, Y.; Zhen, Y.; Chen, N.; Wang, L.; Song, L. The HTIRDB: A resource containing a transcriptional atlas for 105 different tissues from each of seven species of domestic herbivore. iMeta 2025, 4, e267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voight, B.F.; Kudaravalli, S.; Wen, X.; Pritchard, J.K. A map of recent positive selection in the human genome. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-Admetlla, A.; Liang, M.; Korneliussen, T.; Nielsen, R. On detecting incomplete soft or hard selective sweeps using haplotype structure. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 1275–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, R.; Williamson, S.; Kim, Y.; Hubisz, M.J.; Clark, A.G.; Bustamante, C. Genomic scans for selective sweeps using SNP data. Genome Res. 2005, 15, 1566–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpiech, Z.A.; Hernandez, R.D. selscan: An efficient multithreaded program to perform EHH-based scans for positive selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 2824–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpiech, Z.A. selscan 2.0: Scanning for sweeps in unphased data. Bioinformatics 2024, 40, btae006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garud, N.R.; Messer, P.W.; Buzbas, E.O.; Petrov, D.A. Recent selective sweeps in North American Drosophila melanogaster show signatures of soft sweeps. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Luo, H.; Zhang, P.; Li, Y.; Hao, D.; Zhang, S.; Song, T.; Xu, T.; He, S. Adaptive Selection of Cis-regulatory Elements in the Han Chinese. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2024, 41, msae034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajima, F. Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 1989, 123, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kern, C.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Pan, Z.; Halstead, M.; Chanthavixay, G.; Saelao, P.; Waters, S.; Xiang, R.; Chamberlain, A.; et al. Functional annotations of three domestic animal genomes provide vital resources for comparative and agricultural research. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Gao, Y.; Canela-Xandri, O.; Wang, S.; Yu, Y.; Cai, W.; Li, B.; Xiang, R.; Chamberlain, A.J.; Pairo-Castineira, E.; et al. A multi-tissue atlas of regulatory variants in cattle. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 1438–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lex, A.; Gehlenborg, N.; Strobelt, H.; Vuillemot, R.; Pfister, H. UpSet: Visualization of Intersecting Sets. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2014, 20, 1983–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Kirov, S.; Snoddy, J. WebGestalt: An integrated system for exploring gene sets in various biological contexts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W741–W748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Cui, H.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Ding, J.; Liu, L.; Wen, J.; Zhao, G. Fatty acid metabolism-related genes are associated with flavor-presenting aldehydes in Chinese local chicken. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 902180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Bulgakov, O.V.; Darrow, K.N.; Pawlyk, B.; Adamian, M.; Liberman, M.C.; Li, T. Usherin is required for maintenance of retinal photoreceptors and normal development of cochlear hair cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4413–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, D.C.; Komal, R.; Langel, J.; Ma, J.; Duy, P.Q.; Penzo, M.A.; Zhao, H.; Hattar, S. Retinal innervation tunes circuits that drive nonphotic entrainment to food. Nature 2020, 581, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Trujillo, A.; Hoang, N.; Robinson, L.; McCabe, C.J.; Conklin, D.; Minor, R.C.; Townsend, J.; Plaut, K.; George, U.Z.; Boerman, J.; et al. Effect of circadian system disruption on the concentration and daily oscillations of cortisol, progesterone, melatonin, serotonin, growth hormone, and core body temperature in periparturient dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 2651–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, R.J.; Tamura, H.; Tan, D.X.; Xu, X.Y. Melatonin and the circadian system: Contributions to successful female reproduction. Fertil. Steril. 2014, 102, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, T.; Jensen, M.K.; Slavney, A.; Deane, P.E.; Milano, A.; Raghavan, V.; Ford, B.; Chu, E.T.; Sams, A.J.; Boyko, A.R. R-locus for roaned coat is associated with a tandem duplication in an intronic region of USH2A in dogs and also contributes to Dalmatian spotting. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Tobin, D.J.; Shibahara, S.; Wortsman, J. Melanin pigmentation in mammalian skin and its hormonal regulation. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 1155–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunryd, J.C.; Cheon, B.; Graham, J.B.; Giorda, K.M.; Fissore, R.A.; Hebert, D.N. TMTC1 and TMTC2 are novel endoplasmic reticulum tetratricopeptide repeat-containing adapter proteins involved in calcium homeostasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 16085–16099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherardi, G.; Weiser, A.; Bermont, F.; Migliavacca, E.; Brinon, B.; Jacot, G.E.; Hermant, A.; Sturlese, M.; Nogara, L.; Vascon, F.; et al. Mitochondrial calcium uptake declines during aging and is directly activated by oleuropein to boost energy metabolism and skeletal muscle performance. Cell Metab. 2025, 37, 477–495.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Cole, J.B.; Freebern, E.; Da, Y.; VanRaden, P.M.; Ma, L. Functional annotation and Bayesian fine-mapping reveals candidate genes for important agronomic traits in Holstein bulls. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, B.; Chen, Y.; Gao, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L.; Gao, H.; et al. The eQTL colocalization and transcriptome-wide association study identify potentially causal genes responsible for economic traits in Simmental beef cattle. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 14, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, I.G.; Kumar, P.; Lichtenberg, J.; Wang, P.; Yu, J.; Phillips, J.D.; Kane, M.A.; Bodine, D.; Hamza, I. MRP5 and MRP9 play a concerted role in male reproduction and mitochondrial function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2111617119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dersh, D.; Phelan, J.D.; Gumina, M.E.; Wang, B.; Arbuckle, J.H.; Holly, J.; Kishton, R.J.; Markowitz, T.E.; Seedhom, M.O.; Fridlyand, N.; et al. Genome-wide Screens Identify Lineage- and Tumor-Specific Genes Modulating MHC-I- and MHC-II-Restricted Immunosurveillance of Human Lymphomas. Immunity 2021, 54, 116–131.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Yu, W.Y.; Dai, L.S.; Gao, Y.; Ding, Y.; Yu, X.F.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.B. Expression of microRNA-26b and identification of its target gene EphA2 in pituitary tissues in Yanbian cattle. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 5753–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Guo, X.; Glenn, A.S.; Vuguin, P.M.; Fiallo, A.; Du, Q.; Ko, Y.A.; Yu, Y.; Susztak, K.; et al. In Utero Exposure to a High-Fat Diet Programs Hepatic Hypermethylation and Gene Dysregulation and Development of Metabolic Syndrome in Male Mice. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 2860–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Chen, S.; Mi, B.; Qi, Y.; Jiao, C.; Zhang, M.; Dai, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, J.; Shi, B.; et al. Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Insights into Age-Related Changes in Lung Tissue of Yaks Under Highland Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feicht, J.; Jansen, R.P. The high-density lipoprotein binding protein HDLBP is an unusual RNA-binding protein with multiple roles in cancer and disease. RNA Biol. 2024, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobin, M.B.; Gerstberger, S.; Teupser, D.; Campana, B.; Charisse, K.; Heim, M.H.; Manoharan, M.; Tuschl, T.; Stoffel, M. The RNA-binding protein vigilin regulates VLDL secretion through modulation of Apob mRNA translation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Q.; Li, L.; Zhao, B.; Shi, W.; Hao, X.; Zhang, L.; Miao, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, Q.; Zheng, N. The network regulation mechanism of the effects of heat stress on the production performance and egg quality of Jinding duck was analyzed by miRNA-mRNA. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Qin, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, Z.; Hao, R.; Zhang, S.; Yang, S.; Wang, L.; Cui, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Serum Biochemical Parameters, Rumen Fermentation, and Rumen Bacterial Communities Are Partly Driven by the Breed and Sex of Cattle When Fed High-Grain Diet. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Liu, X.; Xie, P.; Lei, Y.; Yu, H.; Han, A.; Xie, L.; Jia, H.; Lin, S.; Bai, Y. Characterization of volatile profiles and correlated contributing compounds in pan-fried steaks from different Chinese yellow cattle breeds through GC-Q-orbitrap, e-nose, and sensory evaluation. Molecules 2022, 27, 3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Bruce, H.; Kemp, R.A.; Charagu, P.; Miar, Y.; Yang, T.; Plastow, G. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) identify a QTL close to PRKAG3 affecting meat pH and colour in crossbred commercial pigs. BMC Genet. 2015, 16, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidaritabar, M.; Huisman, A.; Krivushin, K.; Stothard, P.; Dervishi, E.; Charagu, P.; Bink, M.; Plastow, G.S. Imputation to whole-genome sequence and its use in genome-wide association studies for pork colour traits in crossbred and purebred pigs. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 1022681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, G.; Chen, L.; Liu, G.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Yan, H.X.; Zhang, H.L.; Tang, J.; Yang, Y.C.; Lin, X.; et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase-2 (ALDH2) opposes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by regulating AMP-activated protein kinase signaling in mice. Hepatology 2017, 65, 1628–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.; Feng, X.; Yang, C.; Ma, C.; Niu, S.; Jia, L.; Yang, X.; Liang, J.; Bo, Y.; Geng, K.; et al. Simulated microgravity reduces quality of ovarian follicles and oocytes by disrupting communications of follicle cells. NPJ Microgravity 2023, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E, F.; Zhang, H.; Yin, W.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zou, C.; et al. CPEB3 deficiency in mice affect ovarian follicle development and causes premature ovarian insufficiency. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Mazzilli, M.; Pennarossa, G.; Brevini, T.A.; Zecconi, A.; Gandolfi, F. Chronic mastitis is associated with altered ovarian follicle development in dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 1885–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Wang, F.; He, C.; Zhang, L.; Tan, D.; Reiter, R.J.; Xu, J.; Ji, P.; Liu, G. Beneficial effects of melatonin on bovine oocytes maturation: A mechanistic approach. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 57, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Yu, S.; Mipam, T.; Yang, F.; Zhao, W.; Liu, W.; Cao, S.; Shen, L.; Zhao, F.; Sun, L.; et al. Comparative analysis of testis transcriptomes associated with male infertility in cattleyak. Theriogenology 2017, 88, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnicka-Turek, O.; Shirneshan, K.; Paprotta, I.; Grzmil, P.; Meinhardt, A.; Engel, W.; Adham, I.M. Inactivation of insulin-like factor 6 disrupts the progression of spermatogenesis at late meiotic prophase. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 4348–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakapenka, D.; Liang, Z.; Da, Y. Genome-Wide Association Study of Age at First Calving in U. S. Holst. Cows. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, D.A.; Ross, P.J. Similarities between bovine and human germline development revealed by single-cell RNA sequencing. Reproduction 2021, 161, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Angulo, B.; Xia, N.; Sukhwani, M.; Wang, Z.; Carey, C.C.; Mazurie, A.; Cui, J.; Wilkinson, R.; Wiedenheft, B.; et al. A PAX5-OCT4-PRDM1 developmental switch specifies human primordial germ cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nixon, B.; Bromfield, E.G.; Cui, J.; De Iuliis, G.N. Heat Shock Protein A2 (HSPA2): Regulatory Roles in Germ Cell Development and Sperm Function. Adv. Anat. Embryol. Cell Biol. 2017, 222, 67–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, L.; Zhang, P.; Yu, B.; Liu, Q.; Liu, C.; Lu, W.; Cheng, L.; Chen, H. Whole-Genome Sequencing Reveals the Role of Cis-Regulatory Elements and eQTL/sQTL in the Adaptive Selection of Hubei Indigenous Cattle. Animals 2025, 15, 1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091301
Shi L, Zhang P, Yu B, Liu Q, Liu C, Lu W, Cheng L, Chen H. Whole-Genome Sequencing Reveals the Role of Cis-Regulatory Elements and eQTL/sQTL in the Adaptive Selection of Hubei Indigenous Cattle. Animals. 2025; 15(9):1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091301
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Liangyu, Pu Zhang, Bo Yu, Qing Liu, Chenhui Liu, Wei Lu, Lei Cheng, and Hongbo Chen. 2025. "Whole-Genome Sequencing Reveals the Role of Cis-Regulatory Elements and eQTL/sQTL in the Adaptive Selection of Hubei Indigenous Cattle" Animals 15, no. 9: 1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091301
APA StyleShi, L., Zhang, P., Yu, B., Liu, Q., Liu, C., Lu, W., Cheng, L., & Chen, H. (2025). Whole-Genome Sequencing Reveals the Role of Cis-Regulatory Elements and eQTL/sQTL in the Adaptive Selection of Hubei Indigenous Cattle. Animals, 15(9), 1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091301






