Effect of Nitrogen Oxide Concentration Levels and Meteorological Variables on Ozone (O3) Formation in the Petrochemical Industry Area in the Monterrey Metropolitan, Mexico †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Area of Study
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
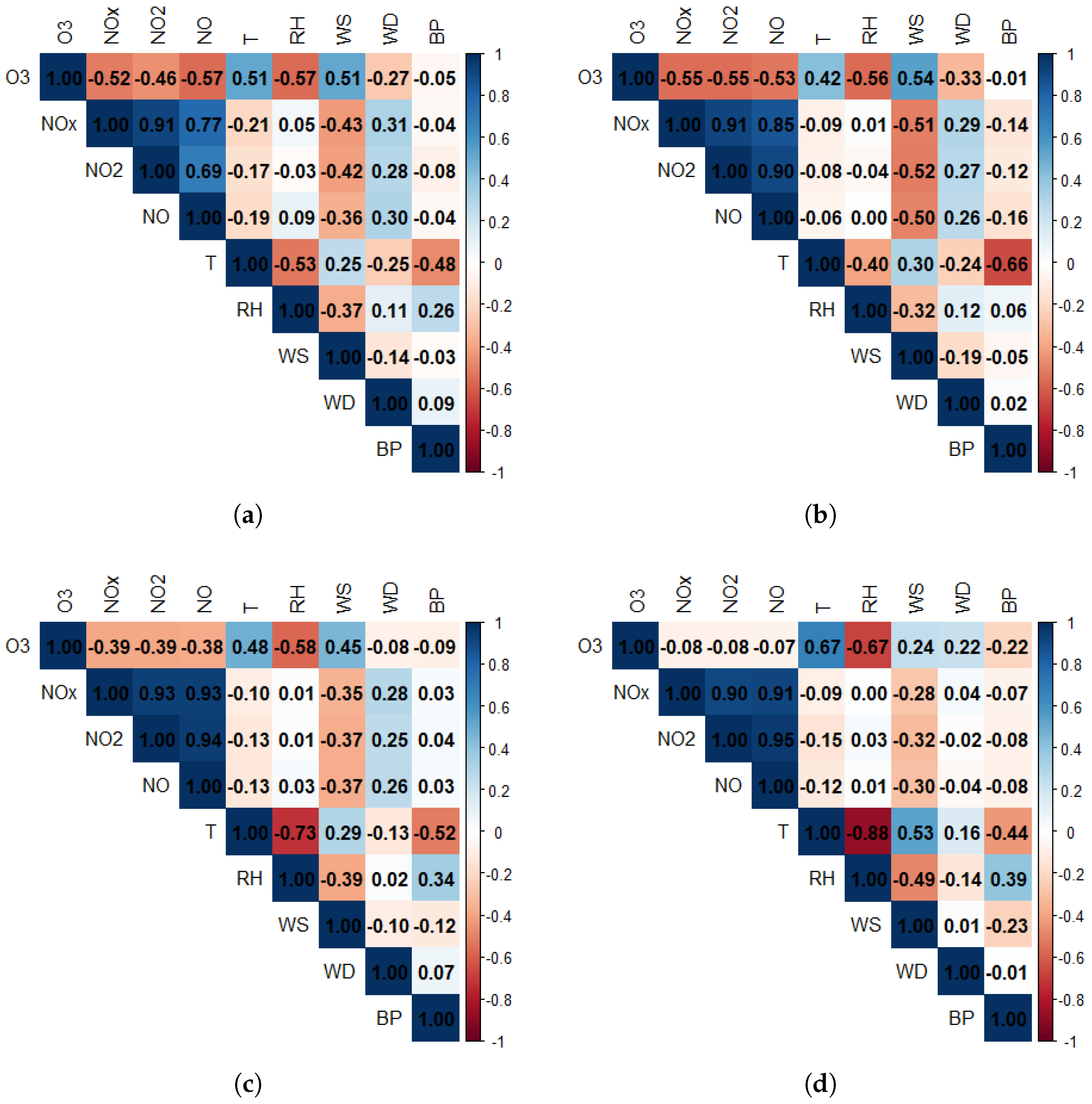
3.1. Correlation Analysis
3.2. O3 Prediction Models
3.3. Residuals
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, W.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, G.; Sun, W.; She, J. Chemical reactivity of volatile organic compounds and their effects on ozone formation in a petrochemical industrial area of Lanzhou, Western China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 155901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinthong, N.; Thepanondh, S.; Kultan, V.; Keawboonchu, J. Characteristics and Impact of VOCs on Ozone Formation Potential in a Petrochemical Industrial Area, Thailand. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Sun, X.; Xu, J.; Ye, D. Improved emissions inventory and VOCs speciation for industrial OFP estimation in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 140838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Shen, H.; Li, H.; Ji, Y.; Zhong, X.; Zhao, M.; Liu, Y.; Guo, M.; Shang, F.; Xue, L. Significant contributions of the petroleum industry to volatile organic compounds and ozone pollution: Insights from year-long observations in the Yellow River Delta. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2024, 17, 100523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Meng, X.; Chen, Q.; Xue, Q.; Wang, L.; Sun, J.; Guo, W.; Tao, H.; Yang, L.; Chen, F. Characteristics of volatile organic compounds under different operating conditions in a petrochemical industrial zone and their effects on ozone formation. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 363, 125254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.; Kim, S.J.; Choi, S.D. Influence of industrial emissions on volatile organic compound levels and secondary formation of organic aerosol and ozone in a multi-industrial city during the warm season. Atmos. Environ. 2025, 343, 120983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Li, Y.; Fu, Q.; Tian, M.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Huang, K. Volatile organic compounds in a typical petrochemical production area in Shanghai, China: Source profiles, human health and environmental impacts. