Continuous Wave Magnetron Technologies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Injection-Locked CW Magnetron
2.1. Magnetron Operation Characteristics
2.1.1. Operating Parameters of Magnetron
2.1.2. Frequency Characteristics of Magnetrons
2.2. Injection-Locked Magnetron
2.2.1. Development of Injection-Locked Magnetron
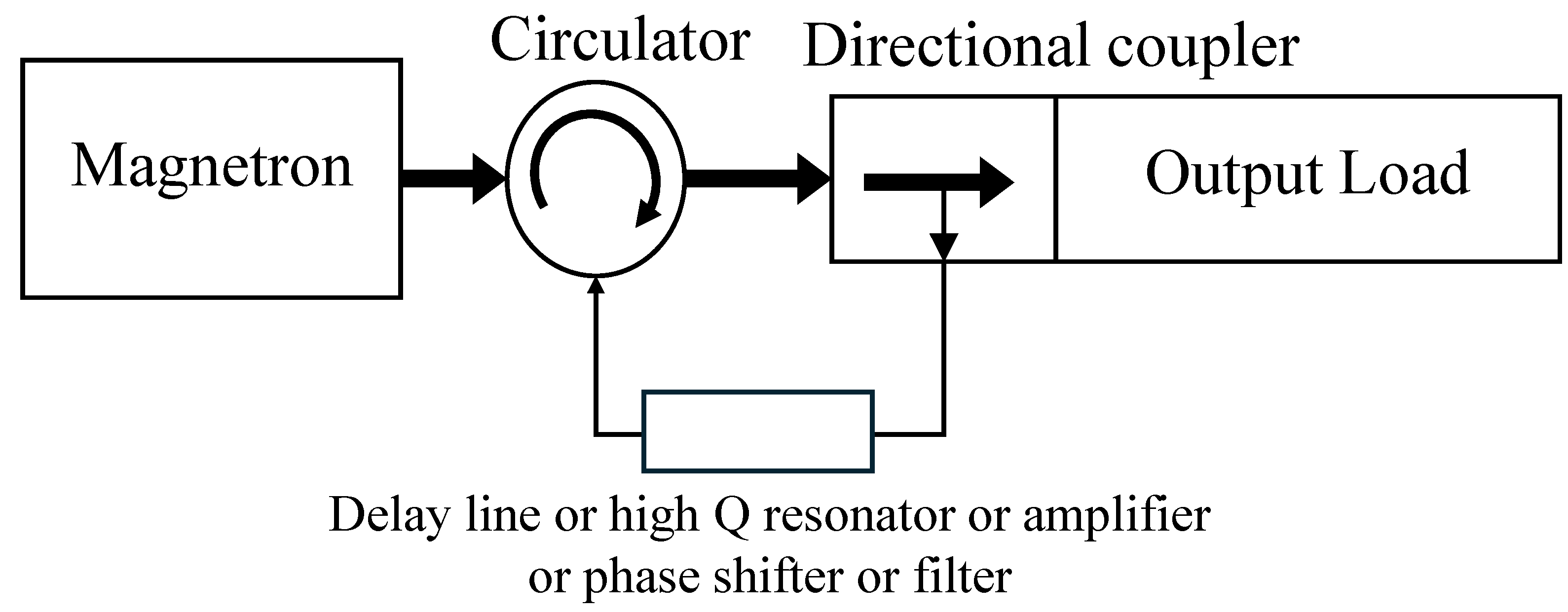
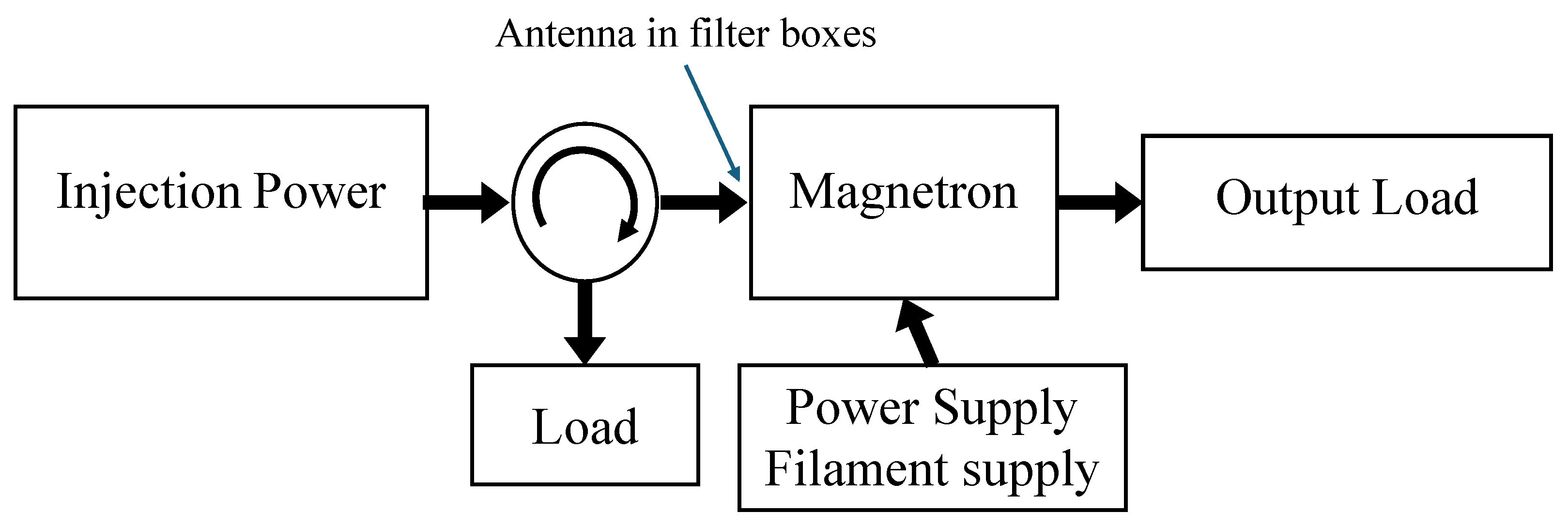
2.2.2. Injection-Locked Magnetron Method
2.3. Phase-Locked CW Magnetron
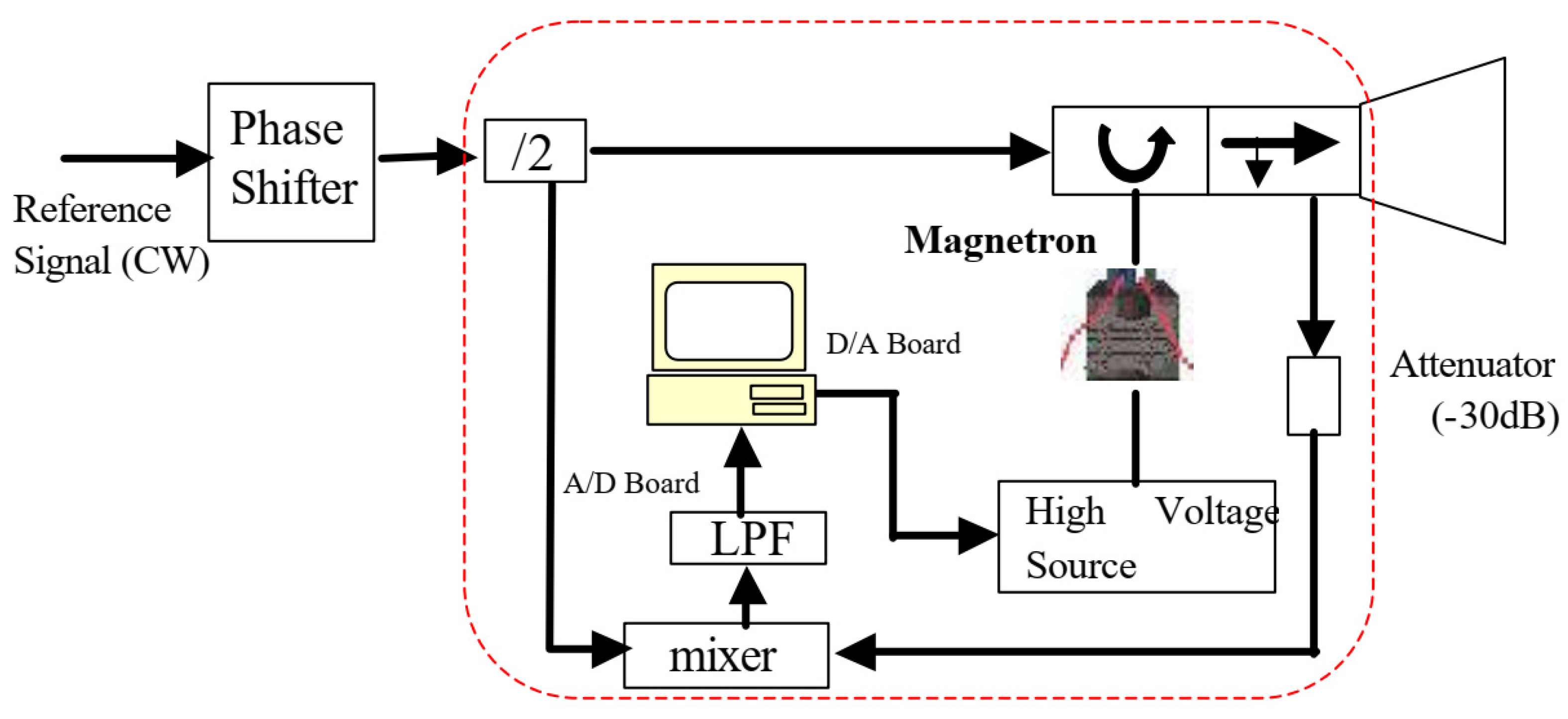
2.3.1. Phase-Locked of Magnetron
2.3.2. Phase-Locked CW Magnetron for Accelerator
2.3.3. Injection-Locked Magnetron Modulator
3. Power Combining of Multiple Magnetrons
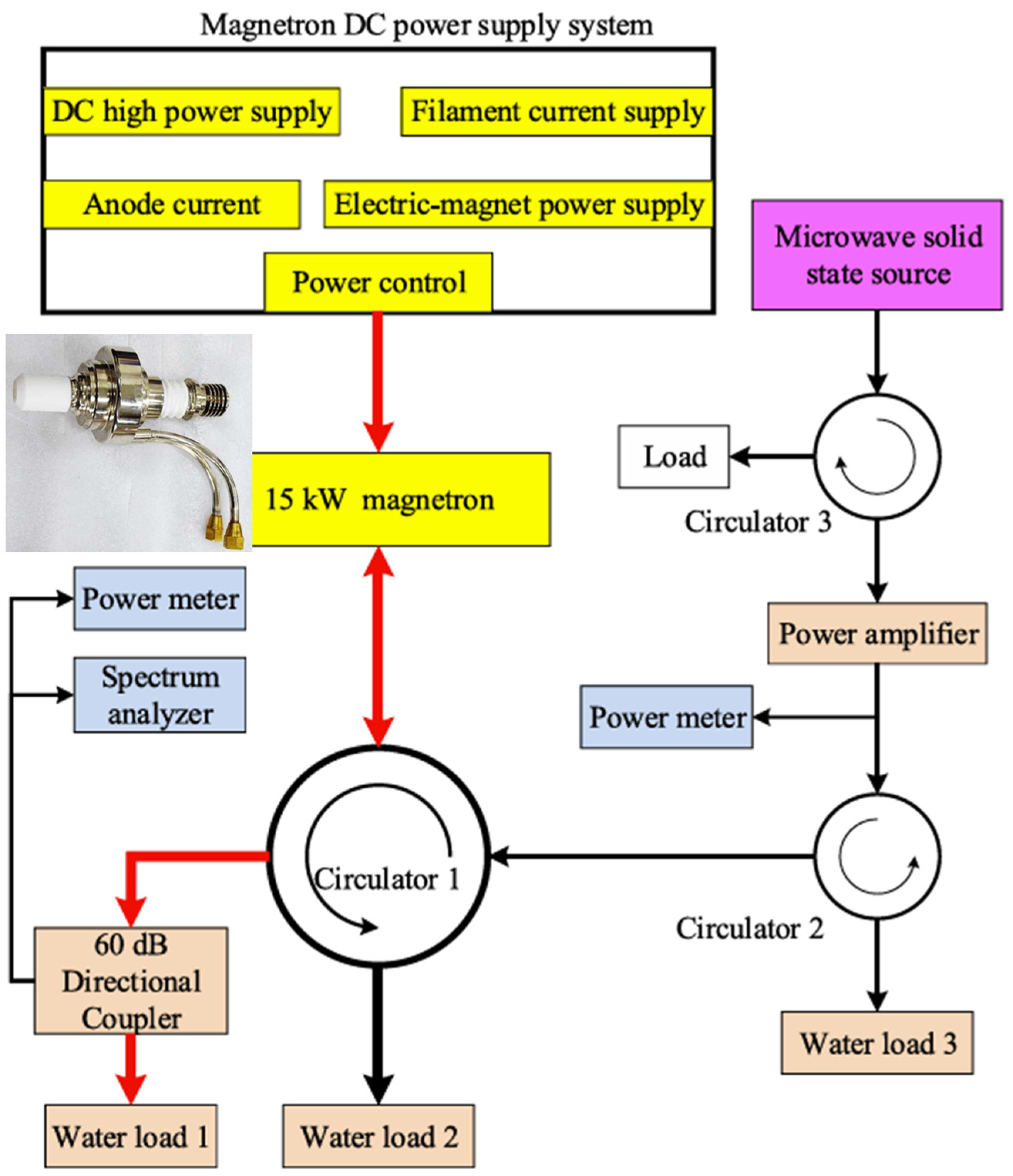
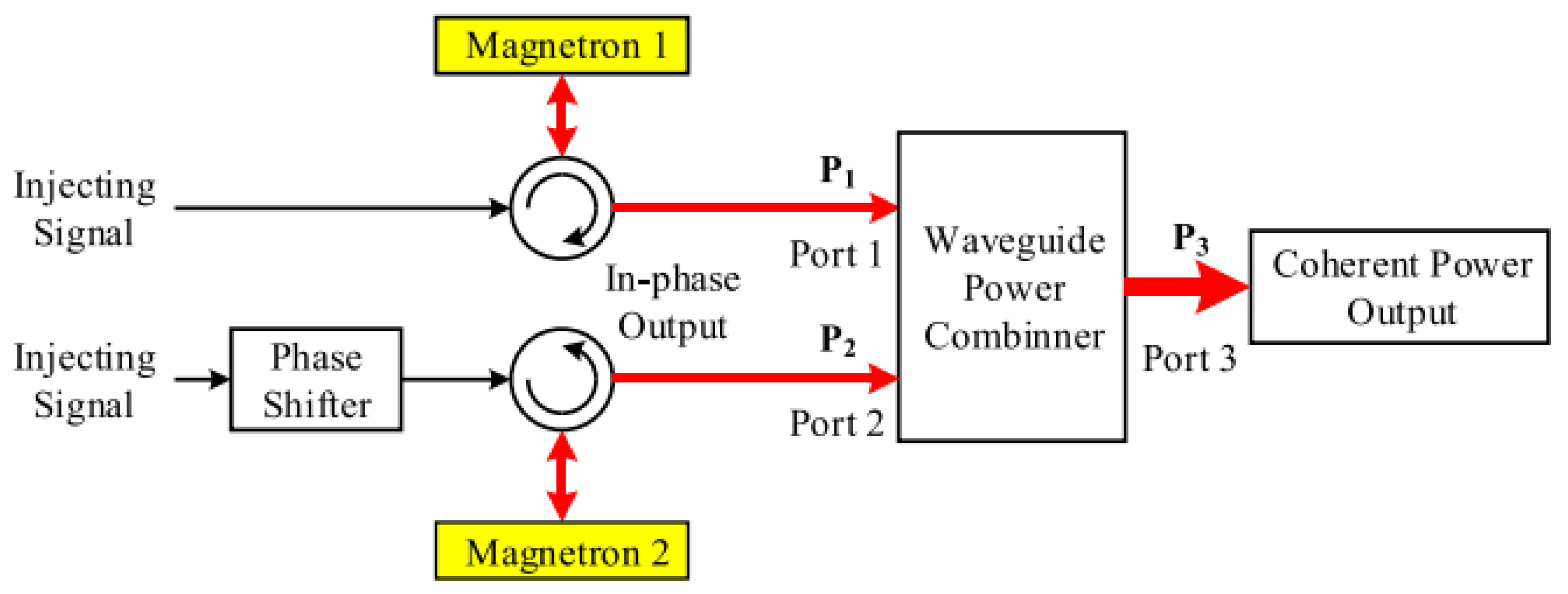
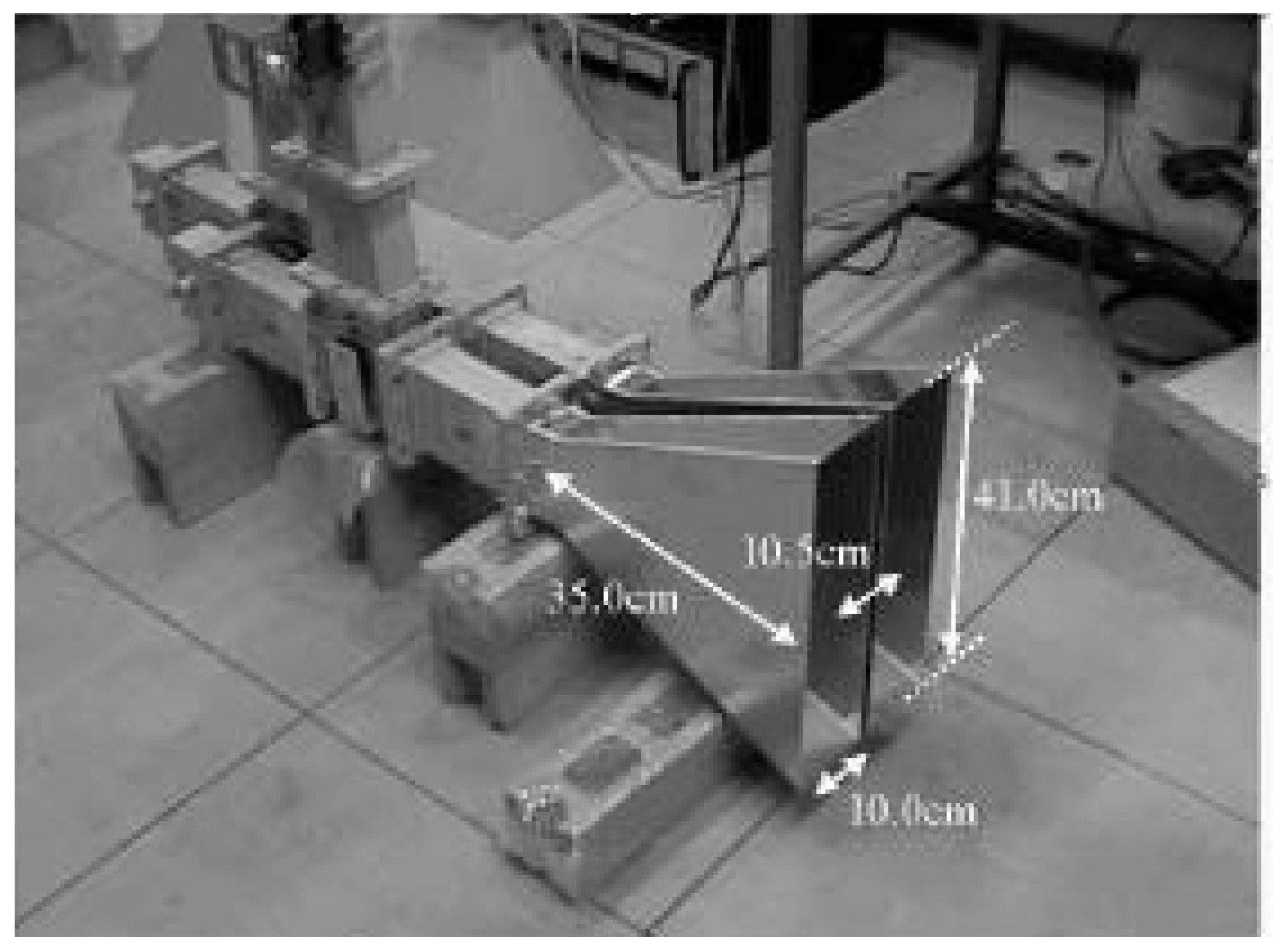
3.1. Injection-Locked Magnetron Power Combining Based on Waveguides
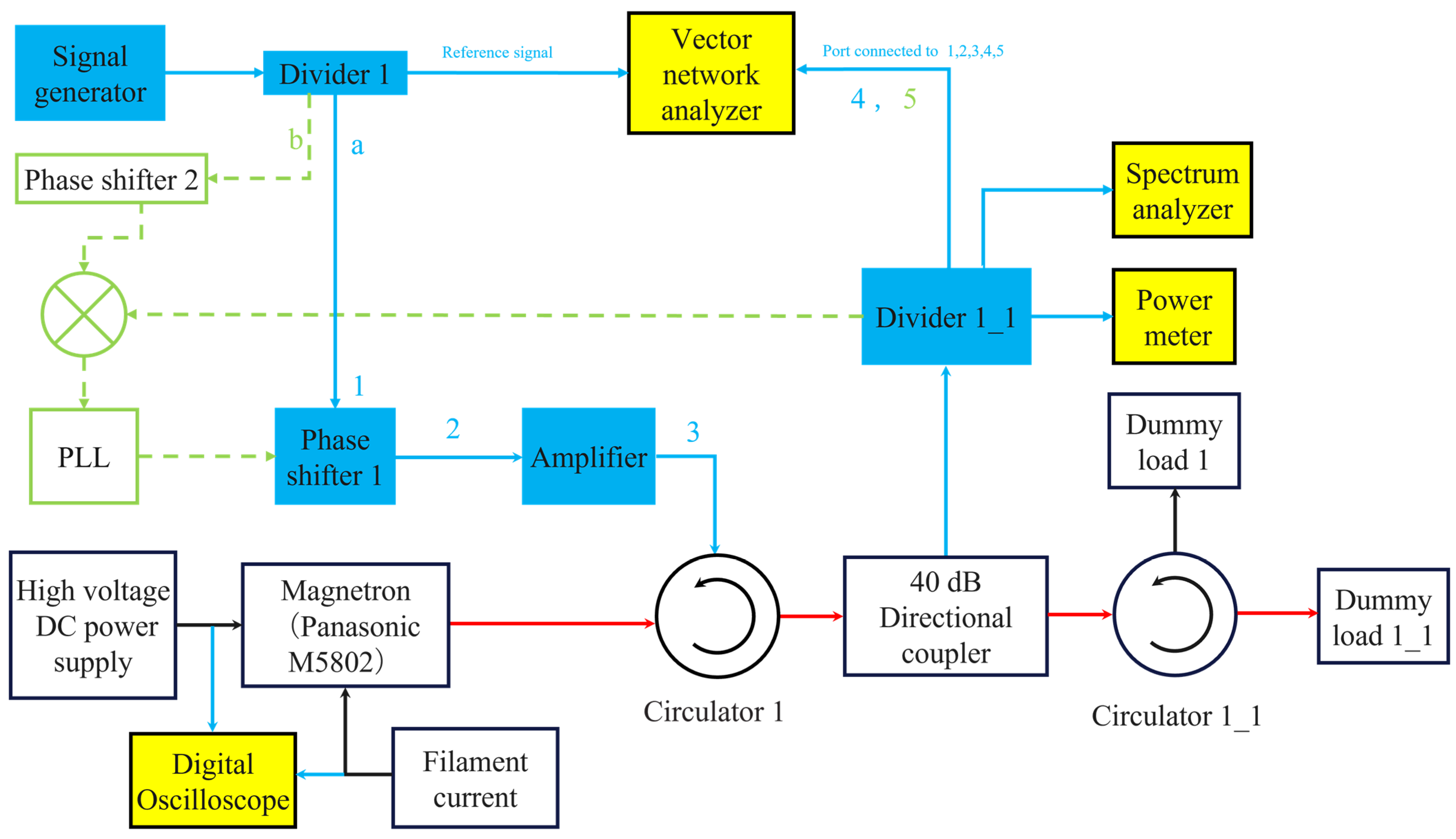
