Multi-Objective Antenna Design Based on BP Neural Network Surrogate Model Optimized by Improved Sparrow Search Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Problem Description
3. Improved Sparrow Search Algorithm
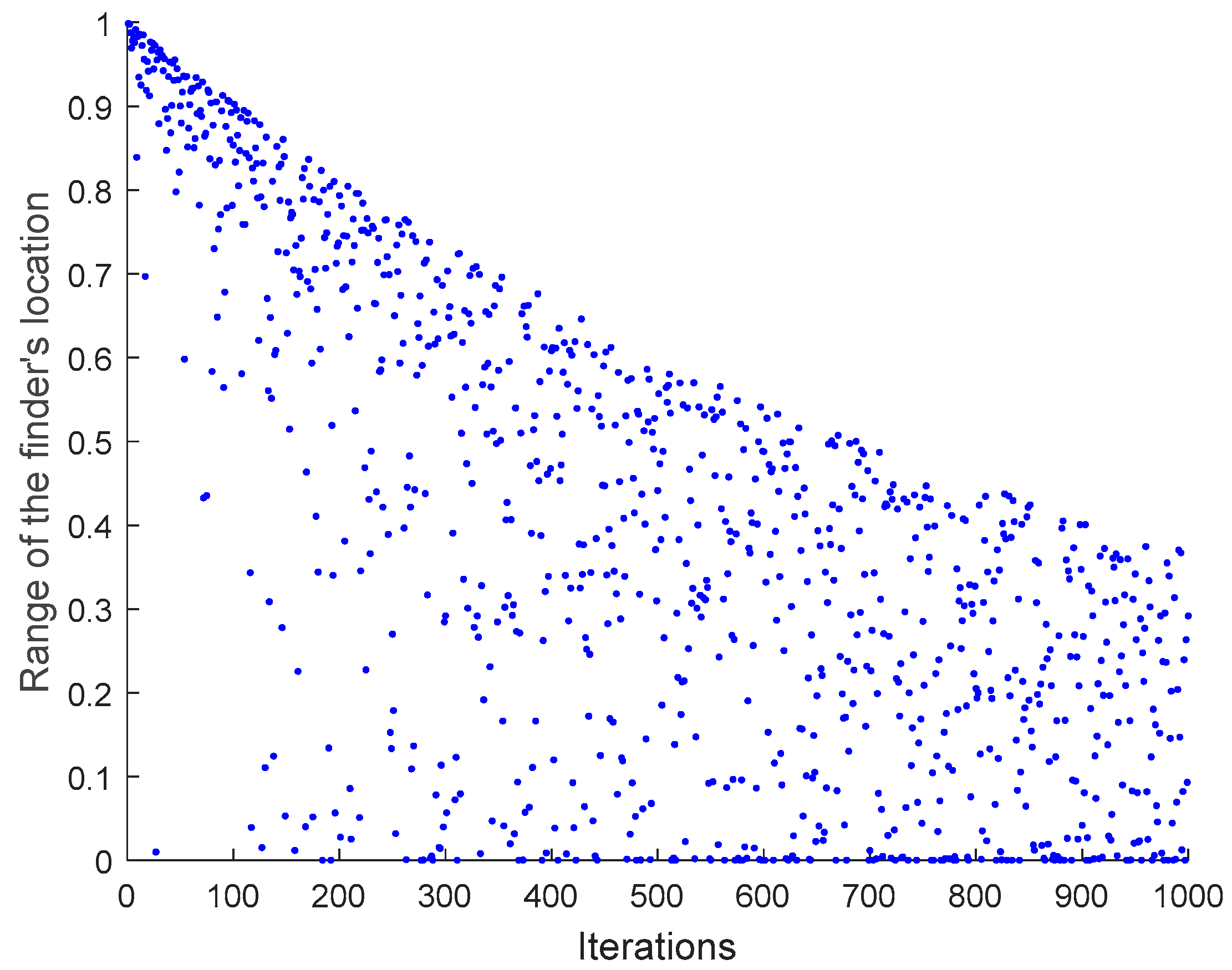
3.1. Sparrow Search Algorithm
3.2. Improved Strategies
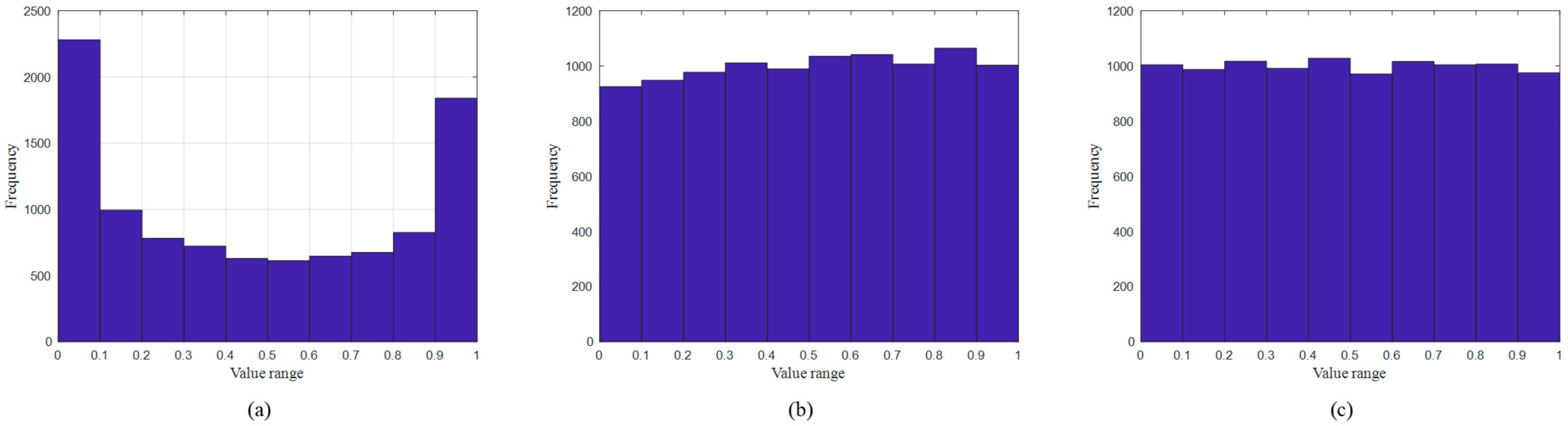
3.2.1. Chaos Mapping Strategy
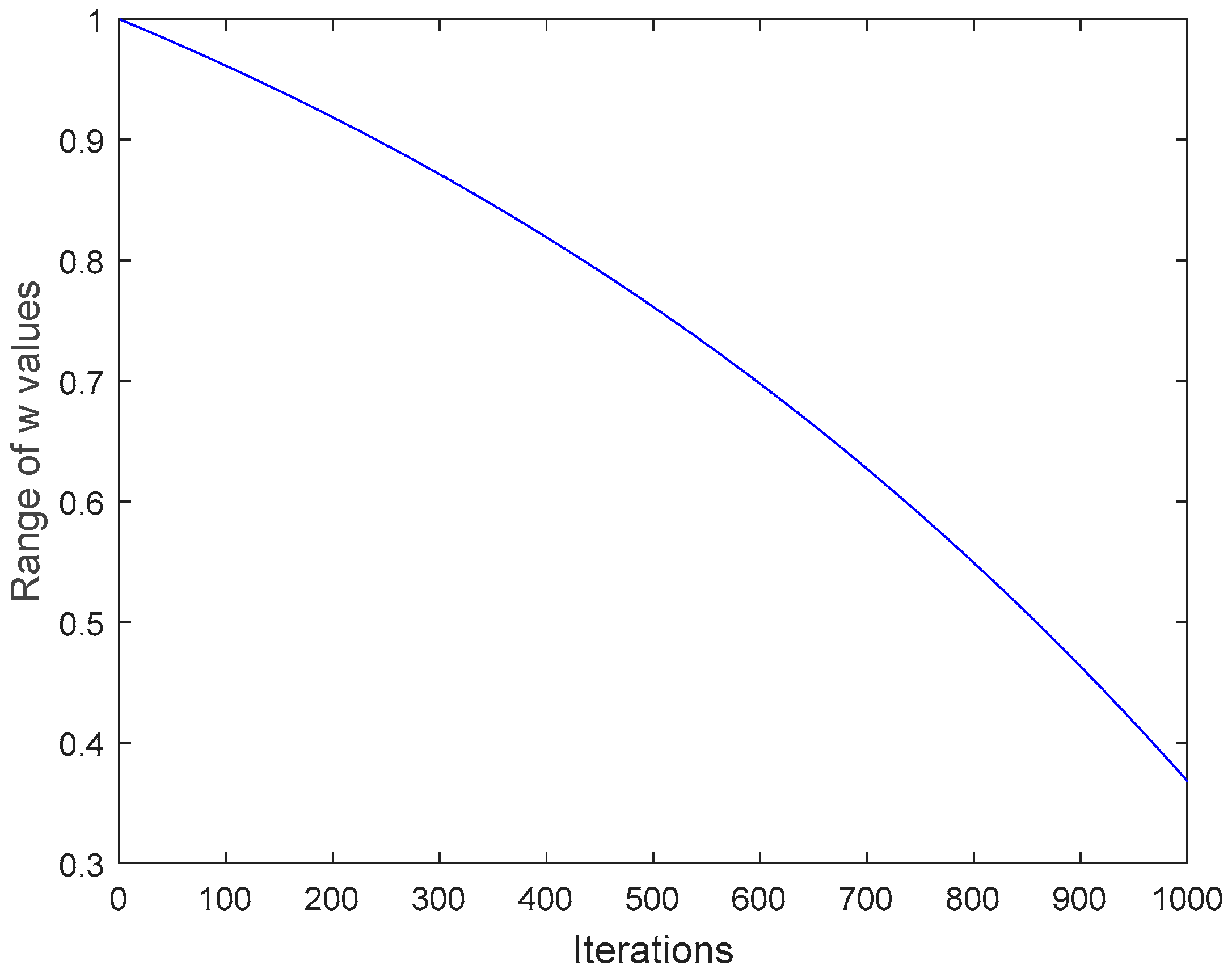
3.2.2. Weight Strategy
3.2.3. Adaptive t-Distribution Strategy
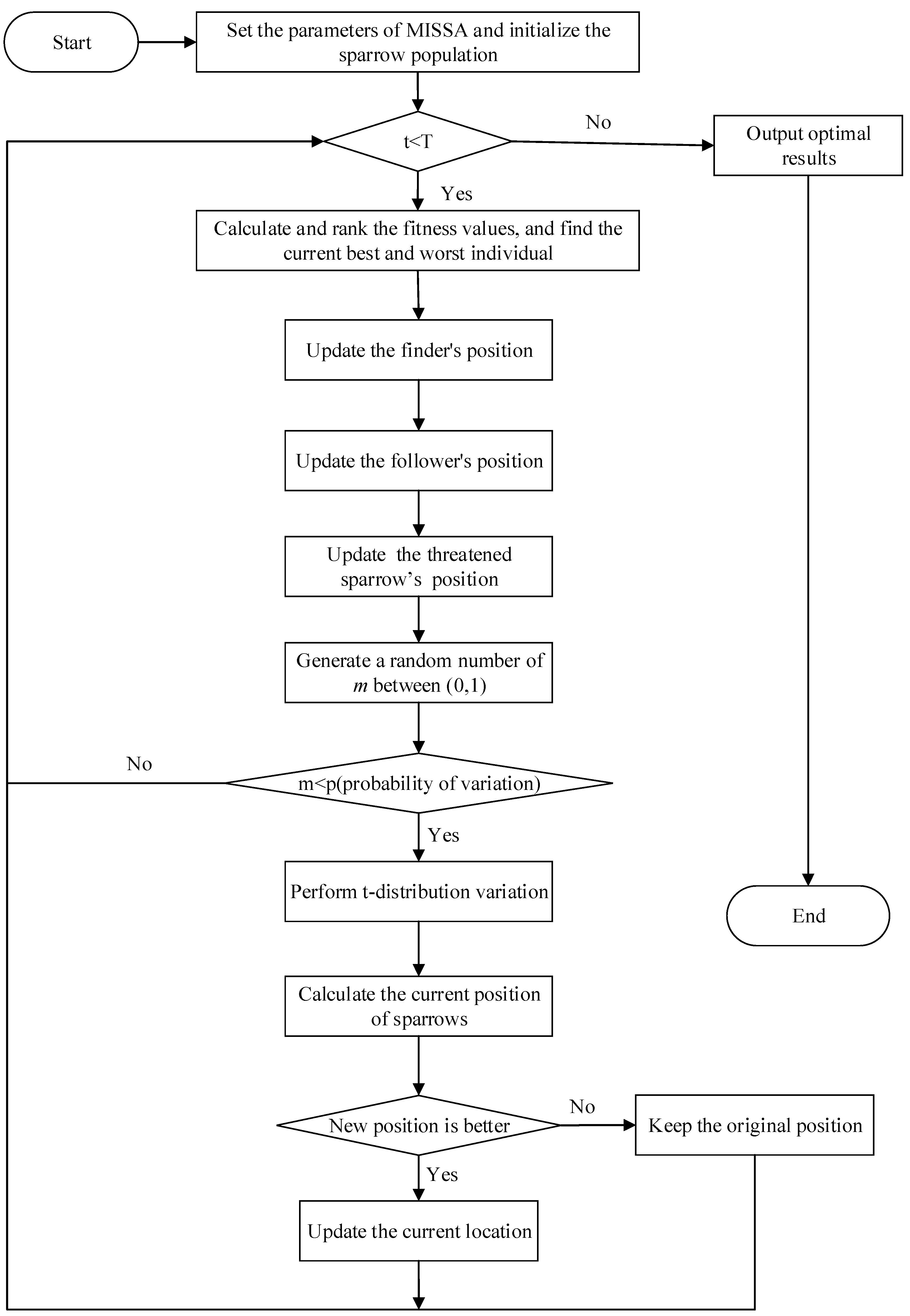
3.3. Improved Sparrow Search Algorithm
| Algorithm 1: The framework of MISSA. |
| /* Initialization */ 1. Set the maximum number of evolutions as T; 2. Set the population number of sparrows as n; 3. Set the warning value as ST; 4. Set the number of finders as PD; 5. Set the number of threatened sparrows as SD; 6. Set the variation