Elevated Alpha-Fetoprotein in Hypothyroidism
Abstract
1. Introduction
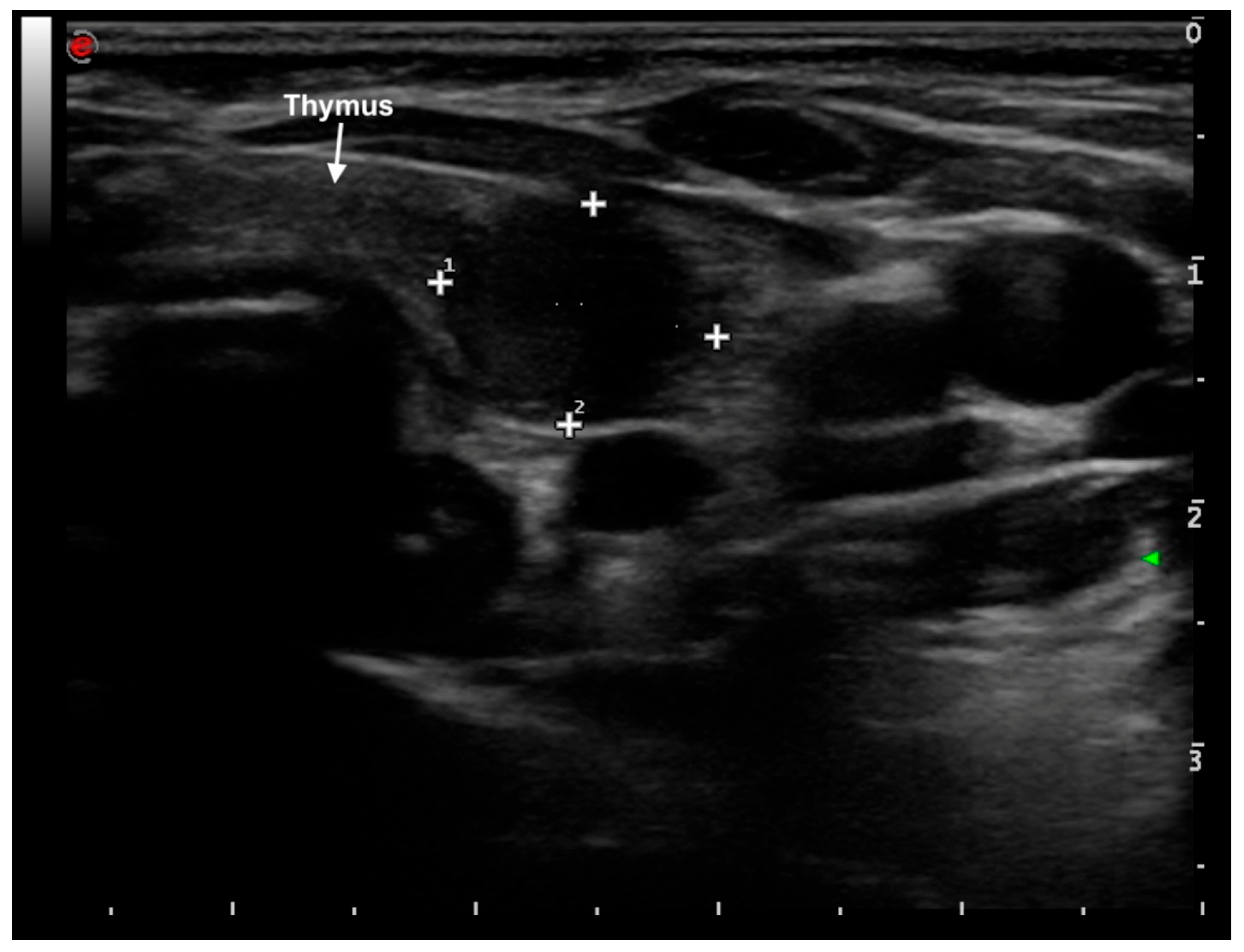
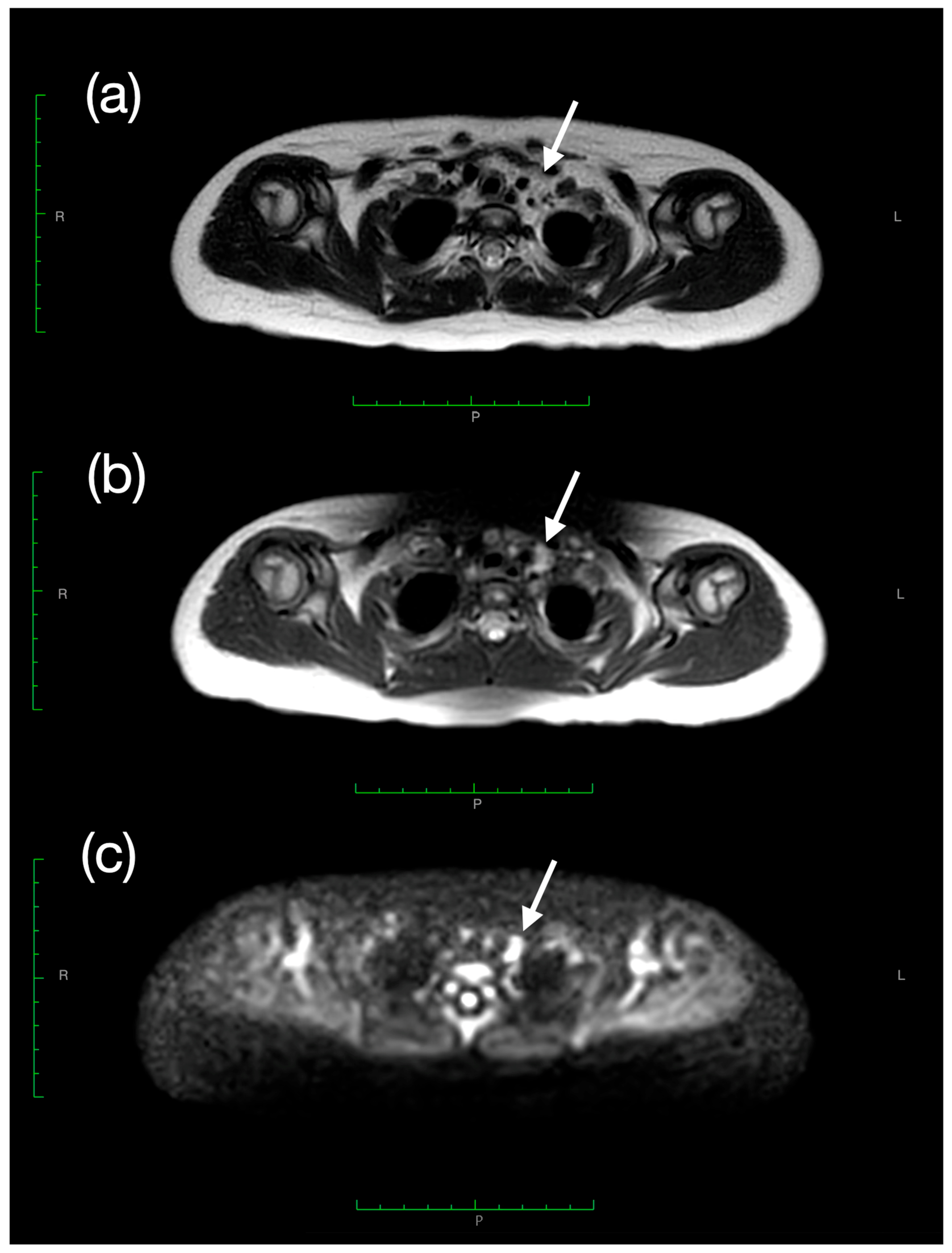
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFP | Alpha-fetoprotein |
| FSH | Follicle-Stimulating Hormone |
| fT3 | free Triiodothyronine |
| fT4 | free Thyroxine |
| LH | Luteinizing Hormone |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| TSH | Thyroid-Stimulating hormone |
References
- Głowska-Ciemny, J.; Szymański, M.; Kuszerska, A.; Rzepka, R.; von Kaisenberg, C.S.; Kocyłowski, R. Role of Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP) in Diagnosing Childhood Cancers and Genetic-Related Chronic Diseases. Cancers 2023, 15, 4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanif, H.; Ali, M.J.; Susheela, A.T.; Yeo, Y.H.; Lee, Y.-T.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, J.D. Update on the Applications and Limitations of Alpha-Fetoprotein for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matonóg, A.; Drosdzol-Cop, A. Alpha-Fetoprotein Level in Fetuses, Infants, and Children with Ovarian Masses: A Literature Review. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1307619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, Y.H.; Lee, Y.-T.; Tseng, H.-R.; Zhu, Y.; You, S.S.; Agopian, V.G.; Yang, J.D. Alpha-Fetoprotein: Past, Present, and Future. Hepatol. Commun. 2024, 8, e0422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, H.; Hızal, G.; Uslu Kızılkan, N.; Gürakan, F.; Talim, B.; Coşkun, T.; Kale, G.; Yüce, A. Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein Levels in Neonatal Cholestasis. Turk. J. Pediatr. 