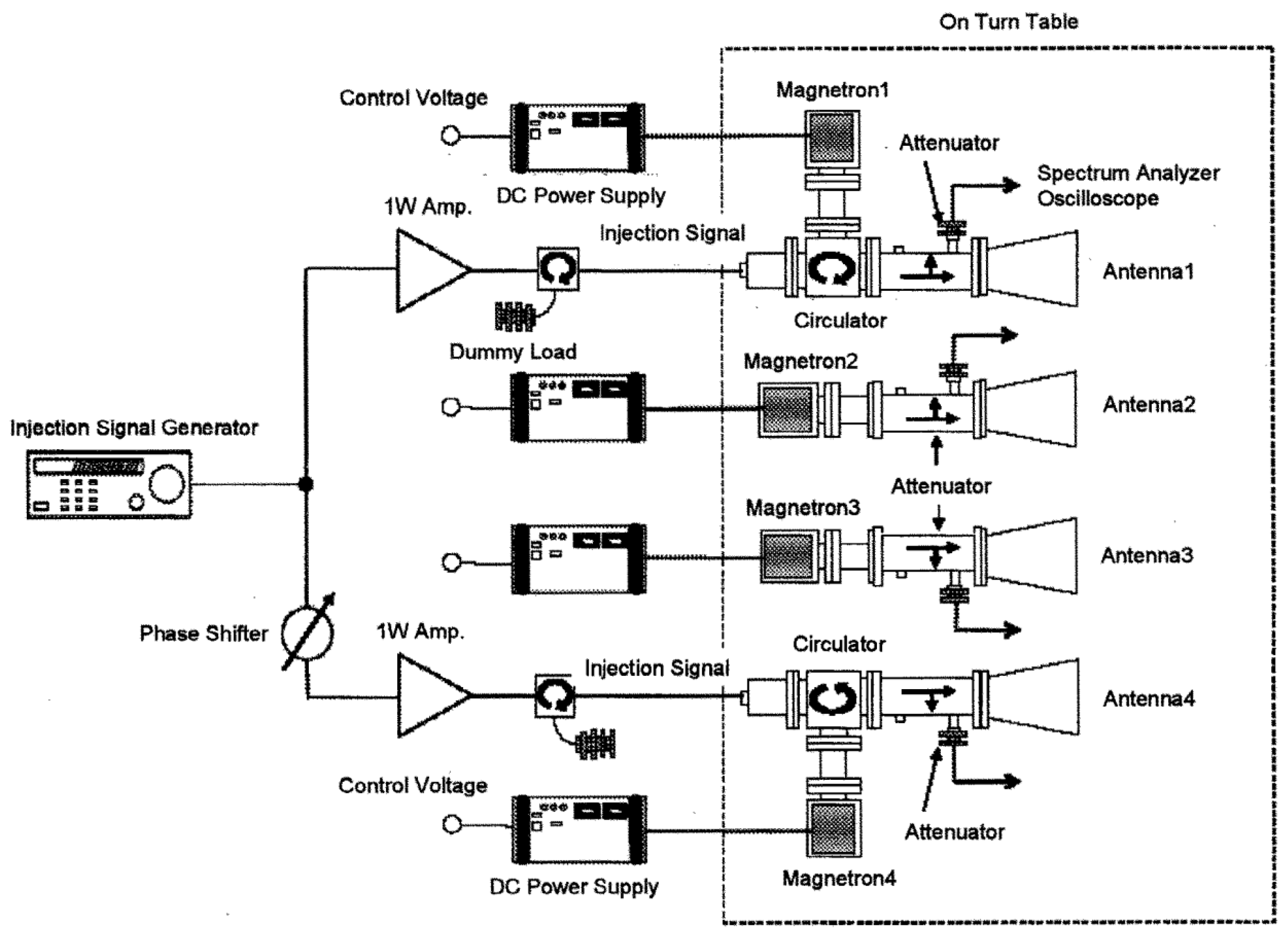
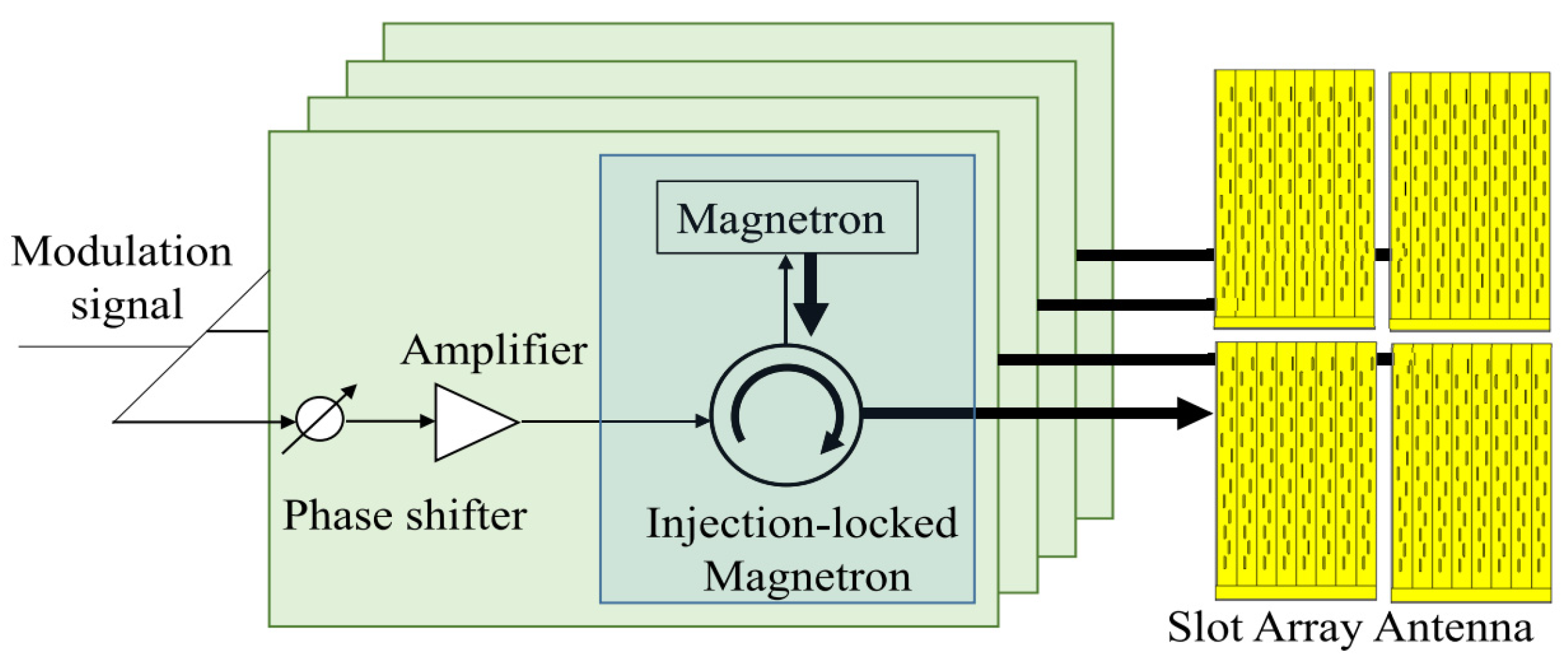
3.2. CW Magnetron Active Phased Array for WPT
4. Next-Generation Magnetron Prospects
4.1. Innovative Operations of CW Magnetron
4.2. Prospects of the Next-Generation Magnetron
- (1)
- Device-level improvements:
- (2)
- External operating-parameter control:
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gilmour, A.S. Microwave and Millimeter-Wave Vacuum Electron Devices: Inductive Output Tubes, Klystrons, Traveling-Wave Tubes, Magnetrons, Crossed-Field Amplifiers, and Gyrotrons; Artech: Tokyo, Japan, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Changjun, L. Microwave—A New Open Access Journal for Microwave Technologies. Microwave 2025, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitani, T.; Shinohara, N.; Matsumoto, H.; Aiga, M.; Kuwahara, N.; Handa, T. Time domain analysis of noises generated from microwave oven magnetron. Electron. Commun. Jpn. Pt. II-Electron. 