Achieving Neuroplasticity in Artificial Neural Networks through Smart Cities
Abstract
1. Introduction
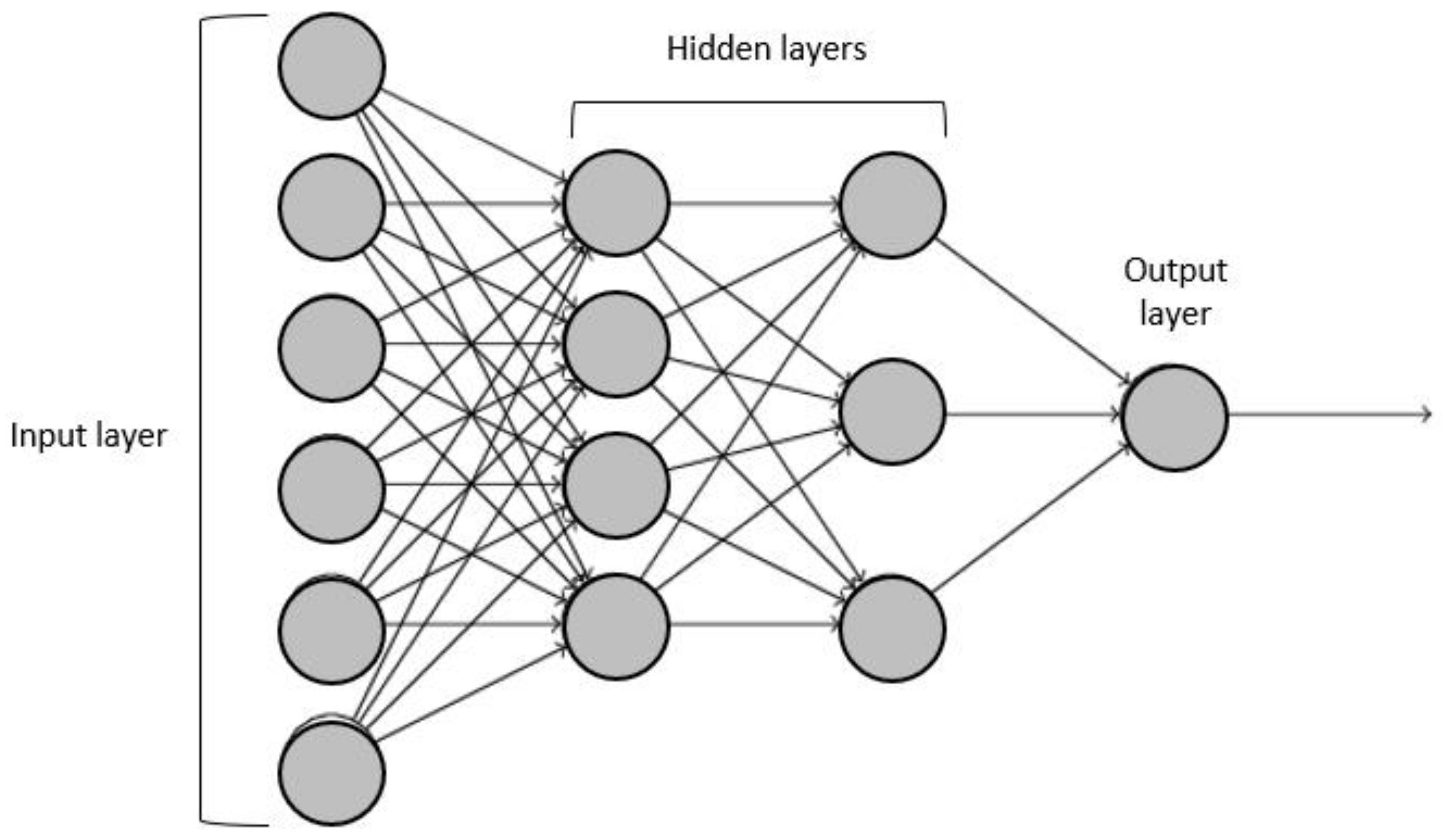
2. Artificial Neural Networks
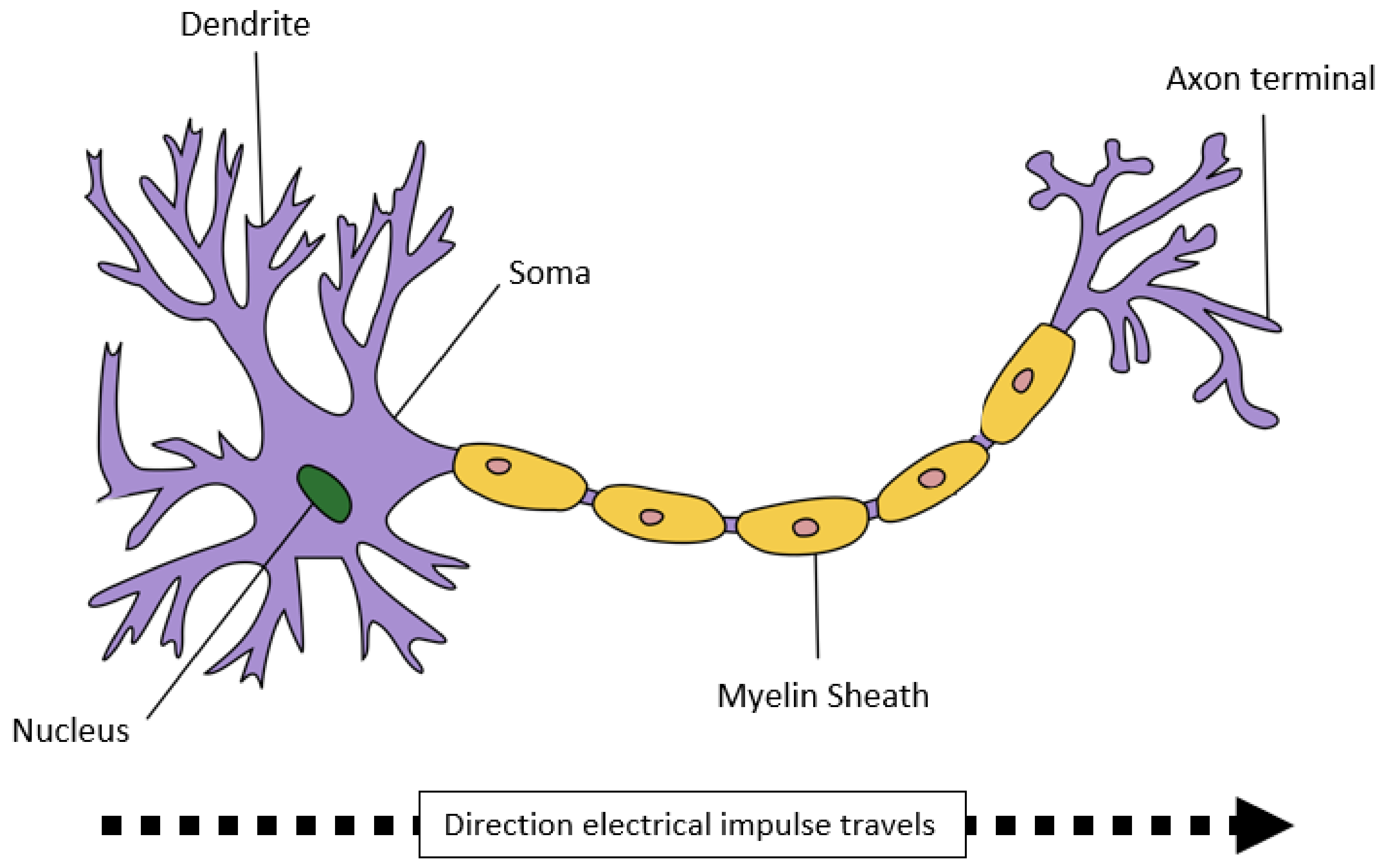
3. Brain Neural Networks and Neuroplasticity
4. Emerging Networks in Smart Cities
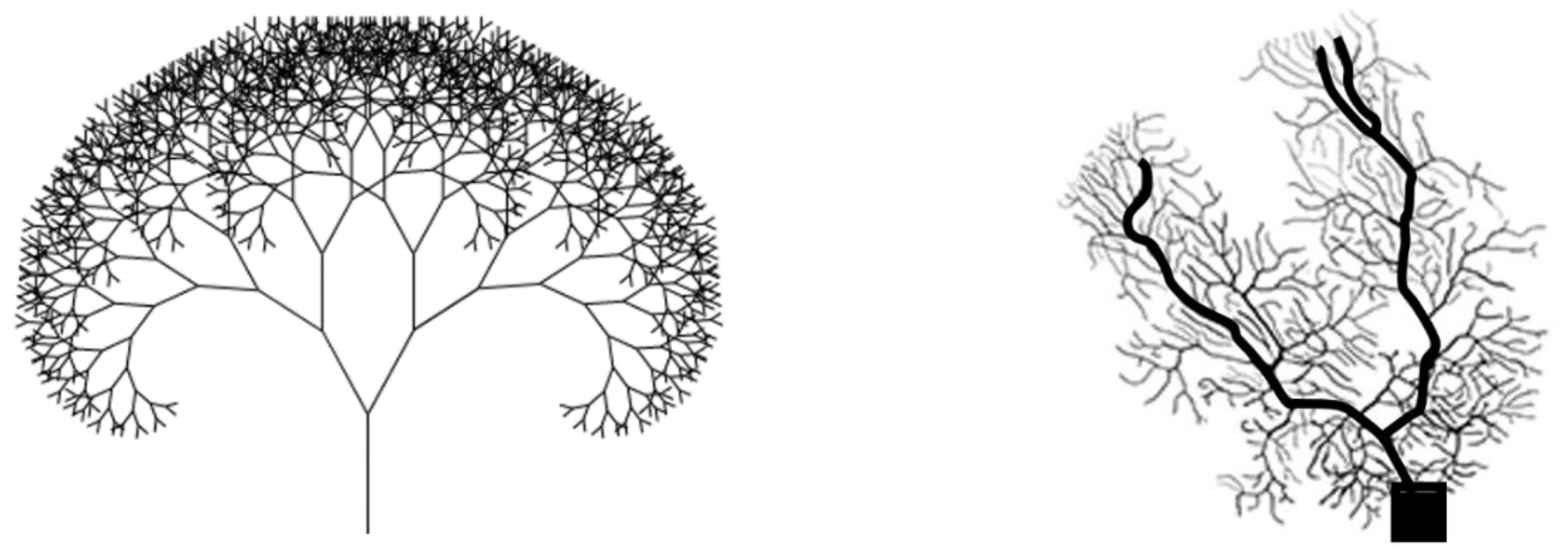
5. On Christopher Alexander’s Pattern Language and Nature of Order
5.1. Complexity
5.2. Achieving Wholeness
5.3. Generated Structures
5.4. Urban Coherence
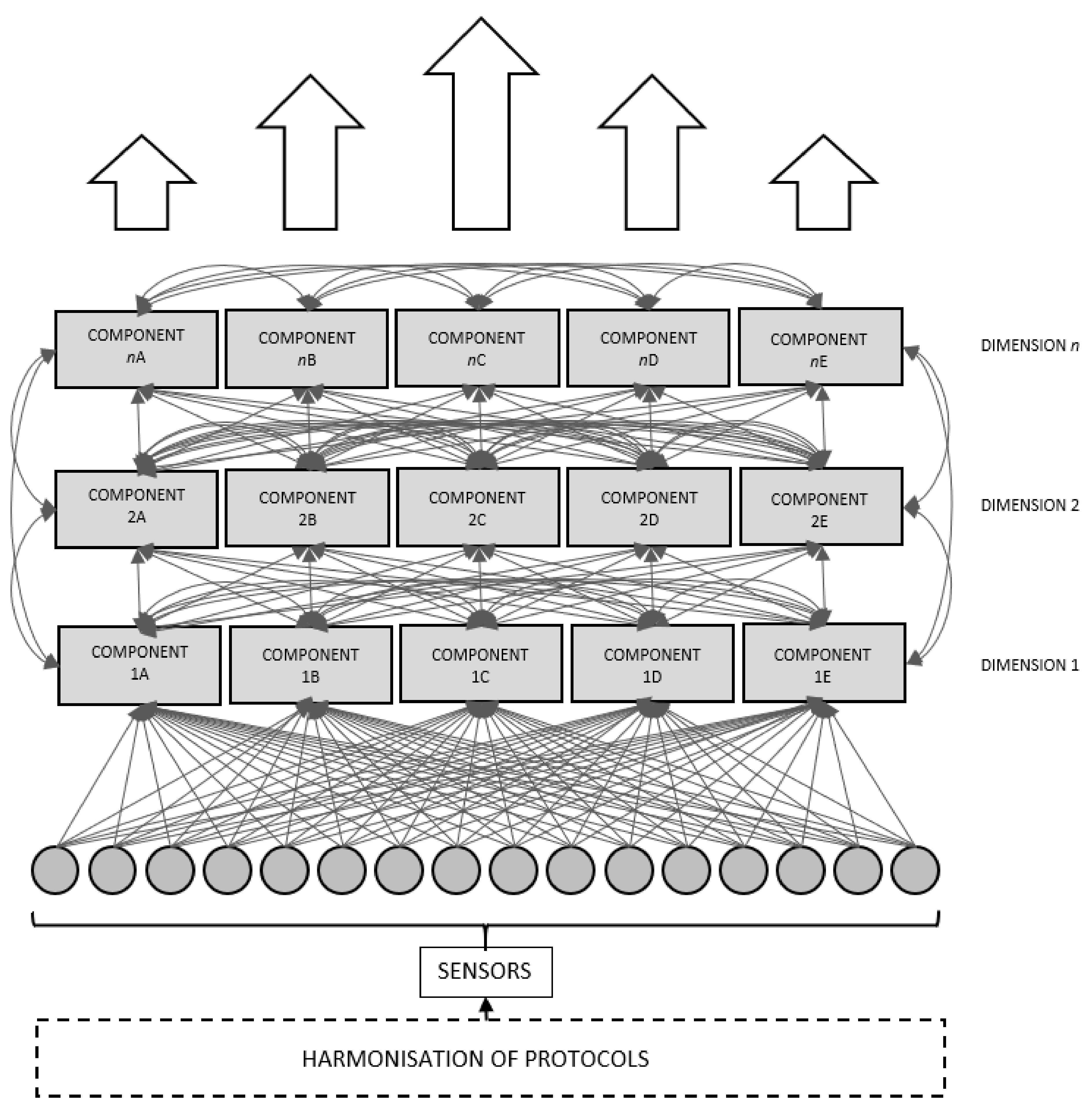
6. A Proposed Theoretical Model
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- OECD. Cities and climate change: National governments enabling local action. In OECD Policy Perspectives; Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development; OECD: Paris, France, 2014; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. Sustainable Development Goals Report; UN: New York, NY, USA, 2018; p. 40. [Google Scholar]