2013, 55, 152–157. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Feng, G. Association between Alpha-Fetoprotein and Metabolic Syndrome in a Chinese Asymptomatic Population: A Cross-Sectional Study. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga-Neto, P.; Dutra, L.A.; Pedroso, J.L.; Barsottini, O.G. Alpha-Fetoprotein as a Biomarker for Recessive Ataxias. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2010, 68, 953–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, T.; Matsubara, F. Changes in the Tumor Marker Concentration in Female Patients with Hyper-, Eu-, and Hypothyroidism. Endocrinol. Jpn. 1989, 36, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawky, R.M.; Abd El-Fattah, S.; El-Din Azzam, M.E.; Rafik, M.M.; Osman, A. Alpha-Fetoprotein in Screening for Congenital Hypothyroidism. East. Mediterr. Health J. 2001, 7, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, J.; Lin-Su, K. Van Wyk–Grumbach Syndrome in a Female Pediatric Patient with Trisomy 21: A Case Report. Int. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2020, 2020, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amr, N.H. Thyroid Disorders in Subjects with Down Syndrome: An Update. Acta Biomed. 2018, 89, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeliga, K.; Antosz, A.; Skrzyńska, K.; Kalina-Faska, B.; Januszek-Trzciakowska, A.; Gawlik, A. Subclinical Hypothyroidism as the Most Common Thyroid Dysfunction Status in Children with Down’s Syndrome. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 12, 782865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalrymple, R.A. Thyroid Disorder in Children and Young People with Down Syndrome: DSMIG Guideline Review. Arch. Dis. Child. Educ. Pract. 