probability of t distribution as p; 7. Initialize the population of sparrows using Equation (5); /* Iterative optimization */ 8. while (t < T) 9. Calculate and rank the fitness values, and find the current best and worst individual; 10. ST = rand (1) 11. for I = 1: PD 12. Use Equation (7) to update the finder’s position; 13. end for 14. for i = (PD + 1): n 15. Use Equation (3) to update the follower’s position; 16. end for 17. for i = 1:SD 18. Use Equation (4) to update the threatened sparrow’s position; 19. end for 20. Generate a random number of m between (0,1); 21. If m < p, use Equation (9) to conduct interference variation on sparrow individuals; 22. Calculate the current new position; 23. If the new position is better than before, update it; 24. t = t + 1; 25. end while 26. Output the best solution |
4. Multi-Objective Antenna Design Method
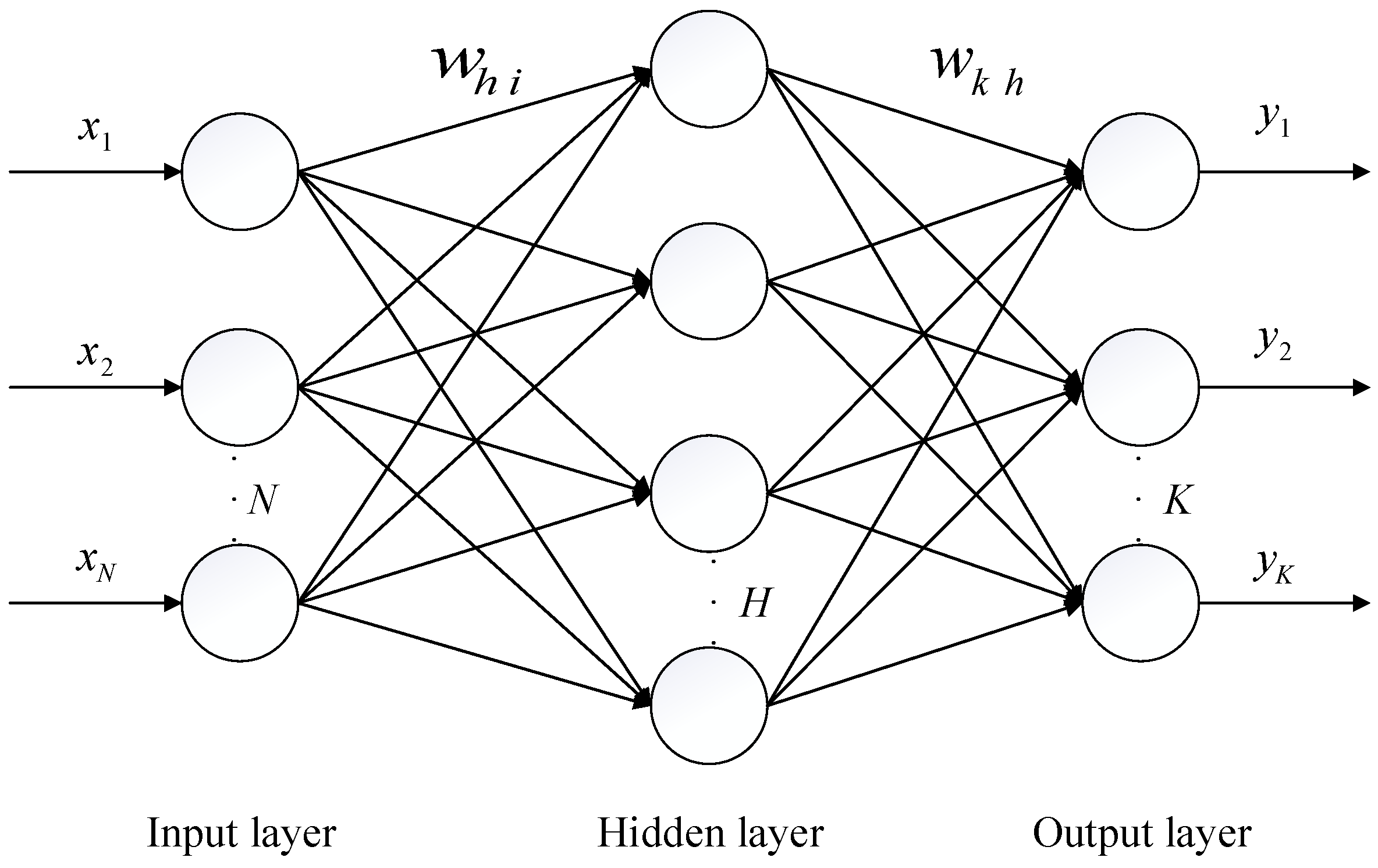
4.1. MISSA-BP Surrogate Model
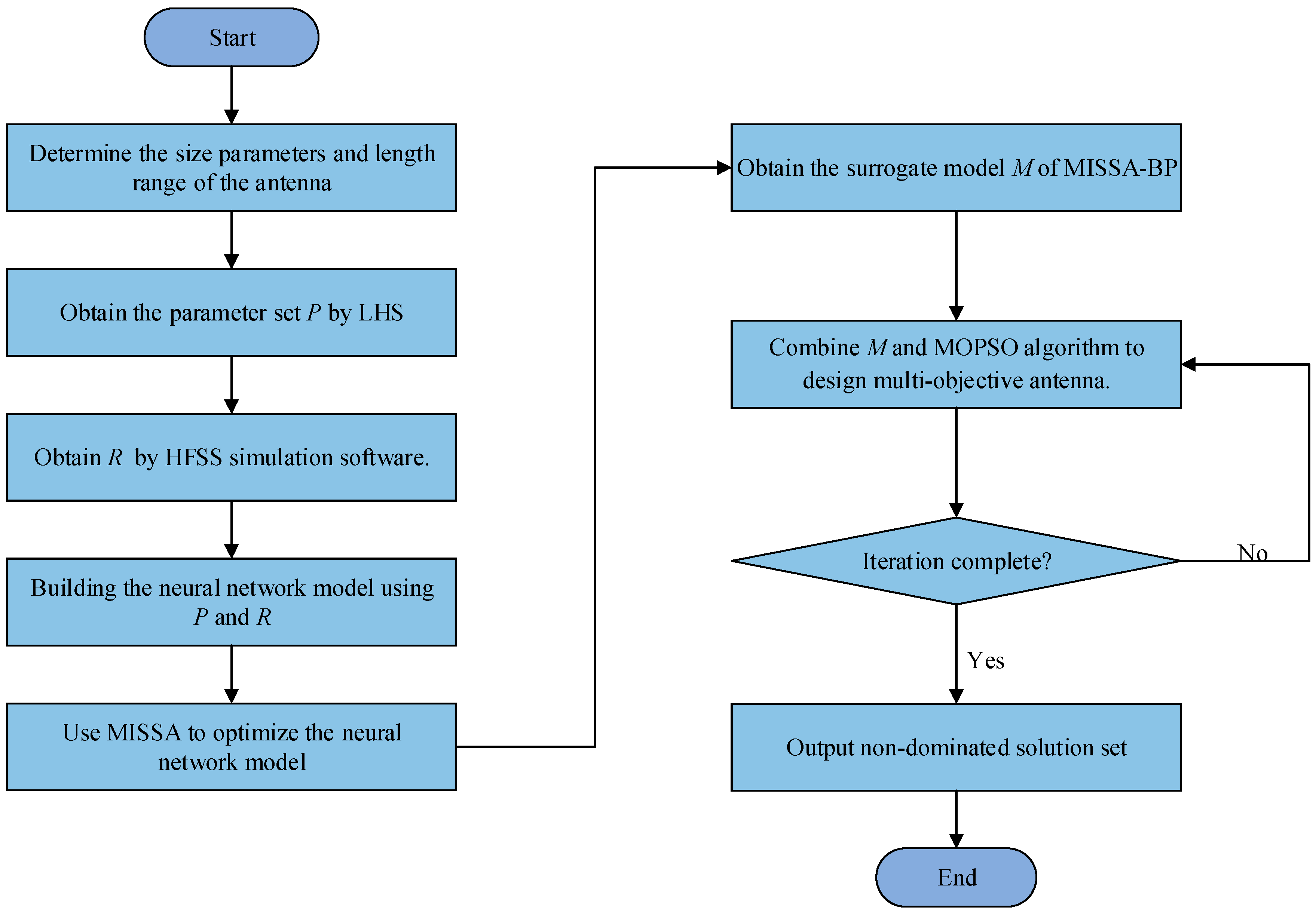
4.2. Multi-Objective Antenna Design Scheme Based on MISSA-BP
- Step 1. Determining the size parameters and length range of the antenna.
- Step 2. Latin hypercube sampling (LHS) is used for uniform sampling within the length range of the antenna, and the parameter set P is obtained.
- Step 3. Substituting P into HFSS simulation software to obtain result set R.
- Step 4. Building the neural network model using P and R.
- Step 5. Using MISSA to optimize the parameters of the neural network, the surrogate model M of MISSA-BP is obtained.
- Step 6. Combine M and the MOPSO algorithm to design the multi-objective antenna.
- Step 7. If the iteration is not completed, continue to step 5. Otherwise, end the optimization and output the non-dominated solution set.
