Application of LiDAR Remote Sensing for Aerosol Monitoring: Case Studies in Cyprus and Greece †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Classification of Aerosol Types in the Vertical Column
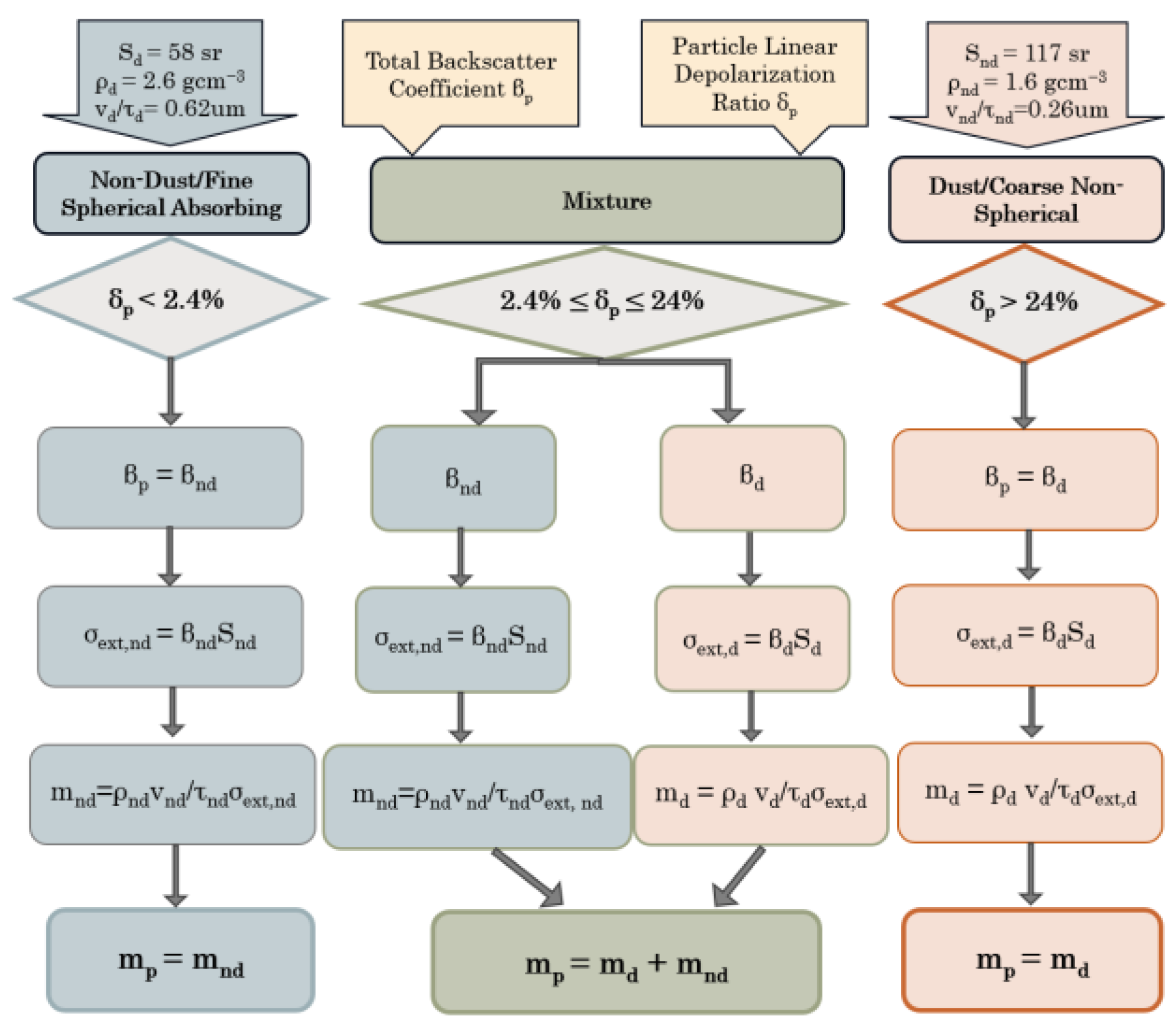
2.2. Backscatter Separation and Quantification of Aerosol Mass Concentration
3. Results
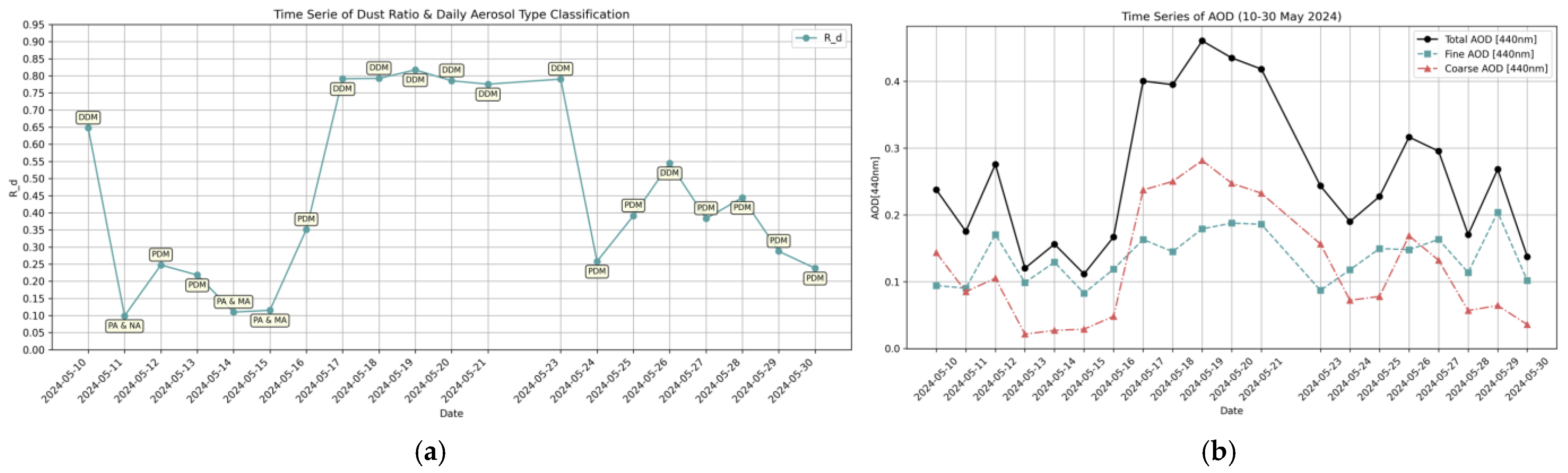
3.1. Results from AERONET
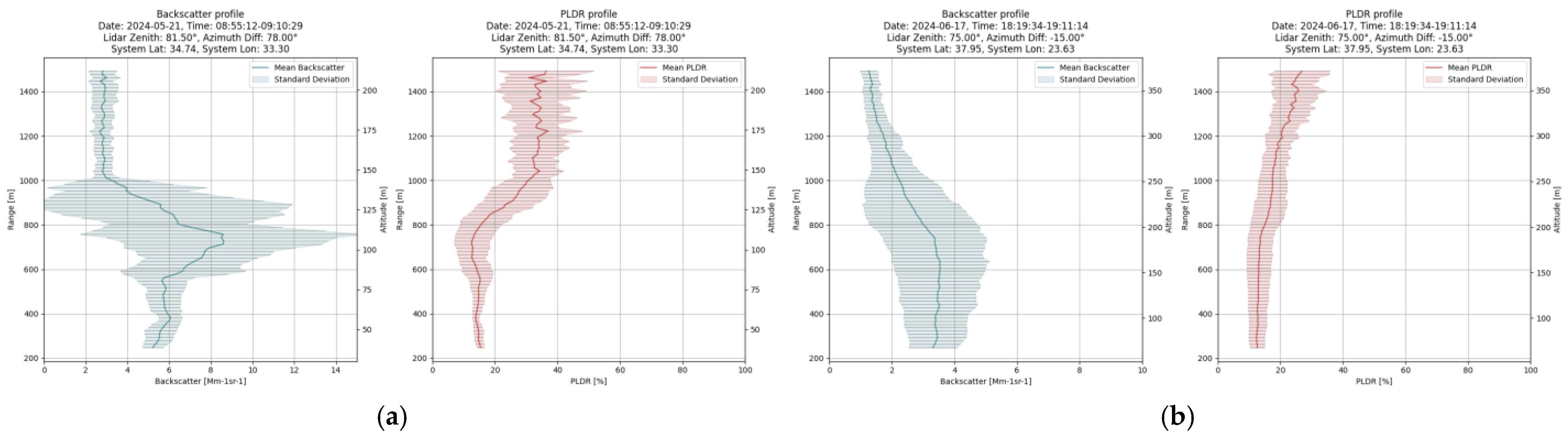
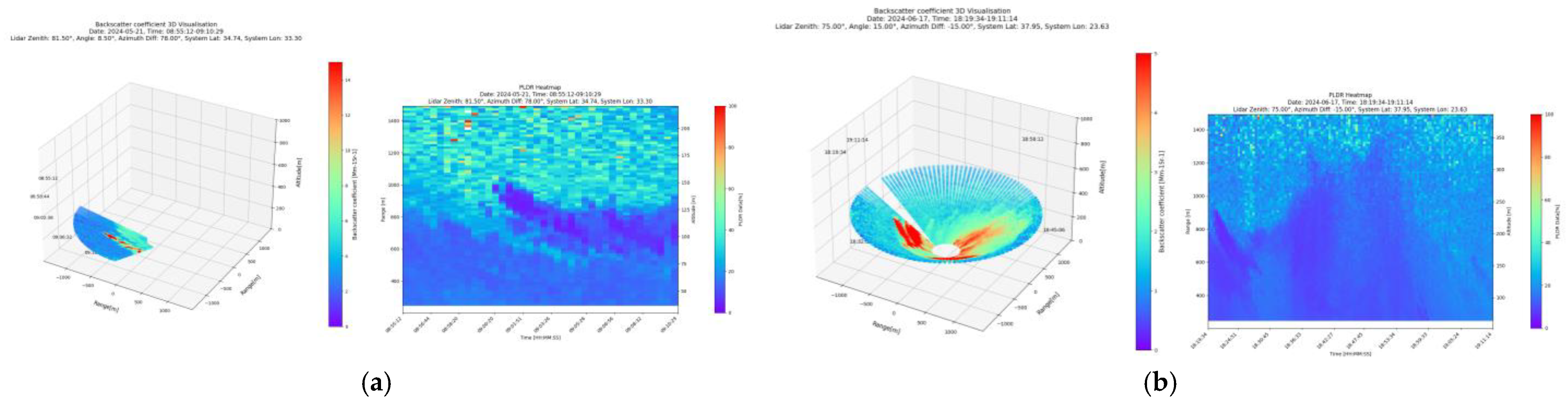
3.2. Results from PMeye Measurments
- Optical properties
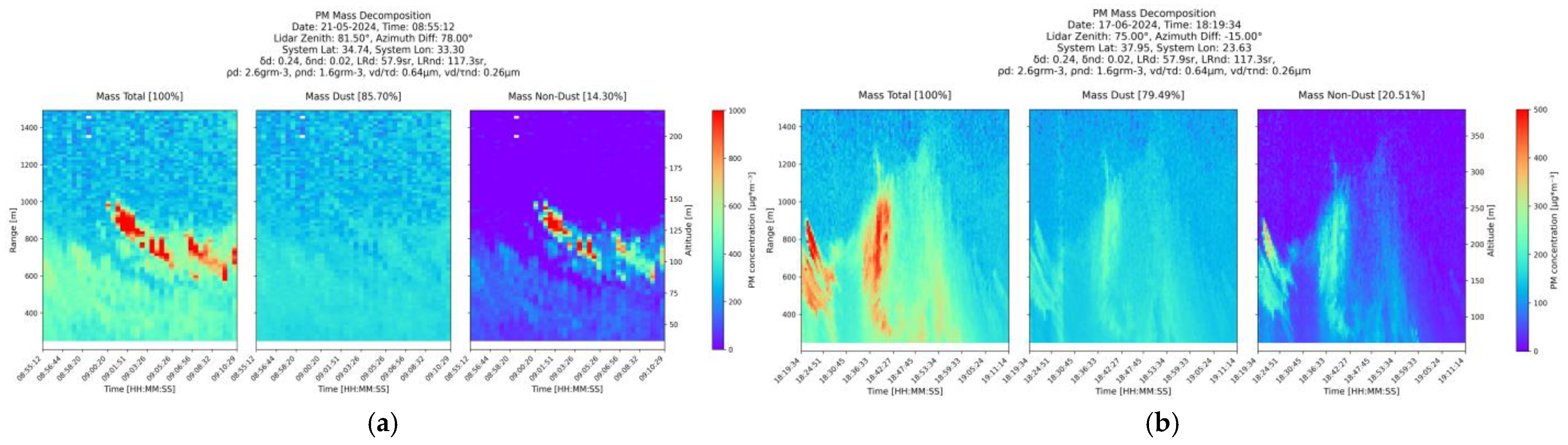
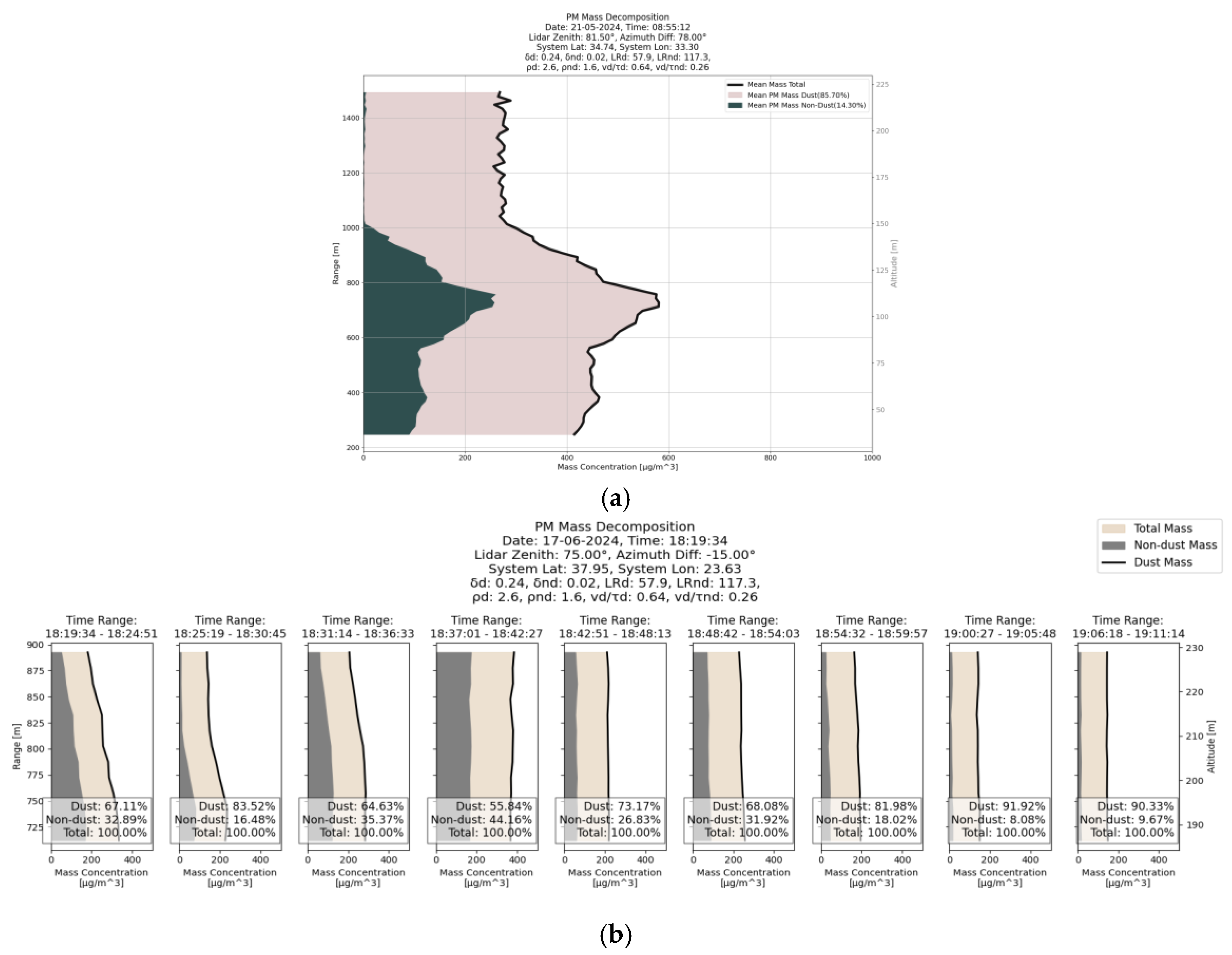
- Quantification and decomposition of Aerosol Mass Concentration
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hinds, W.C. Aerosol Technology: Properties, Behavior, and Measurement of Airborne Particles, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, D.; Ansmann, A.; Mattis, I.; Tesche, M.; Wandinger, U.; Althausen, D.; Pisani, G. Aerosol-type-dependent lidar ratios observed with Raman lidar. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D16202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, R.J.; Schwartz, S.E.; Hales, J.M.; Cess, R.D.; Coakley, J.A.; Hansen, J.E.; Hofmann, D.J. Climate forcing by anthropogenic aerosols. Science 1992, 255, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twomey, S. The influence of pollution on the shortwave albedo of clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 1977, 34, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansmann, A.; Wagner, F.; Müller, D.; Althausen, D.; Herber, A.; Wandinger, U. European pollution outbreaks during ACE-2: Lidar observations of anthropogenic aerosol layers. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, 8126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleanthous, S.; Vrekoussis, M.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Kalabokas, P.; Lelieveld, J. On the temporal and spatial variation of ozone in Cyprus. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 476–477, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.-K.; Tesche, M.; Noh, Y.; Müller, D. Aerosol-type classification based on AERONET version 3 inversion products. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 3789–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, D.M.; Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Sinyuk, A.; Smirnov, A.; Slutsker, I.; Dickerson, R.R.; Thompson, A.M.; Schafer, J.S. An analysis of AERONET aerosol absorption properties and classifications representative of aerosol source regions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.; Eck, T.; Smirnov, A.; Kaufman, Y.; King, M.; Tanré, D.; Slutsker, I. Variability of Absorption and Optical Properties of Key Aerosol Types Observed in Worldwide Locations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 590–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudenthaler, V.; Esselborn, M.; Wiegner, M.; Heese, B.; Tesche, M.; Ansmann, A.; Weinzierl, B. Depolarization ratio profiling at several wavelengths in pure Saharan dust during SAMUM 2006. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2009, 61, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamouri, R.E.; Ansmann, A. Fine and coarse dust separation with polarization lidar. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 3717–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamouri, R.E.; Ansmann, A. Potential of polarization/Raman lidar to separate fine dust, coarse dust, marine, and anthropogenic aerosol profiles. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 3403–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansmann, A.; Tesche, M.; Althausen, D.; Müller, D.; Seifert, P.; Freudenthaler, V.; Heese, B.; Wiegner, M.; Pisani, G.; Knippertz, P.; et al. Influence of Saharan dust on cloud glaciation in southern Morocco during the Saharan