- UNDP. Sustainable Urbanization Strategy: Undp’s Support to Sustainable, Inclusive and Resilient Cites in the Developing World; United Nations Development Programme: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sepasgozar, S.M.E.; Hawken, S.; Sargolzaei, S.; Foroozanfa, M. Implementing citizen centric technology in developing smart cities: A model for predicting the acceptance of urban technologies. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 142, 115–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, M.Z. Redefining the Smart City: Culture, Metabolism and Governance. Case Study of Port Louis, Mauritius; Curtin University: Perth, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Allam, Z. Contextualising the smart city for sustainability and inclusivity. New Des. Ideas 2018, 2, 124–127. [Google Scholar]
- Allam, Z.; Newman, P. Redefining the smart city: Culture, metabolism & governance. Smart Cities 2018, 1, 4–25. [Google Scholar]
- Barns, S.; Cosgrave, E.; Acuto, M.; Mcneill, D. Digital infrastructures and urban governance. Urban Policy Res. 2016, 35, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, D.; Ferrández, A.; Moramora, H.; Peral, J. Internet of things: A review of surveys based on context aware intelligent services. Sensors 2016, 16, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibri, S.E. The ioT for smart sustainable cities of the future: An analytical framework for sensor-based big data applications for environmental sustainability. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 38, 230–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassoo, V.; Ramnarain-Seetohul, V.; Hurbungs, V.; Fowdur, T.P.; Beeharry, Y. Big data analytics for smart cities. In Internet of Things and Big Data Analytics toward Next-Generation Intelligence. Studies in Big Data; Dey, N., Hassanien, A., Bhatt, C., Stapathy, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Batty, M. Big data and the city. Built Environ. 2016, 42, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saqaf, W.; Seidler, N. Blockchain technology for social impact: Opportunities and challenges ahead. J. Cyber Policy 2017, 2, 338–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christidis, K.; Devetsikiotis, M. Blockchains and smart contracts for the internet of things. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 2292–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, Z. On smart contracts and organisational performance: A review of smart contracts through the blockchain technology. Rev. Econ. Bus. Stud. 2018, 11, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bini, S.A. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, deep learning, and cognitive computing: What do these terms mean and how will they impact health care? J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 2358–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, K.; Lu, Y.; Gao, H.; Cao, R. Artificial intelligence-based semantic internet of things in a user-centric smart city. Sensors 2018, 18, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, U.; Peña, O.; Belmonte, O.; López-de-Ipiña, D. Citizen-centric data services for smarter cities. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2017, 76, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Babar, M.; Ahmed, S.H.; Shad, S.C.; Han, K. Smart city designing and planning based on big data analytics. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 35, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, B.N.; Khan, M.; Han, K. Towards sustainable smart cities: A review of trends, architectures, components, and open challenges in smart cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 38, 697–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathaini, S.; Jain, R.K.; Arora, M.K. An artificial neural network based approach for modelling urban spatial growth. ITPI J. 2007, 4, 43–51. [Google Scholar]
- Mathaini, S. A neural network based urban growth model of an Indian city. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2009, 37, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, A.G.; Li, X. Urban simulation using neural networks and cellular automata for land use planning. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Geospatial Theory, Processing and Applications, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 9–12 July 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Sorda, K.R. Artificial Neural Networks—The Future of Smart Cities. Available online: http://www.itwebafrica.com/home-pagex/opinion/244318-artificial-neural-networks--the-future-of-smart-cities (accessed on 1 January 2019).