2005, 88, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Mitani, T.; Shinohara, N.; Zhang, H. High-Power Simultaneous Wireless Information and Power Transfer: Injection-Locked Magnetron Technology. ZTE Commun. 2022, 20, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Mitani, T.; Shinohara, N. Experimental study on frequency modulation of an injection-locked magnetron based on full wave voltage doubler. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Vacuum Electronics Conference (IVEC), Monterey, CA, USA, 24–26 April 2018; pp. 251–252. [Google Scholar]
- Middleton, D.; Gottschalk, W.M.; Wiesner, J.B. Noise in CW Magnetrons. J. Appl. Phys. 1953, 24, 1065–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, N.; Matsumoto, H. Design of space solar power system (SSPS) with phase and amplitude controlled magnetron. In Proceedings of the 2004 Asia-Pacific Radio Science Conference, Qingdao, China, 24–27 August 2004; pp. 624–626. [Google Scholar]
- Mitani, T.; Kawasaki, H.; Shinohara, N.; Matsumoto, H. A Study of Oven Magnetrons toward a Transmitter for Space Applications. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Vacuum Electronics Conference, Rome, Italy, 28–30 April 2009; pp. 323–324. [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara, N.; Matsumoto, H. Research of Magnetron Phased Array with Mutual Injection Locking for Space Solar Power Satellite/Station. Electr. Eng. Jpn. 2010, 173, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakevich, G.; Johnson, R.; Flanagan, G.; Marhauser, F.; Yakovlev, V.; Chase, B.; Nagaitsev, S.; Pasquinelli, R.; Wolff, D. High-Power Magnetron RF Source For Superconducting Linacs of ADS and Intensity-Frontier Projects; Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (FNAL): Batavia, IL, USA, 2013.
