An Adaptive Second Order Sliding Mode Inverse Kinematics Approach for Serial Kinematic Chain Robot Manipulators
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Traditional Inverse Kinematics Method
3. The Proposed Approach
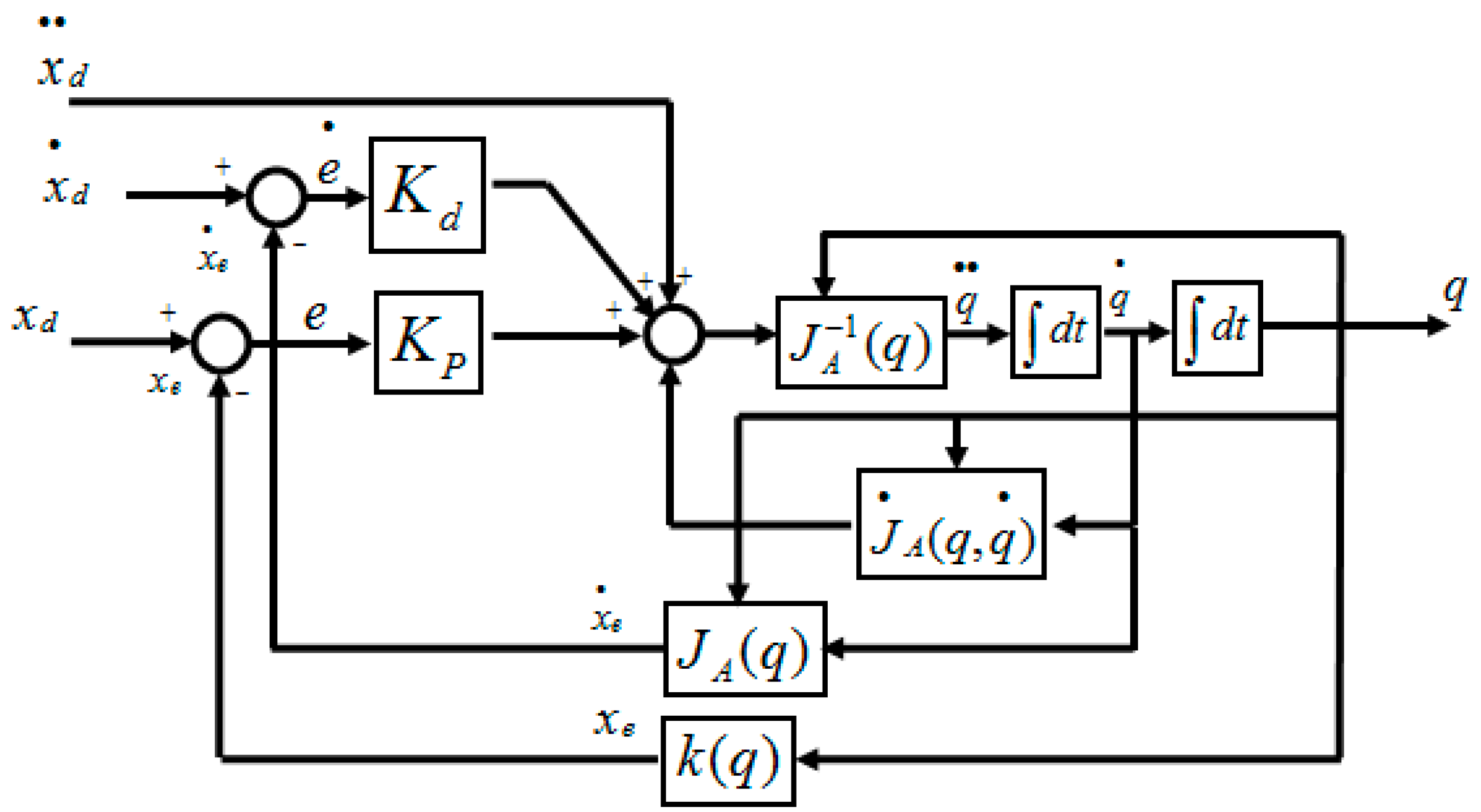
3.1. The Proposed Second Order Sliding Mode-Based Inverse Kinematics Algorithm
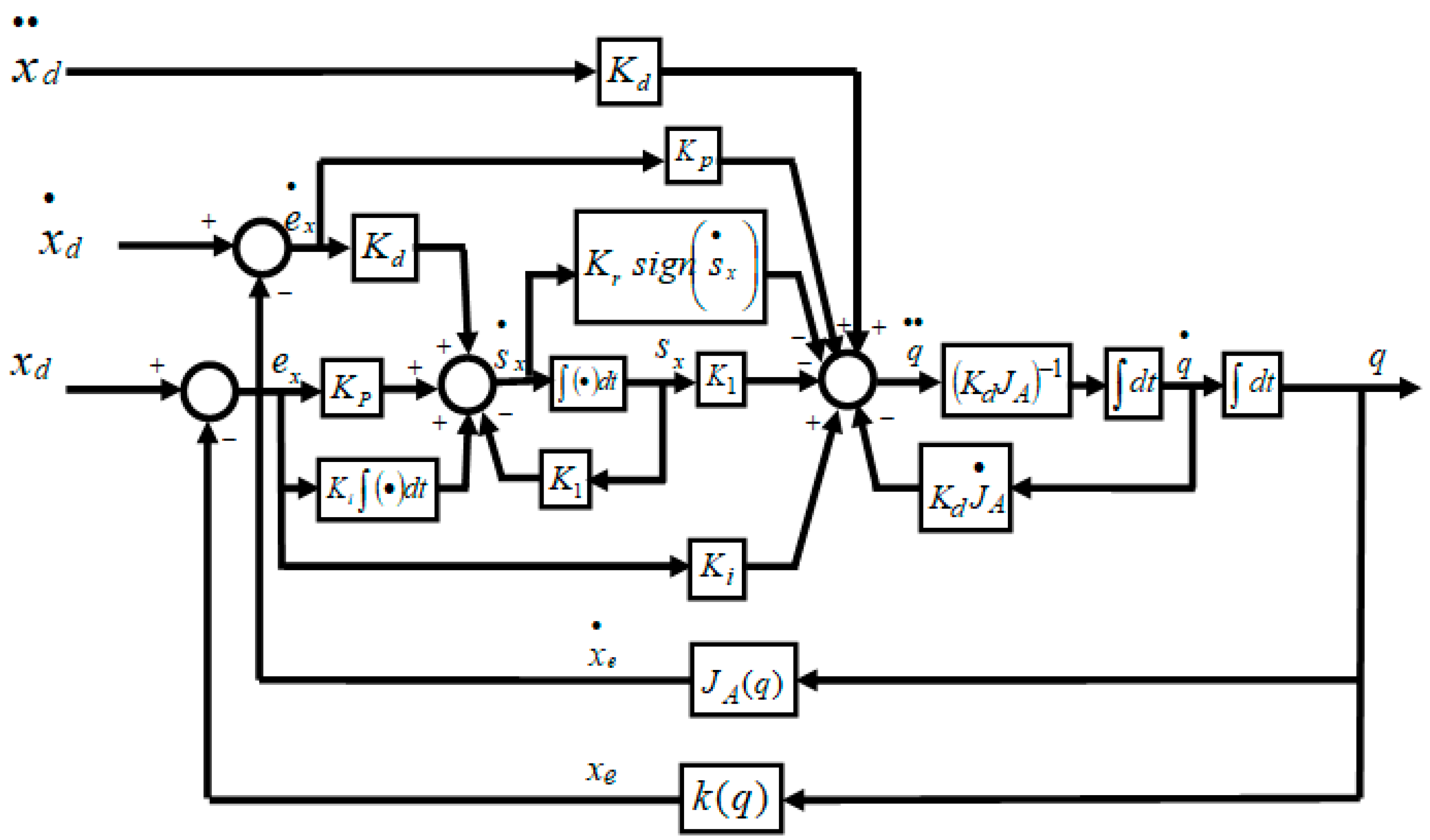
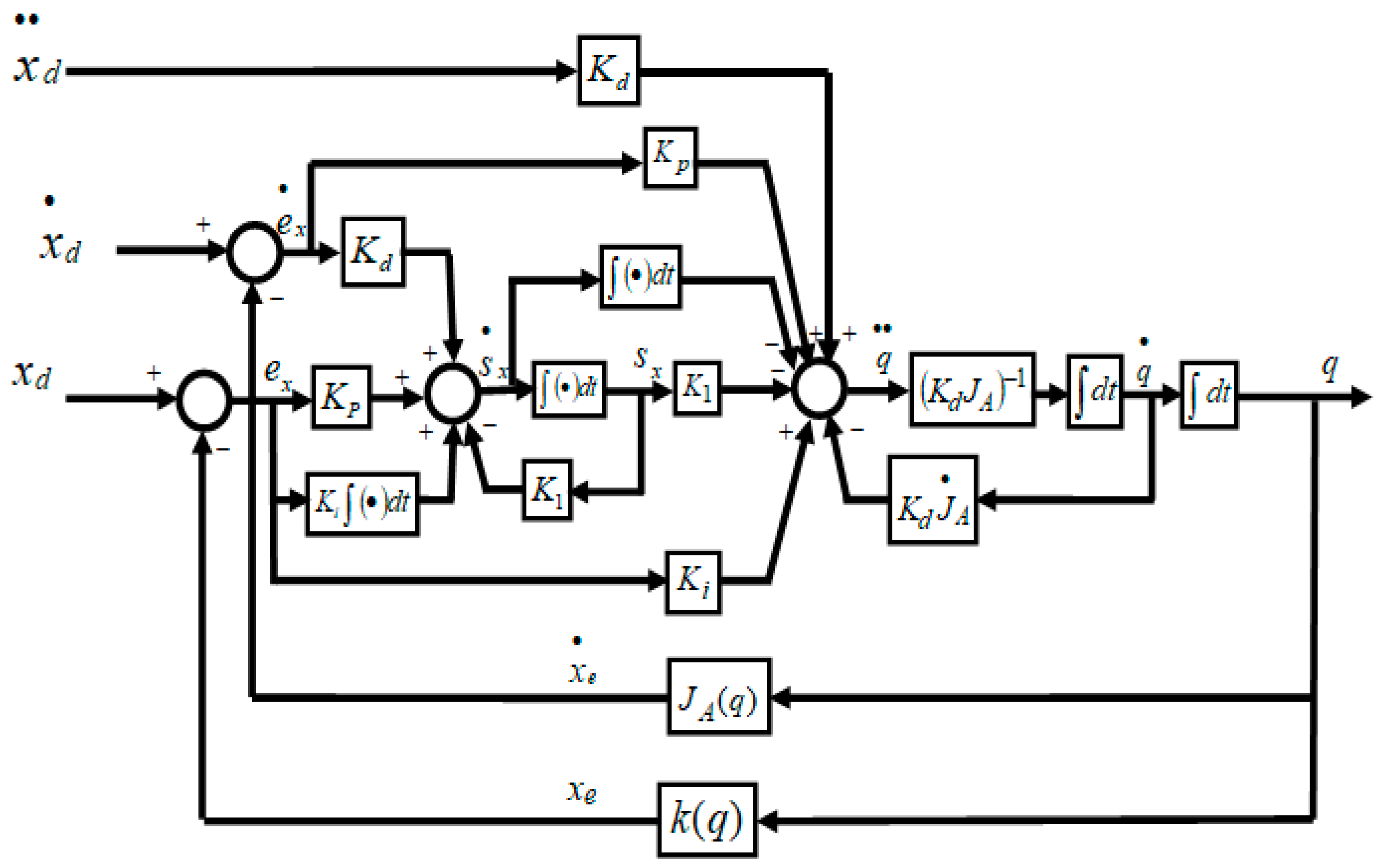
3.2. The Proposed Continuous Second Order Sliding Mode-Based Inverse Kinematics Algorithm
4. Results
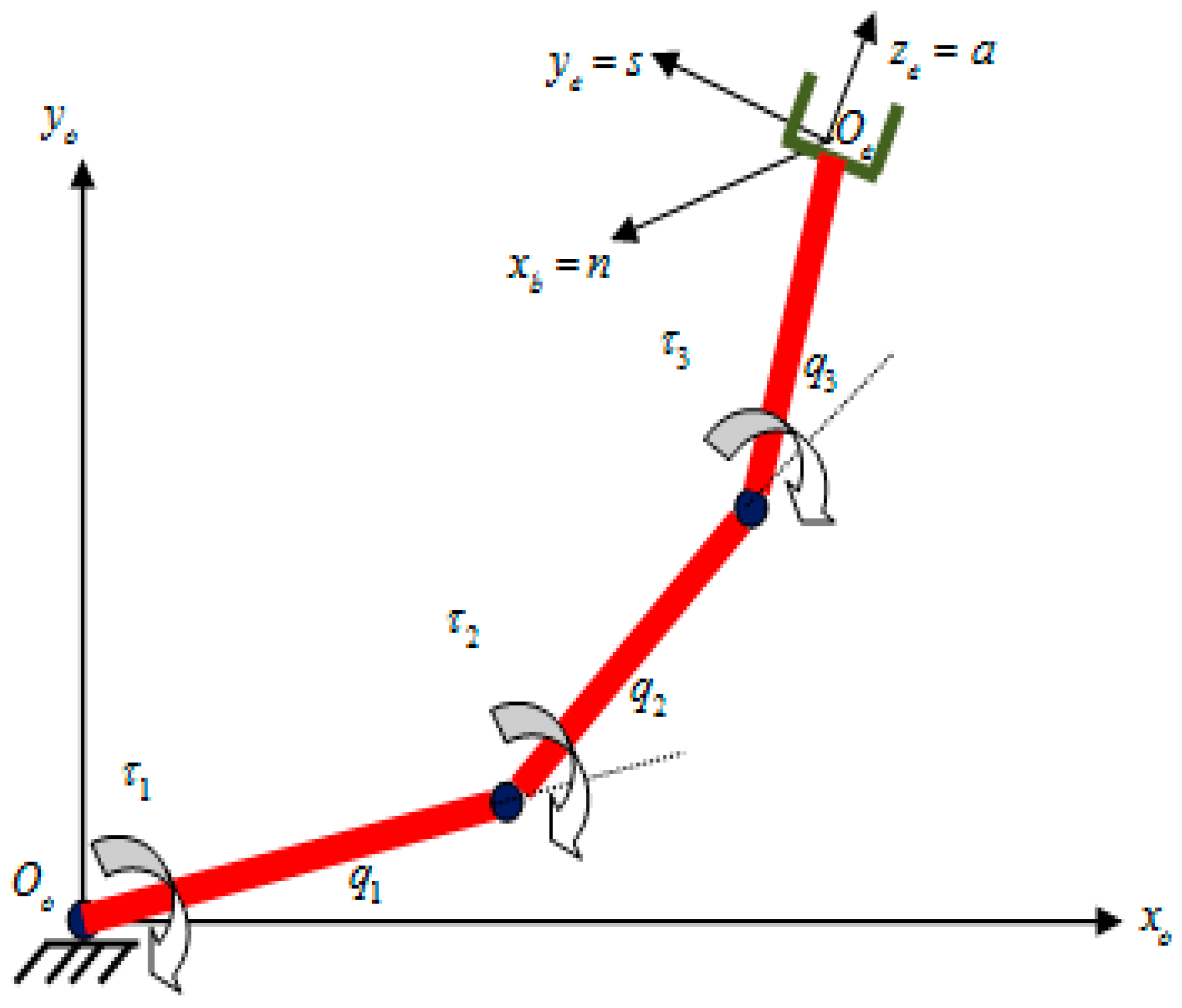
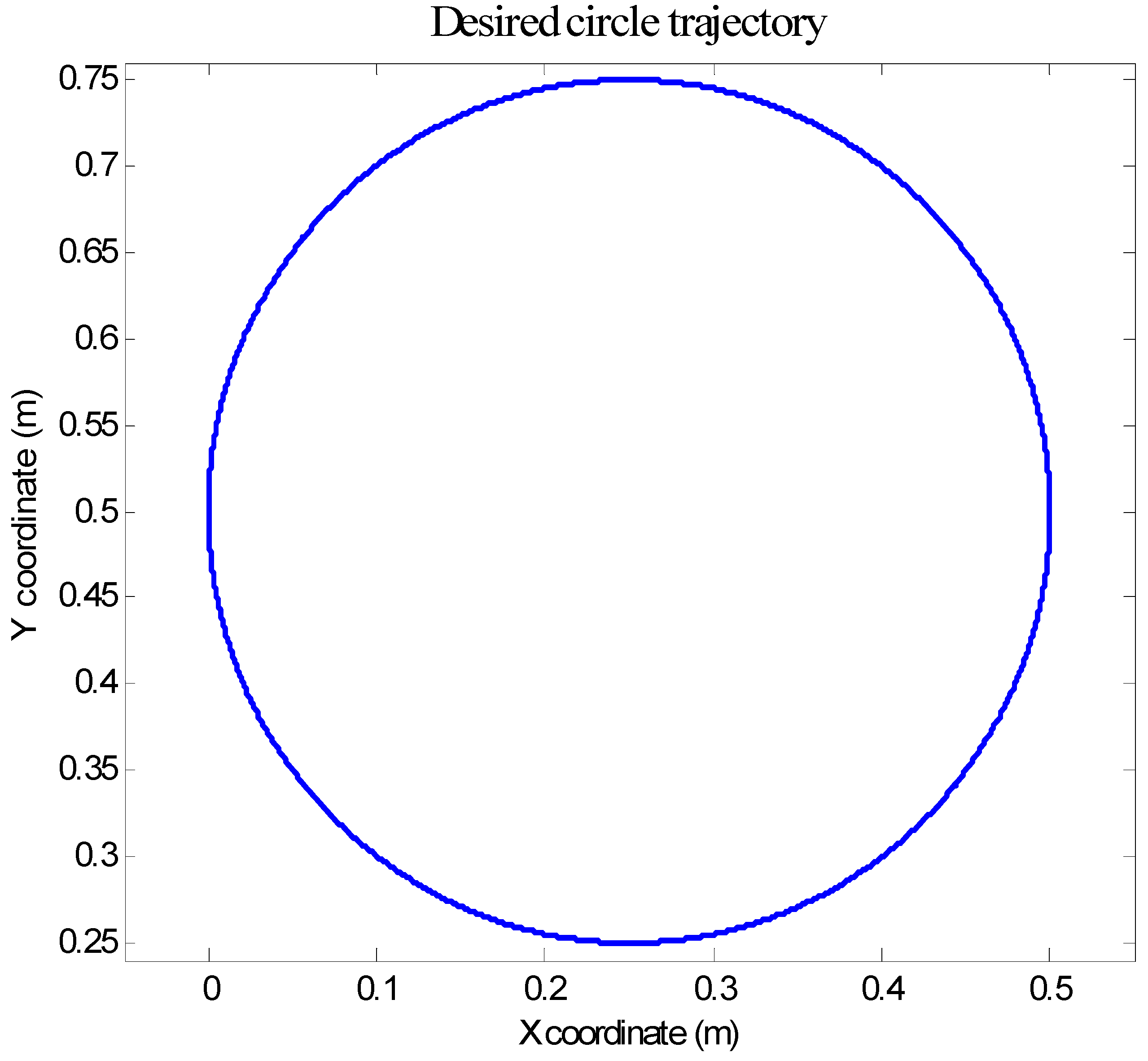
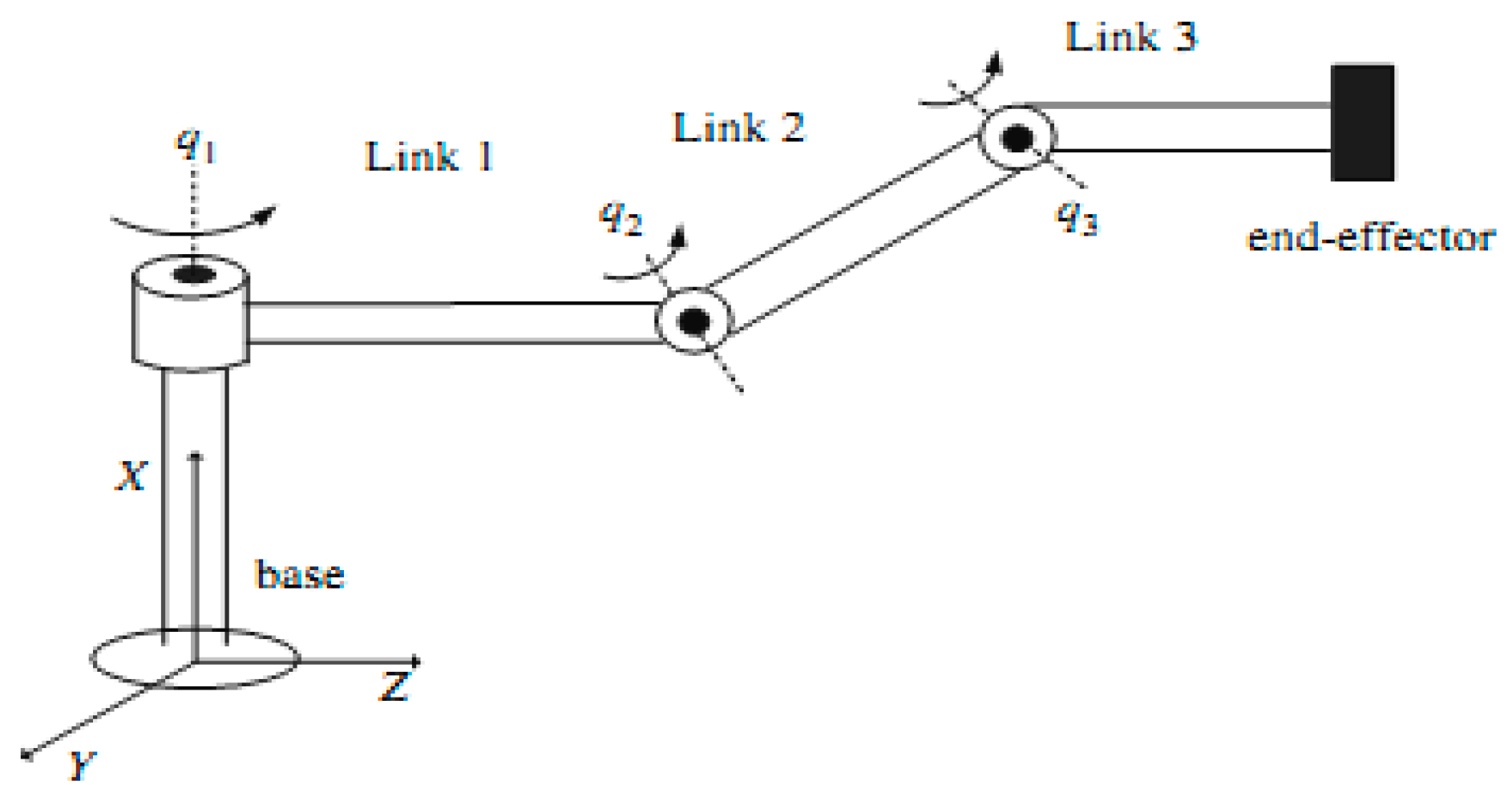
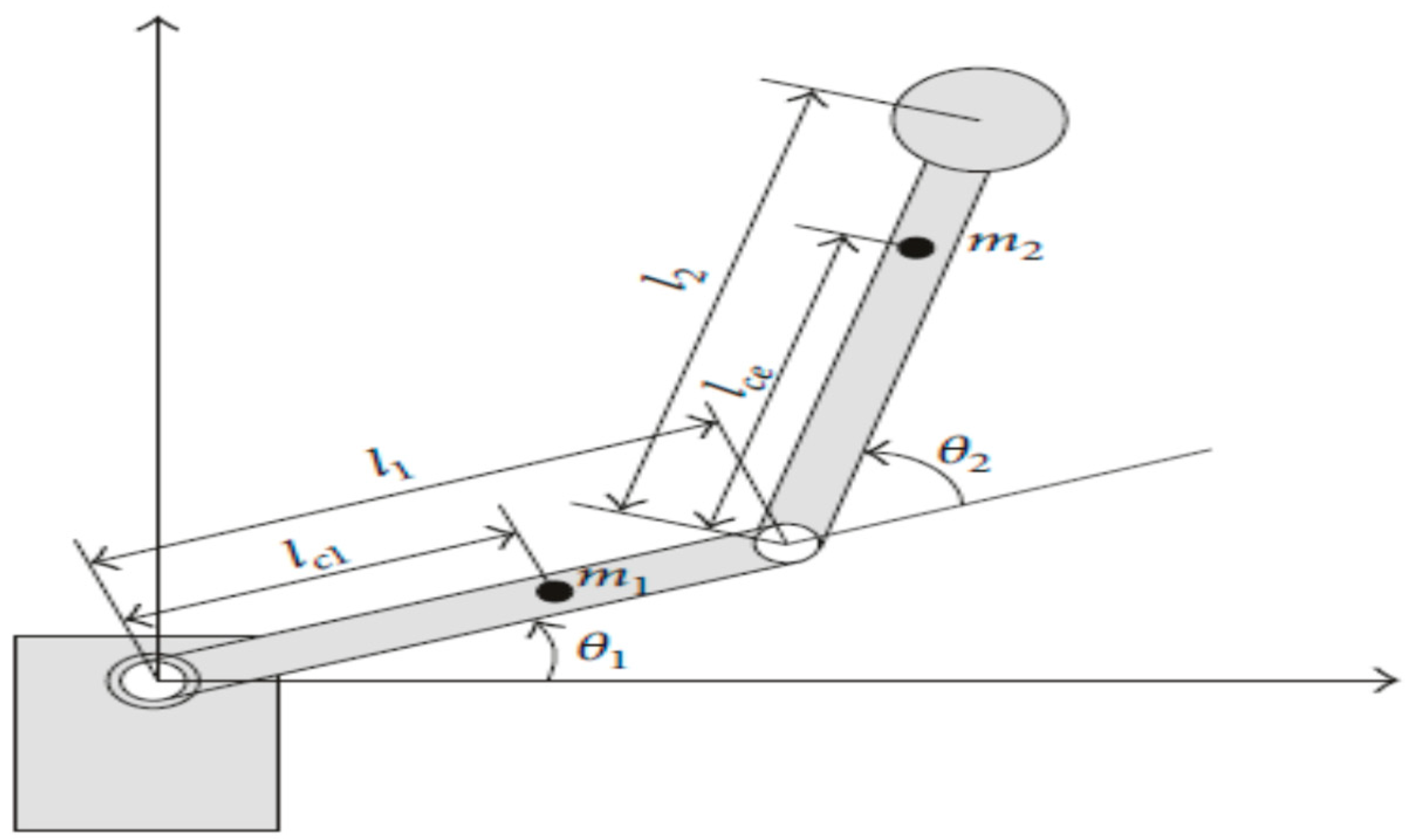
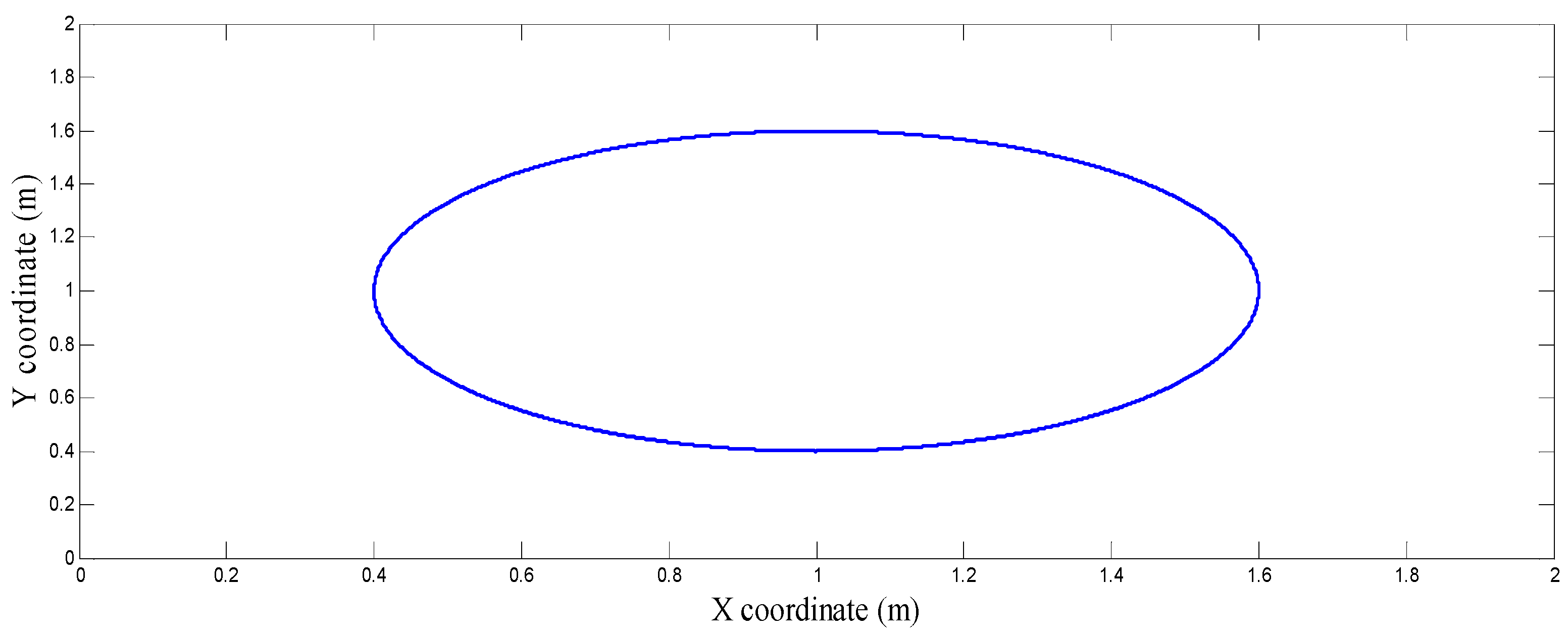
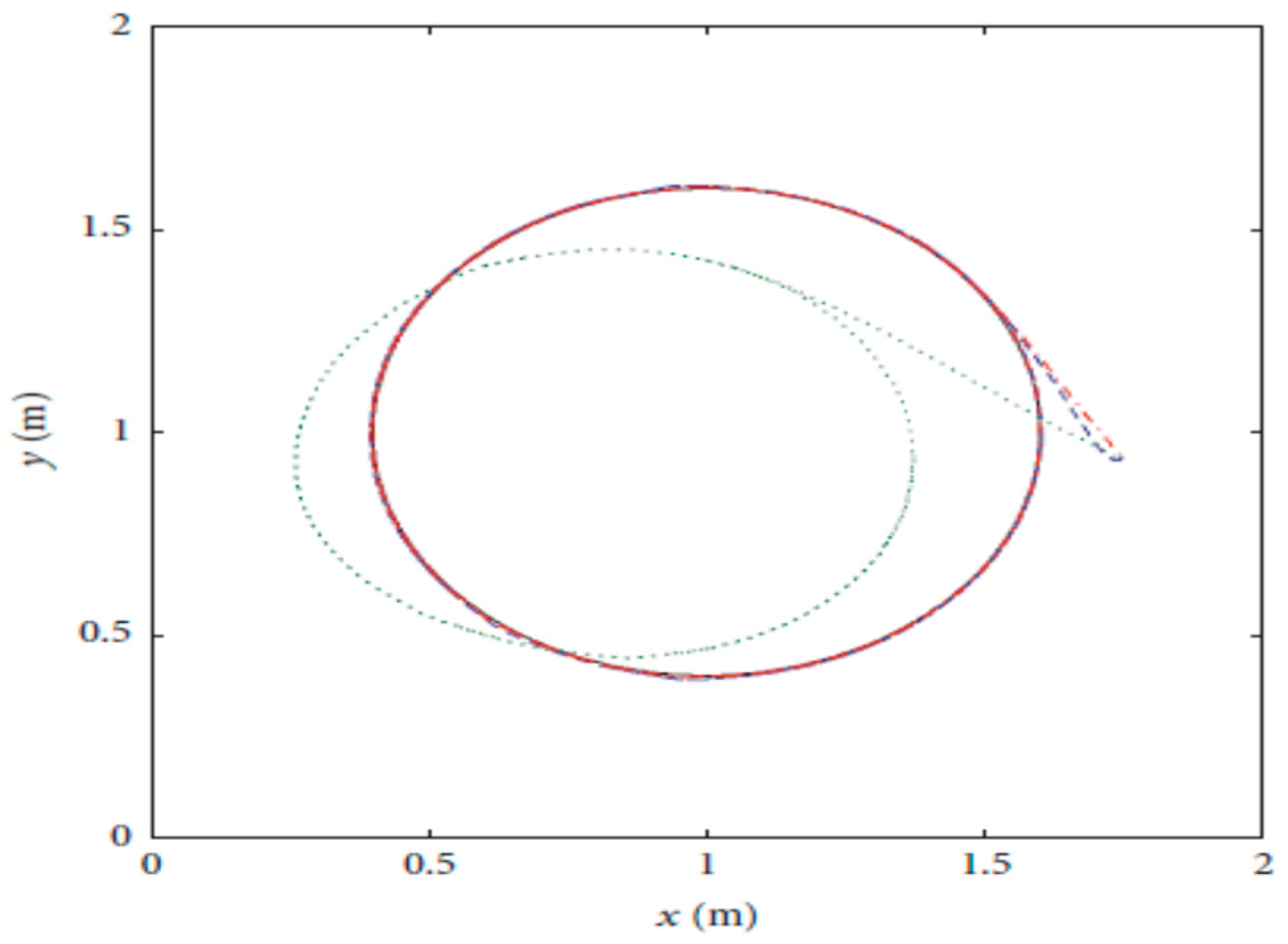
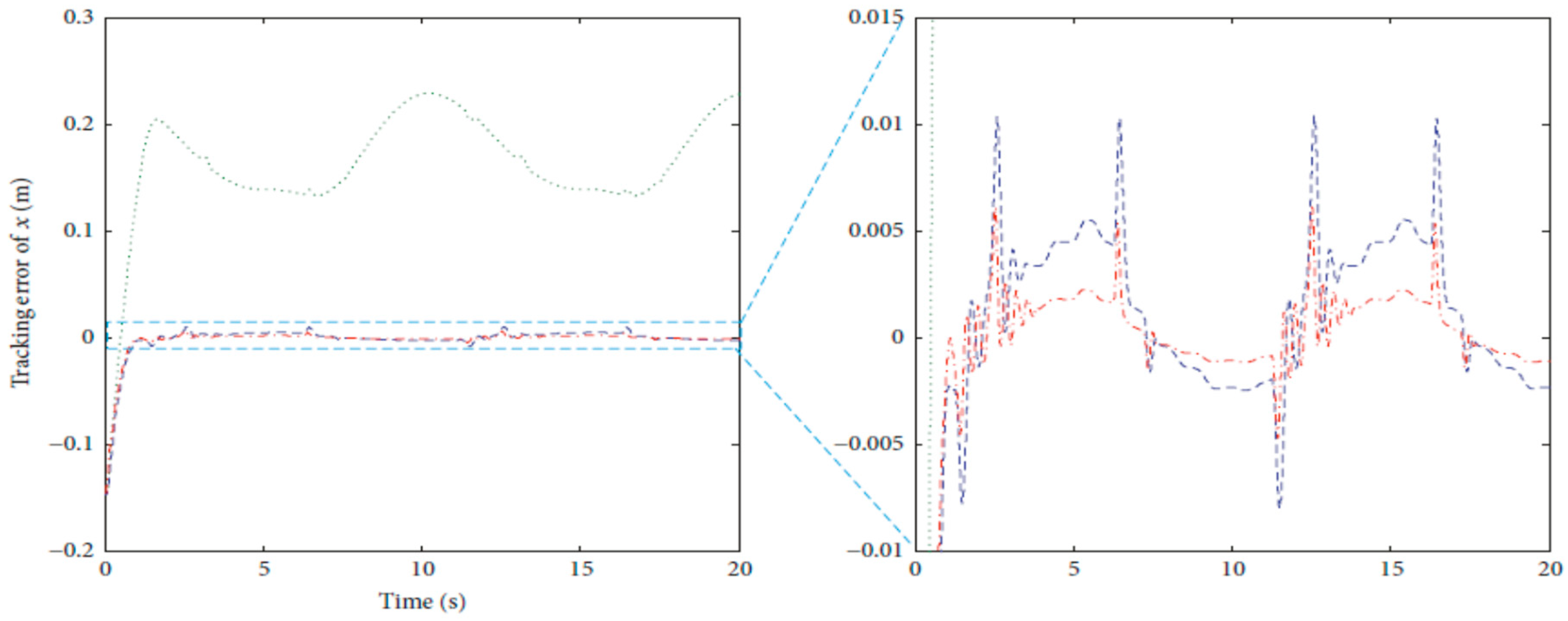
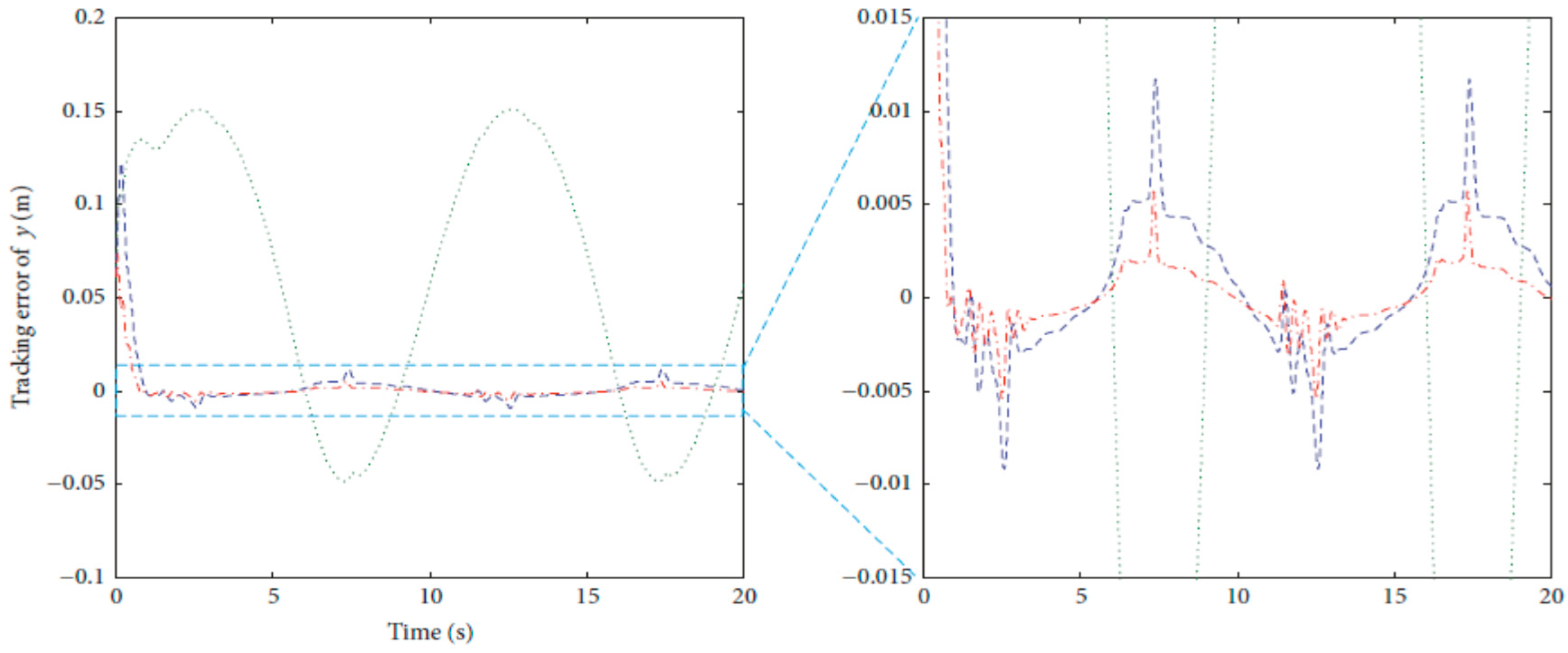
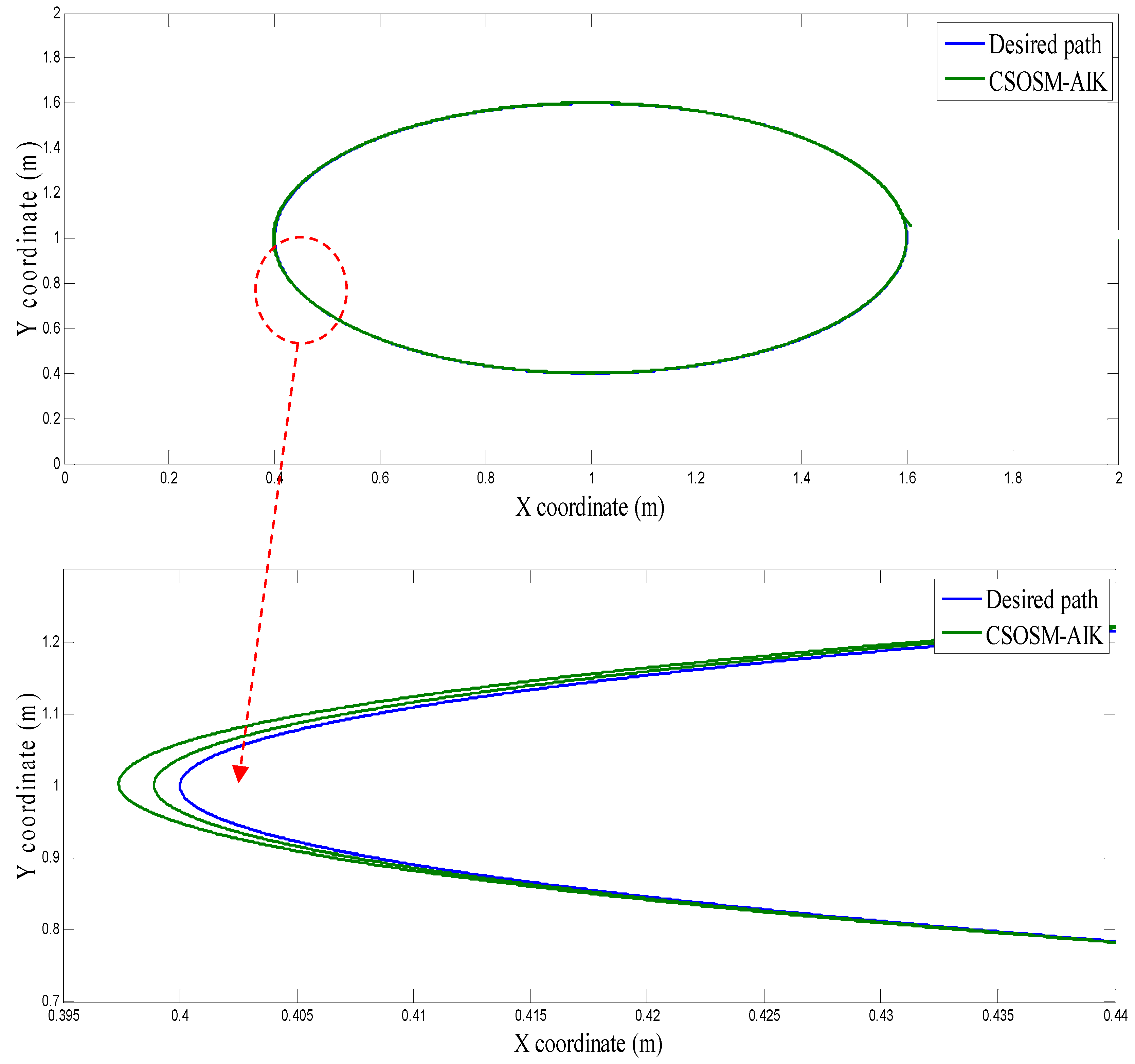
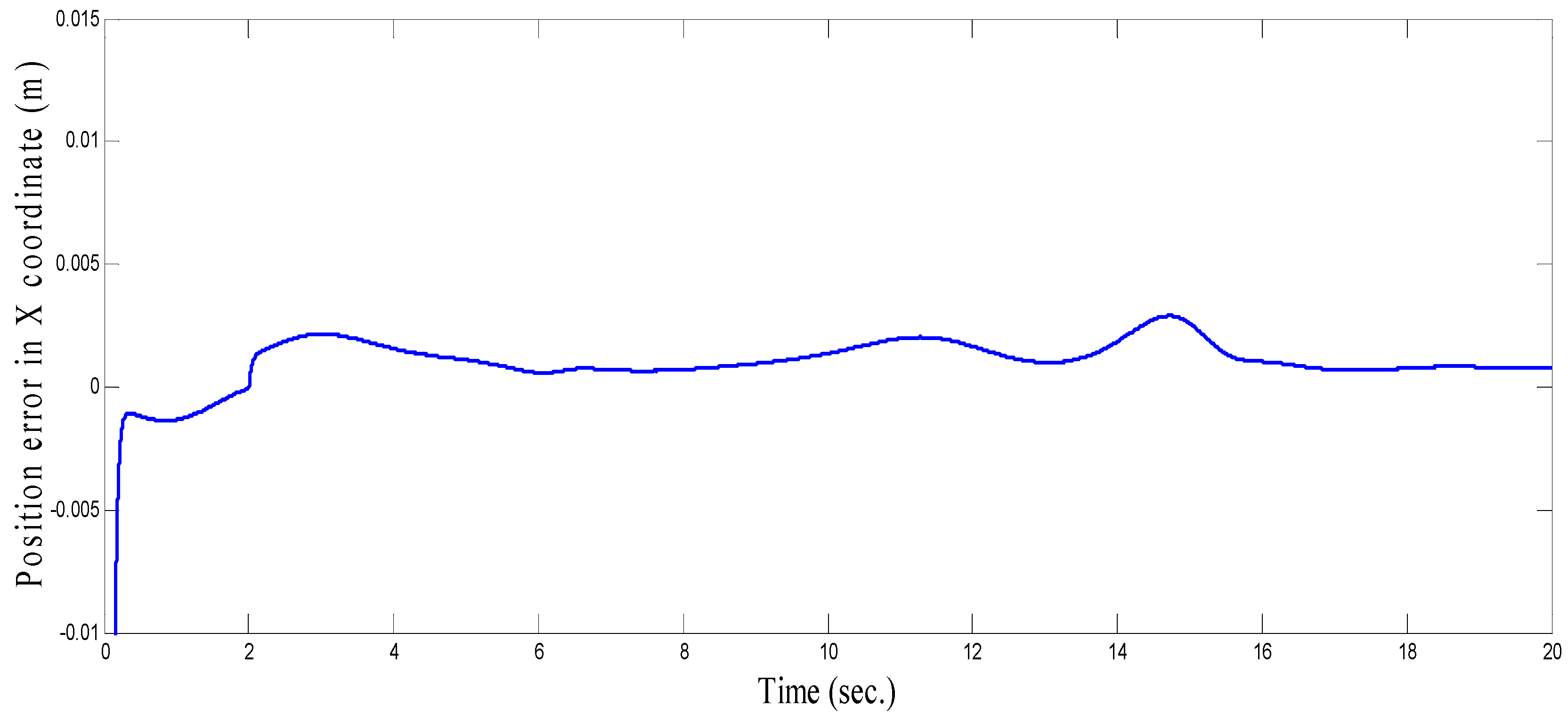
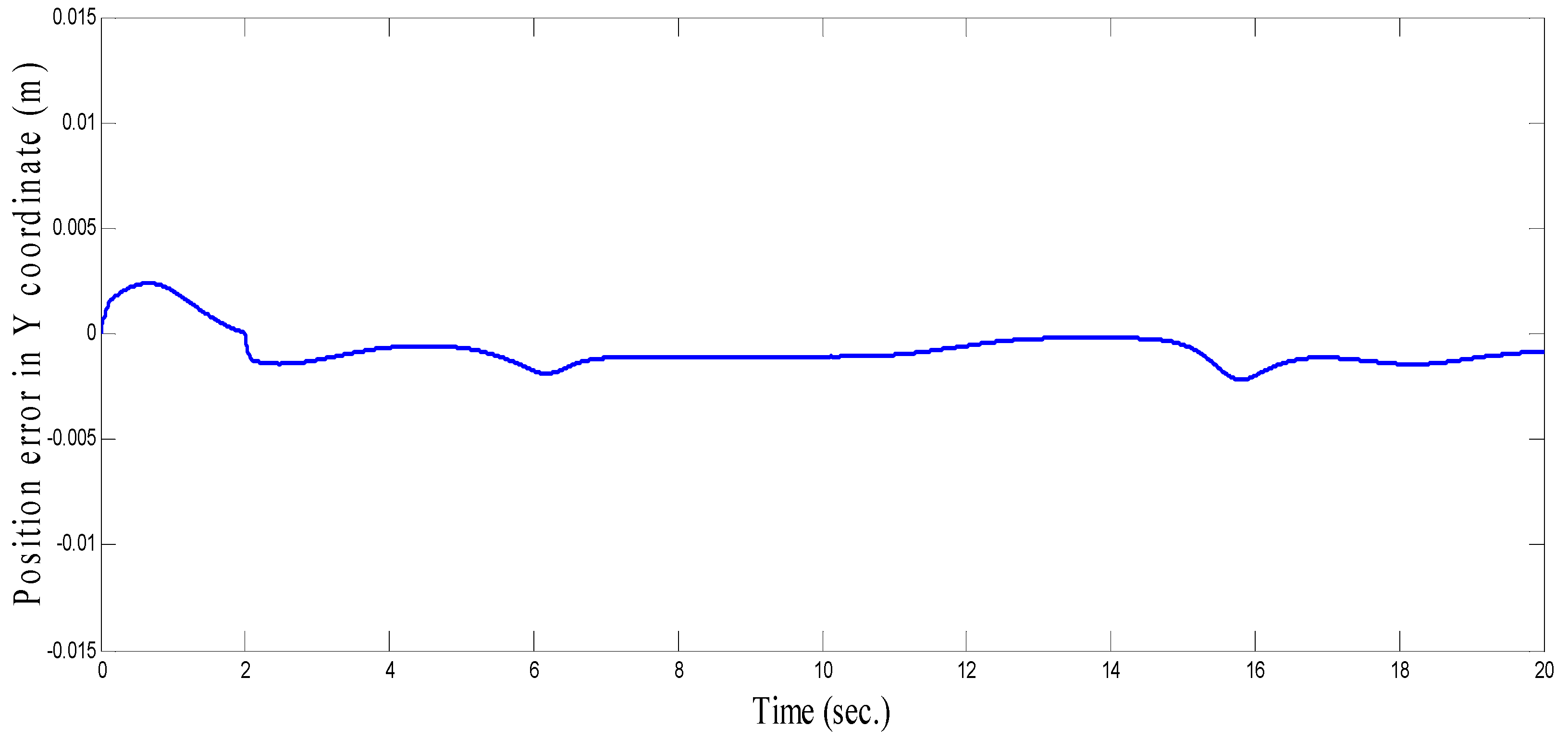
4.1. Three-Link Robot Arm
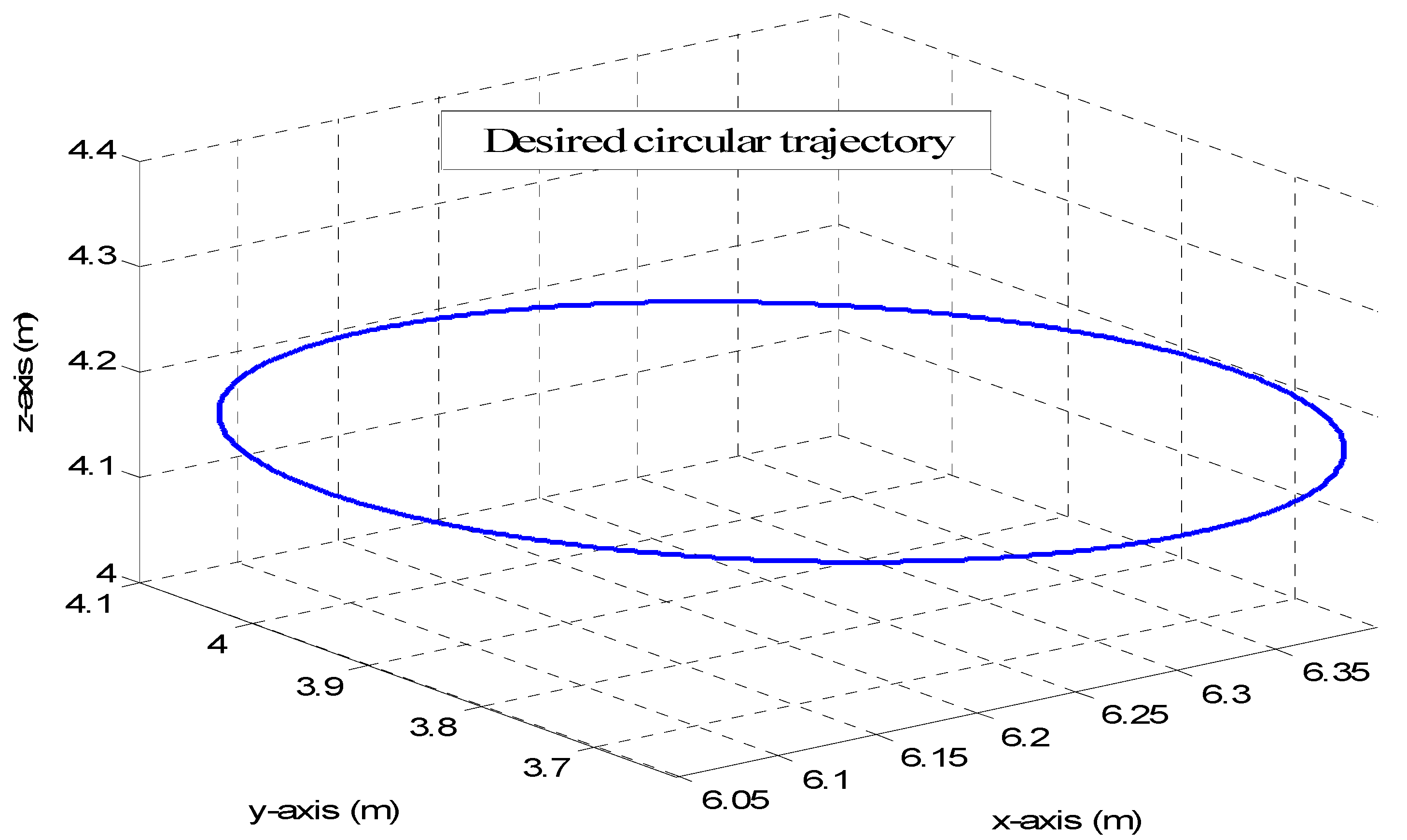
4.2. Anthropomorphic Robot Arm
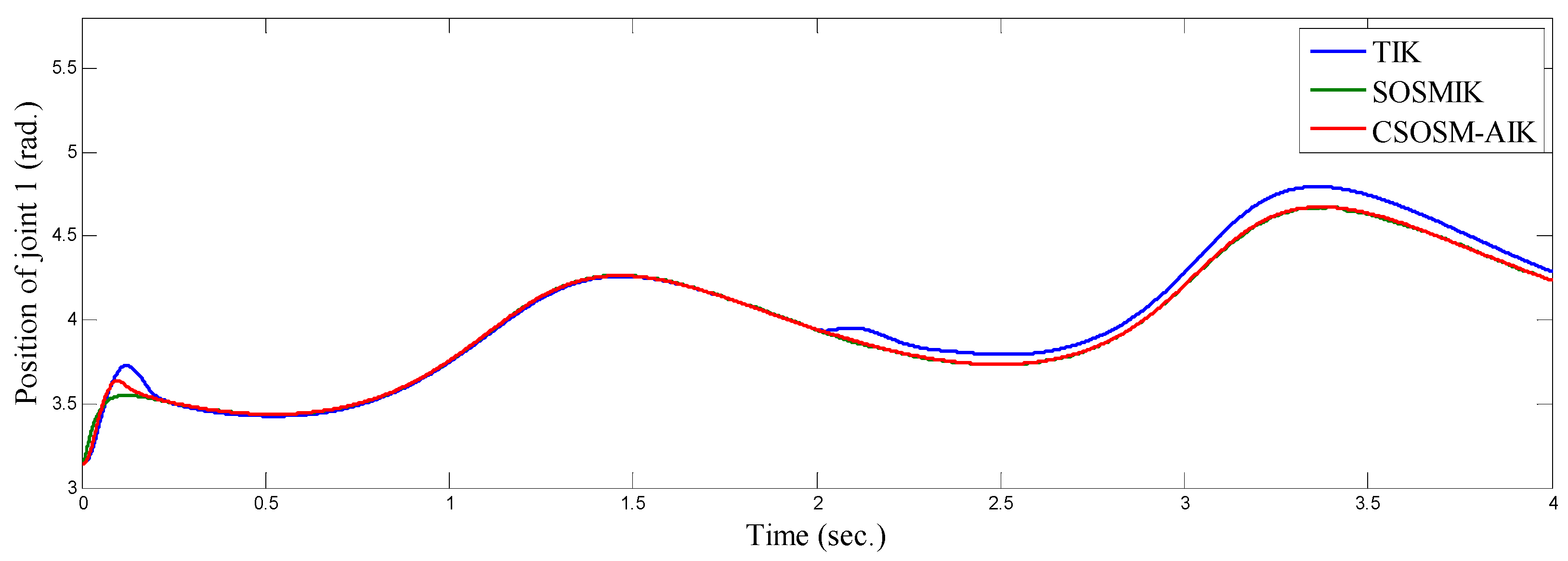
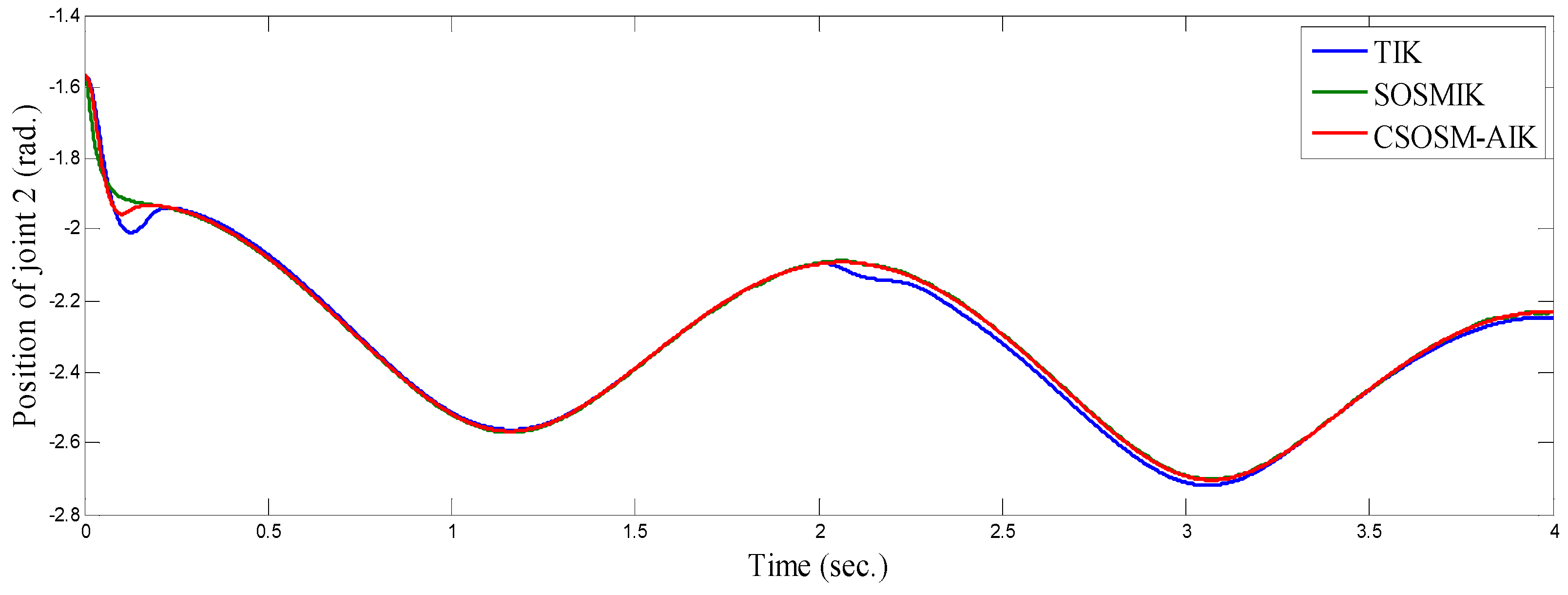
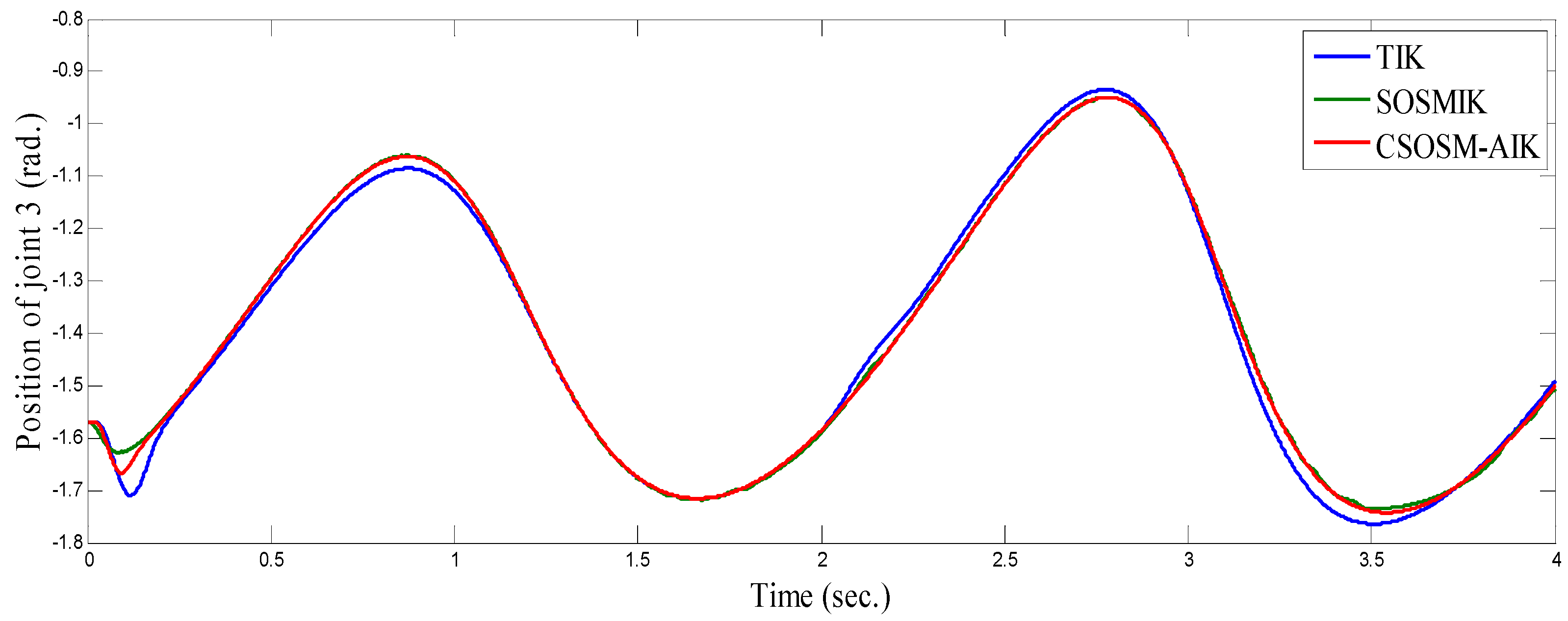
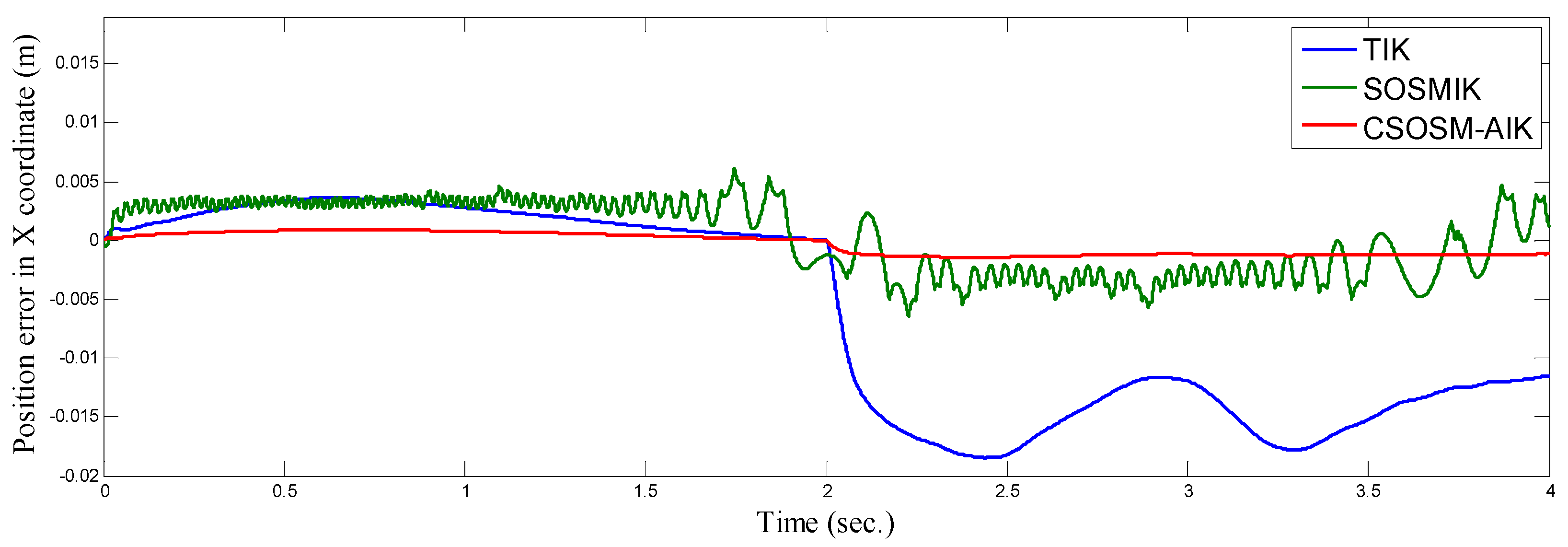
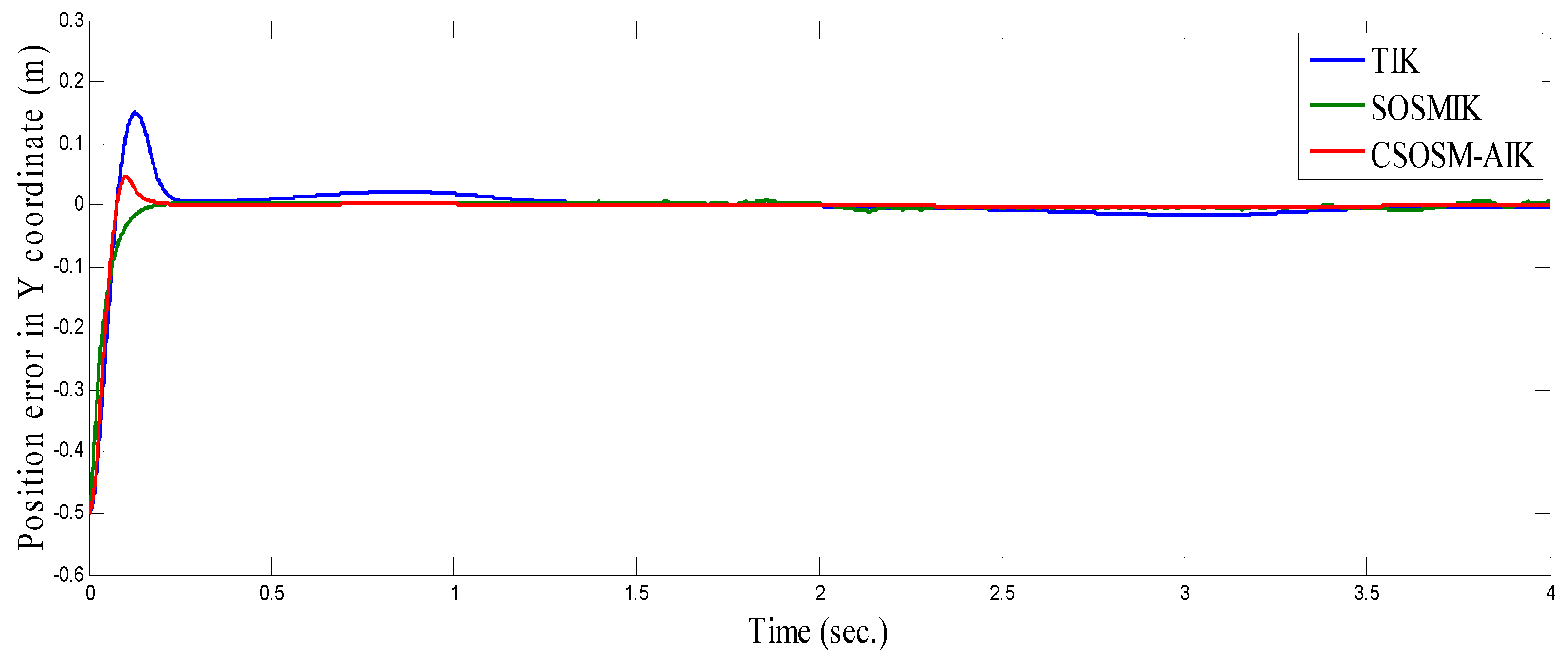
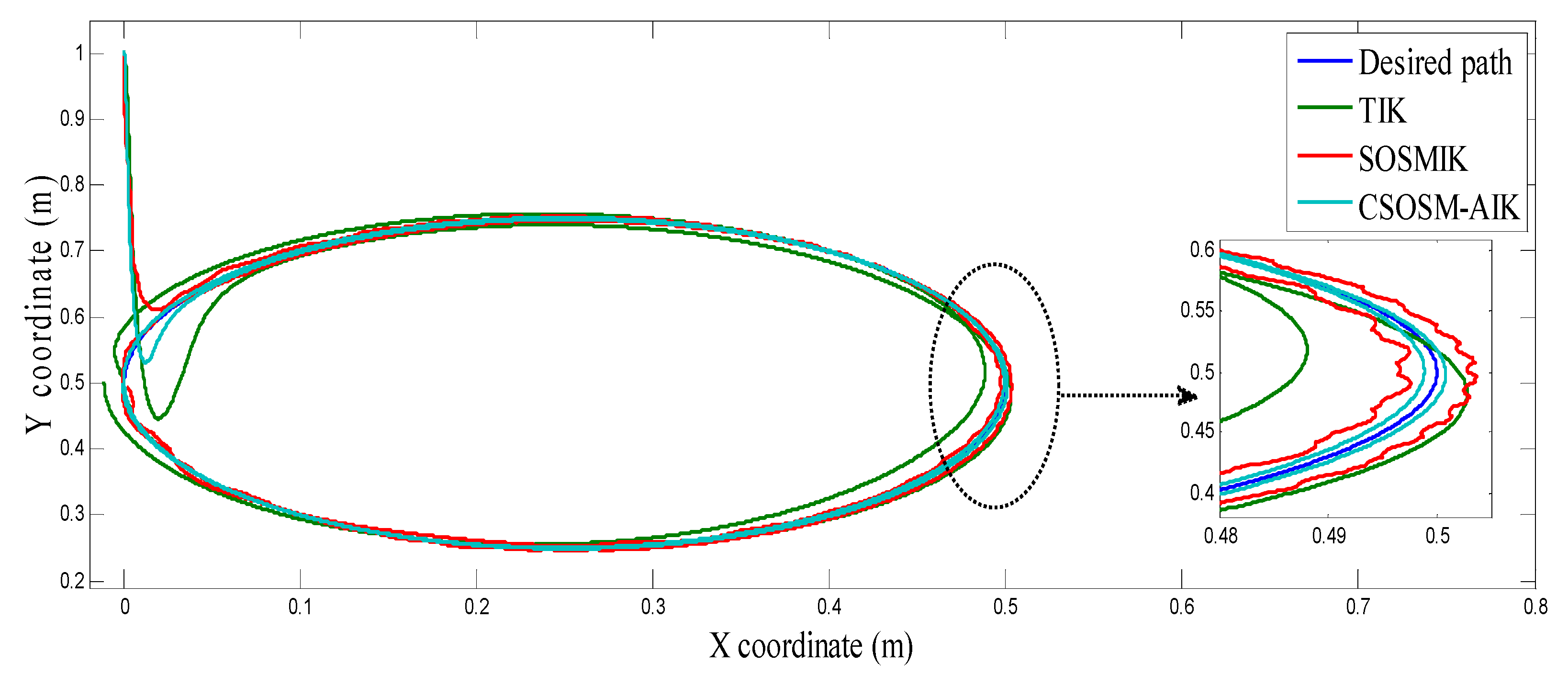
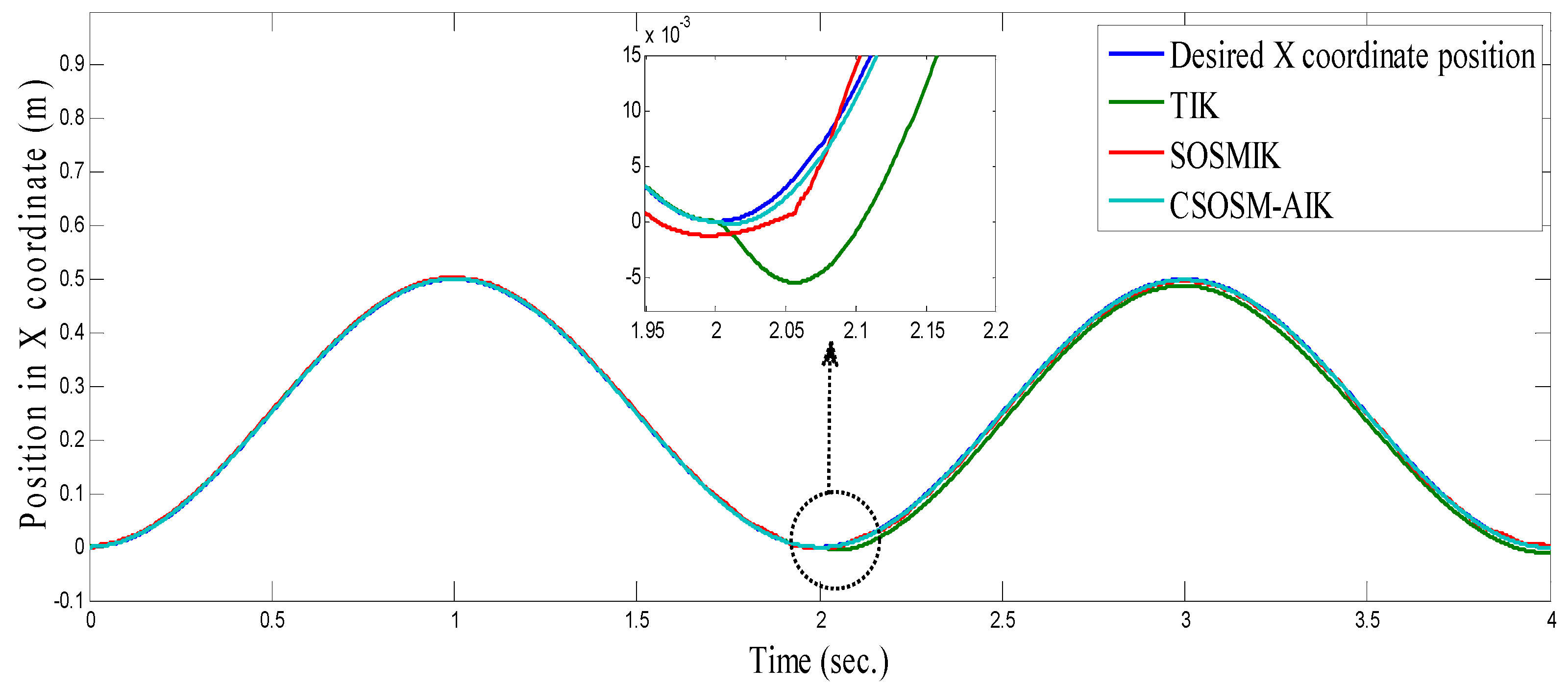
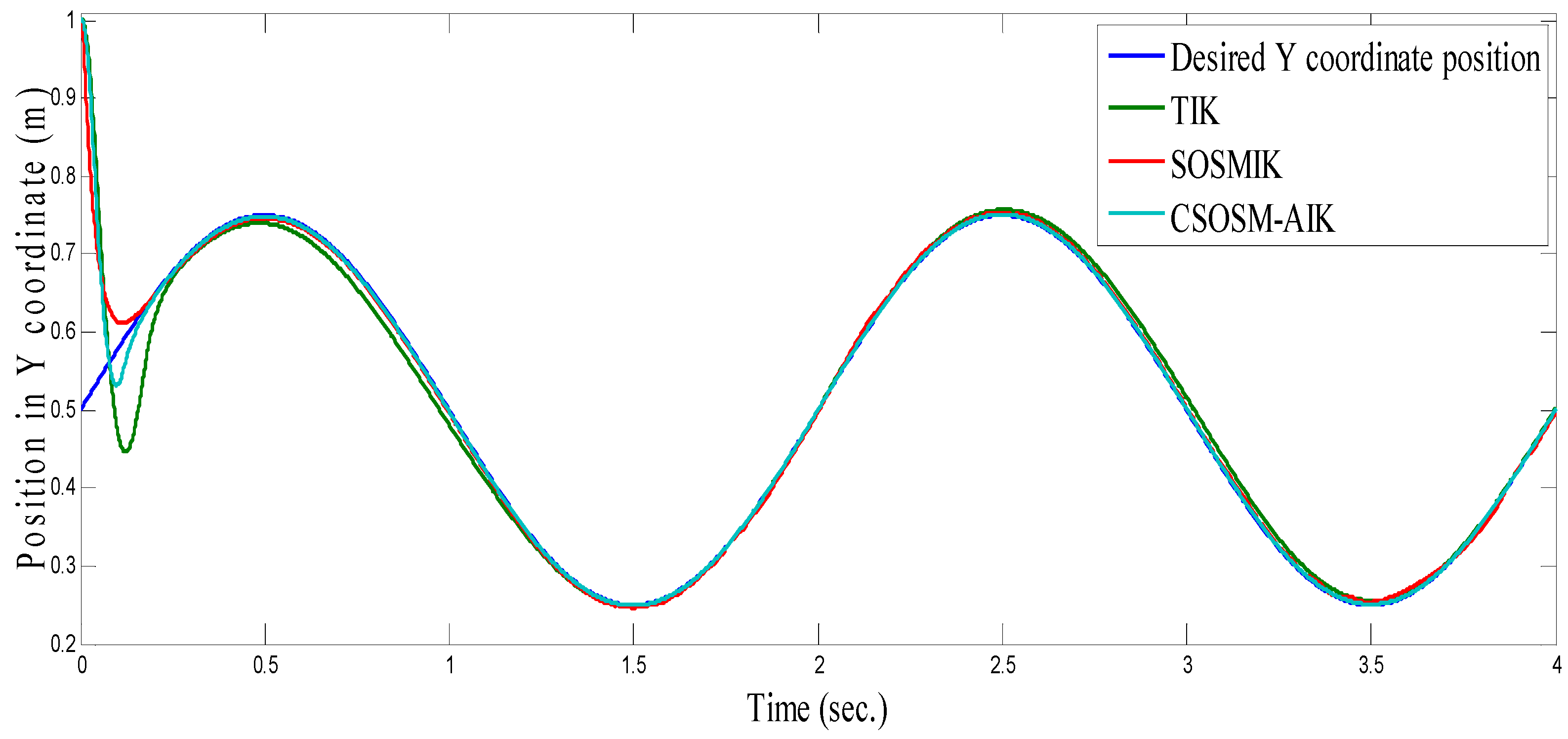
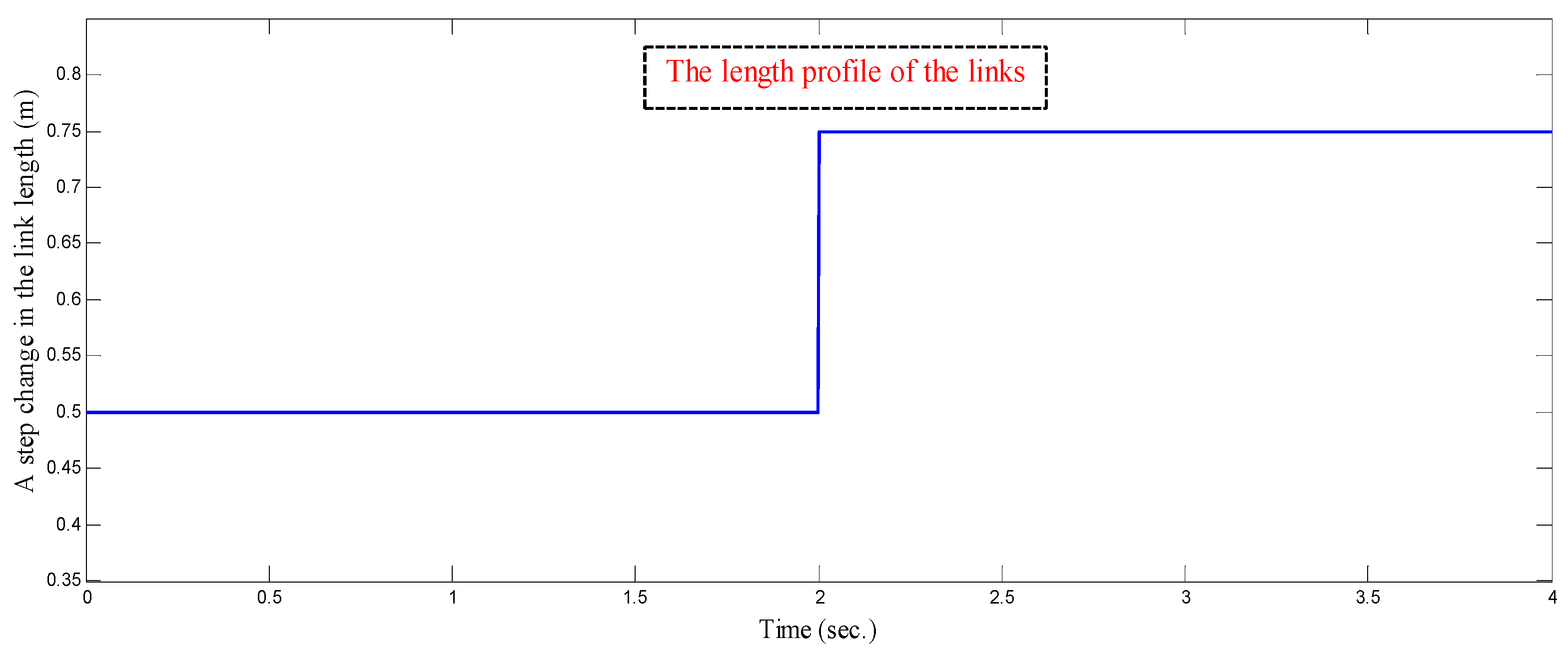
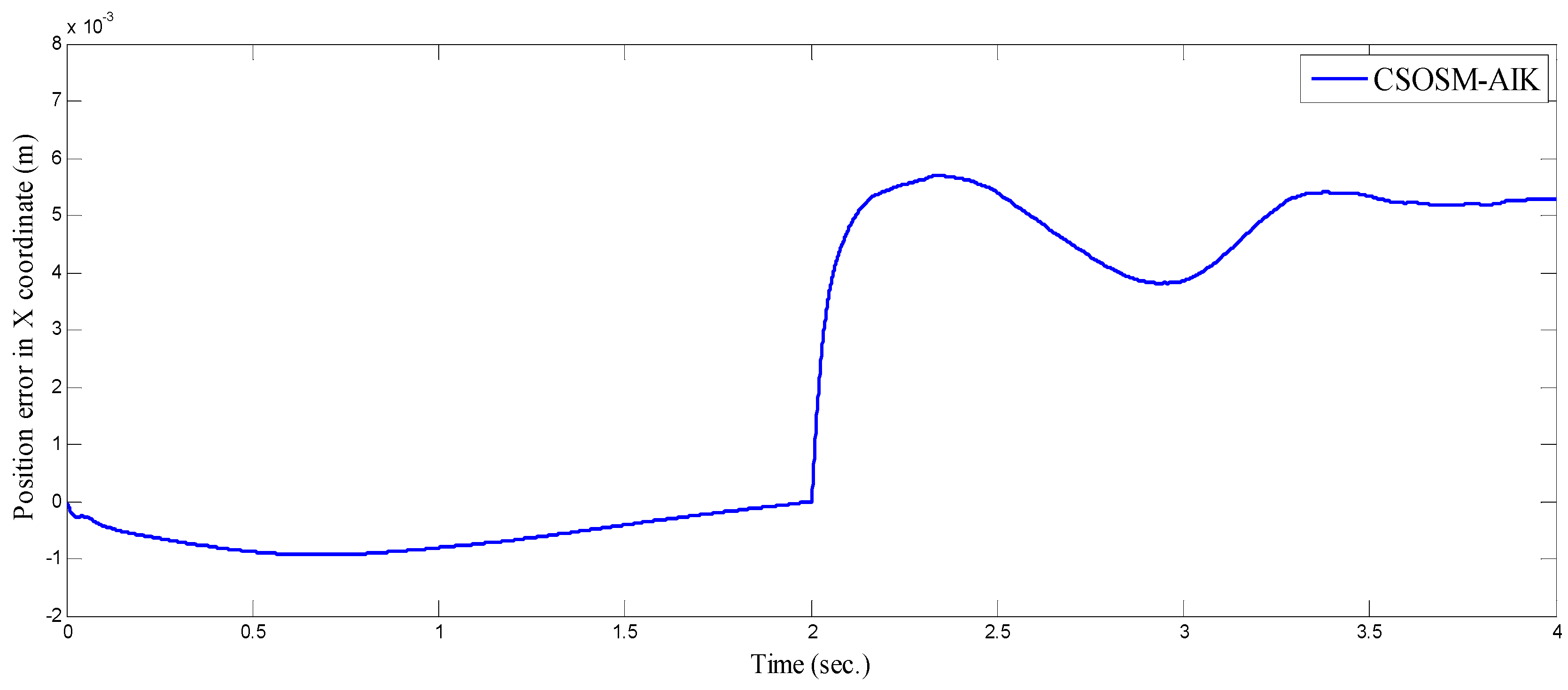
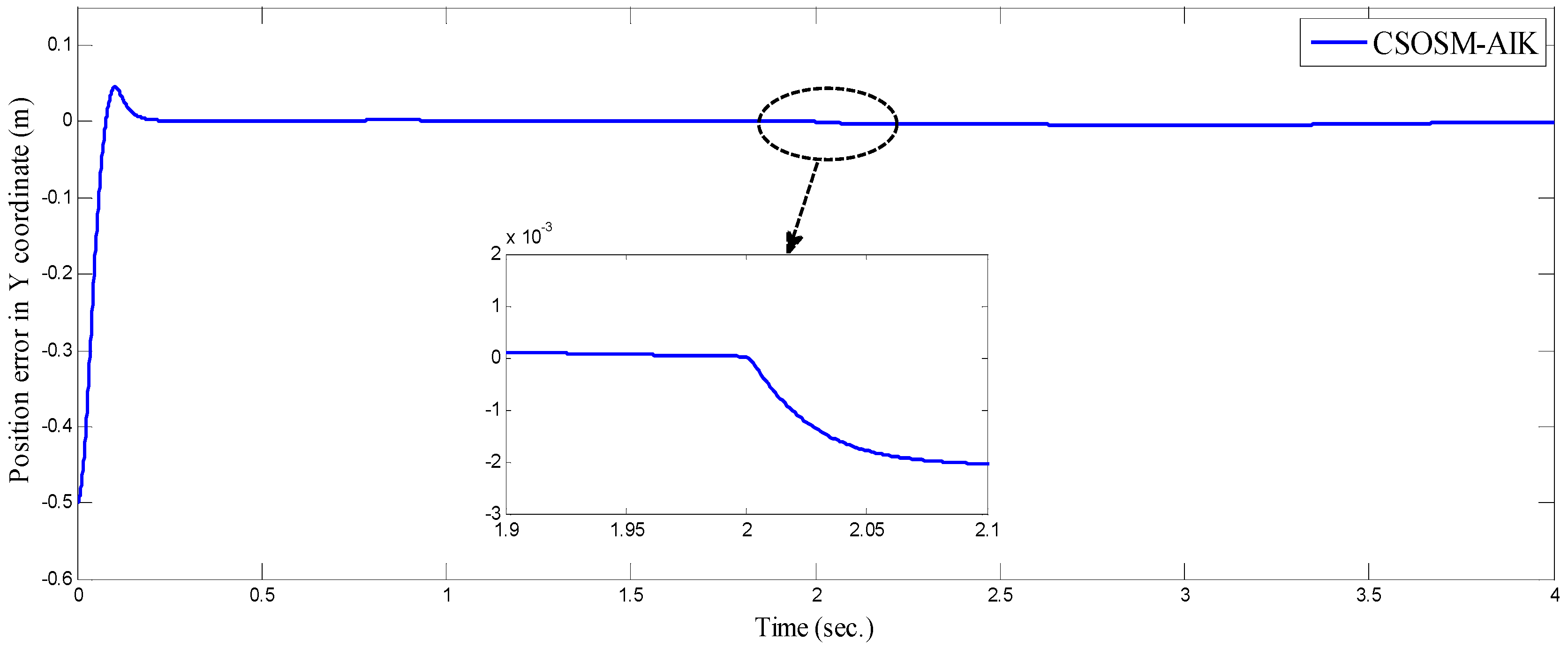
