Abstract
This manuscript describes a novel in situ interfacial dynamic inverse emulsion polymerization process under sonication of aniline in the presence of carbon nanotubes (CNT) and graphene nanoparticles in ethanol. This polymerization method is simple and very rapid (up to 10 min) compared to other techniques reported in the literature. During polymerization, the nanoparticles are coated with polyaniline (PANI), forming a core-shell structure, as confirmed by high-resolution scanning electron microscopy (HRSEM) and Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) measurements. The membrane pore sizes range between 100–200 nm, with an average value of ~119 ± 28.3 nm. The film resistivity decreased when treated with alcohol, and this behavior was used for selection of the most efficient alcohol as a solvent for this polymerization technique. The membrane permeability of the PANI grafted CNT was lower than the CNT reference, thus demonstrating better membranal properties. As measured by water permeability, these are ultrafiltration membranes. An antimicrobial activity test showed that whereas the reference nanoparticle Bucky paper developed a large bacterial colony, the PANI grafted CNT sample had no bacterial activity. The thicker, 2.56 mm membranes exhibited high salt removal properties at a low pressure drop. Such active membranes comprise a novel approach for future water treatment applications.
1. Introduction
The challenge of meeting the global demand for clean water is rising constantly [1]. Purification processes combining innovative filters and membranes are ever-growing. Two major challenges with current purification systems are fouling and biofouling [2,3,4]. Fouling is produced by macromolecule depositions, particles, colloids, and inorganic materials on membranal pores and surfaces. Biofouling involves the deposition of large bacterial clusters, biofilm, and colonies on membrane surfaces and inside pores. Both fouling and biofouling are difficult to clean efficiently. Biofouling can be addressed as a four-step process [5,6]. The first step involves the deposition of polymeric abiotic and biotic elements. This step is the only reversible step and crucial to biofilm formation since microorganisms are affixed to the membrane surface mainly via physical interactions. The other irreversible steps involve chemical adhesion to the membrane surface, biofilm development, and dispersion and propagation of the biofilm.
Anti-biofouling additive efficiency is low as additives need to be durable at any rate of the fluid flux and are located on the membranes or filters interface, or surface, where they can be active [4,6,7,8,9,10]. Recently, electrically conductive polymers have been recommended as biofouling prevention materials [11,12,13,14,15]. Ghaffari-Mogahaddam et al. [16] reported the use of silver particles, pre-treated with NaBH4 and then blended with poly(vinyl-alcohol) (PVOH) and polyaniline (PANI) for antimicrobial activity. Vast numbers of reported techniques involve pre-polymerized PANI followed by adsorption to the membrane surface. However, most studies have not used an “all-in-one” approach, and a latest review indicated the lack of work on PANI as an antimicrobial agent in polymeric membranes [17,18].
Nanocomposites consist of nanoparticles imbedded in synthetic or natural polymers and are a relatively new class of materials. A major challenge is the homogeneous dispersion of nanoparticles in polymers using conventional processing. Nanoparticles have a considerable tendency to agglomerate due to strong Van-der-Waals forces. The search for efficient methods for fine dispersion have been pursued in recent years. One of the most interesting techniques is the in situ polymerization of monomers in the presence of nanoparticles [19,20,21,22,23,24]. There are numerous reports in the literature on CNT, the polymerization of aniline, and the preparation of PANI/CNT nano-composites for different applications [25,26].
Among the family of intrinsically conductive polymers (ICP), PANI has been studied extensively owing to its simple polymerization, high electrical conductivity, and environmental stability [18,26]. PANI can be synthesized using different techniques, in the aqueous or organic phase, using agitation or ultrasonication techniques, as well as static interfacial, emulsion, or inverse emulsion polymerization.
This study further extends an ultra-fast inverse emulsion sonication technique reported previously by the author [27,28]. The PANI combines two anti-biofouling mechanisms: electric current and chemical reactivity [29]. Oxidation or reduction affects the PANI conductivity through a process termed doping [30]. The conductivity of PANI can be reversibly switched from an insulator to a metallic conductor.
Coating with water-treatment membranes comprises drop casting, dip-coating, and interfacial polymerization [31,32]. However, a literature search only indicated one report on inverse emulsion polymerization techniques [17]. The oil-in-water, or emulsion polymerization technique, occurs in systems comprised of a majority of water and a minor amount of oil, monomers, and surfactants. The monomers polymerize within micelles and form stable colloidal dispersions, i.e., emulsions [33]. In the inverse emulsion polymerization process, the major continuous phase is the organic phase containing the aniline monomer, whereas the aqueous solution containing the surfactant and initiator is emulsified by the surfactant.
Carbon nanotubes (CNT) have been well-known for many years since their first observation by Iijima [34]. CNT’s possess a significant combination of mechanical properties including high strength and flexibility with high electrical and thermal conductivity, thus offering new opportunities for the development of nanocomposites [35]. However, the fine dispersion of CNT within the polymeric matrix is hard to achieve due to its poor "solubility" in most solvents.
An inverse emulsion technique has been used successfully for PANI/CNT nanocomposite manufacturing [24,28] where a core-shell structure of PANI coating the CNT was formed. The existence of CNT increased the PANI’s mechanical properties, resulting in higher conductivities exhibited by the PANI/CNT nanocomposites compared to neat PANI.
In the present study, Bucky paper membranes [36] were prepared and analyzed in depth. Bucky paper is prepared by an in situ inverse emulsion polymerization method under sonication of aniline in the presence of nanoparticles, resulting in PANI coated nanoparticles, which then undergo Millipore filtration. A study of the alcohol post-treatment effect on the electrical properties reported better conductivity and better antimicrobial activity [17]. The antimicrobial activity of the PANI coated nanoparticles Bucky-paper led to improved antibacterial properties.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
An aniline monomer was used after purification (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). Dodecyl benzene sulfonic acid (DBSA) (Zohar, Dalia, Israel) was used as received. The Nanocyl 7000 MWNT has an average diameter of 9.5 nm and an average length of 1.5 μm (Nanocyl, Sambreville, Belgium). A selected grade of graphene AO-3 with an average flake thickness of 12 nm and an average particle size of 1.5–10 μm (Graphene Nanopowder, Calverton, NY, USA) was also investigated. Ammonium peroxydisulfate (APS) was used as received (Riedel de-Haën, Sigma-Aldrich, Munich, Germany). Methyl alcohol, 1-butanol, 2-propanol (Frutarom LTD., Haifa, Israel), ethyl alcohol 96% (Gadot chemicals, Haifa, Israel), 1-pentanol (Flucka chemie, Buchs, Switzerland), and iso-propyl alcohol (Finkelman LTD., Afula, Israel) were used to remove impurities from the composite.
2.2. Preparation of Nanocomposites
The inverse emulsion polymerization procedure of aniline in organic solvent was carried out as previously reported [24,28]: 1 g of DBSA was dissolved in 200 mL of alcohol using magnetic stirring. Then, 0.3 g of distilled aniline was added, and a clear solution was formed. A Vibra cell VCX 750 (Sonics & Materials Inc., Newtown, CT, USA), with a 40% amplitude, ultrasonic liquid processor was used to disperse the nanoparticles and to accelerate the polymerization process. Nanoparticles were added to the alcohol solution in situ before polymerization began. The nanoparticle concentration was 0.5% w/v of the dispersion. Next, 0.37 g of ammonium peroxydisulfate (APS) dissolved in 10 mL distilled water was added to the solvent/aniline solution followed by sonication at 4 °C for 10 min. The PANI/nanoparticles dispersion then served for film formation using a 4 μm coating rod to produce a homogenous film (K Hand Coater Large Starter Set, RK Print Coat Instruments, Royston, UK). This step was used to determine the best alcohol for the polymerization procedure. The film’s surface resistivity was measured to determine the preferred solvent for this procedure. A reference CNT sample without PANI and a PANI/CNT physical mixture were prepared using the same procedure. The PANI and PANI/nanoparticle dispersions were mixed in an excess of ethanol followed by filtration under vacuum using the Millipore system (at a diameter of 47 mm, Millipore LTD, Carrigtwohill, Ireland). The hybrid dispersions were filtered with 25, 50, and 100 mL to obtain different thicknesses. The resulted filtration cake, i.e., Bucky paper, was used as a membrane for water filtration experiments and characterization.
All the techniques had the same composition. The dynamic and in situ polymerization involved a chemical reaction in the presence of the nanoparticles, whereas the later mixing with PANI involved the physical contact of the nanoparticles with the pre-polymerized aniline. The Bucky paper membranes were placed in ethanol for 12 h to remove non-grafted PANI.
2.3. Characterization
A two-point probe technique was used to measure the electrical conductivity of the films produced. The morphology of PANI/membrane hybrid was examined using a LEO 982 (Cambridge, UK) high resolution scanning electron microscope (HRSEM), equipped with a high-resolution field emission gun (FEG), operated at a 4 kV accelerating voltage at a 3–4 mm working distance, with an in-lens detector of secondary electrons.