- Huang, H.; Yang, B.; Shinohara, N.; Liu, C. Coherent Power Combining of Four-Way Injection-Locked 5.8-GHz Magnetrons Based on a Five-Port Hybrid Waveguide Combiner. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2024, 72, 4395–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Chen, X.; Chu, J.; Mitani, T.; Shinohara, N. A 5.8-GHz Phased Array System Using Power-Variable Phase-Controlled Magnetrons for Wireless Power Transfer. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2020, 68, 4951–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitani, T. Microwave tube transmitters. In Recent Wireless Power Transfer Technologies via Radio Waves, Proceedings of the Sixth International Vacuum Electronics Conference IVEC, Monterey, CA, USA, 25–29 April 2022; River Publishers: Aalborg, Denmark, 2022; pp. 49–69. [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara, N. Trends in Wireless Power Transfer: WPT Technology for Energy Harvesting, Millimeter-Wave/THz Rectennas, MIMO-WPT, and Advances in Near-Field WPT Applications. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2021, 22, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Liao, C.; He, Z.; Yan, L.; Liu, C. High-Efficiency Ultrawideband Microwave Rectifier Based on Adaptive Harmonic Control. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2025, 73, 10017–10027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, N.; Matsumoto, H.; Hashimoto, K. Phase-controlled magnetron development for SPORTS: Space power radio transmission system. URSI Radio Sci. Bull. 2004, 2004, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitani, T.; Shinohara, N.; Matsumoto, H. Development of a pulse-driven phase-controlled magnetron. In Proceedings of the Eighth IEEE International Vacuum Electronics Conference, Kitakyushu, Japan, 15–17 May 2007; pp. 425–426. [Google Scholar]
- Mitani, T.; Shinohara, N.; Hashimoto, K. A Fundamental Study on Spectral Purity of a CW Magnetron for Microwave Power Transmission. In Proceedings of the XXIX URSI General Assembly, Chicago IL, USA, 7–16 August 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, G.B. Microwave Magnetrons; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1948; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Hull, A.W. The magnetron. Am. Inst. Electr. Eng. J. 1921, 40, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengvanich, P. Theory of Injection Locking and Rapid Start-Up of Magnetrons, and Effects of Manufacturing Errors in Terahertz Traveling Wave Tubes. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Welch, H.W. Prediction of Traveling Wave Magnetron Frequency Characteristics: Frequency Pushing and Voltage Tuning. Proc. IRE 1953, 41, 1631–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Lai, S.; Wang, G.; Zhu, H.; Yang, Y. Influence of Power Supply Ripple on Injection Locking of Magnetron with Frequency Pushing Effect. Processes 2022, 10, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neculaes, V.B.; Jones, M.C.; Gilgenbach, R.M.; Lau, Y.Y.; Luginsland, J.W.; Hoff, B.W.; White, W.M.; Jordan, N.M.; Pengvanich, P.; Hidaka, Y.; et al. Magnetic priming effects on noise, startup, and mode competition in magnetrons. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2005, 33, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Mitani, T.; Shinohara, N. Evaluation of the Modulation Performance of Injection-Locked Continuous-Wave Magnetrons. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2019, 66, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitani, T.; Shinohara, N.; Matsumoto, H.; Hashimoto, K. Experimental study on oscillation characteristics of magnetron after turning off filament current. Electron. Commun. Jpn. (Part II Electron.) 2003, 86, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, W.C. The high signal to noise ratio of the microwave oven magnetron and evidence of a negative feedback loop to control it. In Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop Crossed-Field Devices, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 15–16 August 1995; pp. 178–187. [Google Scholar]
- Neculaes, V.B.; Jones, M.C.; Gilgenbach, R.W.; Lau, Y.Y.; Luginsland, J.W.; Hoff, B.W.; White, W.M.; Jordan, N.M.; Pengvanich, P.; Hidaka, Y.; et al. Magnetic perturbation effects on noise and startup in DC-operating oven magnetrons. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2005, 52, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, R. A study of locking phenomena in oscillators. Proc. IRE 1946, 34, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengvanich, P.; Neculaes, V.B.; Lau, Y.Y.; Gilgenbach, R.M.; Jones, M.C.; White, W.M.; Kowalczyk, R.D. Modeling and experimental studies of magnetron injection locking. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 114903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, I.; Dexter, A.; Carter, R. Frequency and phase modulation performance of an injection-locked CW magnetron. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2006, 53, 1721–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengvanich, P.; Lau, Y.Y.; Luginsland, J.W.; Gilgenbach, R.M.; Cruz, E.; Schamiloglu, E. Effects of frequency chirp on magnetron injection locking. Phys. Plasmas 2008, 15, 073110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vito, P.; Kearns, W.; Seavey, M. Phase pattern control of injection-locked pulsed magnetrons. Proc. IEEE 1969, 57, 1436–1437. [Google Scholar]
- Slater, J.C. The Phasing of Magnetrons; Technical Report NO. 35; Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1947. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, D.H.; Lau, Y.Y.; Greening, G.; Wong, P.; Hoff, B.W.; Gilgenbach, R.M. Stability of Brillouin flow in planar, conventional, and inverted magnetrons. Phys. Plasmas 2015, 22, 082104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, K.D. Inter-injection-locked oscillators for power combining and phased arrays. Microw. Theory Tech. IEEE Trans. 1986, 34, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar]
- Paciorek, L.J. Injection locking of oscillators. Proc. IEEE 1965, 53, 1723–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, E.E. RF phase control in pulsed magnetrons. Proc. IRE 1952, 40, 669–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seavey, M.H. Some properties of an injection-locked pulsed magnetron in a coherent-echo-detection system. Electron. Lett. 1967, 3, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devito, P.A. Some Properties of an Injection-Locked Pulsed Magnetron; DTIC Document: Fort Belvoir, VA, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, W.C. The microwave magnetron and its derivatives. Electron Devices IEEE Trans. 1984, 31, 1595–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, W.C. Phase-Locked Magnetron System. U.S. Patent 4571552A, 18 February 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, W.C. Magnetron Amplifier Power Combiner. U.S. Patent 4634992A, 6 January 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, W.C. Magnetron Amplifier. U.S. Patent 2673306A, 6 July 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, W.C. The Magnetron—A Low Noise, Long Life Amplifier. Appl. Microw. 1990, 117, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Overett, T.; Remsen, D.; Bowles, E.; Thomas, G.; Smith, R., III. Phase Locked Magnetrons as Accelerator RF Sources. In Proceedings of the 12th IEEE Particle Accelerator Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 16–19 March 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Benford, J.; Smith, R.R.; Sze, H.; Harteneck, B.; Woo, W. Phase-locking of relativistic magnetrons. In Proceedings of the Microwave and Particle Beam Sources and Propagation, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 13–15 January 1988; pp. 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Benford, J.; Sze, H.; Woo, W.; Smith, R.R.; Harteneck, B. Phase locking of relativistic magnetrons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1989, 62, 969–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, J.S.; Benford, J.; Cooksey, N.; Harteneck, B.; Smith, R.R.; Sze, H. Phase-locking of multiple relativistic magnetrons. In Proceedings of the IEEE 1989 International Conference on Plasma Science, Buffalo, NY, USA, 22–24 May 1989; p. 122. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.C.; Bekefi, G.; Temkin, R.J. Injection locking of a long-pulse relativistic magnetron. In Proceedings of the 1991 IEEE Particle Accelerator Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 6–9 May 1991; pp. 751–753. [Google Scholar]
- Strassner, B.; Chang, K. Microwave Power Transmission: Historical Milestones and System Components. Proc. IEEE 2013, 101, 1379–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metaxas, A.C.; Meredith, R.J. Industrial Microwave Heating; The Institution of Engineering and Technology: London, UK, 1988; p. 376. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, N.; Fujiwara, T.; Morita, T.; Kishimoto, A.; Hasegawa, K.; Takagi, Y.; Ohta, Y. Phase-Locked Magnetrons for Beam Combining in High Power Antenna Array on MPT System. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference (APMC), Singapore, 10–13 December 2019; pp. 905–907. [Google Scholar]
- Neubauer, M.; Popovic, M.; Johnson, R.P. Phase and Frequency locked magnetron. In Proceedings of the IPAC2012, New Orleans, LA, USA, 20–25 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Heng-Chia, C. Stability analysis of self-injection-locked oscillators. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2003, 51, 1989–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng-Chia, C. Phase noise in self-injection-locked oscillators—Theory and experiment. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2003, 51, 1994–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yuan, P.; Ye, W.; Zhu, H.; Yang, Y.; Huang, K. Frequency qusai locking and noise reduction of the self-injection qusai locked magnetron. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2016, 51, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, E.J.; Hoff, B.W.; Pengvanich, P.; Lau, Y.Y.; Gilgenbach, R.M.; Luginsland, J.W. Experiments on peer-to-peer locking of magnetrons. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 191503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengvanich, P.; Lau, Y.Y.; Cruz, E.; Gilgenbach, R.M.; Hoff, B.; Luginsland, J.W. Analysis of peer-to-peer locking of magnetrons. Phys. Plasmas 2008, 15, 103104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, W.; Zhu, H.; Huang, K.; Yang, Y. Power-combining based on master-slave injection-locking magnetron. Chin. Phys. B 2016, 25, 078402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, N.; Fujiwara, J.; Matsumoto, H. Development of active phased array with phase-controlled magnetrons. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Antennas and Propagations, Beijing, China, 15–18 August 2000; pp. 713–716. [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara, N.; Matsumoto, H. Microwave power transmission system with phase and amplitude controlled magnetrons. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Recent Advances in Space Technologies, Istanbul, Turkey, 9–11 June 2005; pp. 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.J.; Choi, G.W. Experimental observation of frequency locking and noise reduction in a self-injection-locked magnetron. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2007, 54, 3430–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Huang, K.; Liu, C. Experimental Study on the Phase Deviation of 20-kW S-Band CW Phase-Locked Magnetrons. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2018, 28, 509–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cai, Z.; Pei, N.; Tan, Z.; Liu, C. Performance Evaluation of a 20-kW Injection-locked Magnetron with Load-Pull Characterization. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE MTT-S International Wireless Symposium (IWS), Nanjing, China, 23–26 May 2021; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, S.; Maitani, M.M.; Suzuki, E.; Chonan, S.; Fukui, M.; Wada, Y. Injection-Locked Magnetron Using a Cross-Domain Analyzer. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2016, 26, 966–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Liu, L.; Huo, F.; Liu, Z.; Liu, C. Microwave power combining system based on two injection-locked 15 kW CW magnetrons. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 17–22 May 2015; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Huang, H.; Liu, Z.; Huo, F.; Huang, K. Experimental Study on Microwave Power Combining Based on Injection-Locked 15-kW S-Band Continuous-Wave Magnetrons. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2016, 44, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yang, B.; Shinohara, N.; Liu, C. Modeling and Experiments of an Injection-Locked Magnetron With Various Load Reflection Levels. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2020, 67, 3802–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wei, Y.; Chen, X.; Huang, K.; Liu, C. Simulation and Experiments of an S-Band 20-kW Power-Adjustable Phase-Locked Magnetron. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2017, 45, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, M.; Johnson, R.; Moretti, A.; Popovic, M. Phase and Frequency Locked Magnetrons for SRF Sources. In Proceedings of the Particle Accelerator Conference, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 4–8 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Treado, T.A.; Hansen, T.A.; Jenkins, D.J. Power-combining and injection-locking magnetrons for accelerator applications. In Proceedings of the 1991 IEEE Particle Accelerator Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 6–9 May 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.C.; Bekefi, G.; Temkin, R.; de Graff, C. Proposed injection locking of a long pulse relativistic magnetron. In Microwave and Particle Beam Sources and Directed Energy Concepts; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1989; pp. 157–160. [Google Scholar]
- Obata, H.; Tsuji, N.; Furumoto, K. Frequency Bandwidth Narrowing Technology for Pulsed Magnetrons. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2009, 56, 3191–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakevich, G.; Johnson, R.; Yakovlev, V.P.; Chase, B.E.; Pasquinelli, R.J. Modeling of Magnetron Transmitter for the Project X CW 1 GeV Linac; Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (FNAL): Batavia, IL, USA, 2013.