5. Simulation and Verification
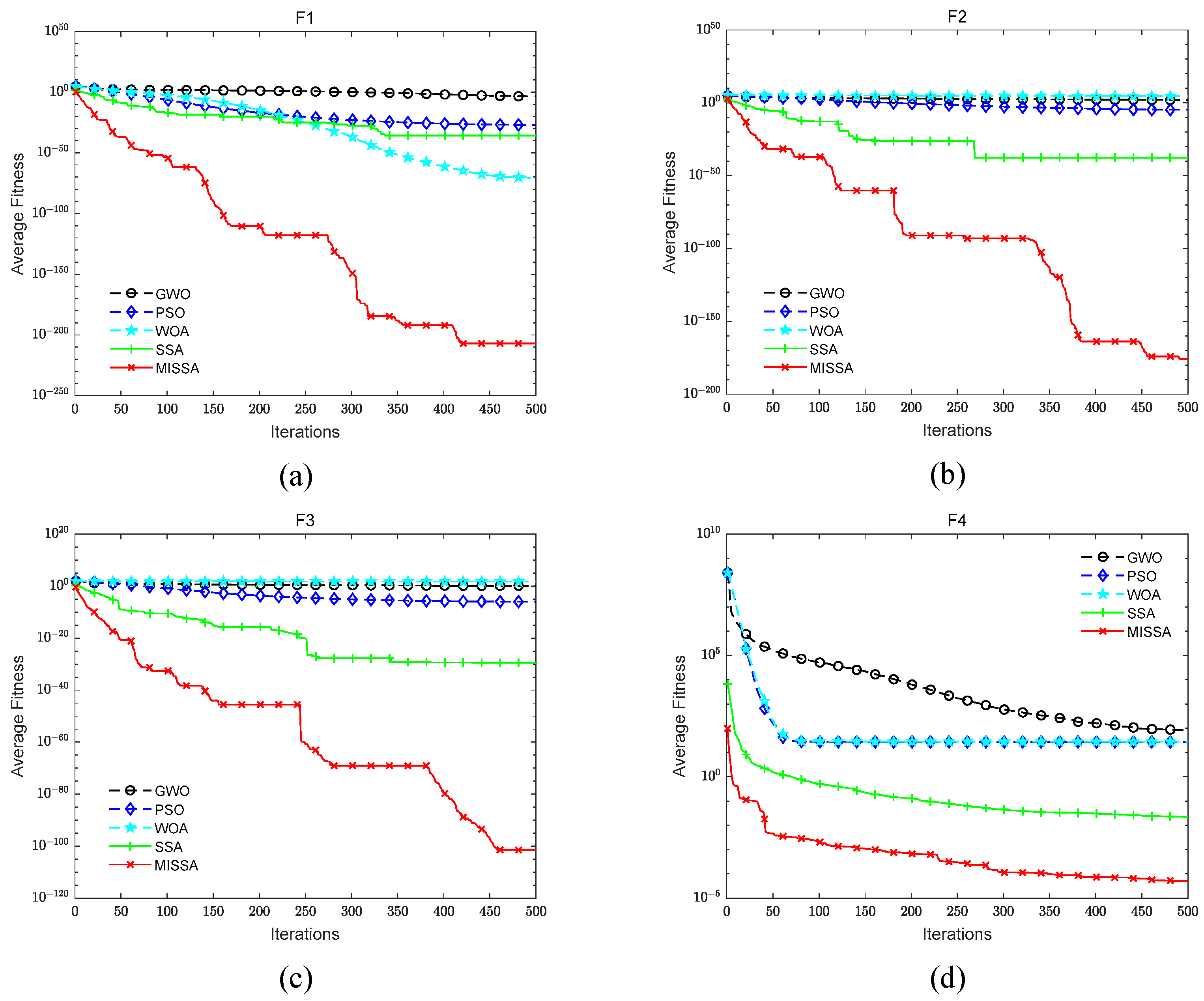
5.1. Verification of MISSA
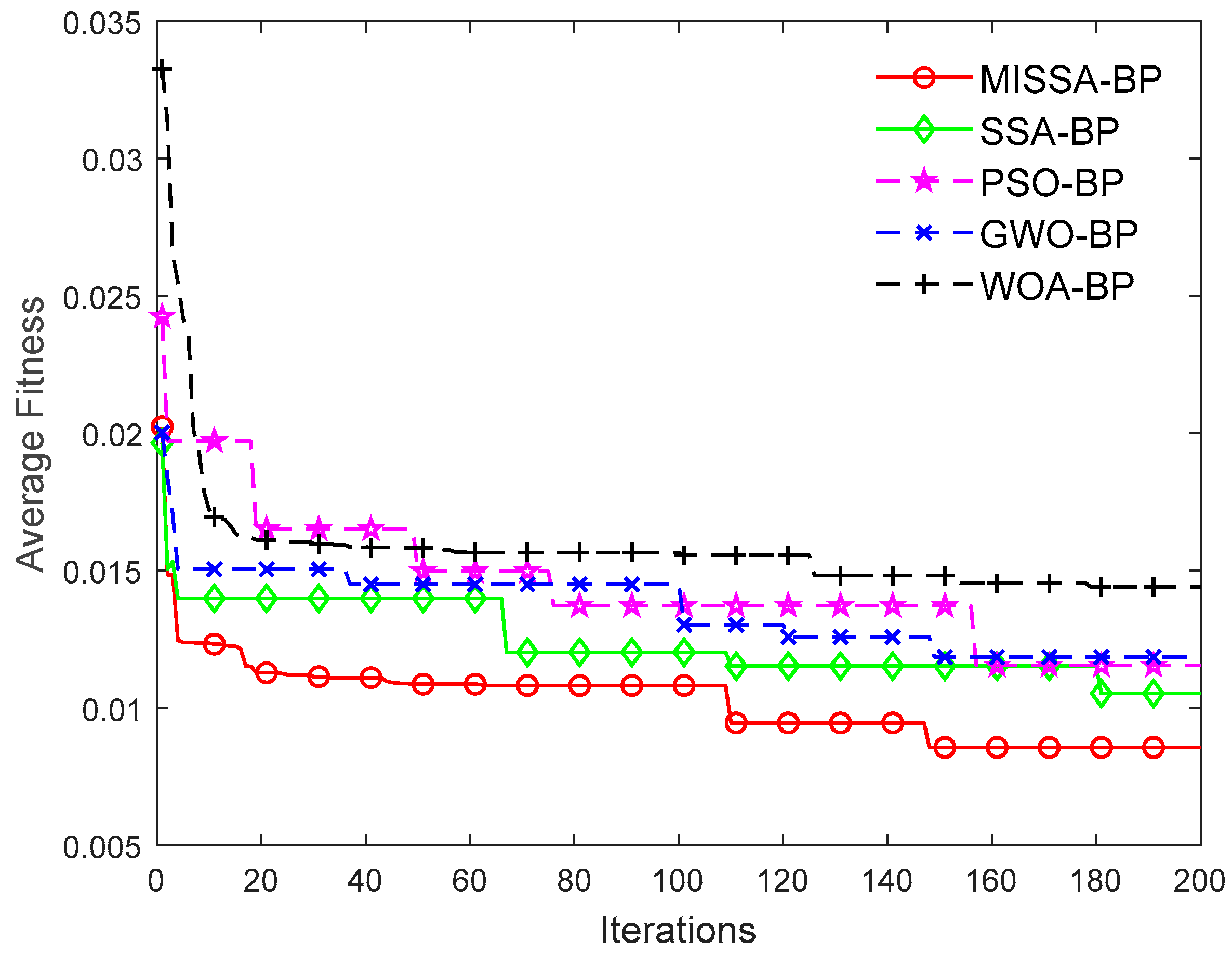
5.2. Validation of MISSA-BP Surrogate Model
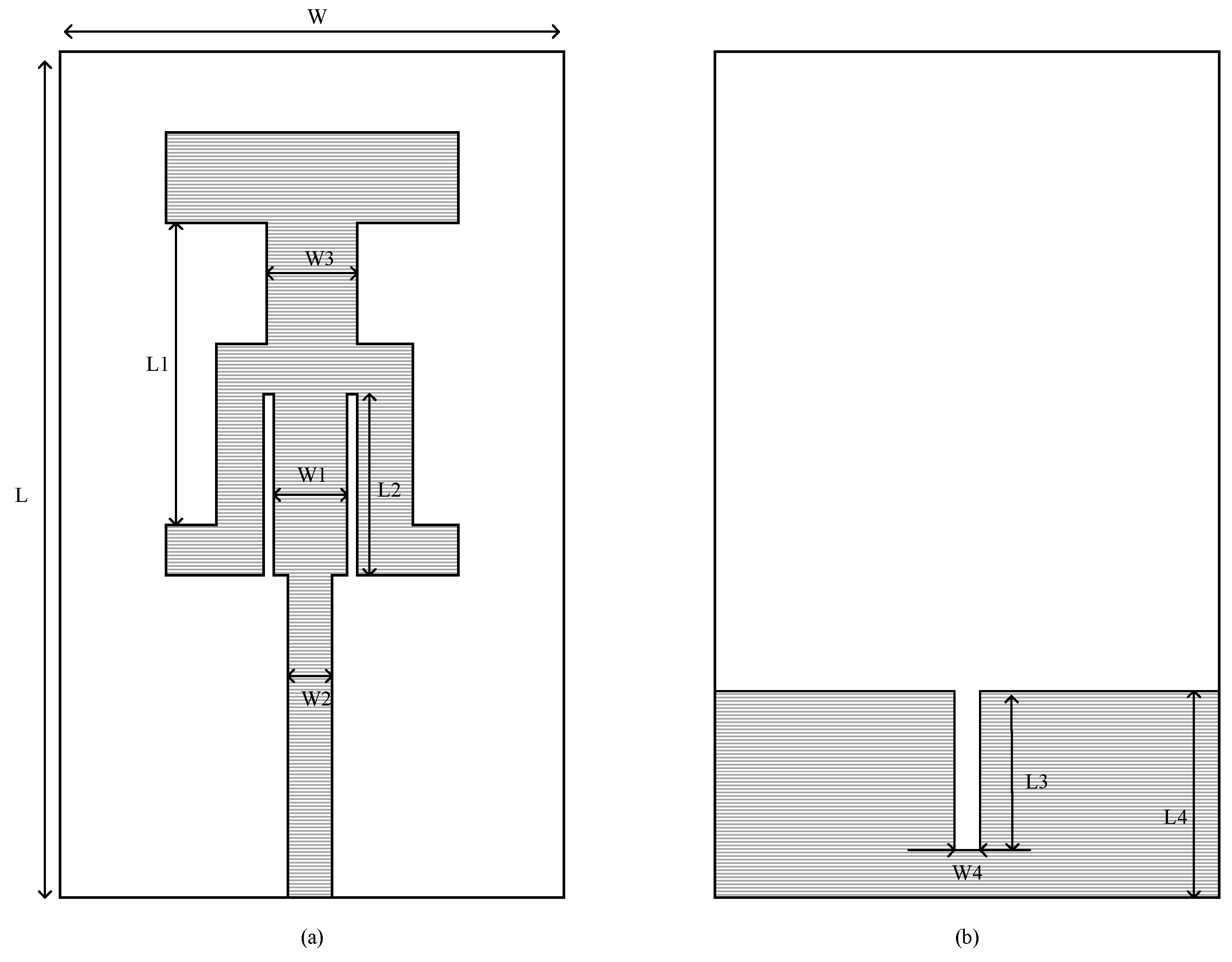
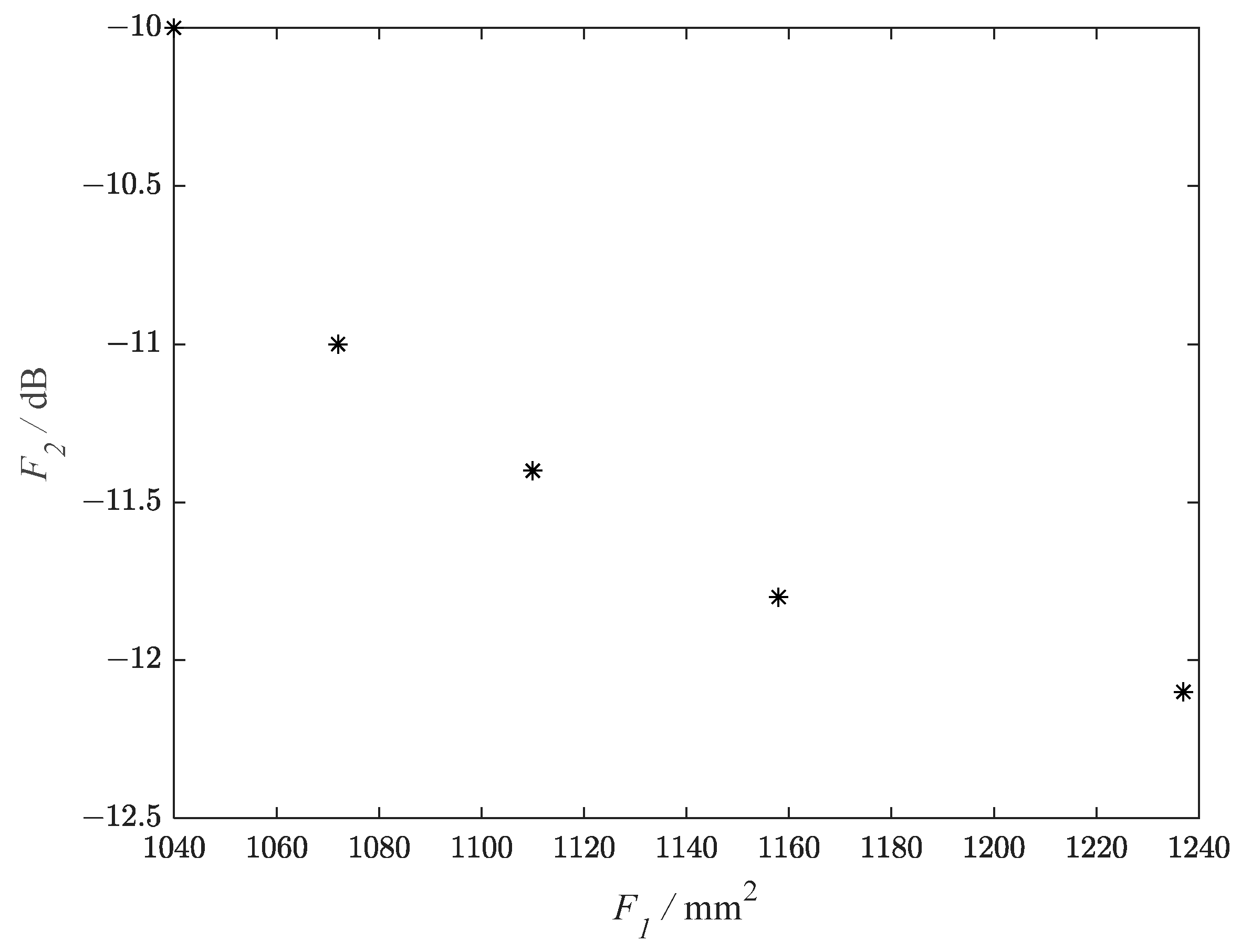
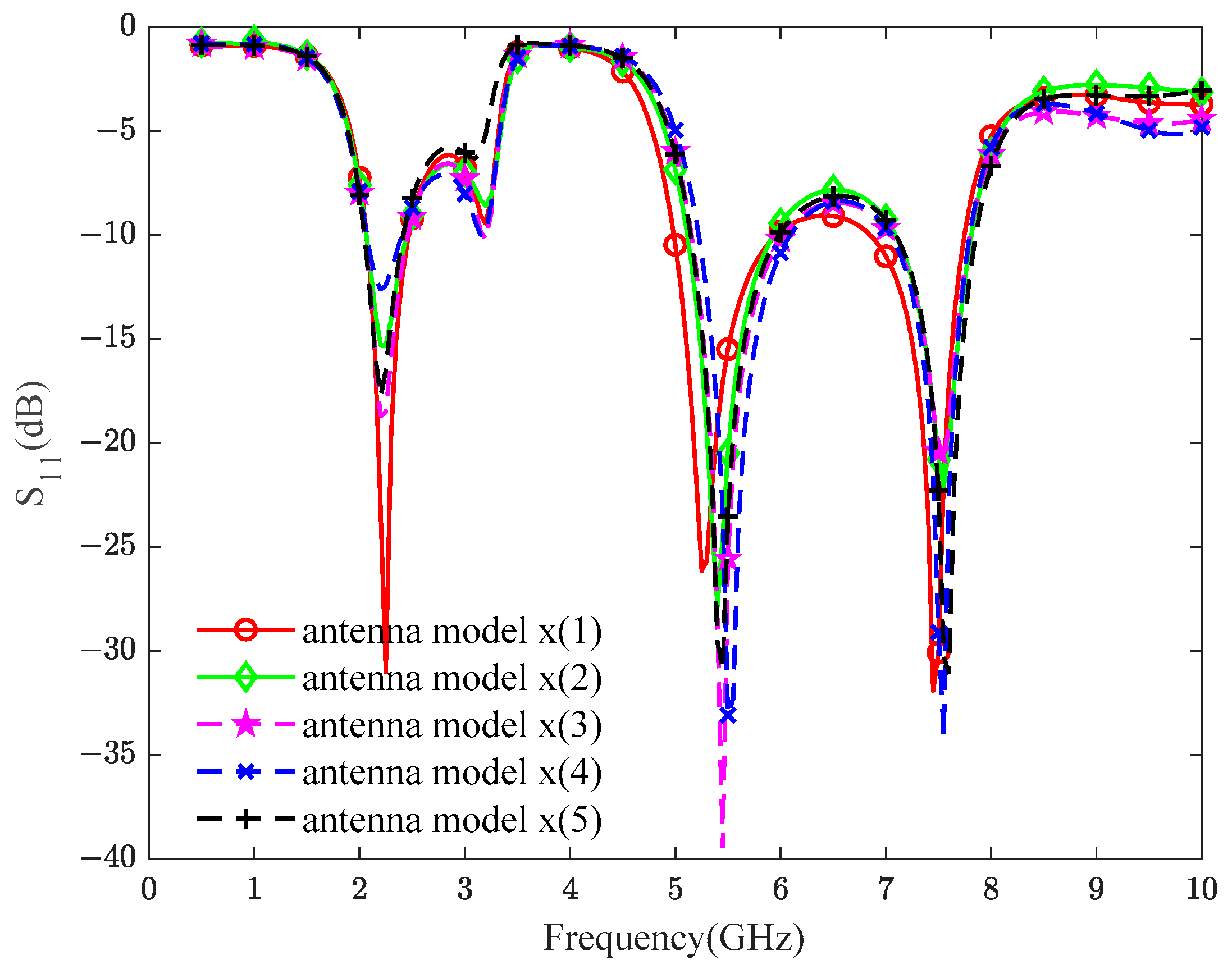
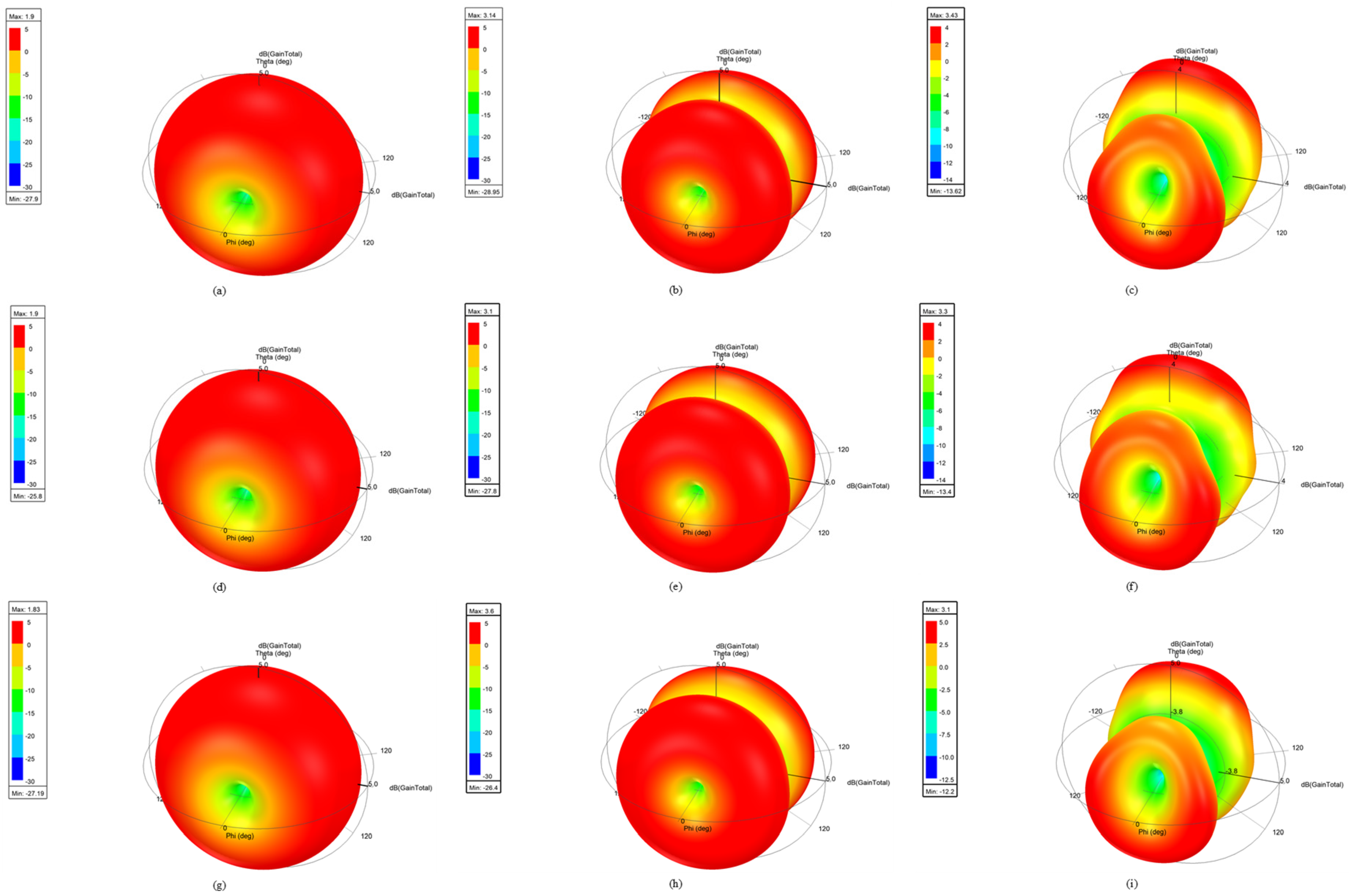
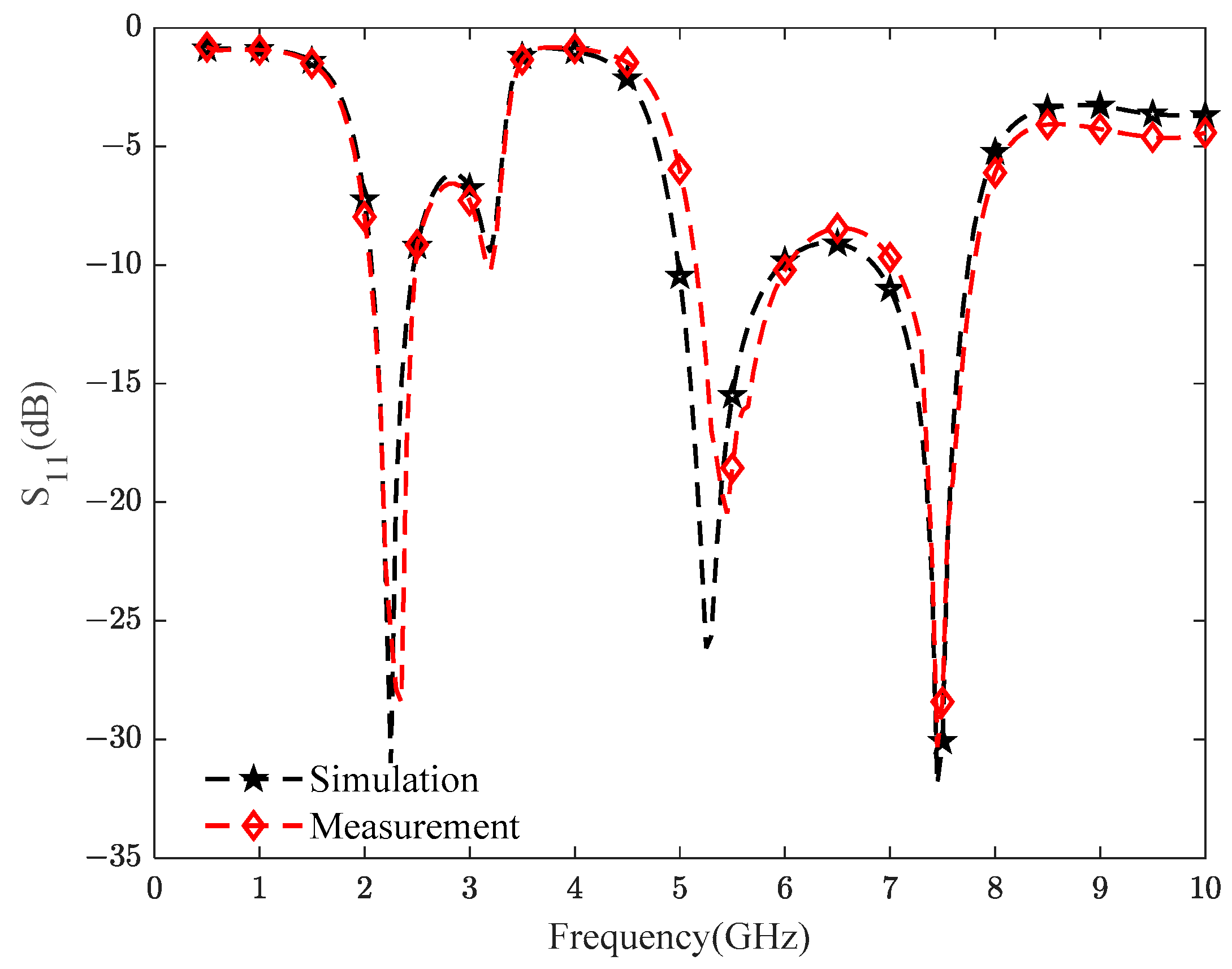
5.3. Design of Multi-Objective Antenna
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, M. Fast Multi-Objective Antenna Optimization Based on RBF Neural Network Surrogate Model Optimized by Improved PSO Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziel, S.; Adrian, B. Rapid multi-objective antenna design using point-by-point Pareto set identification and local surrogate models. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2016, 64, 2551–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekasiewicz, A.; Koziel, S.; Plotka, P.; Zwolski, K. EM-Driven Multi-Objective Optimization of a Generic Monopole Antenna by Means of a Nested Trust-Region Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Qin, W. Fast Multi-Objective Optimization of Multi-Parameter Antenna Structures Based on Improved BPNN Surrogate Model. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 77692–77701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, D.R.; López-Fernández, J.A.; Arrebola, M. Wideband shaped-beam reflect array design using support vector regression analysis. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2019, 18, 2287–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Tian, Y.; Chen, X. Antenna optimization based on co-training algorithm of Gaussian process and support vector machine. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 211380–211390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziel, S.; Bekasiewicz, A. Fast multi-objective surrogate-assisted design of multi-parameter antenna structures through rotational design space reduction. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2016, 10, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, B.; Ren, Z.; Koh, C.S. Utilizing Kriging Surrogate Models for Multi-Objective Robust Optimization of Electromagnetic Devices. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 693–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziel, S.; Ogurtsoy, S. Multi-objective design of antennas using variable-fidelity simulations and surrogate models. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 5931–5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, J.; Kantemur, A.; Sharmma, Y. A 3-D-printed W-band slotted waveguide array antenna optimized using machine learning. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2018, 17, 2008–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, A.; Sinha, S.N. Design of Custom-Made Fractal Multi-Band Antennas Using ANN-PSO Antenna Designer’s Notebook. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2011, 53, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Yadav, R.N.; Singh, R.P. Directivity estimations for short dipole antenna arrays using radial basis function neural networks. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2015, 14, 1219–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.; Vakula, D. Single aperture multiple beams of array antenna using Radial Basis Function Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave and RF Conference (IMaRC), Hyderabad, India, 10–12 December 2015; pp. 388–391. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Ji, W.; Zhao, X. SOC Estimation of E-Cell Combining BP Neural Network and EKF Algorithm. Processes 2022, 10, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Jin, S.; Zhou, J.; Yang, J.; Luo, Y.; Shi, Y.; Sun, C.; Jiang, P. Prediction of the Equivalent Steering Angle of a Front-Wheel, High-Clearance Paddy Field Management Machine. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Qin, W.; Mo, J. Low-cost multi-objective optimization of multi-parameter antenna structures based on the l1 optimization BPNN surrogate model. Electronics 2019, 8, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liang, Z.C.; Pu, Y. Method for Loran-C Additional Secondary Factor Correction Based on Neural Network and Transfer Learning. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2021, 21, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Guo, L.; Jia, Z.; Tian, D.; Xiong, Y. A Surrogate-Model-Based Approach for the Optimization of the Thermal Design Parameters of Space Telescopes. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Luo, M.; Pang, F. An Algorithm for Solving Robot Inverse Kinematics Based on FOA Optimized BP Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Xu, Z.B.; Huang, G.B.; Wang, D.H. Global convergent of online BP training with dynamic learning rate. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2012, 23, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.B.; Zhang, R.; Jing, W.F. When Does Online BP Training Converge? IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2009, 20, 1529–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Shen, B. A novel swarm intelligence optimization approach: Sparrow search algorithm. Syst. Sci. Control. Eng. 2020, 8, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Shang, S.; Zhang, C. Research on the Processing of Coal Mine Water Source Data by Optimizing BP Neural Network Algorithm with Sparrow Search Algorithm. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 108718–108730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, W. Prediction of Mechanical Properties of Thermally Modified Wood Based on TSSA-BP Model. Forests 2022, 13, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.