PMSSO-Hydrogels as a Promising Carrier for B12 Vitamin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. B12 Sorption into PMSSO-Hydrogel
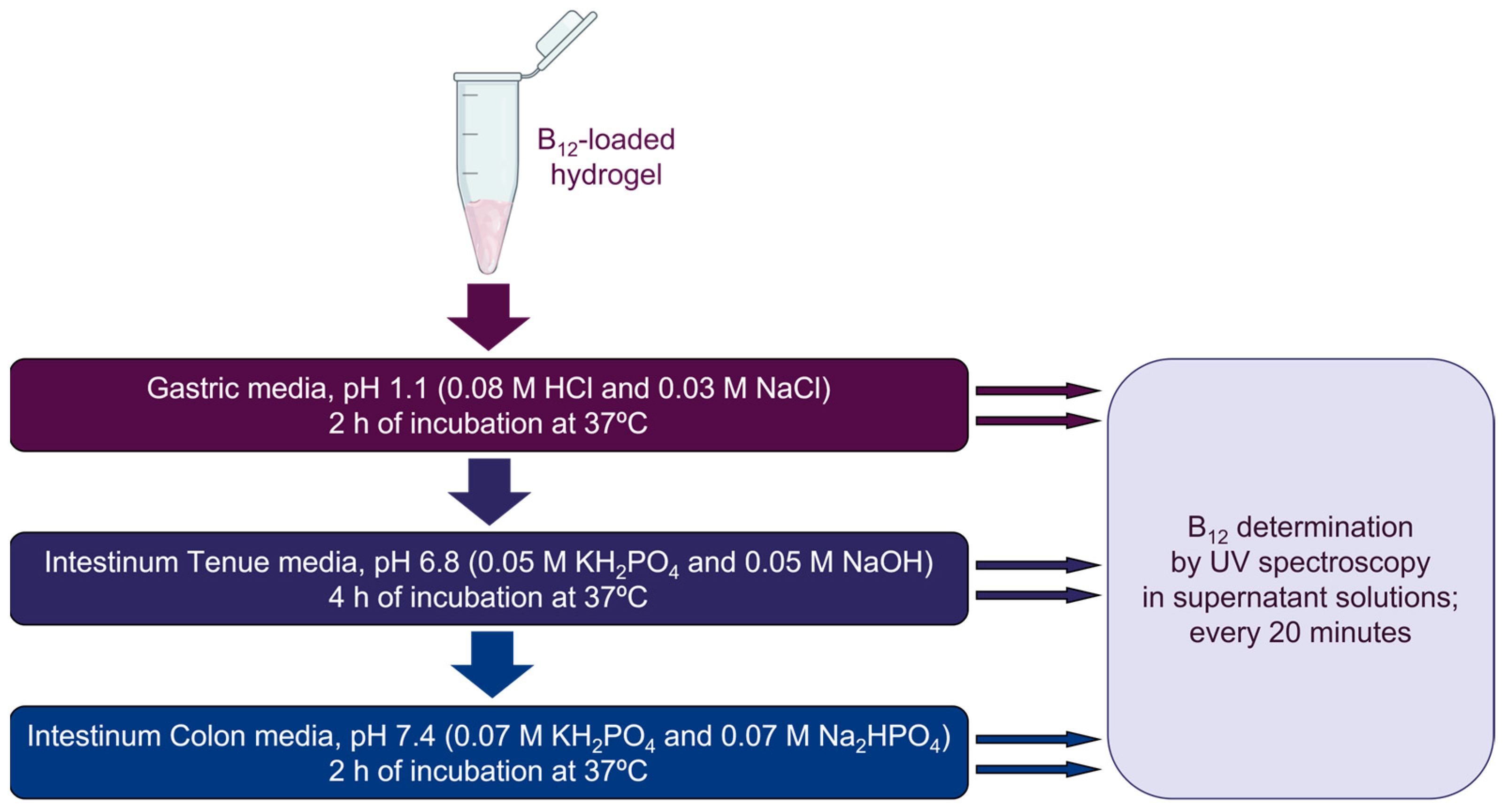
2.2.2. B12 Release
2.2.3. Spectroscopy Studies
2.2.4. Mathematical Processing of the Data
2.2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
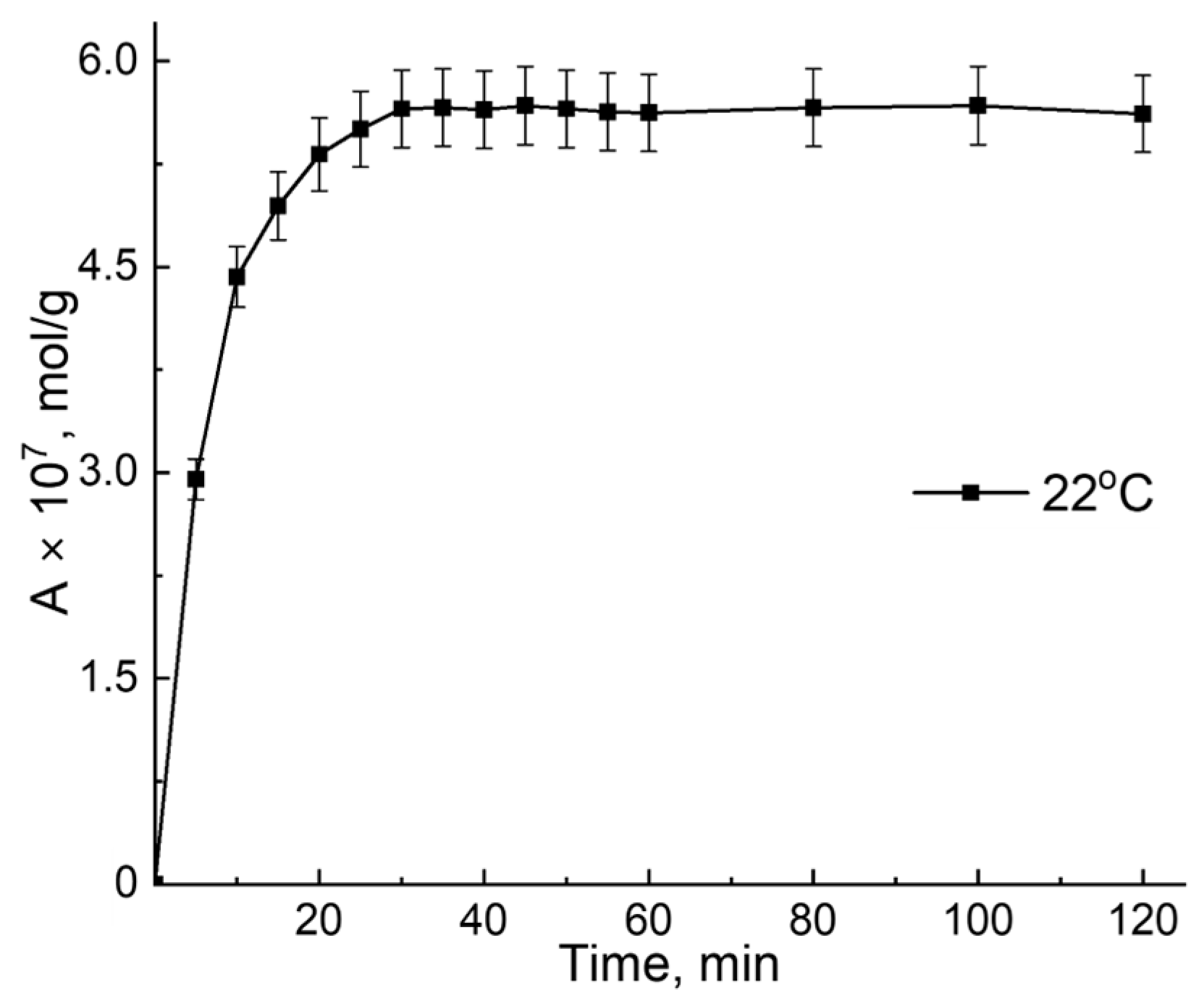
3.1. B12 Vitamin Sorption—Role of the Temperature
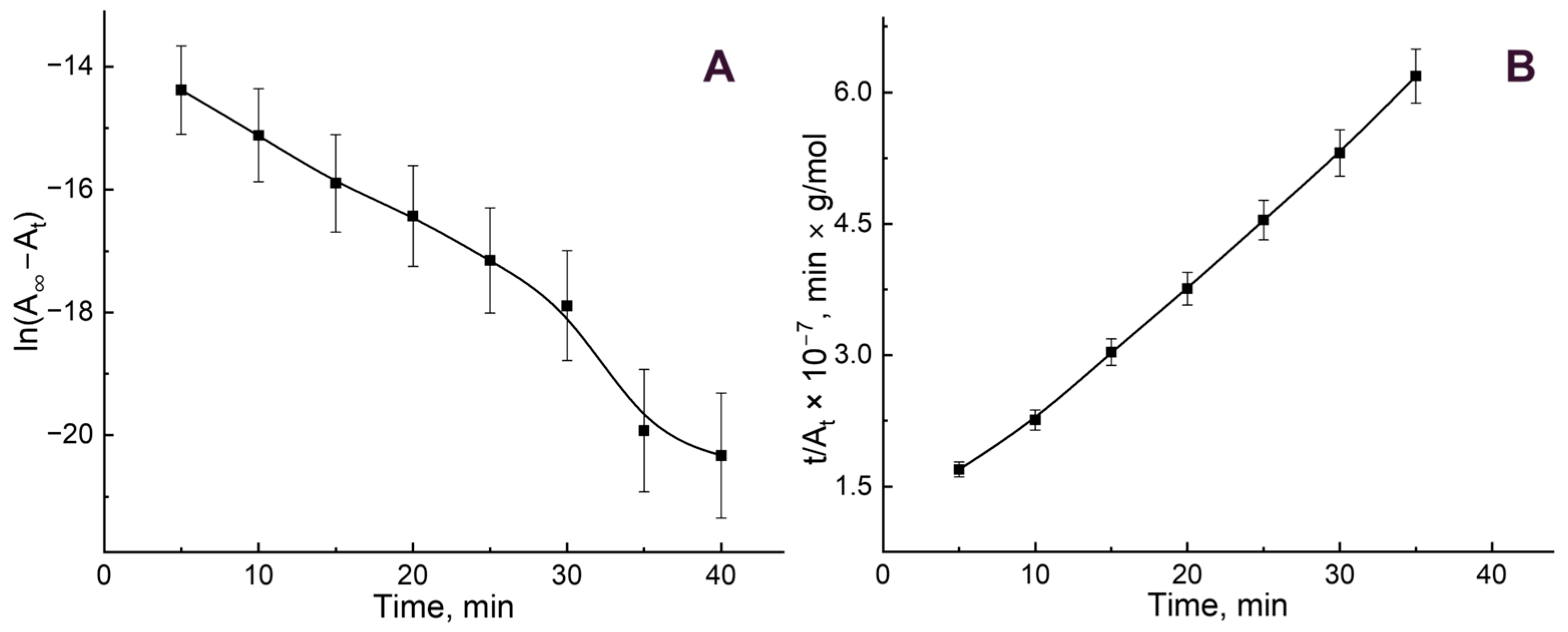
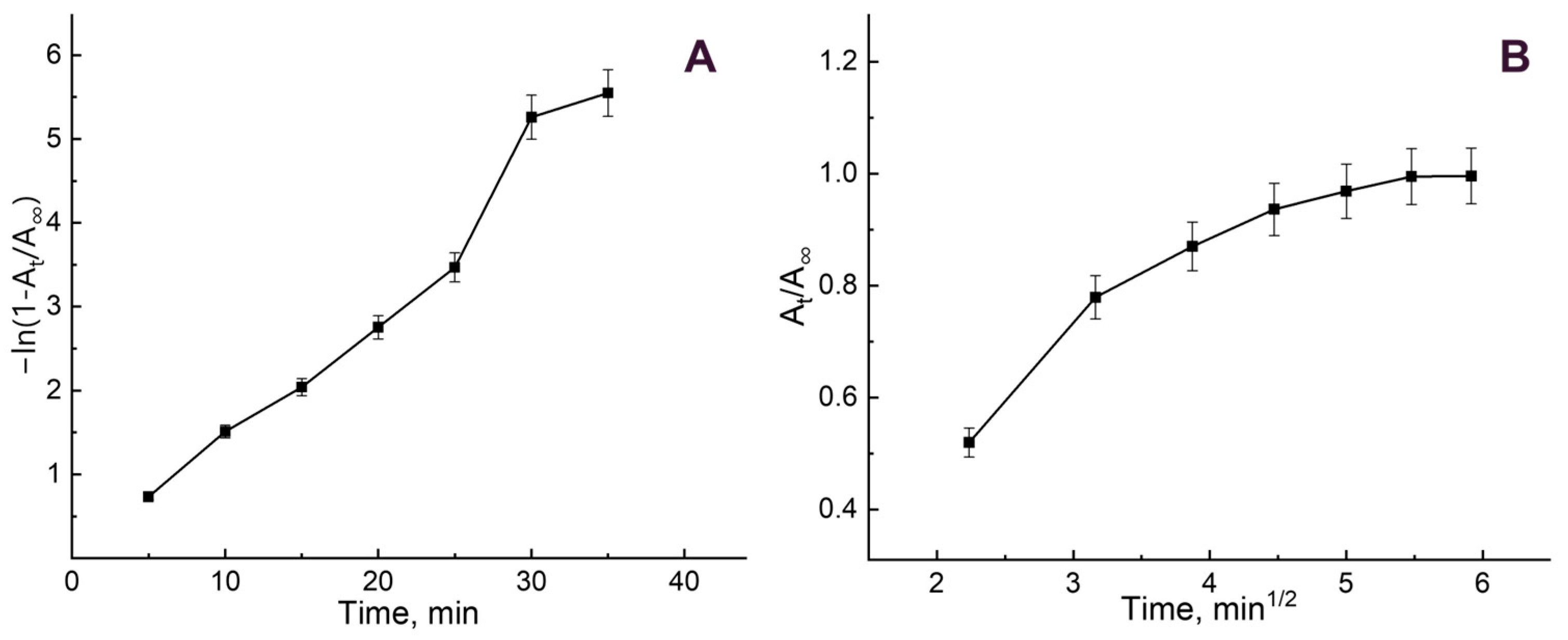
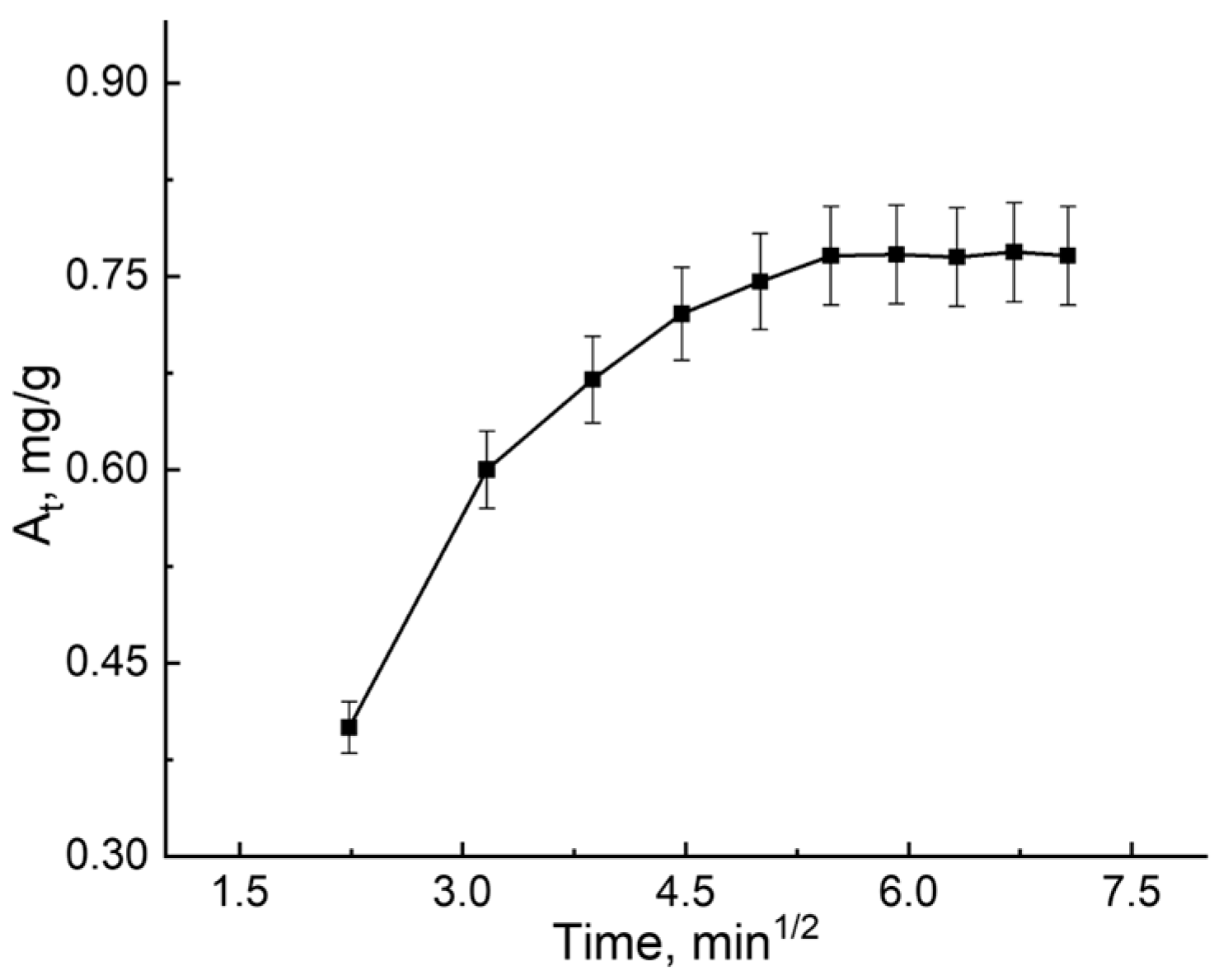
3.2. B12 Vitamin Sorption: Looking for the Mathematical Model
3.3. B12 Vitamin Release from PMSSO-Hydrogel in the Digestive Medium
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| PMSSO-hydrogel | Polymethylsilsesquioxane hydrogel |
| G | Gastric medium |
| IT | Intestinum Tenue medium |
| IC | Intestinum Colon medium |
References
- Emelyanova, A.Y.; Zinovyeva, O.E. Vitamin B12 in the Treatment of Nervous System Diseases. RMJ 2016, 24, 429–433. [Google Scholar]
- WHO European Office for the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases. Plant-Based Diets and Their Impact on Health, Sustainability and the Environment: A Review of the Evidence; WHO Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Doets, E.L.; Veld, P.H.; Szczecińska, A.; Dhonukshe-Rutten, R.A.M.; Cavelaars, A.E.J.M.; van’t Veer, P.; Brzozowska, A.; de Groot, L.C.P.G.M. Systematic Review on Daily Vitamin B12 Losses and Bioavailability for Deriving Recommendations on Vitamin B12 Intake with the Factorial Approach. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 62, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannibal, L.; Lederer, A.K.; Storz, M.A.; Huber, R.; Jacobsen, D.W. Vitamin B12 Status and Supplementation in Plant-Based Diets. Food Nutr. Bull. 2024, 45 (Suppl. S1), 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwahab, O.A.; Abdelaziz, A.; Diab, S.; Khazragy, A.; Elboraay, T.; Fayad, T.; Diab, R.A.; Negida, A. Efficacy of different routes of vitamin B12 supplementation for the treatment of patients with vitamin B12 deficiency: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2024, 193, 1621–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, R.; Allen, L.H.; Bjørke-Monsen, A.L.; Brito, A.; Guéant, J.L.; Miller, J.W.; Molloy, A.M.; Nexo, E.; Stabler, S.; Toh, B.H.; et al. Vitamin B12 deficiency. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17040. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Green, R.; Miller, J.W. Vitamin B12 Deficiency. In Vitamins and Hormones; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 119, pp. 405–439. [Google Scholar]
- Skuredina, A.A.; Ialama, D.E.; Le-Deygen, I.M. Vitamin B12 in Drug Delivery Systems (A Review). Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2024, 50, 2540–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yuan, H.; Luo, X. Fabrication of carboxylated cellulose microspheres via Fe2+/H2O2 oxidation method and their application in vitamin B12 efficient loading and controlled release. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2025, 104, 106515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, S.; Oliveira, L.; Pereira, A.; Costa, M.D.C.; Raposo, A.; Saraiva, A.; Magalhães, B. Exploring Vitamin B12 Supplementation in the Vegan Population: A Scoping Review of the Evidence. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, F.; dos Reis, A.C.; Paludo, K.S.; Tenório-Neto, E.T.; Lima-Tenório, M.K.; Viana, A.G. Designing biocompatible xanthan gum hydrogels for pH-responsive vitamin B12 delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 308, 142449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueoka, H.; Shimomura, O.; Ueda, K.; Inada, K.; Nomura, R. Release behavior of a polyanion-crosslinked chitosan-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) gel thermoresponsive material. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlova, P.; Meshkov, I.B.; Latipov, E.V.; Vasiliev, S.G.; Kalinina, A.A.; Muzafarov, A.M.; Le-Deygen, I.M. Functional Design of Peroral Iron Compound Delivery Systems Based on Polymethylsilsesquioxane Hydrogels for the Therapy of Iron Deficiency Anemia. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 2024, 69, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlova, P.; Meshkov, I.; Latipov, E.; Vasiliev, S.; Mikheev, I.; Ratova, D.-M.; Kalinina, A.; Muzafarov, A.; Le-Deygen, I. Cyclodextrin—Polymethylsilsesquioxane Combined System as a Perspective Iron Delivery System for Oral Administration. Gels 2024, 10, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulikova, G.A.; Parfenyuk, E.V. Surface Properties of Modified Nanoscale Silicas and Their Influence on Human Serum Albumin Immobilization. Phys. Chem. Surf. Mater. Prot. 2010, 46, 473–477. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.; Bhasarkar, J.; Chandan, M.R.; Shaik, A.H.; Kiran, B.; Bal, D.K. Diffusion Kinetics of Vitamin B12 from Alginate and Poly(vinyl acetate) Based Gel Scaffolds for Targeted Drug Delivery. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2020, 59, 713–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrañeta, E.; Domínguez-Robles, J.; Coogan, M.; Heaney, E.; Stewart, S.A.; Thakur, R.R.S.; Donnelly, R.F. Poly(methyl vinyl ether-co-maleic acid) Hydrogels Containing Cyclodextrins and Tween 85 for Potential Application as Hydrophobic Drug Delivery Systems. Macromol. Res. 2019, 27, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Samarrai, M.Q.; Al-Samarrai, K.F. Determination of Riboflavin and Cyanocobalamine Spectrophotometricaly via Area Un-der Curve Method. Tikrit J. Pure Sci. 2023, 22, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afarani, Z.R.; Sarvi, M.N.; Alavijeh, M.A. Modification of montmorillonite nanolayers as a pH-responsive carrier of biomolecules: Delivery of vitamin B12. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 84, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.P.; Yoon, S.-H.; Mochida, I.; Qiao, W.M.; Wang, Y.G.; Ling, L.C. Synthesis of mesoporous carbon and its adsorption property to biomolecules. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 115, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocanu, G.; Nichifor, M.; Picton, L.; About-Jaudet, E.; Le Cerf, D. Preparation and characterization of anionic pullulan thermoassociative nanoparticles for drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 111, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarti, F.; Iqbal, J.; Müller, C.; Shahnaz, G.; Rahmat, D.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Poly(acrylic acid)-cysteine for oral vitamin B12 delivery. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 420, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Field, C.J.; Vine, D.; Chen, L. Intestinal uptake and transport of vitamin B12-loaded soy protein nanoparticles. Pharm. Res. 2015, 32, 1288–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Marín, C.