The PANI/membrane composites were studied using a TA 2050 Thermal Gravimetric Analyzer (TGA). The measurements were conducted under air, at a heating rate of 20 °C min−1. The sample’s weight loss was monitored as a function of temperature. Two types of data can be obtained from TGA thermograms: (a) the degradation temperature zones of the acid and polymer fractions, which are normally between 200 and 350 °C and 400 and 700 °C, respectively, and (b) the membrane fraction.
Absorbance Infrared Fourier-Transform spectra were recorded using a Thermo 6700 FTIR instrument equipped with a Smart iTR diamond ATR device. Each spectrum was recorded at a resolution level of 4 cm−1. The electrical conductivity of the Bucky membranes was measured using a four-point probe apparatus. Continuous linear membrane cell was used to measure the flow parameters. The cell was constructed for a “dead end” filtration procedure. The membrane diameter was 15 cm. The fluid capacity and membranal pressure drop were recorded. A colony counting technique [37] was used for evaluation of the membranes antimicrobial activity. Five (5) neat CNT and PANI grafted CNT membranes were tested. The samples were deposited on agar substrate and E. coli pathogens were implanted. The hybrids were then incubated for 96 h.
A 0.5% NaCl solution in distilled water was used for measurement of the salt removal at different trans-membranal pressure drops. Five membranes were tested for each flux and salt removal measurement.
3. Results and Discussion
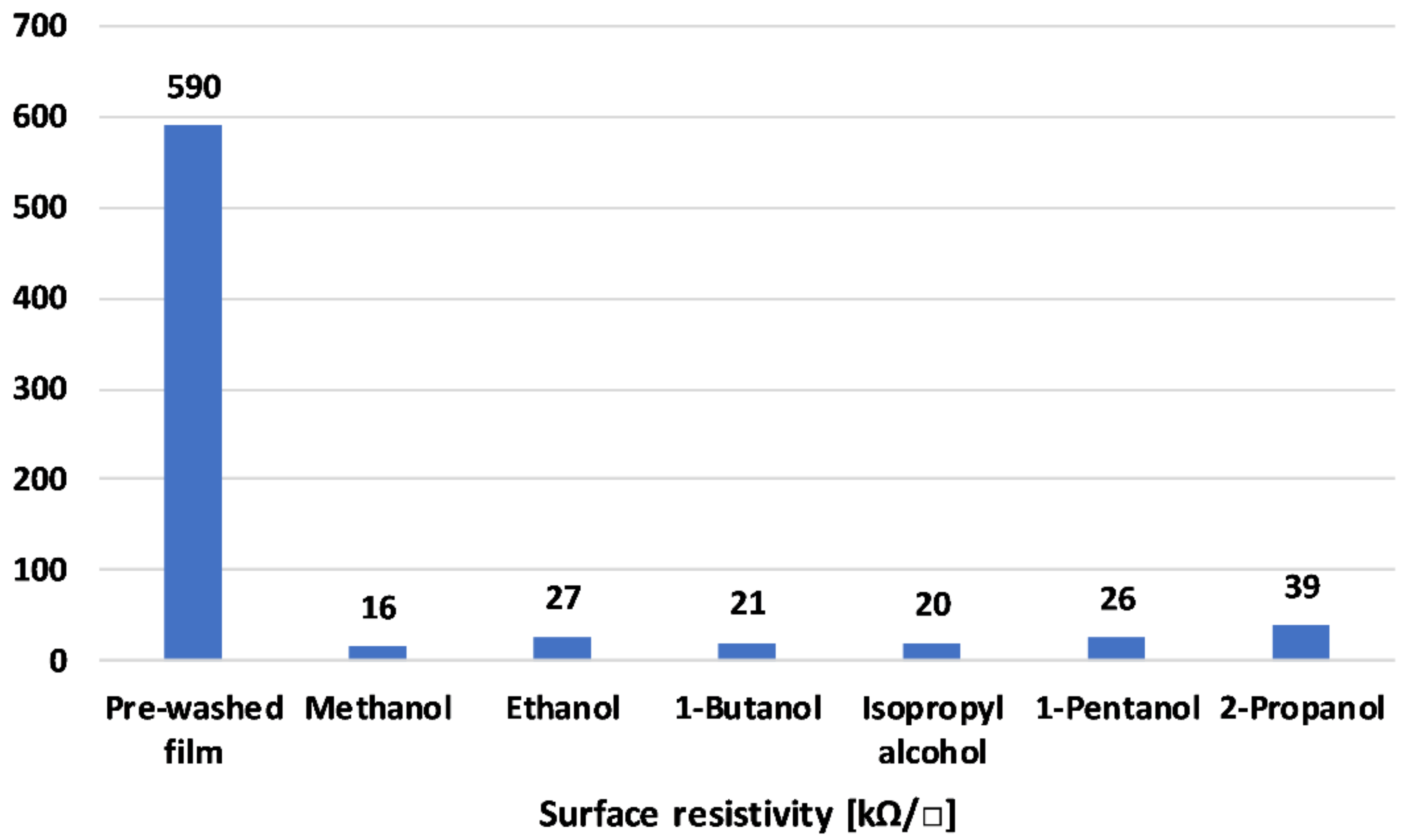
Figure 1 depicts the film resistivity of the different solvent washes. The films were deposited from nanoparticle dispersions on PET substrates using a 4 μm thick coating rod.
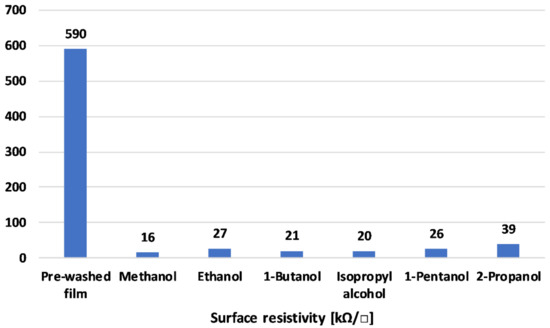
Figure 1.
Film resistivity with different solvents washes.
Figure 1 depicts the film resistivity of the different alcohol washes. The films were deposited from nanoparticle dispersions on PET substrates using a 4 μm thick coating rod. The reference sample exhibited high surface resistivity values of 590 kΩ. All the alcohols exhibited a dramatic reduction in surface resistivity. Alcohol is considered to have washed away the free DBSA fraction and impurities left in the reaction [38]. Ethanol, the least toxic alcohol of the materials studied, exhibited a relatively low resistivity of 27 kΩ sq−1. Thus, further polymerization and characterization was continued using ethanol. The lowered resistivity was due to (1) removal of impurities and (2) the doping effect of the solvents [39]. PANI can exhibit secondary doping effects due to the polymer extended chain effect, as reported earlier [27].
The surface area, measured using the BET technique, of the neat CNT, graphene, and PANI was 140, 115, and 20 m2 g−1, respectively, while the physical mixture of PANI and CNT had a surface area of 147.5 m2 g−1, similar to the neat CNT. The PANI-coated CNT exhibited a higher surface area, ~220 m2 g−1, whereas the PANI-coated graphene exhibited a value of ~17 m2 g−1. The fact that the surface area of the PANI-coated graphene was similar to the neat PANI further supports the claim that graphene Bucky paper is a poor candidate for membranal applications.
A preliminary investigation of the PANI grafted graphene membranes found that the fluid velocity was practically zero, i.e., there was no flux. A report has indicated that graphene platelets exhibit a dense structure without enough cavities for fluid flow [40]. Thus, in the current study, only PANI/CNT hybrids were further analyzed.
