Efficacy and Safety of Polaprezinc (Zinc Compound) on Zinc Deficiency: A Systematic Review and Dose–Response Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials Using Individual Patient Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Risk-of-Bias Assessment
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Statistical Analysis
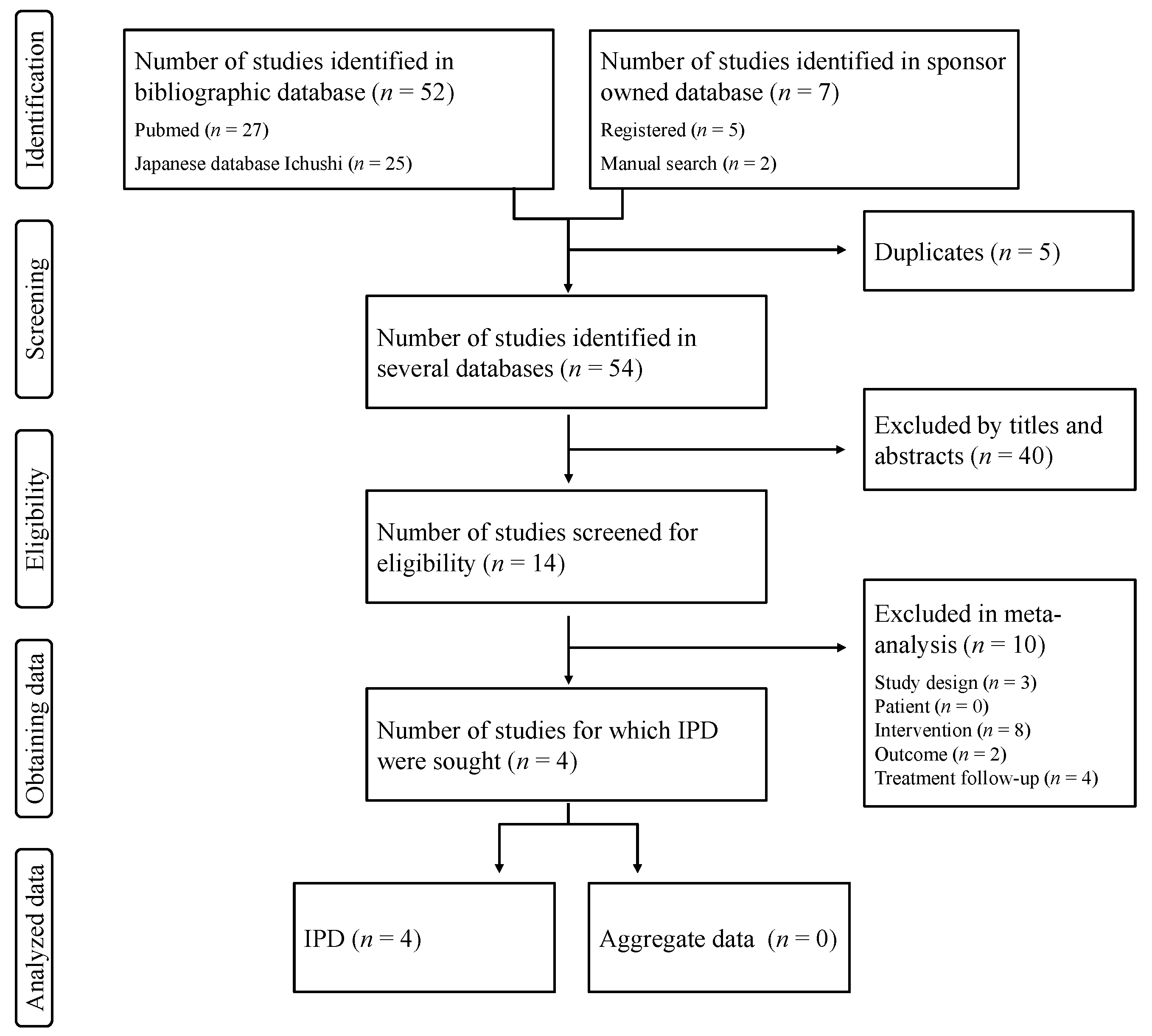
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics
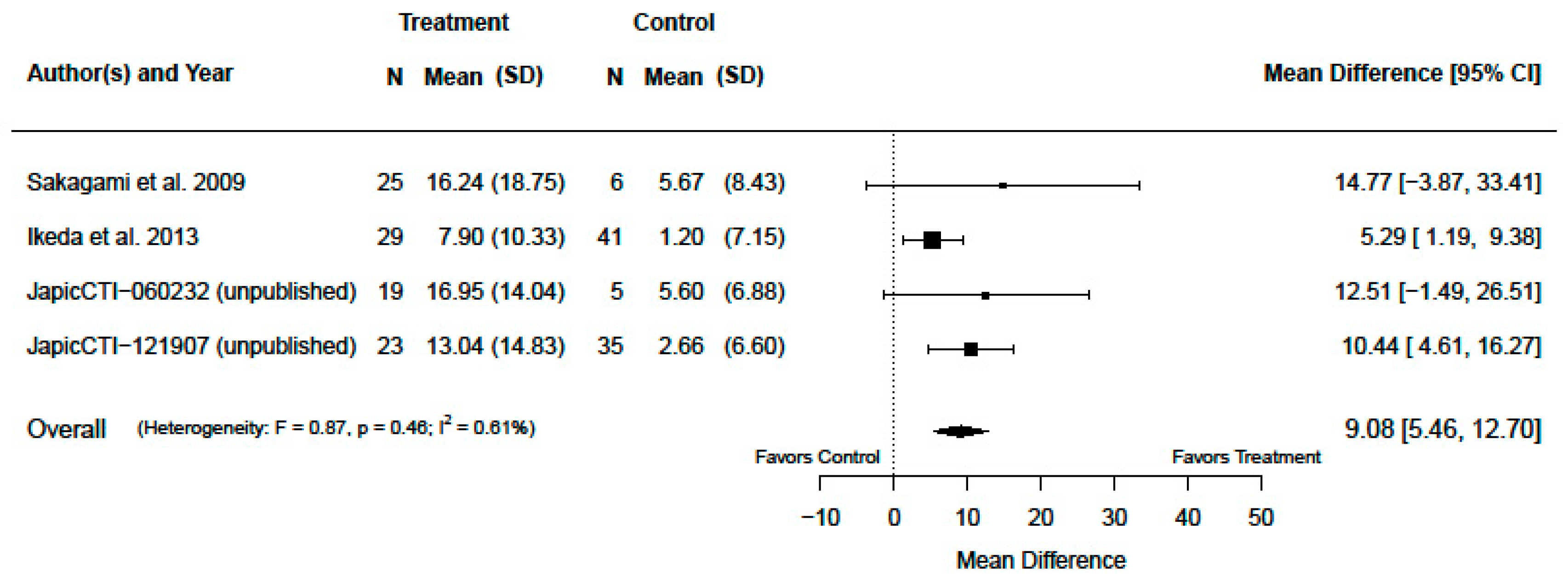
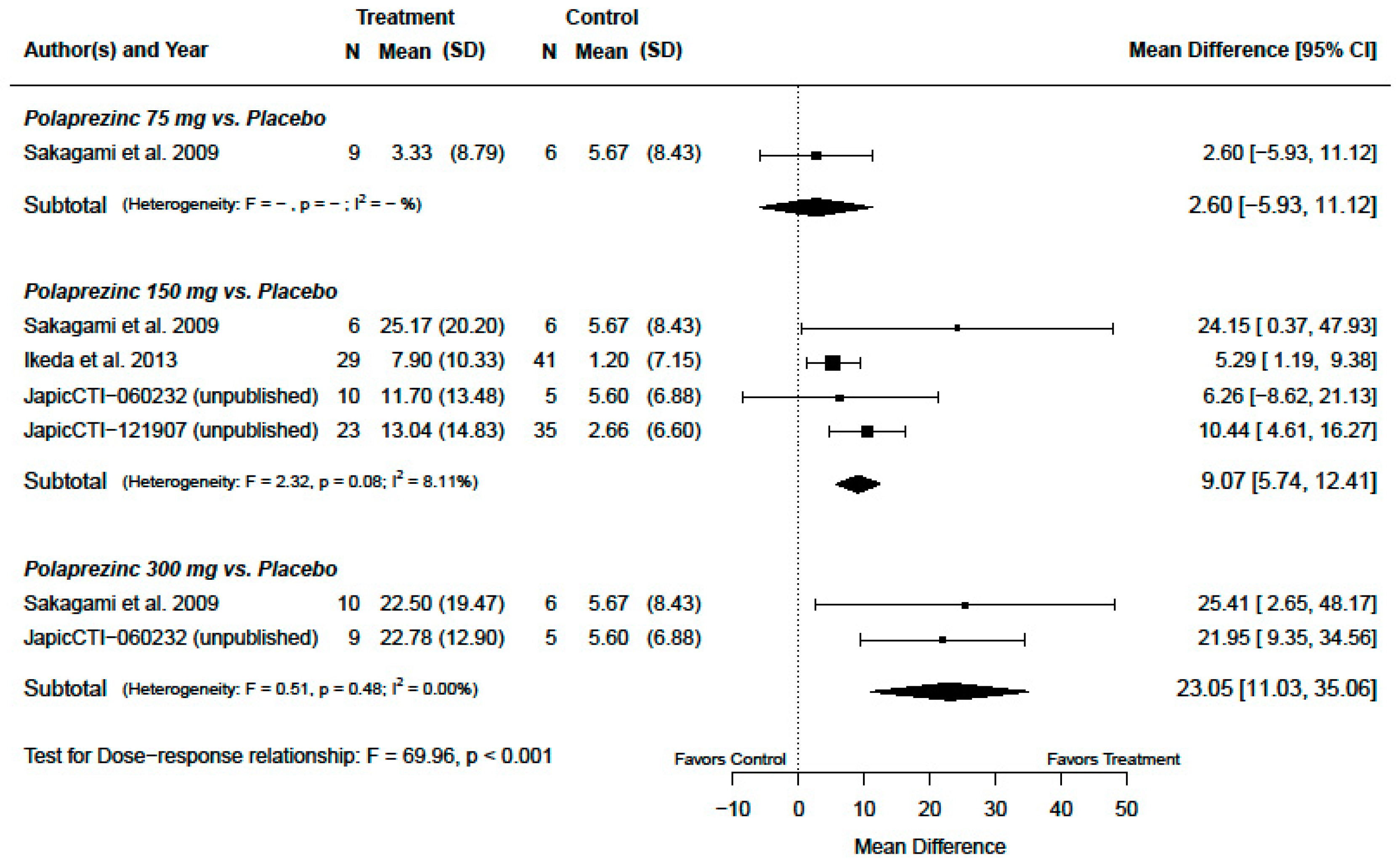
3.2. Serum Zinc Concentration
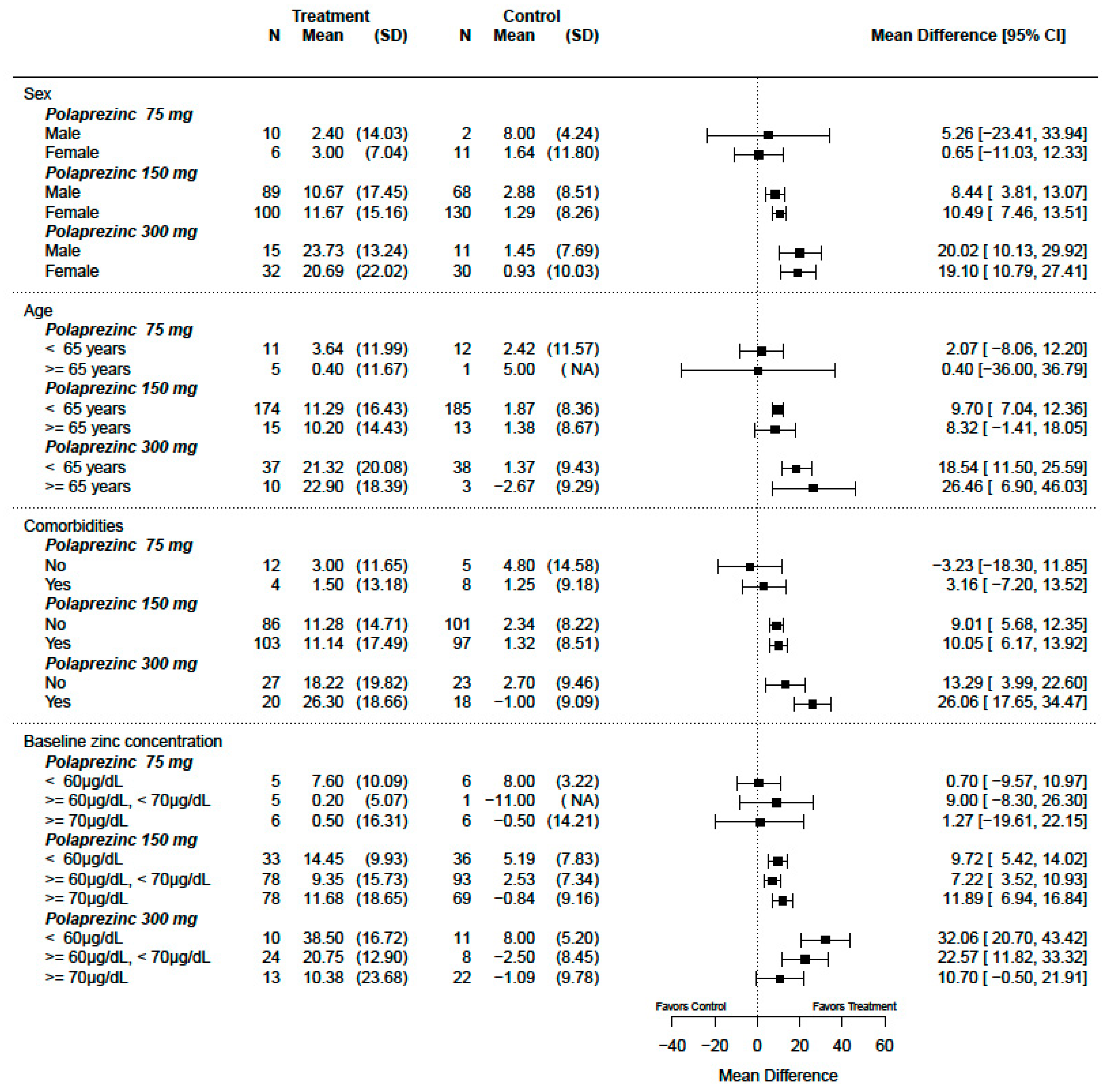
3.3. Interaction Effect and Subgroup Analysis
3.4. Safety
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vallee, B.L.; Falchuk, K.H. The Biochemical Basis of Zinc Physiology. Physiol. Rev. 1993, 73, 79–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valera, P.; Zavattari, P.; Sanna, A.; Pretti, S.; Marcello, A.; Mannu, C.; Targhetta, C.; Bruno, G.; Songini, M. Zinc and Other Metals Deficiencies and Risk of Type 1 Diabetes: An Ecological Study in the High Risk Sardinia Island. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessels, I.; Maywald, M.; Rink, L. Zinc as a Gatekeeper of Immune Function. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna, A.; Firinu, D.; Zavattari, P.; Valera, P. Zinc Status and Autoimmunity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessels, I.; Rink, L. Micronutrients in Autoimmune Diseases: Possible Therapeutic Benefits of Zinc and Vitamin D. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 77, 108240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, C.R.; Lifshitz, F. Zinc Nutrition and Growth Retardation. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Rev. 2008, 5, 889–896. [Google Scholar]