- Dubey, A.; Naik, N.; Parikh, D.; Raskar, R.; Hidalgo, C.A. Deep learning the city: Quantifying urban perception at a global scale. In Proceedings of the ECCV European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kropp, J. A neural network approach to the analysis of city systems. Appl. Geogr. 1998, 18, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorins, A.; Grabusts, P. Artificial Neural Networks and Human Brain: Survey of Improvement Possibilities of Learning. In Proceedings of the 10th International Scientific and Practical Conference, Rezekne, Latvia, 18–20 June 2015; pp. 228–231. [Google Scholar]
- Graupe, D. Principles of Artificial Neural Networks: Advanced Series on Circuits and Systems, 2nd ed.; World Scientific Publishing Co. Ltd.: Singapore, 2007; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, L.; Fanelli, A.M. Recent Advances in Artificial Neural Networks: Design and Applications; CRC Press LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrotra, K.; Mohan, C.K.; Ranka, S. Elements of Artificial Neural Networks; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Botta, A.; Donato, W.D.; Persico, V.; Pescapé, A. Integration of cloud computing and internet of things: A survey. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2016, 56, 684–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, A.S.; Henri, C.; Charles, S.; Melwin, P.; Ninoshka, T. Neuron the memory unit of the brain. IOSR J. Comput. Eng. 2015, 17, 48–61. [Google Scholar]
- Haykin, S. Neural Networks and Learning Machines, 3rd ed.; McMaster University Hamilton: Ontario, ON, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Garcia, E.A. Learning from imbalanced data. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2009, 21, 1260–1284. [Google Scholar]
- Sidiropulou, K.; Pissadaki, E.K.; Poirazi, P. Inside the brain of a neuron. EMBO Rep. 2006, 7, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perwej, Y.; Parwej, F. A neuroplasticity (brain plasticity) approach to use in artificial neural network. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2012, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Abiodun, O.I.; Jantan, A.; Omolara, A.E.; Dada, K.V.; Mahamed, N.A.; Arshad, H. State-of-the-art in artificial neural network applications: A survey. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00938–e00979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.-J. Imitating the brain with neurocomputer: A “new” way towards artificial general intelligence. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 2017, 14, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GK. How Neural Networks Work. Available online: https://chatbotslife.com/how-neural-networks-work-ff4c7ad371f7 (accessed on 2 January 2019).
- Kurama, V. Deep Learning with Python. Available online: https://towardsdatascience.com/deep-learning-with-python-703e26853820 (accessed on 3 January 2019).
- Fukumizu, K. Chapter 17—Geometry of neural networks: Natural gradient for learning. In Handbook of Biological Physics; Moss, F., Gielen, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 731–769. [Google Scholar]
- Hauser, M.; Ray, A. Principles of Riemannian geometry in neural networks. In Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems NIPS, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Triantakonstantis, D.; Stathakis, D. Urban growth prediction in Athens, Greece, using artificial neural networks. Int. J. Archit. Environ. Eng. 2015, 9, 234–238. [Google Scholar]
- Jafar, R.; Shahrour, I.; Juran, I. Application of artificial neural networks (ANN) to model the failure of urban water mains. Math. Comput. Model. 2010, 51, 1170–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Chung, N.; Hwang, S. Application of an artificial neural network (ANN) model for predicting mosquito abundances in urban areas. Ecol. Inform. 2016, 36, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Seto, K.C. Using the ART-MMAP neural network to model and predict urban growth: A spatio-temporal data mining approach. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2008, 35, 296–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, M.; Ngah, I.; Hashim, M.; Pradhan, B.; Pour, A.B. A hybrid analytic network process and artificial neural network (ANP-ANN) model for urban earthquake vulnerability assessment. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasmita, A.O.; Kuruvilla, J.; Ling, A.P.K. Harnessing neuroplasticity: Modern approaches and clinical future. Int. J. Neurosci. 2018, 128, 1061–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandra, C. How Is a Neuron Adapted to Perform Its Function. Available online: https://socratic.org/questions/how-is-a-neuron-adapted-to-perform-its-function (accessed on 3 January 2019).
- Pascual-Leone, A.; Amedi, A.; Fregni, F.; Merabet, L.B. The plastic human brain cortex. Annual Review of Neuroscience 2005, 28, 377–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, J. Neuroplasticity and clinical practice: Building brain power for health. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, N.; Rotermund, C.; Blumrich, E.-M.; Lourenco, M.V.; Joshi, P.; Hegemann, R.U.; Jamwal, S.; Ali, N.; Romero, E.M.G. The malleable brain: Plasticity of neural circuits and behavior—A review from students to students. J. Neurochem. 2017, 142, 790–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryck, R.L.; Fisher, P.A. Training the brain: Practical applications of neural plasticity from the intersection of cognitive neuroscience, developmental psychology, and prevention science. Am. Psychol. 2012, 67, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertzog, C.; Kramer, A.F.; Wilson, R.S.; Lindenberger, U. Enrichment effects on adult cognitive development: Can the functional capacity of older adults be preserved and enhanced? Psychol. Sci. Public Interest J. Am. Psychol. Soc. 2008, 9, 1–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahncke, H.W.; Bronstone, A.; Merzenich, M.M. Brain plasticity and functional losses in the aged: Scientific bases for a novel intervention. Prog. Brain Res. 2006, 157, 81–109. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M. Mapping the Brain’s Traffic. Available online: https://engineering.cmu.edu/news-events/news/2018/09/06-mapping-brain-traffic.html (accessed on 3 January 2019).