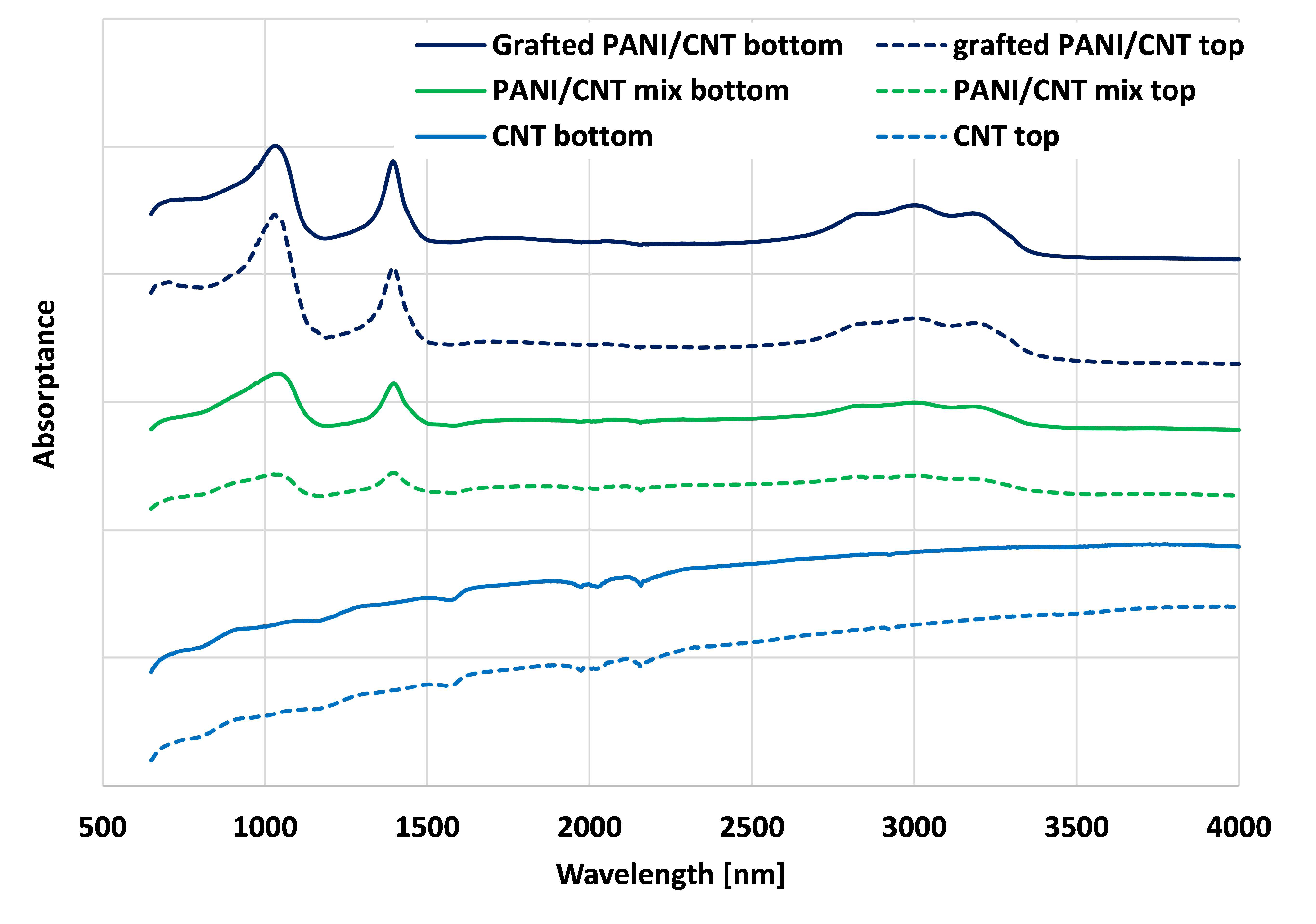
Figure 2 illustrates the FTIR spectra of the neat CNT, the PANI/CNT mixture, and the PANI grafted CNT. The neat CNT had characteristic FTIR peaks at 1475–1600 cm−1 representing the C=C stretching of aromatic rings, as reported elsewhere [41,42]. PANI/CNT had characteristic peaks, similar to previous reports [28,43], at 2800–3400 cm−1, which represent the Nitrogen containing groups such as protonated imine -NH+ = and secondary amine -NH-. The ring-stretching vibrations of quinonoid and benzenoid appear at 1570 cm−1. The bands between 700–900 cm−1 correspond to aromatic ring out-of-plane deformations. The ~1040 cm−1 FTIR peak represents the quinonoid ring, N=Q=N [28]. These peaks confirmed that the dynamic sonication inverse emulsion polymerization alone resulted in doped PANI. The PANI/CNT samples showed similar peaks as the reference PANI and CNT, thus validating that this polymerization technique in the presence of CNT alone resulted in PANI/CNT. Note that the physical PANI/CNT mixture exhibited lower transmittance values than the grafted PANI/CNT. In addition, the bottom part exhibited slightly higher transmittance, suggesting that since there is no chemical bond, the PANI was removed from the Bucky paper during the rinsing step. These results support the author’s previous claims [17,27,28,40] for the grafting of PANI chains to the CNT surface.
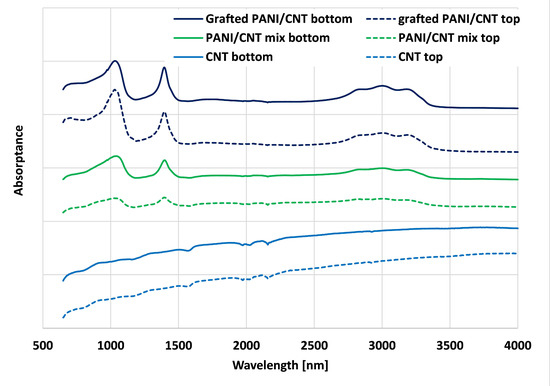
Figure 2.
Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectra of neat CNT, PANI/CNT physical mixture, and PANI grafted CNT Bucky paper.
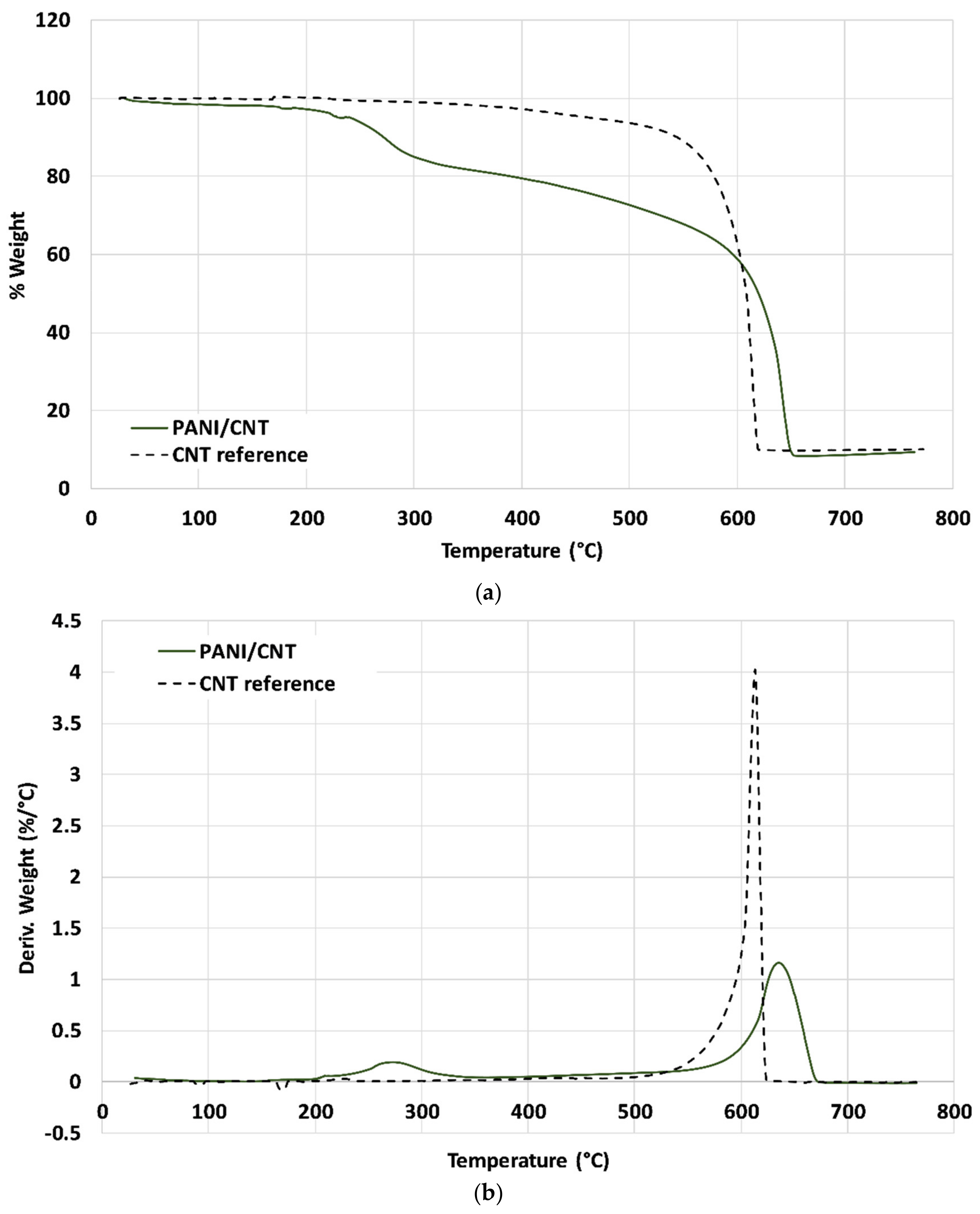
Figure 3a,b depicts the thermal gravimetric analyzer (TGA) thermograms and the first derivative (DTG). The neat CNT (dashed line) exhibited a single weight loss peak at ~610 °C of roughly 90%. The PANI/CNT hybrid exhibited two decomposition peaks, at 275 and 640 °C, with a weight loss of 15% and 75%, respectively. The polymerization process was conducted with excess DBSA to increase the anilinium concentration partially affixed to the PANI chains, whereas the remaining part was unbound. Thus, the 15% weight loss of the PANI/CNT roughly reflects the bound DBSA. Furthermore, the PANI/CNT exhibited higher thermal stability than the neat CNT, suggesting that the chemical grafting of PANI to the CNT surface increased the hybrid’s thermal stability. The TGA results further support the grafting process of PANI chains to the CNT surface, adding to its thermal stability.