- Tahir, I.; Dexter, A.; Carter, R. Noise performance of frequency- and phase-locked CW magnetrons operated as current-controlled oscillators. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2005, 52, 2096–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Plawski, T.; Rimmer, R.; Dexter, A.; Tahir, I.; Neubauer, M.; Dudas, A. System study using injection phase locked magnetron as an alternative source for superconducting radio frequency accelerator. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Vacuum Electronics Conference, Monterey, CA, USA, 22–24 April 2014; pp. 443–444. [Google Scholar]
- Dexter, A.C.; Burt, G.; Carter, R.G.; Tahir, I.; Wang, H.; Davis, K.; Rimmer, R. First demonstration and performance of an injection locked continuous wave magnetron to phase control a superconducting cavity. Phys. Rev. Spec. Top.-Accel. Beams 2011, 14, 032001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakevich, G.; Johnson, R.; Flanagan, G.; Marhauser, F.; Neubauer, M.; Yakovlev, V.; Chase, B.; Nagaitsev, S.; Pasquinelli, R.; Solyak, N. A Two-stage injection-locked magnetron for accelerators with superconducting cavities. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1301.6100. [Google Scholar]
- Chase, B.; Pasquinelli, R.; Cullerton, E.; Varghese, P. Precision vector control of a superconducting RF cavity driven by an injection locked magnetron. J. Instrum. 2015, 10, P03007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakevich, G.; Johnson, R.; Khabiboulline, T.; Romanov, G.; Yakovlev, V. Novel Magnetron Operation and Control Methods for Superconducting RF Accelerators; Fermi National Accelerator Lab. (FNAL): Batavia, IL, USA, 2021.
- Yang, B.; Mitani, T.; Shinohara, N. Study on a 5.8GHz Injection-locked Magnetron for Transferring Data. In Proceedings of the 31st International Vacuum Nanoelectronics Conference (IVNC), Kyoto, Japan, 9–13 July 2018; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Mitani, T.; Shinohara, N. Injection-Locked CW Magnetron for a wirelessly-powered TV. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Vacuum Electronics Conference (IVEC), Busan, Republic of Korea, 28 April–1 May 2019; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Chu, J.; Mitani, T.; Shinohara, N. High-Power Simultaneous Wireless Information and Power Transfer System Based on an Injection-Locked Magnetron Phased Array. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2021, 31, 1327–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, S.K.; Maurya, S.; Singh, V.P. Electromagnetic and Particle-in-Cell Simulation Studies of a High Power Strap and Vane CW Magnetron. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2014, 42, 3373–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, J.A.; LeBorgne, R.H.; Eanes, R.M.; Davison, W.W. Broadband power combining of 5.0 kW coupled-cavity communication TWTs. In Proceedings of the 1974 International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), Washington, DC, USA, 9–11 December 1974; pp. 495–497. [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann, R.J.; Borrego, J.M. Power Combining in an Array of Microwave Power Rectifiers. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1979, 27, 958–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, K.J. Microwave Power Combining Techniques. Microw. Theory Tech. IEEE Trans. 1979, 27, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treado, T.A.; Zurk, L.M.; Smith, R.S., III; Hansen, T.A.; Barry, J.D.; Jenkins, D.J.; Thomas, G.E. Experimental results of power combining and phase-locking magnetrons for accelerator applications. In Proceedings of the International Technical Digest on Electron Devices, San Francisco, CA, USA, 9–12 December 1990; pp. 541–544. [Google Scholar]
