Exploring Various Techniques for the Chemical and Biological Synthesis of Polymeric Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods for Producing PNPs
2.1. Formation of NPs from Preformed Polymers
2.1.1. Nanoprecipitation
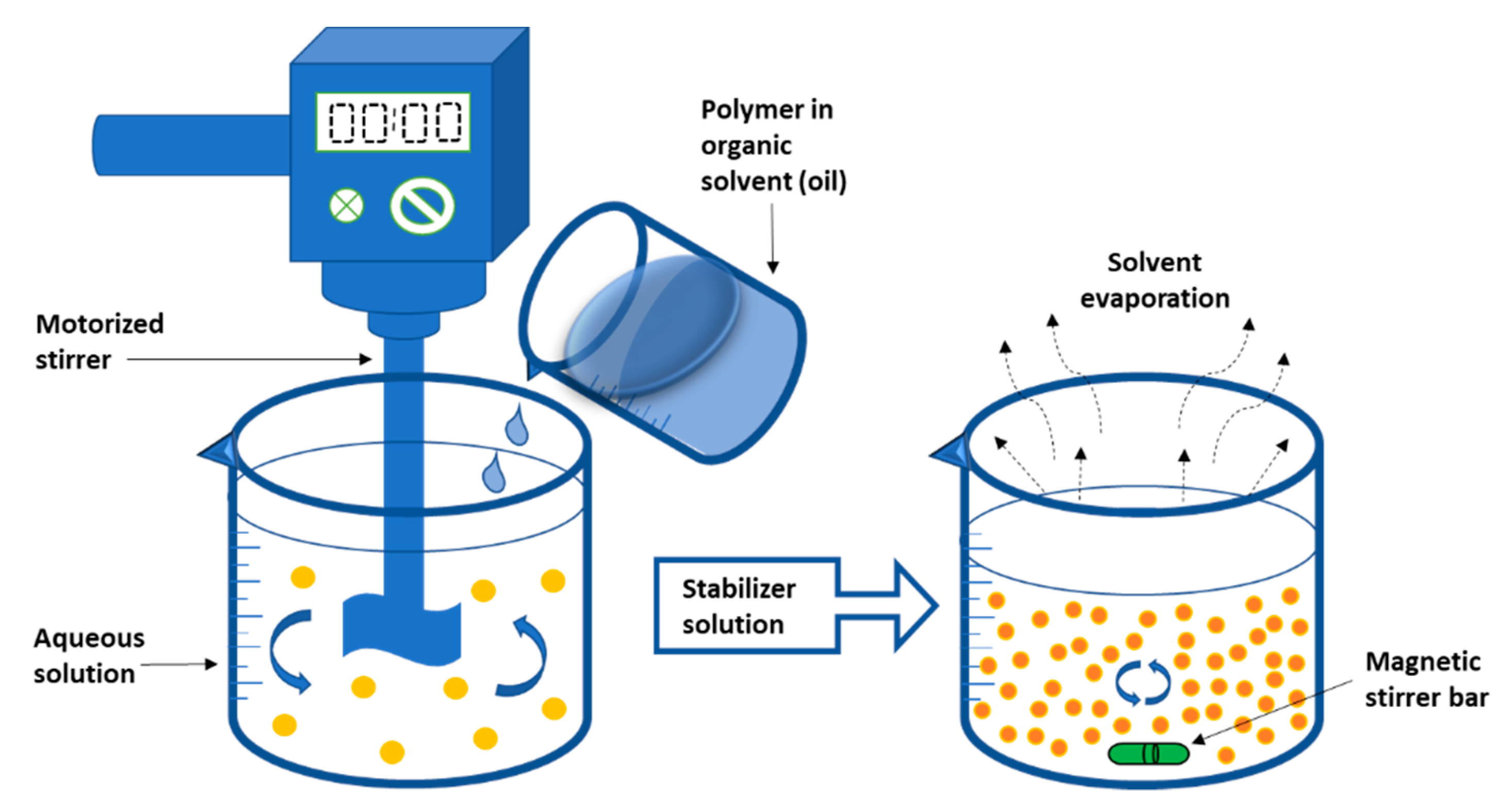
2.1.2. Emulsification-Solvent Evaporation
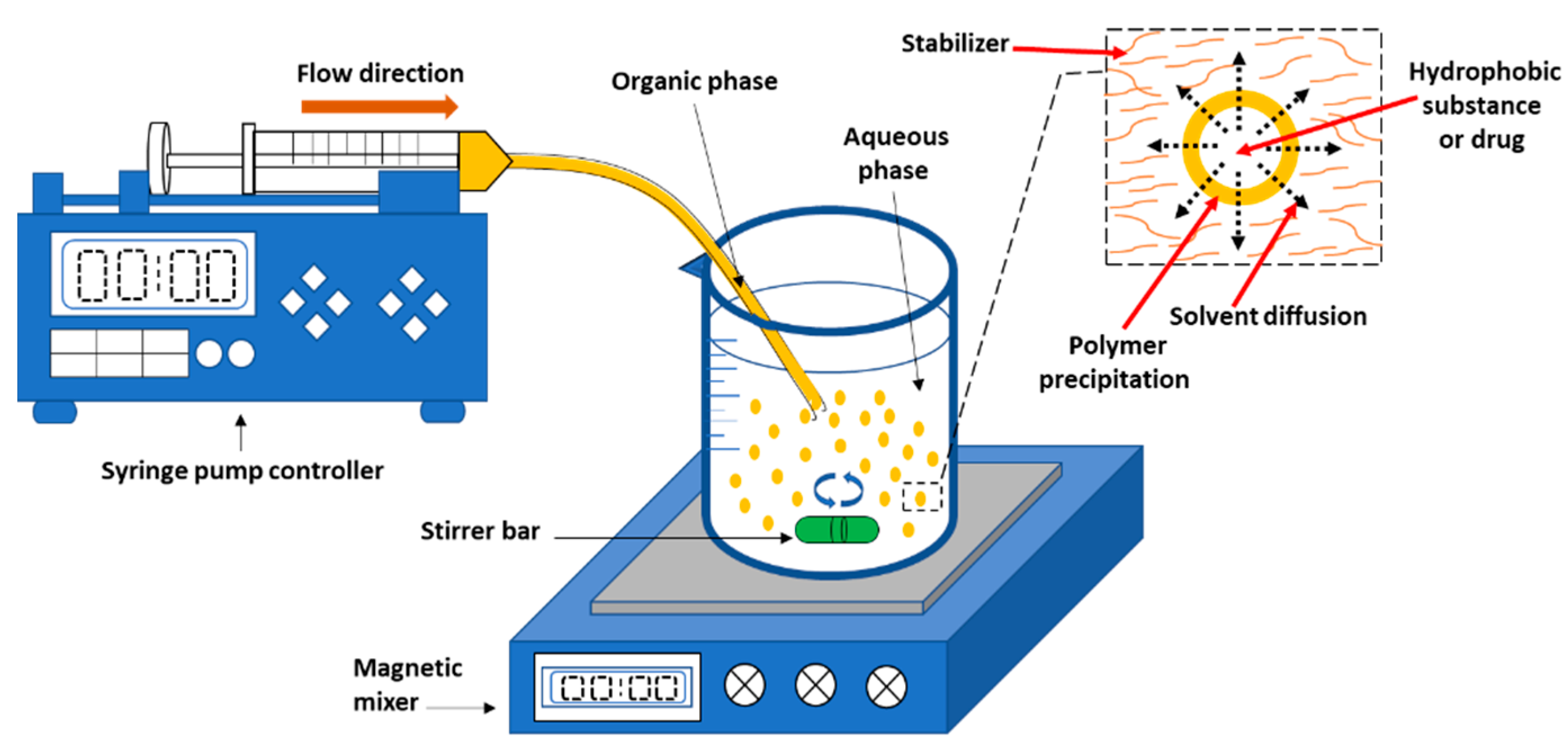
2.1.3. Emulsification Solvent Diffusion
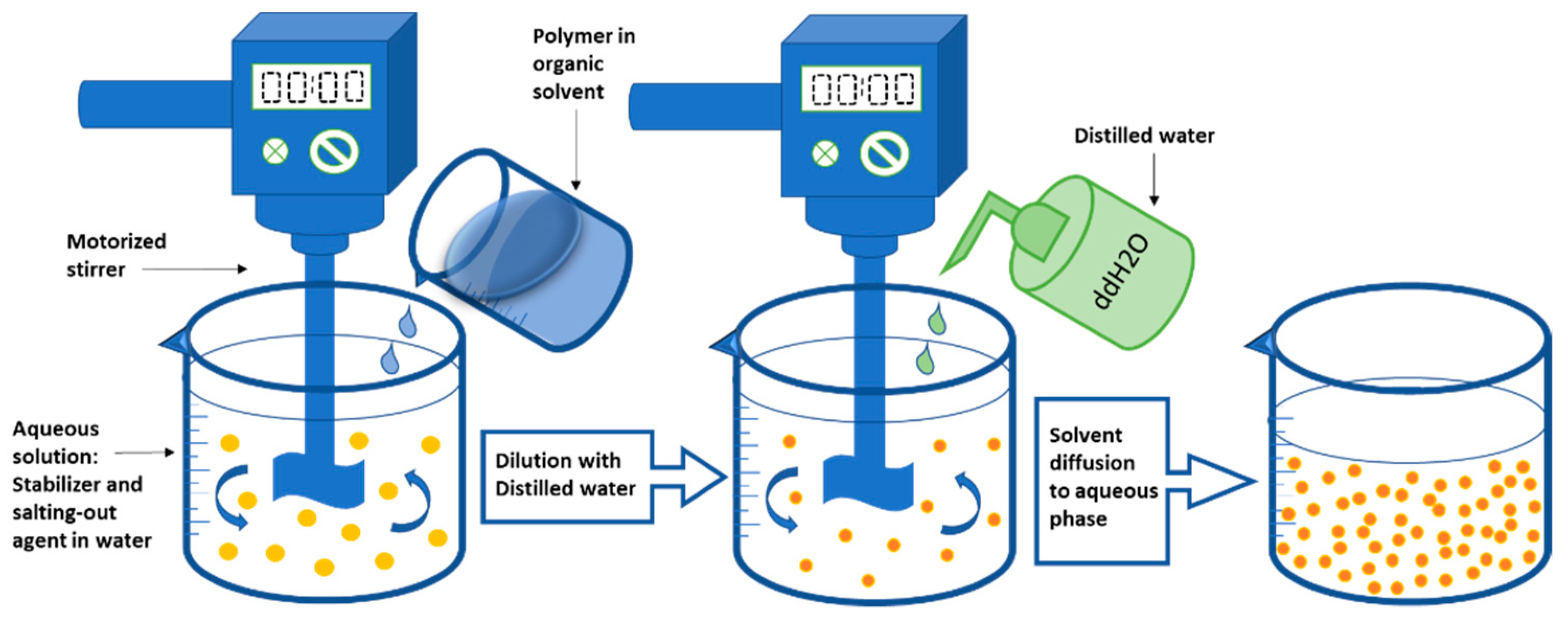
2.1.4. Salting-Out Technique
2.2. Formation of Nanoparticles by Polymerization of Monomers
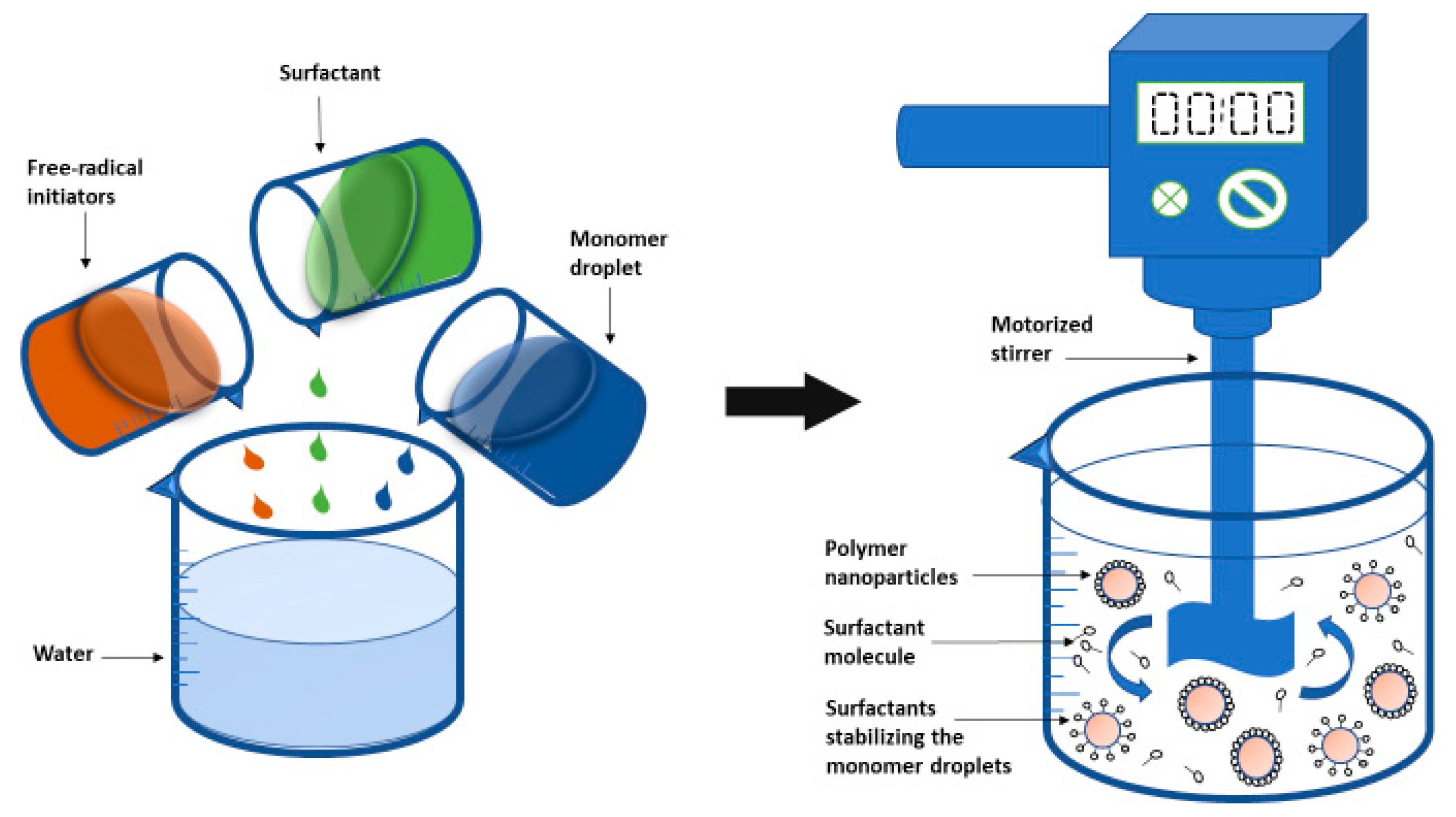
2.2.1. Emulsion Polymerization
2.2.2. Surfactant-Free Emulsion Polymerization
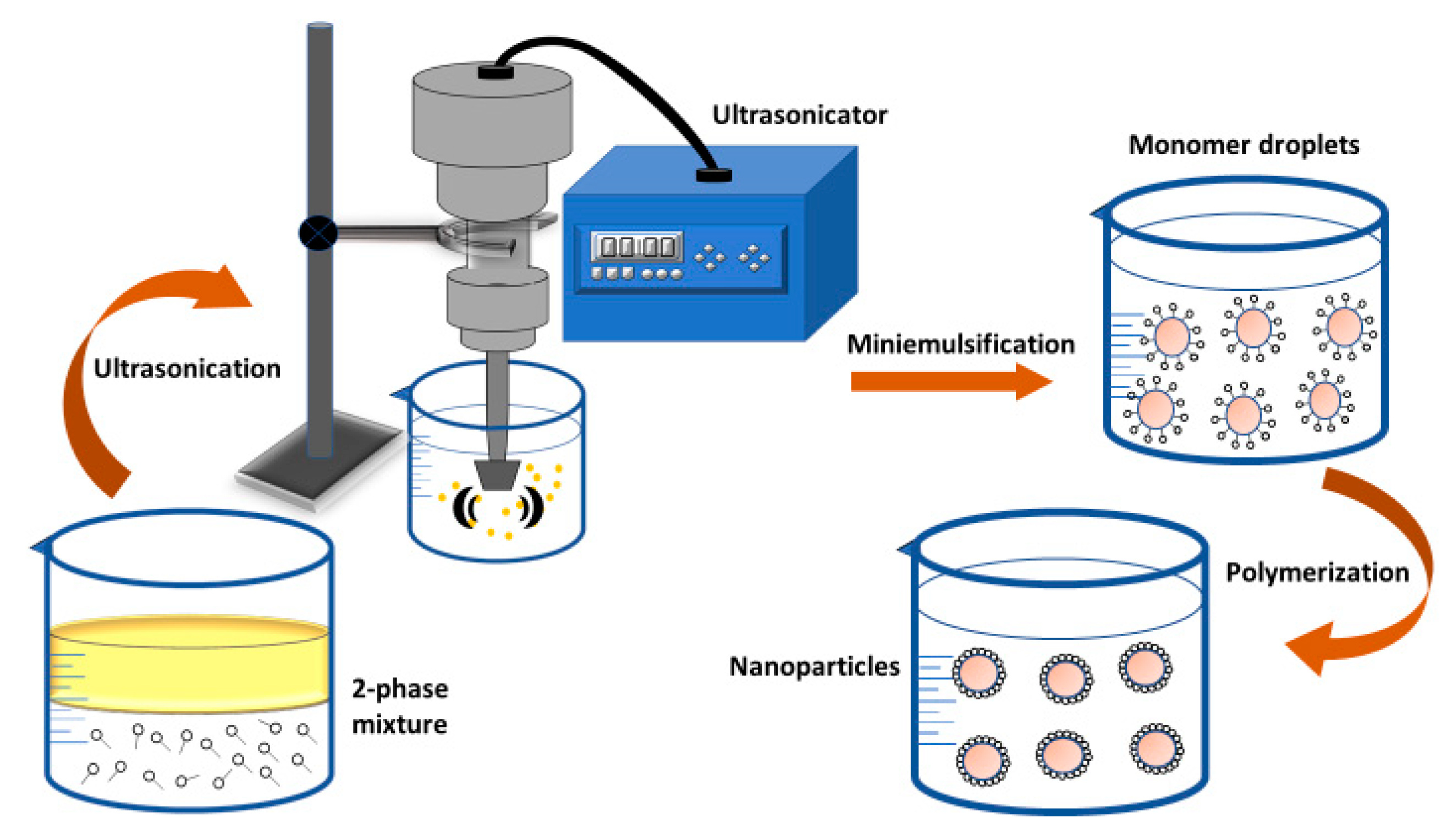
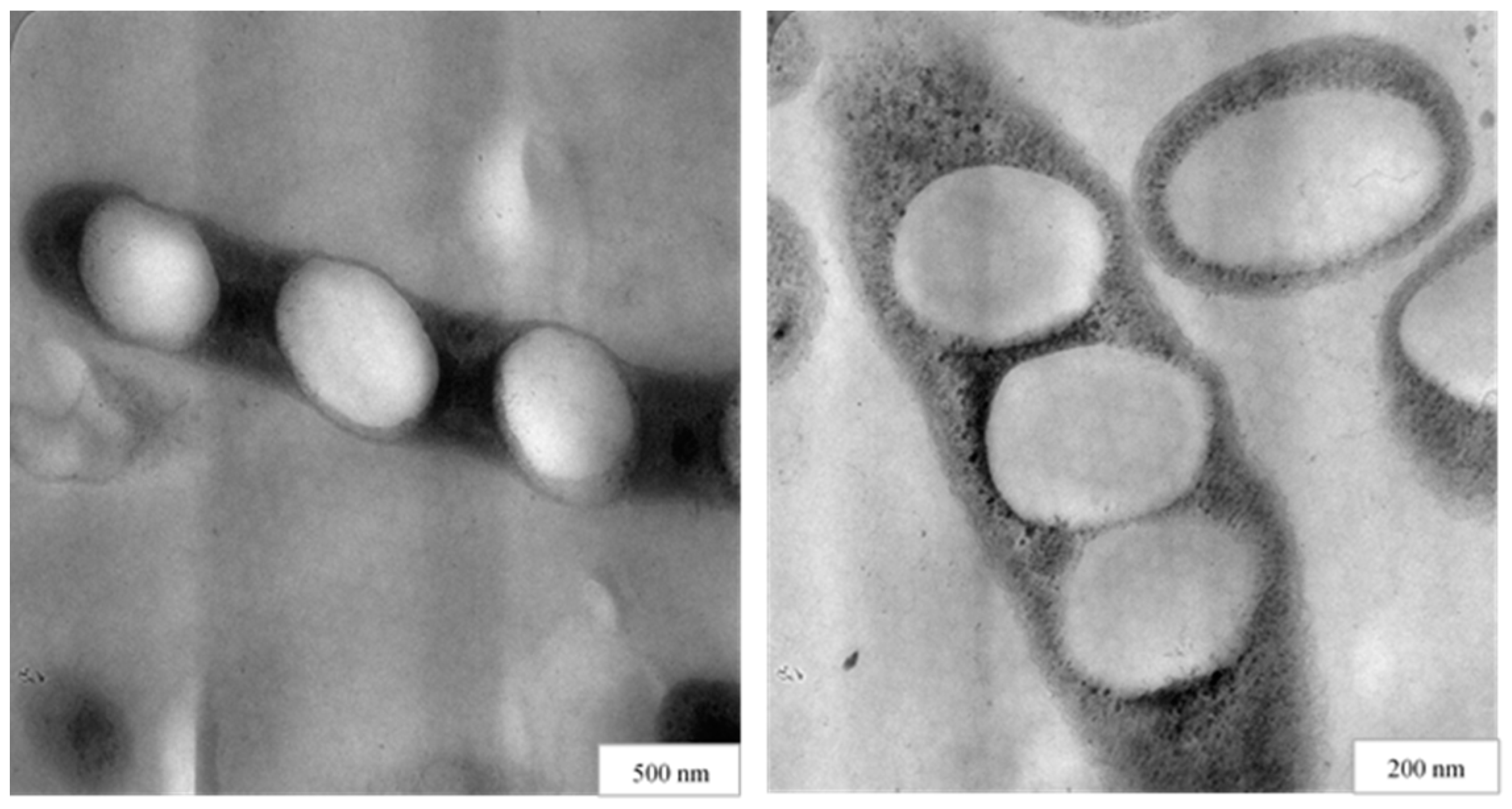
2.2.3. Mini-Emulsion Polymerization
2.2.4. Micro-Emulsion Polymerization
3. Biologically Synthesized Biodegradable Polyhydroxyalkanoate-Based Nanoparticles
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhatia, S. Nanoparticles Types, Classification, Characterization, Fabrication Methods and Drug Delivery Applications. In Natural Polymer Drug Delivery Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 33–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, A.; Tang, P.S.; Chan, W.C. The Effect of Nanoparticle Size, Shape, and Surface Chemistry on Biological Systems. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docter, D.; Strieth, S.; Westmeier, D.; Hayden, O.; Gao, M.; Knauer, S.K.; Stauber, R.H. No king without a crown—impact of the nanomaterial-protein corona on nanobiomedicine. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 503–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joye, I.J.; McClements, D.J. Production of Nanoparticles by Anti-Solvent Precipitation for Use in Food Systems. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 34, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Laurent, S.; Tawil, N.; Yahia, L.H.; Mahmoudi, M. Nanoparticle and Protein Corona. In Protein-nanoparticle interactions; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 21–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Lynch, I.; Ejtehadi, M.R.; Monopoli, M.P.; Bombelli, F.B.; Laurent, S. Protein−Nanoparticle Interactions: Opportunities and Challenges. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5610–5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezhilarasi, P.N.; Karthik, P.; Chhanwal, N.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Nanoencapsulation Techniques for Food Bioactive Components: A Review. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 628–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripriyalakshmi, S.; Jose, P.; Ravindran, A.; Anjali, C.H. Recent Trends in Drug Delivery System Using Protein Nanoparticles. Cell Biophys. 2014, 70, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifácio, B.V.; Silva, P.B.; Ramos, M.A.; Negri, K.M.; Bauab, T.M.; Chorilli, M. Nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems and herbal medicines: A review. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, J.; Takhistov, P.; McClements, D.J. Functional Materials in Food Nanotechnology. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, R107–R116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlbusch, T.A.; Asbach, C.; Fissan, H.; Göhler, D.; Stintz, M. Nanoparticle exposure at nanotechnology workplaces: A review. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2011, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanguansri, P.; Augustin, M.A. Nanoscale Materials Development–A Food Industry Perspective. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Ingle, A. Role of nanotechnology in agriculture with special reference to management of insect pests. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 94, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justin, C.; Philip, S.A.; Samrot, A.V. Synthesis and characterization of superparamagnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) and utilization of SPIONs in X-ray imaging. Appl. Nanosci. 2017, 7, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, P.; Hall, J.B.; McLeland, C.B.; Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; McNeil, S.E. Nanoparticle interaction with plasma proteins as it relates to particle biodistribution, biocompatibility and therapeutic efficacy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharazian, B.; Hadipour, N.; Ejtehadi, M. Understanding the nanoparticle–protein corona complexes using computational and experimental methods. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 75, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöttler, S.; Landfester, K.; Mailänder, V. Controlling the Stealth Effect of Nanocarriers through Understanding the Protein Corona. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 8806–8815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirshafiee, V.; Mahmoudi, M.; Lou, K.; Cheng, J.; Kraft, M.L. Protein corona significantly reduces active targeting yield. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 2557–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K.; Choi, E.-J.; Webster, T.J.; Kim, S.-H.; Khang, D. Effect of the protein corona on nanoparticles for modulating cytotoxicity and immunotoxicity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 10, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rak, J. Microparticles in Cancer. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2010, 36, 888–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mause, S.F.; Weber, C. Microparticles. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, S.A.; Saleh, A.M. Applications of nanoparticle systems in drug delivery technology. Saudi Pharm. J. 2017, 26, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenthamara, D.; Subramaniam, S.; Ramakrishnan, S.G.; Krishnaswamy, S.; Essa, M.M.; Lin, F.H.; Qoronfleh, M.W. Therapeutic efficacy of nanoparticles and routes of administration. Biomater. Res. 2019, 23, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Peng, Z.; Seven, E.S.; Leblanc, R.M. Crossing the blood-brain barrier with nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2017, 270, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Ahmad, E.; Zaman, M.; Qadeer, A.; Rabbani, G. Nanoparticles in relation to peptide and protein aggregation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 899–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magazù, S.; Migliardo, F.; Telling, M. Structural and dynamical properties of water in sugar mixtures. Food Chem. 2008, 106, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samrot, A.; Burman, U.; Philip, S.A.; Shobana, N.; Chandrasekaran, K. Synthesis of curcumin loaded polymeric nanoparticles from crab shell derived chitosan for drug delivery. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2018, 10, 159–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panhwar, A.H.; Tuzen, M.; Hazer, B.; Kazi, T.G. Solid phase microextraction method using a novel polystyrene oleic acid imidazole polymer in micropipette tip of syringe system for speciation and determination of antimony in environmental and food samples. Talanta 2018, 184, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honarkar, H.; Barikani, M. Applications of Biopolymers I: Chitosan. Monatsh. Chem. 2009, 140, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A.; Tuzen, M.; Sarı, A. Polyamide magnetic palygorskite for the simultaneous removal of Hg(II) and methyl mercury; with factorial design analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 211, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, A.; Kausar, A.; Younus, A. A Review on Preparation, Properties and Applications of Polymeric Nanoparticle-Based Materials. Polym. Technol. Eng. 2014, 54, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geckeler, K.E.; Nishide, H. Advanced Nanomaterials; Wiley Online Library: Weinheim, Germany, 2010; Volume 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derman, S.; Kizilbey, K.; Akdeste, Z.M. Polymeric Nanoparticles. Sigma J. Eng. Nat. Sci. 2013, 31, 107–120. [Google Scholar]