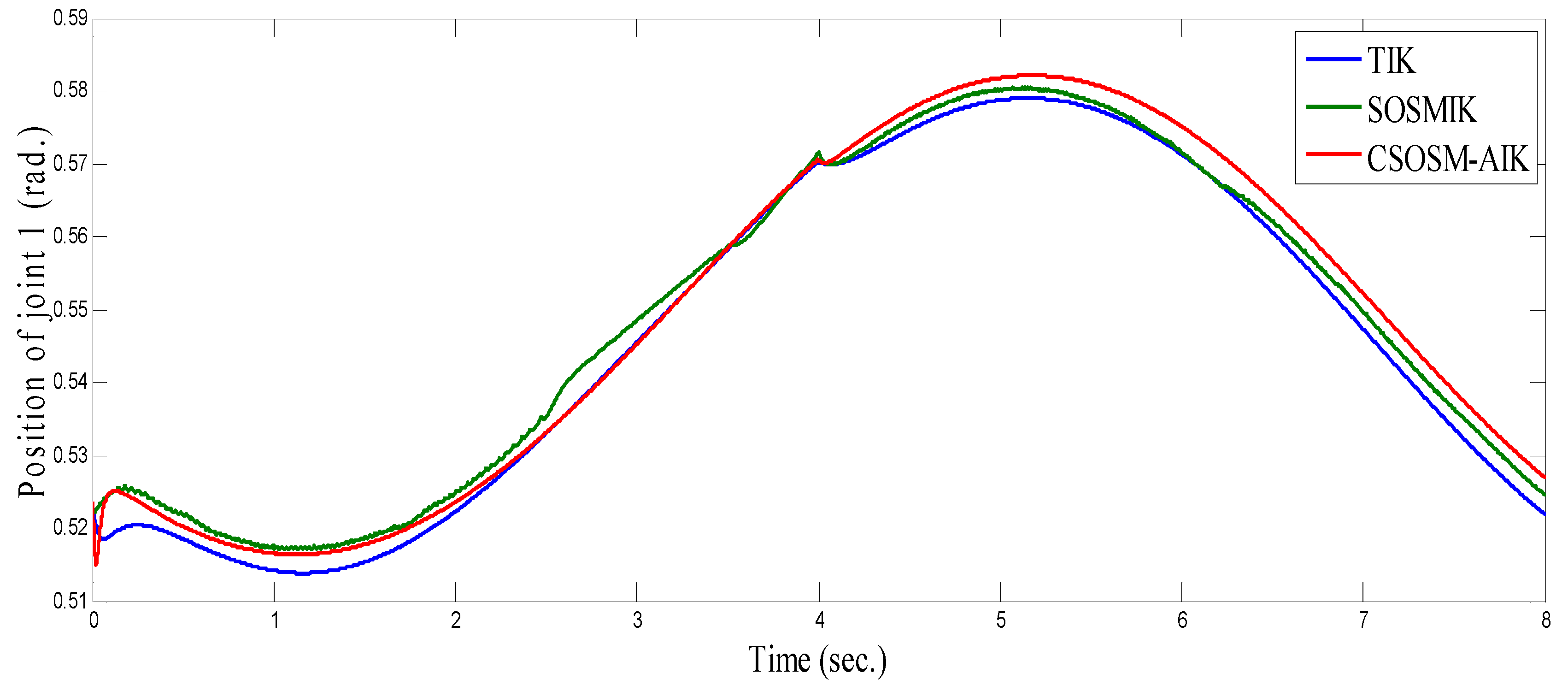
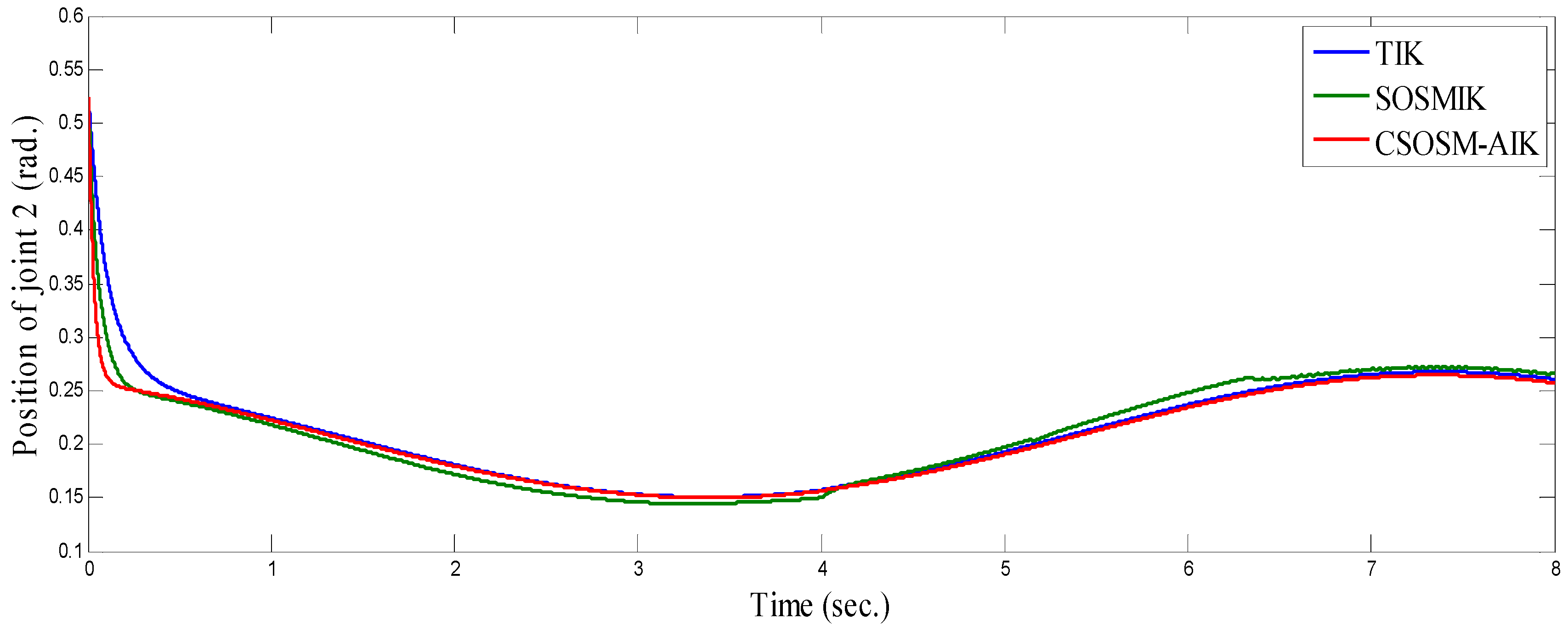
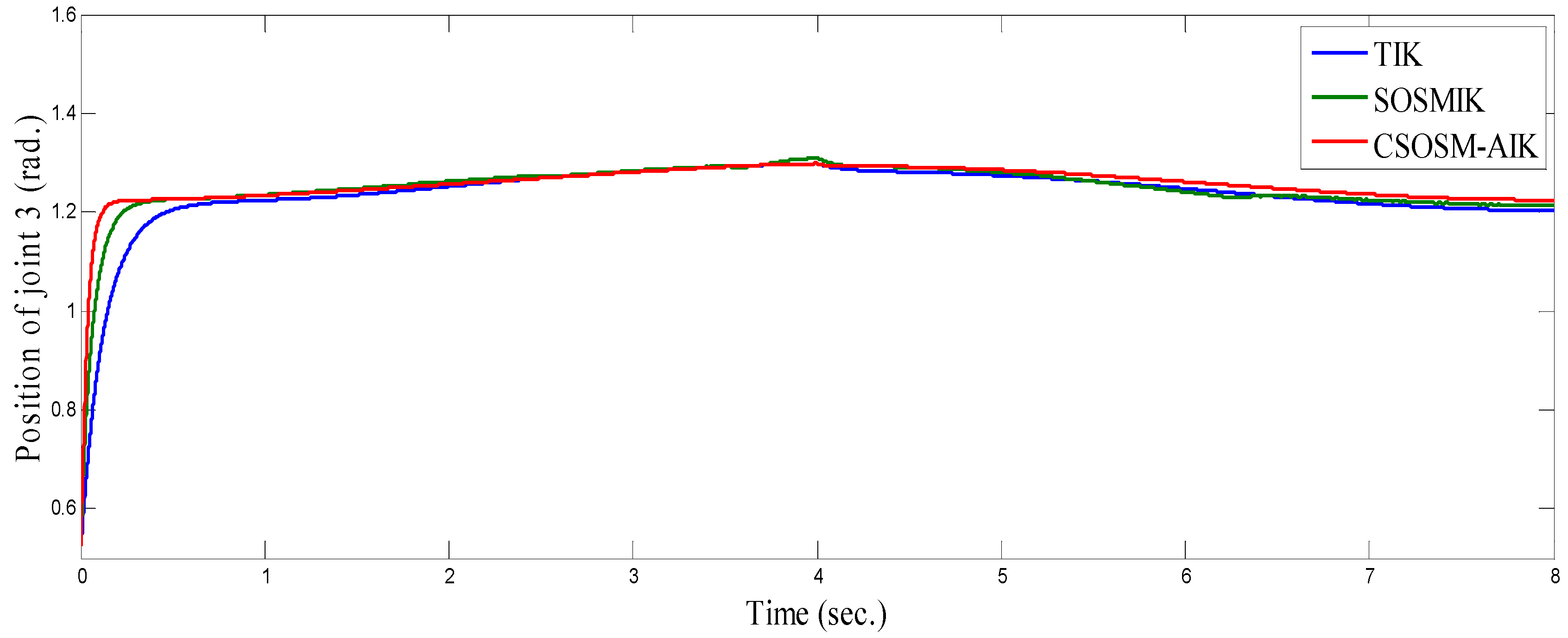
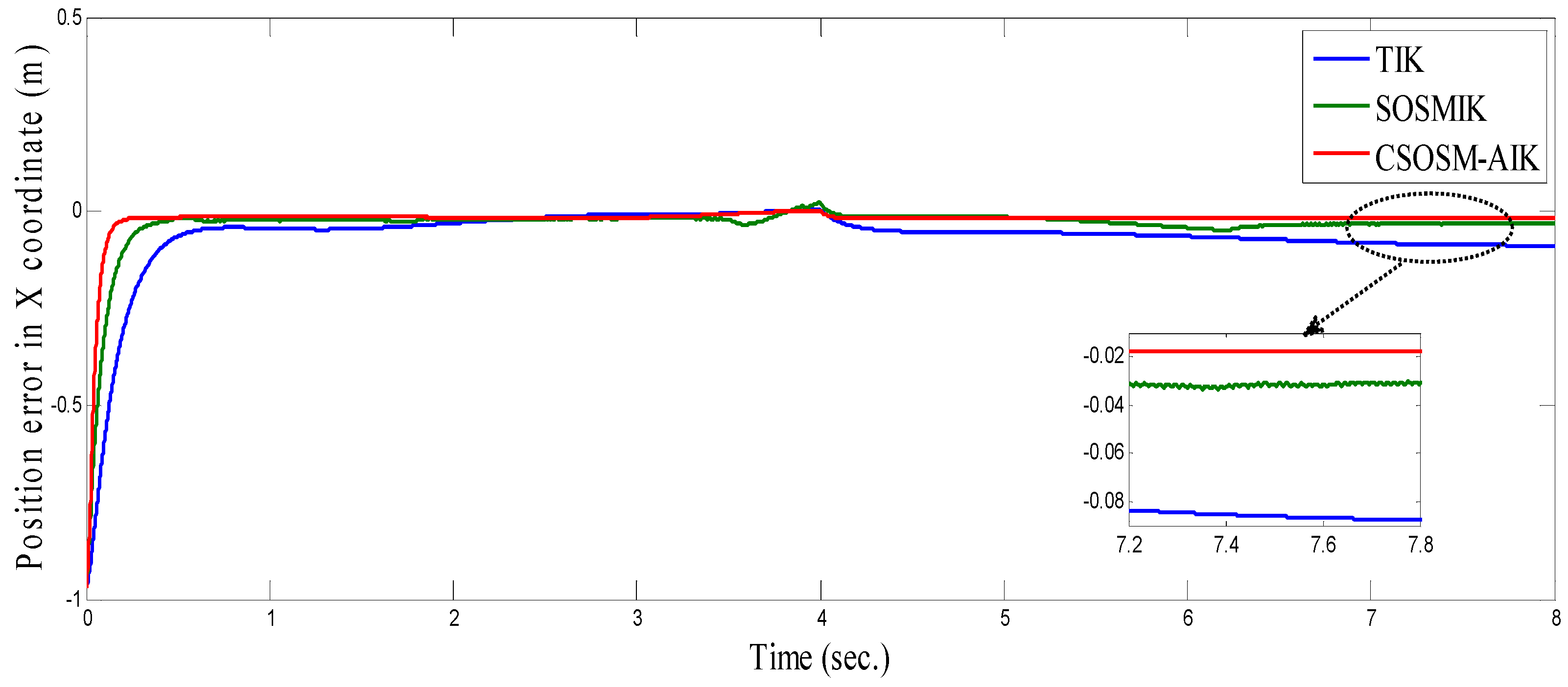
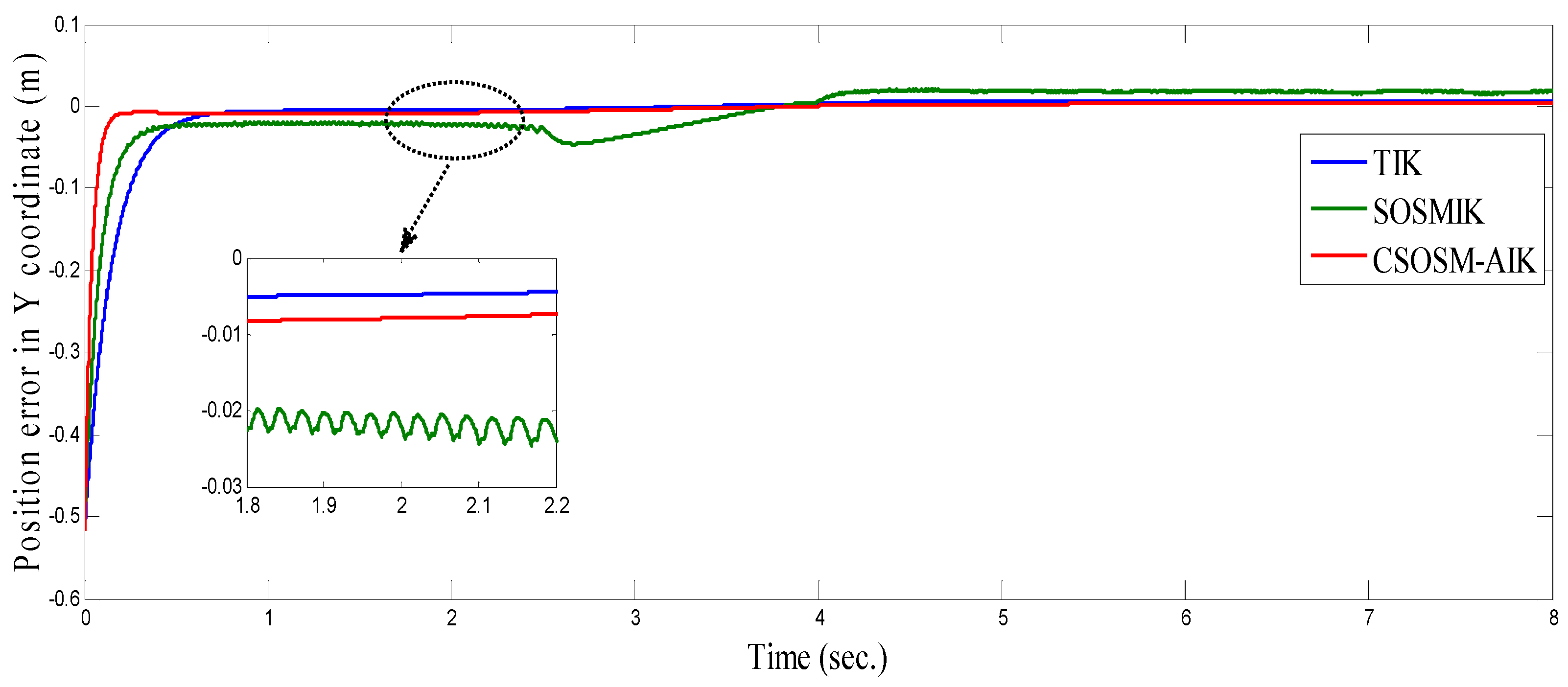
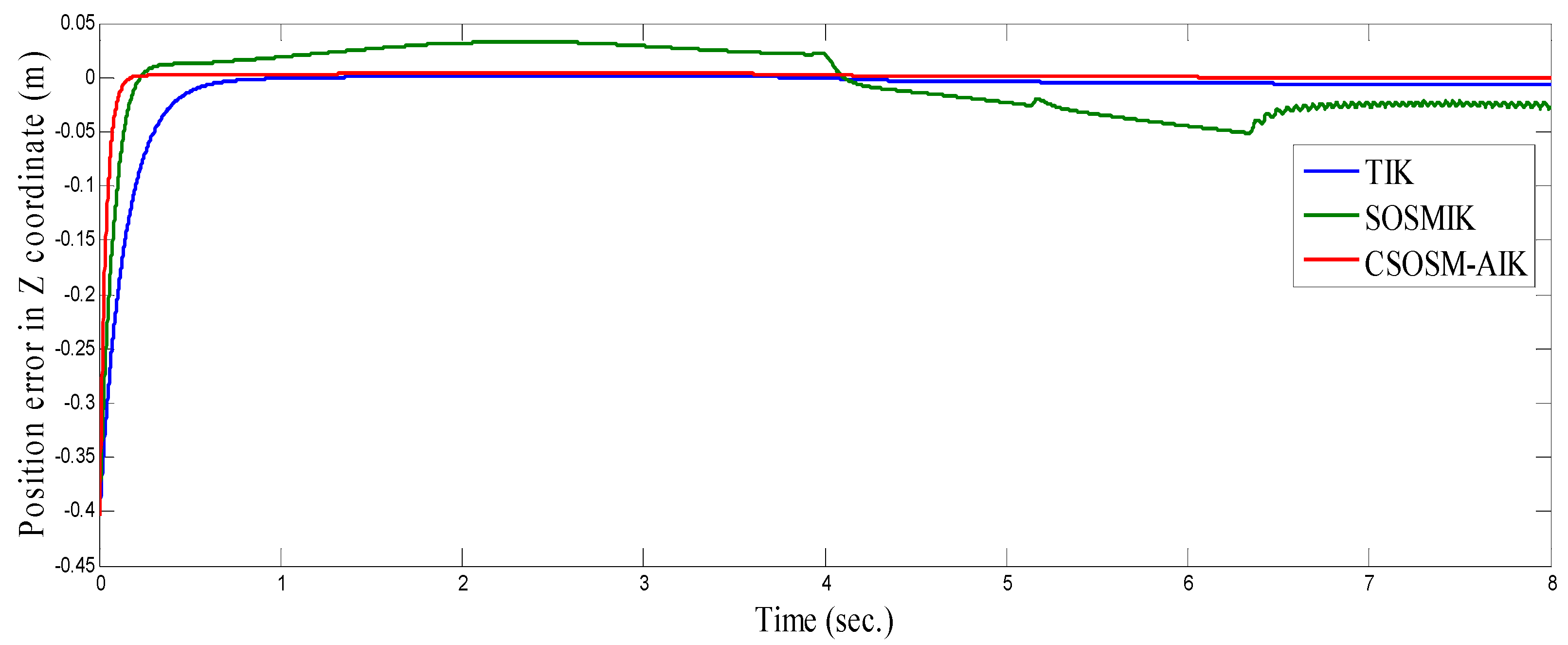
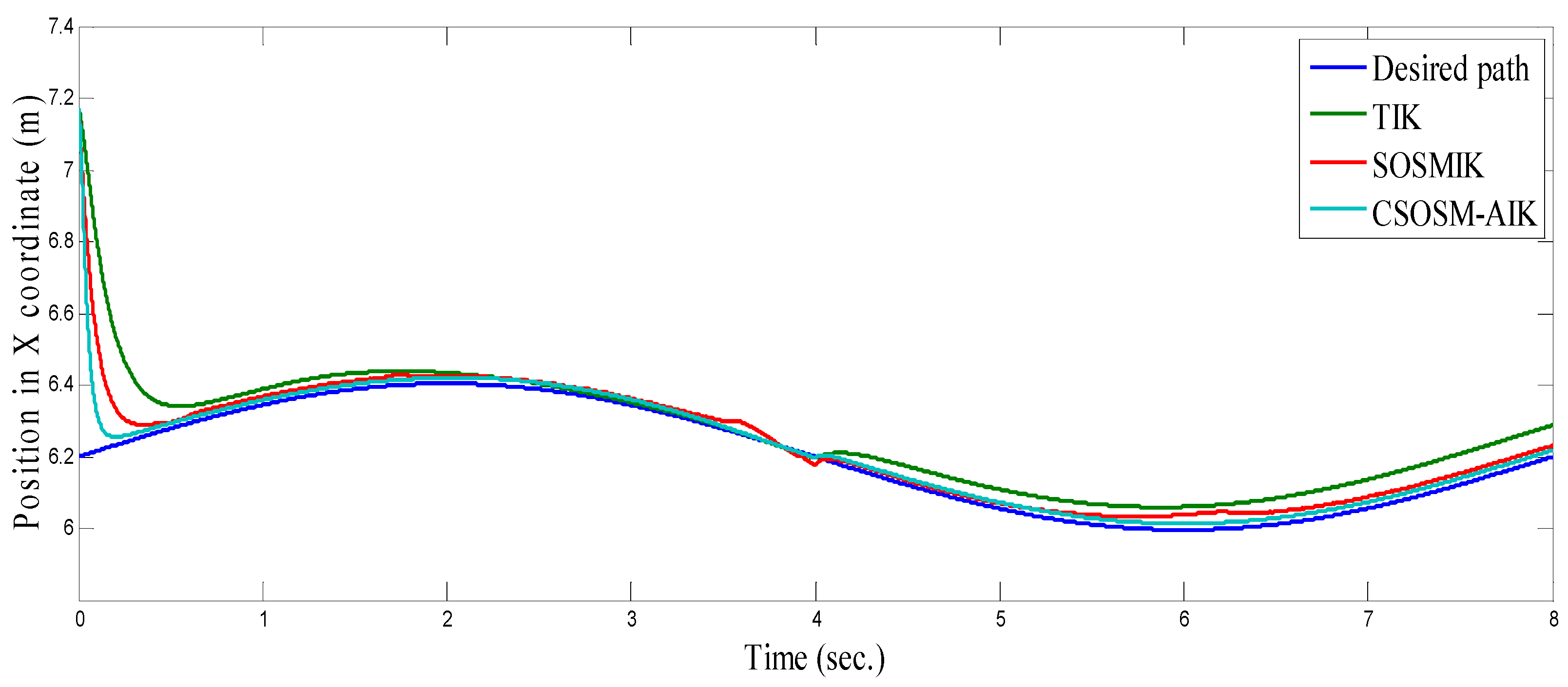
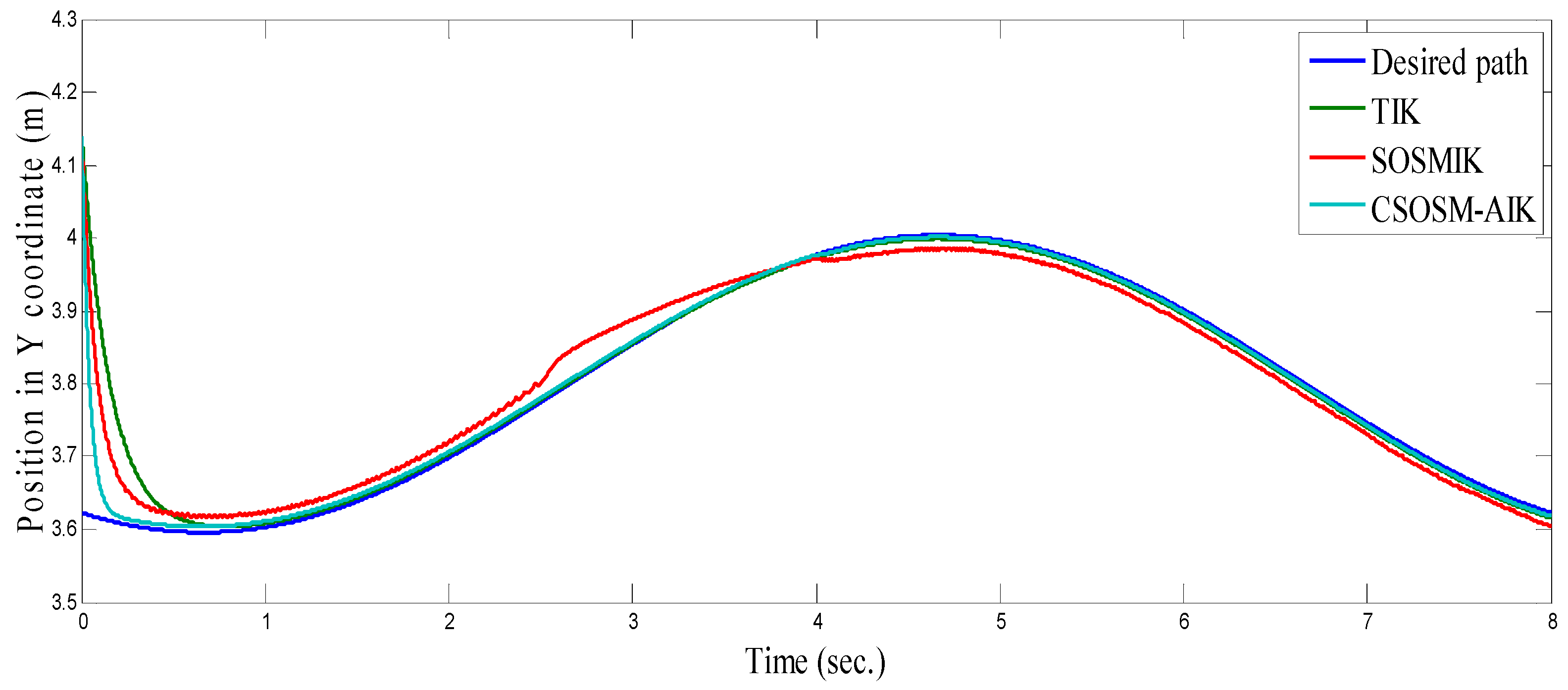
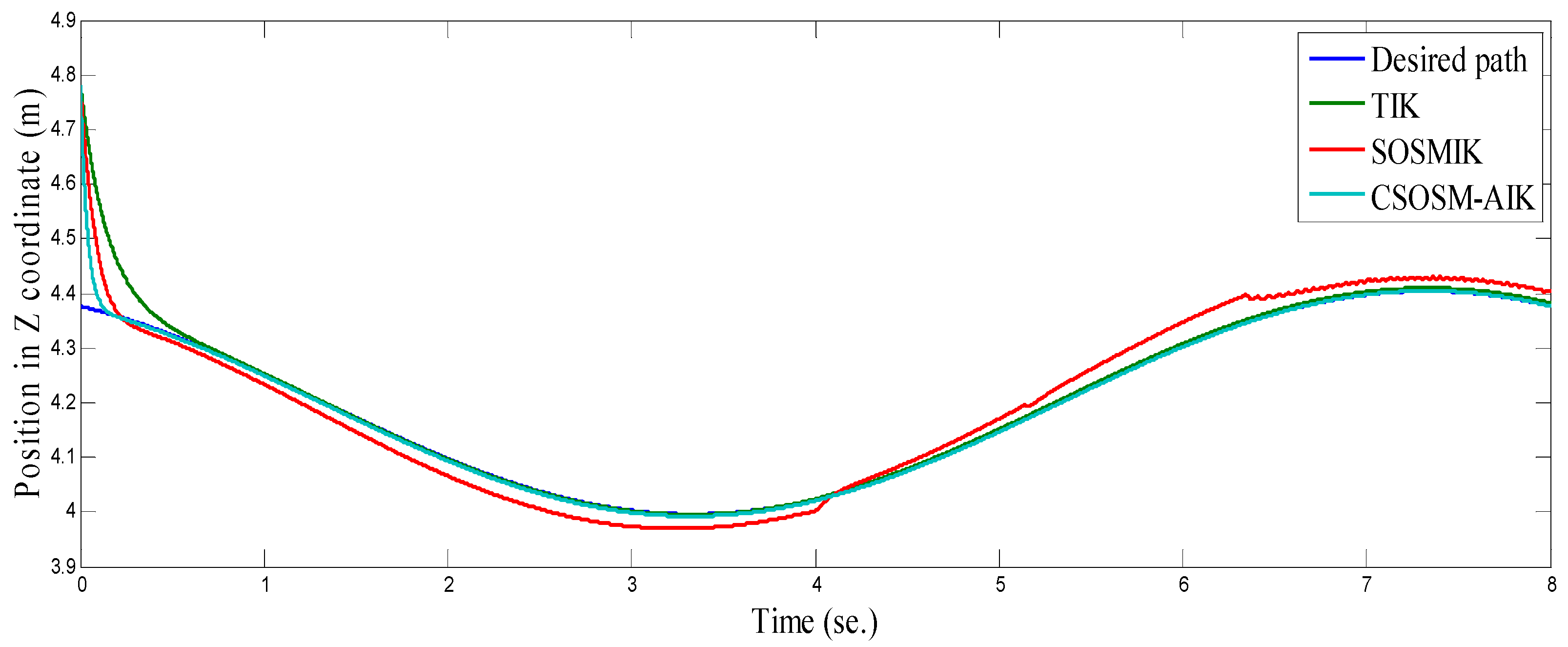
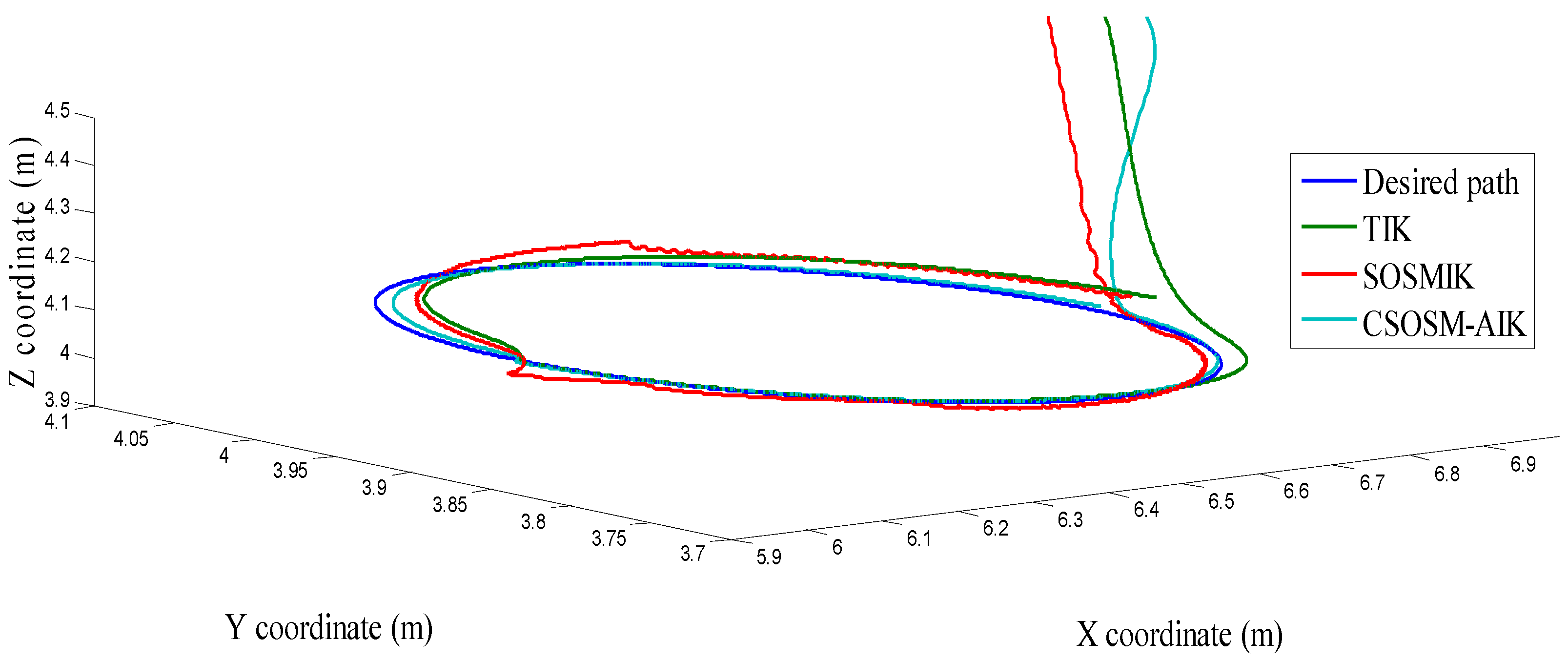
4.3. Comparison between CSOSM-AIK and Other Approaches
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siciliano, B.; Sciavicco, L.; Villani, L.; Oriolo, G. Robotics, Modeling, Planning and Control; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Siciliano, B.; Sciavicco, L.; Khatib, O. Springer Handbook of Robotics; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kütük, M.; Taylan, M.; Canan, L. Forward and Inverse Kinematics Analysis of Denso Robot. In Proceedings of the International Symposium of Mechanism and Machine Science, Baku, Azerbaijan, 11–14 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, M. Fundamentals of Robotics: Linking Perception to Action; World Scientific Publishing, Co., Pte, Ltd.: Singapore, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pasquale, C.; Stefano, C.; Lorenzo, S.; Bruno, S. Closed-Loop Inverse Kinematics Schemes for Constrained Redundant Manipulators with Task Space Augmentation and Task Priority Strategy. Int. J. Robot. Res. 1991, 10, 410–425. [Google Scholar]