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Z.; Alshrah, M.; Grossman, J.; Wang, E. Kinetics of Sorption in Hygroscopic Hydrogels. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 1100–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorshkova, R.M.; Slobodova, D.A.; Gladyshev, P.P. Diffusion Kinetics of Sorption Processes on Sorbents Based on Pectinic Polysaccharides. Fibre Chem. 2024, 55, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fufaeva, V.A.; Nikiforova, T.E. Extraction of Copper Ions by Chitosan-Based Sorbents Modified with Nickel 2-Ethylimidazolate. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf. 2022, 58, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Montelongo, R.; Salazar-Araya, J.; Hernandez-Montelongo, J.; Garcia-Sandoval, J.P. Mathematical Modeling of Recursive Drug Delivery with Diffusion, Equilibrium, and Convection Coupling. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, A.; Bano, S.; Fahim, A.; Parveen, R.; Khurshid, S. Efficient removal of crystal violet eosin B from aqueous solution using Syzygium cumini leaves: Acomparative study of acidic basic dyes on a single adsorbent. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 32, 882–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, K.; Babar, Z.B.; Munir, S.; Arshad, A.; Rauf, A. Recent advancements in engineered biopolymeric-nanohybrids: A greener approach for adsorptive-remediation of noxious metals from aqueous matrices. Environ. Res. 2022, 215 Pt 3, 114398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meshkov, I.B.; Mazhorova, N.G.; Bakirov, A.V.; Vasil’ev, S.G.; Kalinina, A.A.; Bystrova, A.V.; Muzafarov, A.M. Evolution of