- Öztürk, K. Serbest Radikal Temizleyici Madde İçeren Nanopartiküler Taşıyıcı Sistemlerin Tasarımı Ve Değerlendirilmesi. Master’s Thesis, Hacettepe University, Ankara, Turkey, 2010. Available online: http://nek.istanbul.edu.tr:4444/ekos/TEZ/47041.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Wang, Y.-J.; Larsson, M.; Huang, W.-T.; Chiou, S.-H.; Nicholls, S.J.; Chao, J.-I.; Liu, D.-M. The use of polymer-based nanoparticles and nanostructured materials in treatment and diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases: Recent advances and emerging designs. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 57, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.-W.; Edirisinghe, M.; Stride, E. Ultrasound mediated release from stimuli-responsive core–shell capsules. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 3962–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, R.H.; Keck, C.M. Challenges and Solutions for the Delivery of Biotech Drugs–A Review of Drug Nanocrystal Technology and Lipid Nanoparticles. J. Biotechnol. 2004, 113, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, C.; Neufeld, R.J.; Ribeiro, A.; Veiga, F. Nanoencapsulation, I. Methods for preparation of drug-loaded polymeric nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2006, 2, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.G.; Burdick, J.A.; Langer, R. Smart Biomaterials. Science 2004, 305, 1923–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klodzinska, S.N.; Wan, F.; Jumaa, H.; Sternberg, C.; Rades, T.; Nielsen, H.M. Improved drug loading and antibacterial activity of minocycline-loaded PLGA nanoparticles prepared by solid/oil/water ion pairing method. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornig, S.; Heinze, T.; Becer, C.R.; Schubert, U.S. Synthetic polymeric nanoparticles by nanoprecipitation. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 3838–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarwal, R.C.; Kant, S.; Singh, P.N.; Maiti, P.; Pandit, J.K. Polymeric nanoparticulate system: A potential approach for ocular drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2009, 136, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Vega, A.-I.; Gómez-Quintero, T.; Nuñez-Anita, R.E.; Acosta-Torres, L.-S.; Castaño, V. Polymeric and Ceramic Nanoparticles in Biomedical Applications. J. Nanotechnol. 2012, 2012, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, H.K.; Almokdad, A.A.; Shaluf, S.I.; Debe, M.S. Polymer-Based Nanomaterials for Drug-Delivery Carriers. In Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 531–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailaja, A.K. A Review on Biomedical Applications of Polymeric Nanoparticles. Drug Des. Intellect. Prop. Int. J. 2018, 2, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, S.; Misra, R.; Sahoo, S.K. Nanoparticles: A Boon to Drug Delivery, Therapeutics, Diagnostics and Imaging. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2012, 8, 147–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, W.H.; Borm, P.J.A. Drug delivery and Nanoparticles: Applications and Hazards. Int. J. Nanomed. 2008, 3, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos, E.V.R.; del Pilar Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S.; et al. Nano based drug delivery systems: Recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatello, R.; Impallomeni, G.; Cupri, S.; Puzzo, G.; Curcio, C.; Rizzo, M.G.; Guglielmino, S.; Ballistreri, A. Unsaturated Poly(Hydroxyalkanoates) for the Production of Nanoparticles and the Effect of Cross-Linking on Nanoparticle Features. Materials 2019, 12, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umesh, M.; Priyanka, K.; Thazeem, B.; Preethi, K. Biogenic PHA nanoparticle synthesis and characterization from Bacillus subtilis NCDC0671 using orange peel medium. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2017, 67, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koosha, F.; Muller, R.; Washington, C. Production of Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) Nanoparticles for Drug Targeting. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1987, 39, 136P. [Google Scholar]
- Koosha, F.; Muller, R.; Davis, S.S.; Davies, M.C. The surface chemical structure of poly(β-hydroxybutyrate) microparticles produced by solvent evaporation process. J. Control. Release 1989, 9, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyler, I.; Appel, M.; Devissaguet, J.-P.; Legrand, P.; Barratt, G. Macrophage Activation by a Lipophilic Derivative of Muramyldipeptide within Nanocapsules: Investigation of the Mechanism of Drug Delivery. J. Nanopart. Res. 1999, 1, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, P.; Lesieur, S.; Bochot, A.; Gref, R.; Raatjes, W.; Barratt, G.; Vauthier, C. Influence of polymer behaviour in organic solution on the production of polylactide nanoparticles by nanoprecipitation. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 344, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, M.; Kreuter, J. Optimization of the preparation of loperamide-loaded poly (L-lactide) nanoparticles by high pressure emulsification-solvent evaporation. J. Microencapsul. 1997, 14, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehilla, B.J.; Bergkvist, M.; Popat, K.C.; Desai, T.A. Purified and surfactant-free coenzyme Q10-loaded biodegradable nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 348, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yallapu, M.M.; Gupta, B.K.; Jaggi, M.; Chauhan, S.C. Fabrication of curcumin encapsulated PLGA nanoparticles for improved therapeutic effects in metastatic cancer cells. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 351, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, L.B.; Huber, S.C.; Barnabé, A.; Bassora, F.D.S.; Paixão, D.S.; Durán, N.; Annichino-Bizzacchi, J.M. Characterization of PCL and Chitosan Nanoparticles as Carriers of Enoxaparin and Its Antithrombotic Effect in Animal Models of Venous Thrombosis. J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 2017, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajiboye, A.L.; Trivedi, V.; Mitchell, J. Preparation of polycaprolactone nanoparticles via supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of emulsions. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2017, 8, 1790–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri, N.; Javar, H.A.; Fouladdel, S.; Khalaj, A.; Khoshayand, M.R.; Dinarvand, R.; Atyabi, F.; Nomani, A.; Azizi, E. Preparation and Evaluation of Poly (Caprolactone Fumarate) Nanoparticles Containing Doxorubicin HCl. Daru J. Fac. Pharm. Tehran Univ. Med. Sci. 2011, 19, 12–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kateb, B.; Chiu, K.; Black, K.L.; Yamamoto, V.; Khalsa, B.; Ljubimova, J.Y.; Ding, H.; Patil, R.; Portilla-Arias, J.A.; Modo, M.; et al. Nanoplatforms for constructing new approaches to cancer treatment, imaging, and drug delivery: What should be the policy? NeuroImage 2011, 54, S106–S124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, H.M.; Sohn, M.; Al-Ghananeem, A.; DeLuca, P.P. Materials for Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms: Molecular Pharmaceutics and Controlled Release Drug Delivery Aspects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 3298–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, S.; Kundu, J.; Kundu, S.C. Biopolymeric Nanoparticles. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2010, 11, 014104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, A. The use of mucoadhesive polymers in ocular drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1595–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanz-Landázuri, A.; Portilla-Arias, J.; De Ilarduya, A.M.; Álvarez, M.G.; Holler, E.; Ljubimova, J.; Muñoz-Guerra, S. Nanoparticles of Esterified Polymalic Acid for Controlled Anticancer Drug Release. Macromol. Biosci. 2014, 14, 1325–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Loyer, P.; Cammas-Marion, S. Natural and synthetic poly(malic acid)-based derivates: A family of versatile biopolymers for the design of drug nanocarriers. J. Drug Target. 2014, 22, 556–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutul, T.; Rusu, E.; Condur, N.; Ursaki, V.; Goncearenco, E.; Vlazan, P. Preparation of poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone)-stabilized ZnO colloid nanoparticles. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, A.; Solanki, P.; Mitra, S. Curcuminoid-loaded poly(methyl methacrylate) nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, A.N.; Hubber, I.; Siqueira, M.; Barbosa, G.M.; Moreira, D.D.L.; Holandino, C.; Pinto, J.C.; Nele, M. Preparation and Cytotoxicity of Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) Nanoparticles for Drug Encapsulation. Macromol. Symp. 2012, 319, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasen, S.; Chong, S.-F.; Wohl, B.M.; Goldie, K.N.; Zelikin, A.N. Poly(vinyl alcohol) Physical Hydrogel Nanoparticles, Not Polymer Solutions, Exert Inhibition of Nitric Oxide Synthesis in Cultured Macrophages. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 1687–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madlova, M.; Jones, S.; Zwerschke, I.; Ma, Y.; Hider, R.; Forbes, B. Poly(vinyl alcohol) nanoparticle stability in biological media and uptake in respiratory epithelial cell layers in vitro. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 72, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Ding, Y.; Ge, H.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, C. Synthesis and characterization of chitosan–poly(acrylic acid) nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 3193–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, R.M.; Bodnar, M.; Hartmann, J.F.; Borbely, J. Preparation and characterization of poly(acrylic acid)-based nanoparticles. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2009, 287, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualdesi, M.; Igarzabal, C.A.; Vara, J.; Ortiz, C. Synthesis and physicochemical properties of polyacrylamide nanoparticles as photosensitizer carriers. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 512, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuntini, F.; Dumoulin, F.; Daly, R.; Ahsen, V.; Scanlan, E.M.; Lavado, A.S.P.; Aylott, J.W.; Rosser, G.A.; Beeby, A.; Boyle, R.W. Orthogonally bifunctionalised polyacrylamide nanoparticles: A support for the assembly of multifunctional nanodevices. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 2034–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Muñoz, R.; Treviño, M.E.; Morales, G.; Valdez-Garza, J.A.; de León, R.D.; Saade, H.; Enríquez-Medrano, F.J.; López, R.G. Ultrafine Nanoparticles of Poly(Methyl Methacrylate-co-Methacrylic Acid) Loaded with Aspirin. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.X.; Clegg, J.R.; Ander, E.W.; Peppas, N.A. Tunable poly(methacrylic acid-co-acrylamide) nanoparticles through inverse emulsion polymerization. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2018, 106, 1677–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Tran, T.T.-D.; Zhang, J.; Kong, L. Manufacturing Techniques and Surface Engineering of Polymer Based Nanoparticles for Targeted Drug Delivery to Cancer. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, A.; Carreiró, F.; Oliveira, A.; Neves, A.; Pires, B.; Venkatesh, D.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Eder, P.; Silva, A.; et al. Polymeric Nanoparticles: Production, Characterization, Toxicology and Ecotoxicology. Molecules 2020, 25, 3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crucho, C.I.C.; Barros, M.T. Polymeric nanoparticles: A study on the preparation variables and characterization methods. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 80, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibraheem, D.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A. DNA Encapsulation via Double Emulsion Like Process. J. Colloid Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 2, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, B.; Guo, T. Preparation of Eudragit L 100-55 enteric nanoparticles by a novel emulsion diffusion method. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 108, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranya, S.; Radha, K.V. Review of Nanobiopolymers for Controlled Drug Delivery. Polym. Technol. Eng. 2014, 53, 1636–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, I.M.; Moreira, M.M.; Neves, P.; Da Fé, T.; Gonçalves, L.M.; Almeida, P.J.; Rodrigues, J.A. An Insight on Salting-out Assisted Liquid-Liquid Extraction for Phytoanalysis. Phytochem. Anal. 2017, 28, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, A.M.; Zultanski, S.L.; Waldman, J.H.; Zhong, Y.-L.; Shevlin, M.; Peng, F. General Principles and Strategies for Salting-Out Informed by the Hofmeister Series. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2017, 21, 1355–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distler, D.; Neto, W.S.; Machado, F. Emulsion Polymerization. Ref. Modul. Mater. Sci. Mater. Eng. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamak, H.B. Emulsion Polymerization: Effects of Polymerization Variables on The Properties of Vinyl Acetate Based Emulsion Polymers. In Polymer Science; Yilmaz, F., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2013; pp. 35–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yao, H.; Ma, J. Recent advances in RAFT-mediated surfactant-free emulsion polymerization. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 2532–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgin, S.; Tomovska, R.; Asua, J.M. Surfactant-free high solids content polymer dispersions. Polymer 2017, 117, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faucheu, J.; Gauthier, C.; Chazeau, L.; Cavaillé, J.-Y.; Mellon, V.; Lami, E.B. Miniemulsion polymerization for synthesis of structured clay/polymer nanocomposites: Short review and recent advances. Polymer 2010, 51, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespy, D.; Landfester, K. Miniemulsion polymerization as a versatile tool for the synthesis of functionalized polymers. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2010, 6, 1132–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Zafar, N.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A. Double emulsion solvent evaporation techniques used for drug encapsulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 496, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa, N.; Peralta, R.; López, R.; Ramos, L.; Katime, I.; Cesteros, C.; Mendizábal, E.; Puig, J. A comparison of the characteristics of poly(vinyl acetate) latex with high solid content made by emulsion and semi-continuous microemulsion polymerization. Polymer 2001, 42, 6923–6928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehm, B.H.A. Bacterial polymers: Biosynthesis, modifications and applications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 578–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradali, M.F.; Rehm, B.H.A. Bacterial biopolymers: From pathogenesis to advanced materials. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Niu, A.; Peng, S.; Jiang, M.; Tu, Y.; Li, M.; Wu, C. Formation of Novel Polymeric Nanoparticles. Accounts Chem. Res. 2001, 34, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintanar-Guerrero, D.; Allémann, E.; Fessi, H.; Doelker, E. Preparation Techniques and Mechanisms of Formation of Biodegradable Nanoparticles from Preformed Polymers. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1998, 24, 1113–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couvreur, P.; Dubernet, C.; Puisieux, F. Controlled Drug Delivery with Nanoparticles: Current Possibilities and Future Trends. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1995, 41, 2–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, P.; Ren, W.; Xin, K.; Yang, Y.; Xie, C.; Yang, C.; Liu, Q.; Yu, L.; Jiang, X.; et al. Comparative studies of salinomycin-loaded nanoparticles prepared by nanoprecipitation and single emulsion method. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kumar, A.; Sawant, K. Encapsulation of exemestane in polycaprolactone nanoparticles: Optimization, characterization, and release kinetics. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2013, 4, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthi, C.; Kathiresan, K. Fabrication of Dual Drug Loaded Polymeric Nanosuspension: Incorporating Analytical Hierarchy Process and Data Envelopment Analysis in the Selection of A Suitable Method. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 5, 499–504. [Google Scholar]
- Mora-Huertas, C.E.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A. Polymer-based nanocapsules for drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 385, 113–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noriega-Peláez, E.K.; Mendoza-Muñoz, N.; Ganem-Quintanar, A.; Quintanar-Guerrero, D. Optimization of the emulsification and solvent displacement method for the preparation of solid lipid nanoparticles. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2010, 37, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, K.; Bugnicourt, E.; Latorre, M.; Jorda, M.; Echegoyen Sanz, Y.E.; Lagaron, J.M.; Miesbauer, O.; Bianchin, A.; Hankin, S.; Bölz, U.; et al. Review on the Processing and Properties of Polymer Nanocomposites and Nanocoatings and Their Applications in the Packaging, Automotive and Solar Energy Fields. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, A.D.; Beatrice, C.A.G. Polymer Nanocomposites with Different Types of Nanofiller. In Nanocomposites-Recent Evolutions; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 103–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parambath, A. Engineering of Biomaterials for Drug Delivery Systems: Beyond Polyethylene Glycol; Woodhead Publishing: Kidlington, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sailaja, A.K.; Shreya, M. Preparation and Characterization of Naproxen Loaded Niosomes by Ether Injection Method. Nano Biomed. Eng. 2018, 10, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuah, J.-A.; Kaplan, D.L.; Numata, K. Engineering Peptide-based Carriers for Drug and Gene Delivery. In Engineering in Translational Medicine; Springer: London, UK, 2013; pp. 667–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mascolo, D.; Basnett, P.; Palange, A.L.; Francardi, M.; Roy, I.; Decuzzi, P. Tuning core hydrophobicity of spherical polymeric nanoconstructs for docetaxel delivery. Polym. Int. 2016, 65, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshyar, N.; Gray, S.; Han, H.; Bao, G. The effect of nanoparticle size on in vivo pharmacokinetics and cellular interaction. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 673–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Trase, I.; Ren, M.; Duval, K.; Guo, X.; Chen, Z. Design of Nanoparticle-Based Carriers for Targeted Drug Delivery. Available online: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/jnm/2016/1087250/ (accessed on 14 February 2021).
- Ageitos, J.M.; Chuah, J.-A.; Numata, K. Chapter Design Considerations for Properties of Nanocarriers on Disposition and Efficiency of Drug and Gene Delivery. In Nanomedicines: Design, Delivery and Detection; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2016; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaram, M.; Krishnasamy, K. Application of Plackett-Burman Factorial Design in The Development of Curcumin Loaded Eudragit E 100 Nanoparticles. Nano Biomed. Eng. 2013, 5, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, J.; Santos, J.L.; Williford, J.-M.; Mao, H.-Q. Control of polymeric nanoparticle size to improve therapeutic delivery. J. Control. Release 2015, 219, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, Applications and Toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Serra, C.A.; Vandamme, T.F.; Yu, W.; Anton, N. Double Emulsions Prepared by Two–Step Emulsification: History, State-Of-The-Art and Perspective. J. Control. Release 2019, 295, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodarzi, F.; Zendehboudi, S. A Comprehensive Review on Emulsions and Emulsion Stability in Chemical and Energy Industries. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 97, 281–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubry, J.; Ganachaud, F.; Addad, J.-P.C.; Cabane, B. Nanoprecipitation of Polymethylmethacrylate by Solvent Shifting:Boundaries. Langmuir 2009, 25, 1970–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Huertas, C.E.; Garrigues, O.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A. Nanocapsules prepared via nanoprecipitation and emulsification–diffusion methods: Comparative study. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 80, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepeltier, E.; Bourgaux, C.; Couvreur, P. Nanoprecipitation and the “Ouzo effect”: Application to Drug Delivery Devices. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 71, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoyav, B.; Benny, O. Controlled and tunable polymer particles’ production using a single microfluidic device. Appl. Nanosci. 2018, 8, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vauthier, C.; Dubernet, C.; Fattal, E.; Pinto-Alphandary, H.; Couvreur, P. Poly(alkylcyanoacrylates) as biodegradable materials for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 519–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.; Patel, B.B.; Tiwari, S. Colloidal nanocarriers: A review on formulation technology, types and applications toward targeted drug delivery. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2010, 6, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshfeghi, A.A.; Peyman, G.A. Micro-and Nanoparticulates. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 2047–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Román, R.; Cavazos-Rodríguez, M.; Chávez-Montes, A.; Castro-Ríos, R.; Waksman de Torres, N.; Salazar-Cavazos, M.; Galindo Rodríguez, S. Formulación y caracterización de nanocápsulas con un antioxidante natural para su aplicación cutánea (Formulation and Characterization of Nanocapsules as a Natural Antioxidant for Cutaneous Application). Química Hoy (Chem. Sci.) 2011, 1, 29–35. Available online: http://eprints.uanl.mx/13446/1/Art6.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2021).