- Michele, P.; Olga, H. Zinc and Taste Disturbances in Older Adults: A Review of the Literature. Consult. Pharm. 2016, 31, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, Y.; Kinoshita, M.; Shimada, S.; Kawamura, T. Zinc and Skin Disorders. Nutrients 2018, 10, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessells, K.R.; Brown, K.H. Estimating the Global Prevalence of Zinc Deficiency: Results Based on Zinc Availability in National Food Supplies and the Prevalence of Stunting. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, D.L.; Fauci, A.S.; Kasper, D.L.; Hauser, S.L.; Jameson, J.L.; Loscalzo, J. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine; McGraw Hill Professional: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Nutrition Board, Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silicon, Vanadium, and Zinc; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Takei, M. The Development of Polaprezinc Research. Yakugaku Zasshi 2012, 132, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Doi, H.; Kuribayashi, K.; Kijima, T. Utility of Polaprezinc in Reducing Toxicities during Radiotherapy: A Literature Review. Future Oncol. 2018, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagisawa, H. Zinc Deficiency and Clinical Practice. J. Jpn. Med. Assoc. 2004, 47, 359–364. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, L.A.; Clarke, M.; Rovers, M.; Riley, R.D.; Simmonds, M.; Stewart, G.; Tierney, J.F. Preferred Reporting Items for a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Individual Participant Data The PRISMA-IPD Statement. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2015, 313, 1657–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A Revised Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Randomised Trials. BMJ 2019, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, H.; Itakura, H.; Ohmori, H.; Sasaki, M.; Sando, K.; Takamura, T.; Fuse, Y.; Hosoi, T.; Yoshida, H. Aenketsubosho No Shinryoshishin 2018 [Clinical Guideline for Zinc Deficiency 2018]. J. Jpn. Soc. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 40, 120–167. [Google Scholar]
