Congenital Syphilis: A U.S. Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
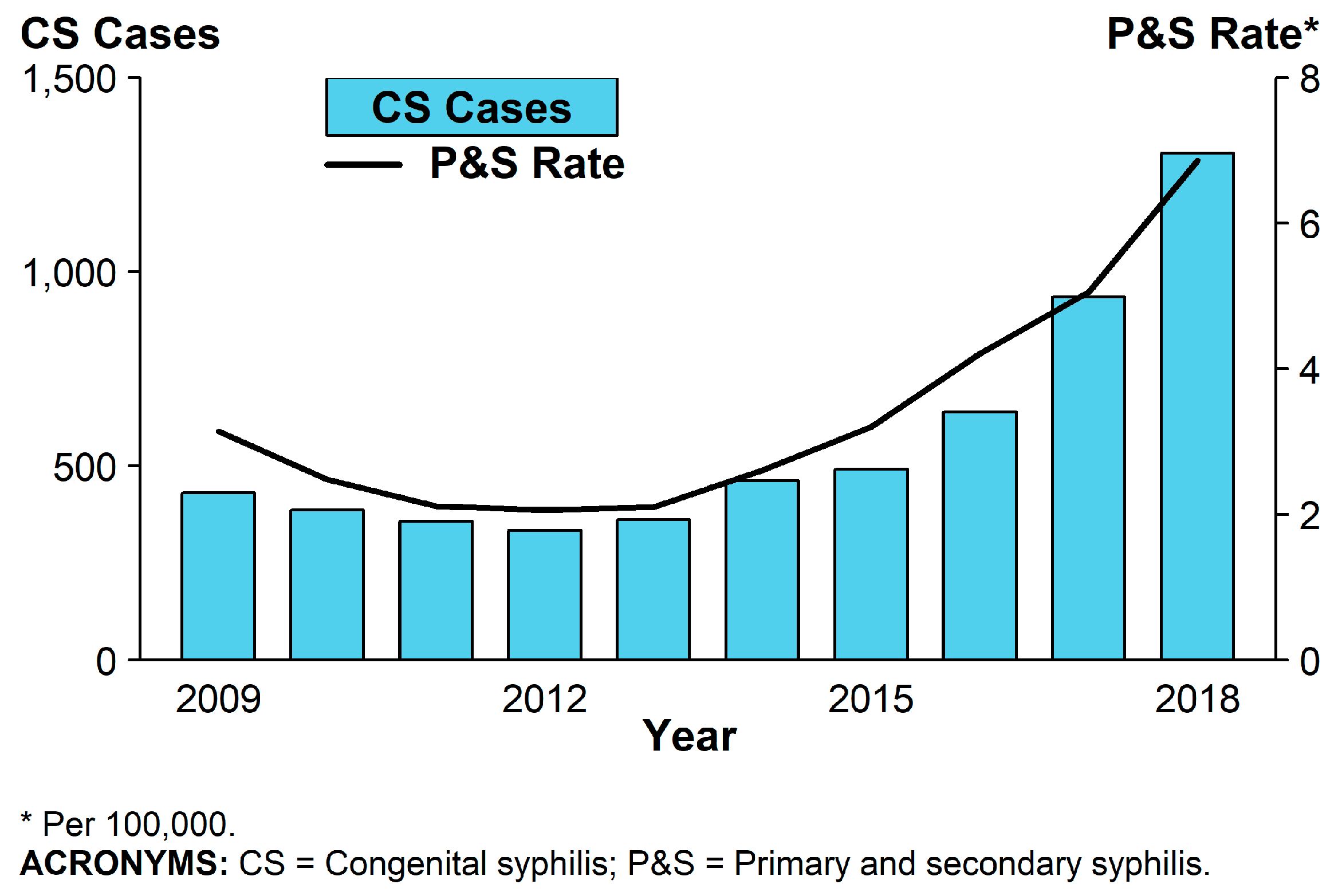
2. Epidemiology