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 372, 126074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Liang, J.; Li, S.; Chen, G.; Chen, Z.; Tang, B.; Zhu, J.; Li, X. Diurnal emission variation of ozone precursors: Impacts on ozone formation during Sep. 2019. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 929, 172591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Lau, A.K.; Fung, J.C.; Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Tao, M.; Lu, X.; Ma, J.; Lao, X.Q. Removing the effects of meteorological factors on changes in nitrogen dioxide and ozone concentrations in China from 2013 to 2020. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Hong, Y.; Lin, Y.; Xu, K.; Chen, G.; Liu, T.; Xu, L.; Li, M.; Fan, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Impacts of Synoptic Patterns and Meteorological Factors on Distribution Trends of Ozone in Southeast China During 2015–2020. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2023, 128, e2022JD037961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Luo, S.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Qu, C.; Liu, X.; Wen, X. Impacts of Meteorological Factors, VOCs Emissions and Inter-Regional Transport on Summer Ozone Pollution in Yuncheng. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Kang, P.; Jaffe, D.A.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Wu, K.; Zhou, M. Understanding the impact of meteorology on ozone in 334 cities of China. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 248, 118221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borhani, F.; Shafiepour Motlagh, M.; Stohl, A.; Rashidi, Y.; Ehsani, A.H. Tropospheric Ozone in Tehran, Iran, during the last 20 years. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 3615–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, J.; Ma, J.; Liu, X.; Han, D.; Gao, H.; Huang, T. Predicting ozone formation in petrochemical industrialized Lanzhou city by interpretable ensemble machine learning. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 318, 120798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Li, R.; Chen, D.; Zhuang, Y.; Gao, B.; Yang, L.; Li, M. Understanding the causal influence of major meteorological factors on ground ozone concentrations across China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumaningtyas, S.D.A.; Tonokura, K.; Muharsyah, R.; Gunawan, D.; Sopaheluwakan, A.; Iriana, W.; Lestari, P.; Permadi, D.A.; Rahmawati, R.; Samputra, N.A.R. Comprehensive analysis of long-term trends, meteorological influences, and ozone formation sensitivity in the Jakarta Greater Area. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.H.; Lin, C.; Vu, C.T.; Cheruiyot, N.K.; Nguyen, M.K.; Le, T.H.; Lukkhasorn, W.; Vo, T.D.H.; Bui, X.T. Tropospheric ozone and NOx: A review of worldwide variation and meteorological influences. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, L.; Luo, H.; Li, W. Impact of Extreme Meteorological Events on Ozone in the Pearl River Delta, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 1307–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Liu, J.; Shu, L.; Wang, T.; Yuan, H. Local and synoptic meteorological influences on daily variability in summertime surface ozone in eastern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancilla, Y.; Paniagua, I.H.; Mendoza, A. Spatial differences in ambient coarse and fine particles in the Monterrey metropolitan area, Mexico: Implications for source contribution. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2019, 69, 548–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allu, S.K.; Srinivasan, S.; Maddala, R.K.; Reddy, A.; Anupoju, G.R. Seasonal ground level ozone prediction using multiple linear regression (MLR) model. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 6, 1981–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Abdullah, L.C.; Sobri, S.; Md Said, M.S.; Hussain, S.A.; Aun, T.P.; Hu, J. Long-Term Air Pollution Characteristics and Multi-scale Meteorological Factor Variability Analysis of Mega-mountain Cities in the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Circle. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidrulhisham, S.E.; Noor, N.M.; Hassan, Z.; Sandu, A.V.; Vizureanu, P.; Ul-Saufie, A.Z.; Zainol, M.R.R.M.A.; Kadir, A.A.; Deák, G. Effects of Weather and Anthropogenic Precursors on Ground-Level Ozone Concentrations in Malaysian Cities. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraschiv, S.; Barbuta-Misu, N.; Paraschiv, S.L. Influence of NO2, NO and meteorological conditions on the tropospheric O3 concentration at an industrial station. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, J. Analysis of the Spatial–Temporal Variation of the Surface Ozone Concentration and Its Associated Meteorological Factors in Changchun. Environments 2019, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Ji, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, M.; Li, H.; Wang, H. Characteristics and Meteorological Effects of Ozone Pollution in Spring Season at Coastal City, Southeast China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Wang, L.; Lu, C.; Liu, J.; Li, M.; Tang, G.; Ji, D.