-T.; Ngo, T.-G.; Dao, T.-K.; Nguyen, T.-T.-T. Microgrid Operations Planning Based on Improving the Flying Sparrow Search Algorithm. Symmetry 2022, 14, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Fu, X.; Dong, Z. A Novel Sparrow Search Algorithm for the Traveling Salesman Problem. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 153456–153471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Yang, P.; Zhu, D. Improved sparrow search algorithm based on iterative local search. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2021, 2021, 6860503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jianhua, L.; Zhiheng, W. A hybrid sparrow search algorithm based on constructing similarity. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 117581–117595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the ICNN’95-International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, WA, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; Volume 4, pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Lewis, A. Grey wolf optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2014, 69, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Lewis, A. The Whale Optimization Algorithm. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2016, 95, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.H.; Salawudeen, A.T.; Kamel, S.; Salau, H.B.; Habil, M.; Shouran, M. Single- and Multi-Objective Modified Aquila Optimizer for Optimal Multiple Renewable Energy Resources in Distribution Network. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Wei, W.; Qin, T.; Fan, Y.; Long, F.; Yang, J. A Hybrid Bald Eagle Search Algorithm for Time Difference of Arrival Localization. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; He, Z.; Zheng, J. Improved flower pollination algorithm and its application in user identification across social networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 44359–44371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Yang, T.; Li, T.; Zhan, Y.; Fu, S. Path Tracking of Underground Mining Boom Roadheader Combining BP Neural Network and State Estimation. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Zhang, M.; Browne, W.N. Particle swarm optimization for feature selection in classification: A multi-objective approach. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2012, 43, 1656–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, P.; Tripathy, A. Triple Band Planar Antenna for Wireless Communication. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2012, 48, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

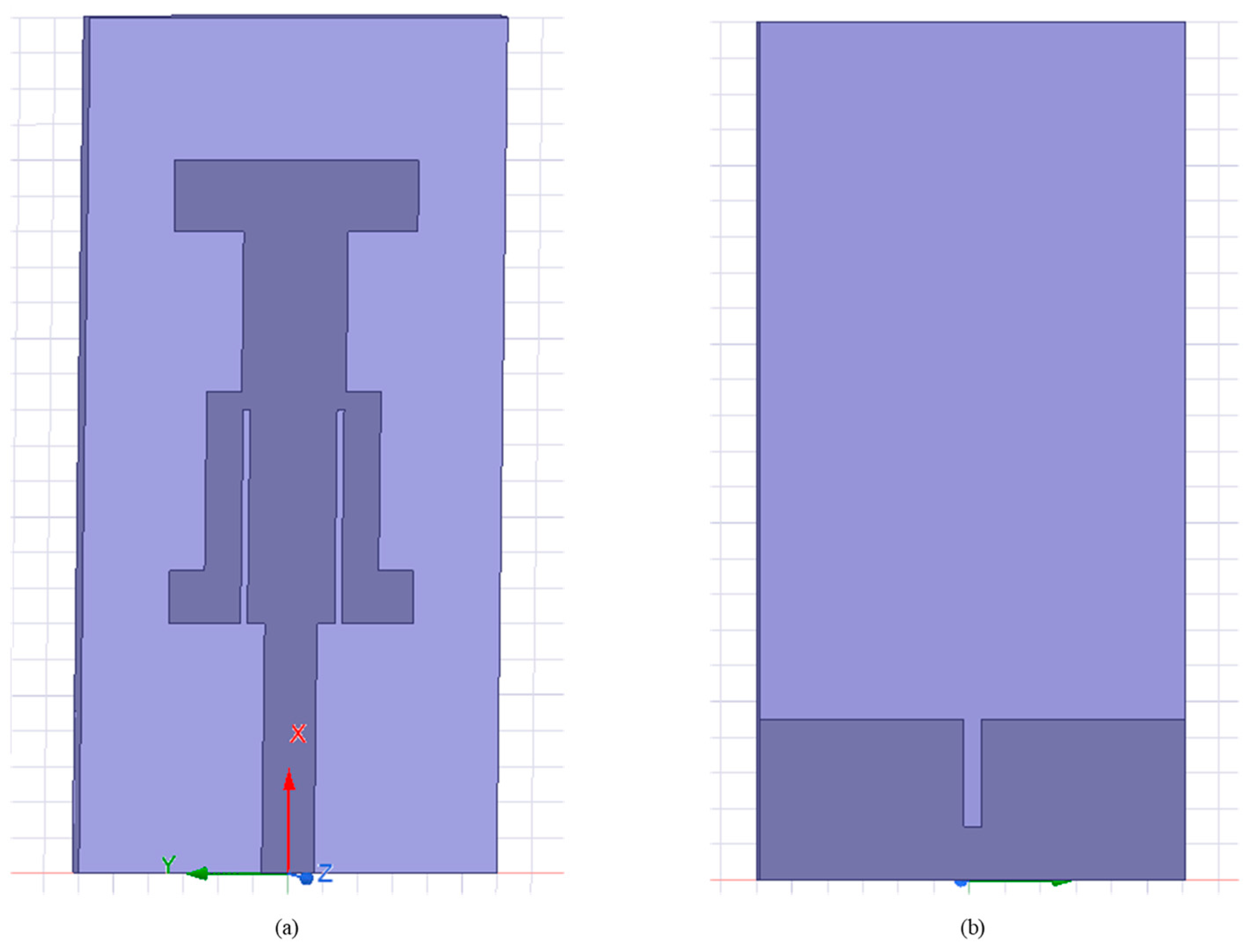


| Type | Expression | Dimension | Range | Optimal Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | [−100, 100] | 0 | ||
| Unimodal function | 30 | [−100, 100] | 0 | |
| 30 | [−100, 100] | 0 | ||
| 30 | [−30, 30] | 0 | ||