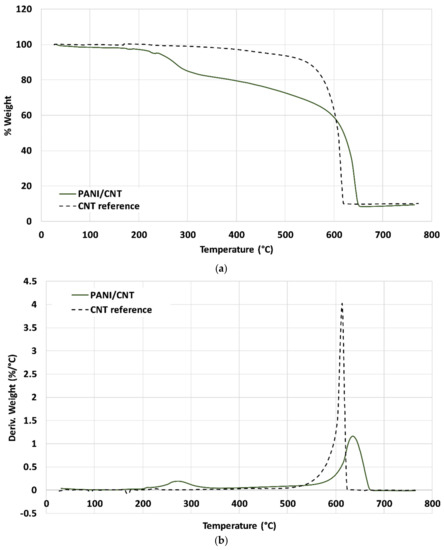
Figure 3.
(a) Thermal gravimetric analyzer (TGA) thermograms of neat CNT and PANI grafted CNT Bucky paper. (b) derivative thermal gravimetric (DTG) thermograms of neat CNT and PANI grafted CNT Bucky paper.
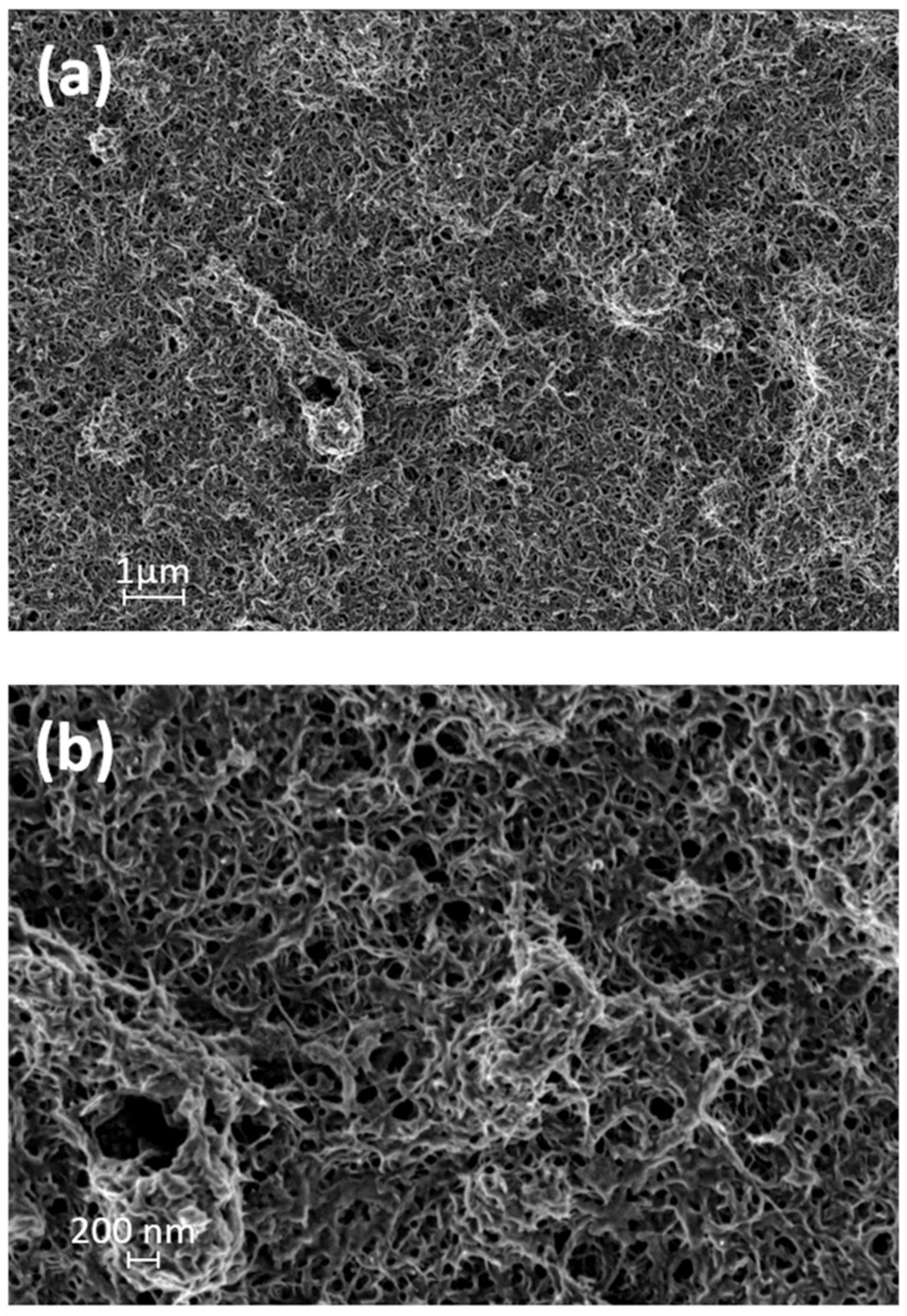
Figure 4a,b illustrates HRSEM images of the PANI grafted CNT sample. The sample presented as a smooth surface with a highly porous structure. A thin PANI coating had formed on the CNT surface, as the HRSEM images show, acting as a physical barrier to fluid transport, thus adding microbial properties. According to the HRSEM images, the membrane pore size ranged between 100–200 nm, with an average value of ~119 ± 28.3 nm. The HRSEM images contribute to the scientific study of the morphology obtained as a result of the presence of ethanol [27,39]. Further, the grafting of PANI chains to the CNT surface is crucial for the stability and durability of the overall membranal structure.
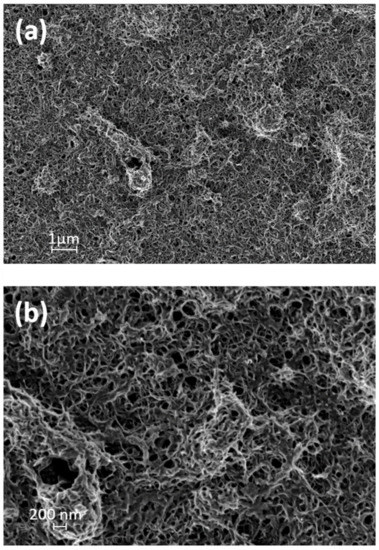
Figure 4.
High-resolution scanning electron microscopy (HRSEM) images of PANI/CNT Bucky paper.
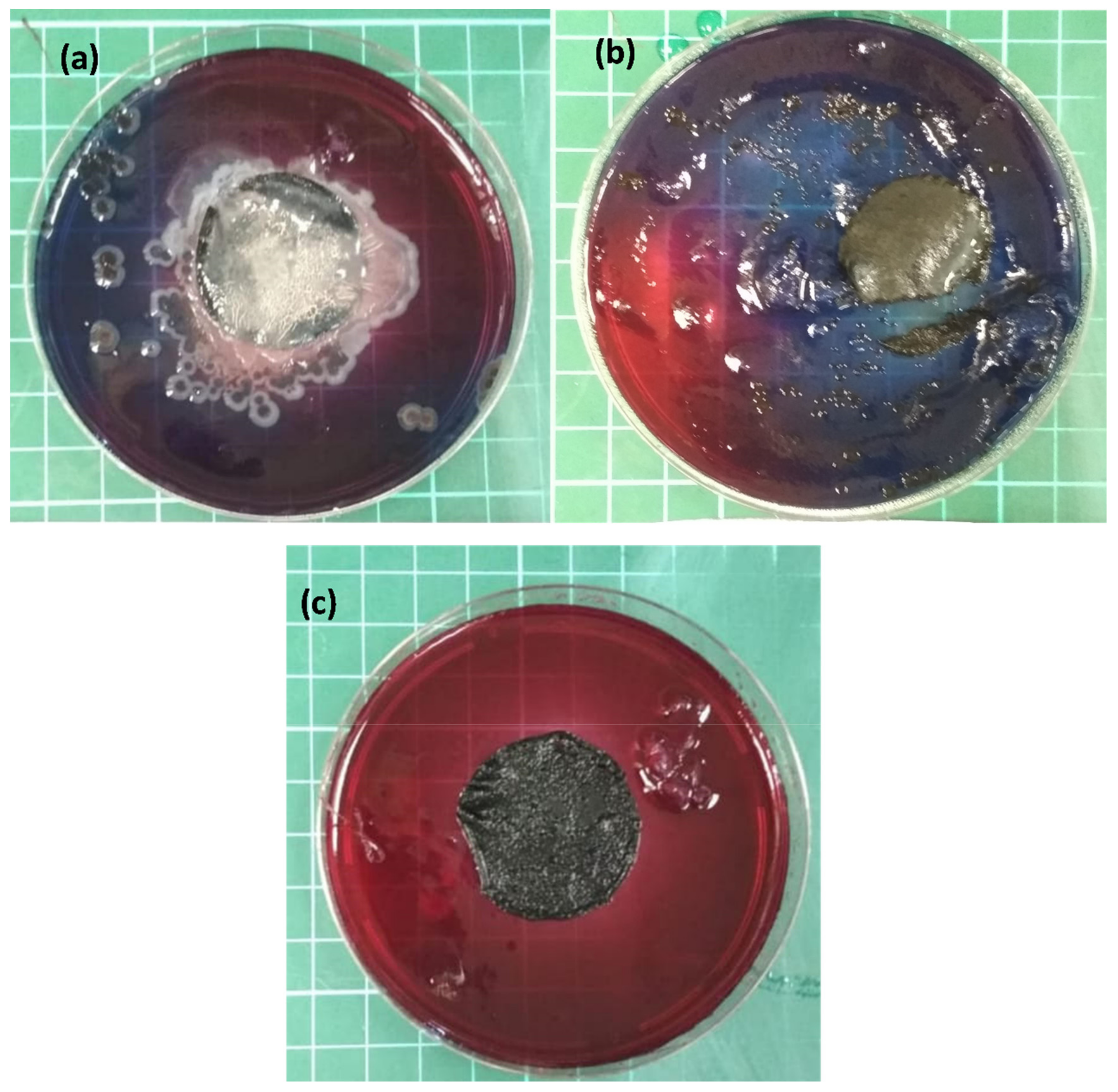
As part of the membrane activity analysis, an antimicrobial test was performed. Figure 5 illustrates an antimicrobial activity test, performed according to the colony counting technique [37], composed of: (a) the reference CNT, (b) the PANI/CNT physical mixture, and (c) the PANI-coated CNT membrane. E. coli bacteria were used as a model. The neat CNT and the PANI/CNT physical mixture membranes formed a large bacterial colony after 96 h of incubation. As expected, the PANI-coated membrane exhibited zero colonies, further demonstrating the antimicrobial activity of the in situ polymerized PANI. This result further supports the claim that the unattached PANI was removed from the physical mixture membrane when rinsing. The successful antibacterial results are important for increasing the membrane lifetime by reducing biofouling.