- Xanthidis, M.; Kyriakopoulos, K.J.; Rekleitis, I. Dynamically efficient kinematics for hyper-redundant manipulators. In Proceedings of the 24th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation, Athens, Greece, 10 March 2018; pp. 207–213. [Google Scholar]
- Cheah, C.; Liaw, H. Inverse Jacobian Regulator with Gravity Compensation: Stability and Experiment. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2005, 21, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, C.; Hirano, M.; Kawamura, S.; Arimoto, S. Approximated Jacobian control for robots with uncertain kinematics and dynamics. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 2003, 19, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeles, J. Fundamentals of Robotic Mechanical Systems, 2nd ed.; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Spong, M.W.; Hutchinson, S.; Vidyasagar, M. Robot Dynamics and Control; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Arimoto, S.; Miyazaki, F. Asymptotic stability of feedback control for robot manipulators. IFAC Proc. Vol. 1985, 18, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheem, F.A.; Kareem, A.R.; Humaidi, A.J. Inverse Kinematics Solution of Robot Manipulator End-Effector Position Using Multi-Neural Networks. Eng. Technol. J. 2016, 34, 1360–1369. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, Y.; Hanafusa, H. Inverse kinematic solutions with singularity robustness for robot manipulator control. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control. 1986, 108, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wampler, C.W. Manipulator inverse kinematic solutions based on vector formulations and damped least-squares methods. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1986, 16, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bcsi, B.; Nguyen-Tuong, D.; Csat, L.; Schlkopf, B.; Peters, J. Learning inverse kinematics with structured prediction. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, San Francisco, CA, USA, 25–30 September 2011; pp. 698–703. [Google Scholar]
- D’Souza, A.; Vijayakumar, S.; Schaal, S. Learning inverse kinematics in Intelligent Robots and Systems. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE/RSJ International Conference, Maui, HI, USA, 29 October–3 November 2001; pp. 298–303. [Google Scholar]
- Reinhart, R.F.; Steil, J.J. Reaching movement generation with a recurrent neural network based on learning inverse kinematics for the humanoid robotic. In Proceedings of the 2009 9th IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots, Paris, France, 7–10 December 2009; pp. 323–330. [Google Scholar]
- Duka, A.-V. Neural network based inverse kinematics solution for trajectory tracking of a robotic arm. Procedia Technol. 2014, 12, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kker, R. A genetic algorithm approach to a neural-network-based inverse kinematics solution of robotic manipulators based on error minimization. Inf. Sci. 2013, 222, 528–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kker, R.; Cemil, Z.; Akar, T.; Ekiz, H. A study of neural network based inverse kinematics solution for a three-joint robot. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2004, 49, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Barnes, C.; Lu, J.; Yang, J.; Li, H. On the Continuity of Rotation Representations in Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New York, NY, USA, 12 April 2019; pp. 5745–5753. [Google Scholar]
- Slotine, J.J.E.; Li, W. Adaptive manipulator control: A case study. IEEE Trans. Autom. Contol. 1988, 33, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollerbach, J.M. A recursive Lagrangian formulation of manipulator dynamics and a comparative study of dynamics formulation complexity. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1980, SMC-10, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luh, J.Y.S.; Walker, M.H.; Paul, R.P. On-line computational scheme for mechanical manipulator. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control. 1980, 102, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejomurtula, S.; Kak, S. Inverse kinematics in robotics using Neural networks. Inf. Sci. 1999, 116, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Hou, Z.; Tan, M. Adaptive neural network tracking control for manipulators with uncertain kinematics, dynamics and actuator model. Automatica 2009, 45, 2312–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayebihaghighi, S.; Piltan, F.; Kim, J. Control of an Uncertain Robot Manipulator Using an Observation-based Modified Fuzzy Sliding Mode Controller. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, S.; Piltan, F.; Kim, J. Robust composite high-order super-twisting sliding mode control of robot manipulators. J. Robot. 2018, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Yang, X.; Zhao, D.; Spurgeon, S.; Yan, X. Sliding Mode Control for Nonlinear Manipulator Systems. IFAC 2017, 50, 5127–5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzuki, Z.; Mardiyah, N. Two-Link Flexible Manipulator Control Using Sliding Mode Control Based Linear Matrix Inequality. Proc. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 190, 012008. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Zhang, P. Composite learning sliding mode control of flexible-link manipulator. J. Complex. 2017, 2017, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, C.; Spurgeon, S. Sliding Mode Control: Theory and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Mobayen, S.; Tchier, F. A novel robust adaptive second-order sliding mode tracking control technique for uncertain dynamical systems with matched and unmatched disturbances. Int. J. Control. Autom. Syst. 2017, 15, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobayen, S. Design of LMI-based global sliding mode controller for uncertain nonlinear systems with application to Genesio’s chaotic system. Complexity 2015, 21, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobayen, S.; Tchier, F. Design of an adaptive chattering avoidance global sliding mode tracker for uncertain non-linear time-varying systems. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control. 2017, 39, 1547–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofid, O.; Mobayen, S. Adaptive sliding mode control for finite-time stability of quad-rotor UAVs with parametric uncertainties. ISA Trans. 2018, 72, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, J. Introduction to Robotics: Mechanics and Control, 3rd ed.; Prentice-Hall: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Spong, M.; Hutchinson, S.; Vidyasagar, M. Robot Modeling and Control; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Eker, I. Second-order sliding mode control with experimental application. ISA Trans. 2010, 49, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, C. Task Space Trajectory Tracking Control of Robot Manipulators with Uncertain Kinematics and Dynamics. Math. Probl. Eng. 2017, 2017, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
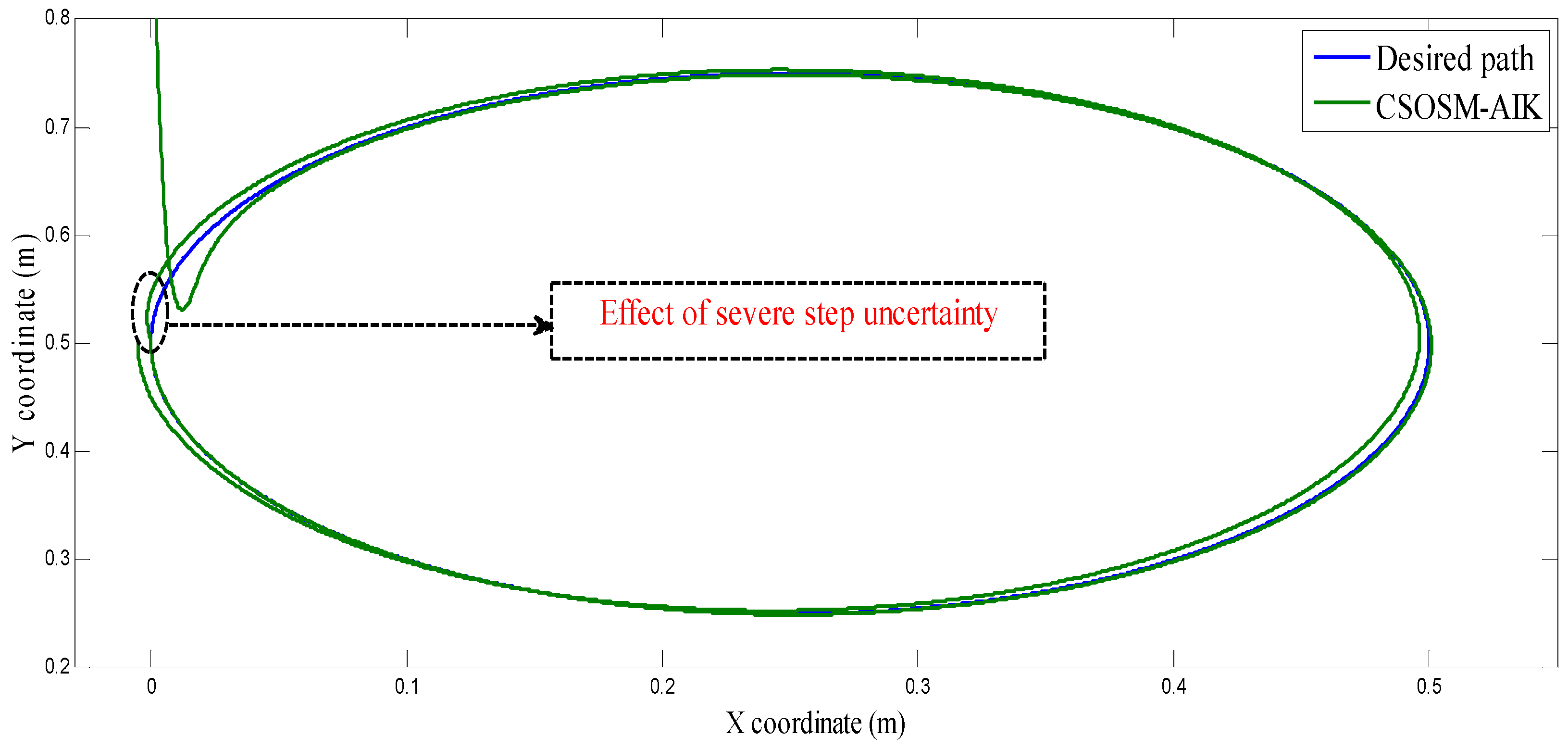
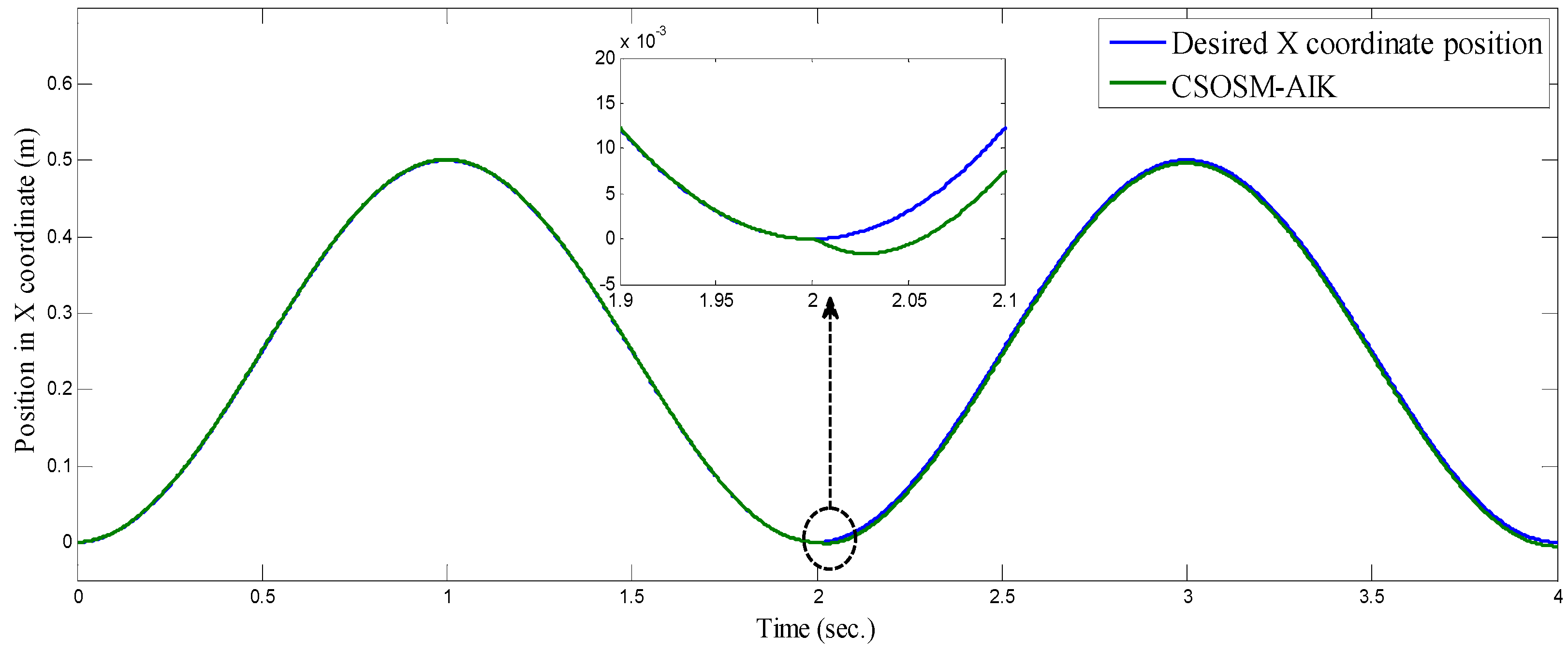
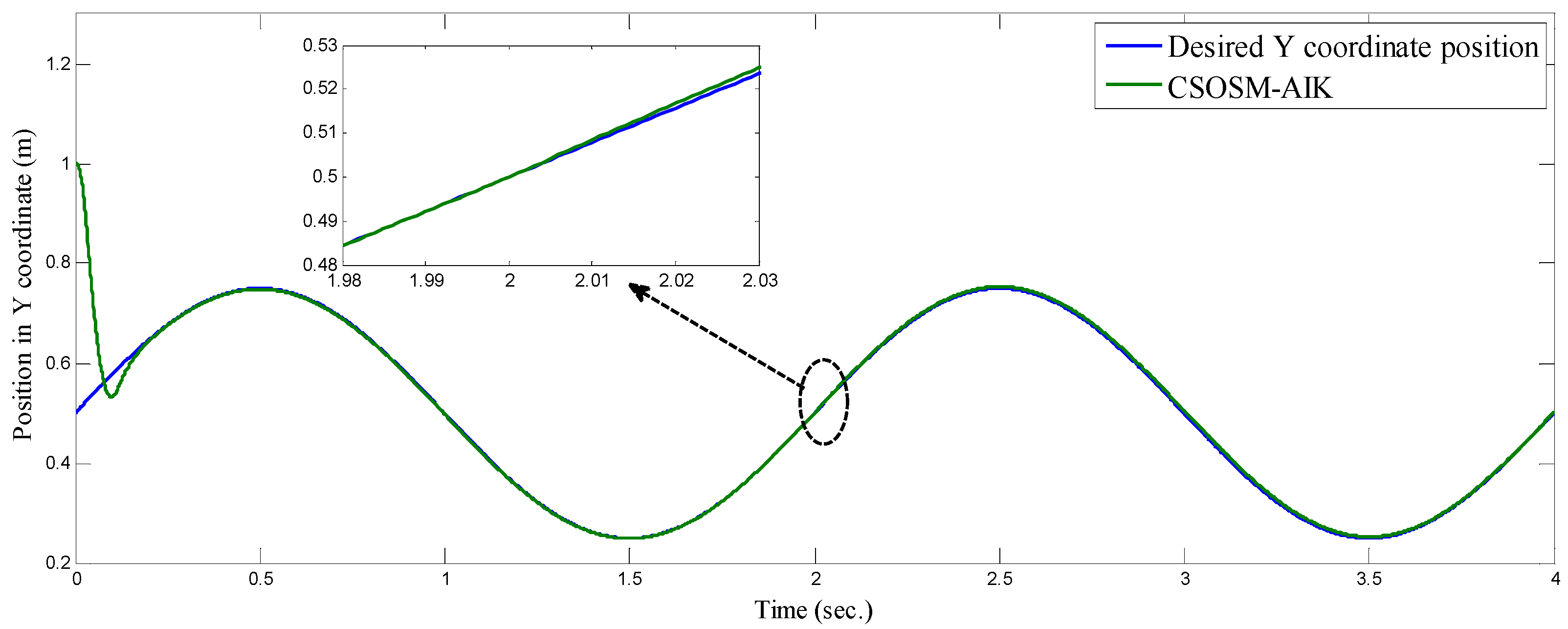
| Algorithm | Parameters |
|---|---|
| TIK | and |
| SOSMIK | , , |
| CSOSM-AIK | , , and |
| Algorithm | ISE | IAE | ITAE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X-Coordin. | Y-Coordin. | X-Coordin. | Y-Coordin. | X-Coordin. | Y-Coordin. | |
| TIK | 3.75 | 1.995 | 4.5878 | 5.7294 | 7.8871 | 7.8772 |
| SOSMIK | 0.85 | 0.79 | 2.9450 | 3.6575 | 4.5473 | 4.0754 |
| CSOSM-AIK | 0.0632 | 0.0478 | 0.8645 | 1.0122 | 2.2461 | 2.2039 |
