Modelling the Outdoor Thermal Benefit of Urban Trees: A Case Study in Lecce, Italy †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
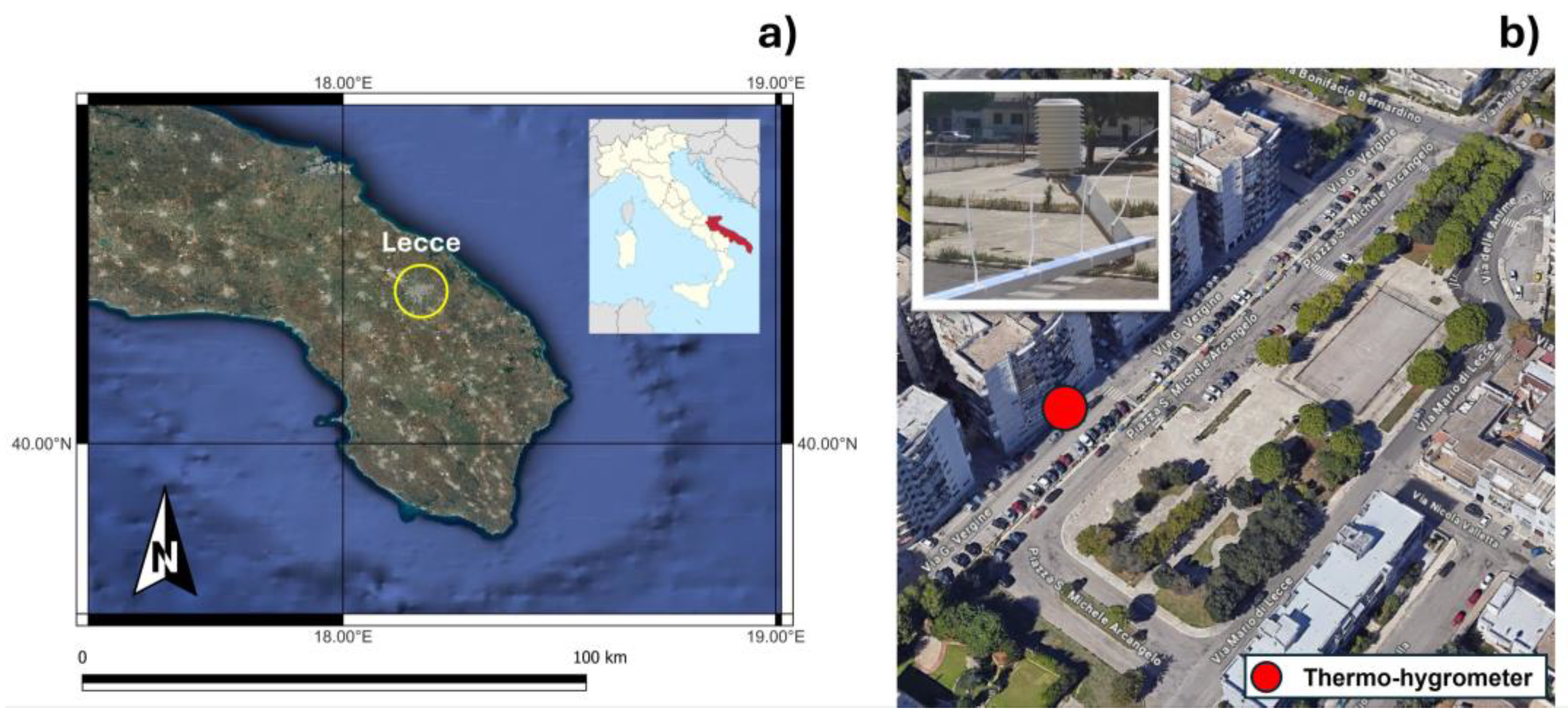
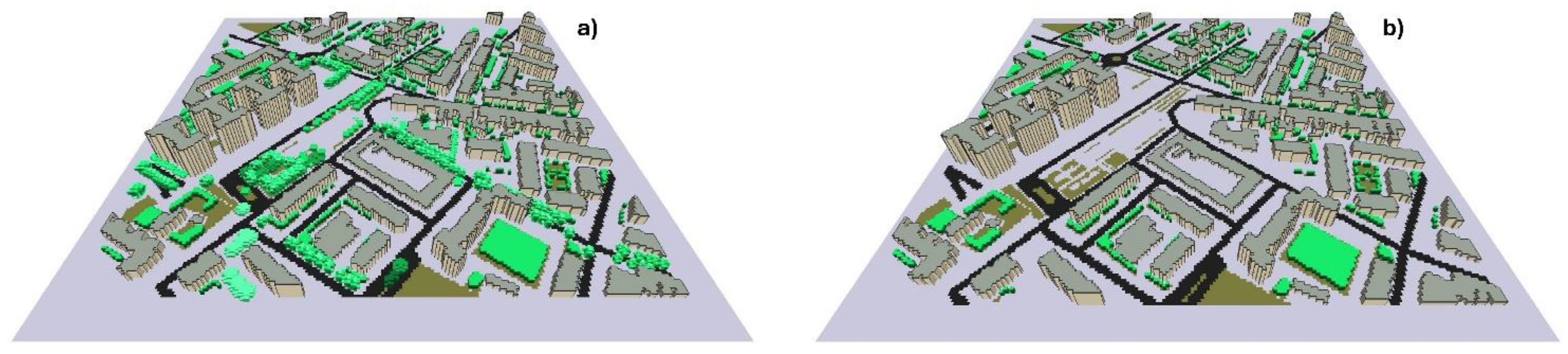
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Meteorological Data and Modelling Setup in ENVI-Met
3. Results
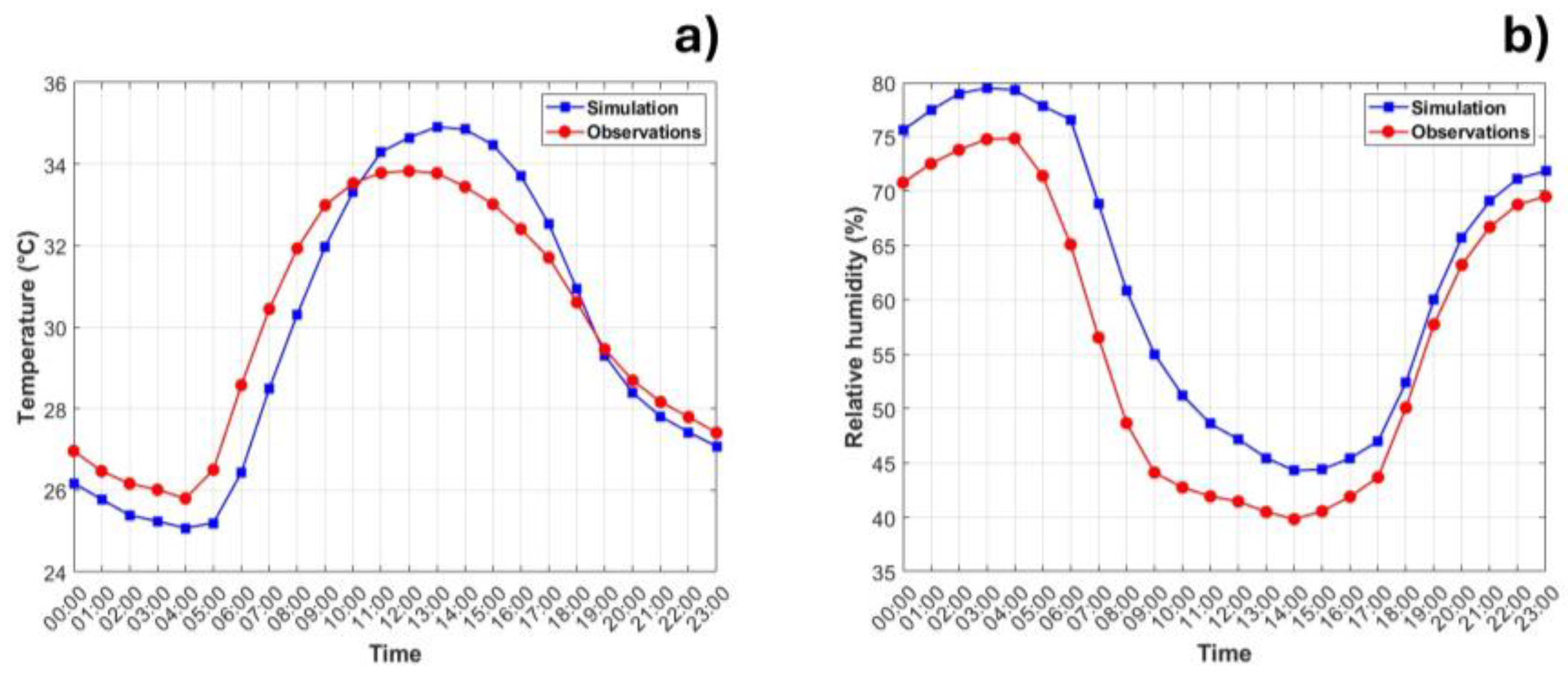
3.1. Model Validation
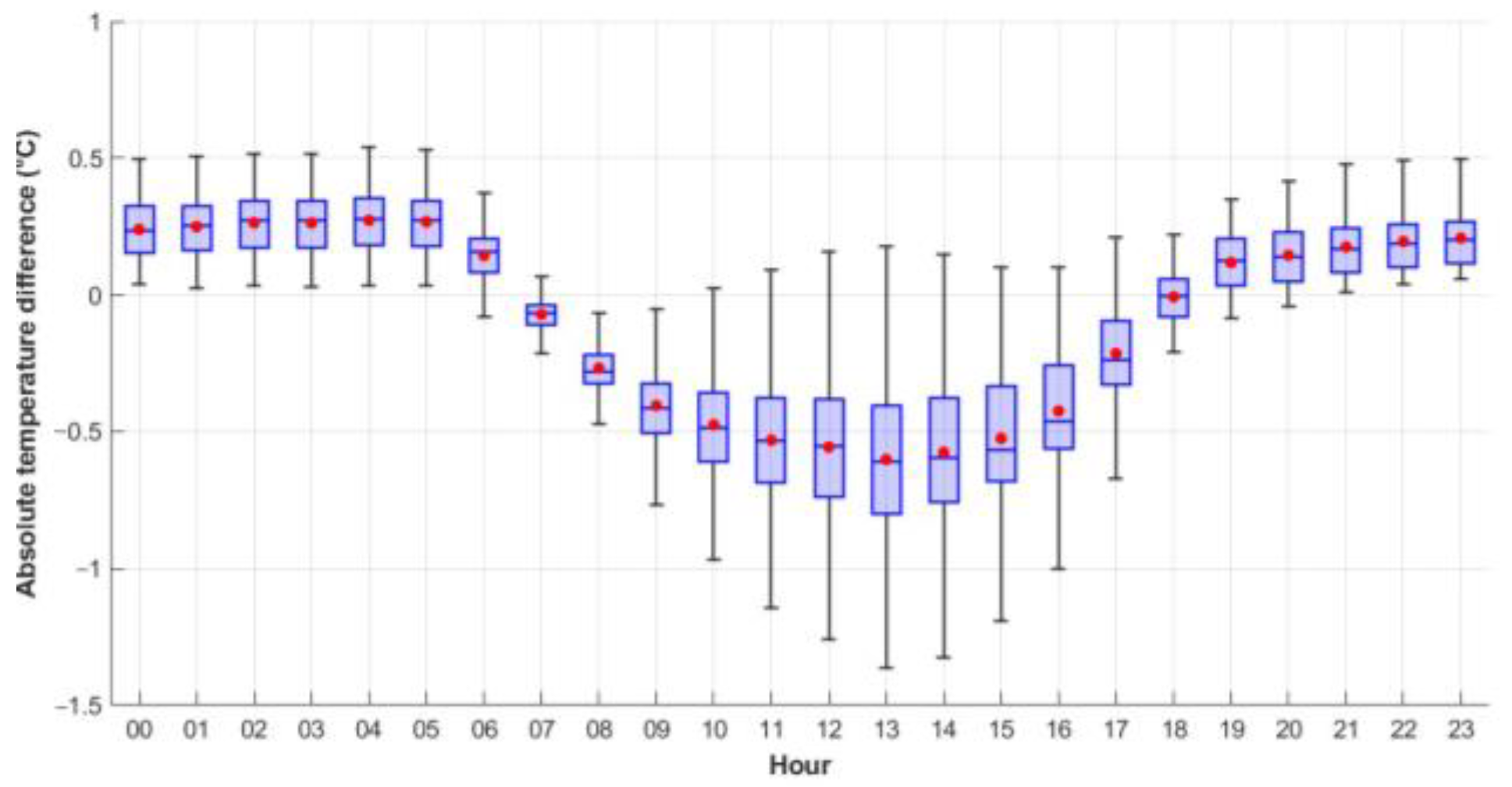
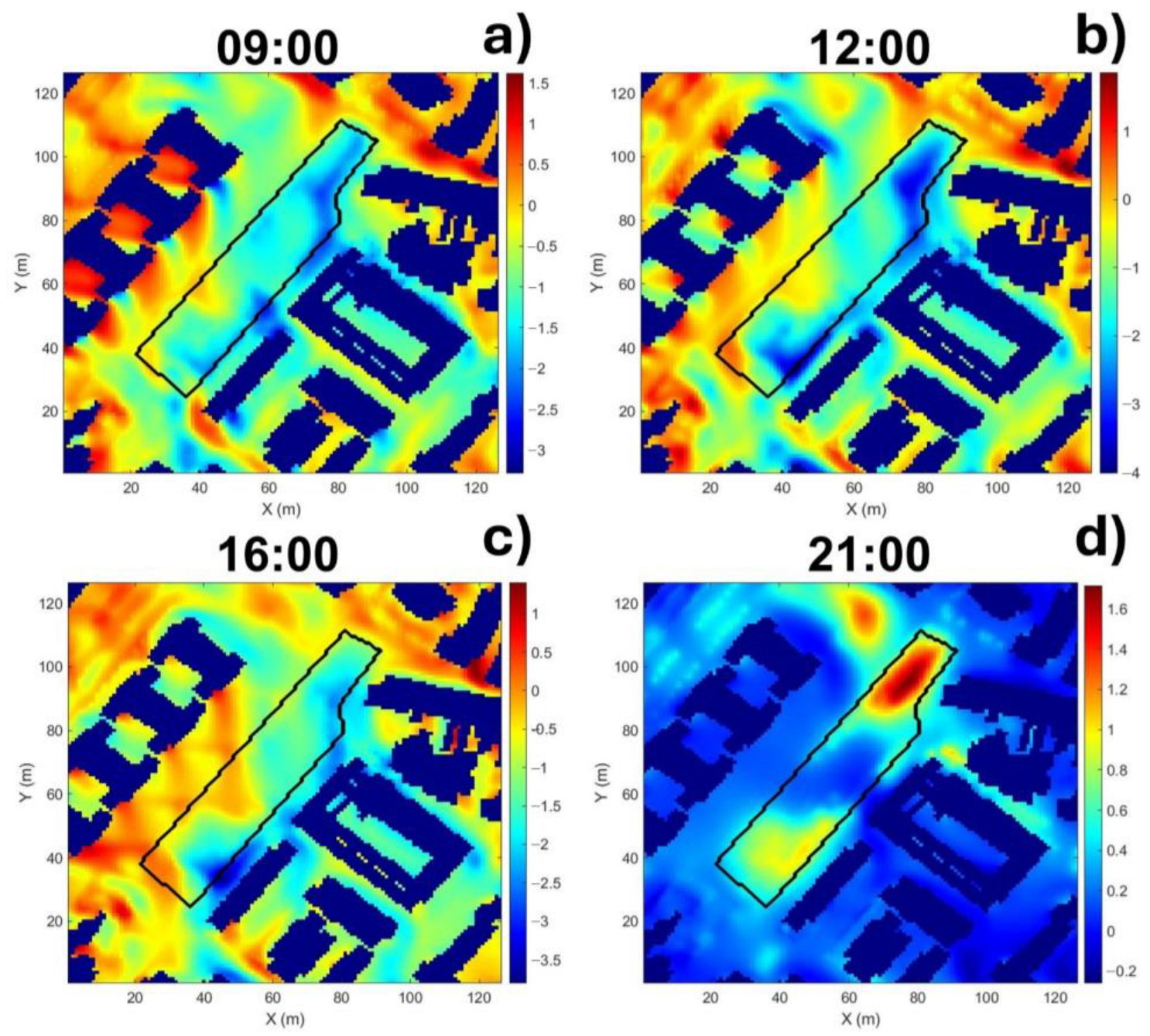
3.2. Analysis of Temperature Differences
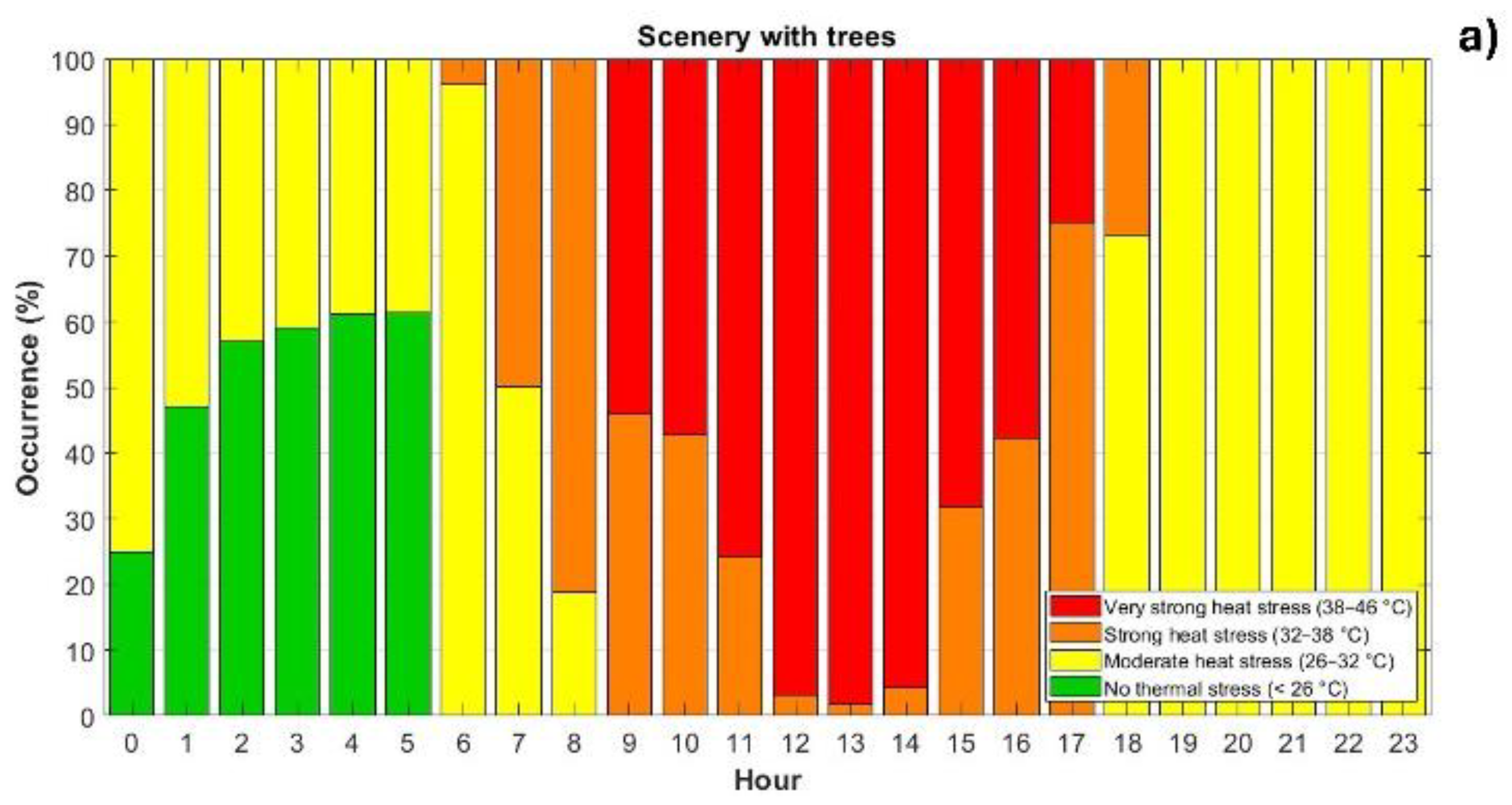
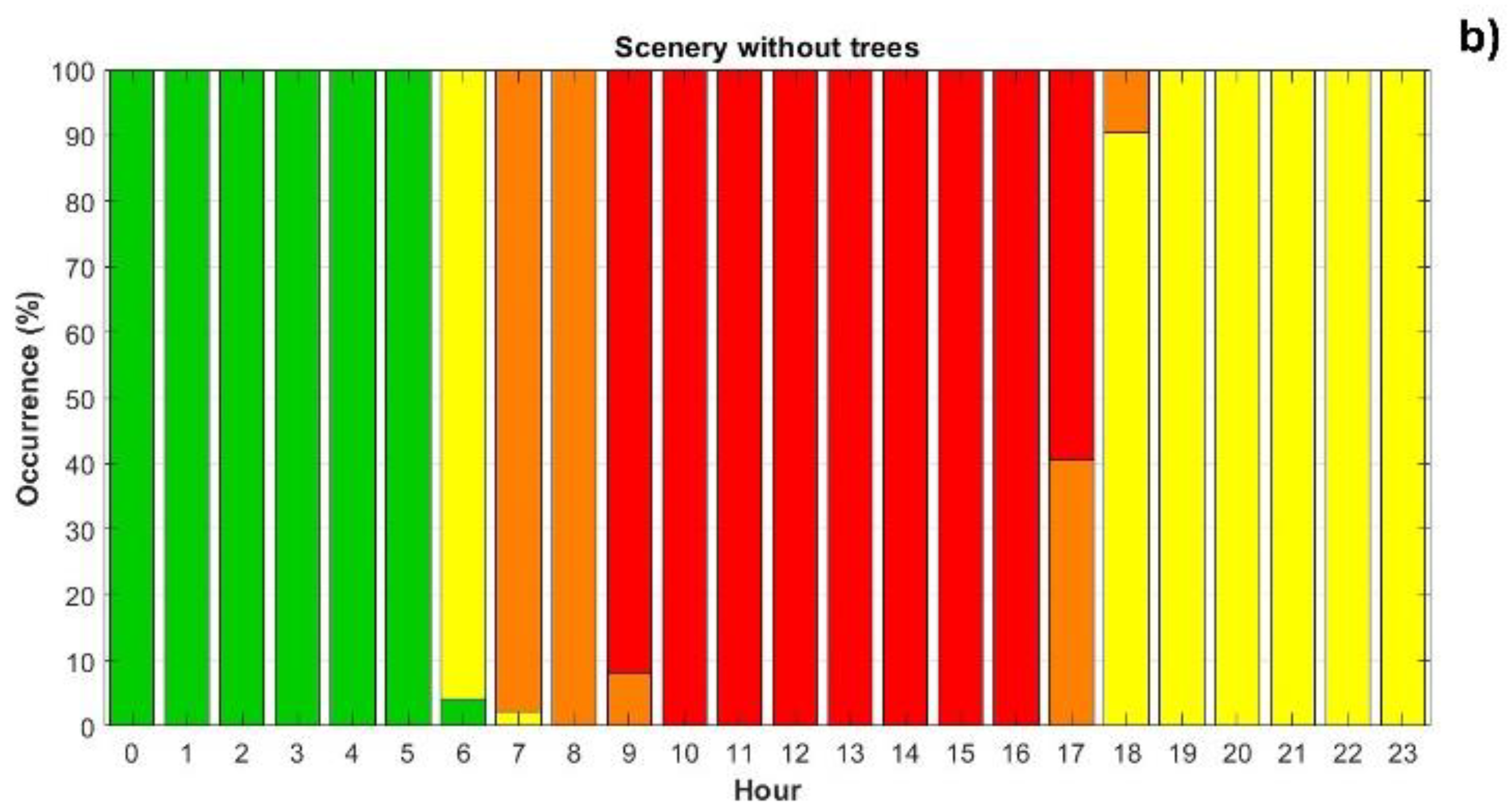
3.3. Outdoor Thermal Comfort Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salehi, A.; Nasrollahi, N. Assessing vegetation distribution based on geometrical and morphological characteristics of the urban fabric to provide thermal comfort for pedestrians: A case study in Sanandaj. