- Review
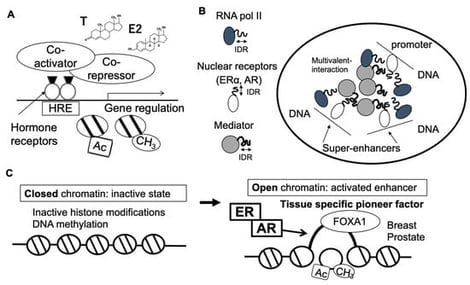
Sex steroid hormones play a pivotal role in maintaining systemic homeostasis throughout life. Their age-related decline is closely associated with the onset of frailty, including sarcopenia and dementia. Here, this article provides a narrative review of the existing literature about the multifaceted roles of sex steroid hormones, particularly estrogens and androgens, in aging and age-related diseases. Sex steroid action is mediated by nuclear receptors such as estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) and androgen receptor (AR). Transcriptional activation through these receptors is orchestrated by epigenetic mechanisms, including histone modifications and chromatin remodeling. Beyond their reproductive functions, sex hormones also influence systemic physiology, metabolism, immune responses, and neuroplasticity. Clinical studies on hormone-deprivation therapies for prostate and breast cancers, as well as animal models, have revealed the key contributions of AR and ER activity to muscle integrity, bone density, and cognitive function. The sexual dimorphism in cognitive decline, especially in postmenopausal women, suggests the therapeutic potential of hormone supplementation and receptor-targeted strategies. Thus, AR- and ER-associated genes are considered promising targets for preventing frailty, sarcopenia, osteoporosis, and dementia. This review summarizes the current knowledge on sex hormone signaling in aging, with an emphasis on translational implications and future research directions.
3 February 2026