Green Synthesis and Catalytic Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Based on Piper chaba Stem Extracts
Abstract
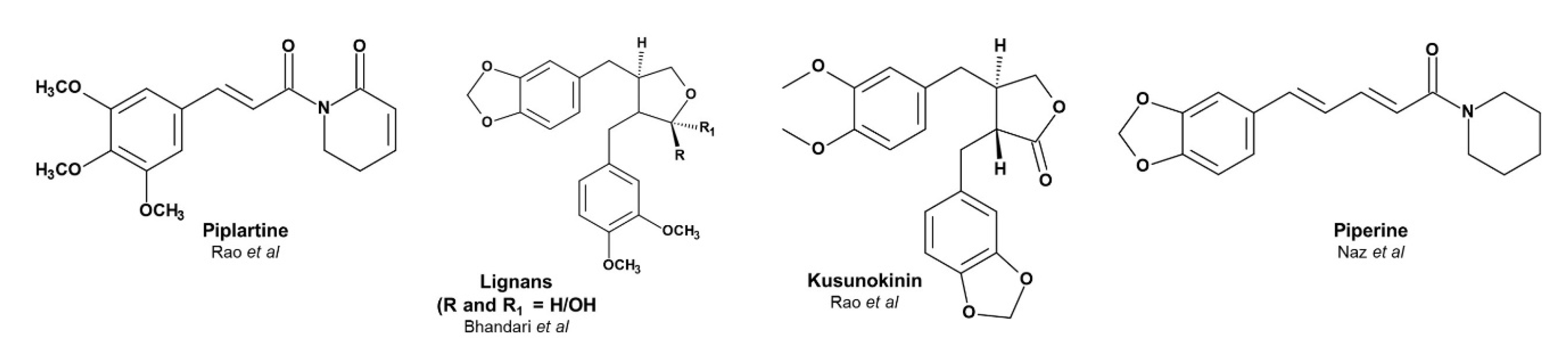
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Plant Materials
2.2. Preparation of Plant Extract
2.3. Materials
2.4. Measurements
2.5. Green Synthesis of AgNPs
2.6. Catalytic Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol to 4-Aminophenol
2.7. Degradation of MB
3. Results and Discussion
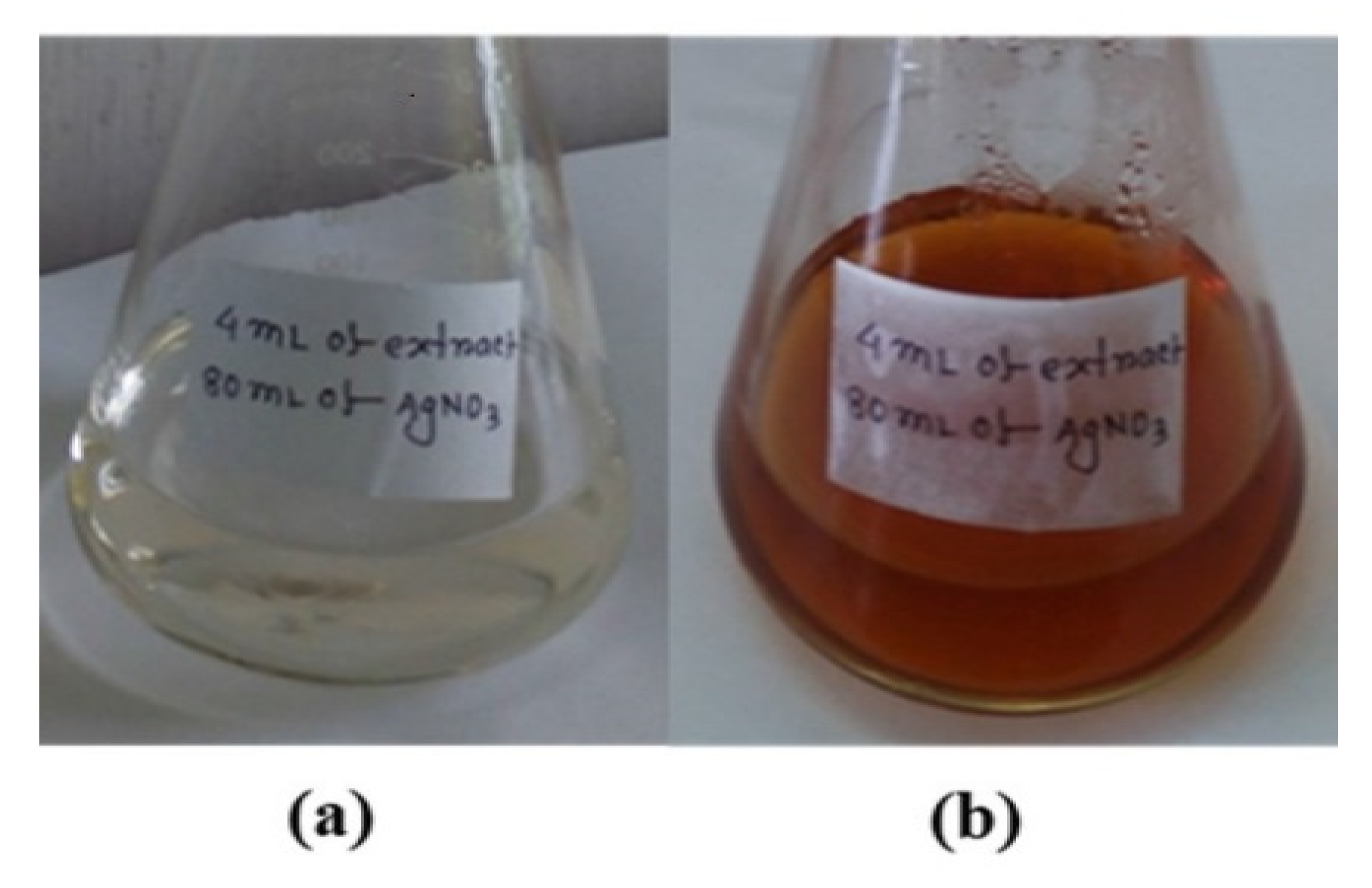
3.1. Formation of AgNPs
3.2. Effect of the Synthesis Conditions
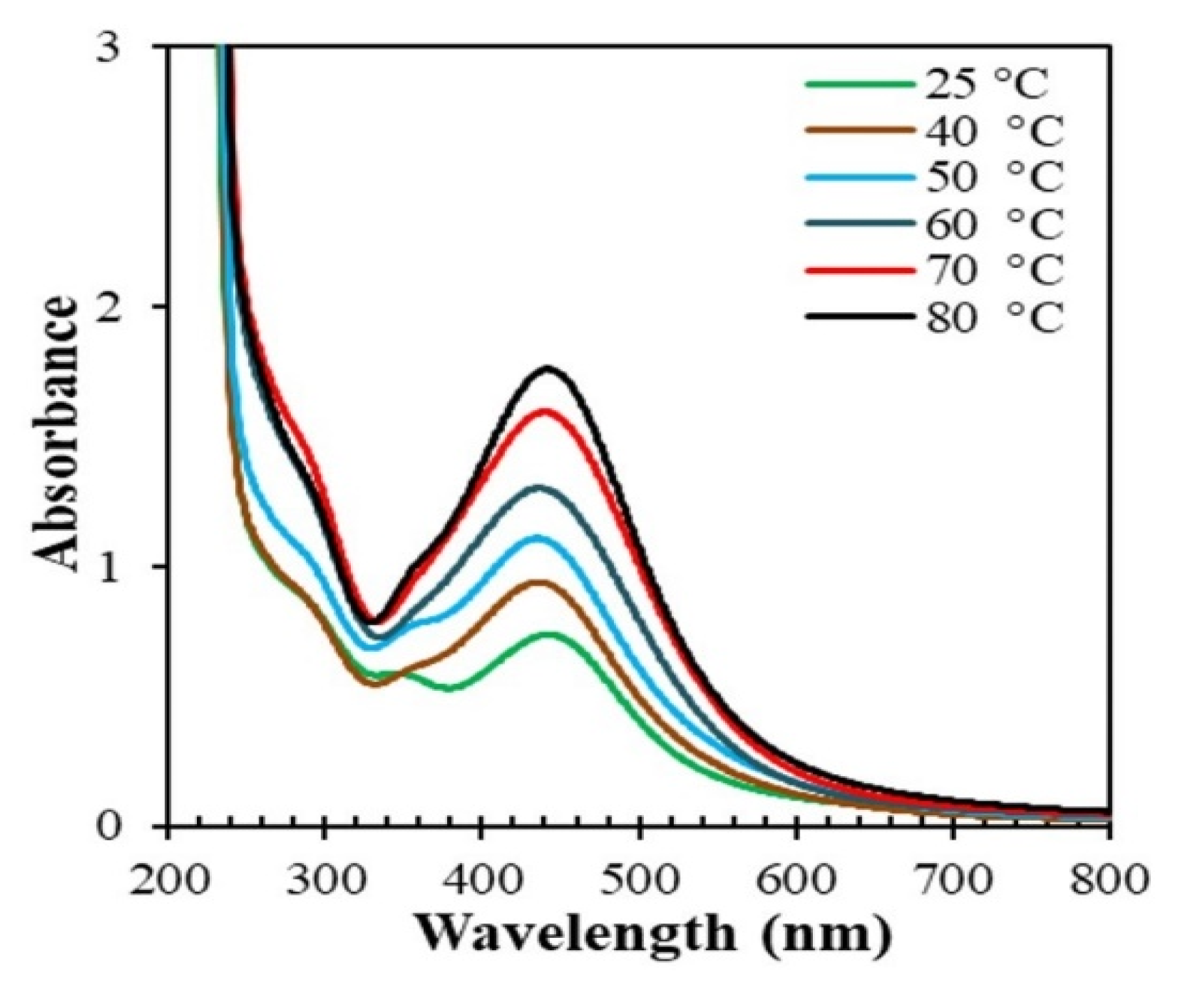
3.2.1. Effect of Temperature
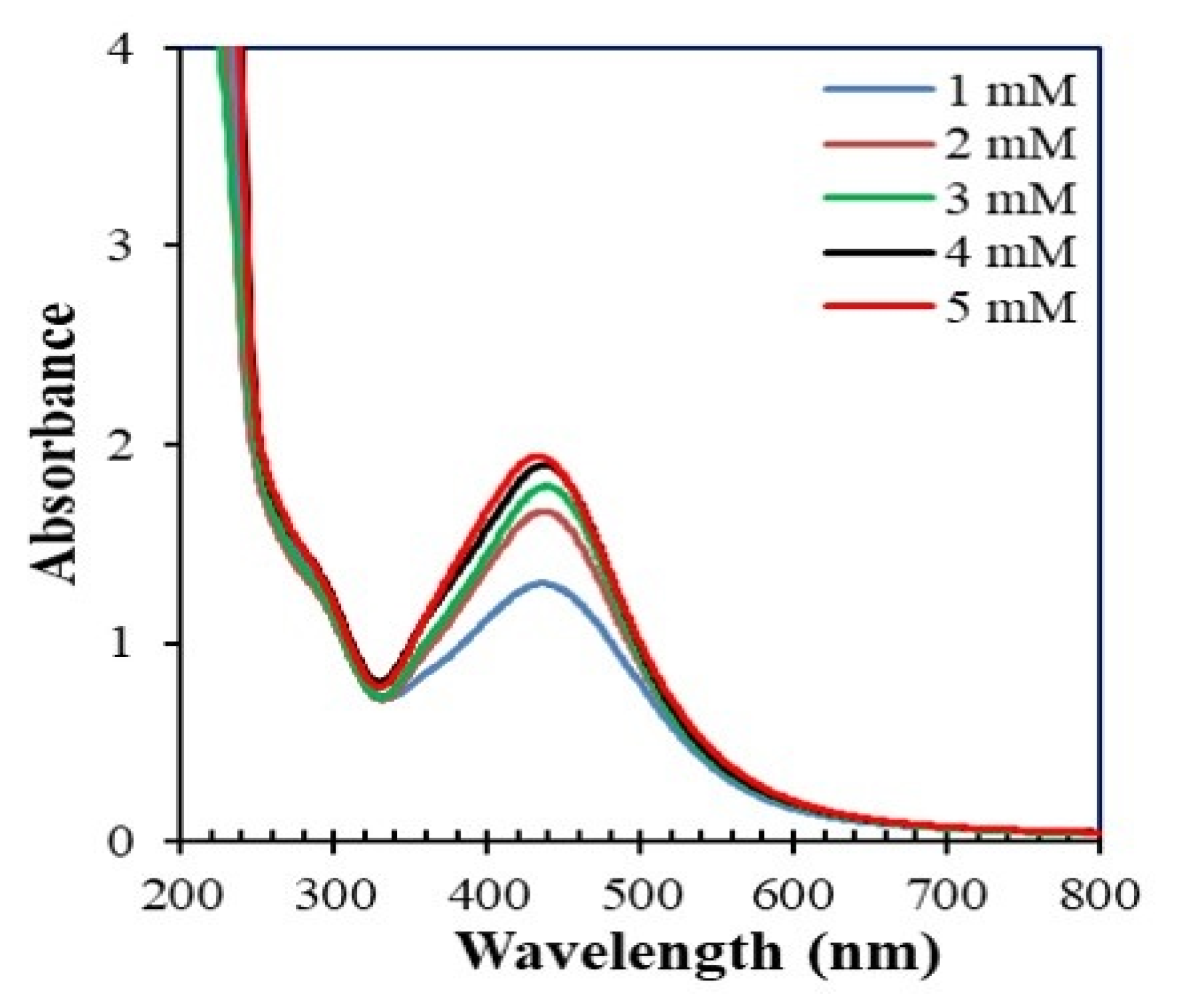
3.2.2. Effect of AgNO3 Concentration
3.2.3. Effect of Plant Extract Concentration
3.2.4. Effect of Reaction Time
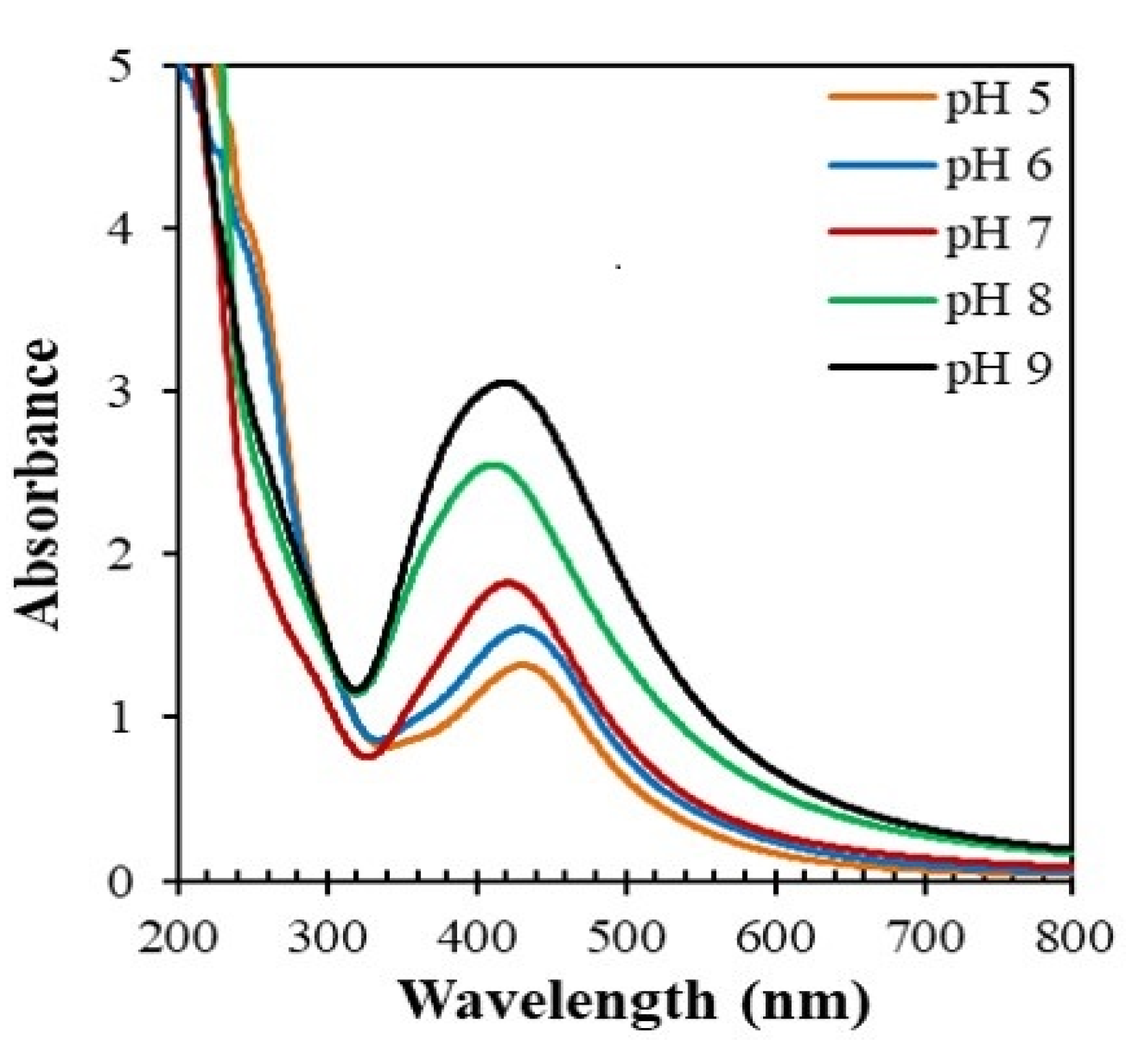
3.2.5. Effect of pH on the Formation of AgNPs
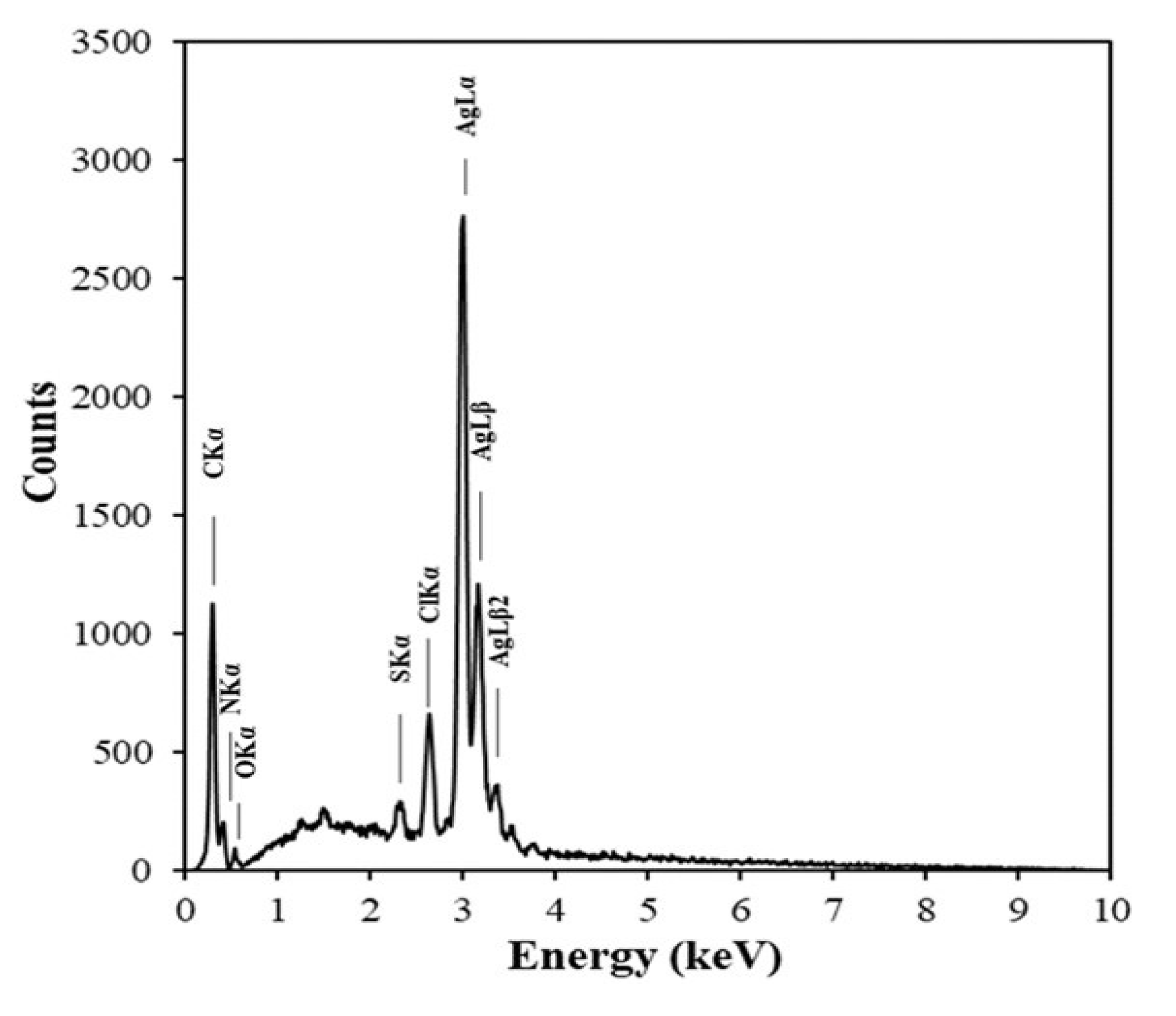
3.3. Structure of AgNPs
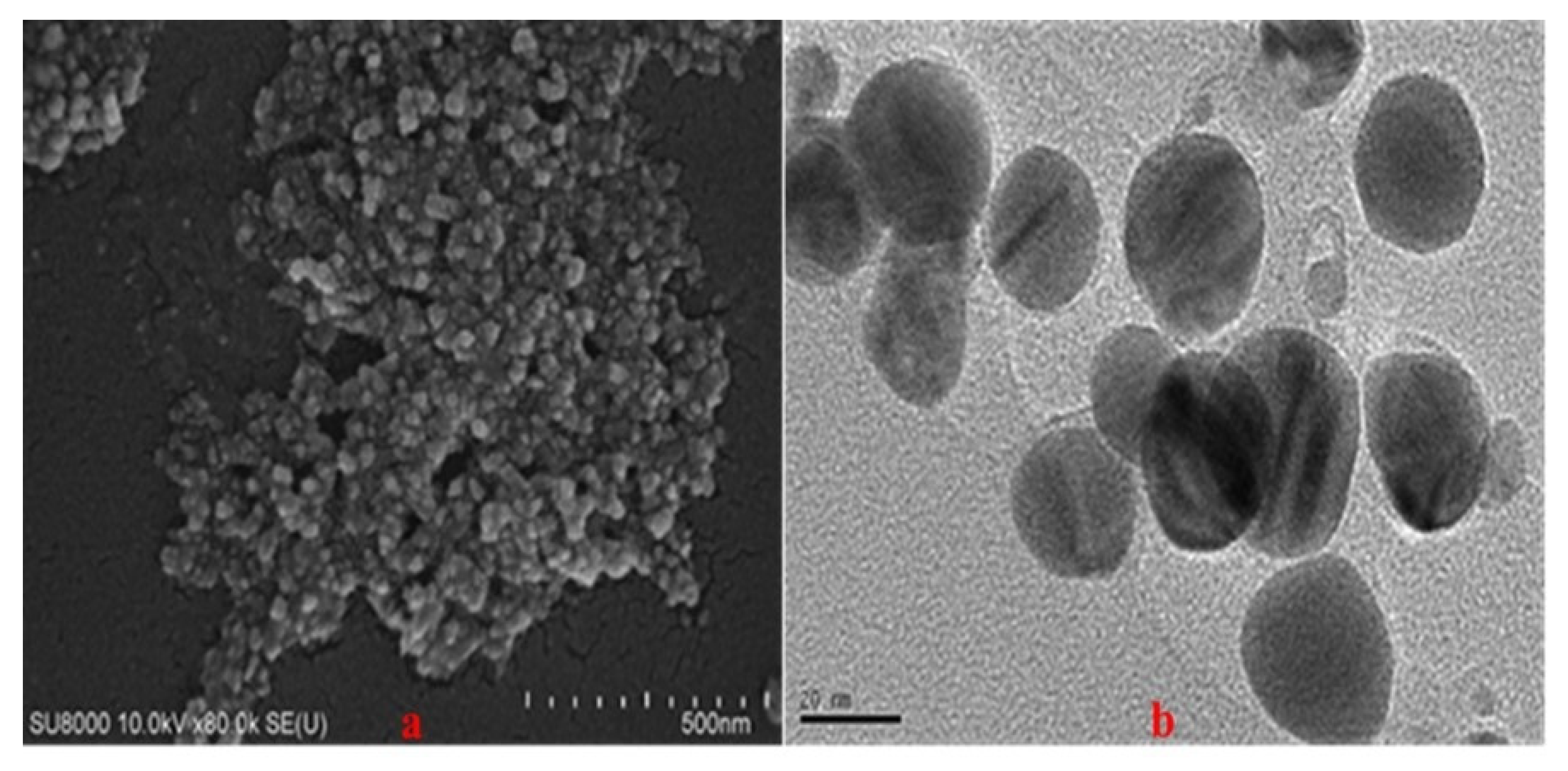
3.4. SEM and TEM Results
3.5. XRD Analysis
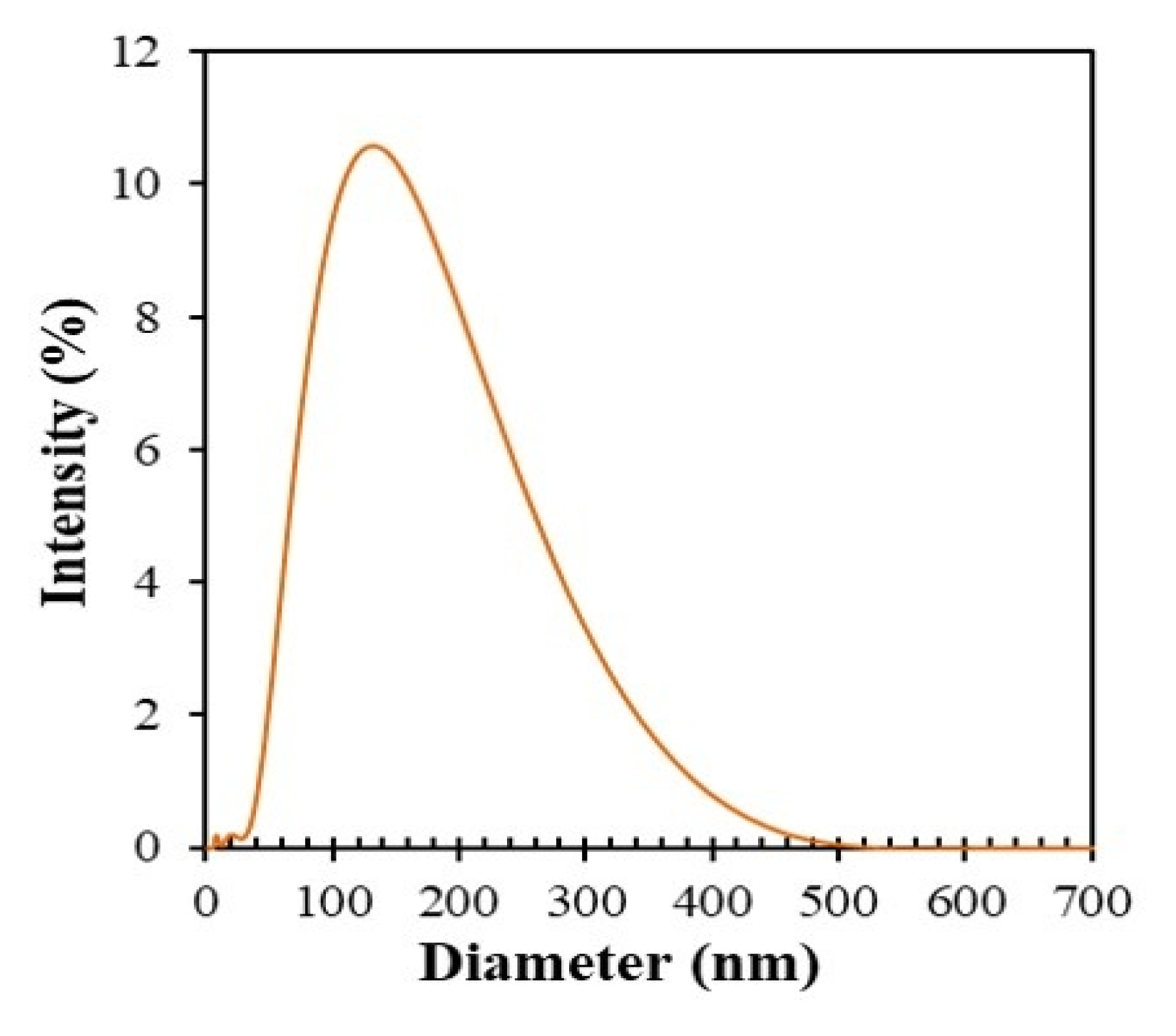
3.6. DLS Study and Zeta Potential Study
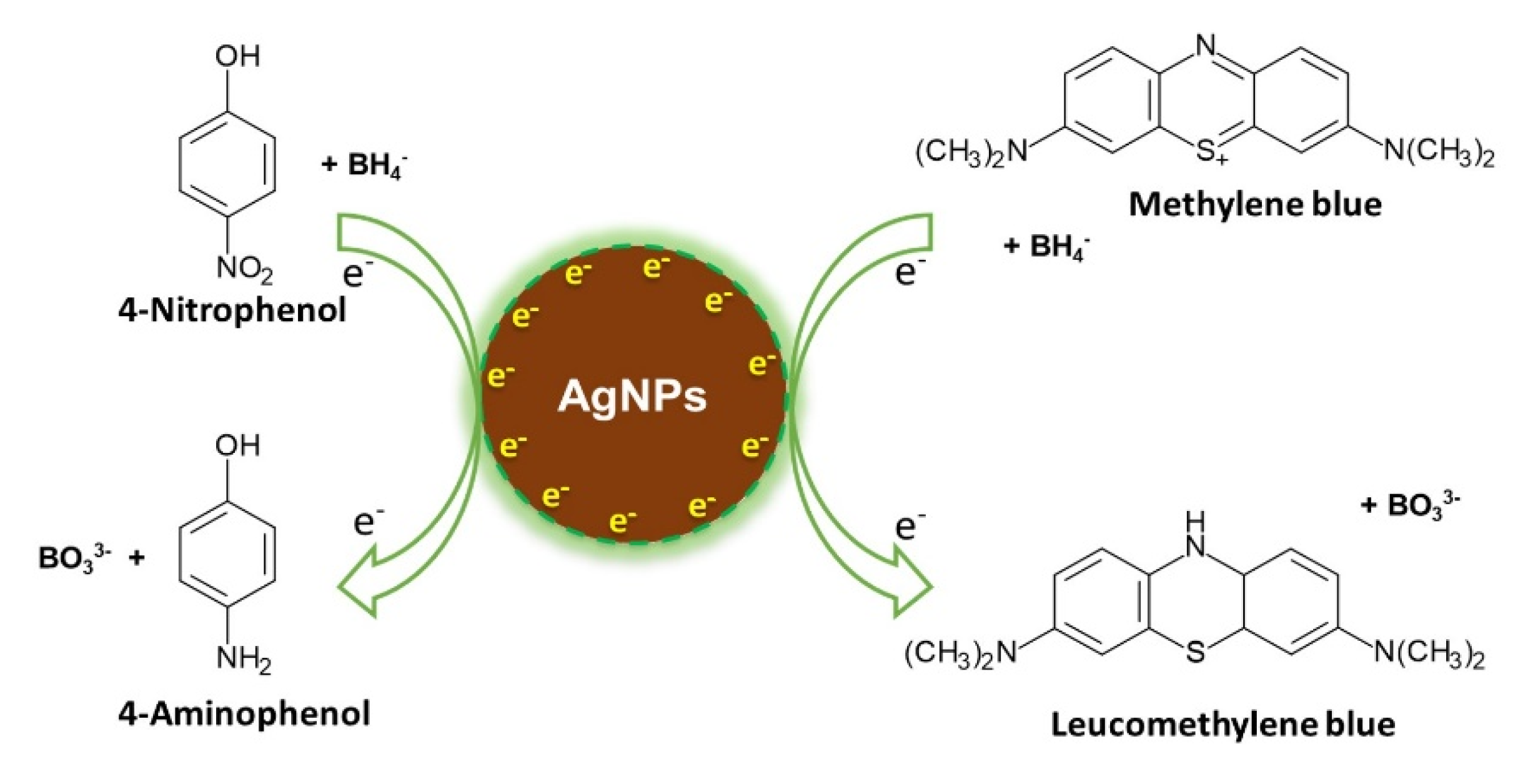
3.7. Application of the Synthesized AgNPs in the Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol (4-NP)
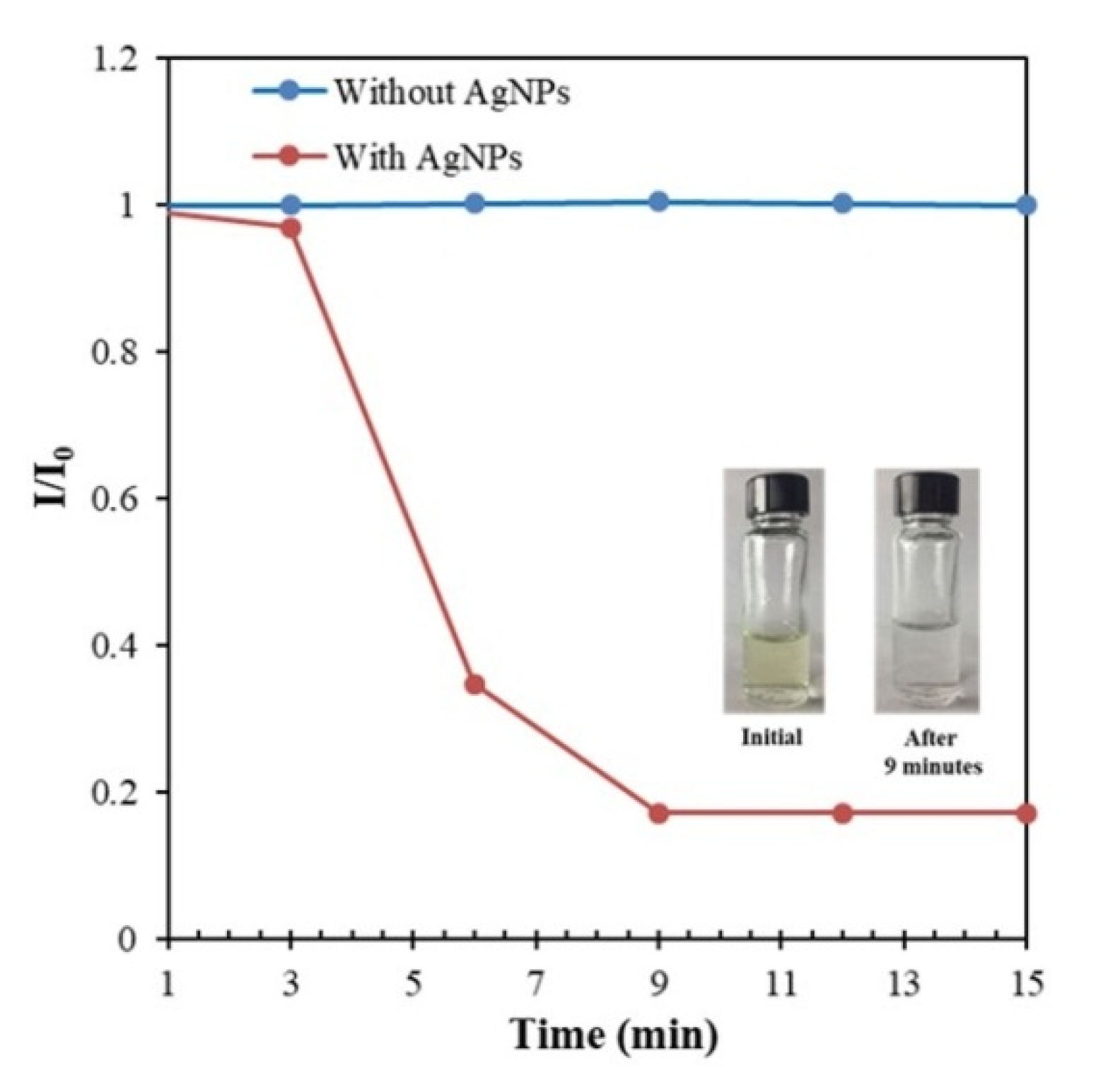
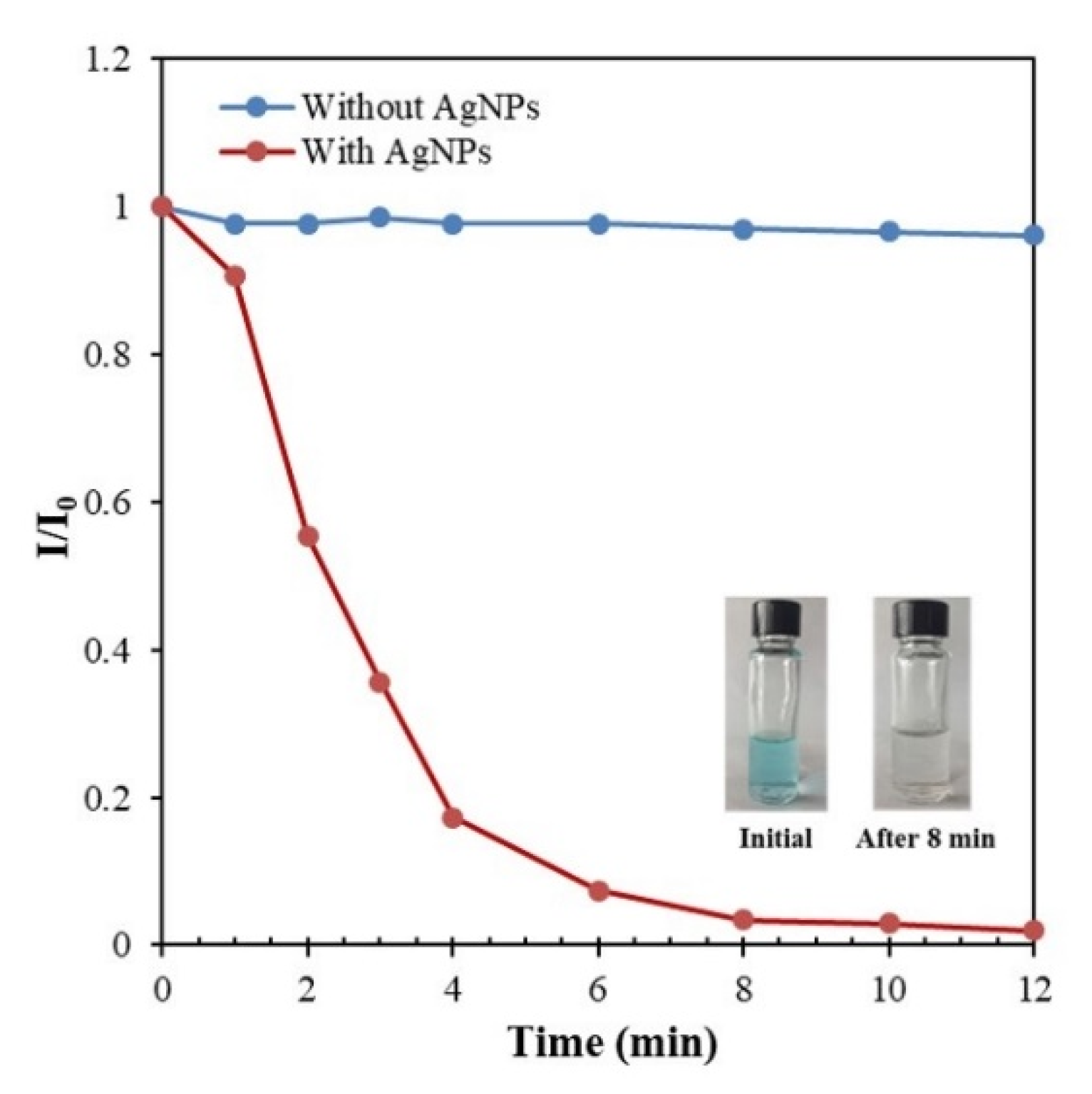
3.8. Application of the Synthesized AgNPs in the Catalytic Degradation of MB
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raveendran, P.; Fu, J.; Wallen, S.L. Completely “Green” Synthesis and Stabilization of Metal Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 13940–13941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iravani, S. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.S.; Panwar, J.; Yun, Y.-S. Biogenic Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles by Plant Extracts. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, S.; Smith, D.R.; Mock, J.J.; Schultz, D.A. Single-target molecule detection with nonbleaching multicolor optical immunolabels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Morrill, A.R.; Moskovits, M. Hot Spots in Silver Nanowire Bundles for Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2200–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Lai, W.; Cui, M.; Liang, L.; Lin, Y.; Fang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Xie, L. An Evaluation of Blood Compatibility of Silver Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panáček, A.; Kvítek, L.; Prucek, R.; Kolář, M.; Večeřová, R.; Pizúrová, N.; Sharma, V.K.; Nevěčná, T.; Zbořil, R. Silver Colloid Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Their Antibacterial Activity. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 16248–16253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krithiga, N.; Rajalakshmi, A.; Jayachitra, A. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extracts of Clitoria ternatea and Solanum nigrum and Study of Its Antibacterial Effect against Common Nosocomial Pathogens. J. Nanosci. 2015, 2015, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanaja, M.; Annadurai, G. Coleus aromaticus leaf extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its bactericidal activity. Appl. Nanosci. 2013, 3, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wei, F.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Q.; Yao, B.; Huang, Z.; Li, J.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, Q. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using seed extract of Alpinia katsumadai, and their antioxidant, cytotoxicity, and antibacterial activities. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 39842–39851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaraj, C.; Jagan, E.G.; Rajasekar, S.; Selvakumar, P.; Kalaichelvan, P.T.; Mohan, N. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Acalypha indica leaf extracts and its antibacterial activity against water borne pathogens. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 76, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathishkumar, M.; Sneha, K.; Won, S.W.; Cho, C.-W.; Kim, S.; Yun, Y.-S. Cinnamon zeylanicum bark extract and powder mediated green synthesis of nano-crystalline silver particles and its bactericidal activity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2009, 73, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, X.; Zhu, P. Antibacterial and catalytic activities of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles prepared by using an aqueous extract of green coffee bean as a reducing agent. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 12144–12149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Pal, A.; Kundu, S.; Basu, S.; Pal, T. Photochemical Green Synthesis of Calcium-Alginate-Stabilized Ag and Au Nanoparticles and Their Catalytic Application to 4-Nitrophenol Reduction. Langmuir 2010, 26, 2885–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, A.; Kim, W.-S.; Yu, T. Synthesis, stabilization, growth behavior, and catalytic activity of highly concentrated silver nanoparticles using a multifunctional polymer in an aqueous-phase. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 28652–28661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamanikandan, R.; Shanmugaraj, K.; Ilanchelian, M. Concentration Dependent Catalytic Activity of Glutathione Coated Silver Nanoparticles for the Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol and Organic Dyes. J. Clust. Sci. 2017, 28, 1009–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, S.; Mathew, B. Microwave-assisted green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and the study on catalytic activity in the degradation of dyes. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 204, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangula, A.; Podila, R.; Karanam, L.; Janardhana, C.; Rao, A.M. Catalytic Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol using Biogenic Gold and Silver Nanoparticles Derived from Breynia rhamnoides. Langmuir 2011, 27, 15268–15274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarland, A.D.; Van Duyne, R.P. Single Silver Nanoparticles as Real-Time Optical Sensors with Zeptomole Sensitivity. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, K.S.B.; Adam, J.K.; Govender, P. Biomedical Applications and Toxicity of Nanosilver: A Review. Med. Technol. SA 2015, 29, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, K.; Banerjee, S.L.; Kundu, P.P.; Madras, G.; Chatterjee, K. Biofunctionalized surface-modified silver nanoparticles for gene delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 5266–5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Wen, L.; Zeng, P.; Zhang, L.; Huang, W.; Wang, H. Symbiosis theory-directed green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their application in infected wound healing. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokura, S.; Handa, O.; Takagi, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Naito, Y.; Yoshikawa, T. Silver nanoparticles as a safe preservative for use in cosmetics. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2010, 6, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metak, A.M.; Ajaal, T.T. Investigation on Polymer Based Nano-Silver as Food Packaging Materials. Int. J. Chem. Mol. Eng. 2013, 7, 780–786. [Google Scholar]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Mahmoudi-Gom Yek, S.; Motahharifar, N.; Gorab, M.G. Recent Developments in the Plant-Mediated Green Synthesis of Ag-Based Nanoparticles for Environmental and Catalytic Applications. Chem. Rec. 2019, 19, 2436–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Park, H.G.; Choi, S.-H. γ-Irradiation-induced preparation of Ag and Au nanoparticles and their characterizations. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2007, 105, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, Y.S. Gamma-radiation induced synthesis of silver nanoparticles in gelatin and its application for radiotherapy dose measurements. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2014, 102, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hyning, D.L.; Zukoski, C.F. Formation Mechanisms and Aggregation Behavior of Borohydride Reduced Silver Particles. Langmuir 1998, 14, 7034–7046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Saifullah; Ahmad, M.; Swami, B.L.; Ikram, S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Azadirachta indica aqueous leaf extract. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2016, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Kumari, S.; Cumbal, L.; Debut, A. Lantana camara berry for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2015, 5, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.M.H.; Ismail, E.H.; El-Baghdady, K.Z.; Mohamed, D. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using olive leaf extract and its antibacterial activity. Arab. J. Chem. 2014, 7, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veisi, H.; Azizi, S.; Mohammadi, P. Green synthesis of the silver nanoparticles mediated by Thymbra spicata extract and its application as a heterogeneous and recyclable nanocatalyst for catalytic reduction of a variety of dyes in water. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 170, 1536–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, J.; Begum, A.; Mukherjee, A.; Kumar, S. A novel green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their catalytic action in reduction of Methylene Blue dye. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2017, 27, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.J.; Murtaza, G.; Mehmood, A.; Bhatti, T.M. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaves extract of Skimmia laureola: Characterization and antibacterial activity. Mater. Lett. 2015, 153, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouvaris, P.; Delimitis, A.; Zaspalis, V.; Papadopoulos, D.; Tsipas, S.A.; Michailidis, N. Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles produced using Arbutus Unedo leaf extract. Mater. Lett. 2012, 76, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, L.; Moldovan, B. Green Synthesis of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles for Efficient Catalytic Removal of Harmful Organic Dyes. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanase, C.; Berta, L.; Coman, N.A.; Roșca, I.; Man, A.; Toma, F.; Mocan, A.; Nicolescu, A.; Jakab-Farkas, L.; Biró, D.; et al. Antibacterial and Antioxidant Potential of Silver Nanoparticles Biosynthesized Using the Spruce Bark Extract. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajitha, B.; Reddy, Y.A.K.; Lee, Y.; Kim, M.J.; Ahn, C.W. Biomimetic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Syzygium aromaticum (clove) extract: Catalytic and antimicrobial effects. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 33, e4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, F.; Begum, Z.; Uddin, M.; Haider, A.; Barman, R. Effects of Methanol Extract of Piper chaba Stem Bark on Acute Inflammation in rats. Faridpur Med. Coll. J. 2012, 7, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taufiq-Ur-Rahman, M.; Shilpi, J.A.; Ahmed, M.; Hossain, C.F. Preliminary pharmacological studies on Piper chaba stem bark. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 99, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sireeratawong, S.; Itharat, A.; Lerdvuthisopon, N.; Piyabhan, P.; Khonsung, P.; Boonraeng, S.; Jaijoy, K. Anti-Inflammatory, Analgesic, and Antipyretic Activities of the Ethanol Extract of Piper interruptum Opiz. and Piper chaba Linn. ISRN Pharmacol. 2012, 2012, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, V.R.S.; Suresh, G.; Babu, K.S.; Raju, S.S.; Vishnu vardhan, M.V.P.S.; Ramakrishna, S.; Rao, J.M. Novel dimeric amide alkaloids from Piper chaba Hunter: Isolation, cytotoxic activity, and their biomimetic synthesis. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 1885–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, S.P.S.; Babu, U.V. A lignan from Piper chaba stems. Phytochemistry 1998, 47, 1435–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, T.; Mosaddik, A.; Rahman, M.M.; Muhammad, I.; Haque, M.E.; Cho, S.K. Antimicrobial, antileishmanial and cytotoxic compounds from Piper chaba. Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 26, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukachaisirikul, T.; Prabpai, S.; Champung, P.; Suksamrarn, A. Chabamide, a Novel Piperine Dimer from Stems of Piper chaba. Planta Med. 2002, 68, 853–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal Bis, S.; Chakrabort, N.; Chakrabort, P.; Sarkar, S. Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities of the Hot Pungent Chabbarin are Responsible for the Medicinal Properties of Piper chaba, Hunter. Res. J. Med. Plant 2012, 6, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Roy, A.C.; Haque, M.E.; Rahman, S.; Al-Mansur, M.A.; Haque, C.M.E. Piperine and isoflavan-4-one from the stems of Piper chaba Hunter and their In vitro antimicrobial activities. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2018, 7, 2653–2662. [Google Scholar]
- Mulfinger, L.; Solomon, S.D.; Bahadory, M.; Jeyarajasingam, A.V.; Rutkowsky, S.A.; Boritz, C. Synthesis and Study of Silver Nanoparticles. J. Chem. Educ. 2007, 84, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, K.; Kaviyarasu, K.; Muniyasamy, S.; Roopan, S.M.; Gengan, R.M.; Chuturgoon, A.A. Bio-Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Agroforestry Residue and Their Catalytic Degradation for Sustainable Waste Management. J. Clust. Sci. 2017, 28, 2279–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollick, M.M.R.; Rana, D.; Dash, S.K.