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 104, 105297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotharkar, R.; Dongarsane, P. Investigating outdoor thermal comfort variations across Local Climate Zones in Nagpur, India, using ENVI-met. Build. Environ. 2024, 249, 111122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, N.; Montazeri, H.; Blocken, B.; Neophytou, M. On the impact of climate change on urban microclimate, thermal comfort, and human health: Multiscale numerical simulations. Build. Environ. 2024, 244, 111690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeri, T.; Hassan, N.; Ghaffarianhoseini, A. Evaluation of microclimate mitigation strategies in a heterogenous street canyon in Kuala Lumpur from outdoor thermal comfort perspective using Envi-met. Urban Clim. 2023, 52, 101719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labdaoui, K.; Mazouz, S.; Reiter, S.; Teller, J. Thermal perception in outdoor urban spaces under the Mediterranean climate of Annaba, Algeria. Urban Clim. 2021, 39, 100970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dontu, E.K.K.; Kyriakodis, G.E.; Zhang, X.; Long, Y.P.; Wan, M.P.; Bozonnet, E. Simulation advances with EnviBatE: A case study on urban heat island mitigation in Singapore. Build. Environ. 2024, 258, 111580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meili, N.; Acero, J.A.; Peleg, N.; Manoli, G.; Burlando, P.; Fatichi, S. Vegetation cover and plant-trait effects on outdoor thermal comfort in a tropical city. Build. Environ. 2021, 195, 107733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wang, Z. Impacts of mesic and xeric urban vegetation on outdoor thermal comfort and microclimate in Phoenix, AZ. Build. Environ. 2015, 94, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoka, S.; Tsikaloudaki, A.; Theodosiou, T. Analyzing the ENVI-met microclimate model’s performance and assessing cool materials and urban vegetation applications—A review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 