3. Biology of Treponema Pallidum
4. Clinical Manifestations
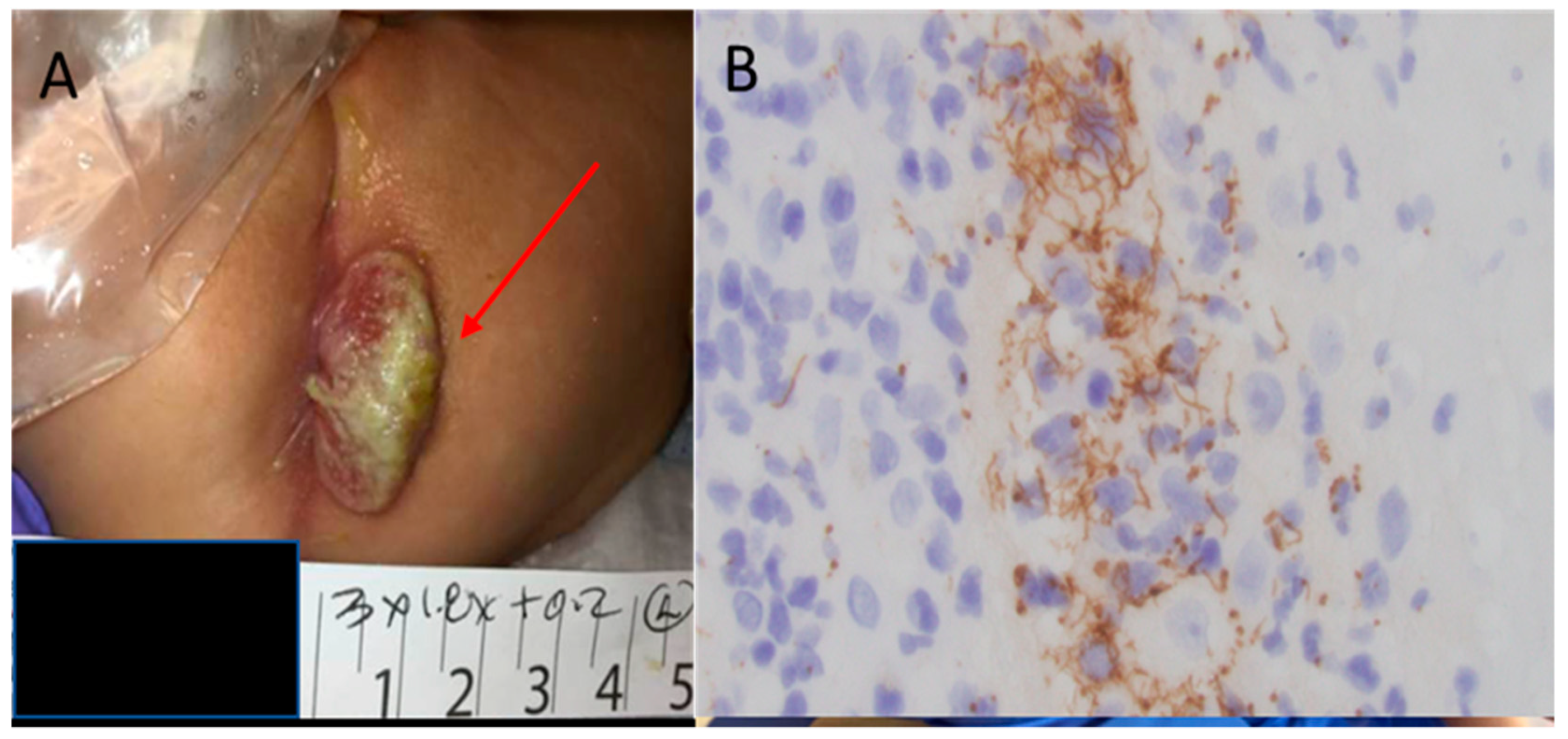
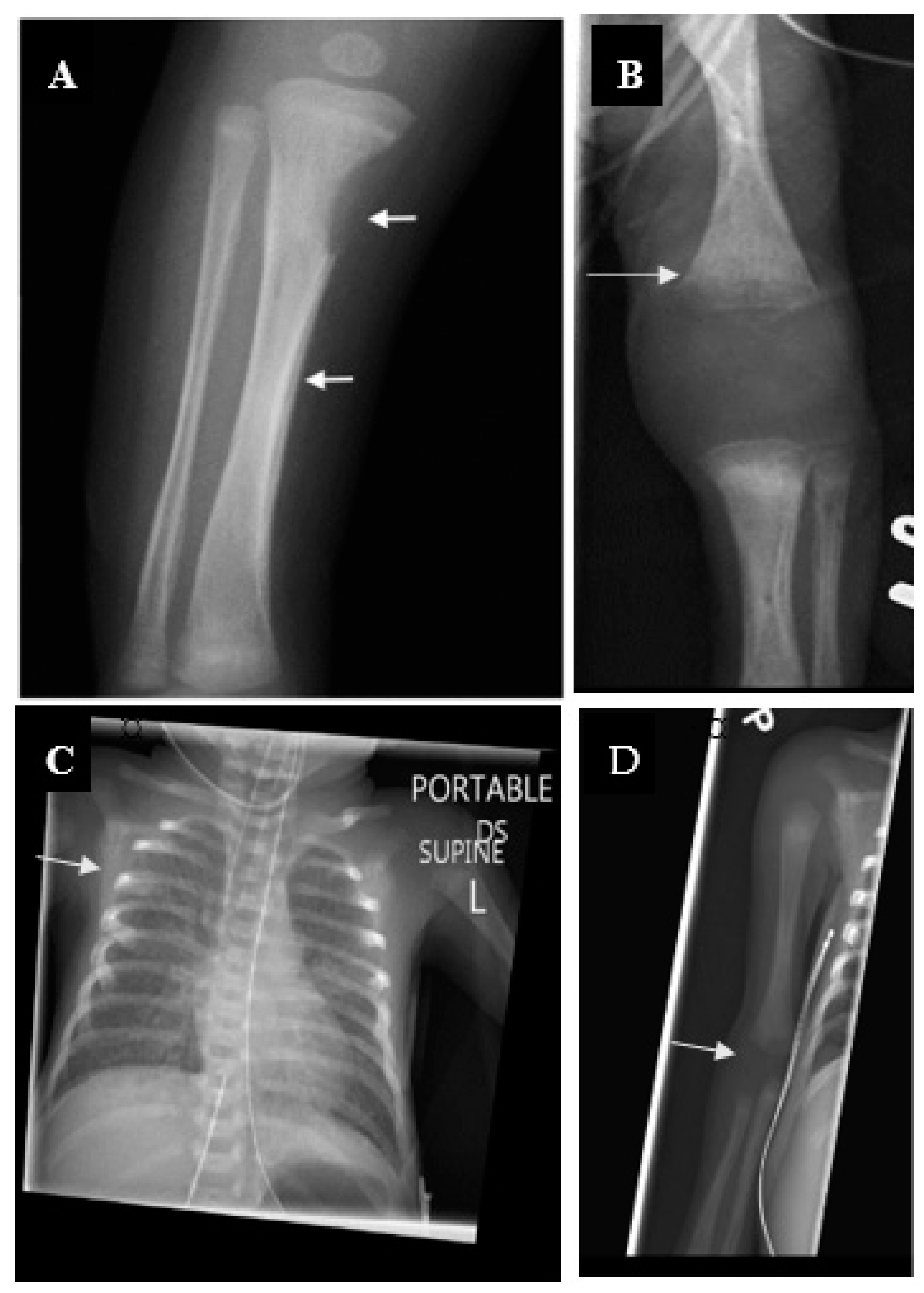