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Bhowmick, B.; Maity, D.; Mondal, D.; Pattanayak, S.; Roy, S.; Chakraborty, M.; et al. Studies on green synthesized silver nanoparticles using Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) pulp extract having anticancer (in vitro) and antimicrobial applications. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 2572–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, A.J.; Oluwafemi, O.S. Plant-mediated synthesis of platinum nanoparticles using water hyacinth as an efficient biomatrix source—An eco-friendly development. Mater. Lett. 2017, 196, 141–144. [Google Scholar]
- Maity, G.N.; Sarkar, J.; Khatua, S.; Mondal, S.; Acharya, K. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using mangrove fruit polysaccharide for bacterial growth inhibition. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2019, 12, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahiuddin, M.; Saha, P.; Ochiai, B. Green Synthesis and Catalytic Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Based on Piper chaba Stem Extracts. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091777
Mahiuddin M, Saha P, Ochiai B. Green Synthesis and Catalytic Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Based on Piper chaba Stem Extracts. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(9):1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091777
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahiuddin, Md., Prianka Saha, and Bungo Ochiai. 2020. "Green Synthesis and Catalytic Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Based on Piper chaba Stem Extracts" Nanomaterials 10, no. 9: 1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091777
APA StyleMahiuddin, M., Saha, P., & Ochiai, B. (2020). Green Synthesis and Catalytic Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Based on Piper chaba Stem Extracts. Nanomaterials, 10(9), 1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091777






