SGLT2 Inhibitors and Kidney Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Clinical Trials
2.1. Major Cardiovascular Outcomes Trials
2.2. Major Kidney-Specific Outcome Trials
2.3. Role of SGLT2 in Non-Diabetic CKD Patients
3. Proposed Renoprotective Mechanisms of SGLT2i
3.1. Tubulo-Glomerular Feedback Mechanism (TGF)
3.2. Non-TGF Mediated Mechanisms
3.3. Antioxidant Properties
3.4. Anti-Inflammatory Properties
3.5. Cortical Hypoxia Reduction
4. Proposed Cardioprotective Mechanisms of SGLT2i
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collins, A.J.; Foley, R.N.; Herzog, C.; Chavers, B.; Gilbertson, D.; Ishani, A.; Kasiske, B.; Liu, J.; Mau, L.W.; McBean, M.; et al. US renal data system 2010 annual data report. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2011, 57, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytvyn, Y.; Bjornstad, P.; van Raalte, D.H.; Heerspink, H.L.; Cherney, D.Z.I. The new biology of diabetic kidney disease—Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 41, 202–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaewput, W.; Thongprayoon, C.; Rangsin, R.; Bathini, T.; Torres-Ortiz, A.; Mao, M.A.; Cheungpasitporn, W. Incidence and risk factors associated with outpatient hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease: A nationwide study. Endocr. Res. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaewput, W.; Thongprayoon, C.; Chewcharat, A.; Rangsin, R.; Satirapoj, B.; Kaewput, C.; Suwannahitatorn, P.; Bathini, T.; Mao, M.A.; Cato, L.D.; et al. Rate of kidney function decline and factors predicting progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with reduced kidney function: A nationwide retrospective cohort study. Ther. Apher.Dial. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaewput, W.; Thongprayoon, C.; Varothai, N.; Sirirungreung, A.; Rangsin, R.; Bathini, T.; Mao, M.A.; Cheungpasitporn, W. Prevalence and associated factors of hospitalization for dysglycemia among elderly type 2 diabetes patients: A nationwide study. World J. Diabetes 2019, 10, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaewput, W.; Thongprayoon, C.; Rangsin, R.; Ruangkanchanasetr, P.; Mao, M.A.; Cheungpasitporn, W. Associations of renal function with diabetic retinopathy and visual impairment in type 2 diabetes: A multicenter nationwide cross-sectional study. World J. Nephrol. 2019, 8, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewput, W.; Thongprayoon, C.; Rangsin, R.; Mao, M.A.; Satirapoj, B.; Cheungpasitporn, W. The association between renal function and neurological diseases in type 2 diabetes: A multicenter nationwide cross-sectional study. Hosp. Pract. 2019, 47, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewput, W.; Thongprayoon, C.; Mungthin, M.; Jindarat, S.; Varothai, N.; Suwannahitatorn, P.; Rangsin, R.; Mao, M.A.; Cheungpasitporn, W. Temporal trends in optimal diabetic care and complications of elderly type 2 diabetes patients in Thailand: A nationwide study. J. Evid. Based Med. 2019, 12, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatz, R.; Meyer, T.W.; Rennke, H.G.; Brenner, B.M. Predominance of hemodynamic rather than metabolic factors in the pathogenesis of diabetic glomerulopathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 5963–5967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Atkin, S.L.; Pirro, M.; Sahebkar, A. A review of the anti-inflammatory properties of antidiabetic agents providing protective effects against vascular complications in diabetes. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 8286–8294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonneijck, L.; Muskiet, M.H.A.; Smits, M.M.; van Bommel, E.J.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; van Raalte, D.H.; Joles, J.A. Glomerular hyperfiltration in diabetes: Mechanisms, clinical significance, and treatment. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2017, 28, 1023–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, A.M.; Knudsen, S.T.; Cooper, M.E. Diabetic nephropathy: An insight into molecular mechanisms and emerging therapies. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2019, 23, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, B.M.; Cooper, M.E.; de Zeeuw, D.; Keane, W.F.; Mitch, W.E.; Parving, H.H.; Remuzzi, G.; Snapinn, S.M.; Zhang, Z.; Shahinfar, S.; et al. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttle, K.R.; Cherney, D.Z. Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition heralds a call-to-action for diabetic kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 15, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Azevedo, M.J.; Ramos, O.L.; Gross, J.L. Lack of effect of captopril on glomerular hyperfiltration in normoalbuminuric normotensive insulin-dependent diabetic patients. Horm. Metab. Res. 1997, 29, 516–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkers, C.C.J.; Gansevoort, R.T. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors: Extending the indication to non-diabetic kidney disease? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, i33–i42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nespoux, J.; Vallon, V. SGLT2 inhibition and kidney protection. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, S.C.; Vallon, V. Renal effects of sodium-glucose co-transporter inhibitors. Am. J. Cardiol. 2019, 124, S28–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tentolouris, A.; Vlachakis, P.; Tzeravini, E.; Eleftheriadou, I.; Tentolouris, N. SGLT2 inhibitors: A review of their antidiabetic and cardioprotective effects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Publ. Health 2019, 16, 2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.H.; Park, E.G.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.G.; Hahn, S.; Kim, N.H. Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinman, B.; Wanner, C.; Lachin, J.M.; Fitchett, D.; Bluhmki, E.; Hantel, S.; Mattheus, M.; Devins, T.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiviott, S.D.; Raz, I.; Bonaca, M.P.; Mosenzon, O.; Kato, E.T.; Cahn, A.; Silverman, M.G.; Zelniker, T.A.; Kuder, J.F.; Murphy, S.A.; et al. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelniker, T.A.; Wiviott, S.D.; Raz, I.; Im, K.; Goodrich, E.L.; Bonaca, M.P.; Mosenzon, O.; Kato, E.T.; Cahn, A.; Furtado, R.H.M.; et al. SGLT2 inhibitors for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet 2019, 393, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnott, C.; Li, Q.; Kang, A.; Neuen, B.L.; Bompoint, S.; Lam, C.S.P.; Rodgers, A.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Cannon, C.P.; Perkovic, V.; et al. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition for the prevention of cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e014908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarova, E.; Górnaś, P.; Konrade, I.; Tirzite, D.; Cirule, H.; Gulbe, A.; Pugajeva, I.; Seglina, D.; Dambrova, M. Acute anti-hyperglycaemic effects of an unripe apple preparation containing phlorizin in healthy volunteers: A preliminary study. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, E.C.; Henry, R.R. SGLT2 inhibition-A novel strategy for diabetes treatment. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Fronzo, R.A.; Norton, L.; Abdul-Ghani, M. Renal, metabolic and cardiovascular considerations of SGLT2 inhibition. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Baar, M.J.B.; van Ruiten, C.C.; Muskiet, M.H.A.; van Bloemendaal, L.; RG, I.J.; van Raalte, D.H. SGLT2 inhibitors in combination therapy: From mechanisms to clinical considerations in type 2 diabetes management. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1543–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.; Perkins, B.A.; Fitchett, D.H.; Husain, M.; Cherney, D.Z. sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in the treatment of diabetes mellitus: Cardiovascular and kidney effects, potential mechanisms, and clinical applications. Circulation 2016, 134, 752–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherney, D.; Perkins, B.A.; Lytvyn, Y.; Heerspink, H.; Rodríguez-Ortiz, M.E.; Mischak, H. The effect of sodium/glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibition on the urinary proteome. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherney, D.Z.I.; Cooper, M.E.; Tikkanen, I.; Pfarr, E.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; Broedl, U.C.; Lund, S.S. Pooled analysis of phase III trials indicate contrasting influences of renal function on blood pressure, body weight, and HbA1c reductions with empagliflozin. Kidney Int. 2018, 93, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjadj, S.; Rosenstock, J.; Meinicke, T.; Woerle, H.J.; Broedl, U.C. Initial combination of empagliflozin and metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 1718–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, R.R.; Murray, A.V.; Marmolejo, M.H.; Hennicken, D.; Ptaszynska, A.; List, J.F. Dapagliflozin, metformin XR, or both: Initial pharmacotherapy for type 2 diabetes, a randomised controlled trial. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2012, 66, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenstock, J.; Chuck, L.; González-Ortiz, M.; Merton, K.; Craig, J.; Capuano, G.; Qiu, R. initial combination therapy with canagliflozin plus metformin versus each component as monotherapy for drug-naïve type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Introduction: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2020. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, S1–S2. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milder, T.Y.; Stocker, S.L.; Abdel Shaheed, C.; McGrath-Cadell, L.; Samocha-Bonet, D.; Greenfield, J.R.; Day, R.O. Combination therapy with an SGLT2 inhibitor as initial treatment for type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bersoff-Matcha, S.J.; Chamberlain, C.; Cao, C.; Kortepeter, C.; Chong, W.H. fournier gangrene associated with sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors: A review of spontaneous postmarketing cases. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 170, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danne, T.; Garg, S.; Peters, A.L.; Buse, J.B.; Mathieu, C.; Pettus, J.H.; Alexander, C.M.; Battelino, T.; Ampudia-Blasco, F.J.; Bode, B.W.; et al. International consensus on risk management of diabetic ketoacidosis in patients with type 1 diabetes treated with sodium-glucose cotransporter (SGLT) inhibitors. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, R.M.; Gilbert, J.D.; Hramiak, I.M.; Woo, V.C.; Zinman, B. Sodium-glucose co-transporter inhibitors, their role in type 1 diabetes treatment and a risk mitigation strategy for preventing diabetic ketoacidosis: The STOP DKA protocol. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 2192–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, C.V.; Schneeweiss, S.; Kim, D.; Fralick, M.; Tong, A.; Patorno, E. Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and the risk for severe urinary tract infections: A population-based cohort study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 171, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanner, C.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Lachin, J.M.; Fitchett, D.; von Eynatten, M.; Mattheus, M.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; Broedl, U.C.; Zinman, B.; et al. Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuen, B.L.; Ohkuma, T.; Neal, B.; Matthews, D.R.; de Zeeuw, D.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Fulcher, G.; Li, Q.; Jardine, M.; Oh, R.; et al. Effect of canagliflozin on renal and cardiovascular outcomes across different levels of albuminuria: Data from the CANVAS program. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 30, 2229–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkovic, V.; Jardine, M.J.; Neal, B.; Bompoint, S.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Charytan, D.M.; Edwards, R.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Bull, S.; et al. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, B.; Perkovic, V.; Mahaffey, K.W.; de Zeeuw, D.; Fulcher, G.; Erondu, N.; Shaw, W.; Law, G.; Desai, M.; Matthews, D.R.; et al. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 644–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkovic, V.; de Zeeuw, D.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Fulcher, G.; Erondu, N.; Shaw, W.; Barrett, T.D.; Weidner-Wells, M.; Deng, H.; Matthews, D.R.; et al. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: Results from the CANVAS program randomised clinical trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 691–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yale, J.F.; Bakris, G.; Cariou, B.; Nieto, J.; David-Neto, E.; Yue, D.; Wajs, E.; Figueroa, K.; Jiang, J.; Law, G.; et al. Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin over 52 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014, 16, 1016–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohan, D.E.; Fioretto, P.; Tang, W.; List, J.F. Long-term study of patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate renal impairment shows that dapagliflozin reduces weight and blood pressure but does not improve glycemic control. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 962–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioretto, P.; del Prato, S.; Buse, J.B.; Goldenberg, R.; Giorgino, F.; Reyner, D.; Langkilde, A.M.; Sjöström, C.D.; Sartipy, P. Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate renal impairment (chronic kidney disease stage 3A): The DERIVE Study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 2532–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, F.A.; Serenelli, M.; Nicolau, J.C.; Petrie, M.C.; Chiang, C.E.; Tereshchenko, S.; Solomon, S.D.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Køber, L.; Kosiborod, M.N.; et al. Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction according to age: Insights from DAPA-HF. Circulation 2020, 141, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherney, D.Z.I.; Dekkers, C.C.J.; Barbour, S.J.; Cattran, D.; Abdul Gafor, A.H.; Greasley, P.J.; Laverman, G.D.; Lim, S.K.; Di Tanna, G.L.; Reich, H.N.; et al. Effects of the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin on proteinuria in non-diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease (DIAMOND): A randomised, double-blind, crossover trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häring, H.U.; Merker, L.; Seewaldt-Becker, E.; Weimer, M.; Meinicke, T.; Woerle, H.J.; Broedl, U.C. Empagliflozin as add-on to metformin plus sulfonylurea in patients with type 2 diabetes: A 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 3396–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, A.H.; Mithal, A.; Manassie, J.; Jones, R.; Rattunde, H.; Woerle, H.J.; Broedl, U.C. Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin added to existing antidiabetes treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halden, T.A.S.; Kvitne, K.E.; Midtvedt, K.; Rajakumar, L.; Robertsen, I.; Brox, J.; Bollerslev, J.; Hartmann, A.; Asberg, A.; Jenssen, T. Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin in renal transplant recipients with posttransplant diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegretti, A.S.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, W.; Thurber, T.K.; Rigby, S.P.; Bowman-Stroud, C.; Trescoli, C.; Serusclat, P.; Freeman, M.W.; Halvorsen, Y.C.; et al. Safety and effectiveness of bexagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and stage 3a/3b CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019, 74, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Thai, K.; Kepecs, D.M.; Gilbert, R.E. Sodium-glucose linked cotransporter-2 inhibition does not attenuate disease progression in the rat remnant kidney model of chronic kidney disease. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0144640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassis, P.; Locatelli, M.; Cerullo, D.; Corna, D.; Buelli, S.; Zanchi, C.; Villa, S.; Morigi, M.; Remuzzi, G.; Benigni, A.; et al. SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin limits podocyte damage in proteinuric nondiabetic nephropathy. JCI Insight 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Steiger, S.; Anders, H.J. Sodium glucose transporter-2 inhibition has no renoprotective effects on non-diabetic chronic kidney disease. Physiol. Rep. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekeran, H.; Reich, H.N.; Hladunewich, M.A.; Cattran, D.; Lovshin, J.A.; Lytvyn, Y.; Bjornstad, P.; Lai, V.; Tse, J.; Cham, L.; et al. Dapagliflozin in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: A combined human-rodent pilot study. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2018, 314, F412–F422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bays, H.E.; Weinstein, R.; Law, G.; Canovatchel, W. Canagliflozin: Effects in overweight and obese subjects without diabetes mellitus. Obesity 2014, 22, 1042–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaikumkao, K.; Pongchaidecha, A.; Chueakula, N.; Thongnak, L.O.; Wanchai, K.; Chatsudthipong, V.; Chattipakorn, N.; Lungkaphin, A. Dapagliflozin, a sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor, slows the progression of renal complications through the suppression of renal inflammation, endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in prediabetic rats. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 2617–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Butler, A.E.; Atkin, S.L.; Katsiki, N.; Sahebkar, A. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and inflammation in chronic kidney disease: Possible molecular pathways. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 234, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, E.J.; Lee, D.H.; Jeon, H.J.; Oh, T.K. Empagliflozin versus dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin, glimepiride and dipeptidyl peptide 4 inhibitors: A 52-week prospective observational study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 151, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGurnaghan, S.J.; Brierley, L.; Caparrotta, T.M.; McKeigue, P.M.; Blackbourn, L.A.K.; Wild, S.H.; Leese, G.P.; McCrimmon, R.J.; McKnight, J.A.; Pearson, E.R.; et al. The effect of dapagliflozin on glycaemic control and other cardiovascular disease risk factors in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A real-world observational study. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrykiv, S.; Sjöström, C.D.; Greasley, P.J.; Xu, J.; Persson, F.; Heerspink, H.J.L. differential effects of dapagliflozin on cardiovascular risk factors at varying degrees of renal function. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, G.C.W.; Tang, S.C.W. SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin: Finally at the latter stage of understanding? Kidney Int. 2018, 93, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škrtić, M.; Cherney, D.Z. Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibition and the potential for renal protection in diabetic nephropathy. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2015, 24, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidokoro, K.; Cherney, D.Z.I.; Bozovic, A.; Nagasu, H.; Satoh, M.; Kanda, E.; Sasaki, T.; Kashihara, N. Evaluation of glomerular hemodynamic function by empagliflozin in diabetic mice using in vivo imaging. Circulation 2019, 140, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eickhoff, M.K.; Dekkers, C.C.J.; Kramers, B.J.; Laverman, G.D.; Frimodt-Møller, M.; Jørgensen, N.R.; Faber, J.; Danser, A.H.J.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Rossing, P.; et al. Effects of dapagliflozin on volume status when added to renin-angiotensin system inhibitors. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karg, M.V.; Bosch, A.; Kannenkeril, D.; Striepe, K.; Ott, C.; Schneider, M.P.; Boemke-Zelch, F.; Linz, P.; Nagel, A.M.; Titze, J.; et al. SGLT-2-inhibition with dapagliflozin reduces tissue sodium content: A randomised controlled trial. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroor, A.R.; Das, N.A.; Carpenter, A.J.; Habibi, J.; Jia, G.; Ramirez-Perez, F.I.; Martinez-Lemus, L.; Manrique-Acevedo, C.M.; Hayden, M.R.; Duta, C.; et al. Glycemic control by the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin decreases aortic stiffness, renal resistivity index and kidney injury. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.M.; Battson, M.L.; Jarrell, D.K.; Hou, S.; Ecton, K.E.; Weir, T.L.; Gentile, C.L. SGLT2 inhibition via dapagliflozin improves generalized vascular dysfunction and alters the gut microbiota in type 2 diabetic mice. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, M.A.; Mansfield, T.A.; Alessi, F.; Iqbal, N.; Parikh, S.; Ptaszynska, A. Effects of dapagliflozin on blood pressure in hypertensive diabetic patients on renin-angiotensin system blockade. Blood Press 2016, 25, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeev, S.P.; Cuthbertson, D.J.; Wilding, J.P.H. Energy balance and metabolic changes with sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibition. Diabetes Obes. Metabol. 2016, 18, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alicic, R.Z.; Johnson, E.J.; Tuttle, K.R. SGLT2 Inhibition for the prevention and treatment of diabetic kidney disease: A review. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 72, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, T.; Furuki, T.; Kobori, H.; Miyakawa, M.; Imachi, H.; Murao, K.; Nishiyama, A. Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on urinary excretion of intact and total angiotensinogen in patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Investig. Med. 2017, 65, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherney, D.Z.; Perkins, B.A.; Soleymanlou, N.; Maione, M.; Lai, V.; Lee, A.; Fagan, N.M.; Woerle, H.J.; Johansen, O.E.; Broedl, U.C.; et al. Renal hemodynamic effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Circulation 2014, 129, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashima, H.; Yoshida, Y.; Nagura, C.; Furukawa, T.; Tei, R.; Maruyama, T.; Maruyama, N.; Abe, M. Renoprotective effects of canagliflozin, a sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor, in type 2 diabetes patients with chronic kidney disease: A randomized open-label prospective trial. Diab. Vasc. Dis. Res. 2018, 15, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, H.; Coronel, I.; Arellano, A.; Pacheco, U.; Bautista, R.; Franco, M.; Escalante, B. Sodium-glucose cotransporter inhibition prevents oxidative stress in the kidney of diabetic rats. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2012, 2012, 542042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Wu, Y.; Tian, M.; Sjöström, C.D.; Johansson, U.; Peng, X.-R.; Smith, D.M.; Huang, Y. Dapagliflozin slows the progression of the renal and liver fibrosis associated with type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metabol. 2017, 313, E563–E576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Xue, M.; Li, X.; Han, F.; Liu, X.; Xu, L.; Lu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Li, T.; et al. SGLT2 inhibition with empagliflozin attenuates myocardial oxidative stress and fibrosis in diabetic mice heart. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boels, M.G.S.; Koudijs, A.; Avramut, M.C.; Sol, W.; Wang, G.; van Oeveren-Rietdijk, A.M.; van Zonneveld, A.J.; de Boer, H.C.; van der Vlag, J.; van Kooten, C.; et al. Systemic monocyte chemotactic protein-1 inhibition modifies renal macrophages and restores glomerular endothelial glycocalyx and barrier function in diabetic nephropathy. Am. J. Pathol. 