4.1. Early Congenital Syphilis
4.2. Late Congenital Syphilis
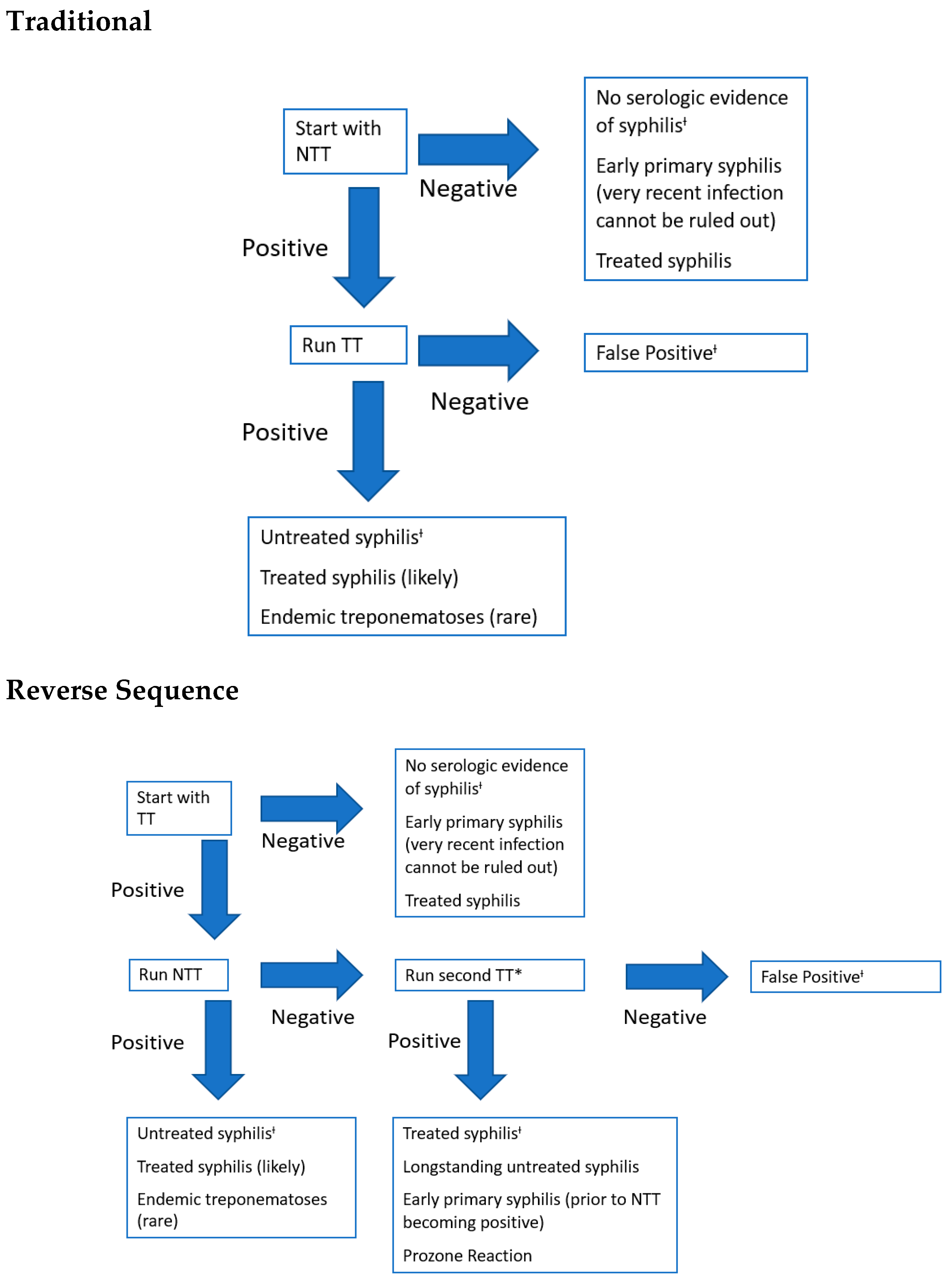
