Assessment of Machine Learning Techniques to Estimate Reference Evapotranspiration at Yauri Meteorological Station, Peru †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
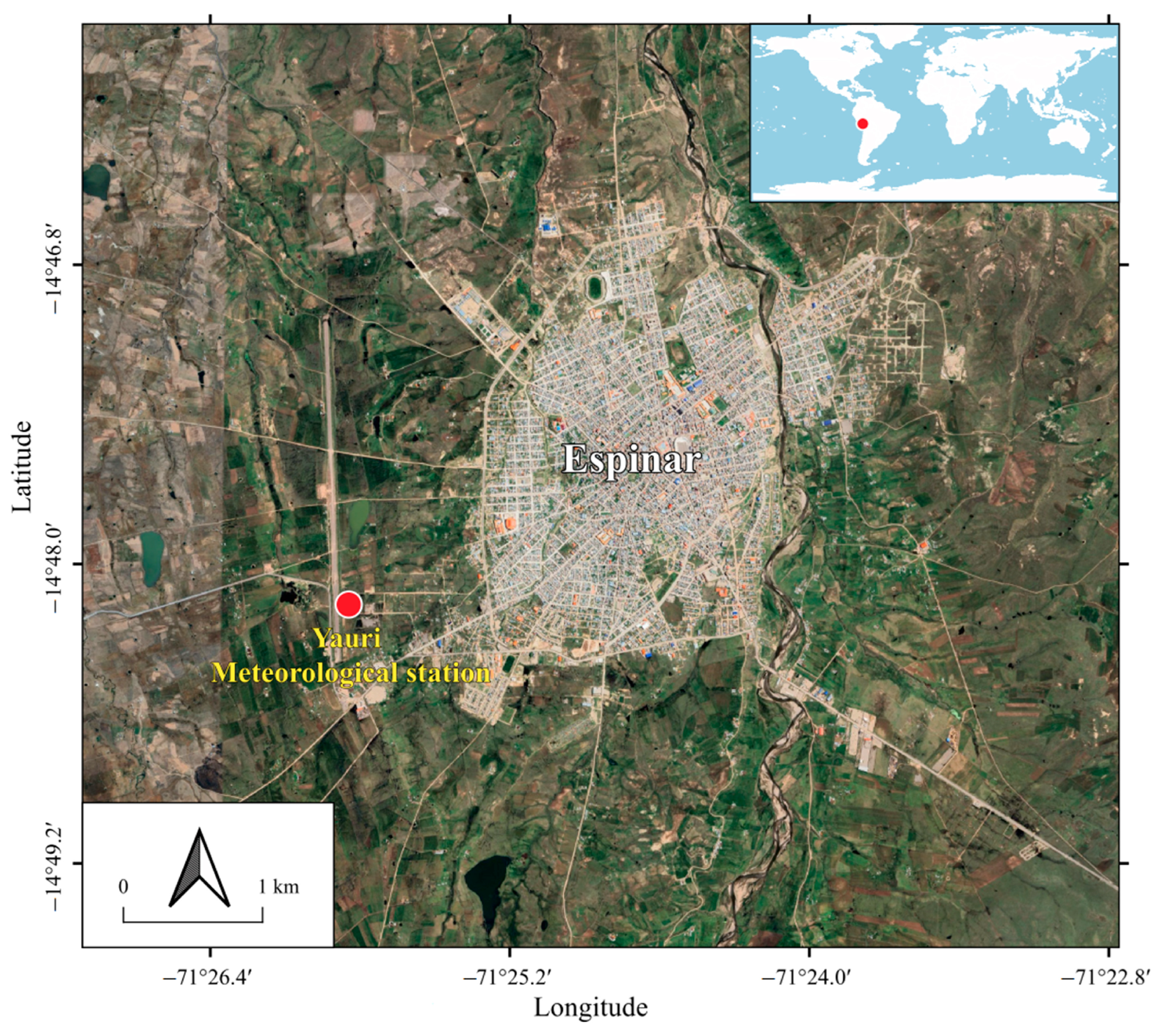
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Standard Estimated of ETo
2.3. Hargreaves–Samani Method
2.4. Machine Learning Algorithms
2.4.1. K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) Algorithm
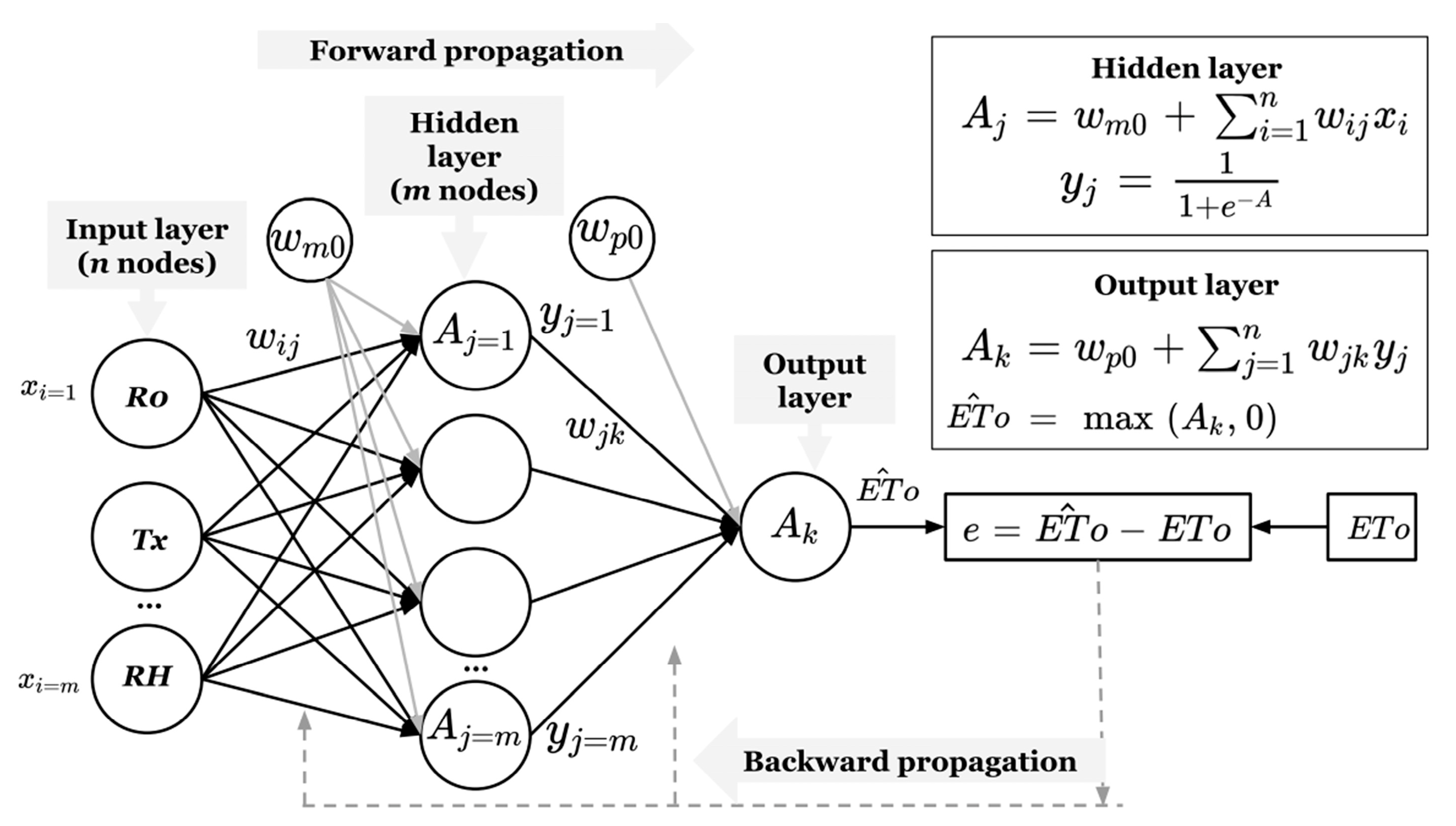
2.4.2. Artificial Neural Network (ANN)
2.5. Model Development
2.6. Goodness-of-Fit Metrics
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jensen, M.E.; Allen, R.G. Evaporation, Evapotranspiration, and Irrigation Water Requirements: Task Committee on Revision of Manual 70; American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE): Reston, VA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Tian, J. Forecasting reference evapotranspiration using data mining and limited climatic data. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 54, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdizadeh, S. Estimation of daily reference evapotranspiration (ETo) using artificial intelligence methods: Offering a new approach for lagged ETo data-based modeling. J. Hydrol. 2018, 559, 794–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Rae, S.D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration: Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; FAO Irrigation and drainage paper 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, P.K.; Dabral, P.P.; Pandey, V. Evaluation of reference evapotranspiration methods for the northeastern region of India. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2016, 4, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavado, W.; Lhomme, J.; Labat, D.; Loup Guyot, J.; Boulet, G. Estimación de la evapotranspiración de referencia (FAO Penman-Monteith) con limitados datos climáticos en la Cuenca Andina Amazónica Peruana. Rev. Peru. Geo-Atmos. 2015, 4, 34–36. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Gao, G.; Xu, C.Y.; Guo, J.; Ren, G. Comparison of the Thornthwaite method and pan data with the standard Penman-Monteith estimates of reference evapotranspiration in China. Clim. Res. 2005, 28, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho Alves, M.; De Carvalho, L.G.; Vianello, R.L.; Sediyama, G.C.; De Oliveira, M.S.; De Sá Junior, A. Geostatistical improvements of evapotranspiration spatial information using satellite land surface and weather stations data. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 113, 155–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, V.Z.; Antonopoulos, A.V. Daily reference evapotranspiration estimates by artificial neural networks technique and empirical equations using limited input climate variables. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 132, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, F. Evapotranspiration evaluation models based on machine learning algorithms: A comparative study. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 217, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, G.H.; Samani, Z.A. Reference Crop Evapotranspiration from Temperature. Appl. Eng. Agric. 1985, 1, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Guo, Z.; Liu, S.; He, X.; Meng, Y.; Xu, Z.; Song, L. Evaluating Different Machine Learning Methods for Upscaling Evapotranspiration from Flux Towers to the Regional Scale. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 8674–8690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demolli, H.; Dokuz, A.S.; Ecemis, A.; Gokcek, M. Wind power forecasting based on daily wind speed data using machine learning algorithms. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 198, 111823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.; Dávila, C.; Laura, W.; Cubas Saucedo, F.; Ávalos, G.; López, C.; Villena, D.; Valdez, M.; Urbiola, J.; Trebejo, I.; et al. Climas del Perú: Mapa de Clasificación Climática Nacional; SENAMHI: Lima, Peru, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Igual, L.; Segui, S. Introduction to Data Science: A Python Approach to Concepts, Techniques and Applications; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.V. Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cover, T.; Hart, P. Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory. 1967, 13, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Kumar, V.; Ross Quinlan, J.; Ghosh, J.; Yang, Q.; Motoda, H.; MCLachlan, G.J.; Ng, A.; Liu, B.; Yu, P.S.; et al. Top 10 Algorithms in Data Mining. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2008, 14, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalev-Shwartz, S.; Ben-David, S. Understanding Machine Learning: From Theory to Algorithms; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, H.R.; Dandy, G.C. Neural networks for the prediction and forecasting of water resources variables: A review of modelling issues and applications. Environ. Model. Softw. 2000, 15, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, H.R.; Jain, A.; Dandy, G.C.; Sudheer, K.P. Methods used for the development of neural networks for the prediction of water resource variables in river systems: Current status and future directions. Environ. Model. Softw. 2010, 25, 891–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulli, A.; Kapoor, A.; Pal, S. Deep Learning with TensorFlow 2 and Keras, 2nd ed.; Packt Publishing Ltd.: Birmingham, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Heddam, S. Modelling hourly dissolved oxygen concentration (DO) using dynamic evolving neural-fuzzy inference system (DENFIS)-based approach: Case study of Klamath River at Miller Island Boat Ramp, OR, USA. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 9212–9227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cybenko, G. Approximation by superpositions of a sigmoidal function. Math. Control Signals Syst. 1989, 2, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornik, K.; Stinchcombe, M.; White, H. Multilayer feedforward networks are universal approximators. Neural Netw. 1989, 2, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, C.C. Neural Networks and Deep Learning: A Textbook; Springer: Ney York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kling, H.; Fuchs, M.; Paulin, M. Runoff conditions in the upper Danube basin under an ensemble of climate change scenarios. J. Hydrol. 2012, 424, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, W.; Williams, G.P.; Jackson, E.; Nelson, E.J.; Ames, D.P. Hydrostats: A Python package for characterizing errors between observed and predicted time series. Hydrology 2018, 5, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Combination | Models | Input Combinations | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | KNN1 | ANN1 | |
| 2 | KNN2 | ANN2 | |
| 3 | KNN3 | ANN3 | |
| Metrics | Equation 1 | Optimal Value |
|---|---|---|
| Anomaly correlation coefficient (ACC) | ±1 | |
| Nash–Sutcliffe Efficiency (NSE) | 1 | |
| Kling–Gupta efficiency (KGE’) | 1 | |
| Mean absolute error (MAE) | 0 | |
| Spectral angle (SA) | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lujano, E.; Lujano, R.; Huamani, J.C.; Lujano, A. Assessment of Machine Learning Techniques to Estimate Reference Evapotranspiration at Yauri Meteorological Station, Peru. Environ. Earth Sci. Proc. 2025, 32, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025032020
Lujano E, Lujano R, Huamani JC, Lujano A. Assessment of Machine Learning Techniques to Estimate Reference Evapotranspiration at Yauri Meteorological Station, Peru. Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings. 2025; 32(1):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025032020
Chicago/Turabian StyleLujano, Efrain, Rene Lujano, Juan Carlos Huamani, and Apolinario Lujano. 2025. "Assessment of Machine Learning Techniques to Estimate Reference Evapotranspiration at Yauri Meteorological Station, Peru" Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings 32, no. 1: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025032020
APA StyleLujano, E., Lujano, R., Huamani, J. C., & Lujano, A. (2025). Assessment of Machine Learning Techniques to Estimate Reference Evapotranspiration at Yauri Meteorological Station, Peru. Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings, 32(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025032020