2017, 187, 2430–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallon, V.; Gerasimova, M.; Rose, M.A.; Masuda, T.; Satriano, J.; Mayoux, E.; Koepsell, H.; Thomson, S.C.; Rieg, T. SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin reduces renal growth and albuminuria in proportion to hyperglycemia and prevents glomerular hyperfiltration in diabetic Akita mice. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2014, 306, F194–F204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Perco, P.; Mulder, S.; Leierer, J.; Hansen, M.K.; Heinzel, A.; Mayer, G. Canagliflozin reduces inflammation and fibrosis biomarkers: A potential mechanism of action for beneficial effects of SGLT2 inhibitors in diabetic kidney disease. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 1154–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkers, C.C.J.; Petrykiv, S.; Laverman, G.D.; Cherney, D.Z.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Heerspink, H.J.L. Effects of the SGLT-2 inhibitor dapagliflozin on glomerular and tubular injury markers. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 1988–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, W.; Ouyang, X.; Lei, X.; Wu, M.; Chen, L.; Wu, Q.; Deng, W.; Liang, Z. The SGLT-2 inhibitor dapagliflozin has a therapeutic effect on atherosclerosis in diabetic ApoE(-/-) mice. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 6305735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchapakesan, U.; Pegg, K.; Gross, S.; Komala, M.G.; Mudaliar, H.; Forbes, J.; Pollock, C.; Mather, A. Effects of SGLT2 inhibition in human kidney proximal tubular cells-renoprotection in diabetic nephropathy? PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Nakano, D.; Guan, Y.; Hitomi, H.; Uemura, A.; Masaki, T.; Kobara, H.; Sugaya, T.; Nishiyama, A. A sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor attenuates renal capillary injury and fibrosis by a vascular endothelial growth factor–dependent pathway after renal injury in mice. Kidney Int. 2018, 94, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessho, R.; Takiyama, Y.; Takiyama, T.; Kitsunai, H.; Takeda, Y.; Sakagami, H.; Ota, T. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α is the therapeutic target of the SGLT2 inhibitor for diabetic nephropathy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambers Heerspink, H.J.; de Zeeuw, D.; Wie, L.; Leslie, B.; List, J. Dapagliflozin a glucose-regulating drug with diuretic properties in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metabol. 2013, 15, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storgaard, H.; Gluud, L.L.; Bennett, C.; Grøndahl, M.F.; Christensen, M.B.; Knop, F.K.; Vilsbøll, T. Benefits and harms of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, W.; Sakaguchi, K. Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis induced by SGLT2 inhibitors: Possible mechanism and contributing factors. J. Diabetes Investig. 2016, 7, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimazu, T.; Hirschey, M.D.; Newman, J.; He, W.; Shirakawa, K.; Le Moan, N.; Grueter, C.A.; Lim, H.; Saunders, L.R.; Stevens, R.D.; et al. Suppression of oxidative stress by β-hydroxybutyrate, an endogenous histone deacetylase inhibitor. Science 2013, 339, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopaschuk, G.D.; Verma, S. Empagliflozin’s fuel hypothesis: Not so soon. Cell Metabolism. 2016, 24, 200–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baartscheer, A.; Schumacher, C.A.; Wüst, R.C.I.; Fiolet, J.W.T.; Stienen, G.J.M.; Coronel, R.; Zuurbier, C.J. Empagliflozin decreases myocardial cytoplasmic Na+ through inhibition of the cardiac Na+/H+ exchanger in rats and rabbits. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, L.A.; Wright, E.M.; Vallon, V. Probing SGLT2 as a therapeutic target for diabetes: Basic physiology and consequences. Diabetes Vasc. Disease Res. 2015, 12, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, W.T.; van Gaal, L.; Leiter, L.A.; Vijapurkar, U.; List, J.; Cuddihy, R.; Ren, J.; Davies, M.J. Effects of canagliflozin versus glimepiride on adipokines and inflammatory biomarkers in type 2 diabetes. Metabolism 2018, 85, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Aizawa, Y.; Yuasa, S.; Kishi, S.; Fuse, K.; Fujita, S.; Ikeda, Y.; Kitazawa, H.; Takahashi, M.; Sato, M.; et al. The effect of dapagliflozin treatment on epicardial adipose tissue volume. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.M.; Chang, N.C.; Lin, S.Z. Dapagliflozin, a selective SGLT2 Inhibitor, attenuated cardiac fibrosis by regulating the macrophage polarization via STAT3 signaling in infarcted rat hearts. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 104, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 - decreased.
- decreased.
 - decreased.