- Shi, W.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Yuan, Y.; Xing, E.-M.; Qin, Y.; Peng, Z.-J.; Zhang, Z.-P.; Yang, K.-Y. Optimization of parameters for preparation of docetaxel-loaded PLGA nanoparticles by nanoprecipitation method. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 33, 754–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.; Luo, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Q. Development and Application of Nanoparticles Synthesized with Folic Acid Conjugated Soy Protein. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 2556–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Kim, Y.S. Production of gliadin-poly(ethyl cyanoacrylate) nanoparticles for hydrophilic coating. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebouille, J.G.J.L.; Stepanyan, R.; Slot, J.J.M.; Stuart Cohen, M.A.; Tuinier, R. Nanoprecipitation of Polymers in a Bad Solvent. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 460, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthi, C.; Kathiresan, K. Fabrication of highly stable sonication assisted curcumin nanocrystals by nanoprecipitation method. Drug Inven. Today 2013, 5, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, Y. Structure Evolution of Curcumin Nanoprecipitation from a Micromixer. Cryst. Growth Des. 2010, 10, 1021–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltonen, L.; Aitta, J.; Hyvönen, S.; Karjalainen, M.; Hirvonen, J. Improved Entrapment Efficiency of Hydrophilic Drug Substance During Nanoprecipitation of Poly(I)Lactide Nanoparticles. AAPS PharmSciTech 2004, 5, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Lu, Y.; Qi, J.; Chen, L.; Hu, F.; Wu, W. Food proteins as novel nanosuspension stabilizers for poorly water-soluble drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 441, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Delgado, M.; Fu, A.; Alcouffe, P.; Gouin, S.G.; Fleury, E.; Katz, J.L.; Ganachaud, F.; Bernard, J. Simple but Precise Engineering of Functional Nanocapsules through Nanoprecipitation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 6910–6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, E.; Sah, H. Recent Trends in Preparation of Poly(lactide- co -glycolide) Nanoparticles by Mixing Polymeric Organic Solution with Antisolvent. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreras-Urbina, C.G.; Ramírez-Wong, B.; López-Ahumada, G.A.; Ibarra, S.E.B.; Martínez-Cruz, O.; Tapia-Hernández, J.A.; Félix, F.R. Nano- and Micro-Particles by Nanoprecipitation: Possible Application in the Food and Agricultural Industries. Int. J. Food Prop. 2016, 19, 1912–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.J.; Alshahrani, S. Nano-encapsulation and characterization of baricitinib using poly-lactic-glycolic acid co-polymer. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Madan, P.; Lin, S. Effect of process and formulation variables on the preparation of parenteral paclitaxel-loaded biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles: A co-surfactant study. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 11, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzoni, E.; Cesaretti, A.; Polchi, A.; Di Michele, A.; Tancini, B.; Emiliani, C. Biocompatible Polymer Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery Applications in Cancer and Neurodegenerative Disorder Therapies. J. Funct. Biomater. 2019, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Jallouli, Y.; Kroubi, M.; Yuan, X.-B.; Feng, W.; Kang, C.-S.; Pu, P.-Y.; Betbeder, D. Characterization of endocytosis of transferrin-coated PLGA nanoparticles by the blood–brain barrier. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 379, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, T.; Rom, A.; Nyska, A.; Benita, S. Novel double coated nanocapsules for intestinal delivery and enhanced oral bioavailability of tacrolimus, a P-gp substrate drug. J. Control. Release 2009, 133, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Assis, D.N.; Mosqueira, V.C.F.; Vilela, J.M.C.; Andrade, M.S.; Cardoso, V.N. Release Profiles and Morphological Characterization by Atomic Force Microscopy and Photon Correlation Spectroscopy of 99mTechnetium-Fluconazole Nanocapsules. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 349, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugheirbi, N.A.; Paluch, K.J.; Tajber, L. Heat induced evaporative antisolvent nanoprecipitation (HIEAN) of itraconazole. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 471, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salatin, S.; Barar, J.; Barzegar-Jalali, M.; Adibkia, K.; Kiafar, F.; Jelvehgari, M. Development of a nanoprecipitation method for the entrapment of a very water soluble drug into Eudragit RL nanoparticles. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, C. Tuning the Size of Poly(lactic-co-glycolic Acid) (PLGA) Nanoparticles Fabricated by Nanoprecipitation. Biotechnol. J. 2017, 13, 1700203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, F.; Esnaashari, S.S.; Mujokoro, B.; Dorkoosh, F.; Khosravani, M.; Adabi, M. Investigation of Effective Parameters on Size of Paclitaxel Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 8, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.K.; Patel, D.K.; Thakur, R.; Mishra, D.P.; Maiti, P.; Haldar, C. Anti-cancer evaluation of quercetin embedded PLA nanoparticles synthesized by emulsified nanoprecipitation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 75, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuddanda, P.R.; Mishra, A.; Singh, S.K. Development of polymeric nanoparticles with highly entrapped herbal hydrophilic drug using nanoprecipitation technique: An approach of quality by design. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2014, 20, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, A.; Ozturk, N.; Sarisozen, C.; Vural, I. Investigation of Formulation Parameters of PLGA Nanoparticles Prepared by Nanoprecipitation Technique. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Nanotechnology: Fundamentals and Application, Prague, Czech Republic, 11–13 August 2014; p. 94. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, P.; Vaysse, M.; Aubry, J.; Mariot, D.; Sonnier, R.; Ganachaud, F. Finest nanocomposite films from carbon nanotube-loaded poly(methyl methacrylate) nanoparticles obtained by the Ouzo effect. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 5528–5531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, K.S.; Sawant, K.K. Modified Nanoprecipitation Method for Preparation of Cytarabine-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Schneider, M. Improvement of Nanoprecipitation Technique for Preparation of Gelatin Nanoparticles and Potential Macromolecular Drug Loading. Macromol. Biosci. 2013, 13, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-Y.; Shen, Z.-G.; Zhong, J.; Hu, T.-T.; Chen, J.-F.; Ma, Z.-Q.; Yun, J. Preparation of amorphous cefuroxime axetil nanoparticles by controlled nanoprecipitation method without surfactants. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 323, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M. Factors Affecting Preparation and Properties of Nanoparticles by Nanoprecipitation Method. Indo Am. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 4, 4854–4858. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, J.; Fang, R.H.; Zhang, L. Preparation of Particulate Polymeric Therapeutics for Medical Applications. Small Methods 2017, 1, 1700147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilati, U.; Allémann, E.; Doelker, E. Development of a nanoprecipitation method intended for the entrapment of hydrophilic drugs into nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 24, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lince, F.; Marchisio, D.; Barresi, A. Strategies to control the particle size distribution of poly-ε-caprolactone nanoparticles for pharmaceutical applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 322, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, Y.C.; Luo, G.S. Modified nanoprecipitation method for polysulfone nanoparticles preparation. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 3414–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, A.M.; Jäger, E.; Jäger, A.; Stepánek, P.; Giacomelli, F.C. Physicochemical aspects behind the size of biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles: A step forward. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 436, 1092–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olenius, T.; Yli-Juuti, T.; Elm, J.; Kontkanen, J.; Riipinen, I. New Particle Formation and Growth: Creating a New Atmospheric Phase Interface. In Physical Chemistry of Gas-Liquid Interface; Faust, J.A., House, J.E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Chapter 11; pp. 315–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.C.; Vigil, R.; Fox, R. A competitive aggregation model for Flash NanoPrecipitation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 351, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.P.; Geckeler, K.E. Polymer nanoparticles: Preparation techniques and size-control parameters. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 887–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorny, M.; Fishbein, I.; Danenberg, H.D.; Golomb, G. Lipophilic drug loaded nanospheres prepared by nanoprecipitation: Effect of formulation variables on size, drug recovery and release kinetics. J. Control. Release 2002, 83, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, H.; Rostamizadeh, K.; Salari, D.; Hamidi, M. Preparation of biodegradable nanoparticles of tri-block PLA–PEG–PLA copolymer and determination of factors controlling the particle size using artificial neural network. J. Microencapsul. 2011, 28, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshamsan, A. Nanoprecipitation is more efficient than emulsion solvent evaporation method to encapsulate cucurbitacin I in PLGA nanoparticles. Saudi Pharm. J. 2013, 22, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.C.; Pramanik, S. Formulation and Characterization of Mefenamic Acid Loaded Polymeric Nanoparticles. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 3, 1391–1405. [Google Scholar]
- Lancheros, R.; Guerrero, C.A.; Godoy-Silva, R.D. Improvement of N-Acetylcysteine Loaded in PLGA Nanoparticles by Nanoprecipitation Method. J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 2018, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaram, M.; Krishnasamy, K. Modifications to the Conventional Nanoprecipitation Technique: An Approach to Fabricate Narrow Sized Polymeric Nanoparticles. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 4, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilati, U.; Allémann, E.; Doelker, E. Nanoprecipitation versus emulsion-based techniques for the encapsulation of proteins into biodegradable nanoparticles and process-related stability issues. AAPS PharmSciTech 2005, 6, E594–E604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Okubo, T.; Nangrejo, M.; Edirisinghe, M. Preparation of polymeric nanoparticles by novel electrospray nanoprecipitation. Polym. Int. 2014, 64, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.-X.; He, L.; Qiao, S.Z.; Middelberg, A.P. Nanoparticle synthesis in microreactors. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 1463–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heshmatnezhad, F.; Nazar, A.R.S. On-chip controlled synthesis of polycaprolactone nanoparticles using continuous-flow microfluidic devices. J. Flow Chem. 2020, 10, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, Q.; Ma, Y.; Sun, J. Microfluidic Methods for Fabrication and Engineering of Nanoparticle Drug Delivery Systems. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2019, 3, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, P.; Dawn, S.S.; Saipriya, C.; Samrot, A.V. Synthesis of polyhydroxybutyrate nanoparticles using surfactant (SPAN20) for hydrophobic drug delivery. Rasayan J. Chem. 2018, 11, 1686–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeri, F.; Shakeri, S.; Hojjatoleslami, M. Preparation and Characterization of Carvacrol Loaded Polyhydroxybutyrate Nanoparticles by Nanoprecipitation and Dialysis Methods. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, N697–N705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, N.; Benoit, J.-P.; Saulnier, P. Design and production of nanoparticles formulated from nano-emulsion templates—A review. J. Control. Release 2008, 128, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.L.; Jana, U.; Manna, P.K.; Mohanta, G.P.; Manavalan, R. Nanoparticle: An Overview of Preparation and Characterization. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 1, 228–234. [Google Scholar]
- Håkansson, A.; Rayner, M. General Principles of Nanoemulsion Formation by High-Energy Mechanical Methods. Nanoemulsions 2018, 103–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A.K.; Garg, T.; Bhandari, S.; Rath, G. Advancement in pulmonary drug delivery systems for treatment of tuberculosis. In Nanostructures for Drug Delivery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 669–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shi, A.; Agyei, D.; Wang, Q. Formulation of water-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) emulsions containing trans-resveratrol. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 35917–35927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauffer, F.; Peter, B.; Alem, H.; Funfschilling, D.; Dumas, N.; Serra, C.; Roques-Carmes, T. Polyelectrolytes layer-by-layer surface modification of PDMS microchips for the production of simple O/W and double W/O/W emulsions: From global to localized treatment. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2019, 146, 107685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadem, B.; Sheibat-Othman, N. Modeling droplets swelling and escape in double emulsions using population balance equations. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 382, 122824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadem, B.; Khellaf, M.; Sheibat-Othman, N. Investigating Swelling-Breakdown in Double Emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 585, 124181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Muñoz, N.; Alcalá-Alcalá, S.; Quintanar-Guerrero, D. Preparation of Polymer Nanoparticles by the Emulsification-Solvent Evaporation Method: From Vanderhoff’s Pioneer Approach to Recent Adaptations. In Polymer Nanoparticles for Nanomedicines; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 87–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Peng, Z.; She, F.H.; Kong, L.X. Microencapsulation of Nanoparticles with Enhanced Drug Loading for pH-Sensitive Oral Drug Delivery for the Treatment of Colon Cancer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosca, I.D.; Watari, F.; Uo, M. Microparticle formation and its mechanism in single and double emulsion solvent evaporation. J. Control. Release 2004, 99, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soppimath, K.S.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Kulkarni, A.R.; Rudzinski, W.E. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles as drug delivery devices. J. Control. Release 2001, 70, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisani, E.; Fattal, E.; Paris, J.; Ringard, C.; Rosilio, V.; Tsapis, N. Surfactant dependent morphology of polymeric capsules of perfluorooctyl bromide: Influence of polymer adsorption at the dichloromethane–water interface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 326, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.