2022, 107, 34–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satgé, D.; Sommelet, D.; Geneix, A.; Nishi, M.; Malet, P.; Vekemans, M. A tumour profile in Down syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1998, 78, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blohm, M.E.; Vesterling-Hörner, D.; Calaminus, G.; Göbel, U. Alpha 1-fetoprotein (AFP) reference values in infants up to 2 years of age. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 1998, 15, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Houwelingen, L.; Sandoval, J.A. Alpha-fetoprotein in malignant pediatric conditions. In Proof and Concepts in Rapid Diagnostic Tests and Technologies; Saxena, S.K., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Caturla, M.; Van Reeth, T.; Drèze, P.; Szpirer, J.; Szpirer, C. The thyroid hormone down-regulates the mouse alpha-foetoprotein promoter. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1997, 135, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Wu, M.-H.; Huang, Y.-H.; Yeh, C.-T.; Lin, K.-H. TUG1 is a regulator of AFP and serves as prognostic marker in non-hepatitis B, non-hepatitis C hepatocellular carcinoma. Cells 2020, 9, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.-S.; Chang, C.-C.; Wang, C.-S.; Lin, K.-H. Functional roles of non-coding RNAs regulated by thyroid hormones in liver cancer. Biomed. J. 2021, 44, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forini, F.; Nicolini, G.; Pitto, L.; Iervasi, G. Novel Insight Into the Epigenetic and Post-transcriptional Control of Cardiac Gene Expression by Thyroid Hormone. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, S.; Furuya, S.; Shiraishi, K.; Shimizu, H.; Akaike, H.; Hosomura, N.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Amemiya, H.; Kawaida, H.; Sudo, M.; et al. miR-122-5p as a Novel Biomarker for Alpha-Fetoprotein-Producing Gastric Cancer. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2018, 10, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Yan, D.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; He, Q. Circulating microRNAs (miR-16, miR-22, miR-122) expression and early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kronquist, K.E.; Dreazen, E.; Keener, S.L.; Nicholas, T.W.; Crandall, B.F. Reduced Fetal Hepatic Alpha-Fetoprotein Levels in Down’s Syndrome. Prenat. Diagn. 1990, 10, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guibourdenche, J.; Leguy, M.-C.; Pidoux, G.; Hebert-Schuster, M.; Laguillier, C.; Anselem, O.; Grangé, G.; Bonnet, F.; Tsatsaris, V. Biochemical Screening for Fetal Trisomy 21: Pathophysiology of Maternal Serum Markers and Involvement of the Placenta. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ning, W.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, H. Diagnostic value of maternal alpha-fetoprotein variants in second-trimester biochemical screening for trisomy 21 and 18. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
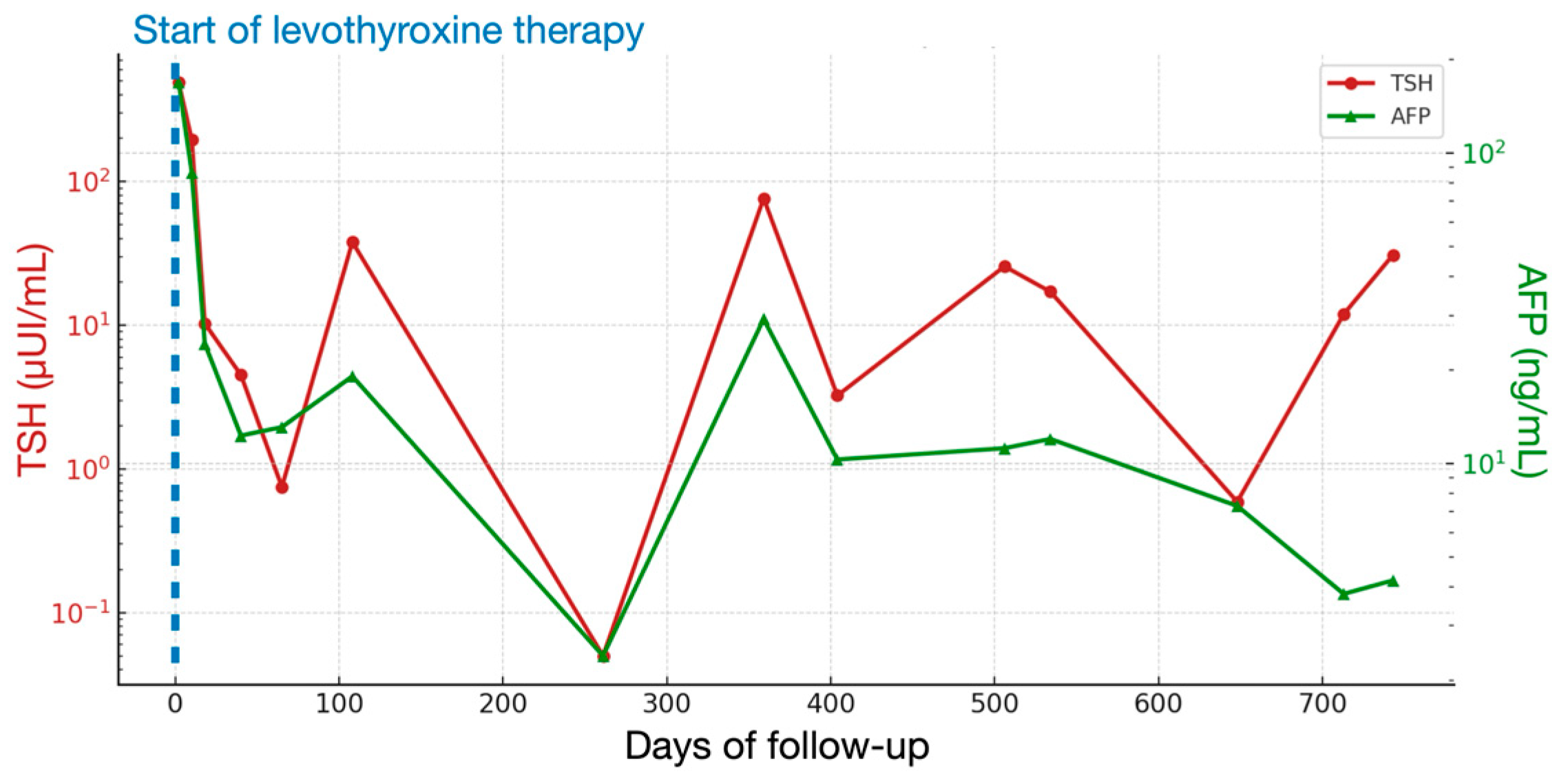
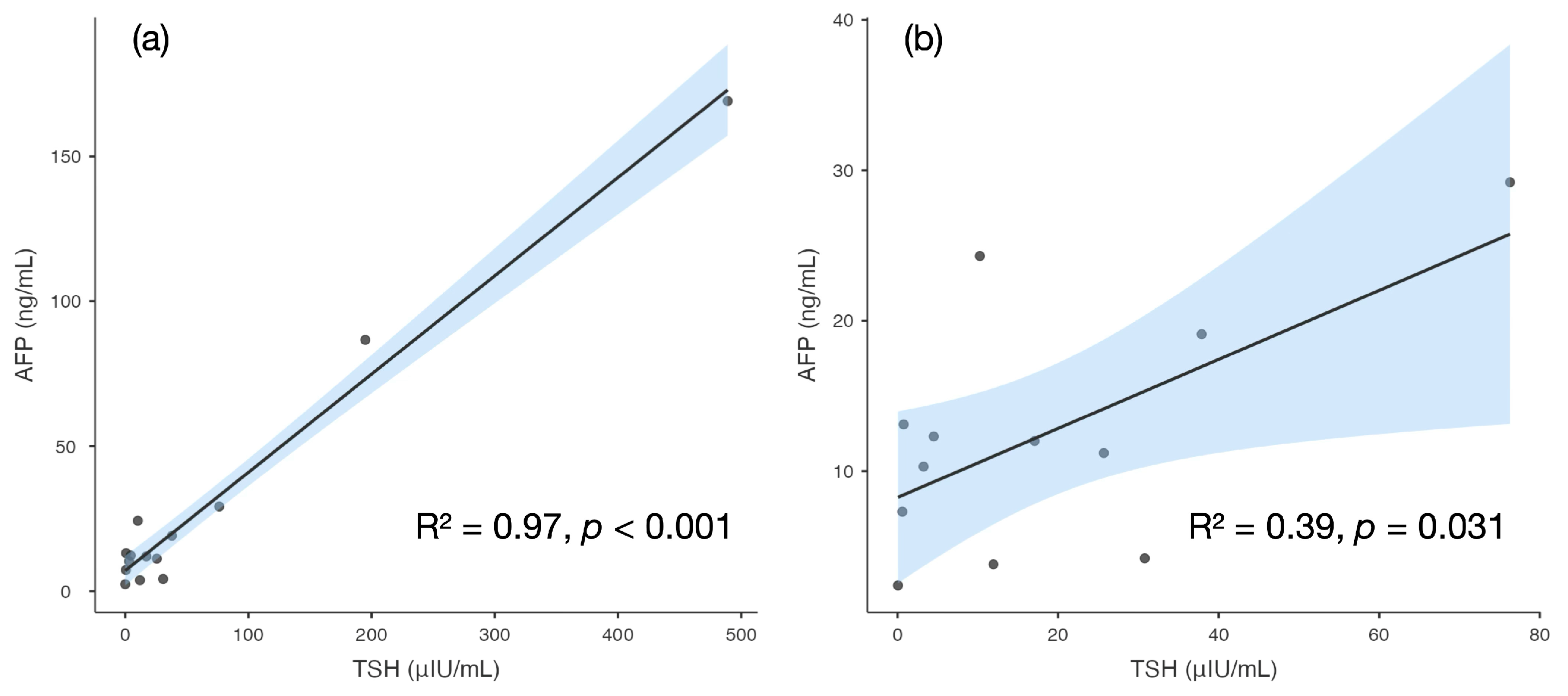
