Occurrence and Characteristics of Salmonella spp., L. monocytogenes, Y. enterocolitica, and Campylobacter spp. in Raw Meat-Based Diets for Pets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Bacterial Screening and Identification
2.2.1. Salmonella spp.
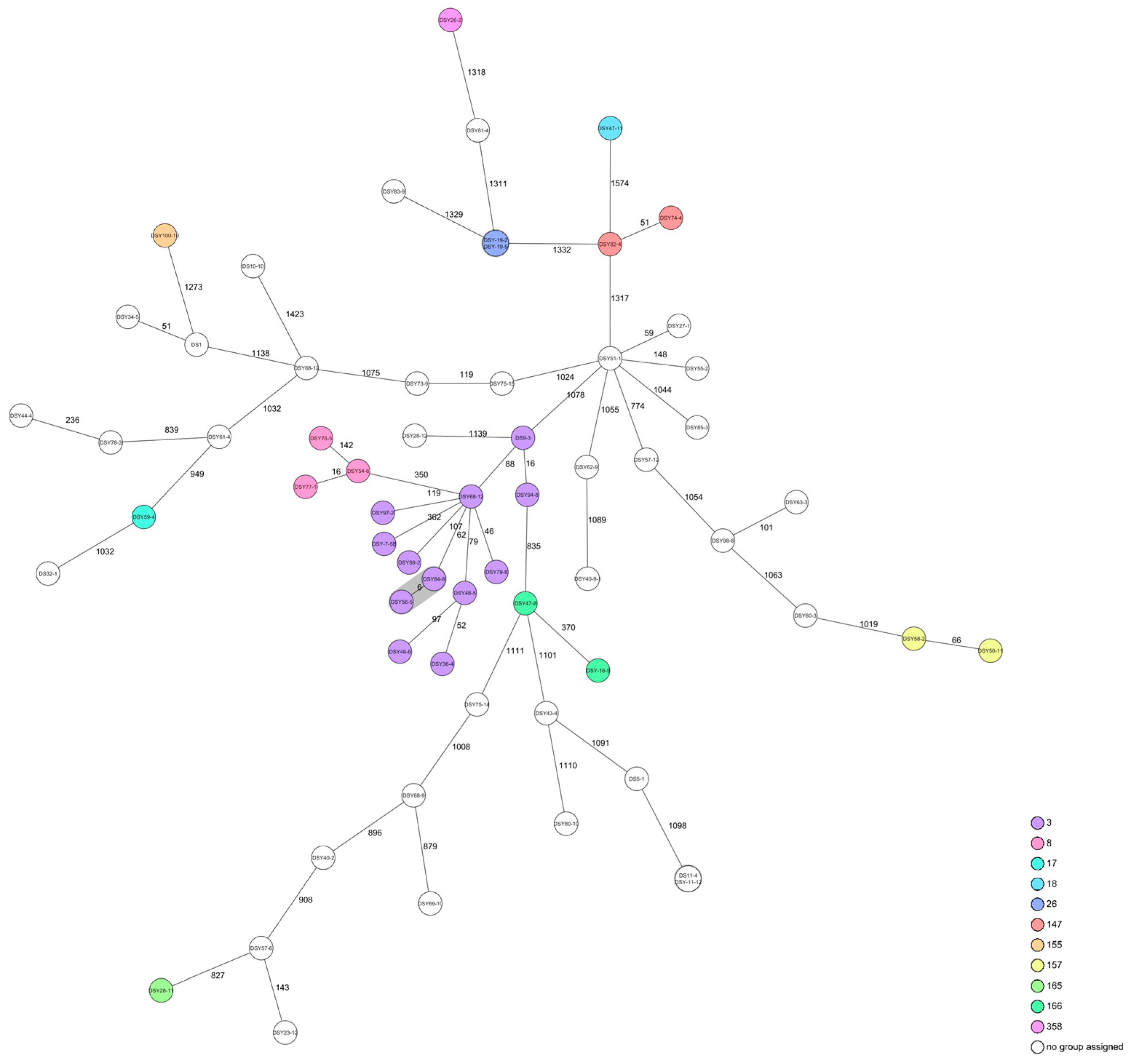
2.2.2. Listeria monocytogenes
2.2.3. Yersinia enterocolitica/Yersinia spp.
2.2.4. Campylobacter spp.
2.3. DNA Extraction and Whole-Genome Sequencing (WGS)
2.4. Descriptive Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Salmonella
3.2. Listeria monocytogenes
3.3. Yersinia enterocolitica
3.4. Campylobacter spp.
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RMBD | raw meat-based diet |
References
- Freeman, L.M.; Chandler, M.L.; Hamper, B.A.; Weeth, L.P. Current Knowledge about the Risks and Benefits of Raw Meat-Based Diets for Dogs and Cats. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2013, 243, 1549–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, G.; Bastianello, S.; Catellani, P.; Ricci, R. Raw Meat-Based Diets for Dogs: Survey of Owners’ Motivations, Attitudes and Practices. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, S.K.; Willis, S.; Shepherd, M.L. Survey of Owner Motivations and Veterinary Input of Owners Feeding Diets Containing Raw Animal Products. PeerJ 2017, 2017, e3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, F.M.; Ramos, C.P.; Xavier, R.G.C.; Lopes, E.O.; Junior, C.A.O.; Bagno, R.M.; Diniz, A.N.; Lobato, F.C.F.; Silva, R.O.S. Fecal Shedding of Salmonella Spp., Clostridium Perfringens, and Clostridioides Difficile in Dogs Fed Raw Meat-Based Diets in Brazil and Their Owners’ Motivation. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlesinger, D.P.; Joffe, D.J. Raw Food Diets in Companion Animals: A Critical Review. Can. Vet. J. 2011, 52, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Köhler, B.; Stengel, C.; Neiger, R. Dietary Hyperthyroidism in Dogs. Br. Small Anim. Vet. Assoc. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2012, 53, 182–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenox, C.; Becvarova, I.; Archipow, W. Metabolic Bone Disease and Central Retinal Degeneration in a Kitten Due to Nutritional Inadequacy of an All-Meat Raw Diet. J. Feline Med. Surg. Open Rep. 2015, 1, 2055116915579682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhakal, J.; Cancio, L.P.M.; Deliephan, A.; Chaves, B.D.; Tubene, S. Salmonella Presence and Risk Mitigation in Pet Foods: A Growing Challenge with Implications for Human Health. In Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernaquez, I.; Dumaresq, J.; Picard, I.; Gaulin, C.; Dion, R.; Weaver, K.; Walker, M.; Kearney, A.; Bharat, A.; Fafard, J.; et al. Dogs Fed Raw Meat-Based Diets Are Vectors of Drug-Resistant Salmonella Infection in Humans. Commun. Med. 2025, 5, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Halloran, C.; Tørnqvist-Johnsen, C.; Woods, G.; Mitchell, J.; Reed, N.; Burr, P.; Gascoyne-Binzi, D.; Wegg, M.; Beardall, S.; Hope, J.; et al. Feline Tuberculosis Caused by Mycobacterium Bovis Infection of Domestic UK Cats Associated with Feeding a Commercial Raw Food Diet. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 2308–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food Safety News. Pet Food Company Refuses to Recall Products Despite Young Girl’s E. coli Infection. Available online: https://www.foodsafetynews.com/2025/07/pet-food-company-refuses-to-recall-products-despite-fda-findings-of-e-coli-and-salmonella-contamination/ (accessed on 5 August 2025).