Methylsilsesquioxane: From Hydrolytic Polycondensation Product to Xerogel. Polymers 2025, 17, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlova, P.; Meshkov, I.; Sharikov, S.; Frolov, V.; Skuredina, A.; Markov, P.; Bobyleva, Z.; Lakienko, G.; Latipov, E.; Kolmogorov, I.; et al. Amidated and Aminated PMSSO-Hydrogels as a Promising Enzyme-Sensitive Vehicle for Antianemic Drugs. Gels 2025, 11, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippova, N.I.; Teslev, A.A. Application of Mathematical Modeling in the Evaluation of in vitro Drug Release. Drug Dev. Regist. 2017, 4, 218–226. [Google Scholar]
- Bhasarkar, J.; Bal, D. Kinetic investigation of a controlled drug delivery system based on alginate scaffold with embedded voids. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2019, 17, 2280800018817462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourtalebi Jahromi, L.; Ghazali, M.; Ashrafi, H.; Azadi, A. A comparison of models for the analysis of the kinetics of drug release from PLGA-based nanoparticles. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guéant, J.L.; Guéant-Rodriguez, R.M.; Alpers, D.H. Vitamin B12 Absorption and Malabsorption. In Vitamins and Hormones; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 119, pp. 241–274. [Google Scholar]



| α, % | At, mg/g | Pseudo-First Order | Pseudo-Second Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25.7 | 0.77 | At, mg/g | , min−1 | R2 | At, mg/g | , g/(mg × min) | R2 |
| 0.766 ± 0.01 | 0.147 ± 0.008 | 0.99 | 0.83 ± 0.06 | 0.303 ± 0.012 | 0.98 | ||
| Step | , mg/(g × min1/2) | c, mg/g | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.216 | 0.08 | 1 |
| 2 | 0.059 ± 0.008 | 0.45 ± 0.04 | 0.96 |
| 3 | 0.045 ± 0.002 | 0.52 ± 0.01 | 0.99 |