| Day | TSH (μUI/mL) (n.v. 0.79–5.85) | fT3 (pg/mL) (n.v. 2.6–4.0) | fT4 (pg/mL) (n.v. 6.1–10.6) | AFP (ng/mL) (n.v. 0.8–5.0) | Levothyroxine Dose (mcg/kg/day) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | >489.00 | 1.9 | <2.5 | - | 3.5 |
| 2 | >489.00 | 2.5 | 4.3 | 169.1 | 3.5 |
| 10 | 194.90 | 3.7 | 6.2 | 86.7 | 3.5 |
| 18 | 10.25 | 4.3 | 14.3 | 24.3 | 3.5 |
| 40 | 4.50 | 4.2 | 11.9 | 12.3 | 2.5 |
| 65 | 0.75 | 4.3 | 14.4 | 13.1 | 1.7 |
| 108 | 37.89 | 3.4 | 9.1 | 19.1 | 2.2 |
| 142 | 40.14 | 3.2 | 7.1 | - | 2.7 |
| 178 | 7.78 | 3.4 | 11.1 | - | 2.7 |
| 231 | 0.69 | 3.4 | 15.2 | - | 2.1 |
| 261 | 0.05 | 2.2 | 10.9 | 2.4 | 1.9 |
| 359 | 76.30 | 3.0 | 7.5 | 29.2 | 2.6 |
| 404 | 3.24 | 3.1 | 10.3 | 10.3 | 2.6 |
| 439 | 38.64 | 3.6 | 7.7 | - | 2.8 |
| 471 | 5.63 | 3.2 | 10.6 | - | 2.6 |
| 506 | 25.68 | 3.1 | 9.1 | 11.2 | 3.2 |
| 534 | 17.08 | 3.6 | 10.9 | 12.0 | 3.6 |
| 586 | 0.78 | 2.3 | 14.4 | - | 2.6 |
| 648 | 0.59 | 4.6 | 13.7 | 7.3 | 2.1 |
| 713 | 11.94 | - | 8.9 | 3.8 | 1.7 |
| 735 | 0.41 | 1.4 | 7.3 | - | 1.5 |
| 743 | 30.78 | 2.8 | 10.7 | 4.2 | 1.7 |
| 762 | 2.16 | 2.7 | 13.0 | - | 1.7 |
| Category | Examples |
|---|---|
| Physiological | Pregnancy (maternal source) Infancy (first year of life) Prematurity |
| Hepatic | Acute or chronic hepatitis Liver regeneration Cirrhosis Neonatal cholestasis Biliary atresia Inherited metabolic liver diseases (e.g., tyrosinemia type I, citrin deficiency) Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) |
| Genetic syndromes | Ataxia-telangiectasia Fanconi anemia Bloom syndrome Nijmegen breakage syndrome Other DNA repair disorders |
| Endocrine/Metabolic | Congenital or acquired hypothyroidism Metabolic syndromes Van Wyk–Grumbach syndrome |