- van Bree, F.P.J.; Bokken, G.C.A.M.; Mineur, R.; Franssen, F.; Opsteegh, M.; van der Giessen, J.W.B.; Lipman, L.J.A.; Overgaauw, P.A.M. Zoonotic Bacteria and Parasites Found in Raw Meat-Based Diets for Cats and Dogs. Vet. Rec. 2018, 182, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís, D.; Toro, M.; Navarrete, P.; Faúndez, P.; Reyes-Jara, A. Microbiological Quality and Presence of Foodborne Pathogens in Raw and Extruded Canine Diets and Canine Fecal Samples. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 799710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matle, I.; Mbatha, K.R.; Madoroba, E. A Review of Listeria Monocytogenes from Meat and Meat Products: Epidemiology, Virulence Factors, Antimicrobial Resistance and Diagnosis. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2020, 87, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellgren, J.; Hästö, L.S.; Wikstrom, C.; Fernström, L.L.; Hansson, I. Occurrence of Salmonella, Campylobacter, Clostridium and Enterobacteriaceae in Raw Meat-Based Diets for Dogs. Vet. Rec. 2019, 184, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. About Pet Food Safety. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/healthy-pets/about/pet-food-safety.html (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- World Small Animal Veterinary Association (WSAVA) Global Nutrition Committee. Raw Meat Based Diets for Pets. Available online: https://wsava.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/Raw-Meat-Based-Diets-for-Pets_WSAVA-Global-Nutrition-Toolkit.pdf (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- Morgan, G.; Pinchbeck, G.; Haldenby, S.; Schmidt, V.; Williams, N. Raw Meat Diets Are a Major Risk Factor for Carriage of Third-Generation Cephalosporin-Resistant and Multidrug-Resistant E. Coli by Dogs in the UK. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1460143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nüesch-Inderbinen, M.; Treier, A.; Zurfluh, K.; Stephan, R. Raw Meat-Based Diets for Companion Animals: A Potential Source of Transmission of Pathogenic and Antimicrobial-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 191170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-Almeida, M.; Mourão, J.; Magalhães, M.; Freitas, A.R.; Novais, C.; Peixe, L.; Antunes, P. Raw Meat-Based Diet for Pets: A Neglected Source of Human Exposure to Salmonella and Pathogenic Escherichia Coli Clones Carrying Mcr, Portugal, September 2019 to January 2020. Eurosurveillance 2024, 29, 2300561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulochova, V.; Evans, E.W. Raw Meat-Based Pet Feeding and Food Safety: Netnography Study of Pet Owner Comments and Review of Manufacturers’ Information Provision. J. Food Prot. 2021, 84, 2099–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6579-1:2017; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection, Enumeration and Serotyping of Salmonella—Part 1: Detection of Salmonella spp. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Grimont, P.A.D.; Weill, F.-X. Antigenic Formulae of the Salmonella Serovars, 9th ed.; WHO Collaborating Centre for Reference and Research on Salmonella, Institut Pasteur: Paris, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 11290-1:2017; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection and Enumeration of Listeria monocytogenes and of Listeria spp.—Part 1: Detection Method. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- ISO 10273:2017; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection of Presumptive Pathogenic Yersinia enterocolitica. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- ISO 10272-1:2017; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for Detection and Enumeration of Campylobacter spp.—Part 1: Detection Method. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Shovill. Available online: https://github.com/tseemann/shovill (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- Souvorov, A.; Agarwala, R.; Lipman, D.J. SKESA: Strategic k-Mer Extension for Scrupulous Assemblies. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinidis, K.T.; Tiedje, J.M. Genomic Insights That Advance the Species Definition for Prokaryotes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2567–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, C.; Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Phillippy, A.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T.; Aluru, S. High Throughput ANI Analysis of 90K Prokaryotic Genomes Reveals Clear Species Boundaries. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppitsch, W.; Pietzka, A.; Prior, K.; Bletz, S.; Fernandez, H.L.; Allerberger, F.; Harmsen, D.; Mellmann, A. Defining and Evaluating a Core Genome Multilocus Sequence Typing Scheme for Whole-Genome Sequence-Based Typing of Listeria Monocytogenes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2869–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nennig, M.; Llarena, A.K.; Herold, M.; Mossong, J.; Penny, C.; Losch, S.; Tresse, O.; Ragimbeau, C. Investigating Major Recurring Campylobacter Jejuni Lineages in Luxembourg Using Four Core or Whole Genome Sequencing Typing Schemes. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 608020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, M.J.A.; Horlbog, J.A.; Diethelm, A.; Stephan, R.; Nüesch-Inderbinen, M. Characteristics and Comparative Genome Analysis of Yersinia Enterocolitica and Related Species Associated with Human Infections in Switzerland 2019–2023. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2024, 123, 105652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federal Office of Public Health. Salmonellosis. Available online: https://www.idd.bag.admin.ch/diseases/salmonellosis/overview (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 2019 NARMS update: Integrated Report Summary. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/animal-veterinary/national-antimicrobial-resistance-monitoring-system/2019-narms-update-integrated-report-summary (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- Nemser, S.M.; Doran, T.; Grabenstein, M.; McConnell, T.; McGrath, T.; Pamboukian, R.; Smith, A.C.; Achen, M.; Danzeisen, G.; Kim, S.; et al. Investigation of Listeria, Salmonella, and Toxigenic Escherichia Coli in Various Pet Foods. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2014, 11, 706–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muchaamba, F.; Eshwar, A.K.; Stevens, M.J.A.; Stephan, R.; Tasara, T. Different Shades of Listeria Monocytogenes: Strain, Serotype, and Lineage-Based Variability in Virulence and Stress Tolerance Profiles. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 792162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurpas, M.; Osek, J.; Moura, A.; Leclercq, A.; Lecuit, M.; Wieczorek, K. Genomic Characterization of Listeria Monocytogenes Isolated From Ready-to-Eat Meat and Meat Processing Environments in Poland. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt-Samoraj, A. Toxigenic Properties of Yersinia Enterocolitica Biotype 1A. Toxins 2022, 14, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillier, L.; Fravalo, P.; Leclercq, A.; Thébault, A.; Kooh, P.; Cadavez, V.; Gonzales-Barron, U. Risk Factors for Sporadic Yersinia Enterocolitica Infections: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Microb. Risk Anal. 2021, 17, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maziero, M.T.; Cristina, T.; De Oliveira, R.M. Effect of Refrigeration and Frozen Storage on the Campylobacter Jejuni Recovery from Naturally Contaminated Broiler Carcasses. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2010, 41, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves-Tenório, A.; Nunes Silva, B.; Rodrigues, V.; Cadavez, V.; Gonzales-Barron, U. Prevalence of Pathogens in Poultry Meat: A Meta-Analysis of European Published Surveys. Foods 2018, 7, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottari, B.; Bancalari, E.; Barera, A.; Ghidini, S.; Gatti, M. Evaluating the Presence of Human Pathogens in Commercially Frozen, Biologically Appropriate Raw Pet Food Sold in Italy. Vet. Rec. 2020, 187, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Public Health England and Animal and Plant Health Agency. Raw Pet Foods: Handling and Preventing Infection. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/guidance/raw-pet-foods-handling-and-preventing-infection (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- Weese, J.S.; Rousseau, J. Survival of Salmonella Copenhagen in Food Bowls Following Contamination with Experimentally Inoculated Raw Meat: Effects of Time, Cleaning, and Disinfection. Can. Vet. J. 2006, 47, 887–889. [Google Scholar]
- Owens, T.G.; King, B.A.; Radford, D.R.; Strange, P.; Arvaj, L.; Pezzali, J.G.; Edwards, A.M.; Ganesh, D.; DeVries, T.J.; McBride, B.W.; et al. Use of 2-Hydroxy-4-(Methylthio)-Butanoic Acid to Inhibit Salmonella and Listeria in Raw Meat for Feline Diets and Palatability in Domestic Cats. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 99, skab253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Maks-Warren, N.; Aguilar, V.; Piszczor, K.; Swicegood, B.; Ye, M.; Warren, J.; O’Neill, E.; Fleck, M.; Tejayadi, S. Inactivation of Salmonella, Shiga Toxin-Producing E. Coli, and Listeria Monocytogenes in Raw Diet Pet Foods Using High-Pressure Processing. J. Food Prot. 2023, 86, 100124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, J.W.; Park, S.C.; Wicklund, A.; Skurnik, M. Bacteriophages Reduce Yersinia Enterocolitica Contamination of Food and Kitchenware. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 271, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, S.; Baker, C.A.; Hamilton, A.N.; Dhulappanavar, G.R.; Jones, S.L.; Gibson, K.E. Aqueous Ozone Efficacy for Inactivation of Foodborne Pathogens on Vegetables Used in Raw Meat-Based Diets for Companion Animals. J. Food Prot. 2023, 86, 100175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiprotich, S.; Altom, E.; Mason, R.; Trinetta, V.; Aldrich, G. Application of Encapsulated and Dry-Plated Food Acidulants to Control Salmonella Enterica in Raw Meat-Based Diets for Dogs. J. Food Prot. 2023, 86, 100077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Product Composition | Samples | Salmonella (%/CI *) | L. monocytogenes (%/CI) | Y. enterocolitica (%/CI) | Campylobacter (%/CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total positive | 11/100 (11%; CI 4.9–17.1%) | 41/100 (41%; 31.4–50.6%) | 58/100 (58%; 48.3–67.7%) | 3/100 (3%; 0–8.5%) | |