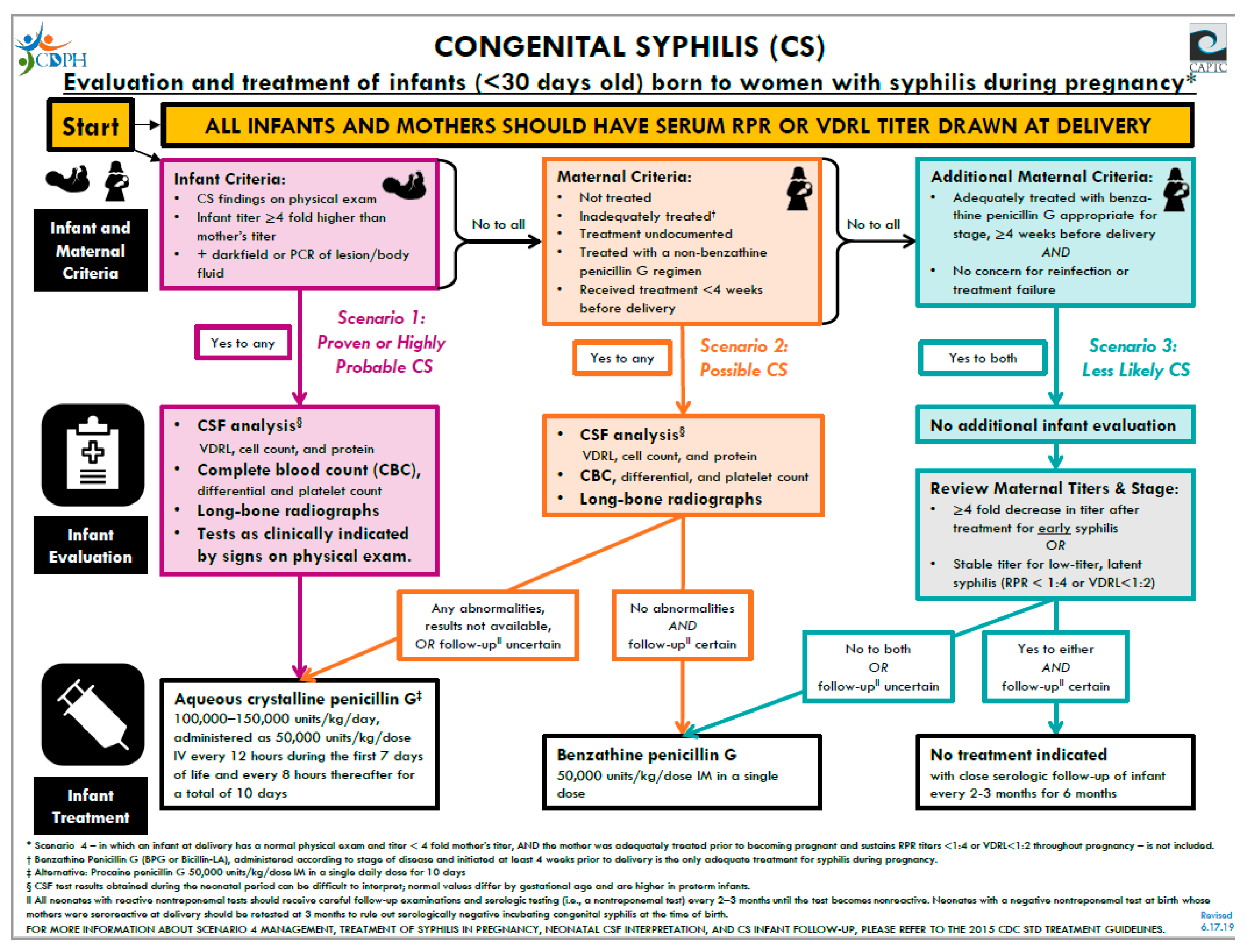
5. Diagnostic Tests and Management
6. Treatment and Follow-Up
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Congenital syphilis--New York City, 1986–1988. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 1989, 38, 825–829.