Mineral Dust Experiment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D04210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakaki, E.; Zyl, P.G.; Müller, D.; Balis, D.; Komppula, M. Optical and microphysical characterization of aerosol layers over South Africa by means of multi-wavelength depolarization and Raman lidar measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2015, 16, 35237–35276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, G.L.; Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.N. Angstrom exponent and bimodal aerosol size distributions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, D07207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floutsi, A.A.; Baars, H.; Wandinger, U. HETEAC-Flex: An optimal estimation method for aerosol typing based on lidar-derived intensive optical properties. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2024, 17, 693–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, M.; Koepke, P.; Schult, I. Optical properties of aerosols and clouds: The software package OPAC. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozic, J.; Verheggen, B.; Weingartner, E.; Crosier, J.; Bower, K.N.; Flynn, M.; Coe, H.; Henning, S.; Steinbacher, M.; Henne, S.; et al. Chemical composition of free tropospheric aerosol for PM1 and coarse mode at the high alpine site Jungfraujoch. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 407–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malesi, C.; Giannakaki, E.; Soupiona, O. Application of LiDAR Remote Sensing for Aerosol Monitoring: Case Studies in Cyprus and Greece. Environ. Earth Sci. Proc. 2025, 35, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025035043
Malesi C, Giannakaki E, Soupiona O. Application of LiDAR Remote Sensing for Aerosol Monitoring: Case Studies in Cyprus and Greece. Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings. 2025; 35(1):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025035043
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalesi, Chara, Elina Giannakaki, and Ourania Soupiona. 2025. "Application of LiDAR Remote Sensing for Aerosol Monitoring: Case Studies in Cyprus and Greece" Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings 35, no. 1: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025035043
APA StyleMalesi, C., Giannakaki, E., & Soupiona, O. (2025). Application of LiDAR Remote Sensing for Aerosol Monitoring: Case Studies in Cyprus and Greece. Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings, 35(1), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025035043