- Salingaros, N.A. Theory of the urban web. J. Urban Des. 1998, 3, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, C. A city is not a tree. Archit. Forum 1965, 122, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Molotch, H. The city as a growth machine: Toward a political economy of place. Am. J. Sociol. 1976, 82, 309–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batty, M.; Longley, P. Fractal Cities: A Geometry of Form and Function; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Allam, Z. Building a conceptual framework for smarting an existing city in Mauritius: The case of Port Louis. J. Biourbanism 2017, 4, 103–121. [Google Scholar]
- Allam, Z.; Newman, P. Economically incentivising smart urban regeneration. Case study of Port Louis, Mauritius. Smart Cities 2018, 1, 53–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-h.; Ramos, C.; Mohammed, S. Smart city and IoT. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2017, 76, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Sheng, Q.Z.; Falkner, N.J.; Dustdar, S.; Wang, H.; Vasilakos, A.V. When things matter: A survey on data-centric internet of things. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2016, 64, 137–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, A.; Pitale, P.; Sanap, S. Industrial automation using internet of things (IoT). Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Eng. Technol. (IJARCET) 2016, 5, 266–269. [Google Scholar]
- Tzafestas, S.G. Synergy of IoT and AI in modern society: The robotics and automation case. Robot. Autom. Eng. J. 2018, 31, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čolaković, A.; Hadžialić, M. Internet of things (IoT): A review of enabling technologies, challenges, and open research issues. Comput. Netw. 2018, 144, 17–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotenko, I.; Saenko, I.; Skorik, F.; Bushuev, S. Neural network approach to forecast the state of the internet of things elements. In Proceedings of the XVIII International Conference on Soft Computing and Measurements (SCM), St. Petersburg, Russia, 19–21 May 2015; pp. 133–135. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdavinejad, M.S.; Rezvan, M.; Barekatain, M.; Adabi, P.; Barnaghi, P.; Sheth, A.P. Machine learning for internet of things data analysis: A survey. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2018, 4, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, R. Expert Systems; Chapman and Hall: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Naganathan, V.; Rao, R.K. The evolution of internet of things: Bringing the power of artificial intelligence to iot, its opportunities and challenges. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Trends ADN Technol. 2018, 6, 94–108. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, K.K.; Patel, S.M. Internet of things-IoT: Definition, characteristics, architecture, enabling technologies, applications and future challenges. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Comput. 2016, 6, 6122–6131. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, J. Semantic framework of internet of things for smart cities: Case studies. Sensors 2016, 16, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnaghi, P.; Bermudez-Edo, M.; Tonjes, R. Challenges for quality of data in smart cities. J. Data Inf. Qual. 2015, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, M. The future of data with the rise of the IoT. RFID J. 2018. Available online: https://www.rfidjournal.com/articles/view?17954 (accessed on 25 January 2019).