- Tomita, H.; Tanaka, M.; Ikui, A. Clinical Standard Value for Diagnosis of Zinc Deficiency by the Serum Zinc Value on the Basis of Evidence. Biomed. Res. Trace Elem. 2007, 18, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, Y.B. A Modified Least-Squares Regression Approach to the Estimation of Risk Difference. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2007, 166, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, Y.; Fukuda, M.; Matsuyama, Y. The Number of Events per Confounder for Valid Estimation of Risk Difference Using Modified Least-Squares Regression. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 187, 2481–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakagami, M.; Ikeda, M.; Tomita, H.; Ikui, A.; Aiba, T.; Takeda, N.; Inokuchi, A.; Kurono, Y.; Nakashima, M.; Shibasaki, Y.; et al. A Zinc-Containing Compound, Polaprezinc, Is Effective for Patients with Taste Disorders: Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Multi-Center Study. Acta Otolaryngol. (Stockh.) 2009, 129, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, M.; Kurono, Y.; Inokuchi, A.; Takeda, N.; Aiba, T.; Nomura, Y.; Sakagami, M. The Effect of Zinc Agent in 219 Patients with Zinc Deficiency-Inductive/Idiopathic Taste Disorder: A Placebo Controlled Randomized Study. Nippon. Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho 2013, 166, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japan Pharmaceutical Information Center. Japic Clinical Trials Information: Japic CTI-060232. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.jp/cti-user/trial/Search.jsp (accessed on 1 November 2019).
- Japan Pharmaceutical Information Center. Japic Clinical Trials Information: Japic CTI-121907. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.jp/cti-user/trial/Search.jsp (accessed on 1 November 2019).