| 30 | [−100, 100] | 0 | ||
| Multimodal function Multimodal function | 30 | [−32, 32] | 0 | |
| 30 | [−600, 600] | 0 | ||
| 2 | [−65, 65] | 1 | ||
| 6 | [−5, 5] | 0.0003 | ||
| 4 | [0, 10] | −10.153 |
| Function | Statistical Value | PSO | GWO | WOA | SSA | CASSA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | Optimal value | 2.121 × 10−6 | 3.455 × 10−29 | 3.409 × 10−84 | 0 | 0 |
| Average value | 3.596 × 10−4 | 1.118 × 10−27 | 1.488 × 10−71 | 1.777 × 10−36 | 8.481 × 10−208 | |
| Standard deviation | 0.001 × 10−1 | 1.843 × 10−27 | 8.126 × 10−71 | 9.732 × 10−36 | 0 | |
| F2 | Optimal value | 2.120 × 101 | 1.148 × 10−08 | 1.715 × 10−4 | 2.485 × 10−150 | 0 |
| Average value | 8.659 × 101 | 1.617 × 10−05 | 4.397 × 10−4 | 2.544 × 10−38 | 1.221 × 10−176 | |
| Standard deviation | 3.380 × 101 | 5.478 × 10−05 | 1.561 × 10−4 | 1.393 × 10−37 | 0 | |
| F3 | Optimal value | 8.659 × 10−1 | 1.308 × 10−7 | 1.343 × 10−2 | 1.475 × 10−125 | 0 |
| Average value | 1.167 × 100 | 9.467 × 10−7 | 5.788 × 101 | 2.822 × 10−30 | 3.130 × 10−102 | |
| Standard deviation | 0.255 × 100 | 9.013 × 10−7 | 2.941 × 101 | 1.546 × 10−29 | 1.715 × 10−101 | |
| F4 | Optimal value | 1.979 × 101 | 2.612 × 101 | 2.705 × 101 | 9.946 × 10−5 | 6.366 × 10−9 |
| Average value | 8.433 × 101 | 2.714 × 101 | 2.774 × 101 | 2.205 × 10−2 | 4.824 × 10−5 | |
| Standard deviation | 6.299 × 101 | 5.031 × 101 | 3.579 × 101 | 1.573 × 10−2 | 7.446 × 10−5 | |
| F5 | Optimal value | 1.439 × 10−5 | 8.346 × 10−5 | 1.032 × 10−1 | 2.512 × 10−5 | 6.265 × 10−12 |
| Average value | 9.862 × 10−5 | 7.996 × 10−1 | 3.877 × 10−1 | 1.128 × 10−4 | 3.552 × 10−7 | |
| Standard deviation | 9.323 × 10−5 | 3.995 × 10−1 | 2.774 × 10−1 | 9.484 × 10−5 | 5.638 × 10−7 | |
| F6 | Optimal value | 2.047 × 10−3 | 6.484 × 10−14 | 8.882 × 10−16 | 8.882 × 10−16 | 8.882 × 10−16 |
| Average value | 1.954 × 10−1 | 9.780 × 10−14 | 4.204 × 10−15 | 8.882 × 10−16 | 8.882 × 10−16 | |
| Standard deviation | 4.740 × 10−1 | 1.706 × 10−14 | 2.072 × 10−15 | 0 | 0 | |
| F7 | Optimal value | 1.225 × 10−6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Average value | 7.894 × 10−3 | 4.795 × 10−3 | 5.600 × 10−3 | 0 | 0 | |
| Standard deviation | 9.217 × 10−3 | 7.407 × 10−3 | 3.067 × 10−2 | 0 | 0 | |
| F8 | Optimal value | 9.980 × 10−1 | 9.980 × 10−1 | 9.980 × 10−1 | 9.980 × 10−1 | 9.980 × 10−1 |
| Average value | 3.619 × 100 | 4.647 × 100 | 2.412 × 100 | 9.047 × 100 | 9.980 × 10−1 | |
| Standard deviation | 3.290 × 100 | 4.597 × 100 | 2.196 × 100 | 4.701 × 100 | 3.172 × 10−8 | |
| F9 | Optimal value | 6.058 × 10−4 | 3.075 × 10−4 | 3.085 × 10−4 | 3.075 × 10−4 | 3.074 × 10−4 |
| Average value | 9.094 × 10−4 | 3.758 × 10−3 | 5.781 × 10−4 | 3.737 × 10−4 | 3.129 × 10−4 | |
| Standard deviation | 1.217 × 10−4 | 7.557 × 10−3 | 3.153 × 10−4 | 1.686 × 10−4 | 5.753 × 10−6 | |