-I.; Cho, C.-S.; Kim, S.-H.; Ko, K.-S.; Kim, S.-I.; Shim, Y.-H.; Nah, J.-W. Preparation of poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles without surfactant. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 80, 2228–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staff, R.H.; Landfester, K.; Crespy, D. Recent Advances in the Emulsion Solvent Evaporation Technique for the Preparation of Nanoparticles and Nanocapsules. In Hierarchical Macromolecular Structures: 60 Years after the Staudinger Nobel Prize II; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, R.; Wagh, P.; Naik, J. Solvent evaporation and spray drying technique for micro- and nanospheres/particles preparation: A review. Dry. Technol. 2016, 34, 1758–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musyanovych, A.; Schmitz-Wienke, J.; Mailänder, V.; Walther, P.; Landfester, K. Preparation of Biodegradable Polymer Nanoparticles by Miniemulsion Technique and Their Cell Interactions. Macromol. Biosci. 2008, 8, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budhian, A.; Siegel, S.J.; Winey, K.I. Haloperidol-loaded PLGA nanoparticles: Systematic study of particle size and drug content. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 336, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilati, U.; Allémann, E.; Doelker, E. Sonication Parameters for the Preparation of Biodegradable Nanocapsules of Controlled Size by the Double Emulsion Method. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2003, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainardes, R.M.; Evangelista, R.C. Praziquantel-loaded PLGA nanoparticles: Preparation and characterization. J. Microencapsul. 2005, 22, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potineni, A.; Lynn, D.M.; Langer, R.; Amiji, M.M. Poly (Ethylene Oxide)-Modified Poly (β-amino ester) Nanoparticles as A pH-Sensitive Biodegradable System for Paclitaxel Delivery. J. Control. Release 2003, 86, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıçay, E.; Demirbilek, M.; Türk, M.; Güven, E.; Hazer, B.; Denkbas, E.B. Preparation and characterization of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) (PHBHHX) based nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 44, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Valour, J.-P.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A. Preparation of biodegradable PCL particles via double emulsion evaporation method using ultrasound technique. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2014, 293, 861–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, L. Folate-decorated Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-co-3-Hydroxyoctanoate) Nanoparticles for Targeting Delivery: Optimization and In Vivo Antitumor Activity. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 1830–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.-Y.; Li, M.; Zhu, X.-L.; Fan, F.; Wang, L.-L.; Ma, J.-G. Microbial synthesized biodegradable PHBHHxPEG hybrid copolymer as an efficient intracellular delivery nanocarrier for kinase inhibitor. BMC Biotechnol. 2014, 14, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.; Ullah, N.; Choi, M.H.; Kim, M.O.; Yoon, S.C. Amorphous Amphiphilic P(3HV-co-4HB)-b-mPEG Block Copolymer Synthesized from Bacterial Copolyester Via Melt Transesterification: Nanoparticle Preparation, Cisplatin-Loading for Cancer Therapy and In Vitro Evaluation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 80, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilicay, E.; Karahaliloglu, Z.; Hazer, B.; Tekin, I.; Denkbas, E.B. Concanavaline A conjugated bacterial polyester-based PHBHHx nanoparticles loaded with curcumin for breast cancer therapy. J. Microencapsul. 2016, 33, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, F.; Chen, P.; Yasin, T.; Fatima, N.; Hasan, F.; Hameed, A. Encapsulation of Ellipticine in poly-(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) based nanoparticles and its in vitro application. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 1054–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.; Ullah, N.; Choi, M.H.; Yoon, S.C. Nanoscale Poly(4-Hydroxybutyrate)-mPEG Carriers for Anticancer Drugs Delivery. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 8416–8421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben David-Naim, M.; Grad, E.; Aizik, G.; Nordling-David, M.M.; Moshel, O.; Granot, Z.; Golomb, G. Polymeric nanoparticles of siRNA prepared by a double-emulsion solvent-diffusion technique: Physicochemical properties, toxicity, biodistribution and efficacy in a mammary carcinoma mice model. Biomaterials 2017, 145, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, S.; Boyd, B.J.; McIntosh, M.P.; Pouton, C.W.; Kaminskas, L.M.; Whittaker, M. Suggested Procedures for The Reproducible Synthesis of Poly(d,l-Lactide-co-Glycolide) Nanoparticles using The Emulsification Solvent Diffusion Platform. Curr. Nanosci. 2018, 14, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baena-Aristizábal, C.M.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A.; Mora-Huertas, C.E. Biodegradable microparticles preparation by double emulsification—Solvent extraction method: A Systematic study. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 492, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, Y.; Sugihara, H.; Nishiura, A.; Kadota, K.; Tozuka, Y.; Takeuchi, H. Appropriate Selection of An Aggregation Inhibitor of Fine Particles Used for Inhalation Prepared by Emulsion Solvent Diffusion. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintanar-Guerrero, D.; Allémann, E.; Doelker, E.; Fessi, H. A mechanistic study of the formation of polymer nanoparticles by the emulsification-diffusion technique. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1997, 275, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanraj, V.; Chen, Y. Nanoparticles-A Review. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2006, 5, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagavarma, B.; Yadav, H.K.; Ayaz, A.; Vasudha, L.; Shivakumar, H. Different Techniques for Preparation of Polymeric Nanoparticles-A Review. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2012, 5, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, C.; Sanchez, A.; Putnam, D.; Ting, D.; Langer, R.; Alonso, M. Poly(lactic acid)-poly(ethylene glycol) nanoparticles as new carriers for the delivery of plasmid DNA. J. Control. Release 2001, 75, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Feng, P.; Ye, C.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y. An improved interfacial coacervation technique to fabricate biodegradable nanocapsules of an aqueous peptide solution from polylactide and its block copolymers with poly(ethylene glycol). Colloid Polym. Sci. 2001, 279, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassou, M. Modélisation et Simulation de la Formation des Nanocapsules Polymériques Par la Méthode D’émulsion-Diffusion. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Claude Bernard-Lyon I, Villeurbanne, France, 2007. Available online: https://tel.archives-ouvertes.fr/tel-00264755v2/document (accessed on 25 August 2021).
- Moinard-Chécot, D.; Chevalier, Y.; Briancon, S.; Beney, L.; Fessi, H. Mechanism of nanocapsules formation by the emulsion–diffusion process. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 317, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramual, S.; Assavanig, A.; Bergkvist, M.; Batt, C.A.; Sunintaboon, P.; Lirdprapamongkol, K.; Svasti, J.; Niamsiri, N. Development and characterization of bio-derived polyhydroxyalkanoate nanoparticles as a delivery system for hydrophobic photodynamic therapy agents. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2015, 27, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.-Y.; Ciraolo, E.; Stefenia, R.; Chen, G.-Q.; Zhang, Y.; Hirsch, E. Sustained release of PI3K inhibitor from PHA nanoparticles and in vitro growth inhibition of cancer cell lines. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 89, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yang, W.; Wang, D.-T.; Chen, C.-L.; Zhuang, Q.-Y.; Kong, X.-D. A modified spontaneous emulsification solvent diffusion method for the preparation of curcumin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles with enhanced in vitro anti-tumor activity. Front. Mater. Sci. 2014, 8, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinebretière, S.; Briancon, S.; Lieto, J.; Mayer, C.; Fessi, H. Study of the emulsion-diffusion of solvent: Preparation and characterization of nanocapsules. Drug Dev. Res. 2002, 57, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimaille, T.; Pichot, C.; Fessi, H.; Delair, T. Poly(d,l-lactic acid) nanoparticle preparation and colloidal characterization. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2003, 281, 1184–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surassmo, S.; Min, S.-G.; Bejrapha, P.; Choi, M.-J. Effects of surfactants on the physical properties of capsicum oleoresin-loaded nanocapsules formulated through the emulsion–diffusion method. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahana, D.; Mittal, G.; Bhardwaj, V.; Kumar, M. PLGA Nanoparticles for Oral Delivery of Hydrophobic Drugs: Influence of Organic Solvent on Nanoparticle Formation and Release Behavior In Vitro and In Vivo Using Estradiol as a Model Drug. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 1530–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K.; Swarnakar, N.K.; Godugu, C.; Singh, R.; Jain, S. The effect of the oral administration of polymeric nanoparticles on the efficacy and toxicity of tamoxifen. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, A.C.; Ferreira, P.; Cordeiro, R.A.; Mendonça, P.V.; Góis, J.R.; Gil, M.H.; Coelho, J.F.J. Drug Delivery Systems for Predictive Medicine: Polymers as Tools for Advanced Applications. In New Strategies to Advance Pre/Diabetes Care: Integrative Approach by PPPM; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 399–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xiong, X. Salting-Out Assisted Liquid–Liquid Extraction (SALLE) in LC-MS Bioanalysis. In Sample Preparation in LC-MS Bioanalysis; Li, W., Jian, W., Fu, Y., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Chapter 5; pp. 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, A.; Bose, R.; Kumar, A.; Mozumdar, S. Targeted Delivery of Pesticides Using Biodegradable Polymeric Nanoparticles; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Ma, L.; Sun, D.; Liu, L.; Qayum, A.; Jiang, Z.; Hou, J. Purification of lactoperoxidase from bovine milk by integrating the technique of salting-out extraction with cation exchange chromatographic separation. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2019, 13, 1400–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eley, J.G.; Pujari, V.D.; McLane, J. Poly (Lactide-co-Glycolide) Nanoparticles Containing Coumarin-6 for Suppository Delivery: In Vitro Release Profile and In Vivo Tissue Distribution. Drug Deliv. 2004, 11, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grumezescu, A.M. Drug Targeting and Stimuli Sensitive Drug Delivery Systems; William Andrew: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Niknafs, M.; Kaviani, R.; Gharekhani, A.; Jouyban, A.; Shayanfar, A. Salting-out liquid–liquid microextraction to the determination of mycophenolic acid in plasma samples. Chem. Pap. 2019, 74, 1663–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, M.; Shivanna, D.K.; Kamate, M.; AB, V.; Tp, K.-V. Single Lysis-Salting Out Method of Genomic DNA Extraction From Dried Blood Spots. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2016, 30, 1009–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Kawasaki, S.-I. Salting-out effects on vanillin extraction by supercritical carbon dioxide from aqueous vanillin solution containing salts. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2019, 152, 104550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.F.; Wang, Y.N.; Ma, J.B. Preparation of insulin nanoparticles and their encapsulation with biodegradable polyelectrolytes via the layer-by-layer adsorption. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 324, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeghere, F.; Allémann, E.; Feijen, J.; Kissel, T.; Doelker, E.; Gurny, R. Cellular Uptake of PEO Surface-Modified Nanoparticles: Evaluation of Nanoparticles Made of PLA: PEO Diblock and Triblock Copolymers. J. Drug Target. 2000, 8, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, K.; Hamid, Z.A. Polymer Nanoparticle Carriers in Drug Delivery Systems: Research Trend. In Applications of Nanocomposite Materials in Drug Delivery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Chapter 10; pp. 217–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.; Mody, N.; Sharma, R.; Agrawal, U.; Vyas, S.P. Nanobiomaterials: Novel Nanoplatforms for Protein and Peptide Delivery. In Nanobiomaterials in Drug Delivery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Chapter 4; pp. 111–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Grijpma, D.W.; Feijen, J. Poly(trimethylene carbonate) and monomethoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(trimethylene carbonate) nanoparticles for the controlled release of dexamethasone. J. Control. Release 2006, 111, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo-Rodriguez, S.; Allémann, E.; Fessi, H.; Doelker, E. Physicochemical Parameters Associated with Nanoparticle Formation in the Salting-Out, Emulsification-Diffusion, and Nanoprecipitation Methods. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 1428–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnasailaja, A.; Sarithareddy, A.; Abbaraju, K.; Aenugu, S. Preparation and Characterisation of Sulfasalazine Loaded Polymeric Nanoparticles by Salting Out Technique. J. Bionanosci. 2017, 11, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, W.; Bi, Y.; Cai, Z.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Hou, S. PLGA nanoparticles simultaneously loaded with vincristine sulfate and verapamil hydrochloride: Systematic study of particle size and drug entrapment efficiency. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 350, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konan, Y.N.; Gurny, R.; Allémann, E. Preparation and characterization of sterile and freeze-dried sub-200 nm nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 233, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazi, A.S.; Sailaja, A.K. Preparation and Characterization of Paracetamol Loaded Eudragit S100 Nanoparticles by Salting Out Technique. J. Dev. Drugs 2018, 7, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweers, M.L.; Engbers, G.H.; Grijpma, D.W.; Feijen, J. Release of anti-restenosis drugs from poly(ethylene oxide)-poly(dl-lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2006, 114, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweers, M.L.; Engbers, G.H.; Grijpma, D.W.; Feijen, J. In vitro degradation of nanoparticles prepared from polymers based on dl-lactide, glycolide and poly(ethylene oxide). J. Control. Release 2004, 100, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.A.; Allémann, E.; Schwach, G.; Doelker, E.; Gurny, R. Synthesis of A Novel Fluorescent Poly (D, L-Lactide) End-Capped with 1-Pyrenebutanol Used for The Preparation of Nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 20, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chern, C. Emulsion polymerization mechanisms and kinetics. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 443–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, G.; Rajagopalan, M.D.; Valluru, R.; Sridhar, K.A. Nanoparticles: A Novel Approach to Target Tumors. In Nano-and Microscale Drug Delivery Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Chapter 7; pp. 113–129. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Fang, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Xie, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, W. An Overview of Pickering Emulsions: Solid-Particle Materials, Classification, Morphology, and Applications. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, F.E.B. Emulsion Polymerization of Superhydrophobic Monomers. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Basque Country, Donostia-San Sebastian, Spain, 2017. Available online: https://addi.ehu.es/bitstream/handle/10810/24229/TESIS_BOSCAN_GUERRA_FREDDY%20ENRIQUE.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Khan, M.U.; Reddy, K.R.; Snguanwongchai, T.; Haque, E.; Gomes, V.G. Polymer brush synthesis on surface modified carbon nanotubes via in situ emulsion polymerization. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2016, 294, 1599–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharieh, A.; Khoee, S.; Mahdavian, A.R. Emulsion and miniemulsion techniques in preparation of polymer nanoparticles with versatile characteristics. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 269, 152–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Bonilla, A.; van Herk, A.M.; Heuts, J.P. Preparation of Hairy Particles and Antifouling Films using Brush-Type Amphiphilic Block Copolymer Surfactants in Emulsion Polymerization. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 2721–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garay-Jimenez, J.C.; Gergeres, D.; Young, A.; Lim, D.V.; Turos, E. Physical properties and biological activity of poly(butyl acrylate–styrene) nanoparticle emulsions prepared with conventional and polymerizable surfactants. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2009, 5, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Qu, R.; Forcada, J. Preparation of magnetic polymeric composite nanoparticles by seeded emulsion polymerization. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 770–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wu, C. Modified Structural Model for Predicting Particle Size in the Microemulsion and Emulsion Polymerization of Styrene under Microwave Irradiation. Langmuir 2004, 21, 782–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.; Santos, A.; Fortuny, M.; Araújo, P.; Sayer, C. Kinetic advantages of using microwaves in the emulsion polymerization of MMA. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.; He, Y. Ultrasonically irradiated emulsion polymerization of styrene in the presence of a polymeric surfactant. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 94, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.-J.; Chun, H.; Lee, M.-S.; Kim, N. Preparation of poly(N-vinylcarbazole) (PVK) nanoparticles by emulsion polymerization and PVK hollow particles. Synth. Met. 2009, 159, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeat-Lami, E.; França, A.J.P.G.; Chaparro, T.C.; Silva, R.D.; Dugas, P.-Y.; Alves, G.M.; Santos, A.M. Synthesis of Polymer/Silica Hybrid Latexes by Surfactant-Free RAFT-Mediated Emulsion Polymerization. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 4431–4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errezma, M.; Ben Mabrouk, A.; Magnin, A.; Dufresne, A.; Boufi, S. Surfactant-free emulsion Pickering polymerization stabilized by aldehyde-functionalized cellulose nanocrystals. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 202, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farias-Cepeda, L.; Herrera-Ordonez, J.; Estevez, M.; Luna-Barcenas, G.; Rosales-Marines, L. New Insights on surfactant-free styrene emulsion polymerization in The presence of sodium styrene sulfonate. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2016, 294, 1571–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahiner, N.; Sengel, S.B. Surfactant Free Synthesis and Characterization of Poly(Vinyl Carbazole) Microgel and its Chemical Modifications. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 514, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, H.J.; Park, I.J.; Lee, S.G.; Ha, J.-W.; Lee, S.-B.; Sohn, E.-H. Surfactant-free preparation of poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanoparticle dispersions and their use as surface coating agents. Green Chem. 2017, 20, 502–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassim, S.; Zahari, S.B.; Tahrin, R.A.A.; Harun, N.A. Co-polymerization of methyl methacrylate and styrene via surfactant-free emulsion polymerization, as a potential material for photonic crystal application. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1885, 20018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Thomas, H.; Zhu, X.; Möller, M. Inclusion of Phase-Change Materials in Submicron Silica Capsules Using a Surfactant-Free Emulsion Approach. Langmuir 2018, 34, 10397–10406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Tang, W.; Hawker, C.J.; Stucky, G.D. One-Step Microwave Preparation of Well-Defined and Functionalized Polymeric Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 15054–15055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, T.; Don, T. Synthesis and characterization of poly(methyl methacrylate) nanoparticles by emulsifier-free emulsion polymerization with a redox-initiated system. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 109, 3622–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.F.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, H.J.; Kim, C.A. Synthesis and electrorheological response of nano-sized laponite stabilized poly(methyl methacrylate) spheres. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2009, 287, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camli, S.T.; Buyukserin, F.; Balci, O.; Budak, G.G. Size controlled synthesis of sub-100nm monodisperse poly(methylmethacrylate) nanoparticles using surfactant-free emulsion polymerization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 344, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Zhong, S.; Wang, H. Emulsifier-free core–shell polyacrylate latex nanoparticles containing fluorine and silicon in shell. Polymer 2007, 48, 7241–7248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faridi-Majidi, R.; Sharifi-Sanjani, N. Emulsifier-free miniemulsion polymerization of styrene and the investigation of encapsulation of nanoparticles with polystyrene via this procedure using an anionic initiator. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 105, 1244–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, N.; Bereli, N.; Akgöl, S.; Denizli, A. High capacity binding of antibodies by poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate) nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2008, 67, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Lee, S.J.; Jung, Y.J.; Kim, J.H. Fabrication of nano-structured polythiophene nanoparticles in aqueous dispersion. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2008, 8, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, H.; Ziener, U.; Landfester, K. Formation of Polyimide Nanoparticles in Heterophase with an Ionic Liquid as Continuous Phase. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 7846–7853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Cho, H.G.; Park, C.R. Fabrication of Unagglomerated Polypyrrole Nanospheres with Controlled Sizes From a Surfactant-Free Emulsion System. Langmuir 2009, 25, 9030–9036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engström, J.; Brett, C.J.; Körstgens, V.; Müller-Buschbaum, P.; Ohm, W.; Malmström, E.; Roth, S.V. Core–Shell Nanoparticle Interface and Wetting Properties. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1907720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedzior, S.A.; Marway, H.S.; Cranston, E.D. Tailoring Cellulose Nanocrystal and Surfactant Behavior in Miniemulsion Polymerization. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 2645–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauman, N.; Zaquen, N.; Junkers, T.; Boyer, C.; Zetterlund, P.B. Particle Size Control in Miniemulsion Polymerization via Membrane Emulsification. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 4492–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.S.J.; Negrell, C.; Ladmiral, V.; Lai-Kee-Him, J.; Bron, P.; Lacroix-Desmazes, P.; Joly-Duhamel, C.; Caillol, S. Cardanol-based polymer latex by radical aqueous miniemulsion polymerization. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 2468–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Smith, K.W. Miniemulsion Polymerization to Prepare Drag Reducers. US20110184121A1, 24 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Landfester, K.; Antonietti, M. The polymerization of acrylonitrile in miniemulsions: “Crumpled latex particles” or polymer nanocrystals. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2000, 21, 820–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landfester, K.; Willert, M.; Antonietti, M. Preparation of Polymer Particles in Nonaqueous Direct and Inverse Miniemulsions. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 2370–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chern, C.-S.; Sheu, J.-C. Effects of carboxylic monomers on the styrene miniemulsion polymerizations stabilized by SDS/alkyl methacrylates. Polymer 2001, 42, 2349–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, J.L.; Gallardo, V.; Gómez-Lopera, S.A.; Plaza, R.; Delgado, A. Synthesis and characterization of poly(ethyl-2-cyanoacrylate) nanoparticles with a magnetic core. J. Control. Release 2001, 77, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, H.T.; Choi, Y.S.; Chee, M.G.; Chung, I.J. Singlewall carbon nanotubes covered with polystyrene nanoparticles byin-situ miniemulsion polymerization. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2005, 44, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, A.; Landfester, K.; Musyanovych, A. Synthesis of phosphonate-functionalized polystyrene and poly(methyl methacrylate) particles and their kinetic behavior in miniemulsion polymerization. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2009, 287, 1261–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- van Herk, A.; Forcada, J.; Pastorin, G. Synthetic Strategies for Synthesis of Polymer Nanoparticles. In Controlled Release Systems; Jenny Stanford Publishing: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; Chapter 5; pp. 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzio, R.A.; Marcato, Y.L.; Gomez, M.L.; Waiman, C.V.; Chesta, C.A.; Palacios, R.E. Crosslinked polymer nanoparticles containing single conjugated polymer chains. Methods Appl. Fluoresc. 2017, 5, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghayempour, S.; Montazer, M. A modified microemulsion method for fabrication of hydrogel Tragacanth nanofibers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cankaya, N. Recent Research in Polymerization; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, J.E.; Rabelero, M. Semicontinuous Microemulsion Polymerization. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 25, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candau, F.; Anquetil, J.-Y. New Developments in Polymerization in Bicontinuous Microemulsions. In Micelles, Microemulsions, and Monolayers; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2018; pp. 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarov, Y.; Capek, I. Kinetic events of (micro)emulsion polymerization of styrene. Polym. Bull. 2019, 77, 4851–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Ramírez, L.G.; Nuño-Donlucas, S.M.; Cesteros, L.C.; Katime, I. Novel Functionalized Nanohydrogels, Synthesis and Some Applications. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. IOP Publ. 2008, 127, 012010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa, N.; Zaragoza, E.A.; Lopez, R.G.; Peralta, R.D.; Katime, I.; Becerra, F.; Mendizabal, E.; Puig, J.E. Unusual Free Radical Polymerization of Vinyl Acetate in Anionic Microemulsion Media. Langmuir 2000, 16, 3612–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrère, M.; da Silva, S.C.; Balic, R.; Ganachaud, F. Synthesis of Monodisperse Poly(dimethylsiloxane) Micro- and Macroemulsions. Langmuir 2001, 18, 941–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanson, K.D.; Kaler, E.W. Kinetics and Mechanism of the Multiple Addition Microemulsion Polymerization of Hexyl Methacrylate. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 1836–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-J.; Chen, F. Semi-Continuous Emulsion Copolymerization of Butyl Methacrylate with Polymerizable Anionic Surfactants. Polymer 2004, 45, 4801–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Oh, J.H.; Stucky, G.D. Fabrication of Ultrafine Conducting Polymer and Graphite Nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 4016–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, A.G.; López, R.G.; Tauer, K. Studies on Semibatch Microemulsion Polymerization of Butyl Acrylate: Influence of the Potassium Peroxodisulfate Concentration. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 2738–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Murphy, M.; Li, C.; Ting, K.; Soo, C.; Zheng, Z. Current development of biodegradable polymeric materials for biomedical applications. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 12, 3117–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, P.Q.; Courchesne, N.M.D.; Duraj-Thatte, A.; Praveschotinunt, P.; Joshi, N.S. Engineered Living Materials: Prospects and Challenges for Using Biological Systems to Direct the Assembly of Smart Materials. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, S. Biological nanoparticles and their influence on organisms. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 28, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertici, G. Introduction to Bioresorbable Polymers for Biomedical Applications. In Bioresorbable polymers for Biomedical Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Chapter 1; pp. 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroe, A.; Chek, M.F.; Hakoshima, T.; Sudesh, K.; Taguchi, S. Synthesis of Polyesters III: Acyltransferase as Catalyst. In Enzymatic Polymerization towards Green Polymer Chemistry; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 199–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zain, N.-A.A.; Ng, L.-M.; Foong, C.P.; Tai, Y.T.; Nanthini, J.; Sudesh, K. Complete Genome Sequence of a Novel Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) Producer, Jeongeupia sp. USM3 (JCM 19920) and Characterization of Its PHA Synthases. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourmentza, C.; Plácido, J.; Venetsaneas, N.; Burniol-Figols, A.; Varrone, C.; Gavala, H.N.; Reis, M.A.M. Recent Advances and Challenges towards Sustainable Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) Production. Bioengineering 2017, 4, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukheem, A.; Hossain, M.; Shahabuddin, S.; Muthoosamy, K.; Manickam, S.; Sudesh, K.; Saidur, R.; Sridewi, N.; Campus, N.M. Bioplastic Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): Recent Advances in Modification and Medical Applications. arXiv 2018, arXiv:10.20944/preprints201808.0271.v1. Available online: https://europepmc.org/article/ppr/ppr48118 (accessed on 30 August 2021).