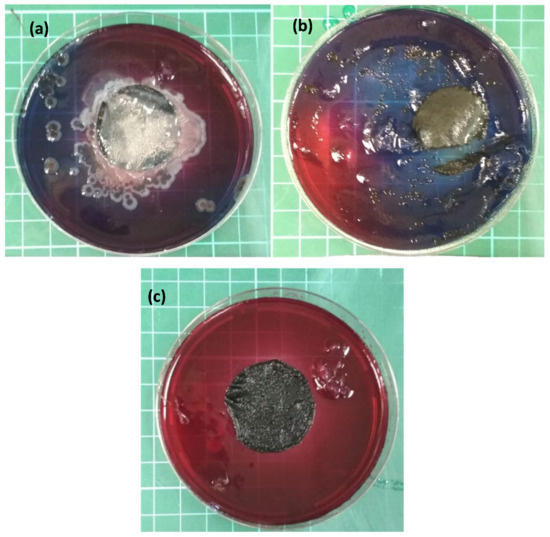
Figure 5.
Antimicrobial activity test, using the colony counting technique for the (a) reference CNT, (b) PANI/CNT physical mixture, and (c) the PANI-coated CNT membranes. Red indicated no bacteria populations at all, whereas blue indicated intense bacterial activity.
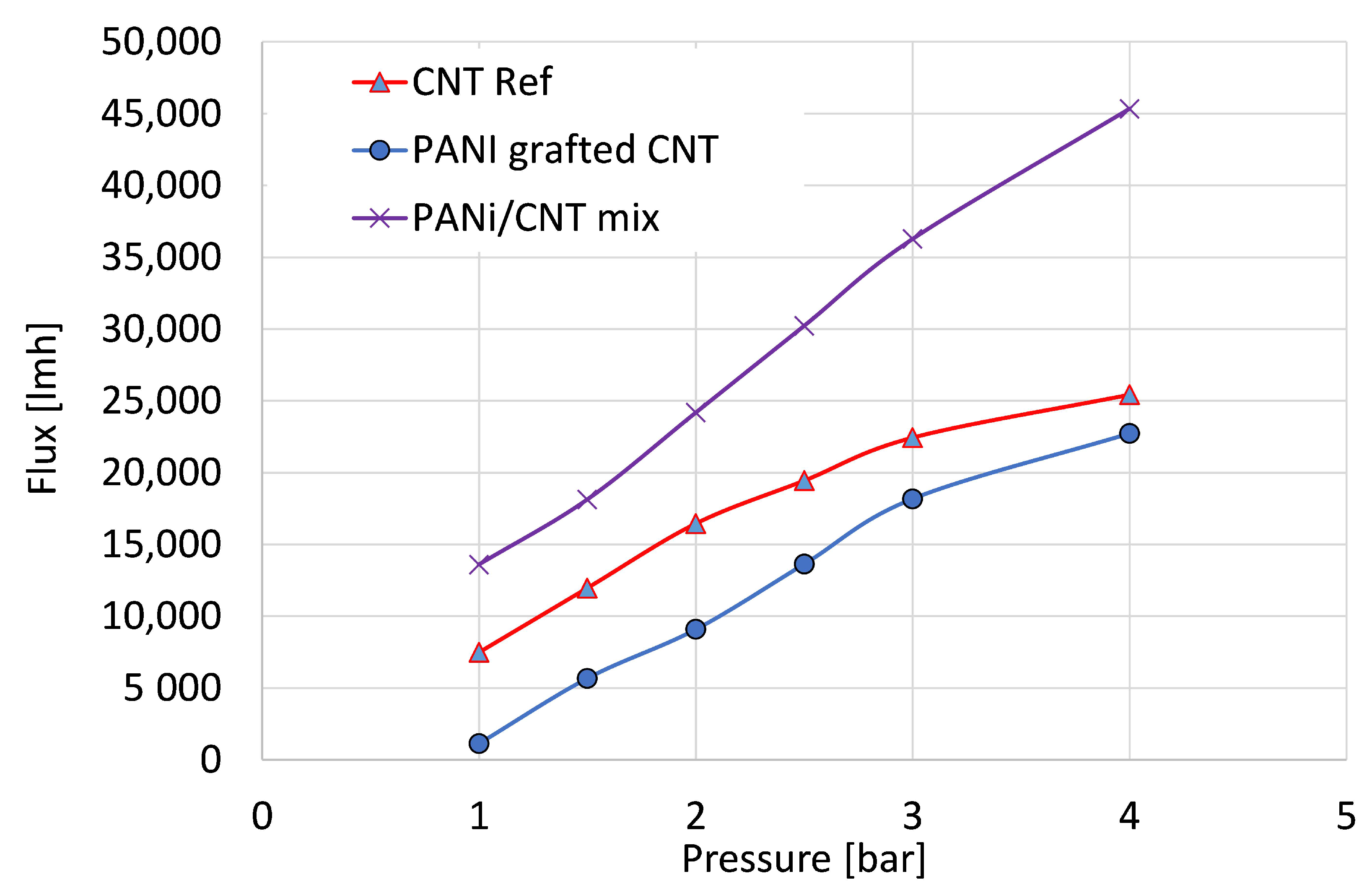
The following results were obtained for an in-depth study of the membrane hydraulic properties. The water flux and salt rejection were measured and analyzed. Figure 6 depicts the flux properties of the reference CNT, the physical mixture of PANI/CNT, and the PANI-coated CNT membranes using distilled water. The flux properties can be used as an indicator of membrane density and permeability since a lower flux is correlated with a denser membrane and smaller pores. The PANI grafted CNT exhibited a lower flux at all measured pressures, thus suggesting that the presence of PANI in the membrane increased its density. The physical mixture exhibited higher flux values since the unattached PANI was removed during rinsing, leaving larger voids and resulting in a poor membrane. Given the higher surface area, the grafted PANI improved the membranal properties. The water permeability for grafted PANI compared to the physical mixture and the pristine CNT membrane was 7595, 11,818, and 5400 L h−1 bar−1 m−2, or 524, 815, and 372 L h−1 psi−1 m−2, respectively. Commercial ultrafiltration membranes exhibit water permeability ranges from 3 up to 750 lmh psi−1 [44], suggesting that we have successfully demonstrated a hybrid membrane using the CNT/PANI material. Similar membranes fabricated from neat CNT [45] exhibited water permeability values of ~1400 L h−1 bar−1 m−2, however, with lower salt removal properties.