- Treado, T.A.; Brown, P.D.; Hansen, T.A.; Aiguier, D.J. Phase locking of two long-pulse, high-power magnetrons. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 1994, 22, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Yang, M.; Wu, P.; Huang, K.; Liu, C. Experimental Studies on a Four-Way Microwave Power Combining System Based on Hybrid Injection-Locked 20-kW S-Band Magnetrons. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2019, 47, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yang, B.; Shinohara, N.; Liu, C. A High-Efficiency Microwave Power Combining System Based on Frequency-Tuning Injection-Locked Magnetrons. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2020, 67, 4447–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yang, B.; Shinohara, N.; Liu, C. Low-Noise Dual-Way Magnetron Power-Combining System Using an Asymmetric H-Plane Tee and Closed-Loop Phase Compensation. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2021, 69, 2267–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Shen, Y.; Liao, C.; Jing, J.; Liu, C. A Novel Injection-Locked S-Band Oven Magnetron System Without Waveguide Isolators. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2023, 70, 1886–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernousov, Y. Novel High Power Pulsed Mode Operation of Commercial Continuous-Wave Magnetron. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2022, 70, 826–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, S.K.; Verma, R.K.; Maurya, S.; Singh, V.V.P. Review of Magnetron Developments. Frequenz 2016, 70, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeryomka, V.D.; Dzyuba, V.P. Coaxial cold-cathode magnetron. In Proceedings of the Technical Digest of the 17th International Vacuum Nanoelectronics Conference (IEEE Cat. No.04TH8737), Cambridge, MA, USA, 16 July 2004; pp. 168–169. [Google Scholar]
- Song, M.; Bi, L.; Meng, L.; Qin, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, B.; Li, H.; Yin, Y. High-efficiency phase-locking of millimeter-wave magnetron for high-power array applications. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2021, 42, 1658–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Shinohara, N. Microwave power transmission technologies for space solar power station. Chin. Space Sci. Technol. 2025, 45, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benford, J. History and future of the relativistic magnetron. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on the Origins and Evolution of the Cavity Magnetron (CAVMAG), Bournemouth, UK, 19–20 April 2010; pp. 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, M.C.; Marder, B.M.; Bacon, L.D. Magnetically insulated transmission line oscillator. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1988, 52, 78–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, J.S.; Aiello, N.; Benford, J.; Harteneck, B. Design and operation of a module of phase-locked relativistic magnetrons. J. Appl. Phys. 1991, 70, 2838–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