43, 55–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cheng, W.; Jim, C.Y.; Morakinyo, T.E.; Shi, Y.; Ng, E. Heat mitigation benefits of urban green and blue infrastructures: A systematic review of modeling techniques, validation and scenario simulation in ENVI-met V4. Build. Environ. 2021, 200, 107939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, R.D.; Audenaert, A.; Verbeke, S. Thermal comfort and indoor overheating risks of urban building stock—A review of modelling methods and future climate challenges. Build. Environ. 2025, 269, 112363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruse, M.; Fleer, H. Simulating surface-plant-air interactions inside urban environments with a three dimensional numerical model. Environ. Model Softw. 1998, 13, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, S.; Lee, G. Analyzing urban thermal comfort changes due to modifications in urban material properties in a large-scale new town: A CFD study based on the Universal Thermal Climate Index (UTCI). Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 130, 106627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jendritzky, G.; de Dear, R.; Havenith, G. UTCI—Why another thermal index? Int. J. Biometeorol. 2012, 56, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bröde, P. Deriving the operational procedure for the universal thermal climate index (UTCI). Int. J. Biometeorol. 2012, 56, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donateo, A.; Palusci, O.; Pappaccogli, G.; Esposito, A.; Martilli, A.; Santiago, J.L.; Buccolieri, R. Analysis of urban heat island and human thermal comfort in a Mediterranean city: A case study of Lecce (Italy). Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 98, 104849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappaccogli, G.; Giangrande, F.; Esposito, A.; Donateo, A.; Lionello, P.; Buccolieri, R. Dynamics of urban heat island intensity in Lecce, Italy: Seasonal, diurnal and heat wave influence. Bull. Atmos. Sci. Technol. 