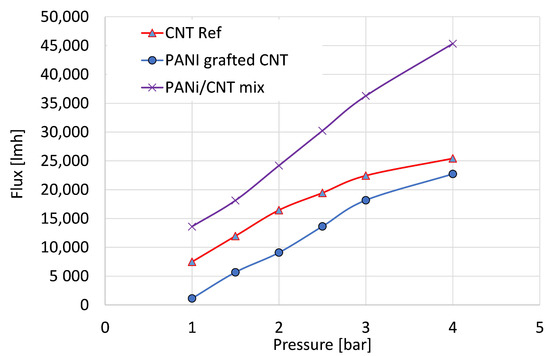
Figure 6.
Distilled water flux properties of the reference CNT (triangle), PANI/CNT physical mixture (X), and PANI-coated CNT (circle) membranes.
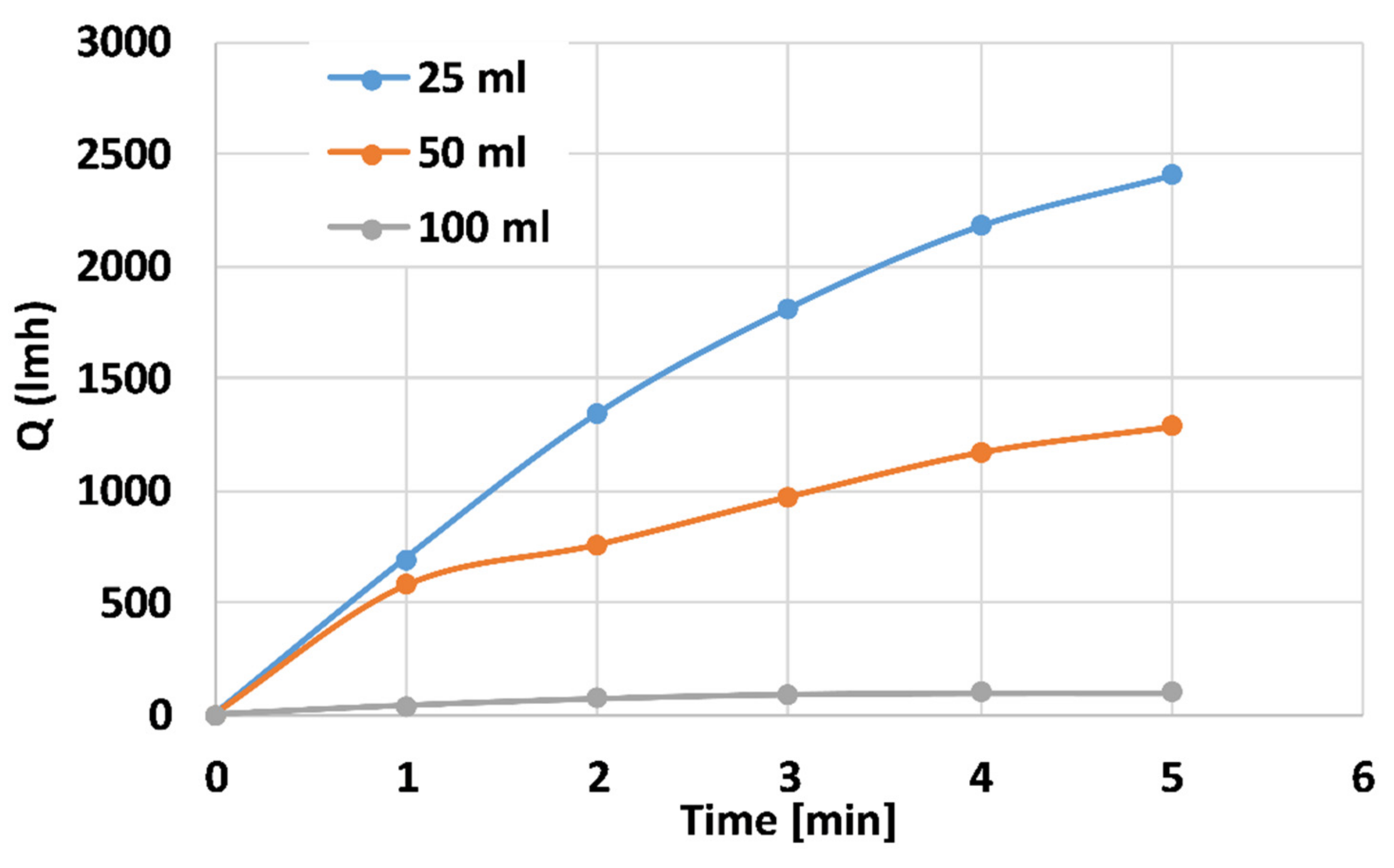
Figure 7 depicts the distilled water flux properties of the 25 mL (blue), 50 mL (orange), and 100 mL (grey) PANI-coated CNT membranes at a trans-membranal pressure drop of 4 bars. The membranes thicknesses are 0.34, 1.45, and 2.56 mm, respectively. The steady-state fluxes for the 25-, 50-, and 100-mL membranes are ~2500, 1300, and 100 L h−1 m−2, respectively. As expected, the flux for the thinner membranes is higher since the membranal flow resistance is smaller. Similar behavior was obtained for 2 and 3 bar pressure drops. The dramatic reduction in flux for the thicker, 100 mL coating indicates that the membrane is promising as an reverse osmosis (RO) membrane with high resistance [46].
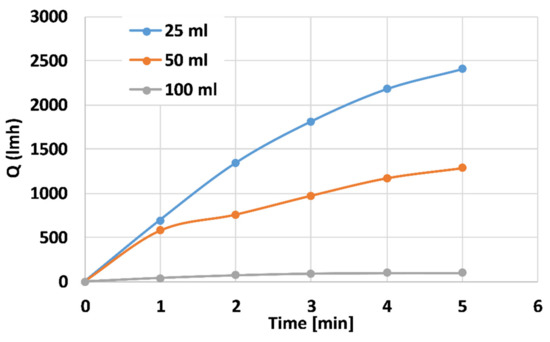
Figure 7.
Distilled water flux properties of the 25 mL (blue), 50 mL (orange), and 100 mL (grey) PANI-coated CNT membranes at the trans-membranal pressure drop of 4 bars.
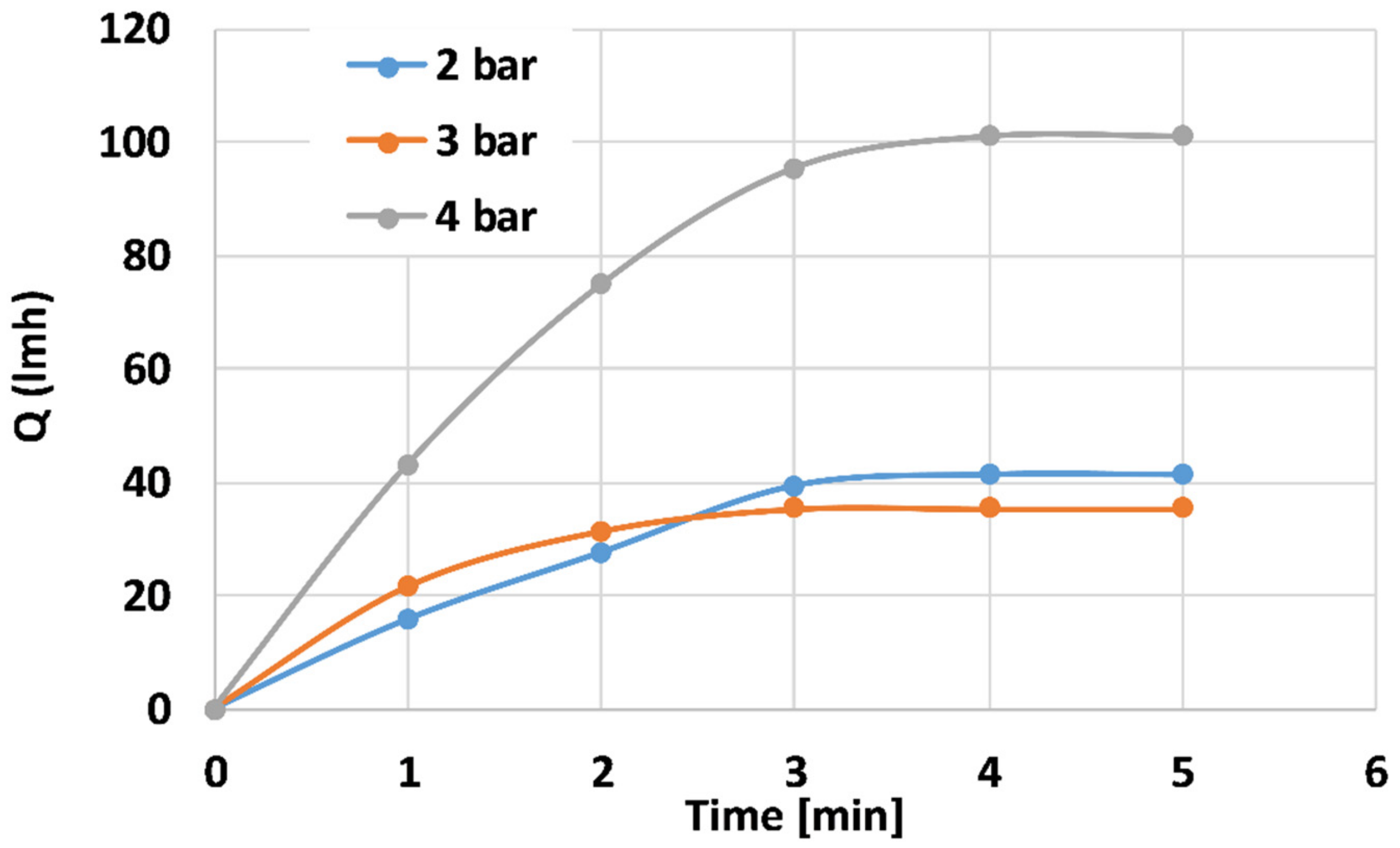
Figure 8 depicts distilled water flux properties of the 100 mL PANI-coated CNT membranes at different trans-membranal pressure drops. The steady-state flux for the 2, 3, and 4 bar pressure drops is ~41, 35, and 100 L h−1 m−2, respectively. The membranes reached steady state after ~3 min. According to this study, one can determine the steady-state operating conditions. Further study of the prolonged effect, including chemical backwash, is currently in progress.