| Algorithm | Parameters |
|---|---|
| TIK | and |
| SOSMIK | , , , |
| CSOSM-MIK | , , and |
| Algorithm | IAE | ITAE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X axis | Y axis | Z axis | X axis | Y axis | Z axis | |
| TIK | 8.9885 | 9.5896 | 8.9884 | 13.8687 | 13.4564 | 13.6091 |
| SOSMIK | 4.6553 | 4.5142 | 5.9203 | 8.2853 | 7.5632 | 8.6541 |
| CSOSM-AIK | 2.6988 | 2.4674 | 2.2541 | 3.6554 | 3.1592 | 3.5628 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohammed Elawady, W.; Bouteraa, Y.; Elmogy, A. An Adaptive Second Order Sliding Mode Inverse Kinematics Approach for Serial Kinematic Chain Robot Manipulators. Robotics 2020, 9, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics9010004
Mohammed Elawady W, Bouteraa Y, Elmogy A. An Adaptive Second Order Sliding Mode Inverse Kinematics Approach for Serial Kinematic Chain Robot Manipulators. Robotics. 2020; 9(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics9010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohammed Elawady, Wael, Yassine Bouteraa, and Ahmed Elmogy. 2020. "An Adaptive Second Order Sliding Mode Inverse Kinematics Approach for Serial Kinematic Chain Robot Manipulators" Robotics 9, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics9010004
APA StyleMohammed Elawady, W., Bouteraa, Y., & Elmogy, A. (2020). An Adaptive Second Order Sliding Mode Inverse Kinematics Approach for Serial Kinematic Chain Robot Manipulators. Robotics, 9(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics9010004