- Lowe, N.M.; Medina, M.W.; Stammers, A.; Patel, S.; Souverein, O.W.; Dullemeijer, C.; Serra-Majem, L.; Nissensohn, M.; Moran, V.H. The Relationship between Zinc Intake and Serum/Plasma Zinc Concentration in Adults: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis by the EURRECA Network. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, 1962–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, V.H.; Stammers, A.; Medina, M.W.; Patel, S.; Dykes, F.; Souverein, O.W.; Dullemeijer, C.; Pérez-Rodrigo, C.; Serra-Majem, L.; Nissensohn, M.; et al. The Relationship between Zinc Intake and Serum/Plasma Zinc Concentration in Children: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2012, 4, 841–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, K.; Hosui, A.; Sakai, Y.; Itou, M.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Takamori, Y.; Hosho, K.; Tsuru, T.; Takikawa, Y.; Michitaka, K.; et al. Effects of Zinc Acetate on Serum Zinc Concentrations in Chronic Liver Diseases: A Multicenter, Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial and a Dose Adjustment Trial. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kambe, T.; Tsuji, T.; Hashimoto, A.; Itsumura, N. The Physiological, Biochemical, and Molecular Roles of Zinc Transporters in Zinc Homeostasis and Metabolism. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 749–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, T.; Kambe, T. The Functions of Metallothionein and ZIP and ZnT Transporters: An Overview and Perspective. IJMS 2016, 17, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoi, K.; Egger, N.G.; Ramanujam, V.M.S.; Alcock, N.W.; Dayal, H.H.; Penland, J.G.; Sandstead, H.H. Association between Plasma Zinc Concentration and Zinc Kinetic Parameters in Premenopausal Women. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 285, E1010–E1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.C.; Brown, K.H.; Gibson, R.S.; Krebs, N.F.; Lowe, N.M.; Siekmann, J.H.; Raiten, D.J. Biomarkers of Nutrition for Development (BOND)—Zinc Review. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 858S–885S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maret, W.; Sandstead, H.H. Zinc Requirements and the Risks and Benefits of Zinc Supplementation. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2006, 20, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, R.S.; Hess, S.Y.; Hotz, C.; Brown, K.H. Indicators of Zinc Status at the Population Level: A Review of the Evidence. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 99, S14–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.C. Assessment of Zinc Status. J. Nutr. 1990, 120, 1474–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author, Year | Sample Size | Studied Population | Treatments | Male (%) | Age (Means ± SD, Year) | Baseline Zinc (Means ± SD, μg/dL) | Duration of Treatment (Week) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sakagami et al., 2009 [21] | 107 | Outpatients with zinc-related taste disorder, aged 20–80 years | Polaprezinc 75 mg/day (n = 27) Polaprezinc 150 mg/day (n = 25) Polaprezinc 300 mg/day (n = 28) Placebo (n = 27) | 47.4 | 45.1 ± 16.2 | 71.0 ± 12.7 | 12 |
| Ikeda et al., 2013 [22] | 219 | Outpatients with zinc-related taste disorder, aged 20–75 years | Polaprezinc 150 mg (n = 108) Placebo (n = 111) | 39.7 | 45.2 ± 12.9 | 72.7 ± 12.6 | 12 |
| JapicCTI-060232 * (unpublished) [23] | 149 | Outpatients with zinc-related taste disorder, aged 20–80 years | Polaprezinc 150 mg (n = 47) Polaprezinc 300 mg (n = 51) Placebo (n = 51) | 45. | 43.3 ± 13.8 | 77.8 ± 11.8 | 12 |
| JapicCTI-121907 * (unpublished) [24] | 269 | Outpatients with zinc-related taste disorder, aged 20–75 years | Polaprezinc 150 mg (n = 134) Placebo (n = 135) | 50.2 | 45.3 ± 12.3 | 76.1 ± 14.1 | 12 |