- Chek, M.F.; Hiroe, A.; Hakoshima, T.; Sudesh, K.; Taguchi, S. PHA synthase (PhaC): Interpreting the functions of bioplastic-producing enzyme from a structural perspective. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 103, 1131–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestro, B.; Sanz, J.M. Polyhydroxyalkanoate-Associated Phasins as Phylogenetically Heterogeneous, Multipurpose Proteins. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1323–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokamura, A.; Fujino, K.; Isoda, Y.; Arizono, K.; Shiratsuchi, H.; Matsusaki, H. Characterization and identification of the proteins bound to two types of polyhydroxyalkanoate granules in Pseudomonas sp. 61-3. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2015, 79, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinjaski, N.; Prieto, M.A. Smart polyhydroxyalkanoate nanobeads by protein based functionalization. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2015, 11, 885–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Carmona, E.; Villaverde, A. Nanostructured bacterial materials for innovative medicines. Trends Microbiol. 2010, 18, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, M.J.M. Biodegradable and Biocompatible Polyhydroxy-alkanoates (PHA): Auspicious Microbial Macromolecules for Pharmaceutical and Therapeutic Applications. Molecules 2018, 23, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, P.; Lee, W.-H.; Loo, C.-Y.; Wong, H.S.J.; Parumasivam, T. Advances in Polyhydroxyalkanoate Nanocarriers for Effective Drug Delivery: An Overview and Challenges. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.F.; Martin, D.P. Applications of Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) in Medicine and Pharmacy. Biopolym 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.-C.; Zhan, X.-Y.; Zhang, J.; Zou, X.-H.; Wang, Z.-H.; Xiong, Y.-C.; Chen, J.; Chen, G.-Q. A specific drug targeting system based on polyhydroxyalkanoate granule binding protein PhaP fused with targeted cell ligands. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4823–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Errico, C.; Bartoli, C.; Chiellini, F.; Chiellini, E. Poly(hydroxyalkanoates)-Based Polymeric Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2009, 2009, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishatskaya, E.I.; Goreva, A.V.; Voinova, O.N.; Inzhevatkin, E.V.; Khlebopros, R.G.; Volova, T.G. Evaluation of antitumor activity of rubomycin deposited in absorbable polymeric microparticles. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2008, 145, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, L.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lin, J.; Chen, Z. Folate-mediated poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyoctanoate) nanoparticles for targeting drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 76, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gursel, I.; Yagmurlu, F.; Korkusuz, F.; Hasirci, V. In vitro antibiotic release from poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) rods. J. Microencapsul. 2002, 19, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Azghani, A.O.; Omri, A. Antimicrobial efficacy of a new antibiotic-loaded poly(hydroxybutyric-co-hydroxyvaleric acid) controlled release system. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 54, 1013–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Itoh, Y.; Hosaka, Y.; Kobayashi, I.; Nakano, Y.; Maeda, I.; Umeda, F.; Yamakawa, J.; Nishimine, M.; Suenobu, T. Mechanism of Enhancement Effect of Dendrimer on Transdermal Drug Permeation Through Polyhydroxyalkanoate Matrix. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2003, 96, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Method | Advantages | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dispersion of preformed polymers | |||
| nanoprecipitation | Requires low energy Reproducible Single step Scalability | Size of NPs can be affected by stirring rate Low efficiency of drug encapsulation | [78,79] |
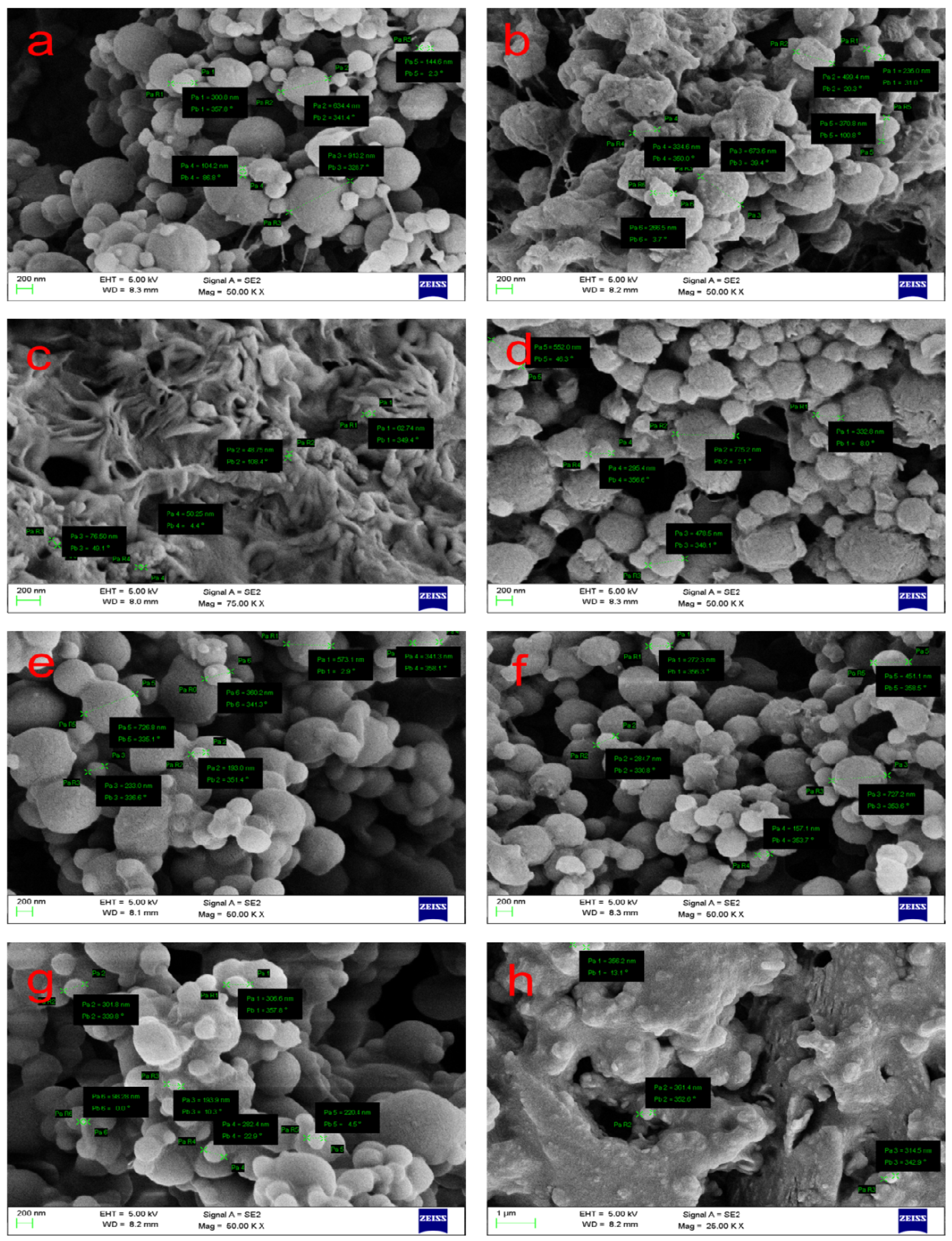
| emulsification solvent evaporation | Scalability Single step emulsion for hydrophobic agents Double or multiple step emulsion for hydrophilic agents | Requires heating or vacuum for evaporation Residual solvent or stabilizer Not stable | [80,81] |
| emulsification solvent diffusion | Does not require homogenizer High reproducibility Easy to scale up | Uses high volumes of water Probable leakage of water-soluble drugs into external phase Lower efficiency in lipophilic drug encapsulation | [82,83] |
| salting out | Does not require heating Avoids chlorinated solvents Suitable for DNA, RNA, and proteins | Requires high speed homogenization Exclusive for the encapsulation of lipophilic drugs Time-consuming Limited scalability | [84,85] |
| Direct polymerization | |||
| emulsion | Produce polymers with high molar mass Uses water as dispersion medium Excellent heat dissipation | Requires removal of surfactant Time consuming High cost | [86,87] |
| surfactant-free emulsion | Does not require surfactant Simple and green process Uses water-soluble initiators | Requires the preparation of monodisperse and uniformly distributed particle sizes | [88,89] |
| mini emulsion | Uses a low molecular mass co-stabilizer Small particle size Low volume of surfactant | Uses a high-shear device Surfactant is retained in the polymer | [90,91] |
| micro-emulsion | Uses water-soluble initiators Thermodynamically stable | Formation of empty micelles Destabilized microdroplets Increased particle size Requires a high ratio of surfactant | [92,93] |
| microbial | Non-toxic Eco-friendly Biocompatible | High production cost | [94,95] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pulingam, T.; Foroozandeh, P.; Chuah, J.-A.; Sudesh, K. Exploring Various Techniques for the Chemical and Biological Synthesis of Polymeric Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030576
Pulingam T, Foroozandeh P, Chuah J-A, Sudesh K. Exploring Various Techniques for the Chemical and Biological Synthesis of Polymeric Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(3):576. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030576
Chicago/Turabian StylePulingam, Thiruchelvi, Parisa Foroozandeh, Jo-Ann Chuah, and Kumar Sudesh. 2022. "Exploring Various Techniques for the Chemical and Biological Synthesis of Polymeric Nanoparticles" Nanomaterials 12, no. 3: 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030576
APA StylePulingam, T., Foroozandeh, P., Chuah, J.-A., & Sudesh, K. (2022). Exploring Various Techniques for the Chemical and Biological Synthesis of Polymeric Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials, 12(3), 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030576