- decreased.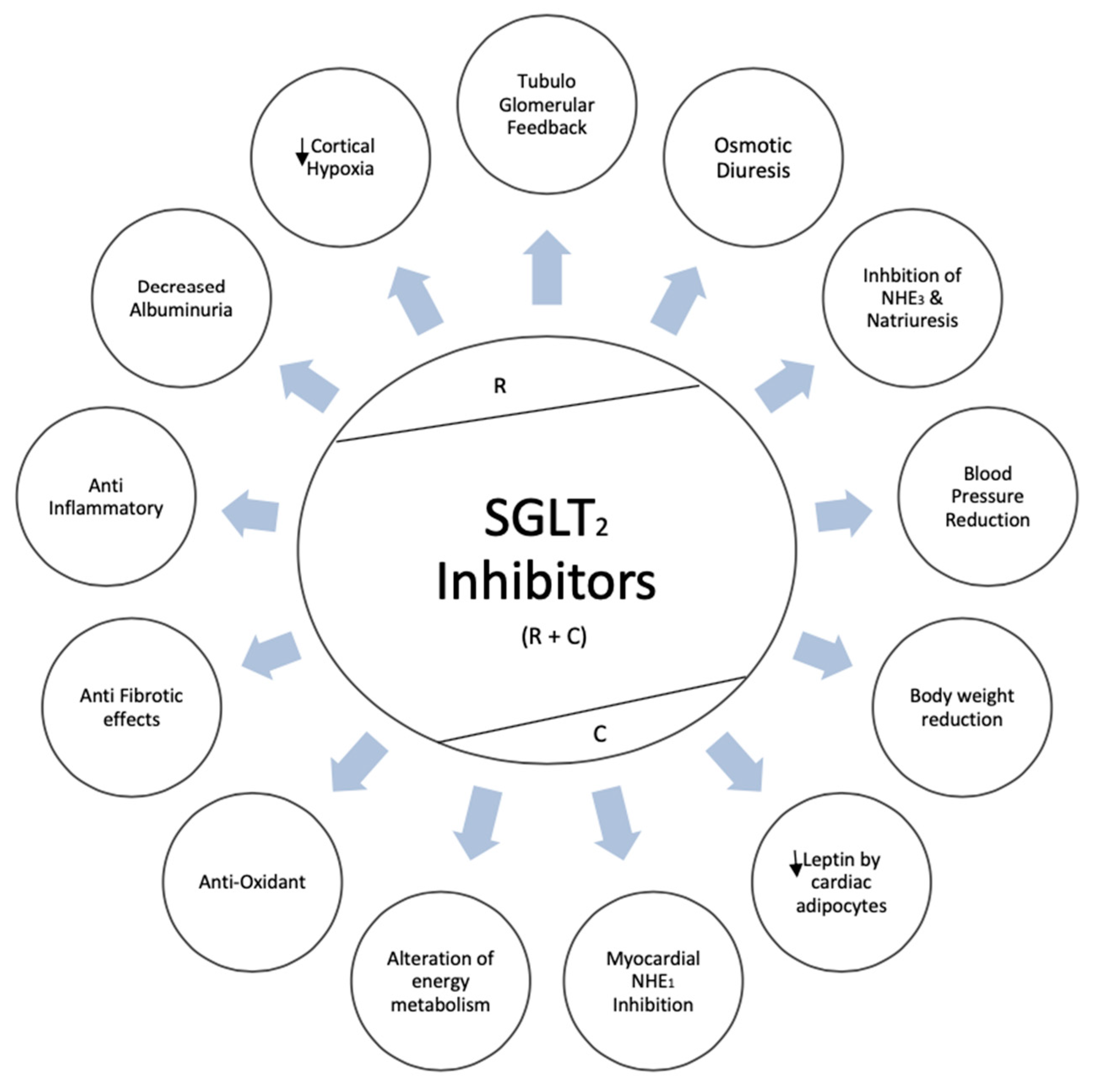
| Clinical Trial | Year | Trial Registration | Total Sample Size | CKD Patients | Kidney Function Inclusion Criteria | Follow-Up | Reported Renal Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Canagliflozin | |||||||
| CANVAS and CANVAS-R [44,45] | 2017 2018 | NCT01032629 NCT01989754 | 10142 | 2039 | eGFR ≥ 30 | 188 wks | ↓ sustained loss of kidney function, eGFR decline, albuminuria, the need for RRT, and death from renal causes |
| DIA3004 [46] | 2014 | NCT01064414 | 269 | 269 | eGFR ≥ 30 and < 50 | 52 wks | ↓ eGFR decline and albuminuria |
| CREDENCE [43] | 2019 | NCT02065791 | 4401 | 2181 | eGFR ≥ 30 | 2.6 yrs | ↓ Renal composite outcomes (ESKD, doubling in SCr, renal or CV death) in both primary and secondary prevention group The trial stopped early due to overwhelming efficacy |
| Dapagliflozin | |||||||
| MB102029 [47] | 2014 | NCT00663260 | 252 | 252 | eGFR ≥ 30 and < 60 | 104 wks | ↓ eGFR decline, albuminuria, and hyperkalemia Slight drop in eGFR during drug initiation |
| DERIVE [48] | 2018 | NCT02413398 | 321 | 321 | eGFR ≥ 45 and < 60 | 24 wks | ↓ Renal related adverse events Slight drop in eGFR during drug initiation |
| DECLARE-TIMI 58 [22] | 2018 | NCT01730534 | 17160 | 1265 | CrCl ≥ 60 mL/min | 4.2 yrs | ↓ Renal composite outcomes ↓ Acute kidney injury |
| DAPA-HF [49] | 2020 | NCT03036124 | 4724 | N/A | eGFR ≥ 30 | 3 yrs | ↓ Doubling in SCr |
| DIAMOND [50] | 2020 | NCT03190694 | 53 | 33 | eGFR ≥ 25 | 6 wks | No effect on proteinuria reduction in CKD without diabetes Reversible decline in eGFR noted |
| Empagliflozin | |||||||
| EMPA-REG OUTCOME [21] | 2015 | NCT01131676 | 7020 | 1819 | eGFR ≥ 30 | 3.1 yrs | ↓ eGFR decline, and renal composite outcomes |
| EMPA-REG METSU [51] | 2013 | NCT01159600 | 666 | 58 | eGFR ≥ 30 | 24 wks | ↓ Renal composite outcomes |
| EMPA-REG RENAL [52] | 2014 | NCT01164501 | 738 | 448 | eGFR ≥ 15 | 52 wks | ↓ Renal composite outcomes |
| Halden, et al. [53] | 2019 | NCT03157414 | 44 | 44 (KTx) | eGFR ≥ 30 | 24 wks | ↓ eGFR within 8 weeks of treatment No change in eGFR from 8-24 weeks |
| Bexagliflozin | |||||||
| Allegretti, et al. [54] | 2019 | NCT02836873 | 312 | 312 | eGFR ≥ 30 and < 60 | 24 wks | ↓ albuminuria Study not designed to evaluate the impact on long-term kidney disease |
| Clinical Trial | Year | Trial Type | Total Sample Size | Kidney Function Inclusion Criteria | Follow-Up | Reported Renal Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dapagliflozin | ||||||