- Khaled, A.E.; Halal, S. Interoperable communication framework for bridging restful and topic—Based communication in IoT. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 92, 628–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fugaha, A.; Guizani, A.M.; Mehdi, M.; Mohammed, A.; Moussa, A. Internet of things: A survey on enabling technologies, protocols, and applications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2015, 17, 2347–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espada, J.P.; Yager, R.; Yu, Z. Communications, collaborations and services in networks of embedded devices. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 92, 560–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bačić, Ž.; Jogun, T.; Majić, I. Integrated sensor systems for smart cities. Teh. Vjesn. 2018, 25, 277–284. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, C. A New Theory of Urban Design; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, C. The Process of Creating Life: An Essay on the Art of Building and the Nature of the Universe; Center for Environmental Structure: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, C. The Phenomenon of Life: An Essay on the Art of Building and the Nature of the Universe; Center for Environmental Structure: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, C. The Luminous Ground: An Essay on the Art of Building and the Nature of the Universe; Center for Environmental Structure: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, C. A Vision of a Living World: An Essay on the Art of Building and the Nature of the Universe; Center for Environmental Structure: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Salingaros, N.A. Complexity in architecture and design. Oz J. 2014, 36, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, R. Understanding complexity through pattern languages in biological and man-made architectures. Archnet Int. J. Archit. Res. 2014, 8, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, C.; Ishikawa, S.; Silverstein, M. A Pattern Language; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Salingaros, N.A. Connecting the fractal city. In 5th Biennial of Towns and Town Planners in Europe; PLANUM: Barcelona, Spain, 2003; pp. 78–101. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, C. The Timeless Way of Building; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Dawes, M.J.; Ostwald, M.J. Christopher Alexander’s a pattern language: Analysing, mapping and classifying the critical response. City Territ. Archit. 2017, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salingaros, N.A. Biophilia and Healing Environments; Off the Common Books: Amherst, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kruhl, J.H. Fractal-geometry techniques in the quantification of complex rock structures: A special view on scaling regimes, inhomogeneity and anisotropy. J. Struct. Geol. 2013, 46, 2–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salingaros, N.A. Fractals and Christopher Alexander’s “fifteen fundamental properties”. In Conscious Cities Anthology 2018; Human-Centred Design: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Seamon, D. Christopher Alexander and a phenomenology of wholeness. In Christopher Alexander Annual Meeting of the Environmental Design Research Association; EDRA: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Grabow, S. Christopher Alexander and the Search for a New Paradigm in Architecture; Oriel Press: London, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Delaney, S. Fractal Scaling. Available online: https://medium.com/@sdelaney32/fractal-scaling-6dc8fa1773a9 (accessed on 3 January 2019).
- Salingaros, N.A.; Fractals in the new architecture. Archimagazine 2001. Available online: http://zeta.math.utsa.edu/~yxk833/fractals.html (accessed on 25 January 2019).
- Alexander, C. The Nature of Order: The Process of Creating Life; The Centre for Environmental Structure: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, B. A new kind of beauty out of the underlying scaling of geographic space. Prof. Geogr. 2014, 66, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B. Wholeness as a hierarchical graph to capture the nature of space. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2015, 29, 1632–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salingaros, N.A. Complexity and urban coherence. J. Urban Des. 2000, 5, 291–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J. The Death and Life of Great American Cities; Random House: New York, NY, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Allam, Z.; Dhunny, A.; Siew, G.; Jones, D. Towards smart urban regeneration: Findings of an urban footprint survey in Port Louis, Mauritius. Smart Cities 2018, 1, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, Z.; Dhunny, Z.A. On big data, artificial intelligence and smart cities. Cities 2019, 89, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, Z.; Jones, D.S. The potential of blockchain within air rights development as a prevention measure against urban sprawl. Urban Science 2019, 3, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Allam, Z. Achieving Neuroplasticity in Artificial Neural Networks through Smart Cities. Smart Cities 2019, 2, 118-134. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities2020009
Allam Z. Achieving Neuroplasticity in Artificial Neural Networks through Smart Cities. Smart Cities. 2019; 2(2):118-134. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities2020009
Chicago/Turabian StyleAllam, Zaheer. 2019. "Achieving Neuroplasticity in Artificial Neural Networks through Smart Cities" Smart Cities 2, no. 2: 118-134. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities2020009
APA StyleAllam, Z. (2019). Achieving Neuroplasticity in Artificial Neural Networks through Smart Cities. Smart Cities, 2(2), 118-134. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities2020009