- Lawn, J.E.; Blencowe, H.; Waiswa, P.; Amouzou, A.; Mathers, C.; Hogan, D.; Flenady, V.; Frøen, J.F.; Qureshi, Z.U.; Calderwood, C.; et al. Stillbirths: Rates, risk factors, and acceleration towards 2030. Lancet 2016, 387, 587–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.M.; Sánchez, P.J. Congenital syphilis. Semin. Perinatol. 2018, 42, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimball, A.; Miele, K.; Bachmann, L.; Thorpe, P.; Weinstock, H.; Bowen, V. Missed Opportunities for Prevention of Congenital Syphilis. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korenromp, E.L.; Rowley, J.; Alonso, M.; Mello, M.B.; Wijesooriya, N.S.; Mahiané, S.G.; Ishikawa, N.; Le, L.-V.; Newman-Owiredu, M.; Nagelkerke, N.; et al. Global burden of maternal and congenital syphilis and associated adverse birth outcomes—Estimates for 2016 and progress since 2012. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually Transmitted Disease Surveillance 2018; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Peeling, R.W.; Hook, E.W. The pathogenesis of syphilis: The Great Mimicker, revisited. J. Pathol. 2005, 208, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šmajs, D.; Strouhal, M.; Knauf, S. Genetics of human and animal uncultivable treponemal pathogens. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 61, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radolf, J.D.; Kumar, S. The Treponema pallidum Outer Membrane. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 415, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radolf, J.D.; Deka, R.K.; Anand, A.; Šmajs, D.; Norgard, R.K.D.M.V.; Yang, X.F. Treponema pallidum, the syphilis spirochete: Making a living as a stealth pathogen. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 14, 744–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wan, D.; Fang, X.; Li, T.; Guo, Y.; Chang, D.; Su, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequence of Staphylococcus aureus Strain LCT-SA112. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gust, D.A.; Levine, W.C.; Louis, M.E.S.; Braxton, J.; Berman, S.M. Mortality associated with congenital syphilis in the United States, 1992–1998. Pediatrics 2002, 109, e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.R.; Brooks, L.C.; Davis, D.W.; Torrone, E.A.; Weinstock, H.S.; Kamb, M.L. Congenital syphilis: Trends in mortality and morbidity in the United States, 1999 through 2013. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 214, 381.e1–381.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorfman, D.H.; Glaser, J.H. Congenital Syphilis Presenting in Infants after the Newborn Period. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 323, 1299–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wozniak, P.S.; Cantey, J.B.; Zeray, F.; Leos, N.K.; Sheffield, J.S.; Wendel, G.D.; Sánchez, P.J. Congenital syphilis in neonates with nonreactive nontreponemal test results. J. Perinatol. 2017, 37, 1112–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Force, U.P.S.T.; Curry, S.J.; Krist, A.H.; Owens, D.K.; Barry, M.J.; Caughey, A.B.; Davidson, K.W.; Doubeni, C.A.; Epling, J.W.; Kemper, A.R.; et al. Screening for Syphilis Infection in Pregnant Women. JAMA 2018, 320, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follett, T.; Clarke, D.F. Resurgence of Congenital Syphilis: Diagnosis and Treatment. Neonatal Netw. 2011, 30, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, S.S.; Pickering, L.K.; Prober, C.G. Principles and Practice of Pediatric Infectious Diseases, 2nd Ed. Shock 2003, 20, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, A.C.; Singh, J. Congenital Syphilis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, J.R.; Arenth, J. Wimberger Sign in Congenital Syphilis. J. Pediatr. 2015, 167, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiumara, N.; Lessell, S. Manifestations of Late Congenital Syphilis. Arch. Derm. 1970, 102, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, M.; De Luca, C.; Mappa, I.; Spagnuolo, T.; Licameli, A.; Straface, G.; Scambia, G. Syphilis Infection during Pregnancy: Fetal Risks and Clinical Management. Infect. Dis. Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 2012, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khetarpal, S.; Kempf, E.; Mostow, E. Congenital Syphilis: Early- and Late-Stage Findings of Rhagades and Dental Anomalies. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2011, 28, 401–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Akinboyo, I.C.; Sue, P.K.; Donohue, P.K.; Ghanem, K.G.; Detrick, B.; Witter, F.R.; Page, K.R.; Arav-Boger, R.; Golden, W.C. Evaluating congenital syphilis in a reverse sequence testing environment. J. Perinatol. 2019, 39, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Academy of Pediatrics. Committee on Infectious, D. Red Book: Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases; American Academy of Pediatrics: Elk Grove Village, IL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Seña, A.C.; White, B.L.; Sparling, P.F. Novel Treponema pallidum Serologic Tests: A Paradigm Shift in Syphilis Screening for the 21st Century. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 51, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Discordant results from reverse sequence syphilis screening--five laboratories, United States, 2006–2010. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2011, 60, 133–137.