| Zhang et al. [55] | 2016 | Pre-clinical | 53 | Subtotal Nephrectomized rats. | 12 weeks | No improvement in proteinuria, tubulointerstitial fibrosis or eGFR. |
| Cassis et al. [56] | 2018 | Pre-clinical | 37 | Non-diabetic proteinuric mice, unilateral nephrectomy. | 23 days | Decrease in podocyte damage, reduction in proteinuria |
| Jaikumkao et al. [60] | 2018 | Pre-clinical | 24 | Obese prediabetic rats | 4 weeks | Decrease in podocyte damage, reduction in proteinuria |
| Rajasekeran et al. [58] | 2018 | Clinical | 10 | Biopsy proven FSGS, eGFR > 45mL/min, proteinuria 30 mg-6 gr | 5 weeks | No effect on bodyweight, eGFR or proteinuria |
| DIAMOND [50] | 2020 | Clinical | 53 | eGFR ≥ 25 | 6 weeks | No effect on proteinuria reduction in CKD without diabetes Reversible decline in eGFR noted |
| Empagliflozin | ||||||
| Ma et al. [57] | 2017 | Pre-clinical | 20 | CKD mice | 7–14 days | No reno-protective benefit |
| Canagliflozin | ||||||
| Bays et al. [59] | 2014 | Clinical | 376 | Non-diabetic obese patients, BMI 30-50 | 12 weeks | No renal benefit |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kanduri, S.R.; Kovvuru, K.; Hansrivijit, P.; Thongprayoon, C.; Vallabhajosyula, S.; Pivovarova, A.I.; Chewcharat, A.; Garla, V.; Medaura, J.; Cheungpasitporn, W. SGLT2 Inhibitors and Kidney Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092723
Kanduri SR, Kovvuru K, Hansrivijit P, Thongprayoon C, Vallabhajosyula S, Pivovarova AI, Chewcharat A, Garla V, Medaura J, Cheungpasitporn W. SGLT2 Inhibitors and Kidney Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(9):2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092723
Chicago/Turabian StyleKanduri, Swetha R., Karthik Kovvuru, Panupong Hansrivijit, Charat Thongprayoon, Saraschandra Vallabhajosyula, Aleksandra I. Pivovarova, Api Chewcharat, Vishnu Garla, Juan Medaura, and Wisit Cheungpasitporn. 2020. "SGLT2 Inhibitors and Kidney Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 9: 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092723
APA StyleKanduri, S. R., Kovvuru, K., Hansrivijit, P., Thongprayoon, C., Vallabhajosyula, S., Pivovarova, A. I., Chewcharat, A., Garla, V., Medaura, J., & Cheungpasitporn, W. (2020). SGLT2 Inhibitors and Kidney Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(9), 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092723