2024, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| UTCI Range (°C) | Thermal Sensation |
|---|---|
| >46 | Extreme heat stress |
| 38 to 46 | Very strong heat stress |
| 32 to 38 | Strong heat stress |
| 26 to 32 | Moderate heat stress |
| 9 to 26 | No heat stress |
| 9 to 0 | Slight cold stress |
| 0 to −13 | Moderate cold stress |
| −13 to −27 | Strong cold stress |
| −27 to −40 | Very strong cold stress |
| <−40 | Extreme cold stress |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giangrande, F.; Pappaccogli, G.; Cesari, R.; Esposito, A.; Emmanuel, R.; Ippolito, F.; Buccolieri, R. Modelling the Outdoor Thermal Benefit of Urban Trees: A Case Study in Lecce, Italy. Environ. Earth Sci. Proc. 2025, 34, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025034008
Giangrande F, Pappaccogli G, Cesari R, Esposito A, Emmanuel R, Ippolito F, Buccolieri R. Modelling the Outdoor Thermal Benefit of Urban Trees: A Case Study in Lecce, Italy. Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings. 2025; 34(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025034008
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiangrande, Francesco, Gianluca Pappaccogli, Rita Cesari, Antonio Esposito, Rohinton Emmanuel, Fabio Ippolito, and Riccardo Buccolieri. 2025. "Modelling the Outdoor Thermal Benefit of Urban Trees: A Case Study in Lecce, Italy" Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings 34, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025034008
APA StyleGiangrande, F., Pappaccogli, G., Cesari, R., Esposito, A., Emmanuel, R., Ippolito, F., & Buccolieri, R. (2025). Modelling the Outdoor Thermal Benefit of Urban Trees: A Case Study in Lecce, Italy. Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings, 34(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025034008