| Cattle | 28/100 | 6/28 | 12/28 | 23/28 | 0/28 |
| Horse | 9/100 | 0/9 | 1/9 | 3/9 | 0/9 |
| Poultry | 21/100 | 3/21 | 11/21 | 9/21 | 3/21 |
| Rabbit | 9/100 | 0/9 | 2/9 | 5/9 | 0/9 |
| Game | 8/100 | 1/8 | 3/8 | 8/8 | 0/8 |
| Lamb | 6/100 | 1/6 | 2/6 | 1/6 | 0/6 |
| Salmon | 3/100 | 0/3 | 2/3 | 1/3 | 0/3 |
| Calf | 1/100 | 0/1 | 0/1 | 0/1 | 0/1 |
| Goat | 1/100 | 0/1 | 0/1 | 0/1 | 0/1 |
| Kangaroo | 1/100 | 0/1 | 0/1 | 1/1 | 0/1 |
| Vegetable | 1/100 | 0/1 | 0/1 | 0/1 | 0/1 |
| Mixed | 12/100 | 0/12 | 8/12 | 7/12 | 0/12 |
| Serovar | Sample ID | Product Composition | Ingredients |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. diarizonae | DS 16 | Cattle | Pure muscle meat |
| DS 44 | Cattle | Mixed: offal | |
| S. dublin | DS 45 | Lamb | Mixed: muscle, bone, fat, vegetable, and fruit |
| S. enteritidis | DS 58 | Cattle | Mixed: offal |
| S. infantis | DS 7 | Game (reindeer) | Pure muscle meat |
| DS 82 | Poultry (chicken) | Mixed: muscle, bone, offal, vegetable, and fruit | |
| S. oranienburg | DS 33 | Cattle | Tripe (omasum) |
| DS 35 | Cattle | Mixed: muscle and tripe (rumen) | |
| S. typhimurium | DS 10 | Poultry (goose) | Pure muscle meat |
| DS 23 | Poultry (duck) | Pure muscle meat | |
| DS 61 | Cattle | Mixed: muscle, bone, offal, vegetable, and fruit |
| ST | cgMLST CT | Sample ID | Product Composition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | n/d 1 | DS 47 | Cattle |
| n/d | DS 67 | Poultry (chicken) and insects | |
| 3 | n/d | DS 94 | Game (bison) |
| 4 | n/d | DS 54 | Salmon |
| n/d | DS 60 | Cattle | |
| 5 | n/d | DS 44 | Cattle |
| n/d | DS 63 | Poultry (chicken) | |
| 6 | n/d | DS 5 | Cattle |
| n/d | DS 18 | Horse | |
| n/d | DS 86 | Poultry (turkey) | |
| n/d | DS 90 | Lamb | |
| 7 | n/d | DS 48 | Poultry |
| 18047 | DS 88 | Rabbit | |
| n/d | DS 98 | Poultry (chicken) | |
| 9 | n/d | DS 22 | Poultry |
| n/d | DS 92 | Poultry (chicken) | |
| 14 | n/d | DS 73 | Poultry (chicken) and cattle |
| 17516 | DS 82 | Poultry (chicken) | |
| 16 | 19781 | DS 91 | Poultry (chicken) |
| 18 | n/d | DS 52 | Poultry (turkey) |
| 29 | 4312 | DS 3 | Game (deer) |
| n/d | DS 6 | Lamb and cattle | |
| 121 | n/d | DS 2 | Poultry (chicken) |
| 20596 | DS 15 | Salmon | |
| 4365 | DS 40 | Poultry (turkey) | |
| 219 | n/d | DS 64 | Poultry (chicken) |
| 388 | 16631 | DS 41 | Cattle and salmon |
| 14230 | DS 46 | Cattle | |
| 451 | n/d | DS 7 | Game (reindeer) |
| n/d | DS 9 | Rabbit | |
| 18488 | DS 12 | Cattle | |
| n/d | DS 51 | Cattle | |
| 14591 | DS 71 | Lamb | |
| 5076 | DS 76 | Poultry (chicken) and cattle | |
| n/d | DS 83 | Cattle | |
| 489 | n/d | DS 74 | Poultry (chicken) and cattle |
| n/d | DS 79 | Cattle | |
| n/d | DS 84 | Cattle | |
| 1000 | n/d | DS 55 | Cattle |
| unknown | n/d | DS 56 | Cattle |
| BT | ST | Sample ID | Isolate Number | Product Composition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1A | n/d * | DS 1 | DS 1 | Horse |
| n/d | DS 5 | DS 5-1 | Cattle | |
| ST 3 | DS 7 | DSY-7-5B | Game (reindeer) | |
| ST 3 | DS 9 | DS 9-3 | Rabbit | |
| n/d | DS 10 | DS 10-10 | Poultry (goose) | |
| n/d | DS 11 | DS 11-4, DSY-11-12 | Poultry (quail) | |
| ST 166 | DS 16 | DSY-16-5 | Cattle | |
| ST 26 | DS 19 | DSY-19-2, DSY-19-5 | Cattle | |
| n/d | DS 23 | DSY 23-12 | Poultry (duck) | |
| ST 358 | DS 26 | DSY 26-2 | Kangaroo | |
| n/d | DS 27 | DSY 27-1 | Rabbit | |
| ST 165 | DS 28 | DSY 28-11 | Game ((roe) deer) | |
| n/d | DSY 28-12 | |||
| n/d | DS 32 | DS 32-1 | Horse | |