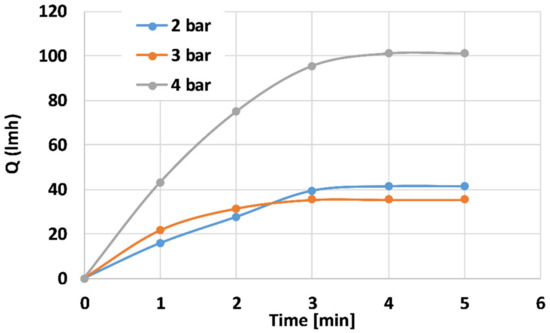
Figure 8.
Distilled water flux properties of the 100 mL PANI-coated CNT membranes at different pressures.
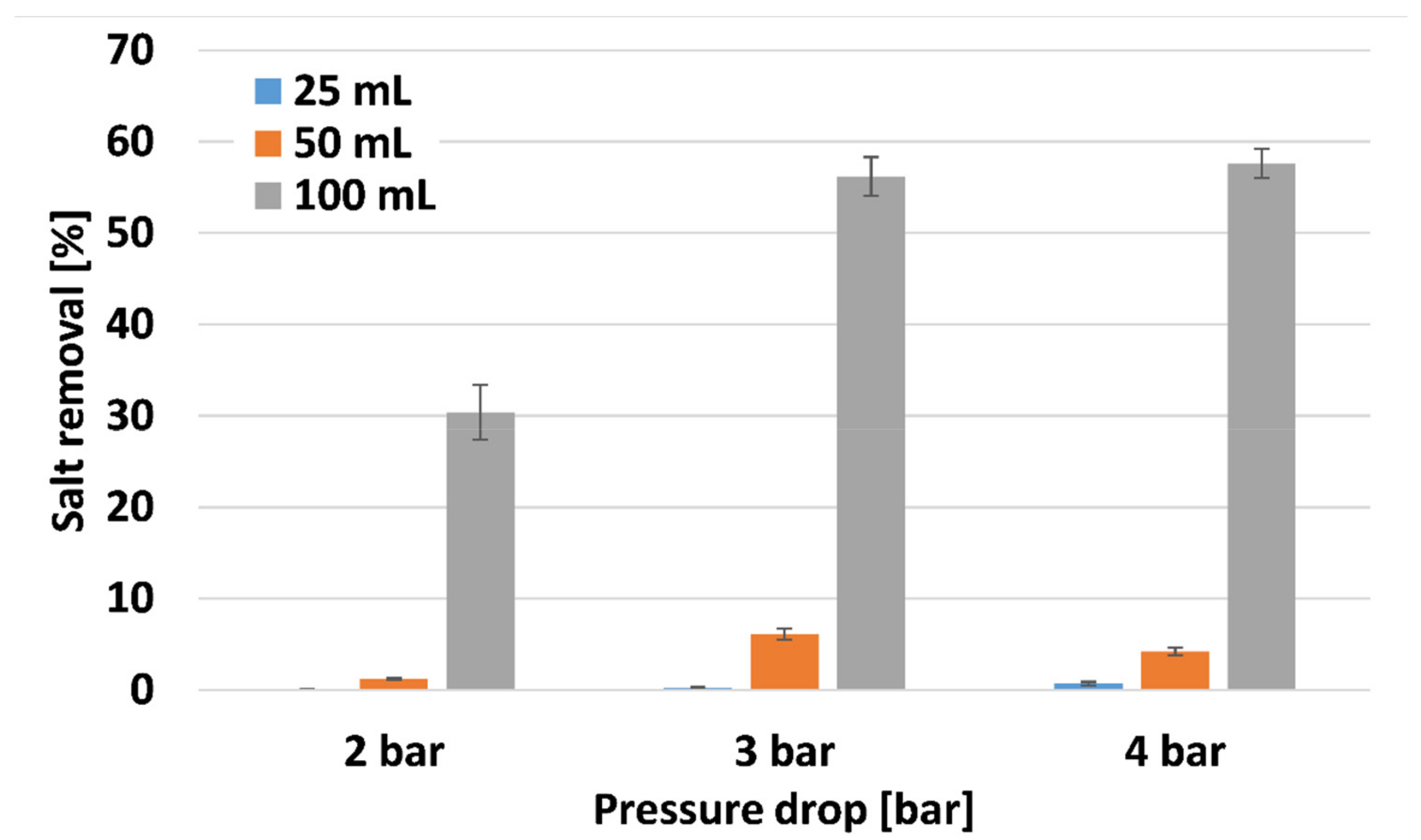
Figure 9 depicts salt removal properties of PANI-coated CNT membranes at different pressure drops. The thinner membranes exhibited low salt removal, since there was not enough membranal resistance to prevent salt penetration. The thicker membrane exhibited high salt removal properties of 30.4, 56.2, and 57.6% for 2, 3, and 4 bars, respectively. Such values would be considered low compared to typical RO processes with ~98% salt removal. However, the process described in this manuscript was conducted with higher initial salt concentration (5% compared to 3.5%) and with much lower pressure drop (4 compared to 70 bar). The higher salt concentration increases the osmotic pressure drop, and the driving force for the filtration process is the pressure drop. Thus, the membranes fabricated are quite efficient for salt removal. The PANI-coated CNT acts as an ionic polymer, removing ions from water, thus increasing the membranal salt removal properties.
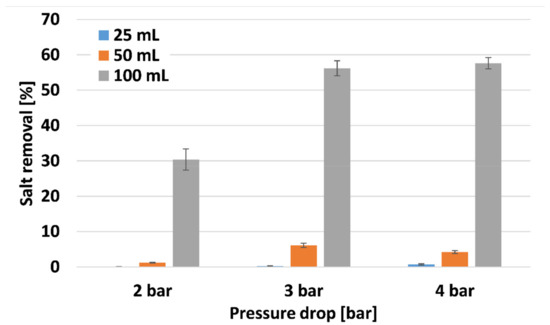
Figure 9.
Salt removal of the PANI-coated CNT membranes.
4. Conclusions
The purpose of this article was to present a study of the key parameters involved in the fabrication of PANI/CNT water filtration membranes characterized by a combination of the preferred flux and antimicrobial properties. Specifically, it analyzed a novel in situ interfacial dynamic inverse emulsion polymerization process under the sonication of aniline in the presence of CNT in ethanol. The polymerization process described in this manuscript is simple and very rapid (10 min) compared to previous reports in the literature. During polymerization, nanoparticles are spontaneously coated with PANI, creating a core-shell structure as demonstrated by HRSEM and FTIR measurements. The membrane pore size ranged between 100–200 nm, with an average value of ~119 ± 28.3 nm. This structure is a key-component for the durability and stability of hybrid membranes. The water flux of PANI grafted CNT was lower than that of the CNT reference, improving membranal activity. The efficacy of PANI grafting to the CNT surface was demonstrated to exhibit improved antimicrobial and flux properties. Film resistivity decreased when the film was treated with alcohol and was used for selection of the most efficient alcohol as the solvent for this polymerization technique. According to the water permeability, these membranes are in the range of ultrafiltration membranes. An antimicrobial activity test demonstrated that while the neat nanoparticles membrane formed a large bacterial colony, the PANI-grafted CNT membrane had zero bacterial activity. The thicker, 2.56 mm membranes exhibited high salt removal properties at a low pressure drop. Such active membranes comprise a novel approach for future water treatment applications. For example, these membranes can perform in countries with low energy availability, allowing for freshwater production for all.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing—original draft preparation, and review and editing: R.Y.S.; formal analysis and investigation I.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially supported by a Kinneret Academic College internal research fund.