- Ghanem, K.G.; Ram, S.; Rice, P.A. The Modern Epidemic of Syphilis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeram, M.R.; Chopde, N.; Dawood, Y.; Siriboe, S.; Abedin, M. Lumbar puncture in the evaluation of possible asymptomatic congenital syphilis in neonates. J. Pediatr. 1996, 128, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, G.B.; Kamb, M.L.; Newman, L.M.; Mark, J.; Broutet, N.; Hawkes, S.J. Untreated maternal syphilis and adverse outcomes of pregnancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Bull. World Health Organ. 2013, 91, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDPH. Congenital Syphilis Algorithm. California Department of Public Health. 2019. Available online: https://www.cdph.ca.gov/Programs/CID/DCDC/Pages/CongenitalSyphilis.aspx (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- Matthias, J.M.; Rahman, M.M.; Newman, D.R.; Peterman, T.A. Effectiveness of Prenatal Screening and Treatment to Prevent Congenital Syphilis, Louisiana and Florida, 2013–2014. Sex. Transm. Dis. 2017, 44, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford, I.A.; Sánchez, P.J.; Stoll, B.J. Ending Congenital Syphilis. JAMA 2019, 322, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Early Congenital Syphilis | Late Congenital Syphilis | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Prenatal | Dentition | ||
| Nonimmune hydrops | Hutchinson’s teeth | ||
| Intrauterine growth retardation | Mulberry molars | ||
| Stillbirth | Eye | ||
| Hematological/ Reticuloendothelial | Interstitial keratitis | ||
| Hepatosplenomegaly | Ear | ||
| Lymphadenopathy | Eight nerve deafness | ||
| Thrombocytopenia | Nose/Face | ||
| Anemia | Saddle nose | ||
| Leukopenia/Leukocytosis (monocytosis) | Impaired maxillary growth | ||
| Mucocutaneous | Cutaneous | ||
| Rhinitis (sniffles) | Rhagades | ||
| Rash (papulovesicular, prominent in palms and sole; pemphigus syphiliticus) | Skeletal | ||
| Mucous patches | Frontal bossing | ||
| Skeletal | Saber shins | ||
| Long bone lesions (Wimberger sign in tibial protuberance) | Clavicle (sternal end) hypertrophy (Higoumenakis’ sign) | ||
| Periostitis (pseudoparalysis) | Clutton’s joints (knees) | ||
| Neurological | Neurological | ||
| Aseptic meningitis | Aseptic meningitis/asymptomatic neurosyphilis | ||
| Ocular | |||
| Retinitis (rare, also cataracts and keratitis) | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galvis, A.E.; Arrieta, A. Congenital Syphilis: A U.S. Perspective. Children 2020, 7, 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7110203
Galvis AE, Arrieta A. Congenital Syphilis: A U.S. Perspective. Children. 2020; 7(11):203. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7110203
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalvis, Alvaro E., and Antonio Arrieta. 2020. "Congenital Syphilis: A U.S. Perspective" Children 7, no. 11: 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7110203
APA StyleGalvis, A. E., & Arrieta, A. (2020). Congenital Syphilis: A U.S. Perspective. Children, 7(11), 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7110203