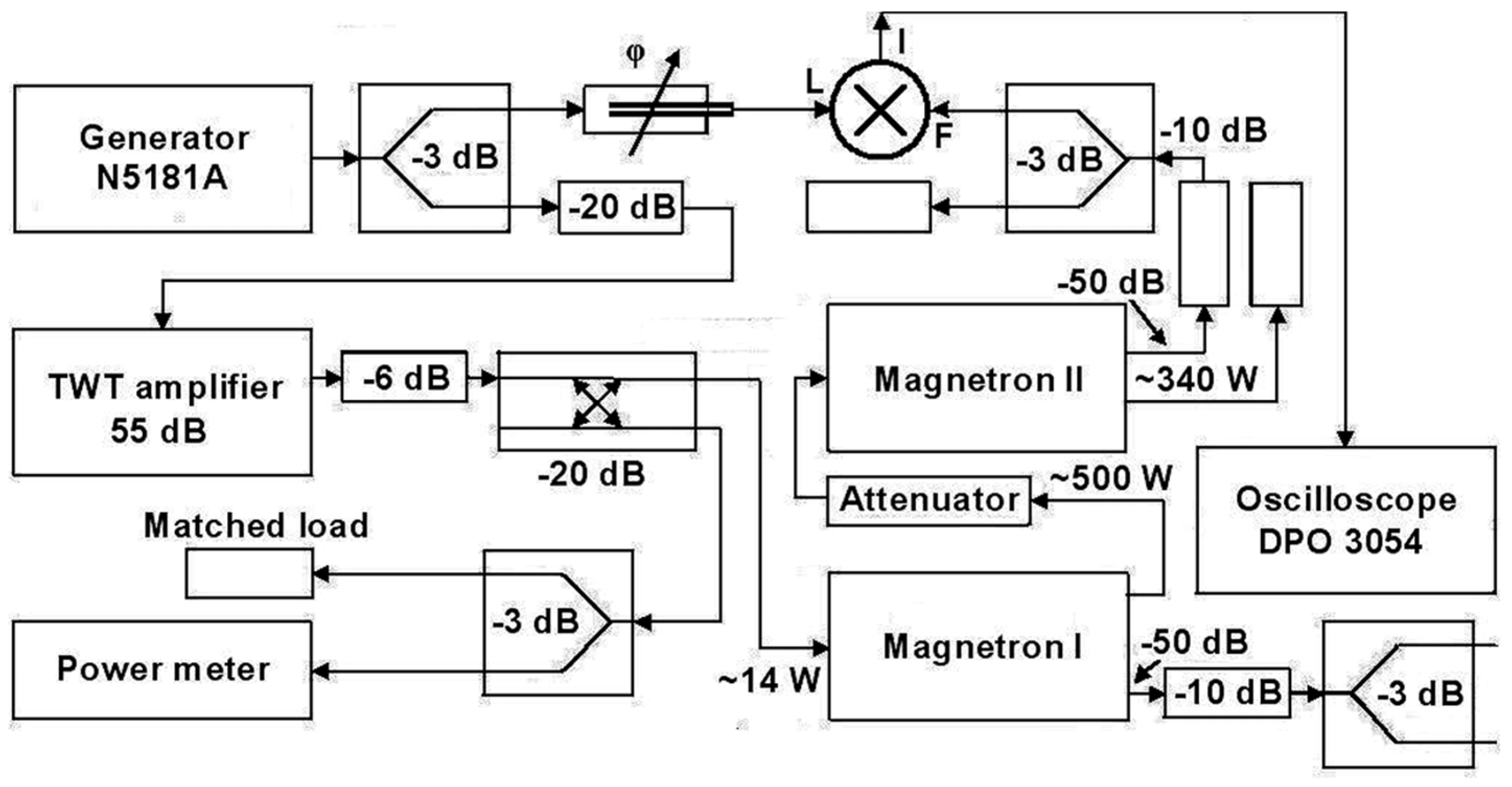
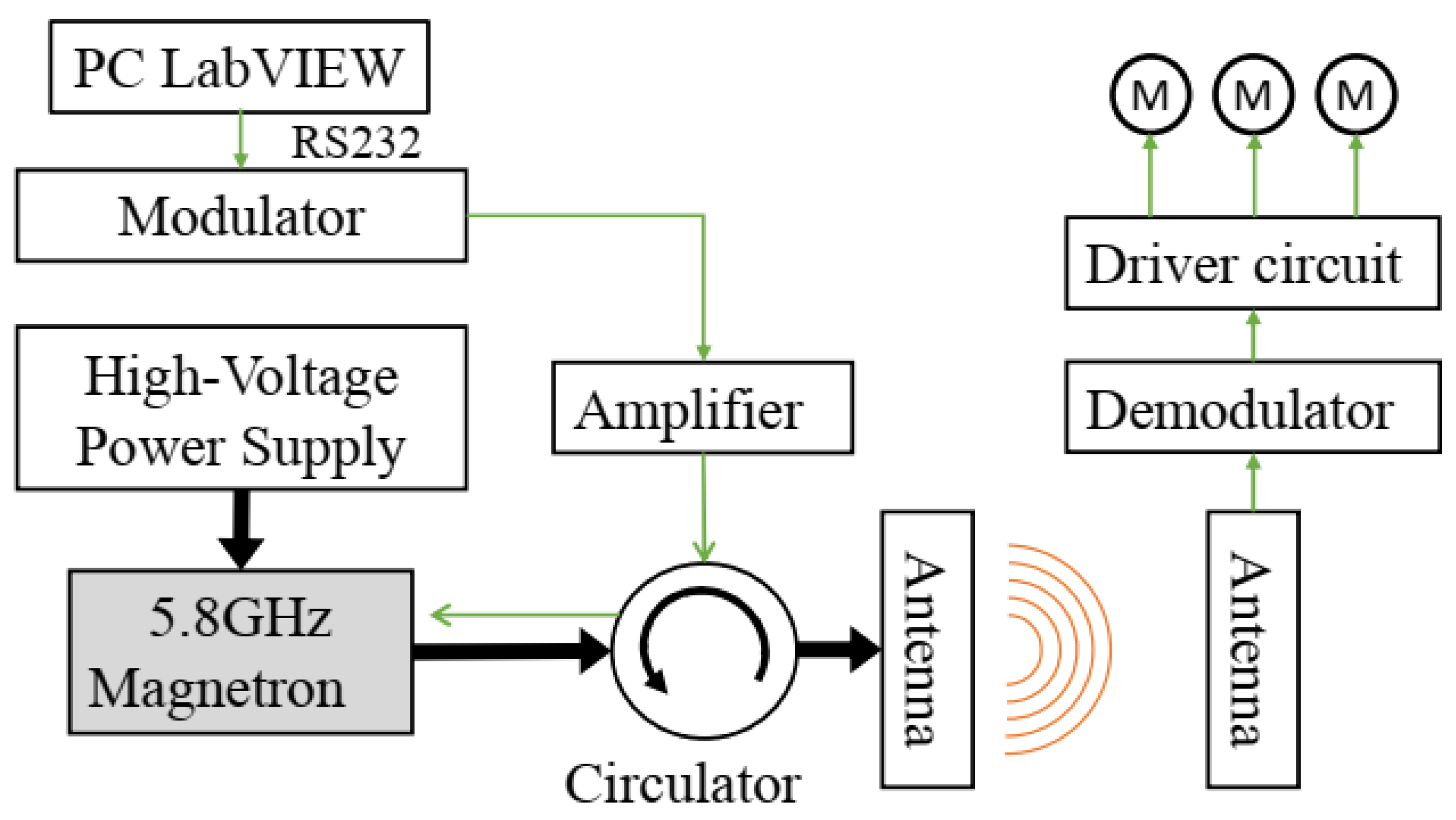
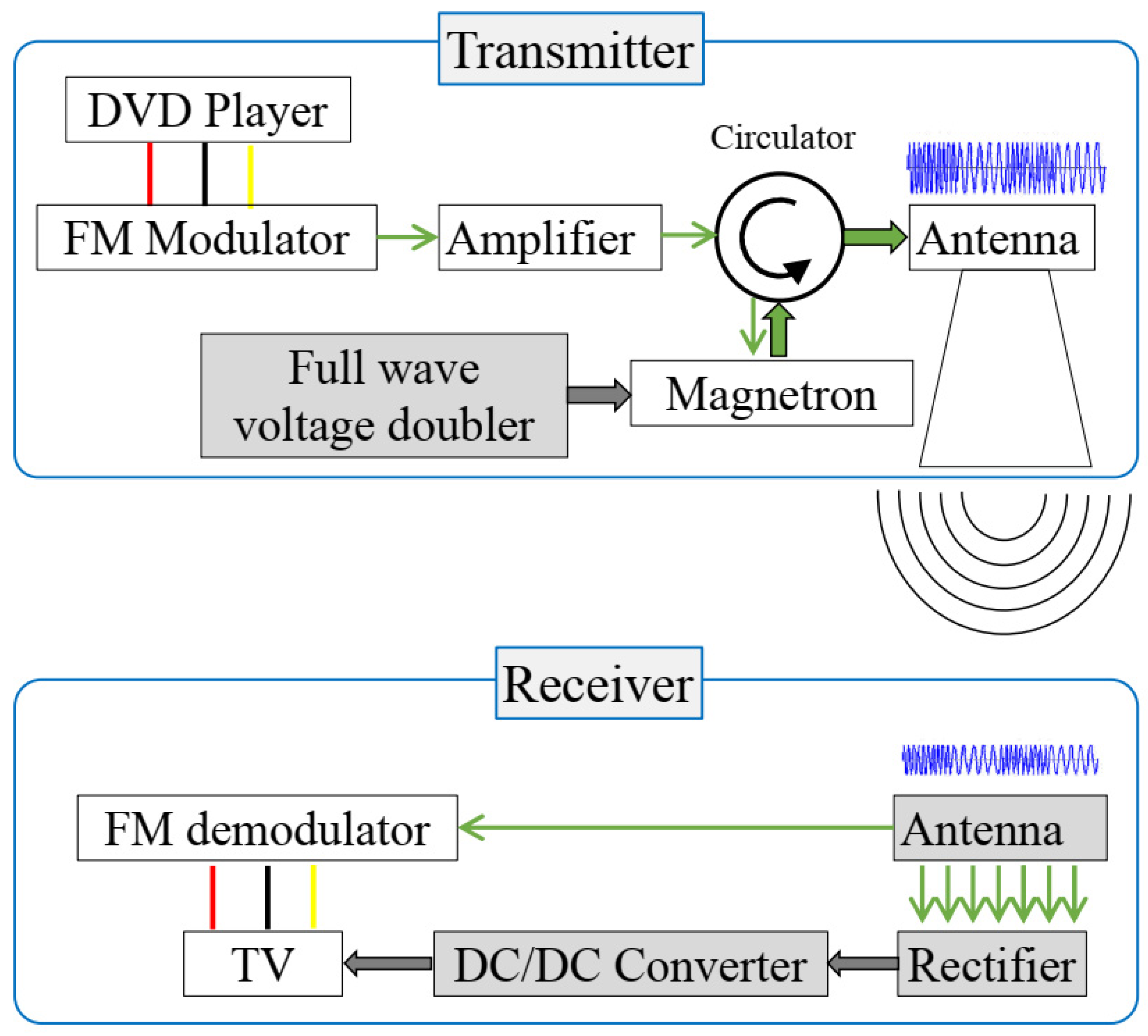
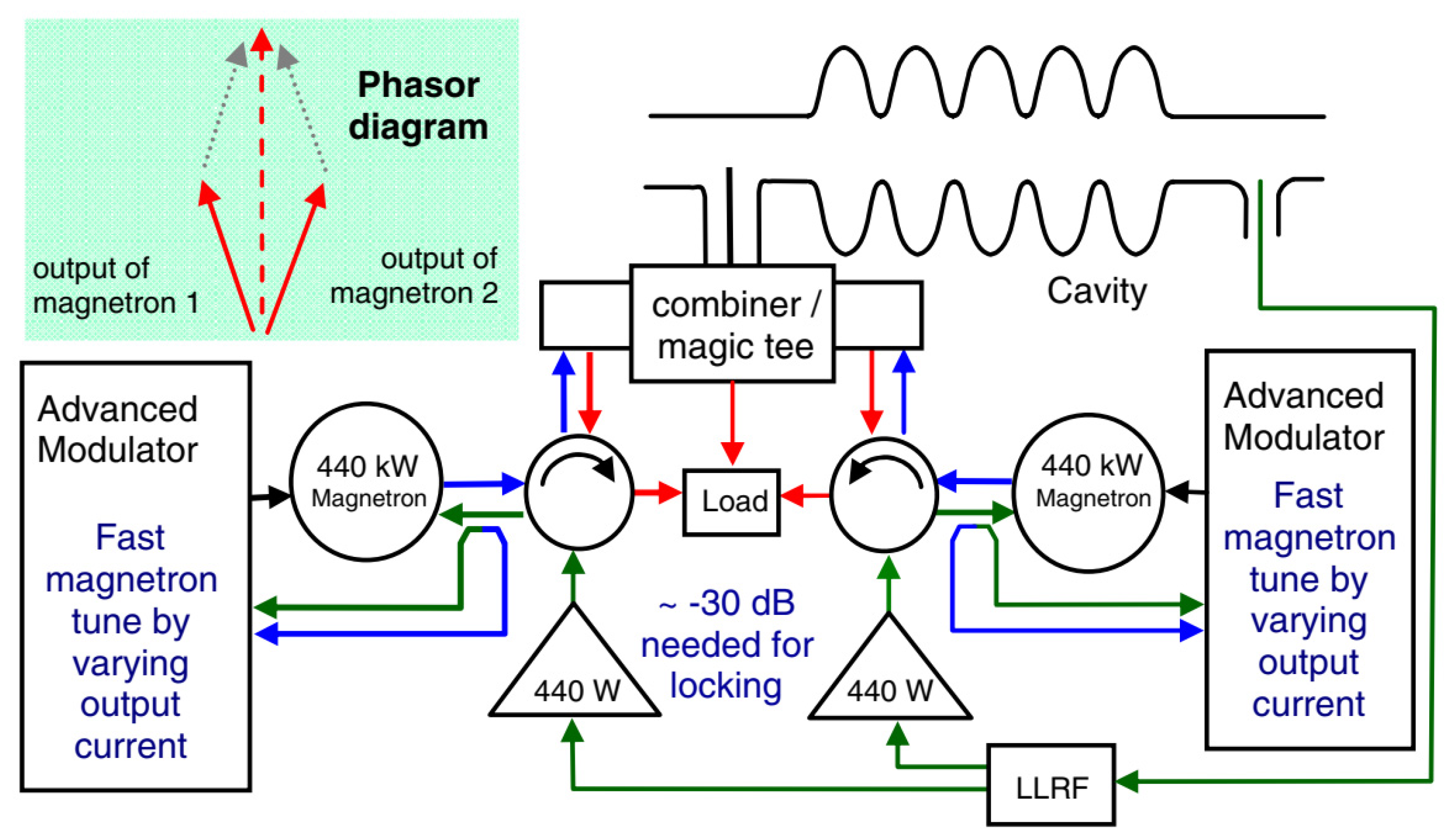
| Reference | Magnetron | Power Output | Injection-Locked Method | Frequency | Injection-Locked Bandwidth |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [63] | LG magnetron | 220 W | Self-injection with a high-Q cavity | 2.455 GHz | 0.12% |
| [30] | National Electronics, SXRH (driver), model HS (oscillator) | 800 W | Oscillator-driver | 2.4478 GHz | / |
| [58] | 2 kW oven magnetron | 300–900 W | Peer-to-peer | 2.44867 GHz; 2.44960 GHz; 2.45067 GHz | / |
| [60] | Panasonic 2M244-M1 | 830 W | Master–slave | 2.4512 GHz | / |
| [57] | Panasonic 2M244-M1 | 1 kW | Self-injection quasi-locked | 2.443 to 2.444 GHz | 0.885–4.7 MHz |
| Ref. | Year | Magnetron Type | Nominal Frequency | Power Output | Injection-Ratio | Locked Frequency | Locked Bandwidth |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [45] | 1990 | Oven magnetron | 2.45 GHz | 500 W | 30 dB | / | / |
| [61] | 2000 | 2M236 | 2.45 GHz | Over 600 W | −30 dB | / | 1.5 MHz |
| [67,68] | 2016 | Nanjing Sanle 15 kW magnetron | 2.45 GHz | Over 12.9 kW | About 0.11 | 2.438–2.4432 GHz | 2–5 MHz |
| [70] | 2017 | Nanjing Sanle 20 kW magnetron | 2.45 GHz | Adjustable | (0.005–0.12 kW)/19.1 kW | 2.439–2.4515 GHz | 11.7–2.4 MHz |
| [69] | 2020 | Panasonic M5802-KRSC1 | 5.8 GHz | 752–768 W; 324–344 W | 0.0075–0.15 | / | About 0~25 MHz |
| [65] | 2021 | Nanjing Sanle 20 kW magnetron | 2.45 GHz | 10–18.3 kW | 0.003 kW/18.3 kW With Load-Pull | 2446 MHz@11.2 kW; 2447.5 MHz@18.3 kW | 3.4–3.9 MHz |
| [11] | 2024 | Panasonic | 5.8 GHz | / | 10 W/300 W | 5.782 GHz | / |
| Refer. | Year | Magnetron | Nominal Frequency | Single Magnetron Power | Combining Ways | Combining Power | Combining Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [67,68] | 2016 | Nanjing Sanle 15 kW magnetron | 2.45 GHz | 12–14 kW | 2 | 25 kW | 95% |
| [91] | 2019 | Nanjing Sanle 20 kW magnetron | 2.45 GHz | 20 kW | 4 | 60 kW | 91.5% |
| [92] | 2020 | Panasonic 2M167B–M32 | 2.45 GHz | 0.98 kW | 2 | 1.8 kW | 94.5% |
| [93] | 2021 | Panasonic 2M167B–M32 | 2.45 GHz | 1 kW | 2 | 1.2–1.58 kW | 95.7% |
| [11] | 2024 | Panasonic M5802 | 5.8 GHz | Adjustable below 360 W | 4 | 1.2 kW | 95–97.7% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Huang, H.; Yang, B.; Shinohara, N. Continuous Wave Magnetron Technologies. Microwave 2026, 2, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/microwave2010003
Huang H, Yang B, Shinohara N. Continuous Wave Magnetron Technologies. Microwave. 2026; 2(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/microwave2010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Heping, Bo Yang, and Naoki Shinohara. 2026. "Continuous Wave Magnetron Technologies" Microwave 2, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/microwave2010003
APA StyleHuang, H., Yang, B., & Shinohara, N. (2026). Continuous Wave Magnetron Technologies. Microwave, 2(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/microwave2010003