| Treatments | Original Sample Size | Primary Analysis Population † | Secondary Analysis Population ‡ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall Polaprezinc | 420 | 97 | 322 |
| Polaprezinc 75 mg | 27 | 9 | 21 |
| Polaprezinc 150 mg | 314 | 69 | 241 |
| Polaprezinc 300 mg | 324 | 19 | 60 |
| Placebo | 79 | 87 | 255 |
| Total | 744 | 184 | 577 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Furihata, K.; Tsuchikawa, M.; Miwa, T.; Naito, Y.; Oba, K.; Sakagami, M. Efficacy and Safety of Polaprezinc (Zinc Compound) on Zinc Deficiency: A Systematic Review and Dose–Response Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials Using Individual Patient Data. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041128
Furihata K, Tsuchikawa M, Miwa T, Naito Y, Oba K, Sakagami M. Efficacy and Safety of Polaprezinc (Zinc Compound) on Zinc Deficiency: A Systematic Review and Dose–Response Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials Using Individual Patient Data. Nutrients. 2020; 12(4):1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041128
Chicago/Turabian StyleFurihata, Kei, Masaru Tsuchikawa, Takaki Miwa, Yuji Naito, Koji Oba, and Masafumi Sakagami. 2020. "Efficacy and Safety of Polaprezinc (Zinc Compound) on Zinc Deficiency: A Systematic Review and Dose–Response Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials Using Individual Patient Data" Nutrients 12, no. 4: 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041128
APA StyleFurihata, K., Tsuchikawa, M., Miwa, T., Naito, Y., Oba, K., & Sakagami, M. (2020). Efficacy and Safety of Polaprezinc (Zinc Compound) on Zinc Deficiency: A Systematic Review and Dose–Response Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials Using Individual Patient Data. Nutrients, 12(4), 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041128






