Cloud Condensation Nuclei (CCN) and Ice Nucleating Particles (INP) Conversion Factors Based on Thessaloniki and Leipzig AERONET Stations Using CALIPSO Aerosol Typing †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. AERONET
2.2. CALIPSO
2.3. Methodology
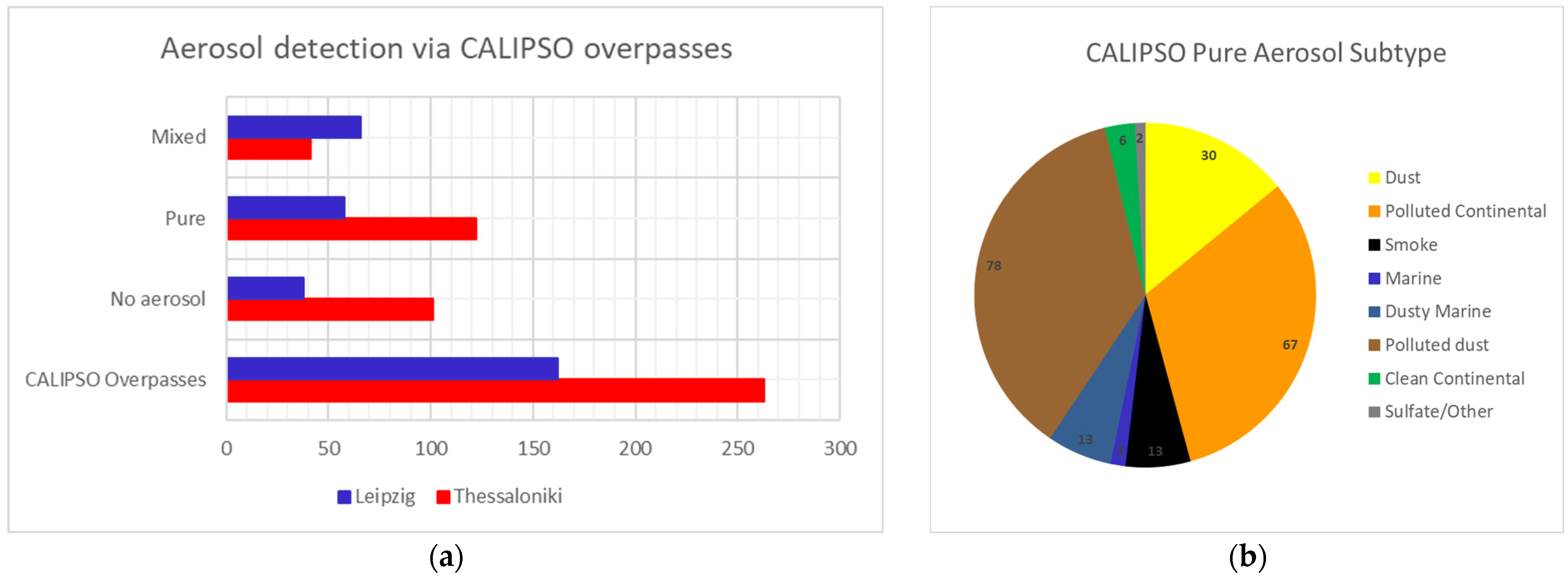
3. Results
3.1. Pure Dust Aerosols
3.2. Pure Polluted Continental Aerosols
3.3. Pure Smoke Aerosols
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AERONET | Aerosol Robotic Network |
| CALIPSO | Cloud-Aerosol LIDAR and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observations |
| CALIOP | Cloud-Aerosol Lidar with Orthogonal Polarization |
| CCN | Cloud Condensation Nuclei |
| INP | Ice-Nucleating Particle |
References
- Mamouri, R.E.; Ansmann, A. Estimated desert-dust ice nuclei profiles from polarization lidar: Methodology and case studies. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 3463–3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamouri, R.E.; Ansmann, A. Potential of polarization lidar to provide profiles of CCN- and INP-relevant aerosol parameters. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 5905–5931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansmann, A.; Ohneiser, K.; Mamouri, R.-E.; Knopf, D.A.; Veselovskii, I.; Baars, H.; Engelmann, R.; Foth, A.; Jimenez, C.; Seifert, P.; et al. Tropospheric and stratospheric wildfire smoke profiling with lidar: Mass, surface area, CCN, and INP retrieval. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 9779–9807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamouri, R.E.; Ansmann, A. Fine and coarse dust separation with polarization lidar. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 3717–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Song, C.; Kim, S.; Chun, Y.; Sohn, B.; Holben, B. Characteristics of aerosol types from AERONET sunphotometer measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 3110–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.A.; Christopher, S.A. MODIS derived fine mode fraction characteristics of marine, dust, and anthropogenic aerosols over the ocean, constrained by GOCART, MOPITT, and TOMS. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D22204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.-K.; Müller, D.; Kim, Y.J.; Noh, Y.M.; Lee, H.; Choi, M. Aerosol-Type Classification Based on AERONET Version 3 Inversion Products. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 3789–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgoulias, A.K.; Marinou, E.; Tsekeri, A.; Proestakis, E.; Akritidis, D.; Alexandri, G.; Zanis, P.; Balis, D.; Marenco, F.; Tesche, M.; et al. A First Case Study of CCN Concentrations from Spaceborne Lidar Observations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinou, E.; Tesche, M.; Nenes, A.; Ansmann, A.; Schrod, J.; Mamali, D.; Tsekeri, A.; Pikridas, M.; Baars, H.; Engelmann, R.; et al. Retrieval of ice-nucleating particle concentrations from lidar observations and comparison with UAV in situ measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 11315–11342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanré, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET—A federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.M.; Pelon, J.; Coakley, J.A., Jr.; Ackerman, S.A.; Charlson, R.J.; Colarco, P.R.; Flamant, P.; Fu, Q.; Hoff, R.M.; Kittaka, C.; et al. The CALIPS mission: A global 3D view of aerosols and clouds. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 1211–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.H.; Winker, D.M.; Kittaka, C.; Vaughan, M.A.; Liu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Trepte, C.R.; Rogers, R.R.; Ferrare, R.A.; Lee, K.P.; et al. The CALIPSO automated aerosol classification and lidar ratio selection algorithm. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1994–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Omar, A.H.; Tackett, J.L.; Vaughan, M.A.; Winker, D.M.; Trepte, C.R.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Poole, L.R.; Pitts, M.C.; et al. The CALIPSO version 4 automated aerosol classification and lidar ratio selection algorithm. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 11, 6107–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