| n/d | DS 34 | DSY 34-5 | Rabbit | |
| ST 3 | DS 36 | DSY 36-4 | Cattle | |
| n/d | DS 40 | DSY 40-2 | Poultry (turkey) | |
| n/d | DSY 40-9-1 | |||
| n/d | DS 43 | DSY 43-4 | Cattle | |
| n/d | DS 44 | DSY 44-4 | Cattle | |
| ST 3 | DS 46 | DSY 46-6 | Cattle | |
| ST 166 | DS 47 | DSY 47-8 | Cattle | |
| ST 3 | DS 48 | DSY 48-5 | Poultry | |
| ST 157 | DS 50 | DSY 50-11 | Cattle | |
| n/d | DS 51 | DSY 51-1 | Cattle | |
| ST 8 | DS 54 | DSY 54-6 | Salmon | |
| n/d | DS 55 | DSY 55-2 | Cattle | |
| ST 3 | DS 56 | DSY 56-5 | Cattle | |
| n/d | DS 57 | DSY 57-6, DSY 57-12 | Game ((roe) deer) | |
| ST 157 | DS 58 | DSY 58-2 | Cattle | |
| ST 17 | DS 59 | DSY 59-4 | Horse | |
| n/d | DS 60 | DSY 60-3 | Cattle | |
| n/d | DS 61 | DSY 61-4 | Cattle | |
| n/d | DS 62 | DSY 62-9 | Lamb | |
| n/d | DS 63 | DSY 63-3 | Poultry (chicken) and insects | |
| n/d | DS 68 | DSY 68-9 | Game (roe deer) | |
| ST 3 | DSY 68-12 | |||
| n/d | DS 69 | DSY 69-10 | Game (deer) | |
| n/d | DS 73 | DSY 73-9 | Poultry (chicken) and cattle | |
| ST 147 | DS 74 | DSY 74-4 | Poultry (chicken) and cattle | |
| n/d | DS 75 | DSY 75-14, DSY 75-15 | Game (deer) and lamb | |
| ST 8 | DS 76 | DSY 76-5 | Poultry (chicken) and cattle | |
| ST 8 | DS 77 | DSY 77-1 | Rabbits and poultry (turkey) | |
| n/d | DS 78 | DSY 78-3 | Cattle | |
| ST 3 | DS 79 | DSY 79-8 | Cattle | |
| n/d | DS 80 | DSY 80-10 | Poultry (turkey) | |
| n/d | DS 81 | DSY 81-4 | Cattle | |
| ST 147 | DS 82 | DSY 82-4 | Poultry (chicken) | |
| n/d | DS 83 | DSY 83-9 | Cattle | |
| ST 3 | DS 84 | DSY 84-8 | Cattle | |
| n/d | DS 85 | DSY 85-3 | Cattle | |
| n/d | DS 88 | DSY 88-12 | Rabbit | |
| ST 3 | DS 89 | DSY 89-2 | Cattle | |
| ST 3 | DS 94 | DSY 94-8 | Game (bison) | |
| ST 3 | DS 97 | DSY 97-2 | Poultry (chicken) | |
| n/d | DS 98 | DSY 98-8 | Poultry (chicken) | |
| ST 155 | DS 100 | DSY 100-10 | Game ((roe) deer), poultry (chicken), and cattle | |
| 4 | ST 18 | DS 47 | DSY 47-11 | Cattle |
| Species | Sample ID | Product Composition | Ingredients |
|---|---|---|---|
| Campylobacter coli | DS 42 | Poultry (chicken) | Neck |
| Campylobacter coli | DS 48 | Poultry | Whole animal |
| Campylobacter jejuni | DS 92 | Poultry (chicken) | Liver |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schmid, D.T.; Barmettler, K.; Stevens, M.J.A.; Stephan, R. Occurrence and Characteristics of Salmonella spp., L. monocytogenes, Y. enterocolitica, and Campylobacter spp. in Raw Meat-Based Diets for Pets. Pets 2025, 2, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/pets2040035
Schmid DT, Barmettler K, Stevens MJA, Stephan R. Occurrence and Characteristics of Salmonella spp., L. monocytogenes, Y. enterocolitica, and Campylobacter spp. in Raw Meat-Based Diets for Pets. Pets. 2025; 2(4):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/pets2040035
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchmid, Désirée Tahnee, Karen Barmettler, Marc J. A. Stevens, and Roger Stephan. 2025. "Occurrence and Characteristics of Salmonella spp., L. monocytogenes, Y. enterocolitica, and Campylobacter spp. in Raw Meat-Based Diets for Pets" Pets 2, no. 4: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/pets2040035
APA StyleSchmid, D. T., Barmettler, K., Stevens, M. J. A., & Stephan, R. (2025). Occurrence and Characteristics of Salmonella spp., L. monocytogenes, Y. enterocolitica, and Campylobacter spp. in Raw Meat-Based Diets for Pets. Pets, 2(4), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/pets2040035