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y. Meteorological mechanism for a large-scale persistent severe ozone pollution event over eastern China in 2017. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 92, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrus, M.; Popa, C.; Bratu, A.M. Temporal Variations in Urban Air Pollution during a 2021 Field Campaign: A Case Study of Ethylene, Benzene, Toluene, and Ozone Levels in Southern Romania. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
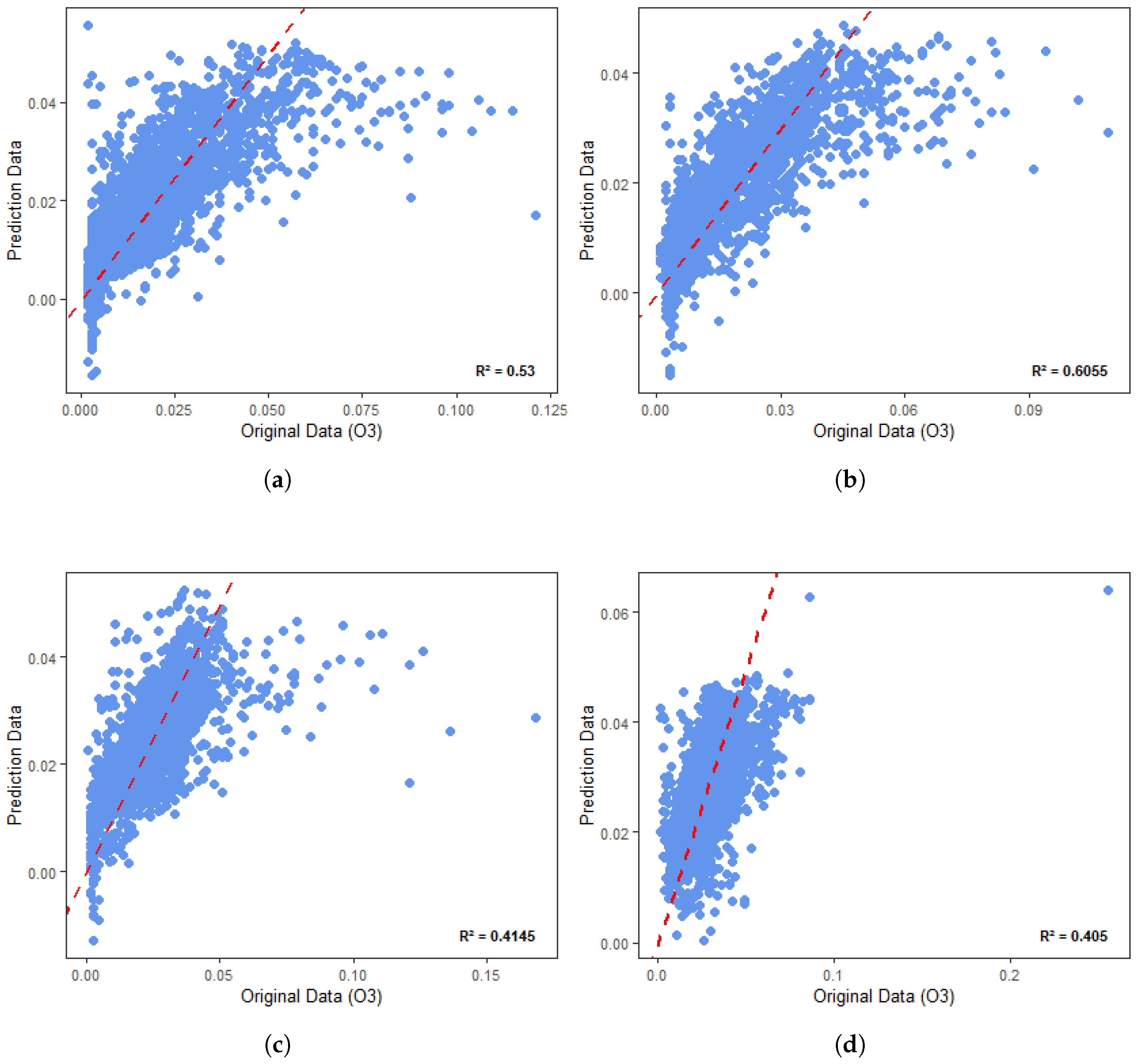

| Season | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|
| Autumn | 0.53 | 0.0115 |
| Winter | 0.60 | 0.0096 |
| Spring | 0.41 | 0.0111 |
| Summer | 0.40 | 0.0111 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaramillo-Perez, J.M.; Macías-Hernández, B.A.; Tello-Leal, E.; Ventura-Houle, R. Effect of Nitrogen Oxide Concentration Levels and Meteorological Variables on Ozone (O3) Formation in the Petrochemical Industry Area in the Monterrey Metropolitan, Mexico. Environ. Earth Sci. Proc. 2025, 34, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025034003
Jaramillo-Perez JM, Macías-Hernández BA, Tello-Leal E, Ventura-Houle R. Effect of Nitrogen Oxide Concentration Levels and Meteorological Variables on Ozone (O3) Formation in the Petrochemical Industry Area in the Monterrey Metropolitan, Mexico. Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings. 2025; 34(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025034003
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaramillo-Perez, Jailene Marlen, Bárbara A. Macías-Hernández, Edgar Tello-Leal, and René Ventura-Houle. 2025. "Effect of Nitrogen Oxide Concentration Levels and Meteorological Variables on Ozone (O3) Formation in the Petrochemical Industry Area in the Monterrey Metropolitan, Mexico" Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings 34, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025034003
APA StyleJaramillo-Perez, J. M., Macías-Hernández, B. A., Tello-Leal, E., & Ventura-Houle, R. (2025). Effect of Nitrogen Oxide Concentration Levels and Meteorological Variables on Ozone (O3) Formation in the Petrochemical Industry Area in the Monterrey Metropolitan, Mexico. Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings, 34(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025034003