Acknowledgments
I am grateful to Esther Segal and Naama Massad-Ivanir from the Department of Biotechnology and Food Engineering, Technion, for the HRSEM, FTIR, and TGA analyses. Thanks to Ofir Menashe, Micha Alkoby, and Ori Zion, Department of Water Industries, Kinneret Academic College, for the anti-biofouling and flow analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sparks, T.; Chase, G. Filters and Filtration Handbook, 6th ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.; Roddick, F.; Fan, L. Biofouling of Water Treatment Membranes: A Review of the Underlying Causes, Monitoring Techniques and Control Measures. Membranes 2012, 2, 804–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kujundzic, E.; Cobry, K.; Greenberg, A.R.; Hernandez, M. Use of Ultrasonic Sensors for Characterization of Membrane Fouling and Cleaning. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2008, 3, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, K.C.; Blainey, B.L. Role of Bacterial Adhesion in Biofilm Formation and Biocorrosion; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, T.S. Microbial Fouling and Corrosion: Fundamentals and Mechanisms. In Operational and Environmental Consequences of Large Industrial Cooling Water Systems; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 95–126. [Google Scholar]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Schaule, G. Biofouling on membranes—A microbiological approach. Desalination 1988, 70, 95–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, M.A. Biofouling prevention in RO polymeric membrane systems. Desalination 1992, 88, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trägårdh, G. Membrane cleaning. Desalination 1989, 71, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.D. Disinfection by-products and other emerging contaminants in drinking water. Trends Anal. Chem. 2003, 22, 666–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhivya, C.; Vandarkuzhali, S.A.A.; Radha, N. Antimicrobial activities of nanostructured polyanilines doped with aromatic nitro compounds. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 3785–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.; Sabzi, M.; Fattahi, A.; Arkan, E. Electrospun silk fibroin/PAN double-layer nanofibrous membranes containing polyaniline/TiO2 nanoparticles for anionic dye removal. J. Polym. Res. 2017, 24, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, J.; Chen, N. Synthesis of DBSA-doped Polyaniline by Emulsion Polymerization and PANI/PLA Electrospun Fiber Membrane Conductivity. J. Text. Inst. 2019, 110, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahadat, M.; Khan, M.Z.; Rupani, P.F.; Embrandiri, A.; Sultana, S.; Ahammad, S.; Ali, S.W.; Sreekrishnan, T. A critical review on the prospect of polyaniline-grafted biodegradable nanocomposite. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 249, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elayappan, V.; Murugadoss, V.; Angaiah, S.; Fei, Z.; Dyson, P.J. Development of a conjugated polyaniline incorporated electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) composite membrane electrolyte for high performance dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Miao, Y.-E.; Liu, T. Electrically Conductive Polyaniline/Polyimide Nanofiber Membranes Prepared via a Combination of Electrospinning and Subsequent In situ Polymerization Growth. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 1206–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaffari-Moghaddam, M.; Eslahi, H. Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial properties of a novel nanocomposite based on polyaniline/polyvinyl alcohol/Ag. Arab. J. Chem. 2014, 7, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suckeveriene, R.Y. Grafting of polyaniline by a dynamic inverse emulsion polymerization technique onto reverse osmosis membranes as an antibiofouling agent. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 30, 1759–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapurina, I.; Stejskal, J. The mechanism of the oxidative polymerization of aniline and the formation of supramolecular polyaniline structures. Polym. Int. 2008, 57, 1295–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuer, O.; Sundararaj, U. Big returns from small fibers: A review of polymer/carbon nanotube composites. Polym. Compos. 2004, 25, 630–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.N.R.; Mueller, A.; Cheetham, A.K. (Eds.) The Chemistry of Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Properties and Applications in 2 Volumes; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 370, 741. [Google Scholar]
- Suckeveriene, R.; Tzur, A.; Narkis, M.; Siegmann, A. Grafting of polystyrene chains on surfaces of nanosilica particles via peroxide bulk polymerization. Polym. Compos. 2009, 30, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelikman, E.; Narkis, M.; Siegmann, A.; Valentini, L.; Kenny, J.M. Polyaniline/multiwalled carbon nanotube systems: Dispersion of CNT and CNT/PANI interaction. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2008, 48, 1872–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelikman, E.; Suckeveriene, R.Y.; Mechrez, G.; Narkis, M. Fabrication of composite polyaniline/CNT nanofibers using an ultrasonically assisted dynamic inverse emulsion polymerization technique. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2009, 21, 150–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suckeveriene, R.Y.; Narkis, M. Hybrid PANI/Carbon Nano-Composites for Production of Thin, Transparent and Conductive Films. U.S. Patent Application 14/016,903, 6 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Suckeveriene, R.Y.; Zelikman, E.; Mechrez, G.; Narkis, M. Literature review: Conducting carbon nanotube/polyaniline nanocomposites. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2011, 27, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suckeveriene, R.Y.; Zelikman, E.; Narkis, M. Hybrid Electrically Conducting Nano-Composites Comprising Carbon Nanotubes/Intrinsically Conducting Polymer Systems; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Suckeveriene, R.Y.; Mechrez, G.; Filiba, O.H.; Mosheev, S.; Narkis, M. Synthesis of hybrid polyaniline/carbon nanotubes nanocomposites in toluene by dynamic interfacial inverse emulsion polymerization under sonication. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 128, 2129–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suckeveriene, R.Y.; Zelikman, E.; Mechrez, G.; Tzur, A.; Frisman, I.; Cohen, Y.; Narkis, M. Synthesis of hybrid polyaniline/carbon nanotube nanocomposites by dynamic interfacial inverse emulsion polymerization under sonication. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 120, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Lalia, B.S.; Kochkodan, V.; Hilal, N.; Hashaikeh, R. Electrically conductive polymeric membranes for fouling prevention and detection: A review. Desalination 2016, 391, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, J.; Palaniappan, S.; Sathyanarayana, D. Conducting polyaniline blends and composites. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1998, 23, 993–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Hou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, M.; He, T.; Liu, J.; Chen, V. Polymeric antimicrobial membranes enabled by nanomaterials for water treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 550, 173–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, M.; De, S. Antibacterial polymeric membranes: A short review. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 1078–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odian, G. Principles of Polymerization, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; p. 768. [Google Scholar]
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nat. Cell Biol. 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginic-Markovic, M.; Matisons, J.G.; Cervini, R.; Simon, G.P.; Fredericks, P.M. Synthesis of New Polyaniline/Nanotube Composites Using Ultrasonically Initiated Emulsion Polymerization. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 6258–6265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Jain, V.; Bajpai, R.; Ghosh, P.; Pente, A.S.; Singh, B.P.; Misra, D.S. Formation of Carbon Nanotube Bucky Paper and Feasibility Study for Filtration at the Nano and Molecular Scale. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 19025–19031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, J.; Khan, W.; Mead, A.; Seal, D.; Sugden, J. Membrane filtration method for bacteriological testing of water: Enhanced colony visualization and stability on purification of phenol red indicator. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1994, 18, 117–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.-Z.; Kim, K.K.; So, K.P.; Lee, Y.H.; Chang, A.Y. Effect of Acid Treatment on Carbon Nanotube-Based Flexible Transparent Conducting Films. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7758–7759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghani, S.A.; Hajar, M.D.S.; Hanif, M.P.M. Effect of type of conductive fillers and poly (ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether on the electrical conductivity and morphology properties of poly (vinyl chloride)/poly (ethylene oxide) conductive films. Polym. Bull. 2016, 73, 2831–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regueira, R.; Suckeveriene, R.Y.; Brook, I.; Mechrez, G.; Tchoudakov, R.; Narkis, M. Investigation of the Electro-Mechanical Behavior of Hybrid Polyaniline/Graphene Nanocomposites Fabricated by Dynamic Interfacial Inverse Emulsion Polymerization. Graphene 2015, 4, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Ma, W.; Zhang, H.-L.; Xu, Z.-G.; Guo, Y.; Xiong, Y. Vinyl-carbon nanotubes for composite polymer materials. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 110, 1915–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-L.; Wang, C.-H.; Ma, C.-C.M.; Chiu, Y.-C.; Chiang, M.-T.; Chiang, C.-L. Preparations and properties of maleic acid and maleic anhydride functionalized multiwall carbon nanotube/poly(urea urethane) nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 1854–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozlívková, Z.; Trchová, M.; Šeděnková, I.; Špírková, M.; Stejskal, J. Structure and stability of thin polyaniline films deposited in situ on silicon and gold during precipitation and dispersion polymerization of aniline hydrochloride. Thin Solid Films 2011, 519, 5933–5941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, I.H.; Dutré, B.; Persson, K.M.; Trägårdh, G. Water permeability in ultrafiltration and microfiltration: Viscous and electroviscous effects. Desalination 1997, 113, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihsanullah, I. Carbon nanotube membranes for water purification: Developments, challenges, and prospects for the future. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 209, 307–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, Y.; Lienhard, J.H. How RO membrane permeability and other performance factors affect process cost and energy use: A review. Desalination 2019, 470, 114064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).