| F10 | Optimal value | −1.015 × 101 | −1.015 × 101 | −1.015 × 101 | −1.015 × 101 | −1.015 × 101 |
| Average value | −7.699 × 100 | −9.315 × 100 | −8.271 × 100 | −1.015 × 101 | −1.015 × 101 | |
| Standard deviation | 2.927 × 100 | 2.216 × 100 | 2.722 × 100 | 6.009 × 10−4 | 3.860 × 10−6 |
| Parameter | W | W1 | W2 | W3 | W4 |
| Range | [22, 26] | [4, 6] | [2.5, 3.5] | [1.5, 2.5] | [0.5, 1.5] |
| Parameter | L | L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 |
| Range | [48, 50] | [18, 20] | [11, 13] | [6, 8] | [8, 10] |
| Surrogate Model | MSE | MAPE/ (%) | Time-Consuming (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SVR [5] | 3.86 | 19.69 | 15.56 |
| Kriging [8] | 3.78 | 16.76 | 14.33 |
| BP | 3.70 | 15.68 | 10.12 |
| PSO-BP | 2.74 | 11.35 | 9.92 |
| GWO-BP | 3.05 | 11.87 | 9.61 |
| WOA-BP | 3.42 | 12.02 | 9.57 |
| SSA-BP | 2.05 | 10.15 | 9.32 |
| MISSA-BP | 0.87 | 7.14 | 7.16 |
| W | W1 | W2 | W3 | W4 | L | L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| antenna model x (1) | 23.26 | 5.96 | 3.32 | 1.81 | 0.99 | 48.63 | 19.87 | 11.05 | 6.49 | 9.88 |
| antenna model x (2) | 22.55 | 5.64 | 3.09 | 1.64 | 1.49 | 48.28 | 18.90 | 11.25 | 7.09 | 9.33 |
| antenna model x (3) | 24.43 | 5.55 | 3.33 | 2.11 | 1.31 | 49.21 | 19.12 | 11.06 | 6.11 | 9.94 |
| antenna model x (4) | 23.39 | 5.03 | 2.93 | 2.10 | 1.19 | 49.20 | 19.11 | 11.09 | 6.36 | 9.96 |
| antenna model x (5) | 23.46 | 5.07 | 3.37 | 1.86 | 0.75 | 48.73 | 18.73 | 11.63 | 7.04 | 9.97 |
| Optimization Method | Surrogate Model | Multi-Objective Optimization | CPU Time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Relative (%) | |||
| HFSS | - | - | 90,630 | 100 |
| Proposed method | 4770 | 798 | 5568 | 6.14 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Qin, J.; Hu, Z.; He, J.; Tang, D. Multi-Objective Antenna Design Based on BP Neural Network Surrogate Model Optimized by Improved Sparrow Search Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12543. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412543
Wang Z, Qin J, Hu Z, He J, Tang D. Multi-Objective Antenna Design Based on BP Neural Network Surrogate Model Optimized by Improved Sparrow Search Algorithm. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(24):12543. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412543
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhongxin, Jian Qin, Zijiang Hu, Jian He, and Dong Tang. 2022. "Multi-Objective Antenna Design Based on BP Neural Network Surrogate Model Optimized by Improved Sparrow Search Algorithm" Applied Sciences 12, no. 24: 12543. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412543
APA StyleWang, Z., Qin, J., Hu, Z., He, J., & Tang, D. (2022). Multi-Objective Antenna Design Based on BP Neural Network Surrogate Model Optimized by Improved Sparrow Search Algorithm. Applied Sciences, 12(24), 12543. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412543