| , µg | Step | Zero-Order Release Model | Korsmeyer-Peppas Release Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 76.6 | , µg | , min−1 | R2 | K, min−1 | n | R2 | |
| 1 | 53.3 ± 3.6 | 0.318 ± 0.096 | 0.85 | 32.1 ± 0.3 | 0.25 ± 0.04 | 0.98 | |
| 2 | 70.6 ± 0.2 | 0.062 ± 0.003 | 0.992 | 52.6 ± 0.1 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.99 | |
| First-Order Release Model | Higuchi Release Model | ||||||
| , µg | , min−1 | R2 | , min−1/2 | R2 | |||
| 1 | 69.8 ± 0.4 | 0.062 ± 0.002 | 0.998 | 5.78 ± 1.28 | 0.98 | ||
| 2 | 76.3 ± 0.7 | 0.025 ± 0.002 | 0.88 | 1.95 ± 0.09 | 0.99 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ialama, D.; Orlova, P.; Skuredina, A.; Meshkov, I.; Muzafarov, A.; Le-Deygen, I. PMSSO-Hydrogels as a Promising Carrier for B12 Vitamin. J. Pharm. BioTech Ind. 2025, 2, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpbi2030010
Ialama D, Orlova P, Skuredina A, Meshkov I, Muzafarov A, Le-Deygen I. PMSSO-Hydrogels as a Promising Carrier for B12 Vitamin. Journal of Pharmaceutical and BioTech Industry. 2025; 2(3):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpbi2030010
Chicago/Turabian StyleIalama, Daniil, Polina Orlova, Anna Skuredina, Ivan Meshkov, Aziz Muzafarov, and Irina Le-Deygen. 2025. "PMSSO-Hydrogels as a Promising Carrier for B12 Vitamin" Journal of Pharmaceutical and BioTech Industry 2, no. 3: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpbi2030010
APA StyleIalama, D., Orlova, P., Skuredina, A., Meshkov, I., Muzafarov, A., & Le-Deygen, I. (2025). PMSSO-Hydrogels as a Promising Carrier for B12 Vitamin. Journal of Pharmaceutical and BioTech Industry, 2(3), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpbi2030010