| Tumoral | Germ cell tumors (yolk sac tumor, mixed germ cell tumor) Hepatoblastoma Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| Iatrogenic/Treatment-related | Liver regeneration after chemotherapy or partial hepatectomy Anabolic steroid therapy Androgen-secreting tumors or exogenous androgen exposure |
| Confirm hypothyroidism and analytical validity |
|
| Reassess AFP after thyroid normalization |
|
| If AFP remains >2–3× upper limit of normal (ULN) or increases: |
|
| Immediate imaging and referral at baseline |
|
| Follow-up |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ceconi, V.; Kiren, V.; Murru, F.M.; Bon, A.; Dragovic, D.; Zandonà, L.; Fachin, A.; Tamaro, G.; Tornese, G. Elevated Alpha-Fetoprotein in Hypothyroidism. LabMed 2025, 2, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/labmed2040024
Ceconi V, Kiren V, Murru FM, Bon A, Dragovic D, Zandonà L, Fachin A, Tamaro G, Tornese G. Elevated Alpha-Fetoprotein in Hypothyroidism. LabMed. 2025; 2(4):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/labmed2040024
Chicago/Turabian StyleCeconi, Viola, Valentina Kiren, Flora Maria Murru, Andrea Bon, Danica Dragovic, Lorenzo Zandonà, Alice Fachin, Gianluca Tamaro, and Gianluca Tornese. 2025. "Elevated Alpha-Fetoprotein in Hypothyroidism" LabMed 2, no. 4: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/labmed2040024
APA StyleCeconi, V., Kiren, V., Murru, F. M., Bon, A., Dragovic, D., Zandonà, L., Fachin, A., Tamaro, G., & Tornese, G. (2025). Elevated Alpha-Fetoprotein in Hypothyroidism. LabMed, 2(4), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/labmed2040024