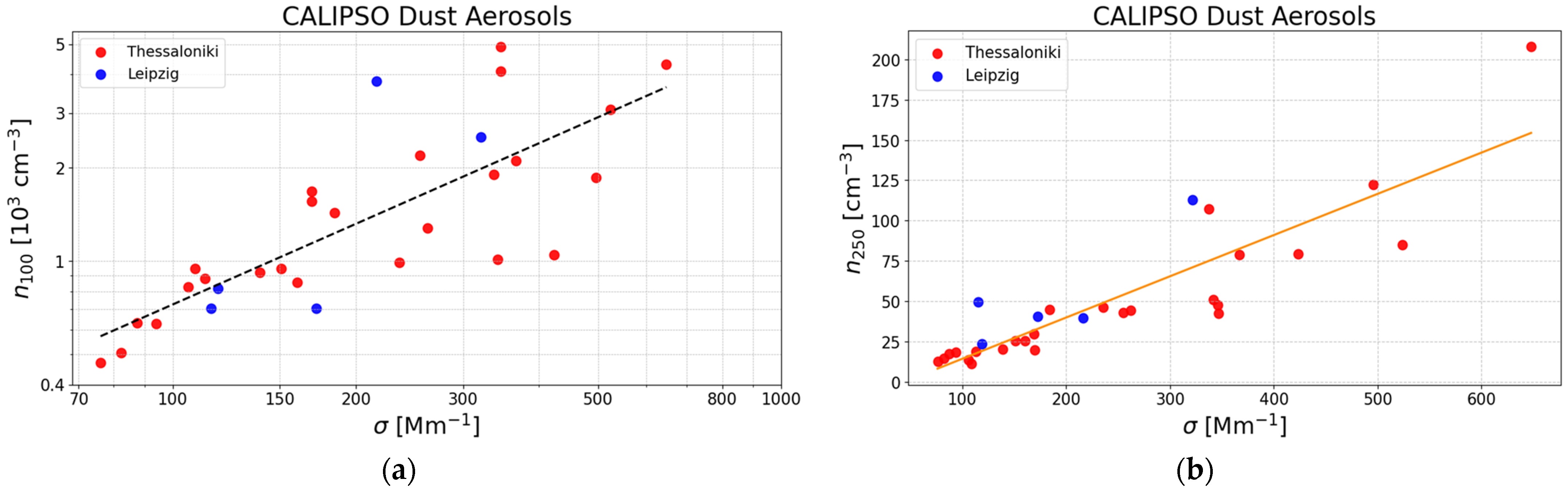
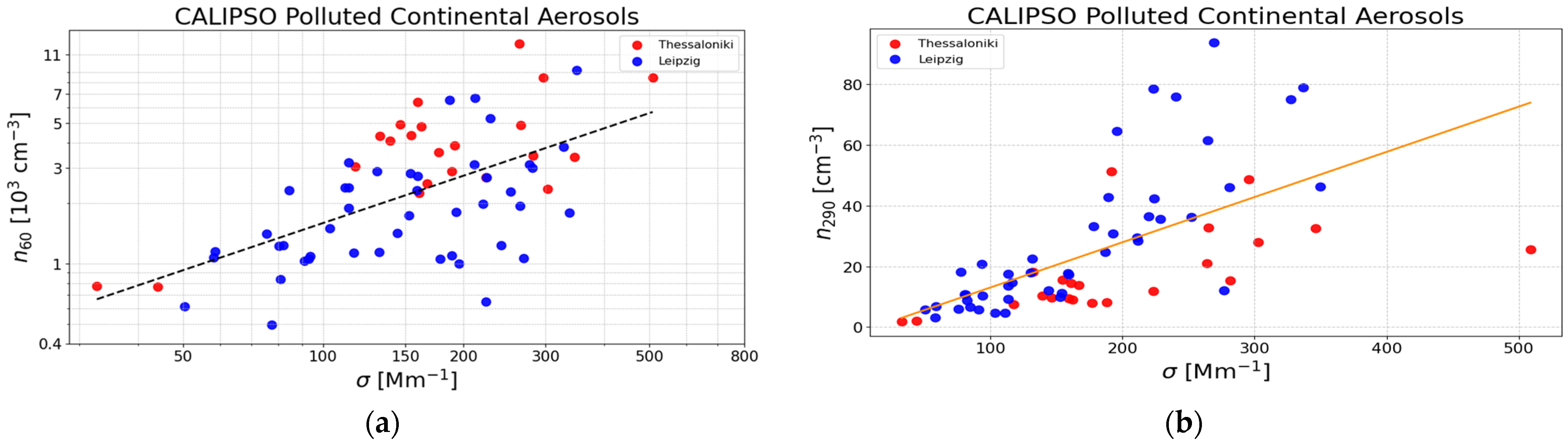

| Desert dust | No. of Data | C100 (cm−3) | xd | C250 (Mm cm−3) |
| Thessaloniki and Leipzig | 30 | 13.6 ± 9.2 | 0.86 ± 0.13 | 0.256 ± 0.026 |
| Polluted continental | No. of Data | C60 (cm−3) | xc | C290 (Mm cm−3) |
| Thessaloniki and Leipzig | 67 | 43.4 ± 28.6 | 0.78 ± 0.13 | 0.149 ± 0.023 |
| Smoke | No. of Data | C50 (cm−3) | xs | C250 (Mm cm−3) |
| Thessaloniki and Leipzig | 13 | 28.2 ± 28.7 | 0.90 ± 0.19 | 0.010 ± 0.004 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karageorgopoulou, A.; Amiridis, V.; Georgiou, T.; Marinou, E.; Giannakaki, E. Cloud Condensation Nuclei (CCN) and Ice Nucleating Particles (INP) Conversion Factors Based on Thessaloniki and Leipzig AERONET Stations Using CALIPSO Aerosol Typing. Environ. Earth Sci. Proc. 2025, 35, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025035033
Karageorgopoulou A, Amiridis V, Georgiou T, Marinou E, Giannakaki E. Cloud Condensation Nuclei (CCN) and Ice Nucleating Particles (INP) Conversion Factors Based on Thessaloniki and Leipzig AERONET Stations Using CALIPSO Aerosol Typing. Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings. 2025; 35(1):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025035033
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarageorgopoulou, Archontoula, Vassilis Amiridis, Thanasis Georgiou, Eleni Marinou, and Eleni Giannakaki. 2025. "Cloud Condensation Nuclei (CCN) and Ice Nucleating Particles (INP) Conversion Factors Based on Thessaloniki and Leipzig AERONET Stations Using CALIPSO Aerosol Typing" Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings 35, no. 1: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025035033
APA StyleKarageorgopoulou, A., Amiridis, V., Georgiou, T., Marinou, E., & Giannakaki, E. (2025). Cloud Condensation Nuclei (CCN) and Ice Nucleating Particles (INP) Conversion Factors Based on Thessaloniki and Leipzig AERONET Stations Using CALIPSO Aerosol Typing. Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings, 35(1), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025035033






